Features
Looking around N0.3 Battery Ruins
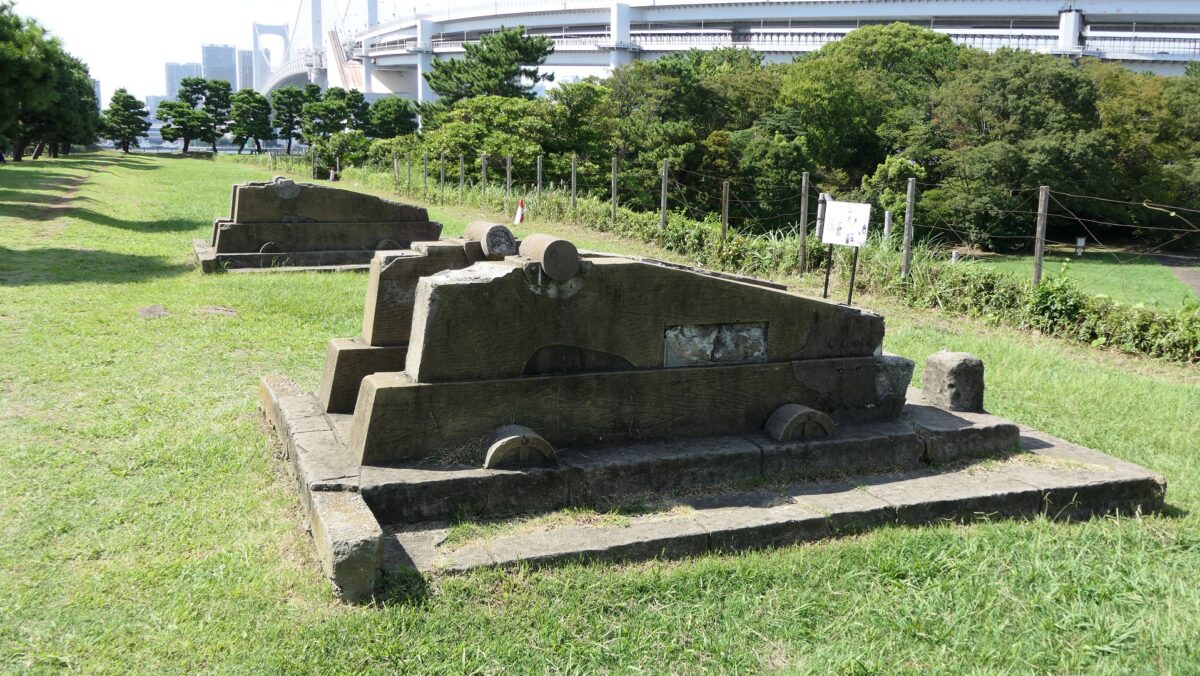
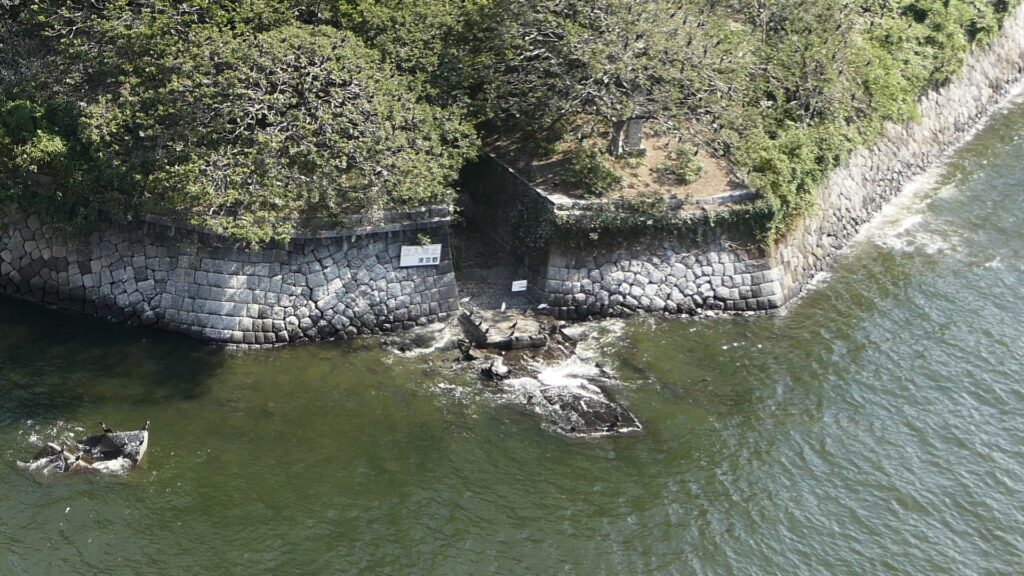
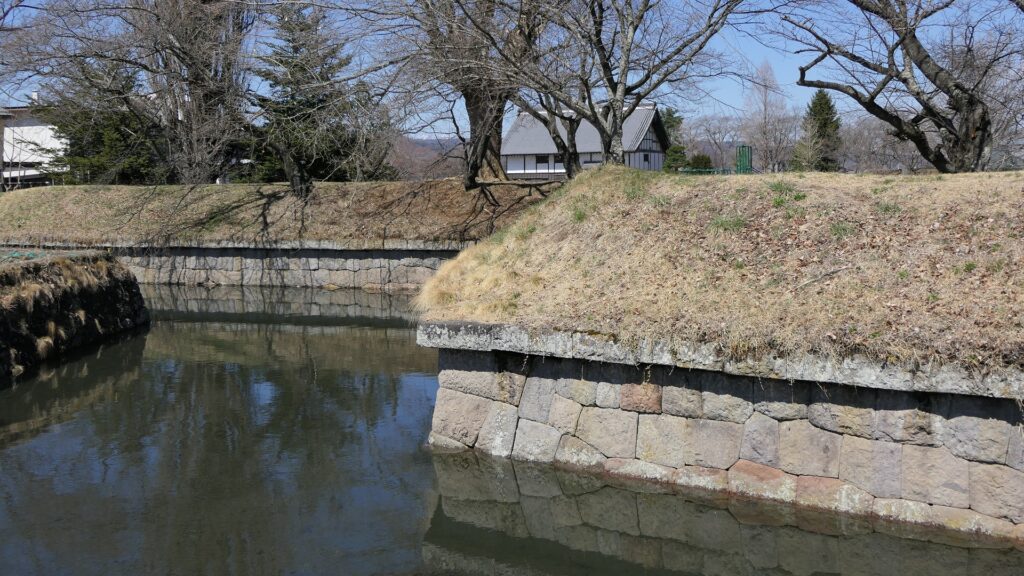
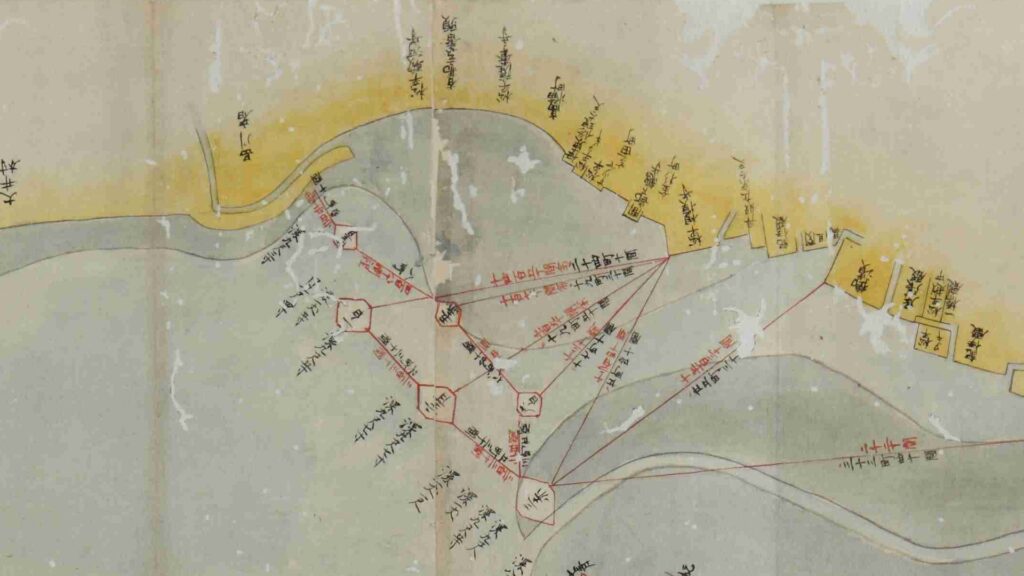
The ruins of the No.3 Battery as the Daiba Park is connected to the seaside by a marine walkway. The walkway was added when the park was established, that means the battery had originally been isolated. As you get close to the battery, you will see its characteristic stone walls using the Hanedashi system. The system refers to all the stones on the top row are layered to prevent enemies from invading, which emulated European castles. This system is rarely seen in other Japanese castles only in Goryokaku, Tatsuoka Castle and Hitoyoshi Castle which were built or renovated at the end of the Edo Period. In fact, this is the only spot where you can see them close by because it is prohibited for visitors to approach the stone walls from the other sides.
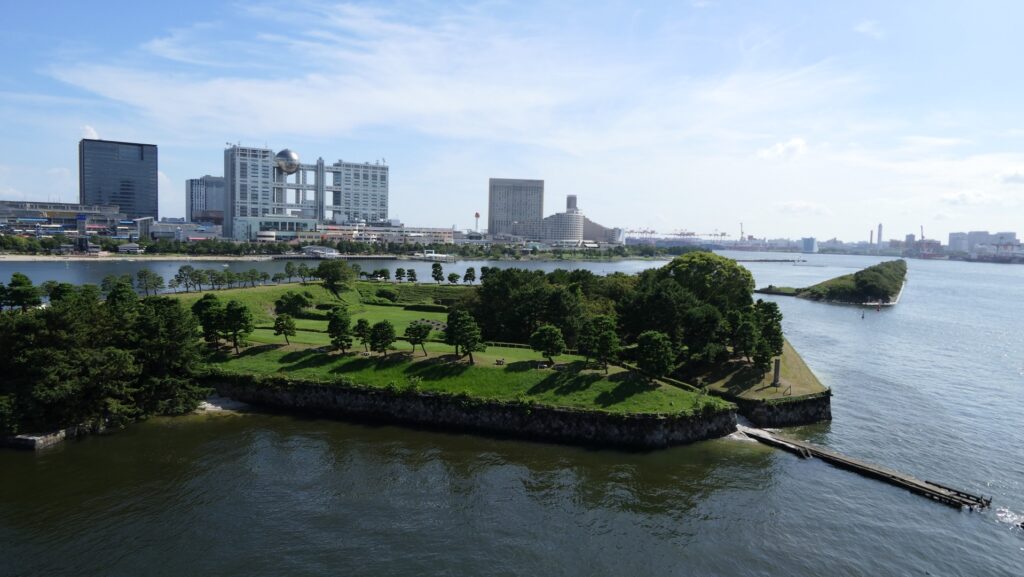
The aerial photo of the No.3 Battery
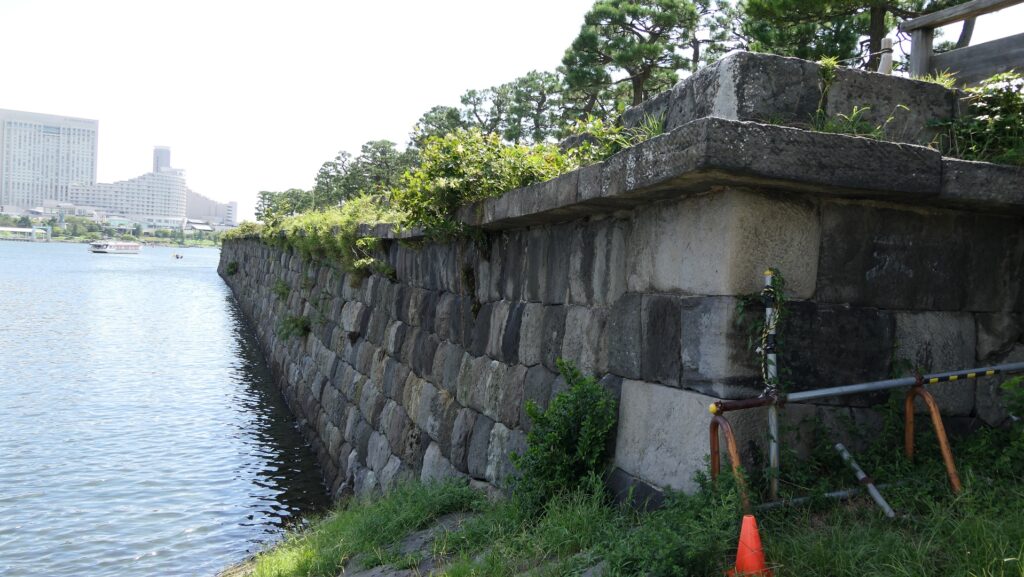
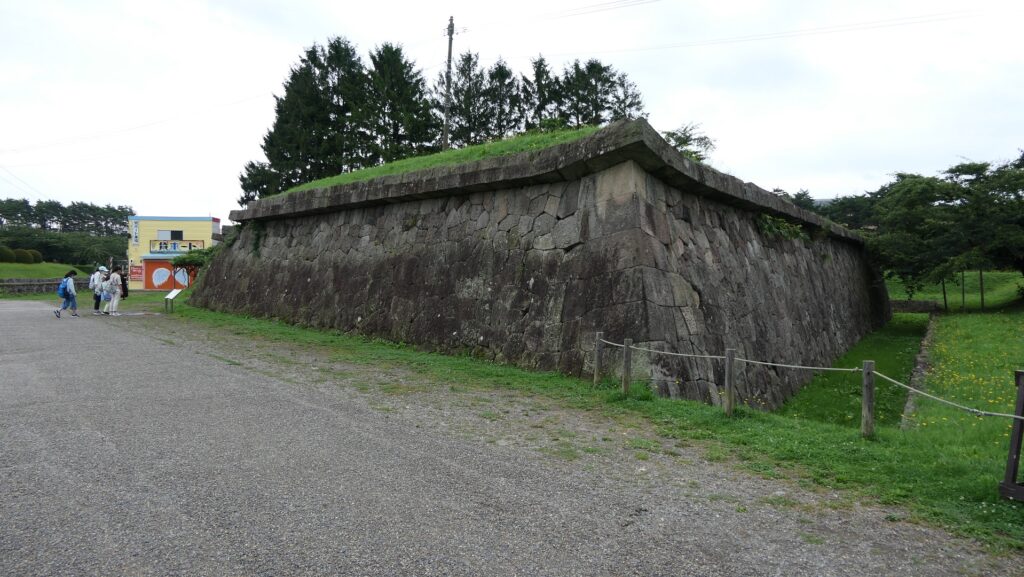



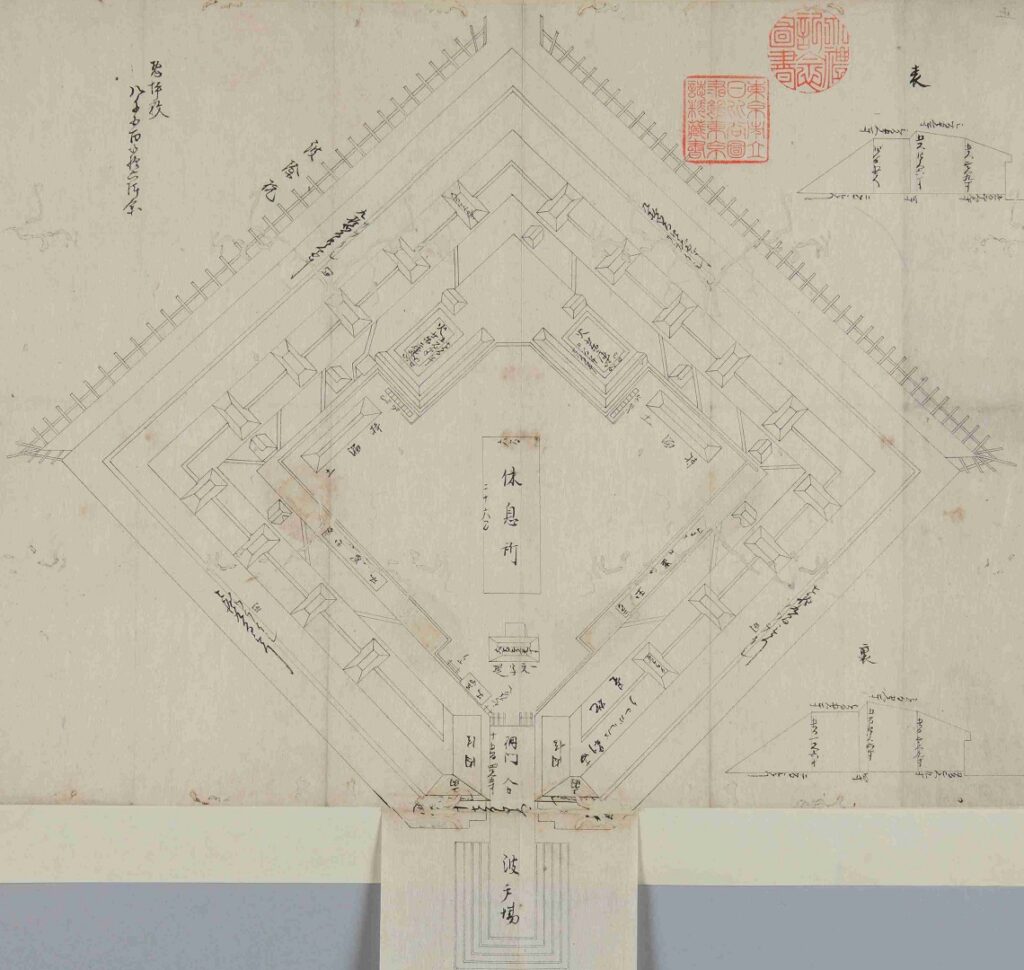
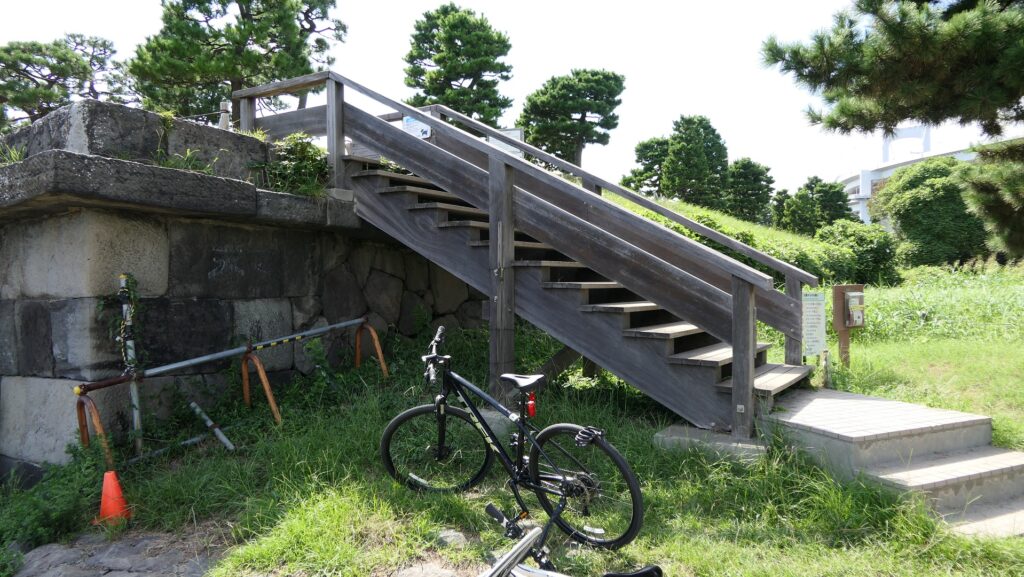
You can land at the battery by using steps like boarding a ship. You can next see a close view of the battery. It is a large square with one side being 160m long and its perimeter is higher than the center. There are few remaining original items, so some visitors might not notice that it is a ruin without the knowledge of its history. If you walk on the perimeter which is made with earthen walls from the entrance, the view is so nice. You can see Odaiba Seaside Park on the left, the Rainbow Bridge and the No.6 Battery on the right, and Tokyo Bay ahead.
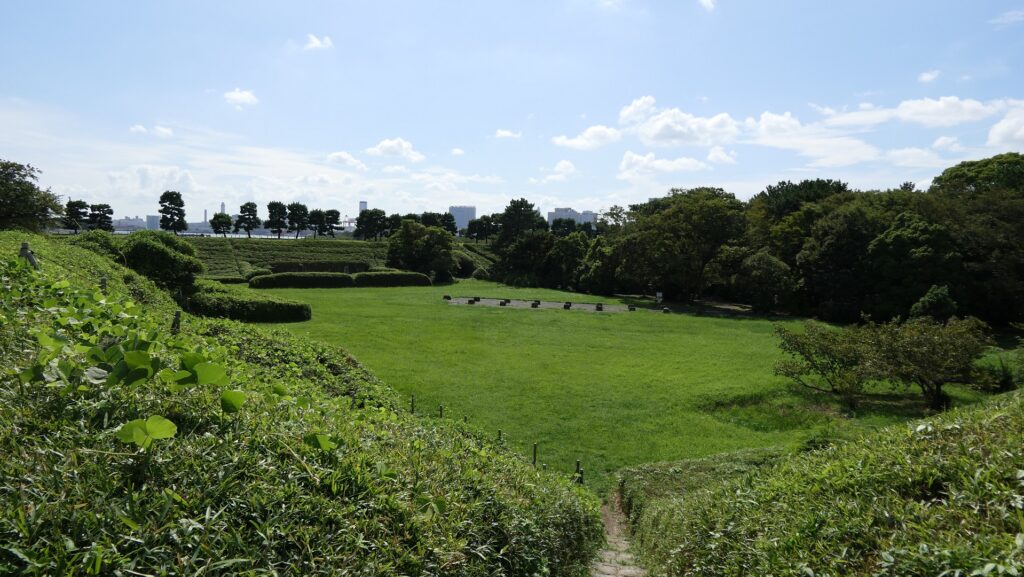
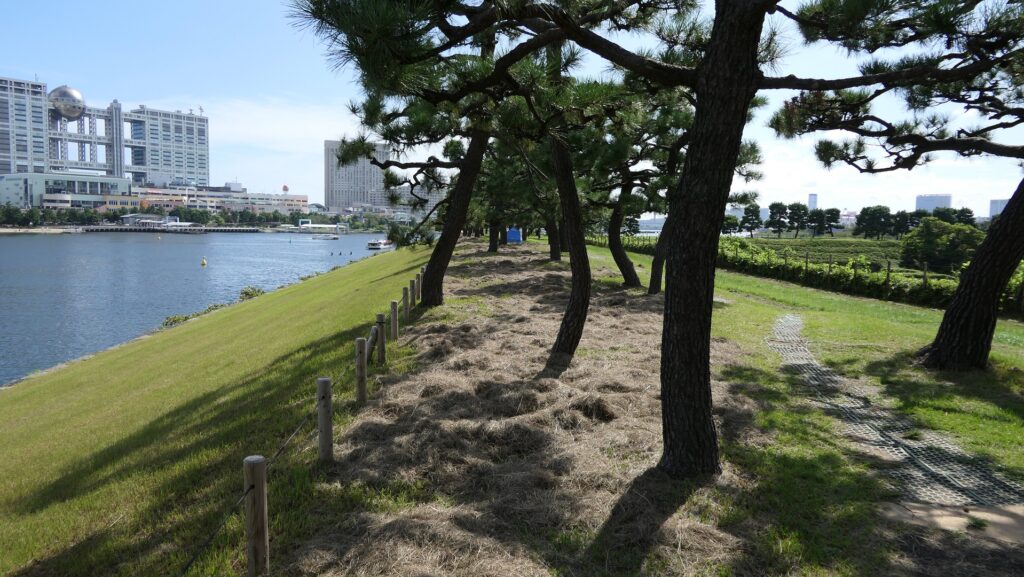
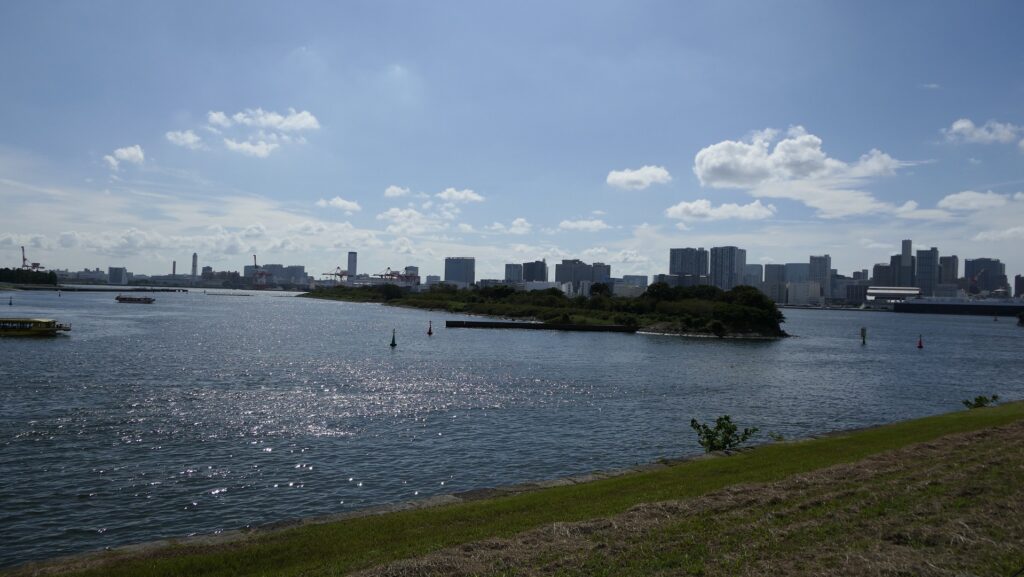
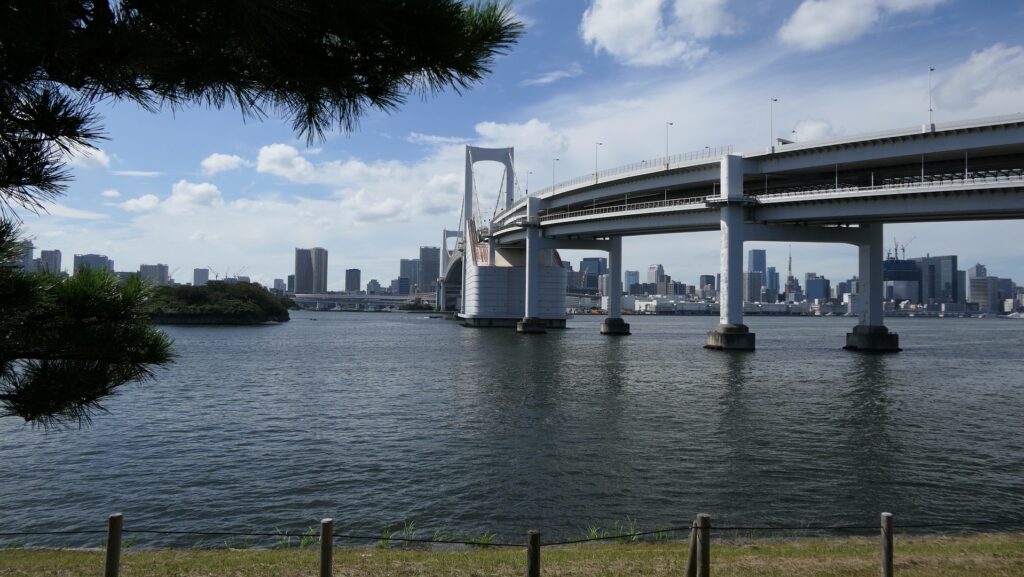





Ruins regarding Guns
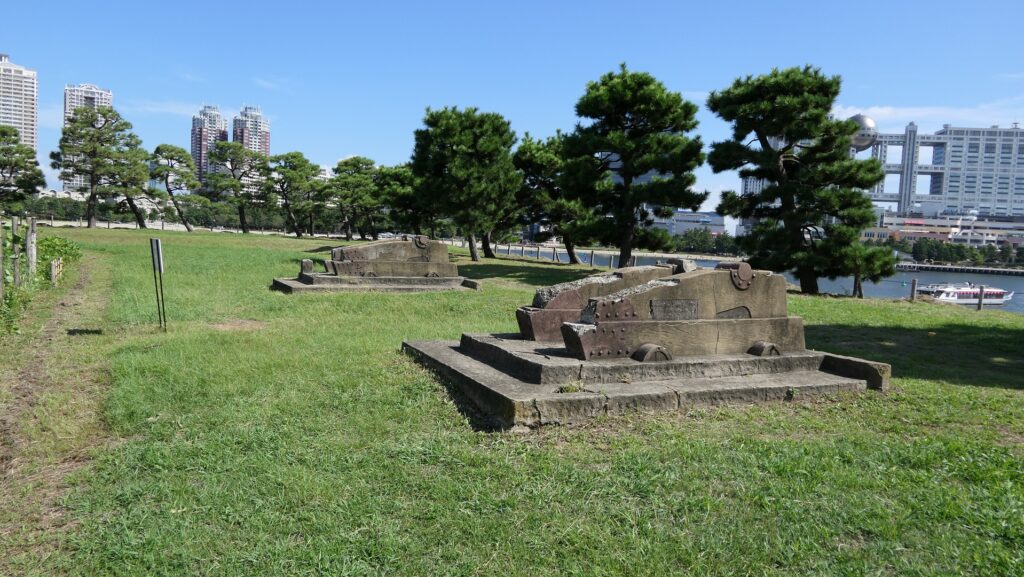
There are two imitations of gun platforms on one side of the perimeter opposite the entrance. However, they are not actually real and should not be considered even as replicas, according to historians. In addition, there were thick and long earthen protective walls called “breastworks” in front of cannons, but they seem to have collapsed. There were also earthen side walls dividing the canons to protect gunners from blasts, but were removed after the battery being abolished. This side was definitely the front line against enemies.
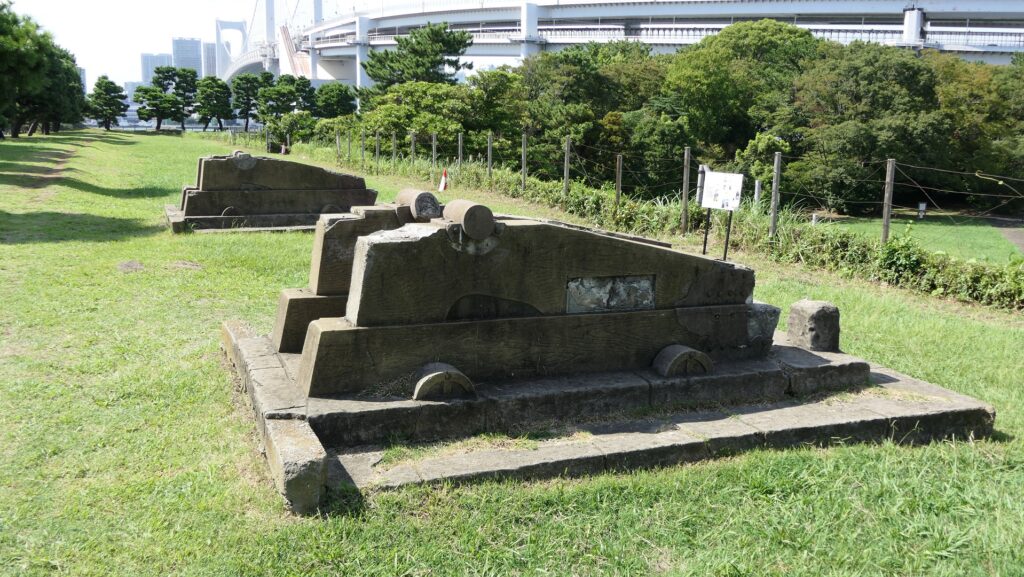
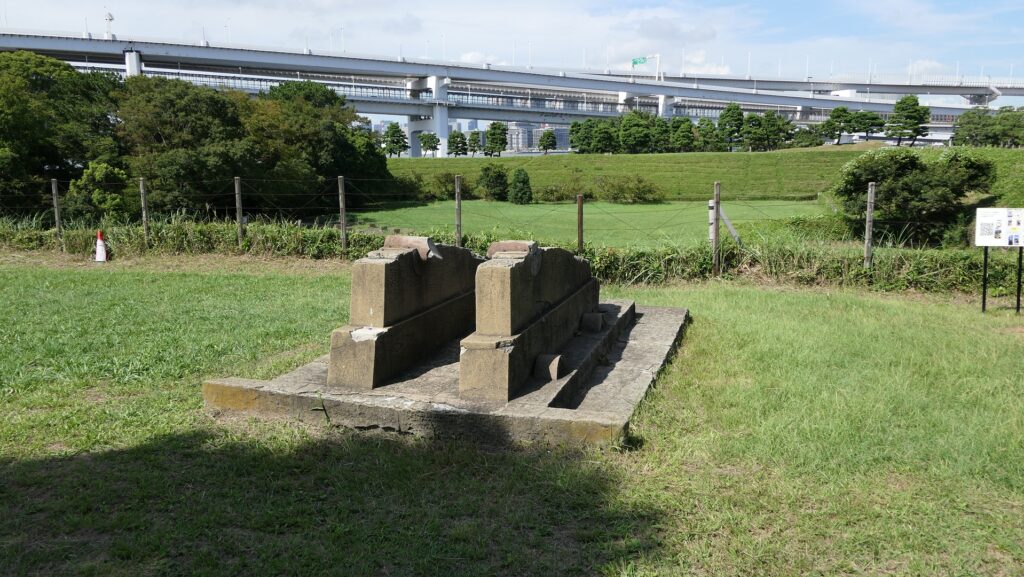


The ruins of the gun powder magazines are facing downward inside the front side walls, which are surrounded by earthen banks. There was the building for the magazine inside the banks, but it was demolished. There is now a stone-made item like a cocking stove instead, but it is not original for the battery. In addition, the banks are partially supported by stone walls which were built to recover them from the damage of the Great Kanto Earthquake of 1923.
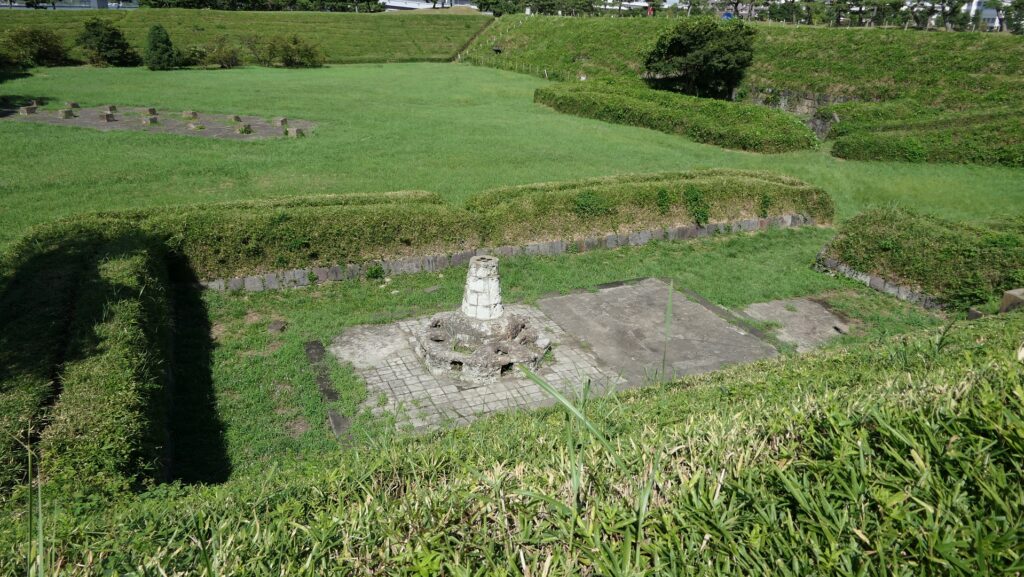
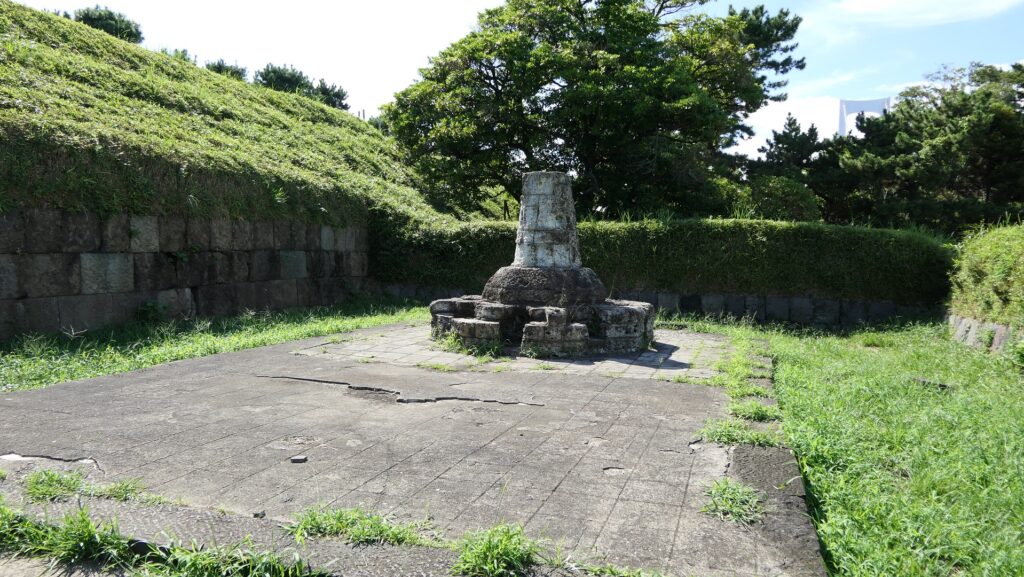
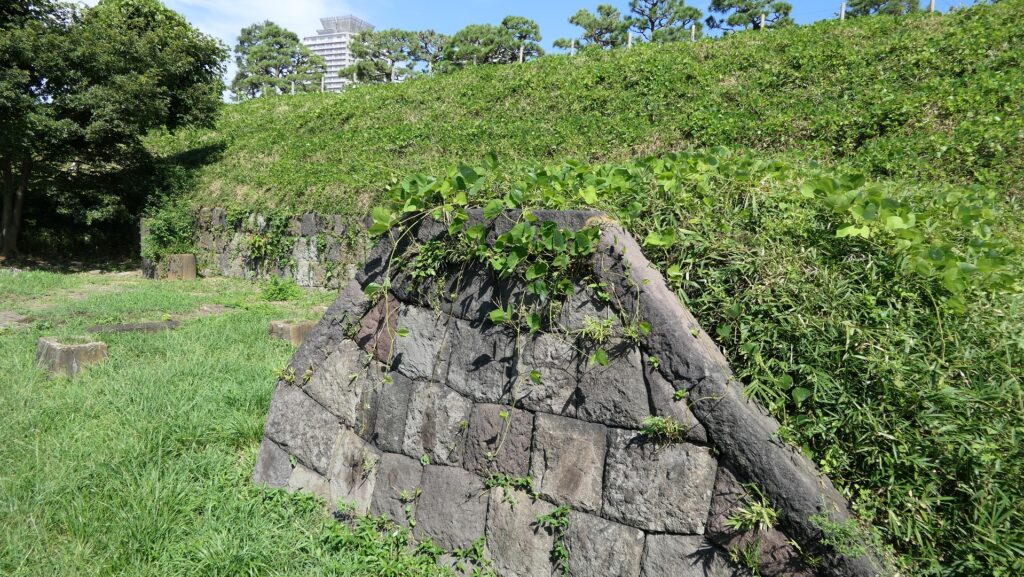



The ruins of the ammunition chambers are at other sides. The chambers were solidly built with a stone hut and wooden racks deep in the earthen walls. This was because ammunition was the most dangerous item in the battery, which might have caused accidents or explosions. We can now see the stone hut ruins behind earthen mounds around which were added later than when the battery was active, maybe for preservation.
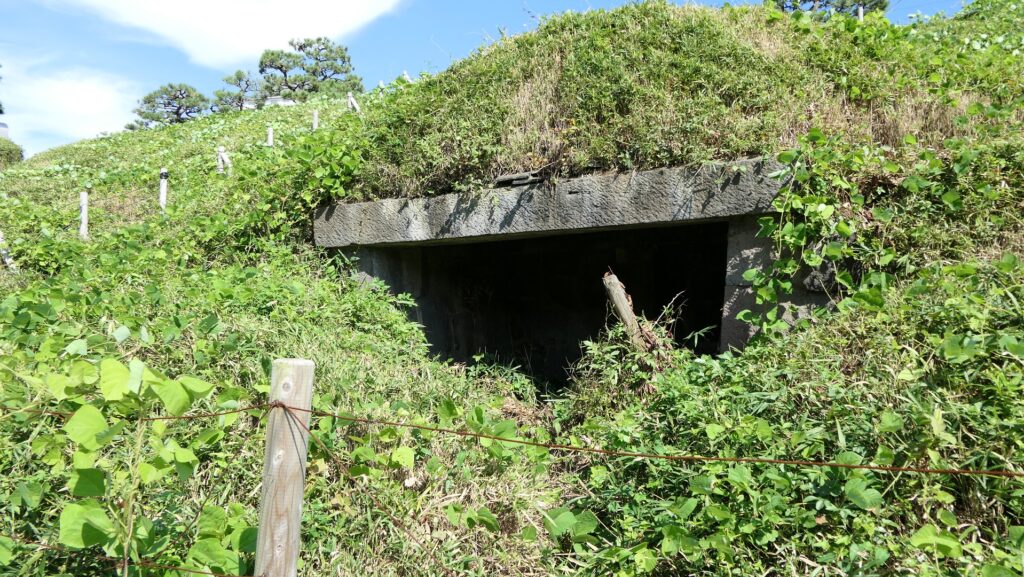

Ruins of Pier and Barrack
In the flat central part of the battery, there are only the stone foundations of the barrack. The barrack was a simple wooden building with no baths for the warriors to rest in. They would escape from the barrack if a battle happened before it would be burned.
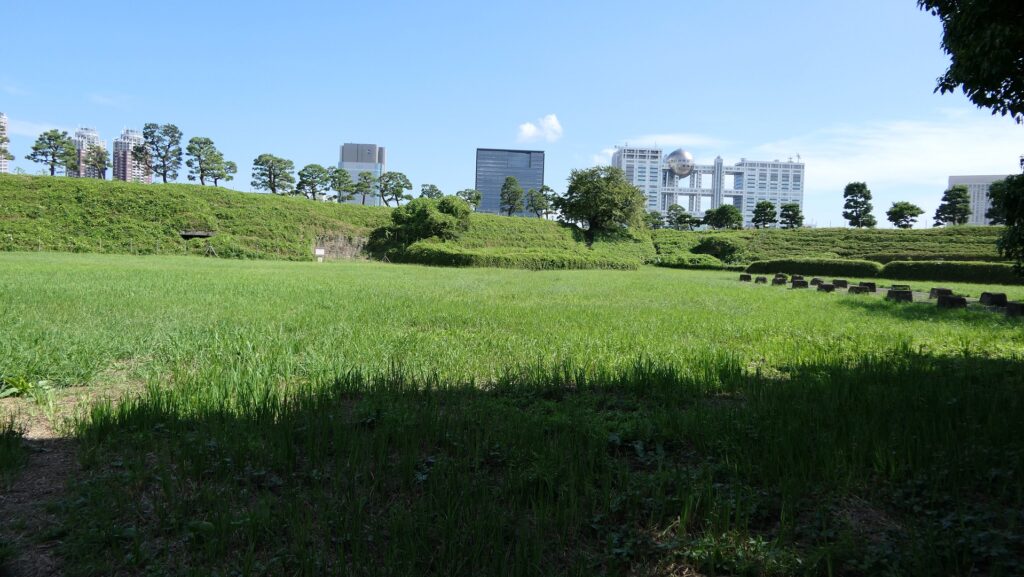
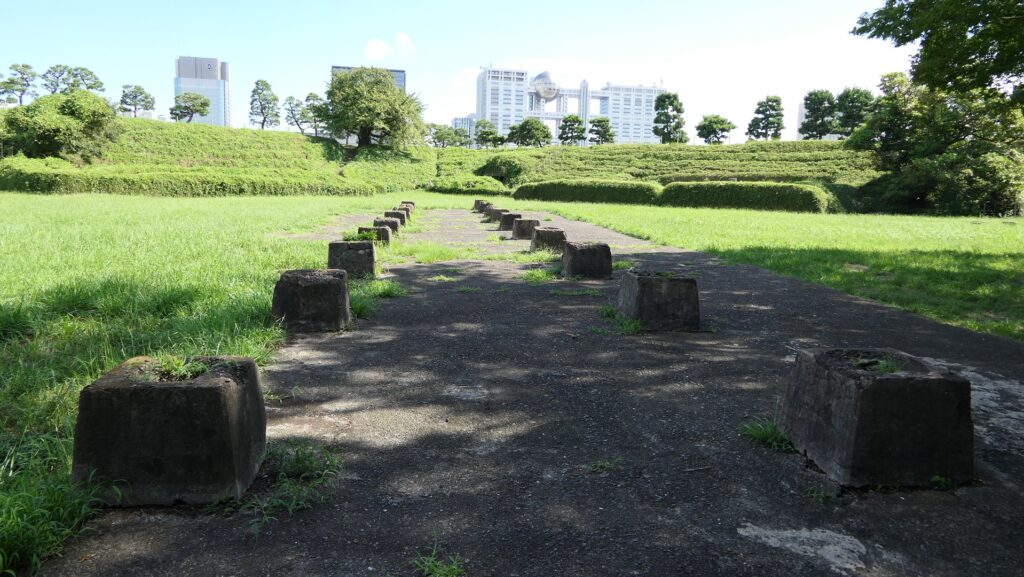


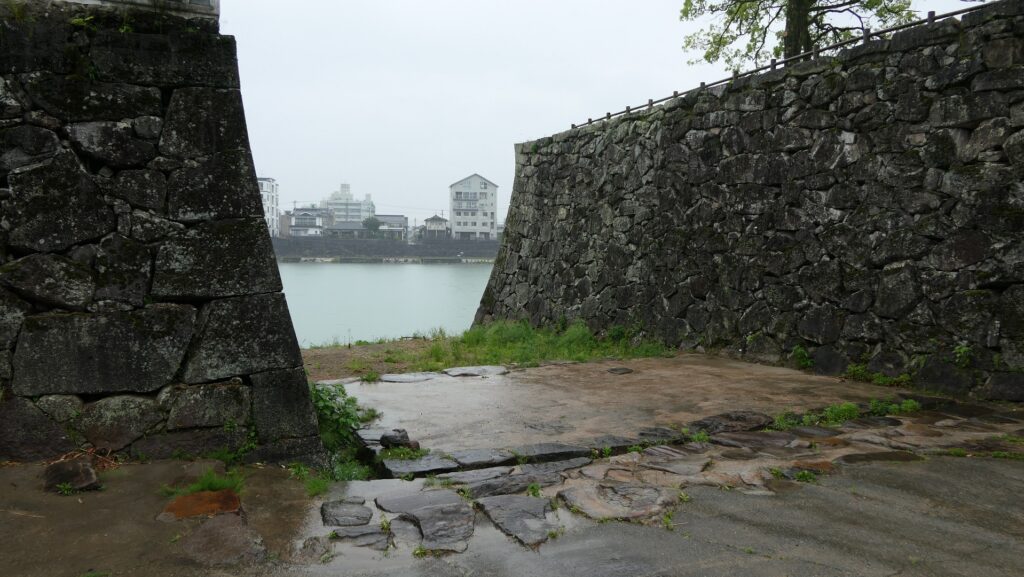
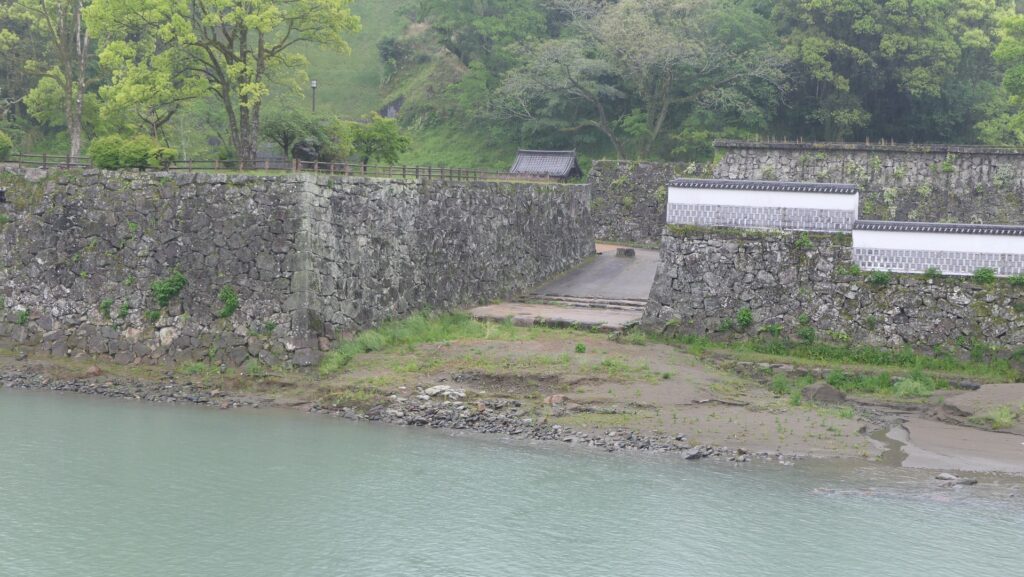
The ruins of the pier are at the next corner to the current entrance. Visitors can not enter it, but only see it from the inside. The concreted part was worked in the later period, which might have been used when the park was developed.
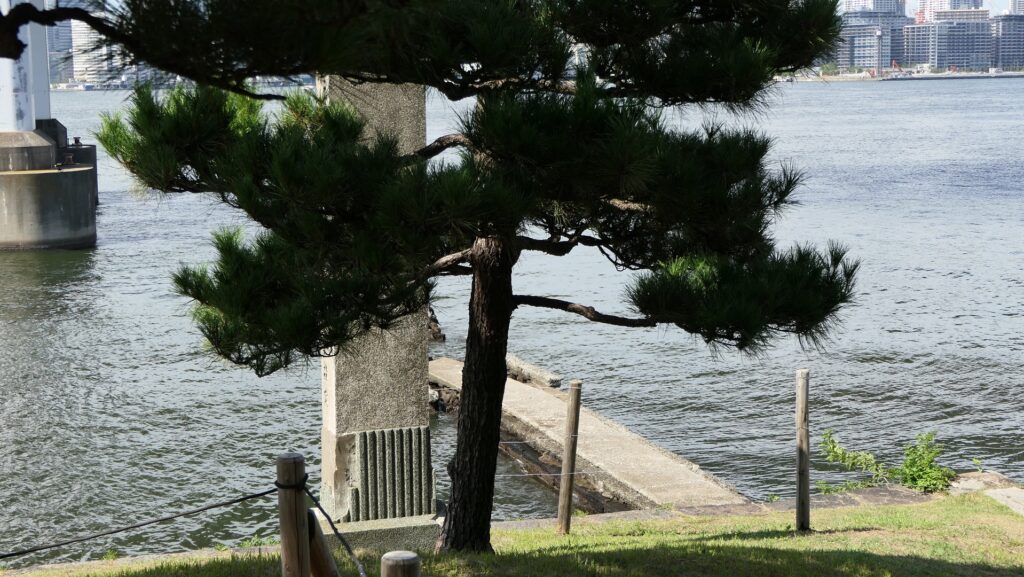
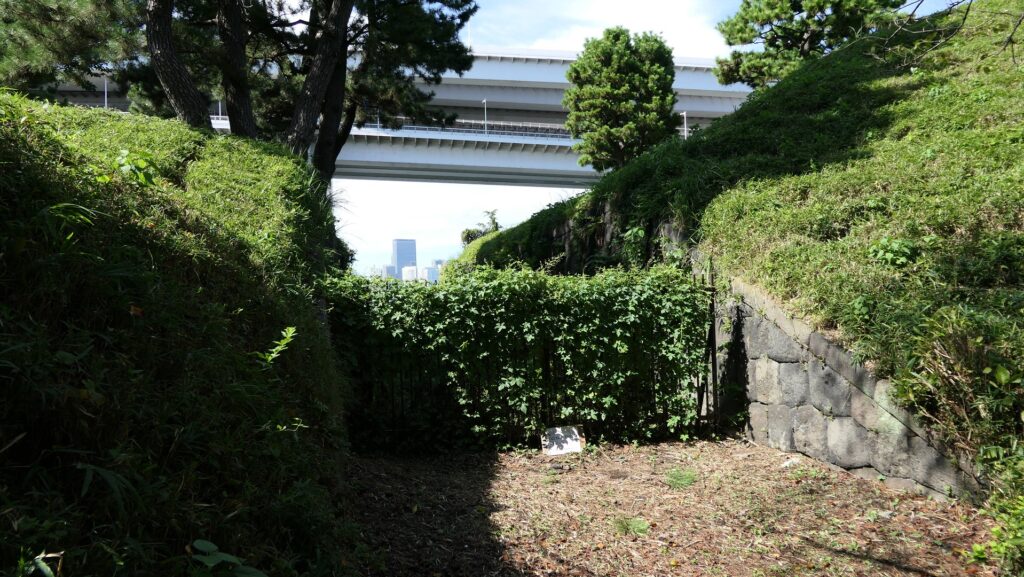


There are also remaining earthen walls in front of the pier, which is called “Ichimonji-tsutsumi” (meaning the bank like the Chinese letter for one which is a horizontal line). This structure was made to ensure visitors could not see inside and the defenders could protect the battery from enemies’ attacks from the tier as the original entrance.

My Impression
I think the ruins of Shinagawa Batteries are very useful for telling people about what happened in the past. Visual historical items are significantly better than only records or explanation boards. The waterfront area of Tokyo has been very important for the economy of the whole country. All the batteries ruins could have been removed. The decision of Tokyo Metropolitan which owns the ruins was so great. Now, just one thing, I would like the government to replace the imitation of gun platforms at the site with realistic replicas to make visitors better understand what the battery would have looked like.

That’s all. Thank you.
Back to “Shinagawa Batteries Part1”
Back to “Shinagawa Batteries Part2”