I introduced the histories and features of Odawara Castle until the Sengoku Period in the previous articles. In this article, I will talk about the histories and features of the castle starting from the Edo Period to the present time. The catchphrase of this article will be “Disaster Recoveries”.
Location and History
Period of Okubo Clan
After the Battle of Odawara Castle in 1590, Ieyasu Tokugawa who captured the Kanto Region chose Edo, not Odawara, as his home. However, he assigned his senior vassal, Tadayo Okubo to Odawara Castle instead as the founder of the Odawara Domain. That meant the castle was still important in order to protect the region from enemies at the western edge of the region. Tadayo lived in the castle while maintaining its stone walls. He used the main hall that the Hojo Clan built, and the Main Tower the clan may have built also. This was because the style of the tower was different from those of the castle later on, but there is no certain evidence of this. Ieyasu often stayed in Odawara Castle when he went hunting or looked around his territories. Despite the close relationship, Tadayo’s successor, Tadachika Okubo was fired by Ieyasu due to a minor violation in 1614. It was actually said that it was caused by the conflicts between the Okubo Clan and the Honda Clan that was another senior vassal family.


Period of Inaba Clan
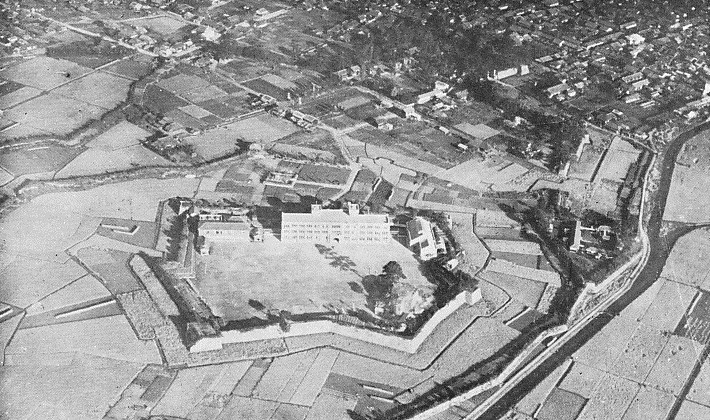
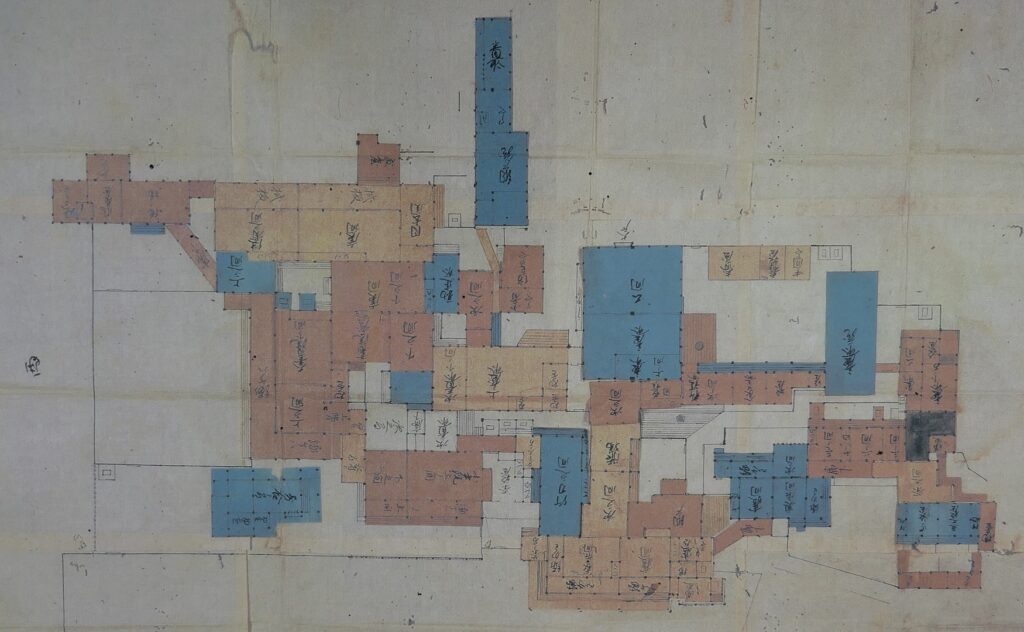
The Odawara Domain was revived in 1632 when Masakatsu Inaba, who was a close vassal of the shogun, became the lord of the castle. He was also a son of Lady Kasuga who was the foster mother of the shogun. Masakatsu was expected to guard the barrier of Hakone near Odawara, which would be the defensive line of the Kanto Region. However, in the following year, Kanei Great Earthquakes happened and it destroyed most of the castle and the castle town. The Tokugawa Shogunate, which planned the shogun’s visit to Kyoto after staying in Odawara in 1634, rapidly launched the reconstructions of the castle. That concluded the basic style of Odawara Castle during the Edo Period. For example, the main tower was rebuilt like the current one, but not the same one. The main portion of the castle was all surrounded by stone walls. The main hall in the main enclosure was built only for the shogun. Therefore, the lord of the castle stayed in his hall in the second enclosure, which was called “Oyakata”.


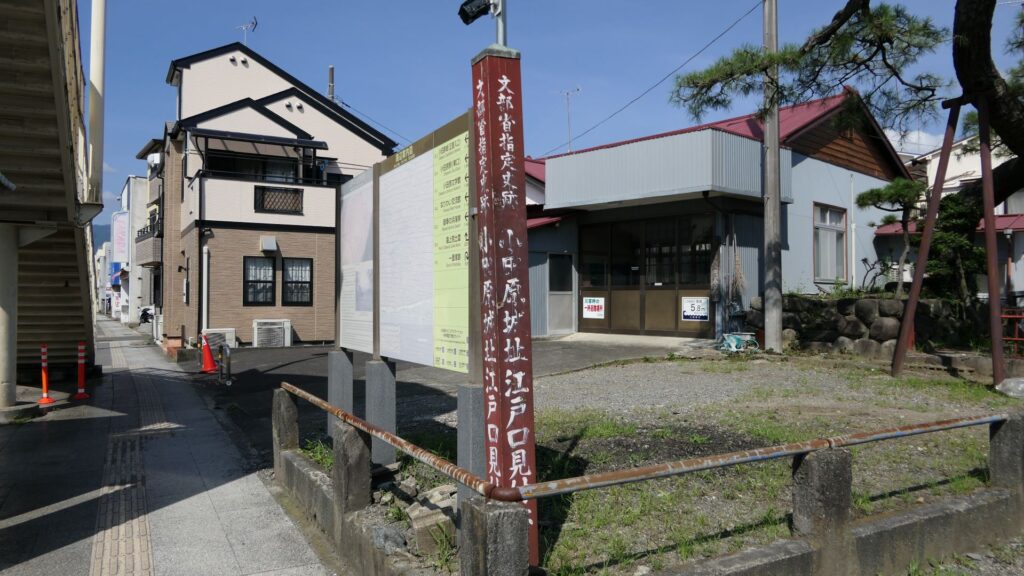
The castle town was also developed as a transportation hub of Tokaido Road, one of the main roads in Japan. On the other hand, the range of the castle was reduced to only on the plain land, compared to that during the Sengoku Period. There were exemptions that some of the So-gamae structure were used as borders of the domain or the town. For instance, the eastern gate of the town to Edo, called “Edoguchi-mitsuke” used the So-gamae earthen walls. In the Yamanokami Ditch on the hill, guards monitored the border of the domain at the gate which was built there.


Period of Okubo Clan again
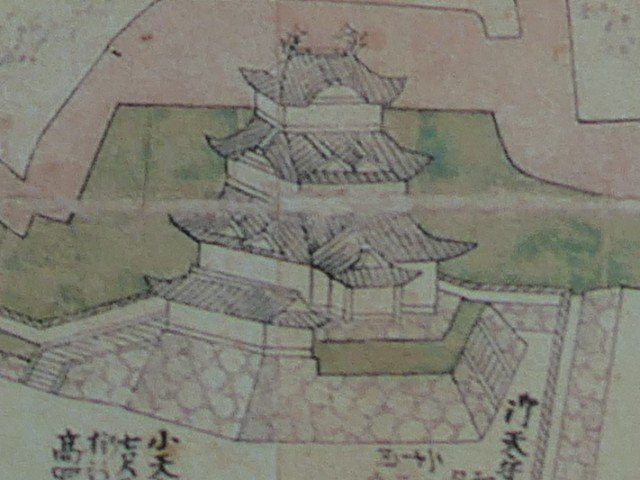
The Okubo Clan became the lord of the Odawara Domain (Odawara Castle) after the Inaba Clan moved to the Takada Domain in 1686. Tadatomo Okubo who was the lord of the clan supported the current shogun as a member of shogun’s council of elders. Few years later, the Genroku Earthquake occurred in 1703 which destroyed the castle and its town again. Mt. Fuji also erupted four years later, which was called “Hoei Eruption”, and its volcanic ash caused serious crop failure to the farms. The castle lost all its main tower and halls, but the shogunate didn’t help the domain in this case. As a result, it took as long as 18 years to restore them except for the main hall for the shogun which was not needed any more. The reconstruction of the main tower was a third generation, which survived until the end of the Edo Period. When the costal defensive system against possible invasions was needed, three batteries were built along the remaining earthen walls of the So-gamae structure beside the sea. However, they were unfortunately demolished until now.
Odawara Castle until Now
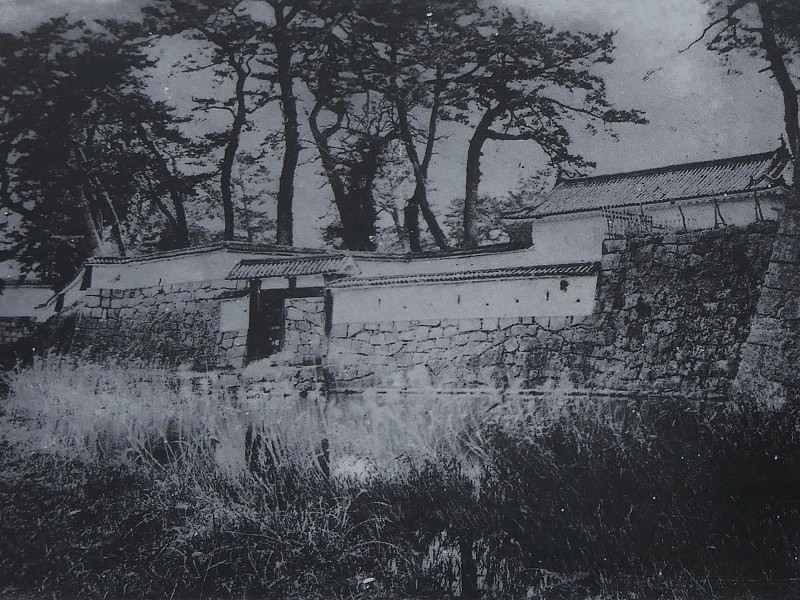
After the Meiji Restoration, Odawara Castle was abandoned and most of the castle buildings were scraped. Meanwhile, the stone walls of the main portion were still used as the base of an imperial villa. However, the Great Kanto Earthquakes, which happened on the 1st of September in 1923, destroyed the villa, the stone walls and the only remaining castle building, was the one-level turret of the second enclosure. This disaster had mostly erased the scenery of the remaining castle. The villa was eventually turned into Odawara Castle Park.
People in Odawara started to restore the castle in 1934 by rebuilding the stone walls and the turret of the second enclosure. The 4th main tower and its stone wall base was rebuilt in 1960. Since then, Tokiwagi-mon Gate in 1970, Akagane-mon Gate in 1997, and Umadashi-mon Gate in 2009 were restored to recreate their scenery during the Edo Period. They could be considered one of the disaster recoveries which the castle experienced again and again.



Features
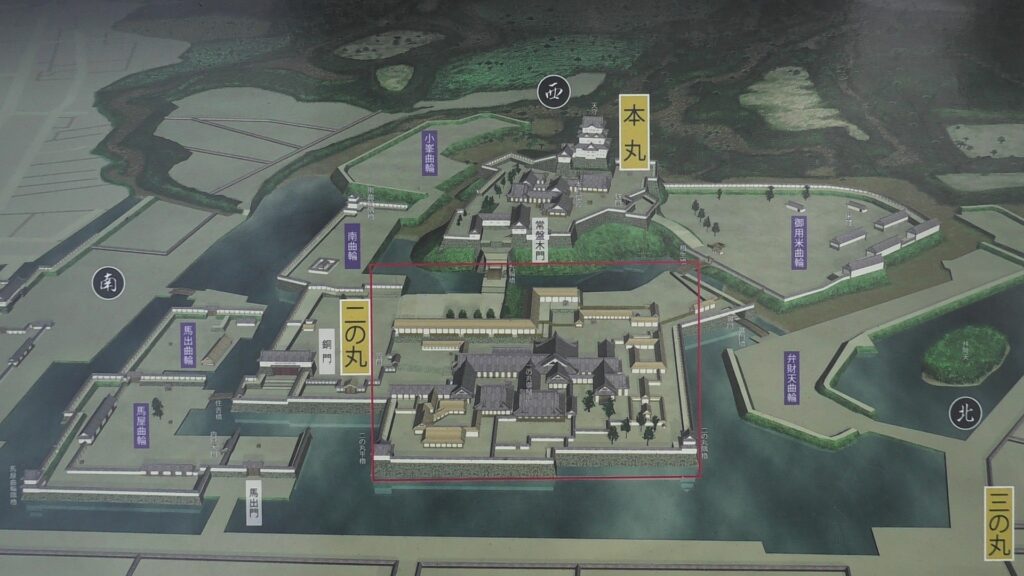
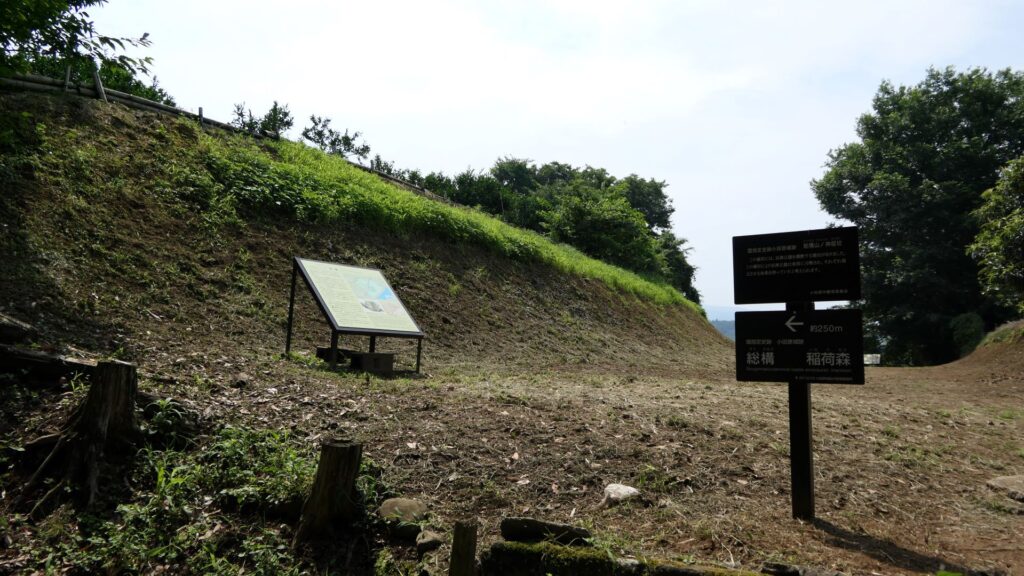
From Third Enclosure to Second Enclosure
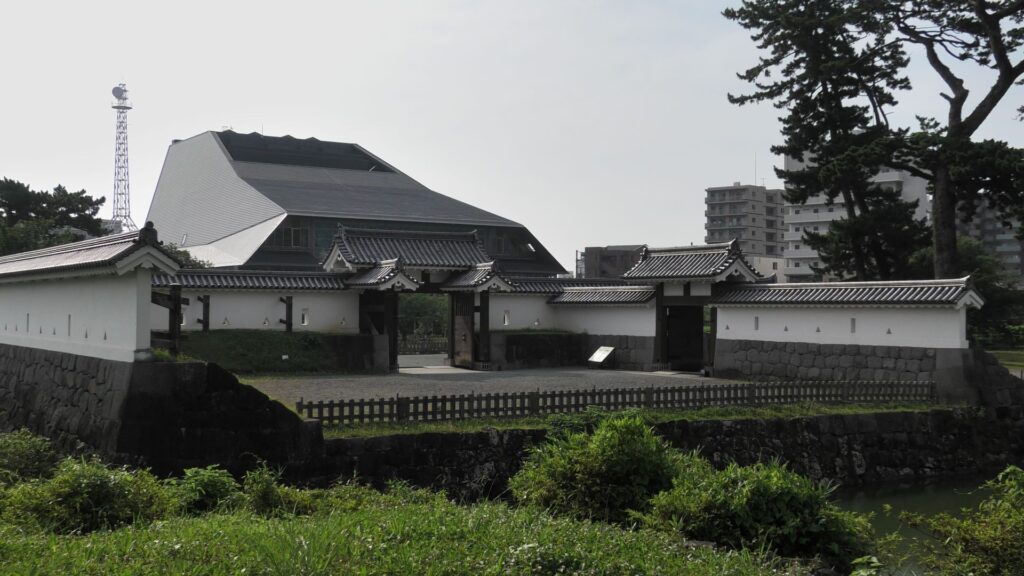
Past visitors to the castle would usually enter the castle from the main gate while current visitors would start from Ohoribata Steet beside the moat of the second enclosure. (Ohoribata means “beside the moat”) However, how about if we take another route instead? This route starts from the entrance to the ruins of Kodamon-guchi Gate beside the Odawara post office. It goes on the few remaining earthen walls of the third enclosure to the Ohoribata Street via the gate ruins. This gate had originally been the main gate of the castle during the Sengoku Period. It was said that Kenshin Uesugi attacked the gate first and followed by Shingen Takeda later on.


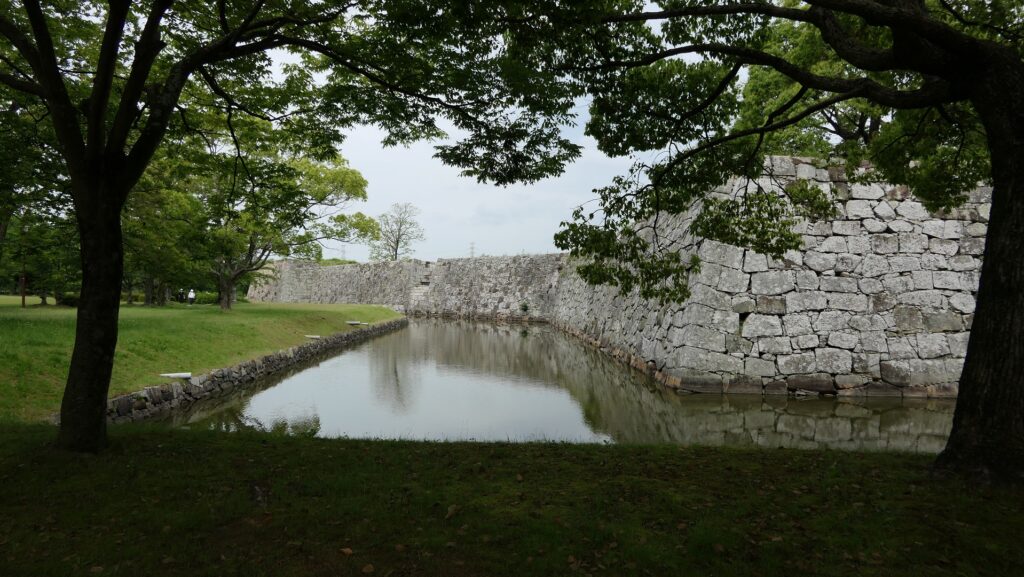
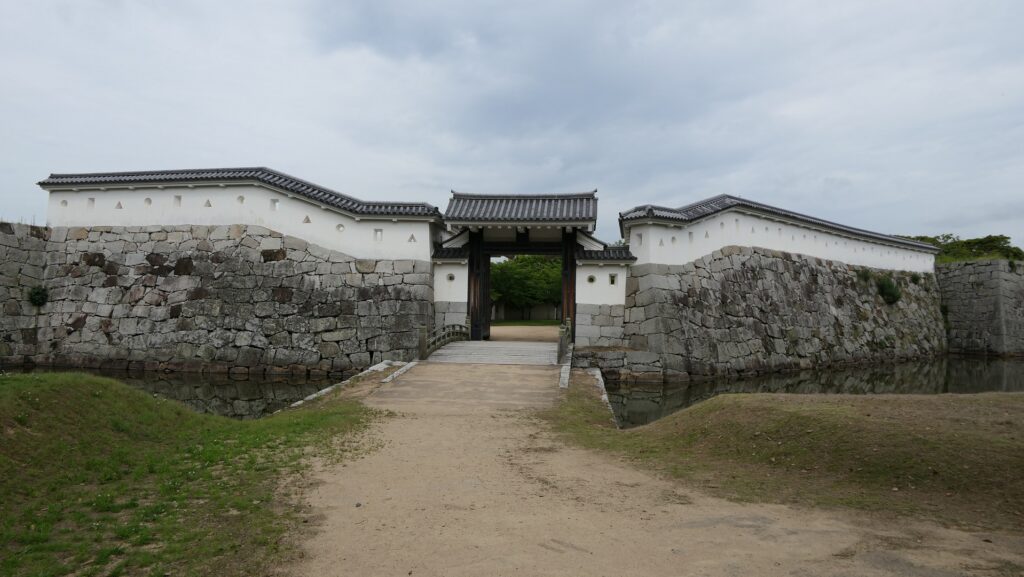
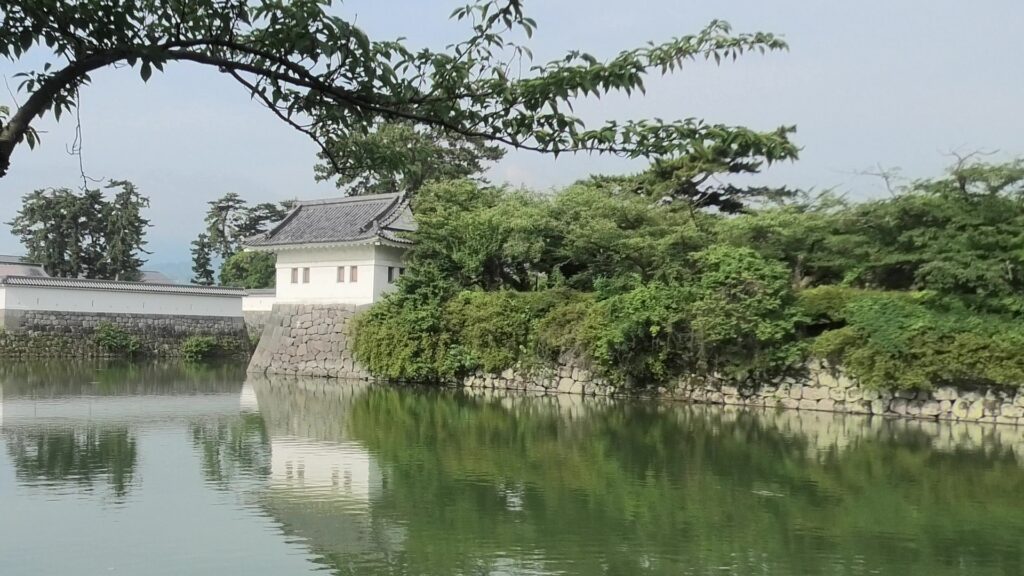
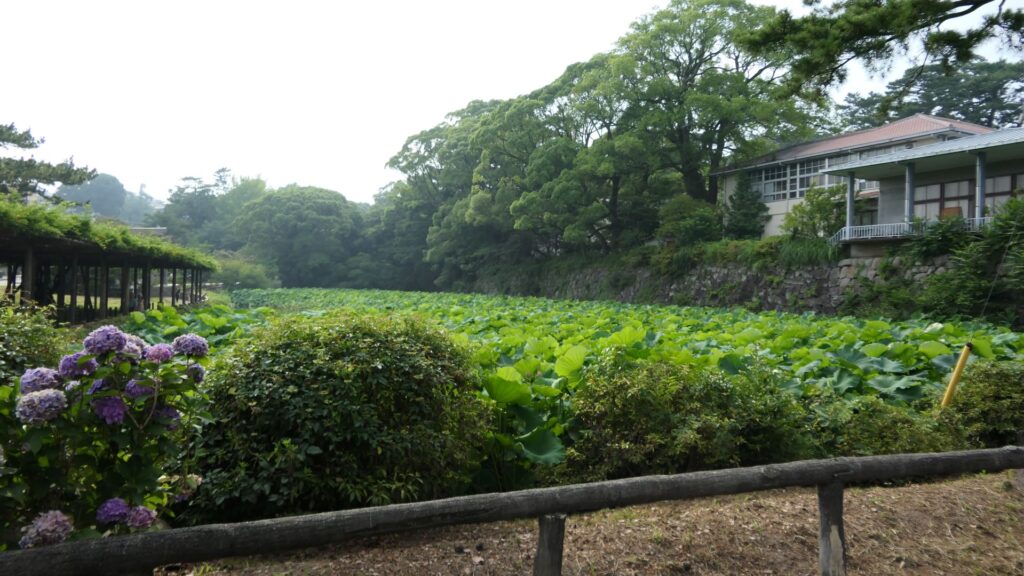
The moat of the second enclosure was originally a pond surrounding the castle, called “Large Pond” or “Lotus Pond”. The stone walls and the single-level turret over the moat were restored after the Great Kanto Earthquakes. The original stone walls, which were destroyed by the earthquakes, were much higher than the current ones.
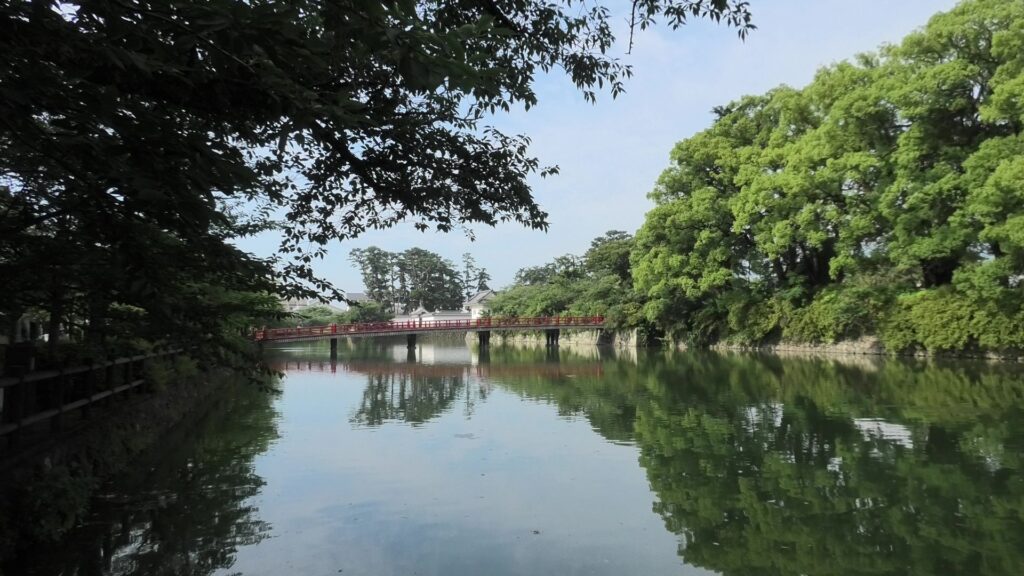


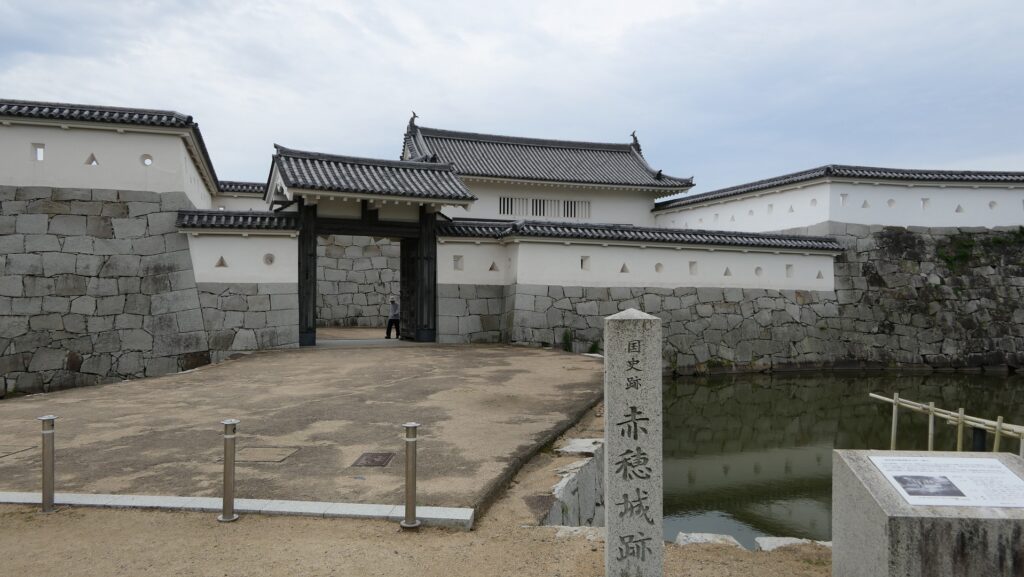
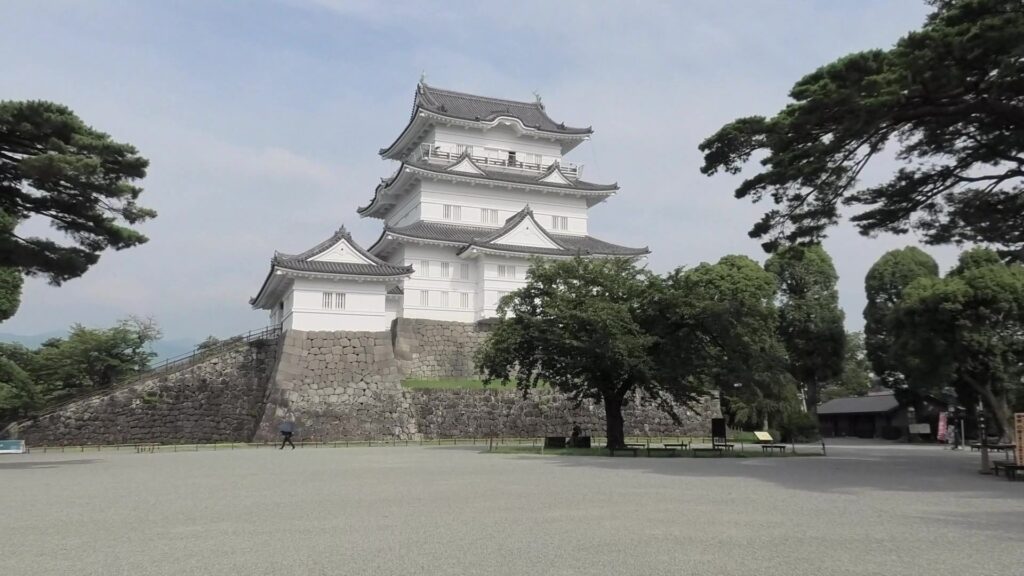
If you enter the front entrance of the Odawara Castle Park, you will enter the Umadashi-mon Gate through the earthen bridge over the moat. This gate was the latest restored gate in the castle, using wooden materials. It has a square space, called Masugata, inside, which makes it tough for enemies to penetrate.

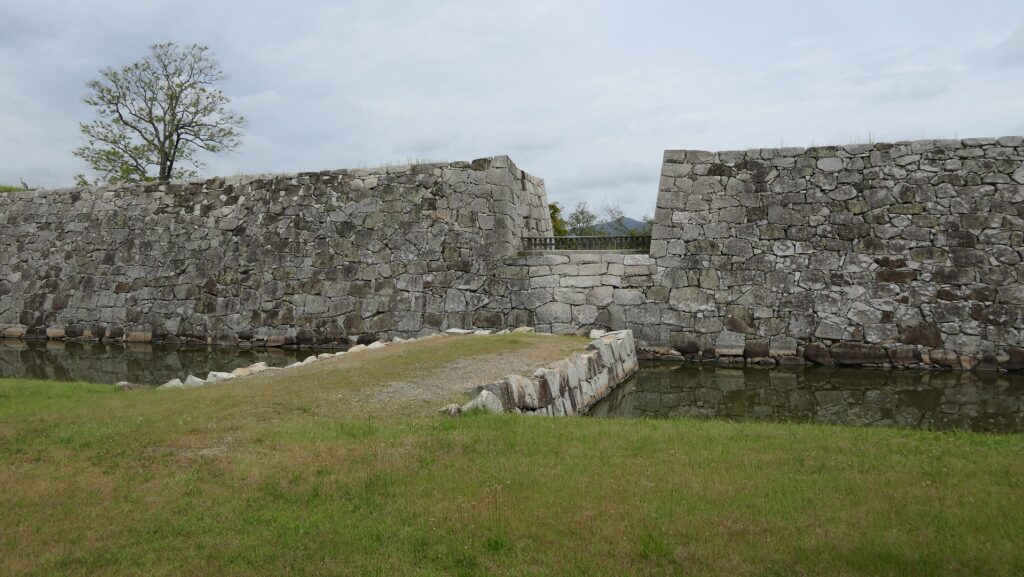
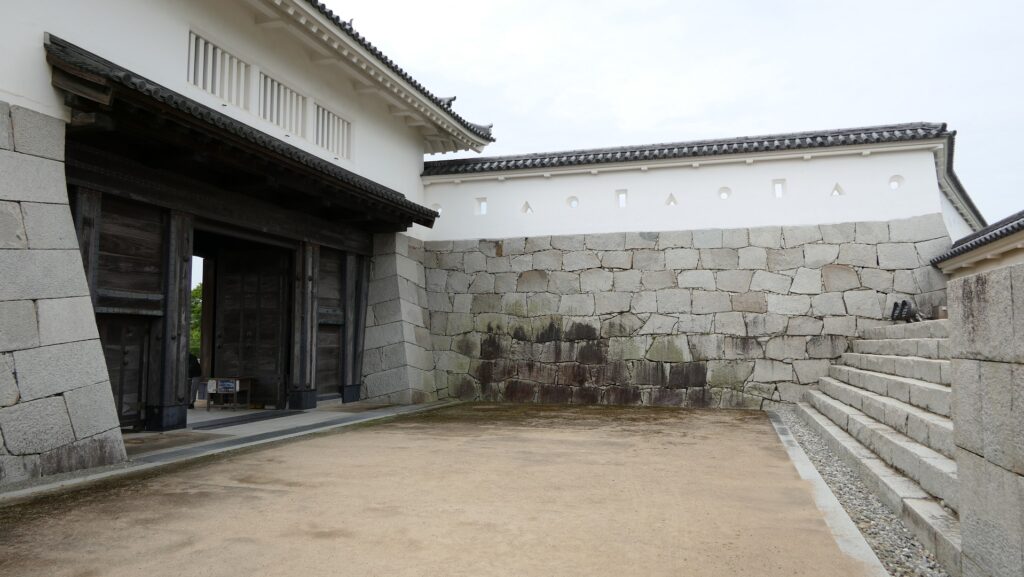
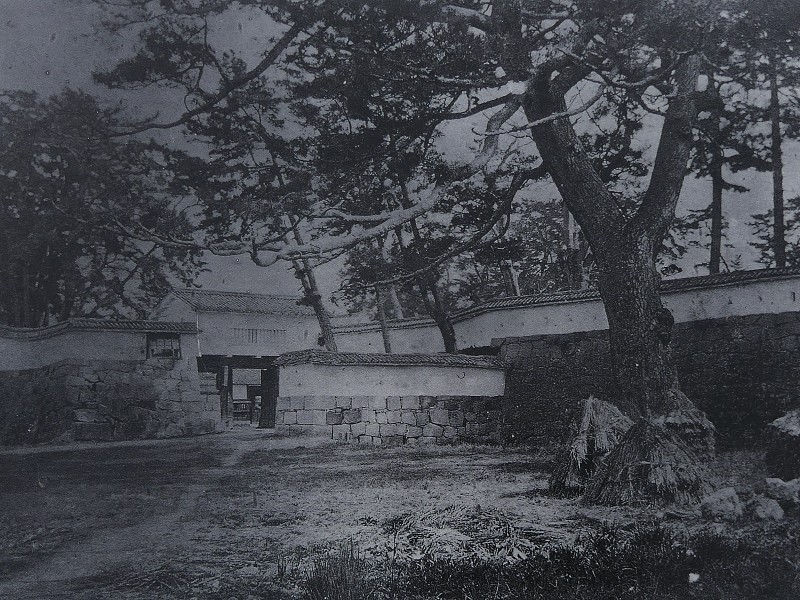
If you pass the gate and walk around the moat again, you will eventually reach the Akagane-mon Gate, which is the front entrance of the second enclosure. You will need to walk across the wooden bridge to go over the moat again, which comes from the castle’s defensive layout. The gate was also restored to its original conditions with the help of old photos, records, and the results of the excavations. This Masugata System looks stronger than The Umadashi-mon Gate, which is surrounded by stone walls and mud walls.
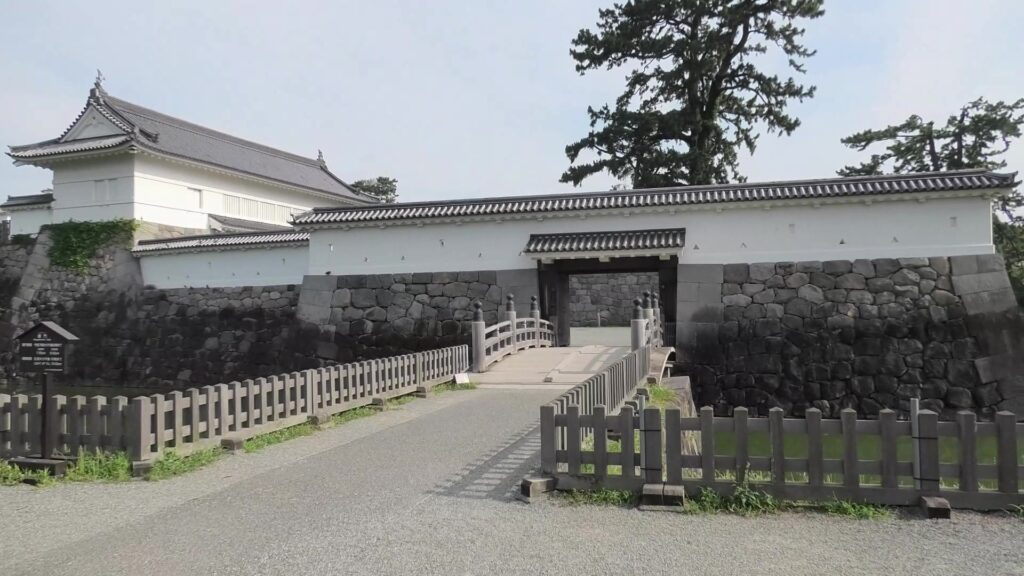

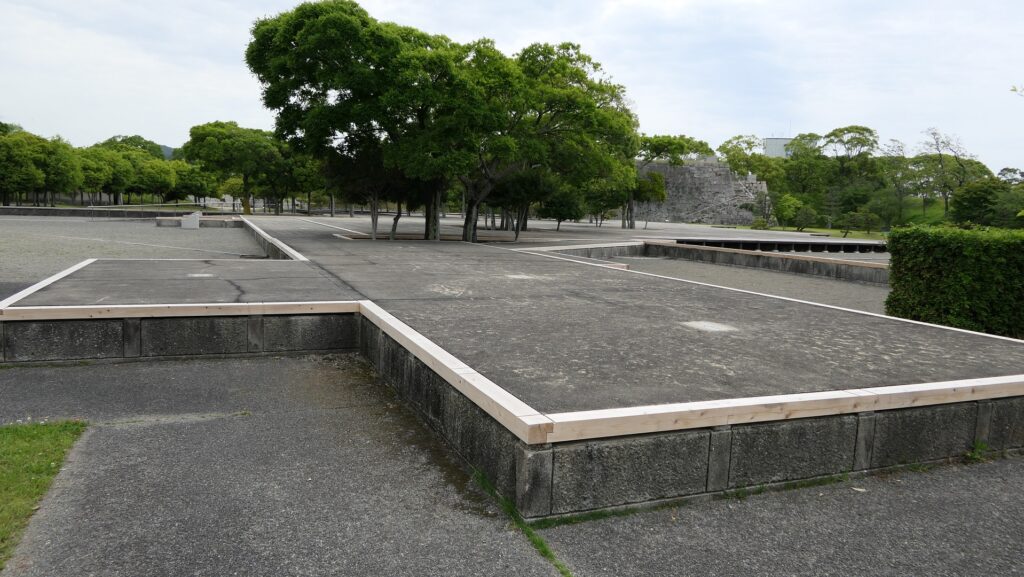
The inside of the second enclosure is mostly an empty space but had the main hall for the lord (during the Edo Period) and the imperial villa (during the Meiji and Taisho Eras).
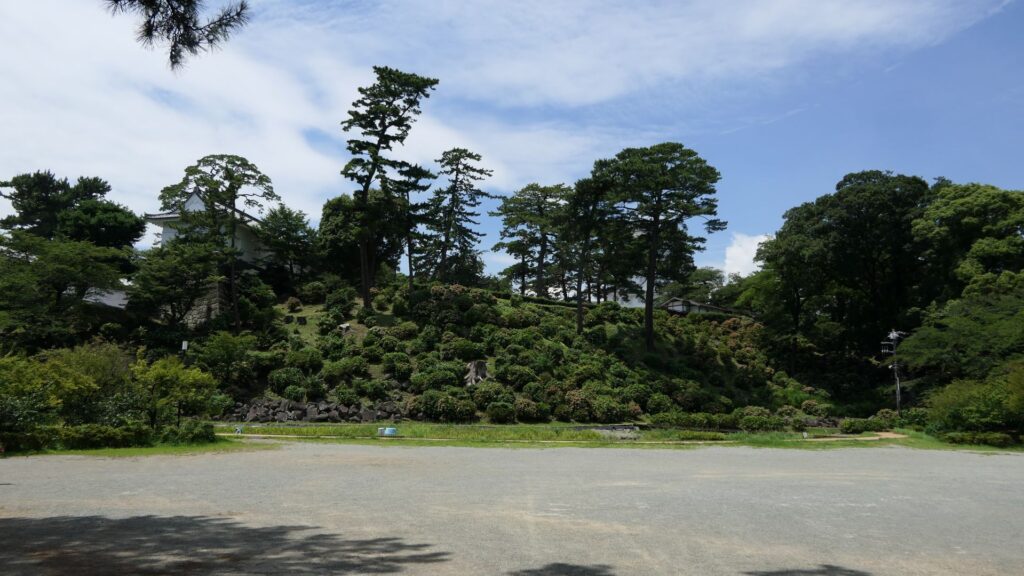

Arriving at Main Enclosure
We will eventually reach the main enclosure from the second enclosure through Tokiwagi-bashi Bridge. There used to be the eastern moat surrounding the main enclosure under the bridge, however, it has been converted into an iris garden which you can enjoy if you walk down to the former bottom of the moat. You can also see many hydrangeas planted on the slopes of the enclosure during the summer season.
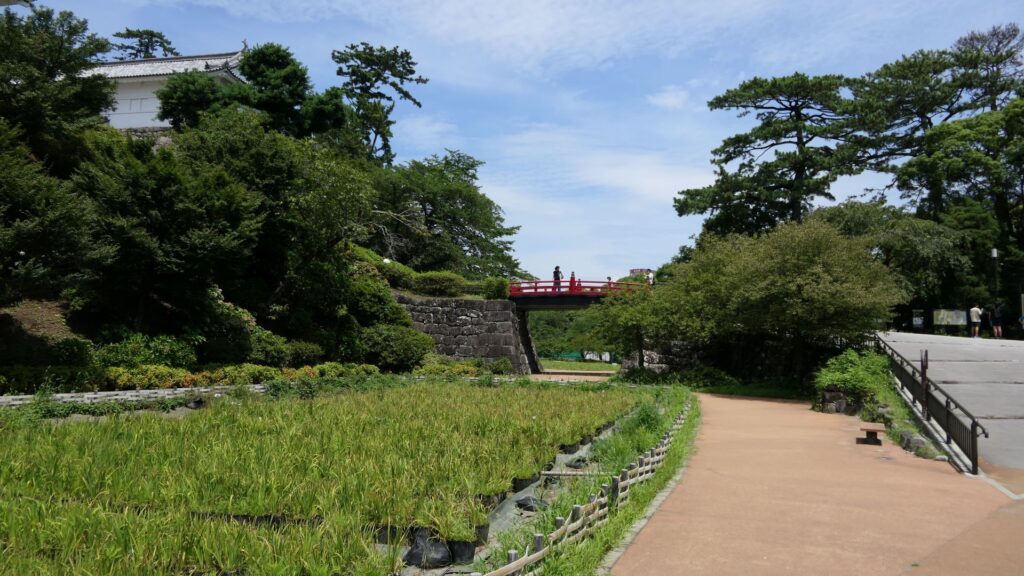

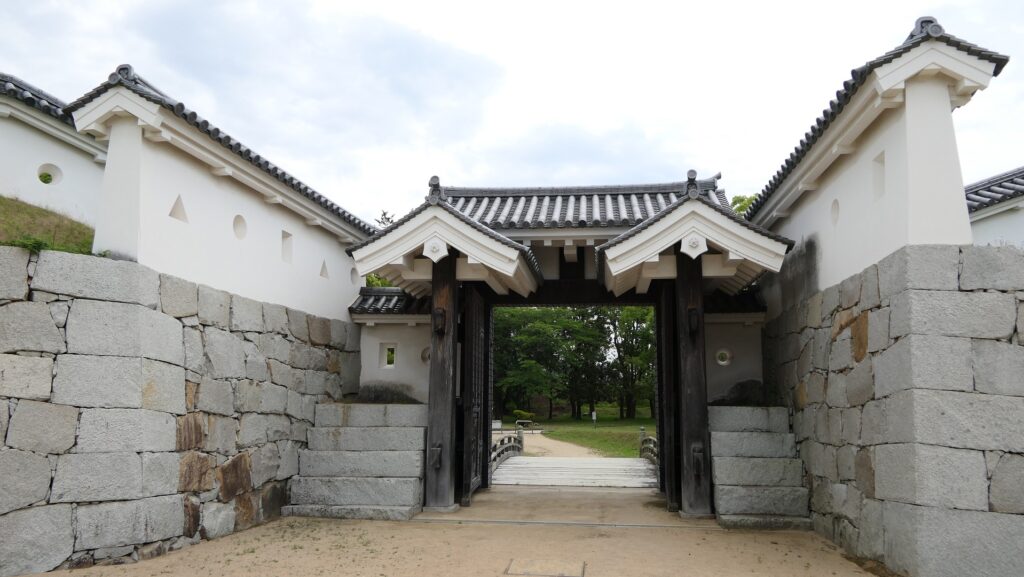
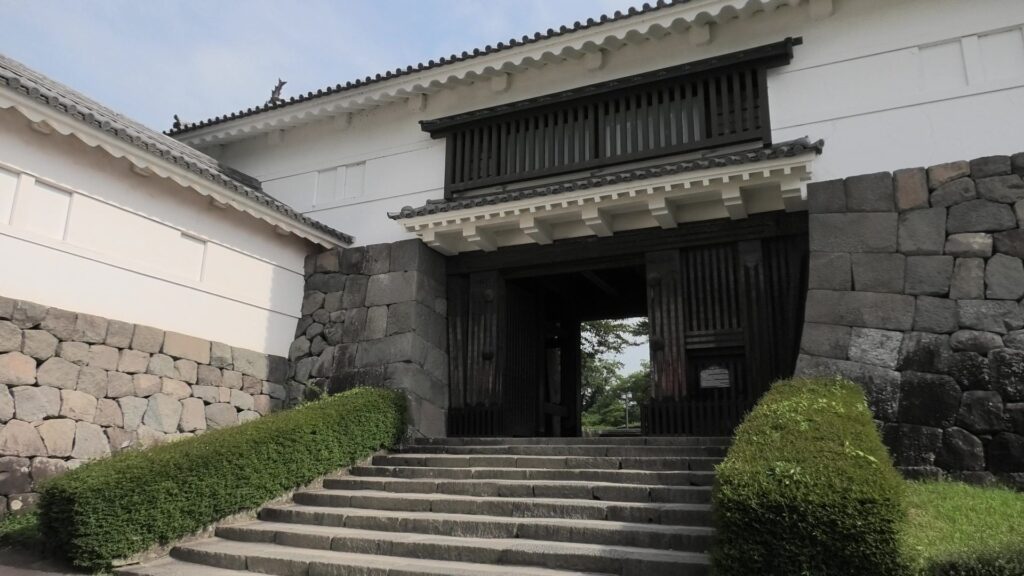
After crossing the bridge, you will finally enter the last gate, called Tokiwagi-mon. It was restored using concrete instead of wood. The original gate had the Masugata system as well, however, the final restoration lacks one side of the walls probably to make it more accessible for visitors.

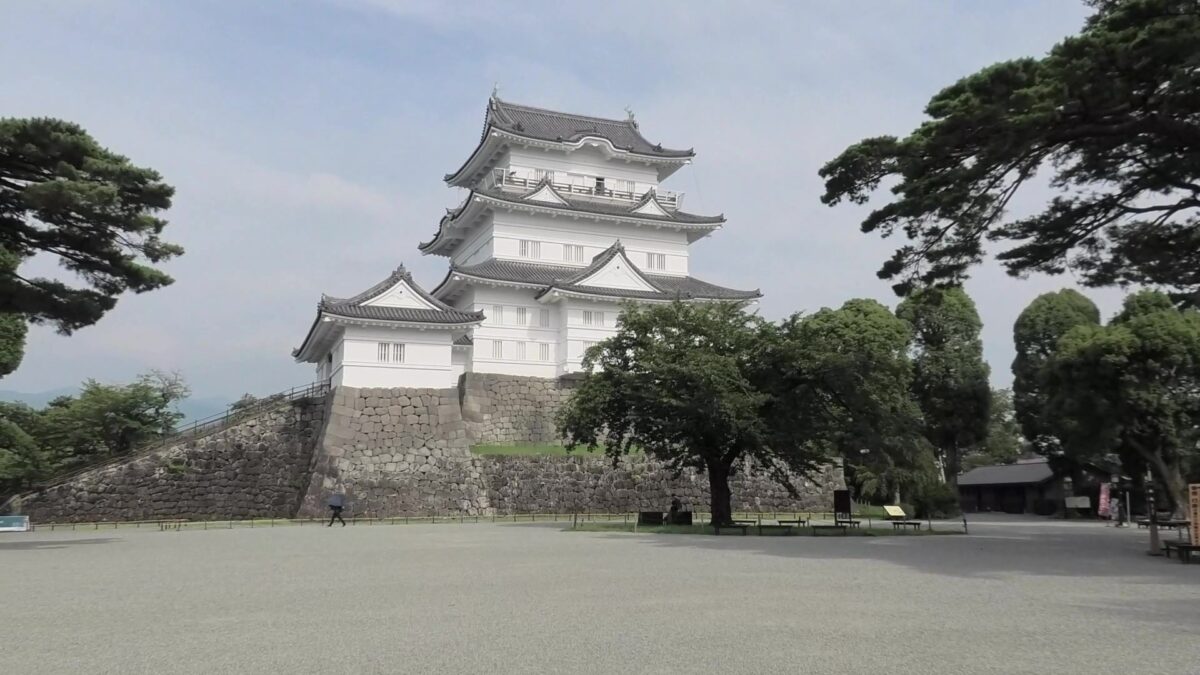
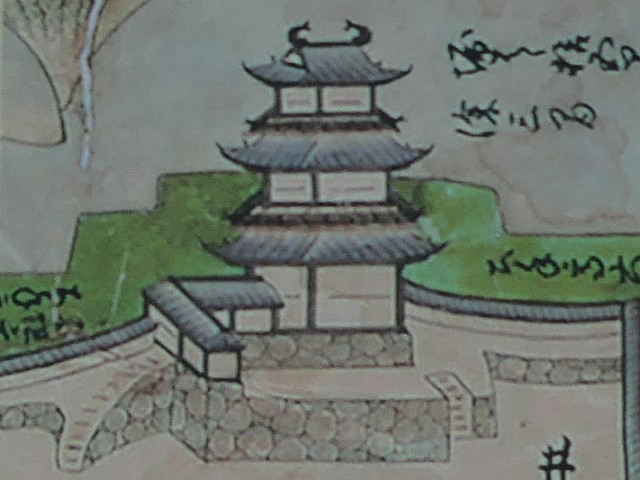
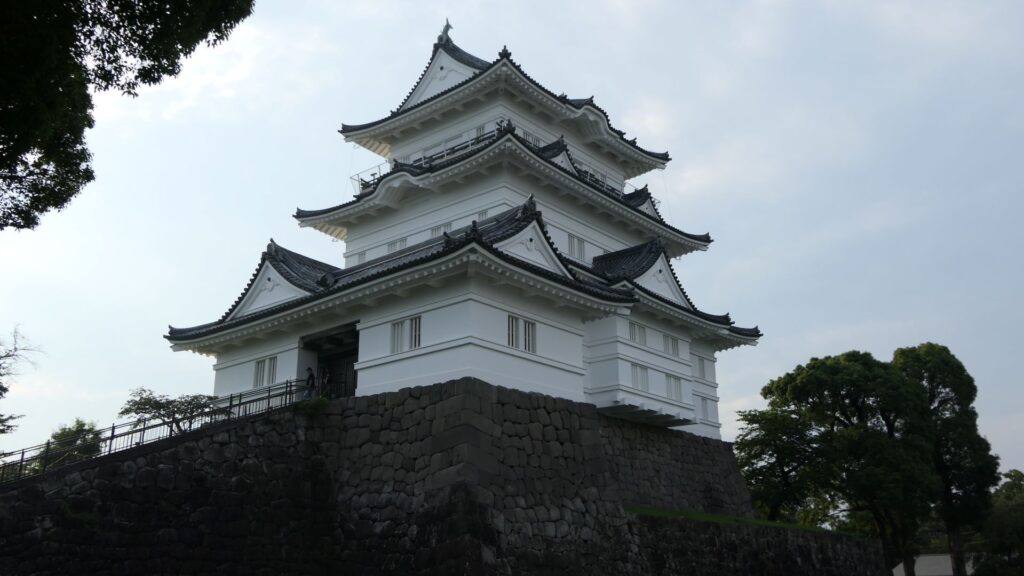
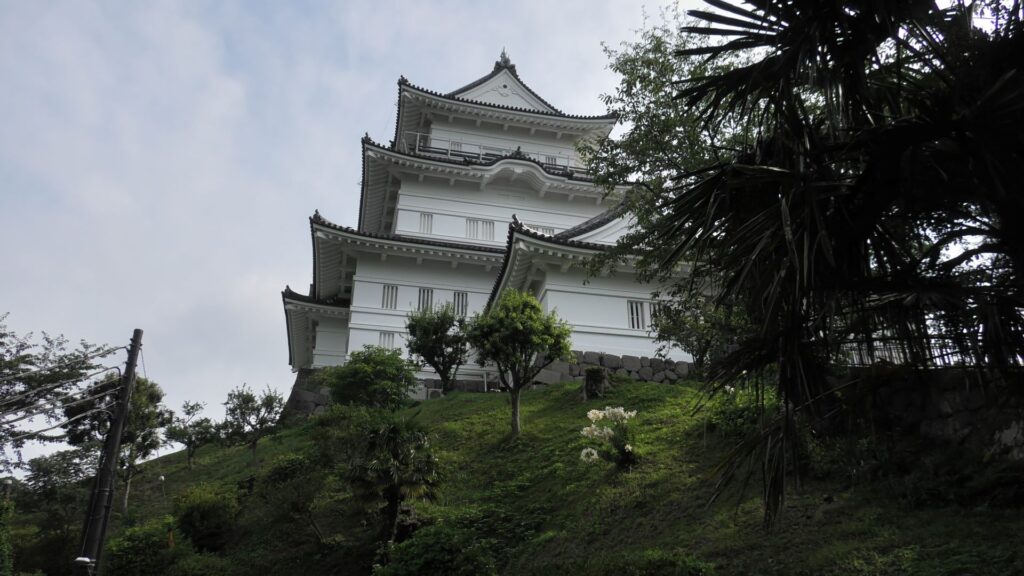
There is the reconstructed main tower in the main enclosure. It is very large for a three-level tower which is 27.2m tall and about 39m tall (including the tower base). The tower has four floors inside. It is the seventh tallest main tower among the existing ones in Japan. It is the fourth generation of the main towers of this castle, which was built emulating the miniature model and records of the third generation. However, the fourth generation has the observation platform for visitors on top, which is different from the design of the third generation tower. For this reason, the current tower is regarded not as “restored” but rather “reconstructed”. The inside of the tower is used as a historical museum, which was renovated are reinforced with earthquake-proof technology back in 2016.


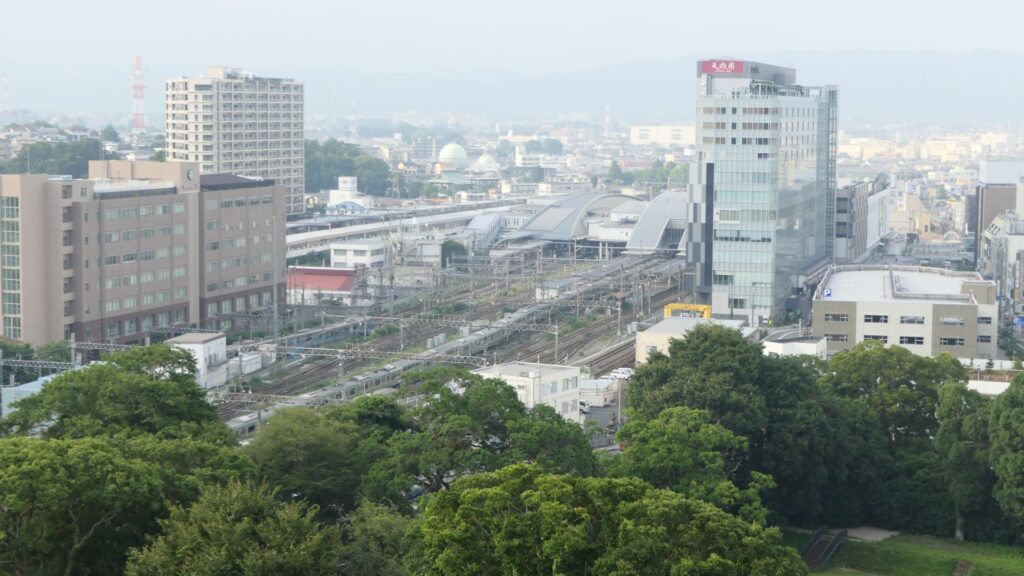
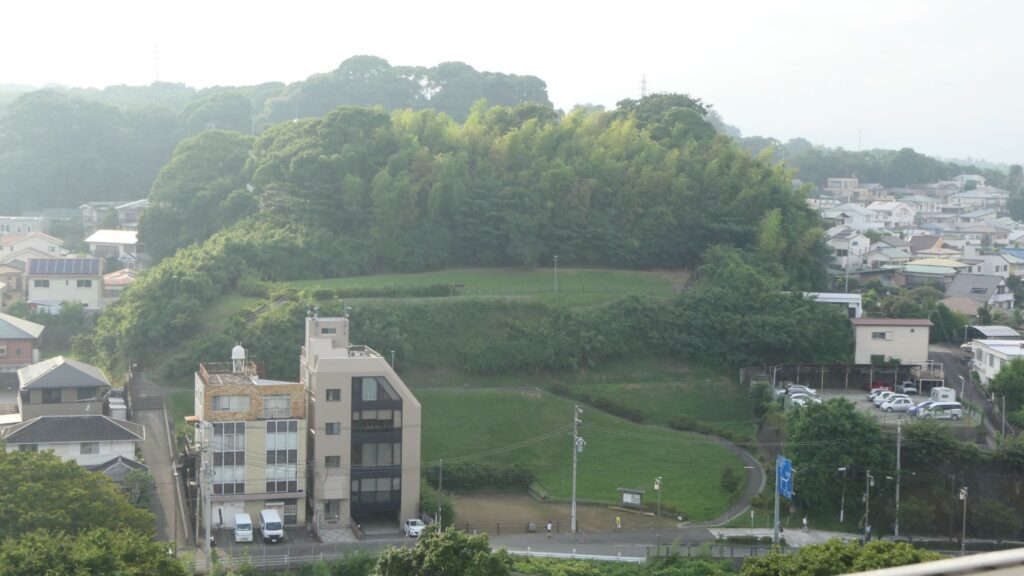
You can see views of Odawara in all directions from the platform, including where you’ve already visited.
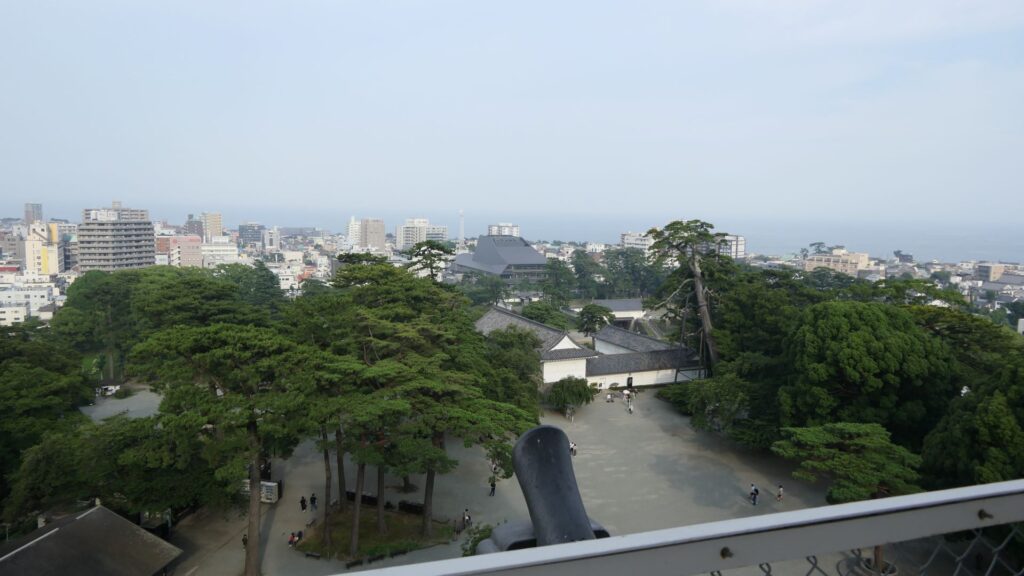
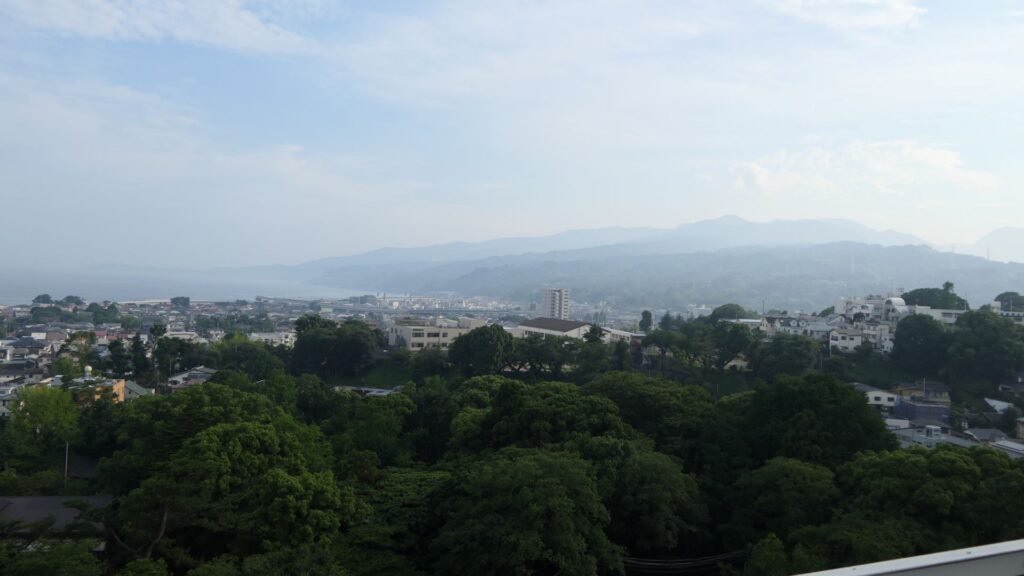




Hopes for the Future and Lessons of the Past
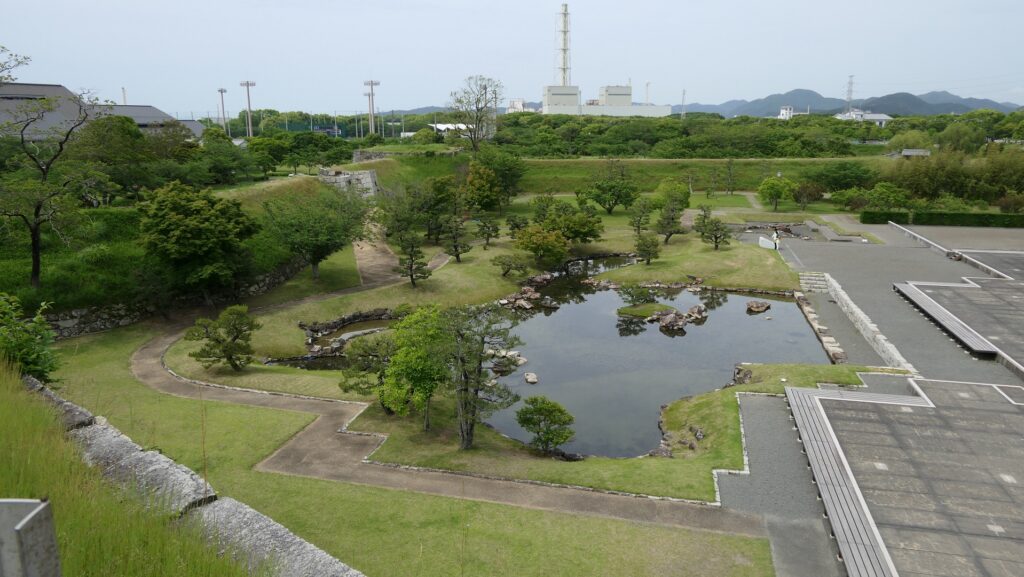
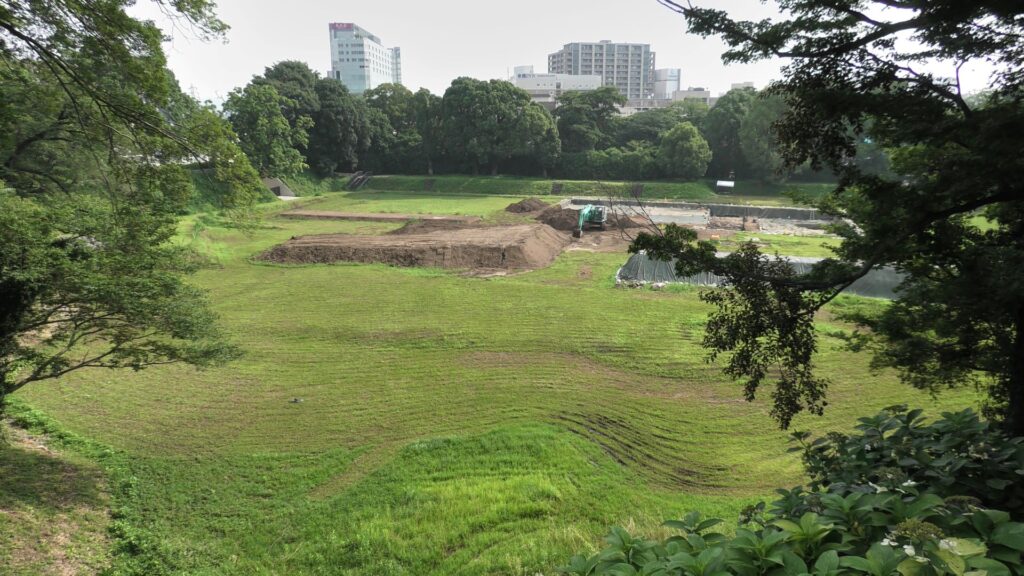
If you get out of the main enclosure through the northern exit, you will reach Goyomai Enclosure. (Goyomai means “official stored rice”) Unfortunately, you can not enter it because of the excavations. Instead, you can see the panels around, which showcases what were found there so far. For example, the ruins of a stone pawed garden, including beautiful cut stones, during the Sengoku Period were discovered. The site was turned into warehouses for rice during the Edo Period, which originated the name of the enclosure. I’m looking forward to seeing this site again after it becomes more developed.



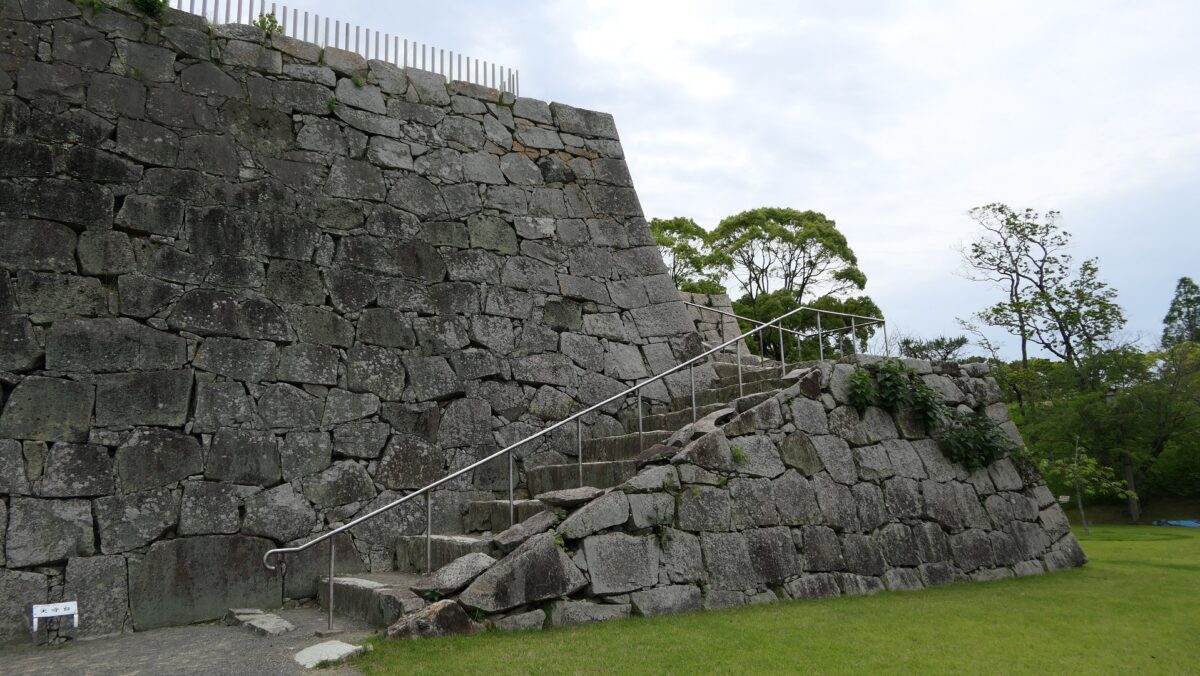
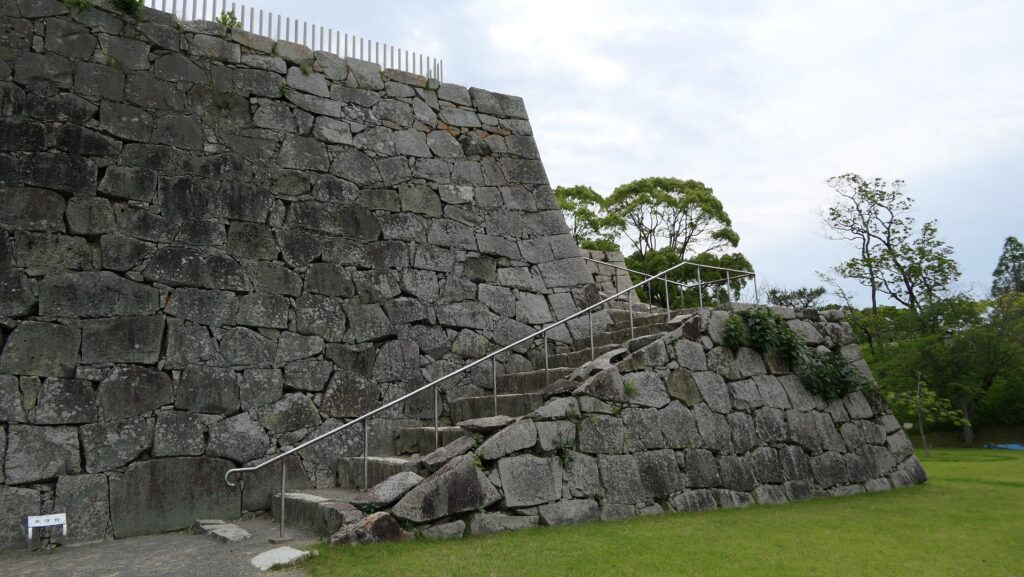
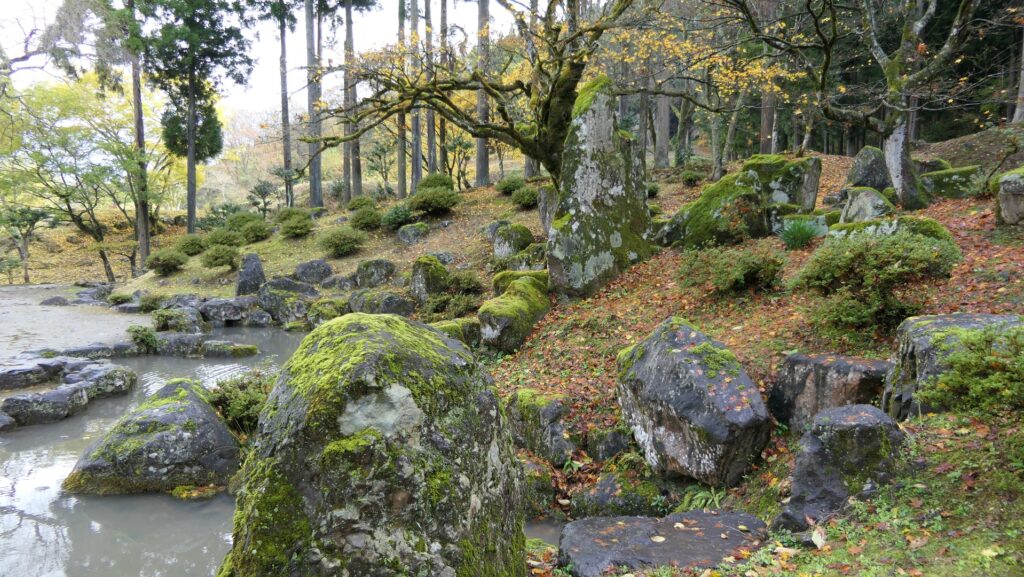
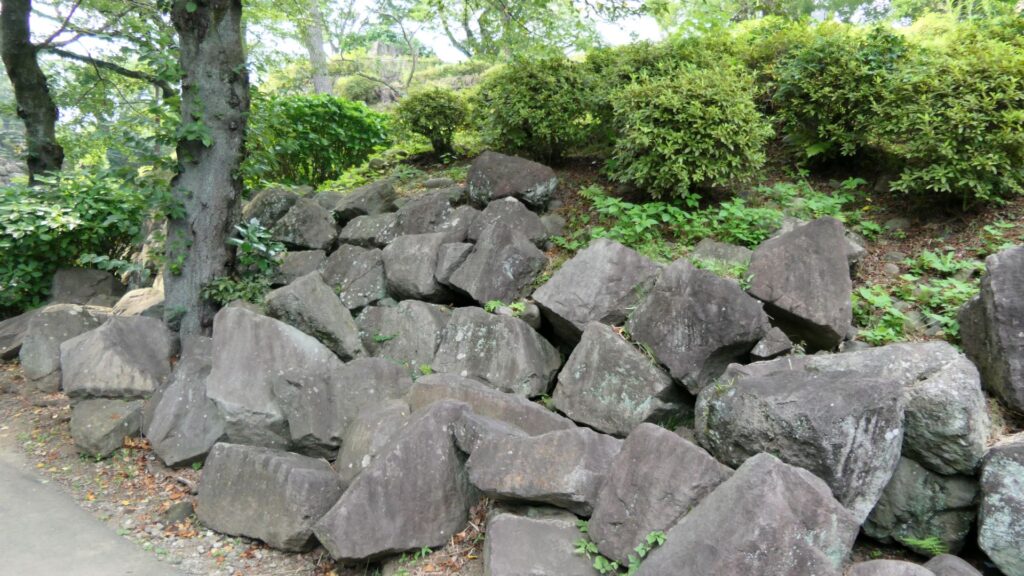
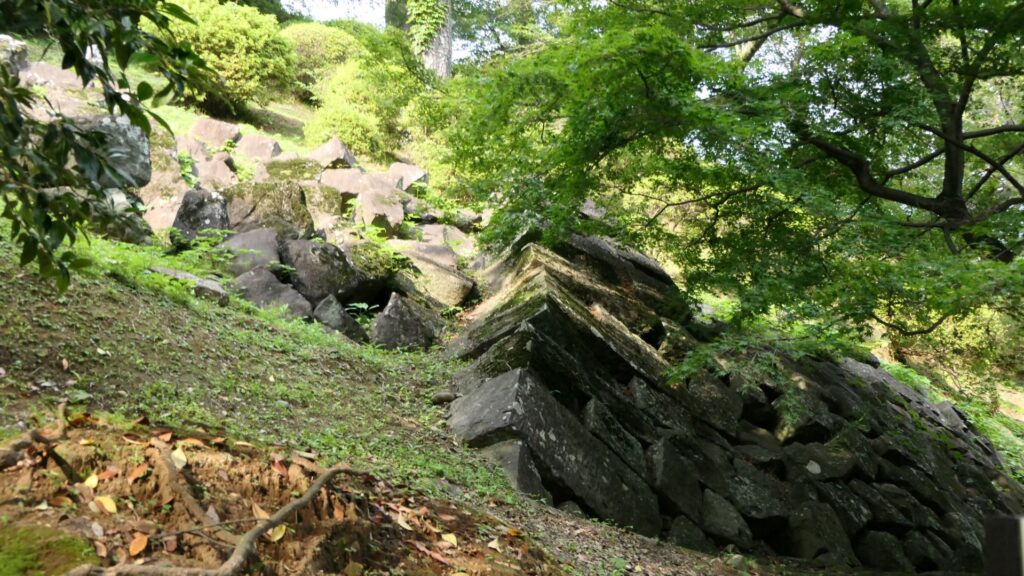
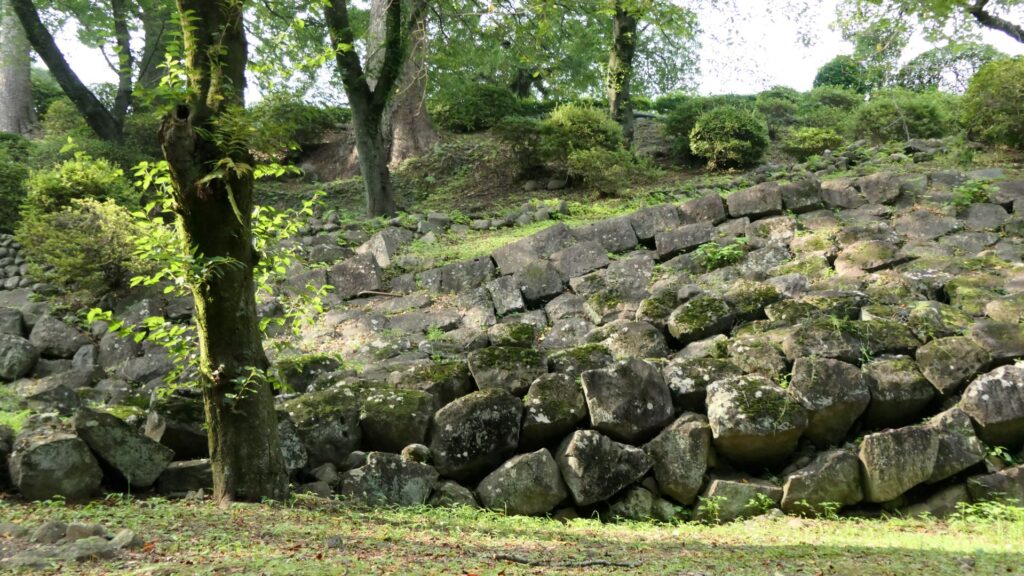
If you go to the southern slopes of the main enclosure, you can see a lot of large stones at the foot which collapsed during the Great Kanto Earthquakes. In fact, the stones were used for the stone walls which covered the top of the enclosure. Some of the stones are still connected to each other forming a curve. That means they slid down from the top to the foot keeping the form when the earthquakes happened. It must have been caused by the enormous strength of the earthquakes. The exhibitions made me realize how important being prepared for disasters is.


Finally, It may be a good idea to visit the southern moat nearby. It is also known as “lotus moat” which uses the same name during the Sengoku Period. You may be seeing the same scenery as people at that time, which shows the castle has a long history.


My Impression
There are a lot of attractions about Odawara Castle from the Sengoku Period to the present time. Maybe you will need more than one day to see all of them. The lords of the castle achieved many things. For instance, they constructed one of the greatest castles and rebuilt the main towers three times. These works were passed down from one lord to the next. It may look simple, but it is difficult to maintain. I speculate that if another disaster happens in the future to Odawara, people there will survive along with Odawara Castle. They could be a role model for other people under similar situations in the future.

That’s all. Thank you.
Back to “Odawara Castle Part1”
Back to “Odawara Castle Part2”