Location and History
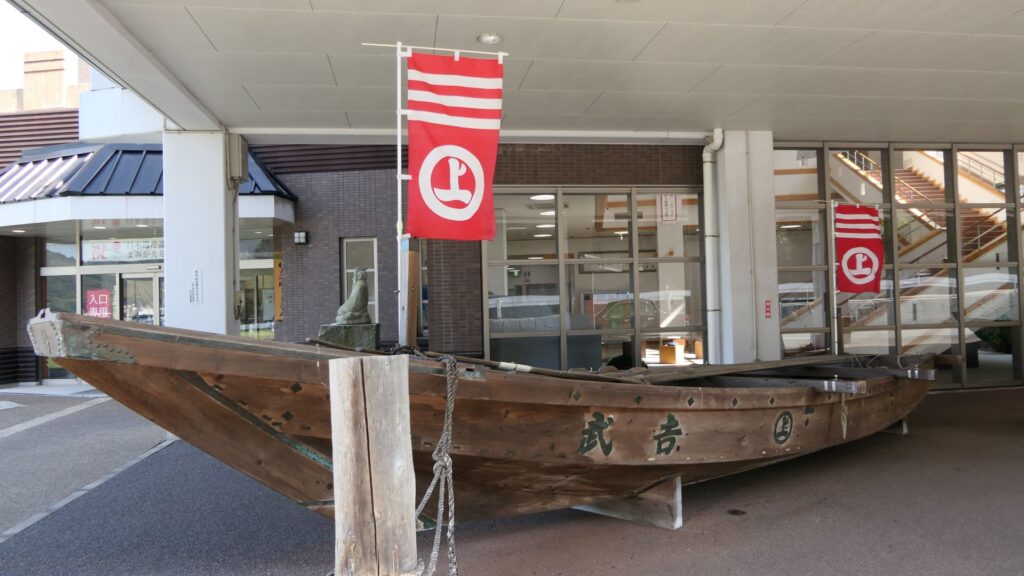
Murakami Navies, Excellent Guides of Seto Inland Sea
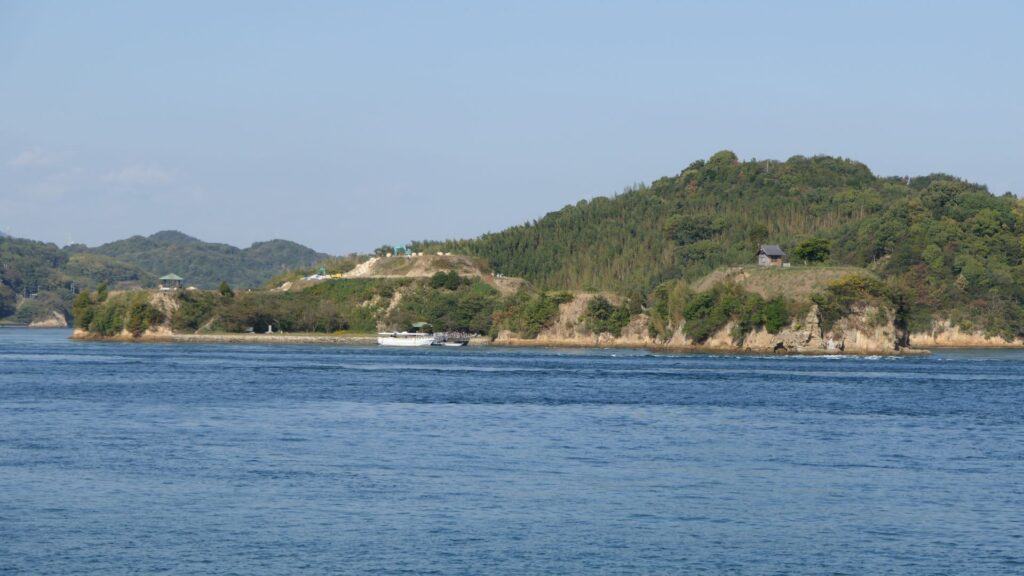
Noshima Castle was located on Noshima Island, which is in a narrow strait called Miyakubo-Seto, and part of the Geiyo Islands in the Seto Inland Sea. It was also built and operated by the Noshima-Murakami Clan, one of the three Murakami Navies which were very active around these islands. Before modern times, sailing along the coast was a major way of transportation. Seto Inland Sea was one of the most important sea routes, which connected central and western Japan. However, the Geiyo Islands area has lots of islands and narrow straits, which made the sea currents fast and difficult. For example, in Kurushima Strait, the direction and speed of the current frequently changes mainly due to the pull of the moon. Ships are still now required to follow instructions from the sea traffic center and its traffic signals.

In the Middle Ages, boatmen and pilots, who sailed there, were required to have great competence instead. In addition, sailing alone could be very dangerous at that time as the police power of the central government was still weak. Each area was governed by a local lord or others, such as pirates. People at that time thought travelers should pay a toll when they passed others’ territories. The Murakami Navies, which were also some of the local lords, came out to guarantee safe travel to ships around the islands. The earliest record about them in 1349 says the Noshima-Murakami Clan guarded the sea around Yuge Island. Their system was roughly as follow: they escorted ships which had paid protection money (basically 10% of the value of the cargo), otherwise, they became pirates by chasing the ship using their boats called Kobayabune (meaning “small fast boat”).

Home of Noshima-Murakami Clan
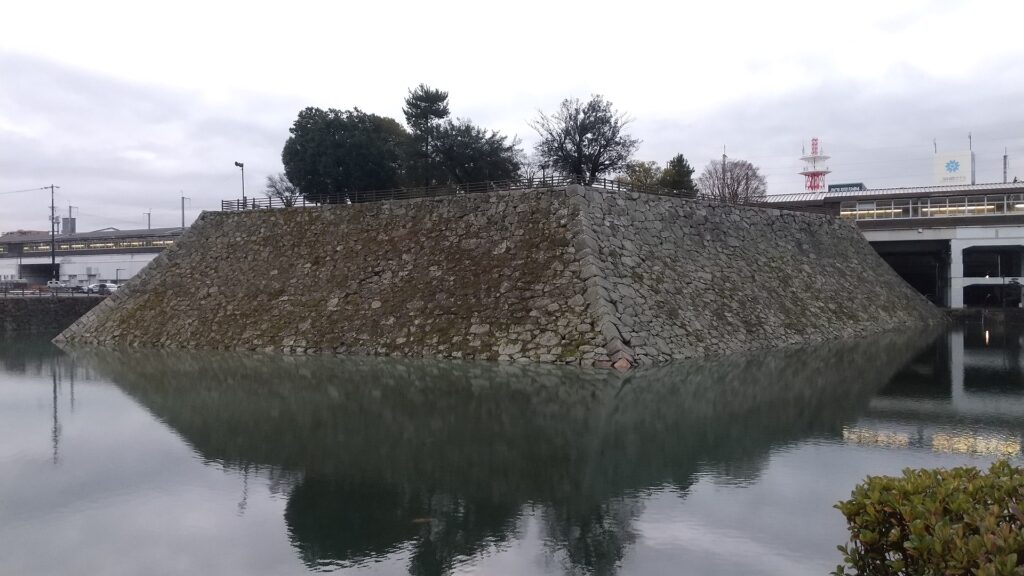
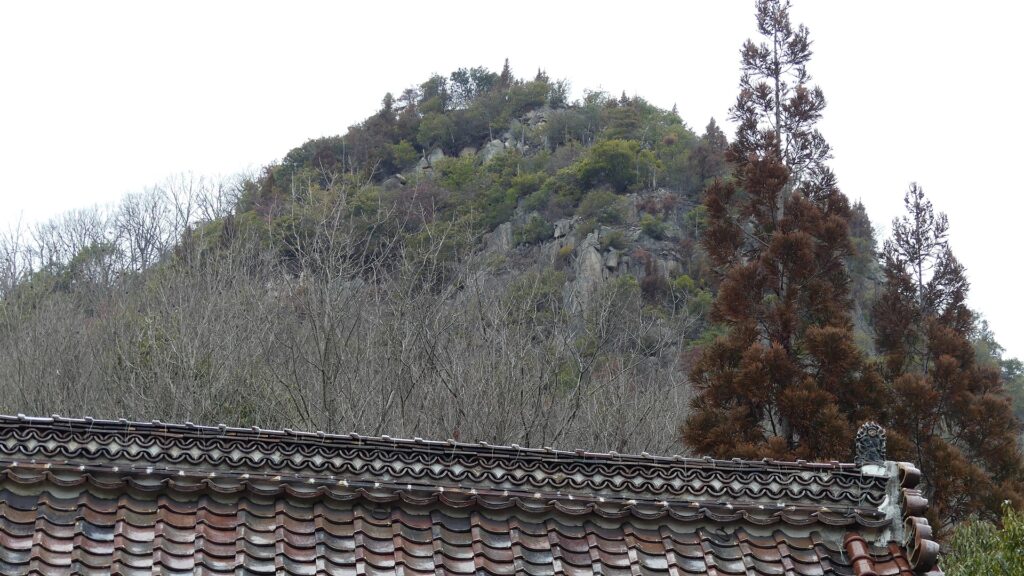
The navies were eventually divided into three clans: the Innoshima-Murakami, Noshima-Murakami, and Kurushima-Murakami Clans. Their territories were based on the northern, middle, and southern Geiyo Islands respectively. Noshima is a small island in the Miyakubo-Seto Strait which is between Ushima Island to the north and Oshima Island to the south. The strait was on one of the shortest paths for ships to pass through the Seto Inland Sea. However, the speed of the current is at most around 10 knots and kept changing constantly. The sea around the island is shallow and kept swirling, which is uncontrollable for regular ships. For the navy members, Noshima is about 300m away from Oshima Island where they usually live, so they could communicate verbally. That meant they could immediately ask or provide help to each other in the event of an emergency. From the top of Noshima, they were able to see the whole strait, beacon fires on mountains of Oshima Island and even Shikoku Island over Oshima between the mountains. Overall, it was suitable for the home base of the Noshima-Murakami Clan.
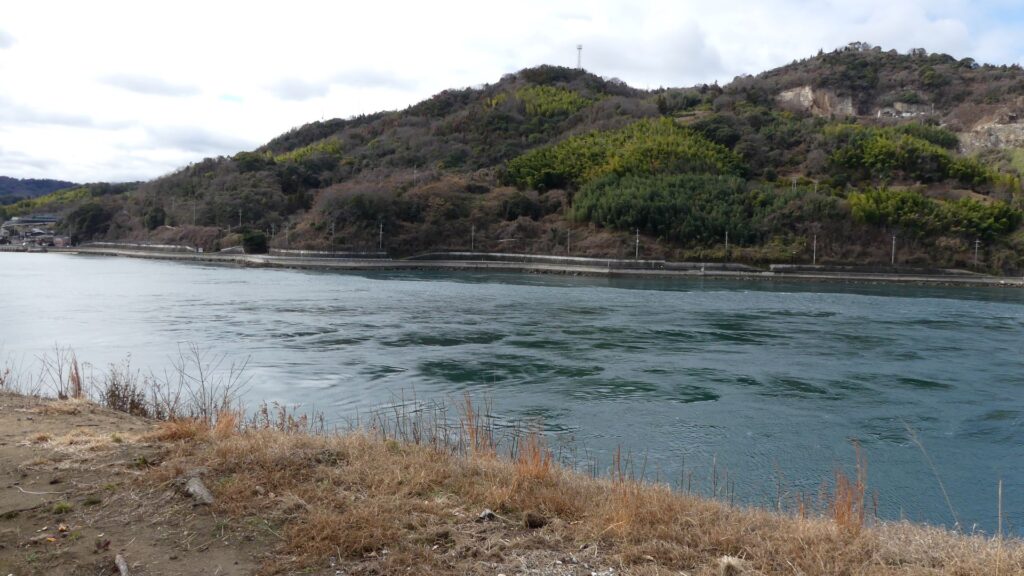
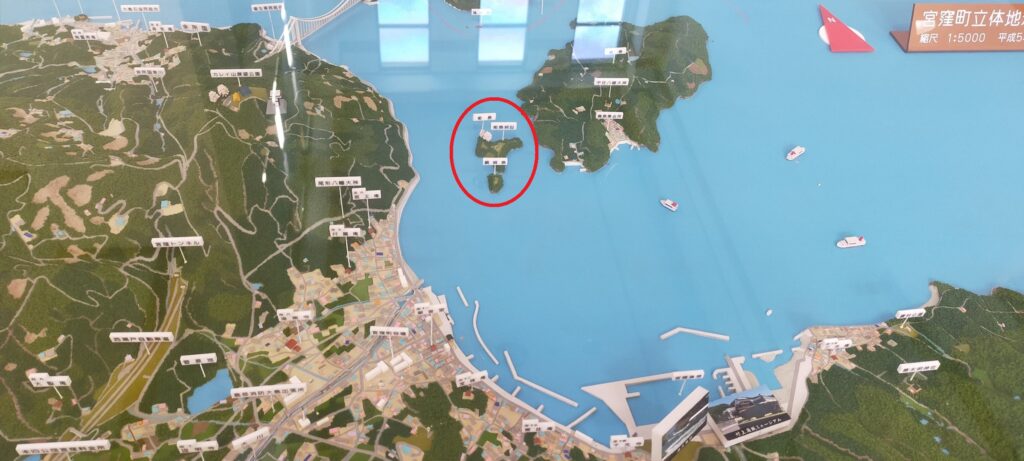


They operated Noshima Castle on the island between the 14th and 16th Centuries. Several enclosures and buildings were built after leveling the land. The navy members lived in or were stationed at the site not only to guard the strait, but also to trade and fish. The defensive systems of the castle were few, excluding artificial vertical cliffs on the sides, because its sea barrier was strong. Instead, they constructed harbors, landing places and maintenance yards at the seaside. On the other hand, the island didn’t provide water, food and other supplies they needed, which had to be brought from other islands.
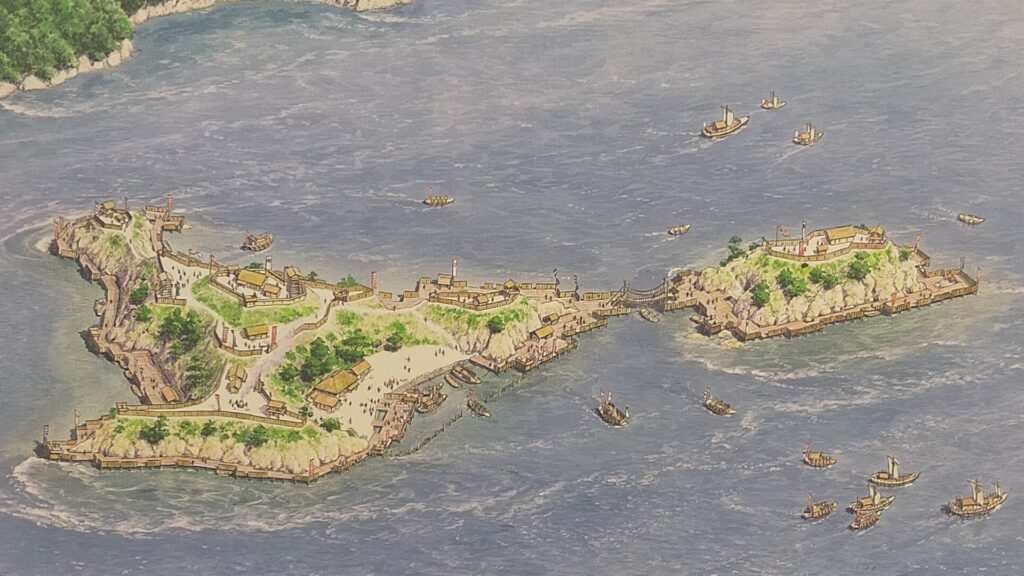

“Largest Pirates of Japan”
The Murakami Navies also often joined battles to support other warlords. In the case of the Noshima-Murakami Clan, it had a good relationship with the Kobayakawa Clan, a branch of the Mori Clan which was the greatest warlord in the Chugoku Region nearby. They needed the superior navy power to survive during the harsh Sengoku Period. Other warlords, such as the Otomo Clan, also invited the Noshima-Murakami Clan. When it once switched to the Otomo’s side, the Kobayakawa Clan, which also had a navy, attacked and blocked Noshima Castle by interrupting the supplies (laying siege) to the castle until it returned to the Kobayakawa’s side.

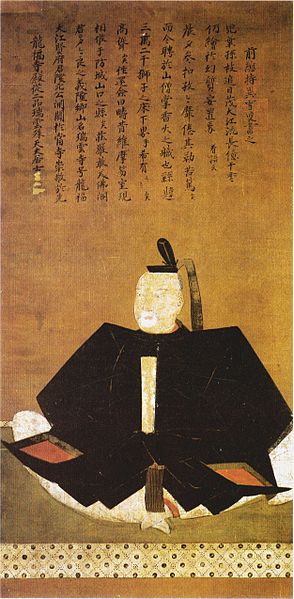
The power of the Noshima-Murakami Clan reached its peak when Takeyoshi Murakami was the lord during the late 16th Century. The most popular battle his navy fought in was the First Battle of Kizugawaguchi between the Mori and Oda Clans in 1576. In this battle, the Mori’s navies, supported by the Takeyoshi’s navy, who tried to bring supplies to Ishiyama Honganji Temple (currently Osaka Castle), and blocked by the Oda’s navies. Tekayoshi’s navy attacked the Oda’s ships with bombs, which eventually burned and sank. The supply operation was a success. In 1586, a Portugal missionary, Luis Frois visited Noshima Castle while sailing the Seto Inland Sea. He recorded in his book “The History of Japan” that they were the largest group of pirates. His crew was given a passport-flag which would guaranteed his safe voyage considerably.
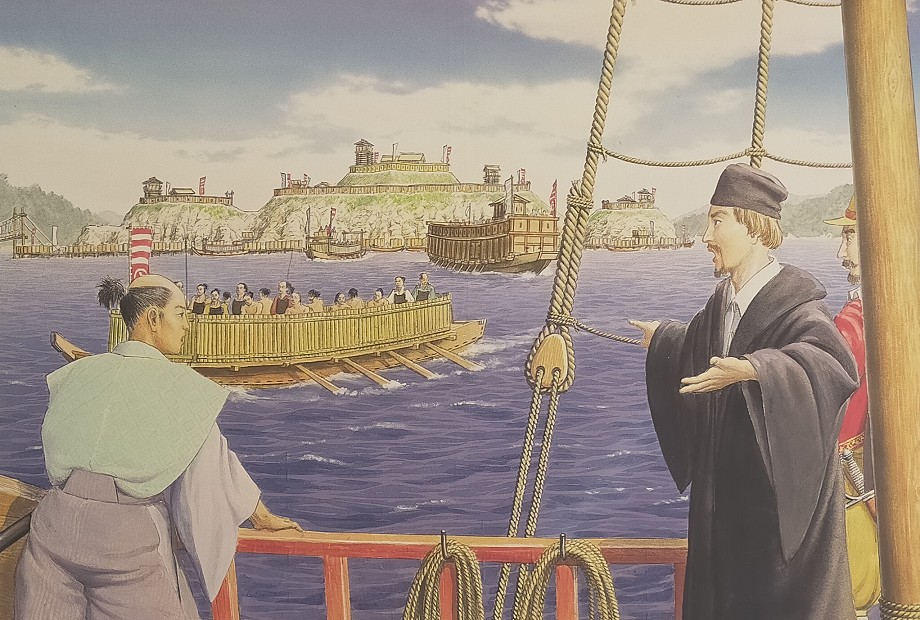



Sudden Ending of Navies and Castle
The three Murakami Navies basically cooperated with each other, however, they eventually took different paths. The Kurushima-Murakami Clan switched to the Oda’s side through the invitation of Hideyoshi Hashiba, who would later be the ruler. Therefore, Takeyoshi occupied the Kurushima’s territory. However, this would be a misfortune for him. In the process of the unification of Japan by Hideyoshi, he was asked to return it to the Kurushima by Hideyoshi. He seemed to want to maintain his clan’s independence. However, when the Kobayakawa Clan, which was the current boss of the Noshima-Murakami Clan, was transferred to the Kushu Region by Hideyoshi, Takeyoshi finally had no choice but to leave all his territories including Noshima Castle.