Features
Is Main Enclosure being improved?
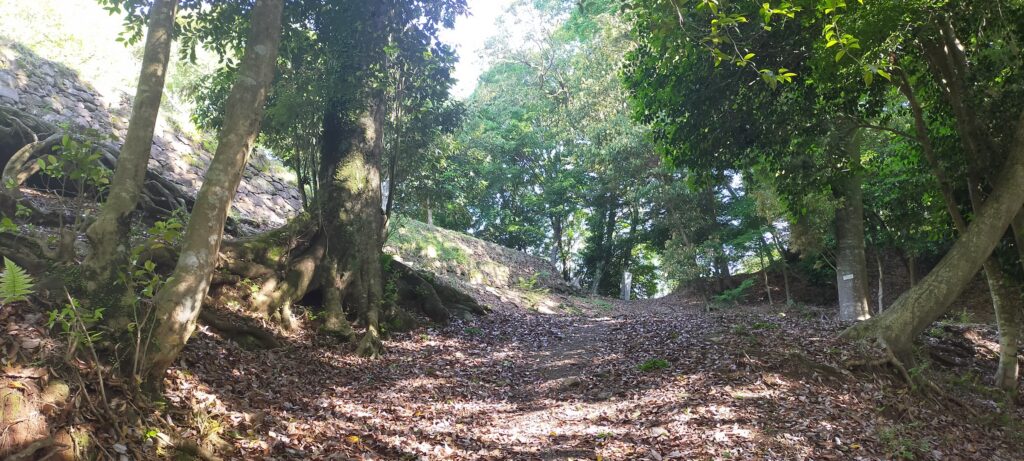
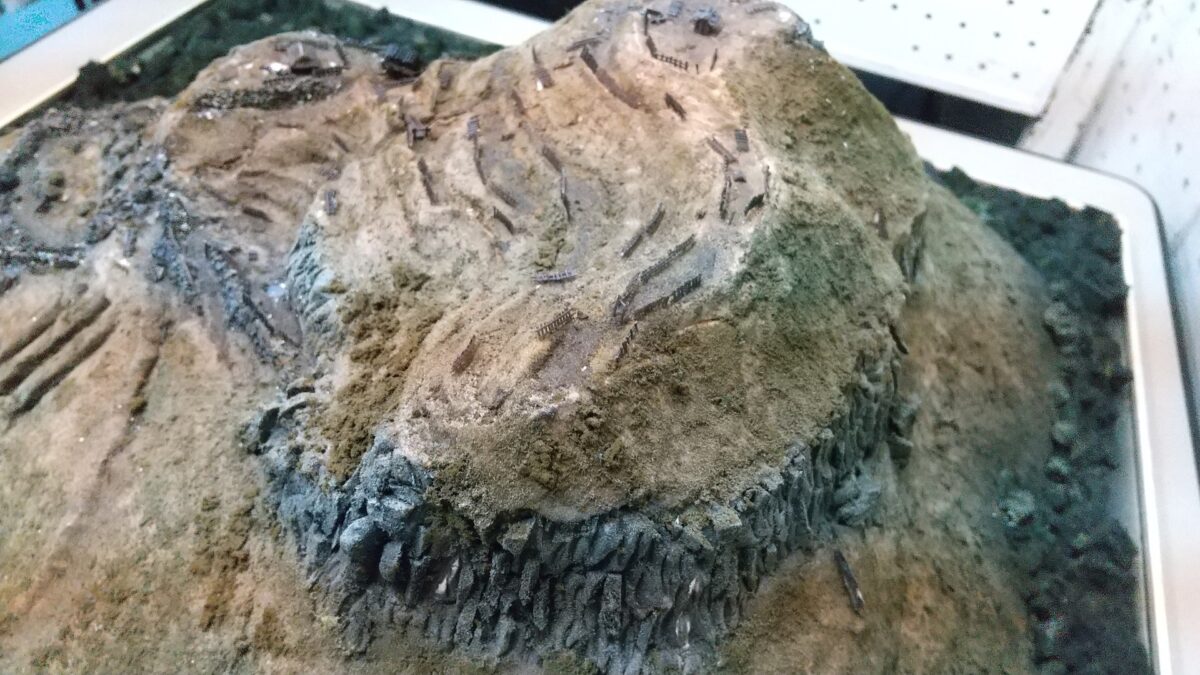
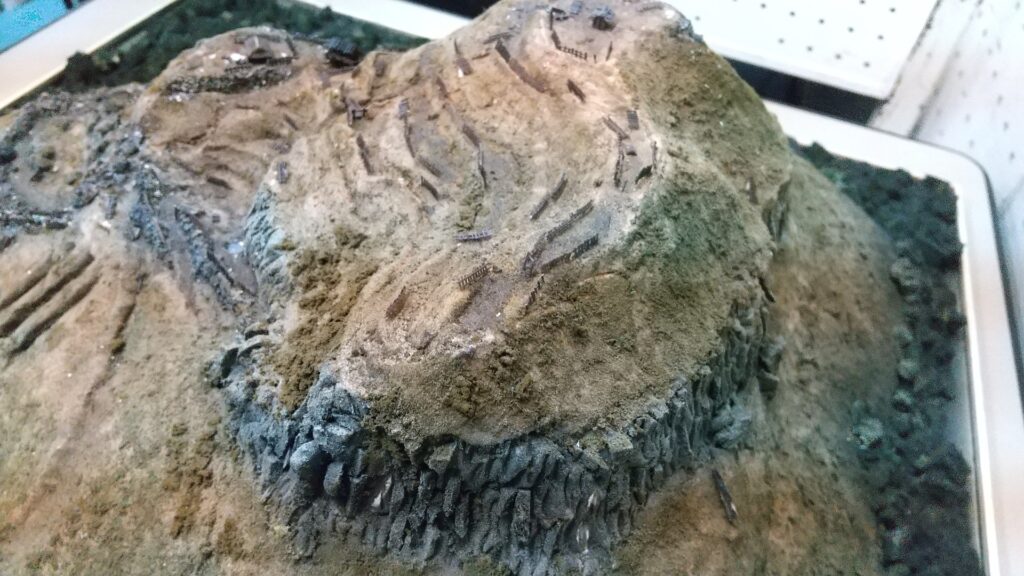
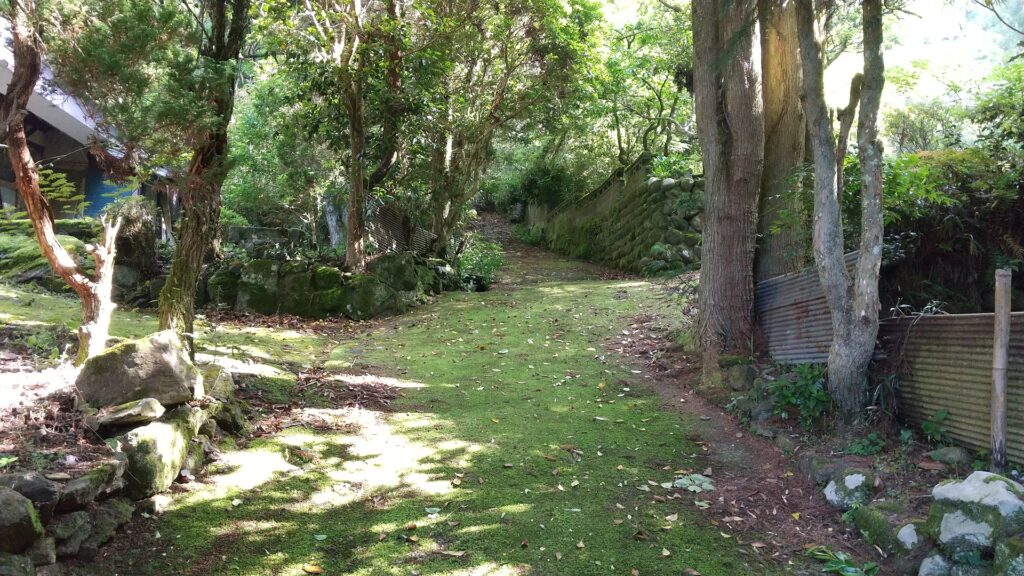
However, the Main Enclosure on the top looks different. Around the Main Enclosure there are no stone walls, but it has the Vertical Cliffs which were artificially cut, made of soil. This method had also been used in the castle before Takamasa Mori came. You will walk around the natural-like path to the enclosure (the straight path for the repair work to it should not be used).
The map around the castle


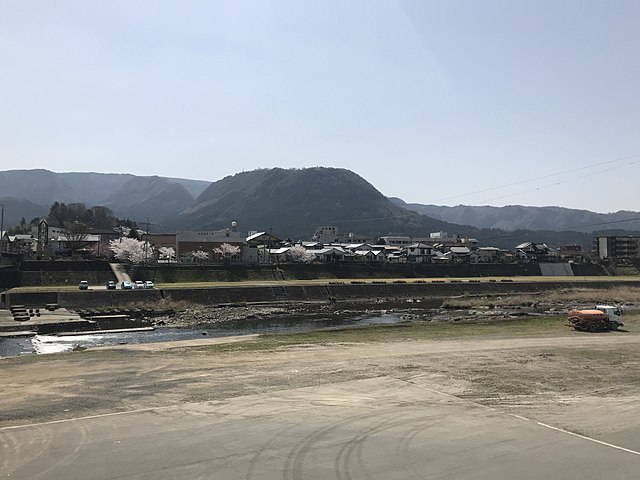
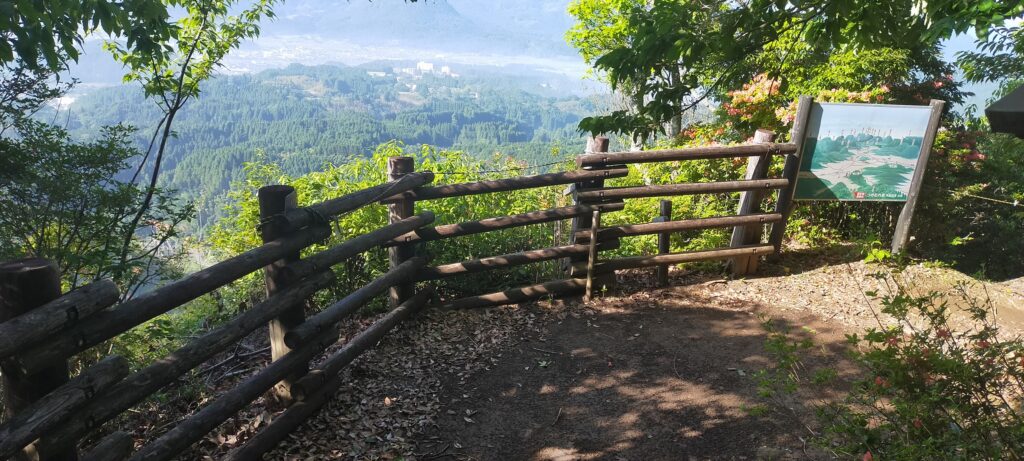
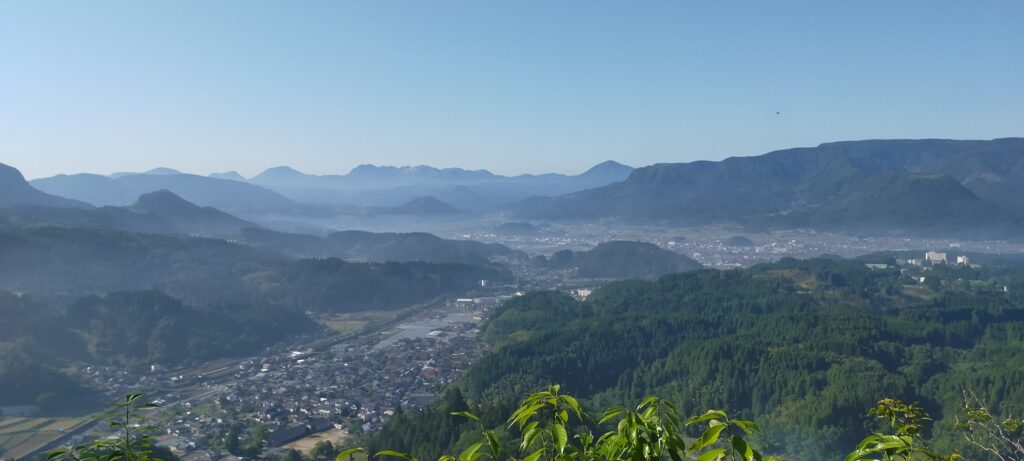
There is the observation platform on the way, where you can enjoy a great view of the Kusu area with lots of mesas or buttes, which look very beautiful.


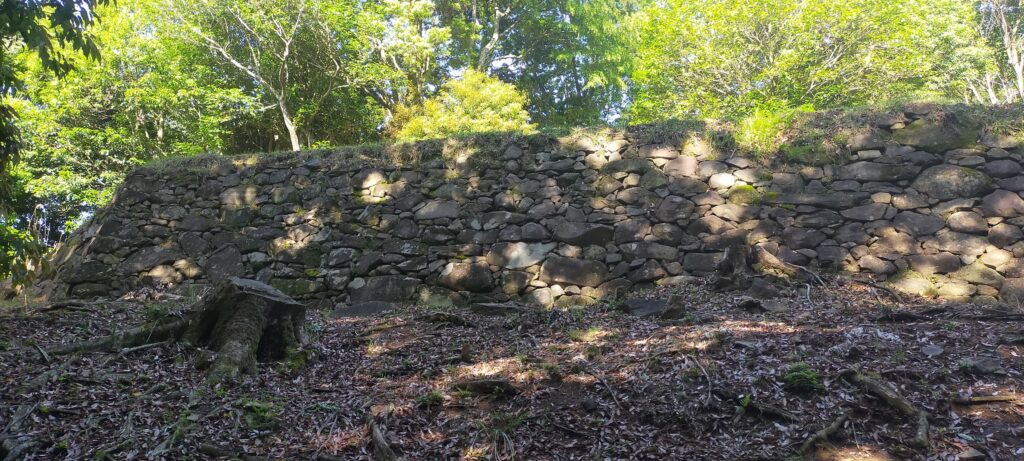
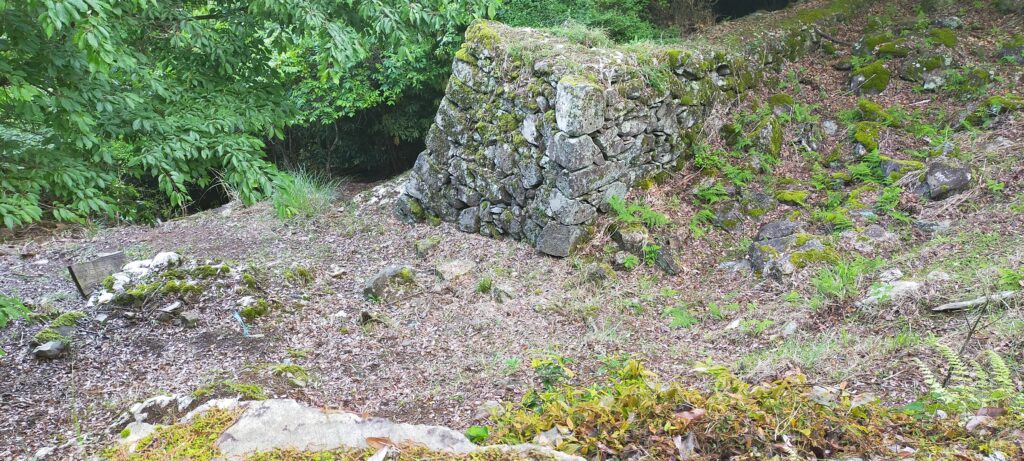
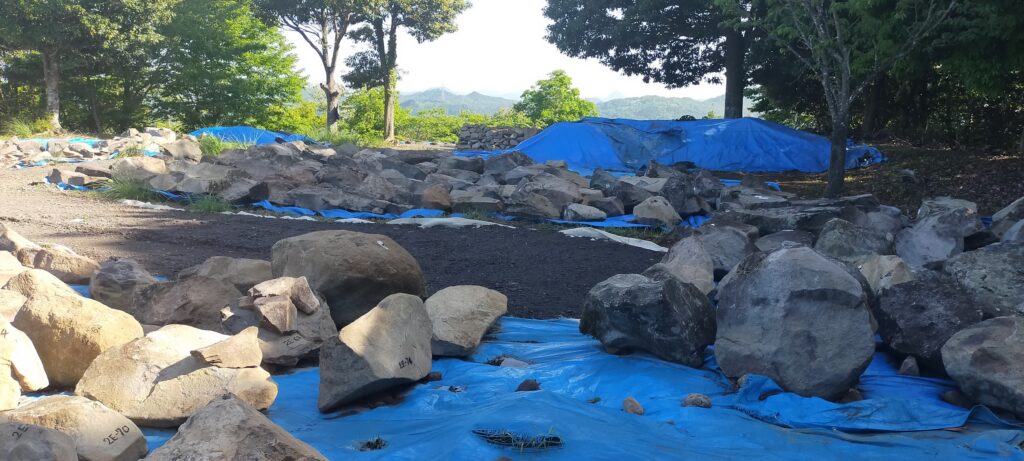
When you arrive at the top of the Main Enclosure, you will see many stones lying on it (as of May of 2023). This is because Takamasa built stone walls only at northern side of the enclosure. The official are repairing them after they collapsed. Maybe Takamasa was also improving the Main Enclosure until he was transferred.



Attractions of Mori Domain
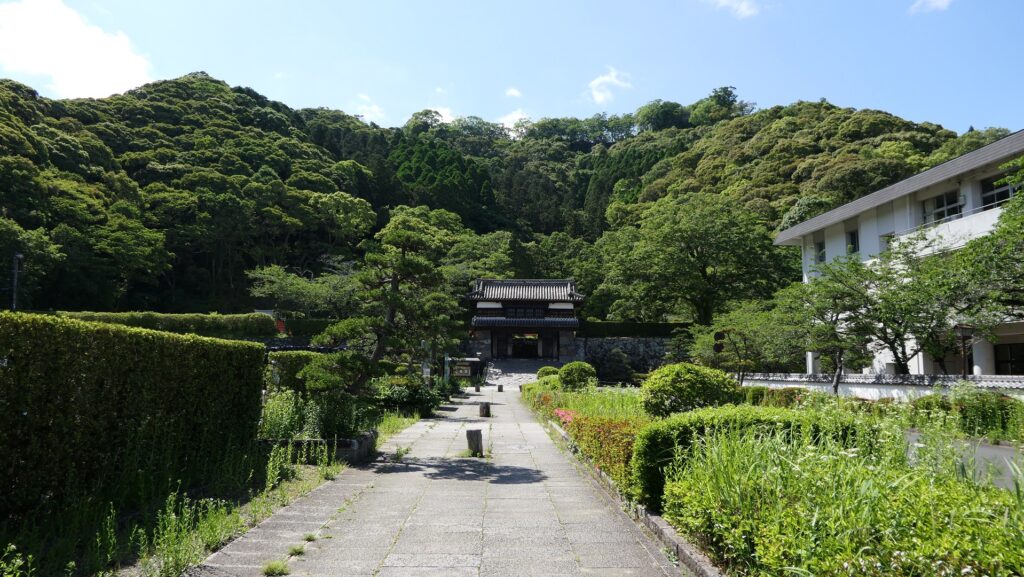
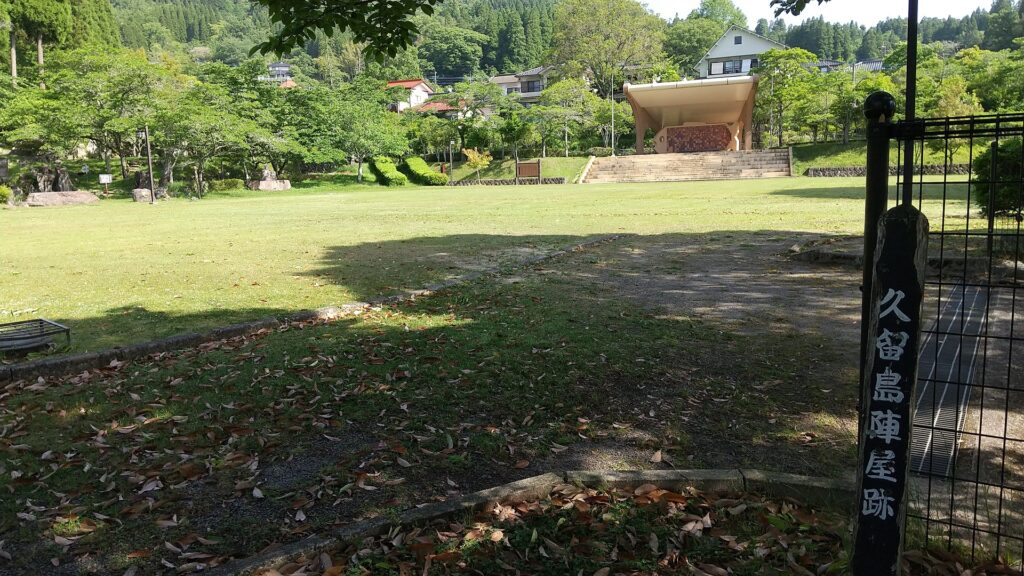
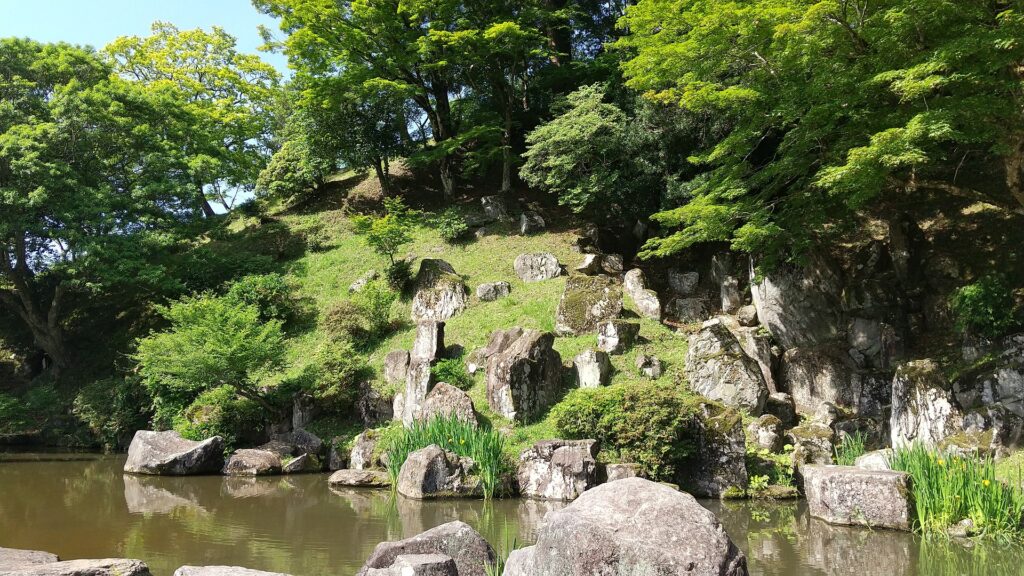
You can also visit the attractions of the Mori Domain which the Kurushima Clan established at the foot of the mountain. The lords of the domain lived in an encampment which was turned into a park. The clan also built a pond garden with a circular promenade beside a hill next to the encampment, which remains now.

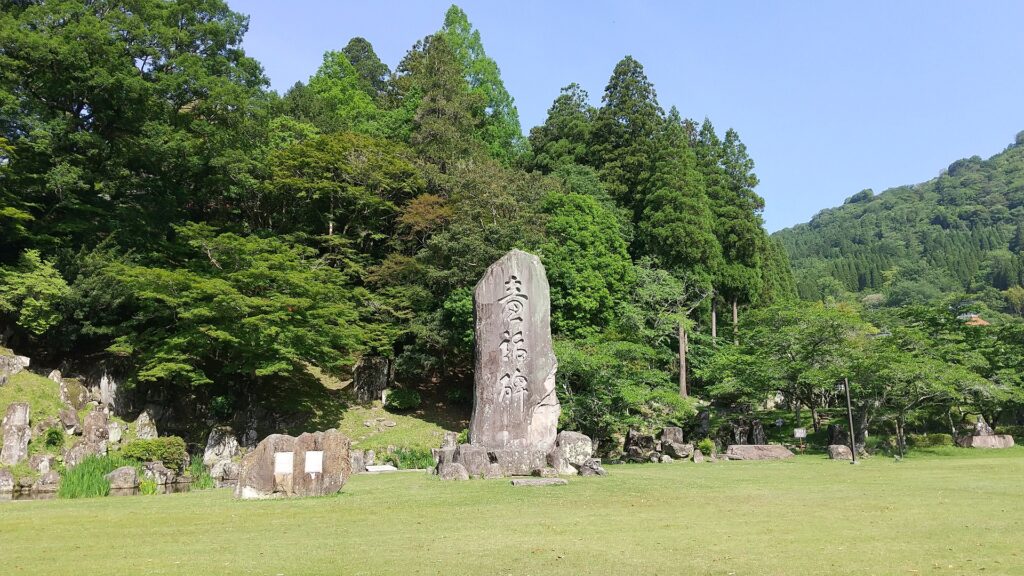
There is a 7m tall monolith standing in front of the garden, called Dowa-hi or the Monument of Fairy Tales. This was not originally part of the encampment, but it was originally used as a stone for the harbor at a river nearby when the domain was thriving. The monolith was moved to the current position and reused as the monument in 1949, named after a famous writer of fairy tales, Takehiko Kurushima who was a descendant of the lord’s family.

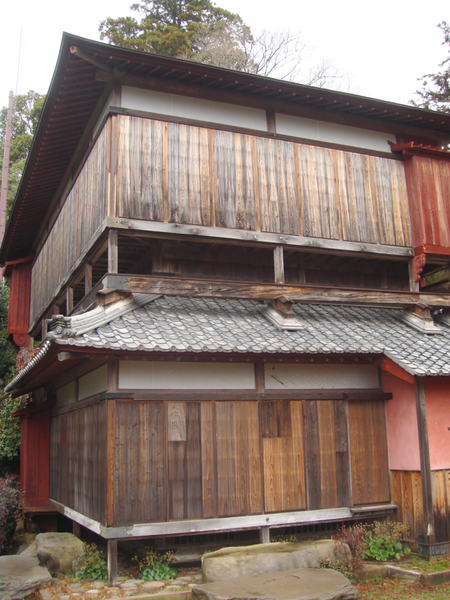
The clan also built a tea room on stone walls, called Seihoro, on the hill, which also remains. It is said that the room was built as a substitute for a Main Tower which was not allowed to be built by the lord of the clan.

Later History
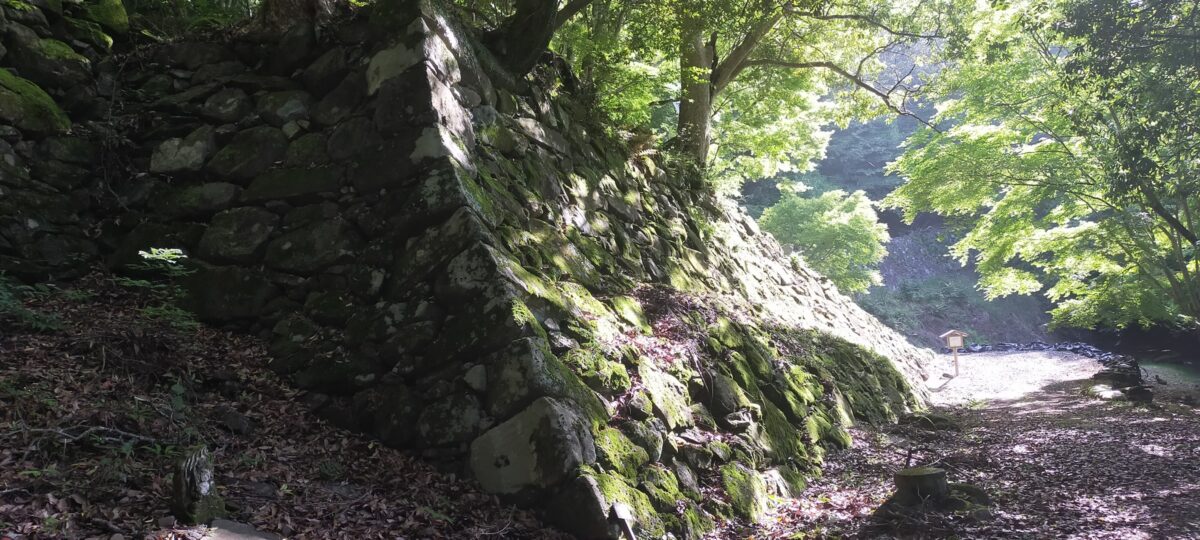
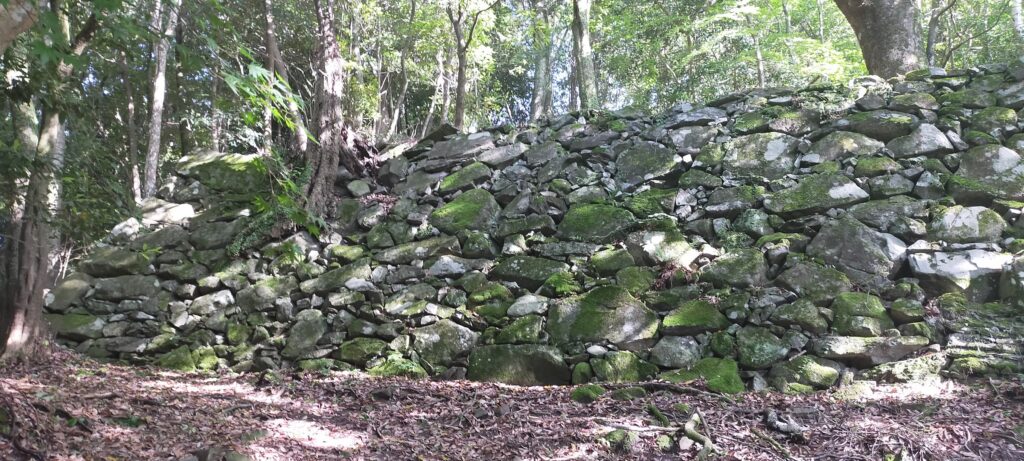
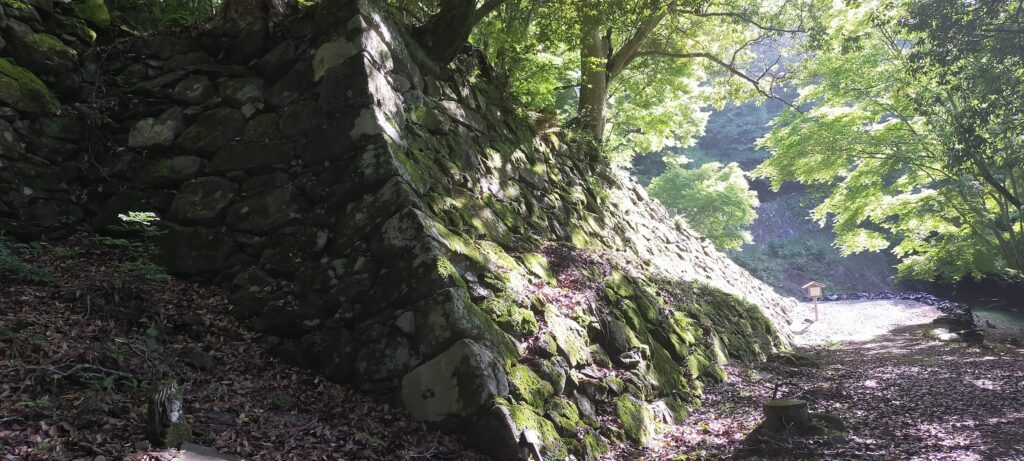
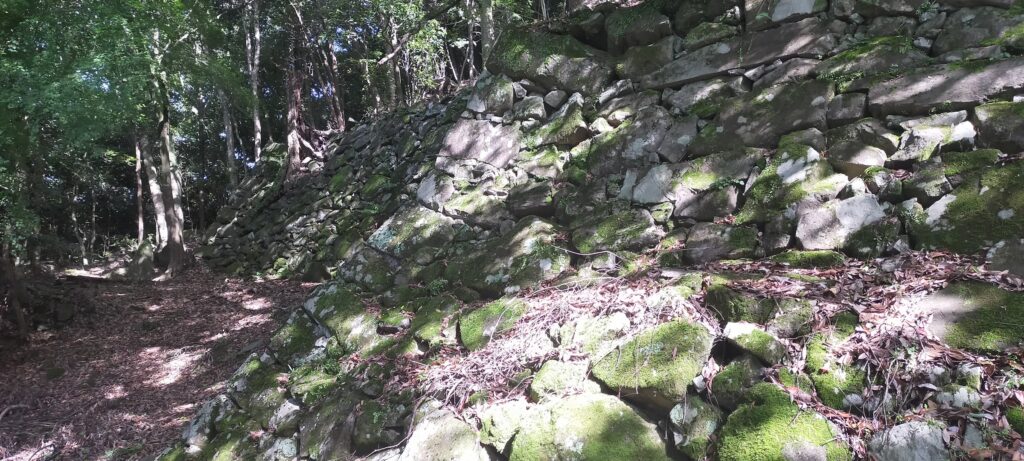
The research of Tsunomure Castle was launched in 1993. It found that the ruins still have an example of the Ano-zumi stone walls in a good condition, which Hideyoshi’s retainers built in many areas during his unification of Japan. It also found that the ruins show the process of castles’ improvement from the Middle Ages to the Edo Period. As a result, the ruins were designated as a National Historic Site in 2005. Kusu Town promoted itself as the hometown of fairy tales and having a castle with the Ano-zumi stone walls.

My Impression
When I visited the Kusu Area, I felt the area has a very unique atmosphere because it is surrounded by mountains, and the small mountains or hills inside are a little strange, which I would learn are called mesas or buttes. These natural features of the area created folk tales about its history, so the town’s nick name, the hometown of fairy tales may be related to them. Tsunomure Castle also came from the area’s features and people from the outside made it more unique. I recommend visiting the Kusu area and Tsunomure Castle Ruins if you travel around there.

How to get There
If you want to visit there by car, it is about a few minutes drive away from Kusu IC on the Oita Expressway. There are several parking lots around the ruins (in the Third Enclosure on the mountain or in the park at the foot of the mountain…).
By public transportation, take the Oita-Kotsu bus bound for Kajiwara from JR Bungomori Station and get off at the Kami-Fushihara bus stop at the foot of the mountain. You can climb the trail to the top from there.
From Tokyo or Osaka to the Station: it may be better to rent a car from Oita Airport or Fukuoka Airport after using a plane.
That’s all. Thank you.
Back to “Tsunomure Castle Part1”
Back to “Tsunomure Castle Part2”