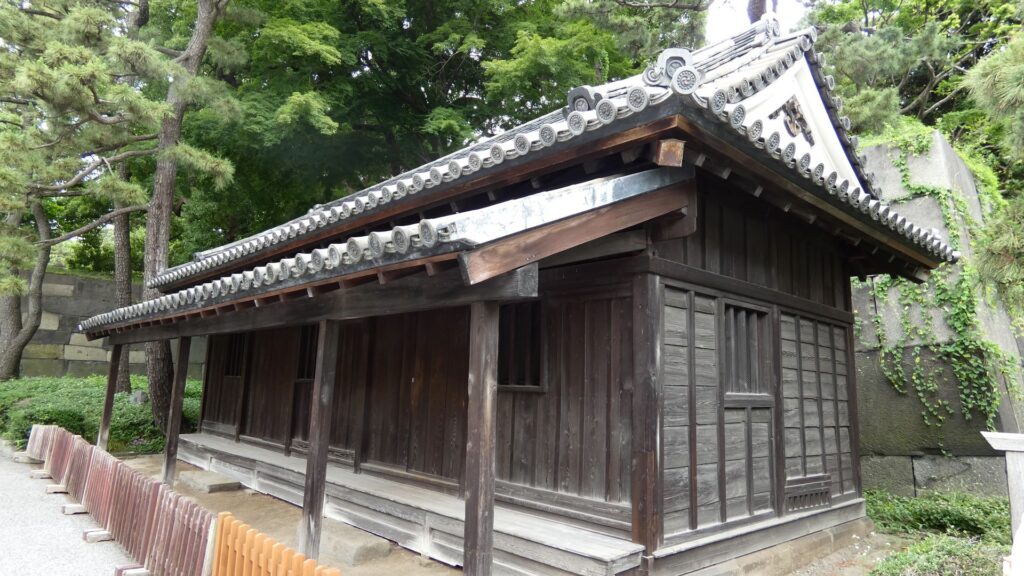
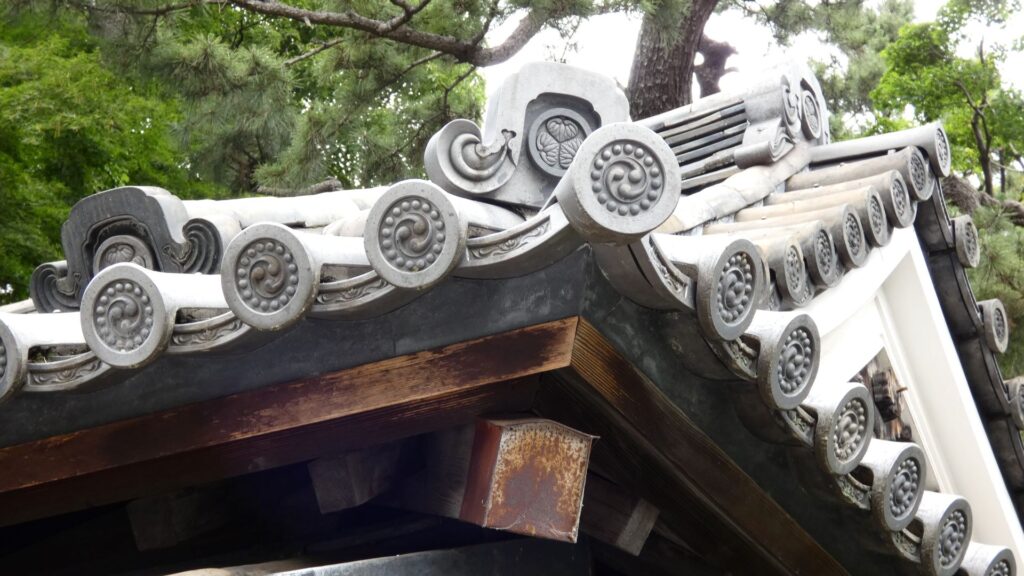
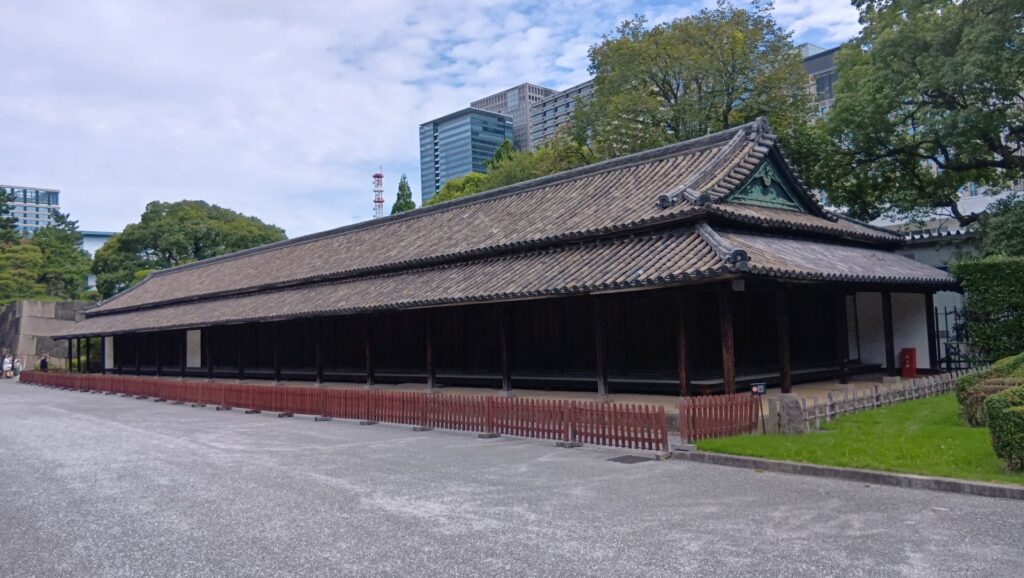
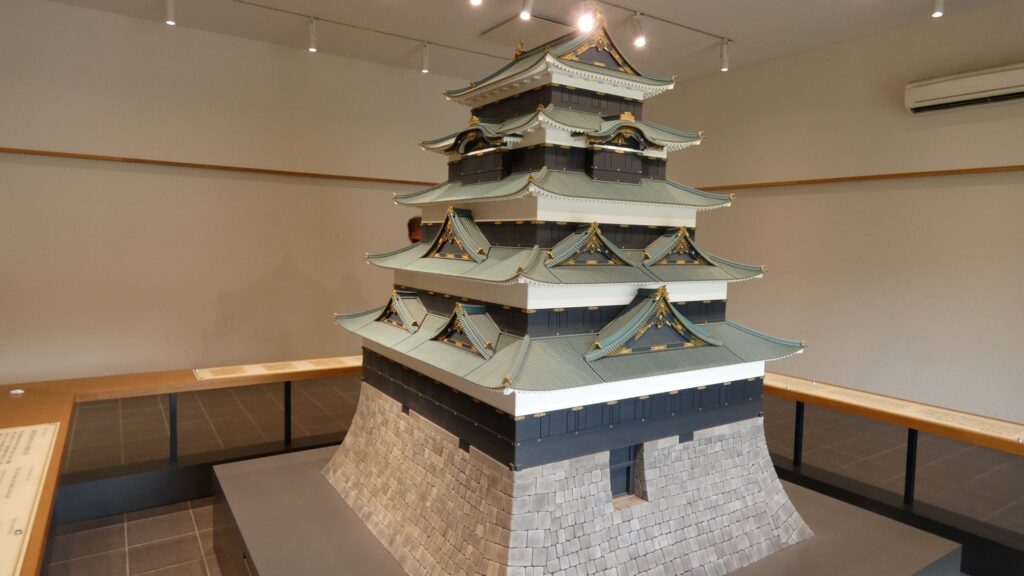
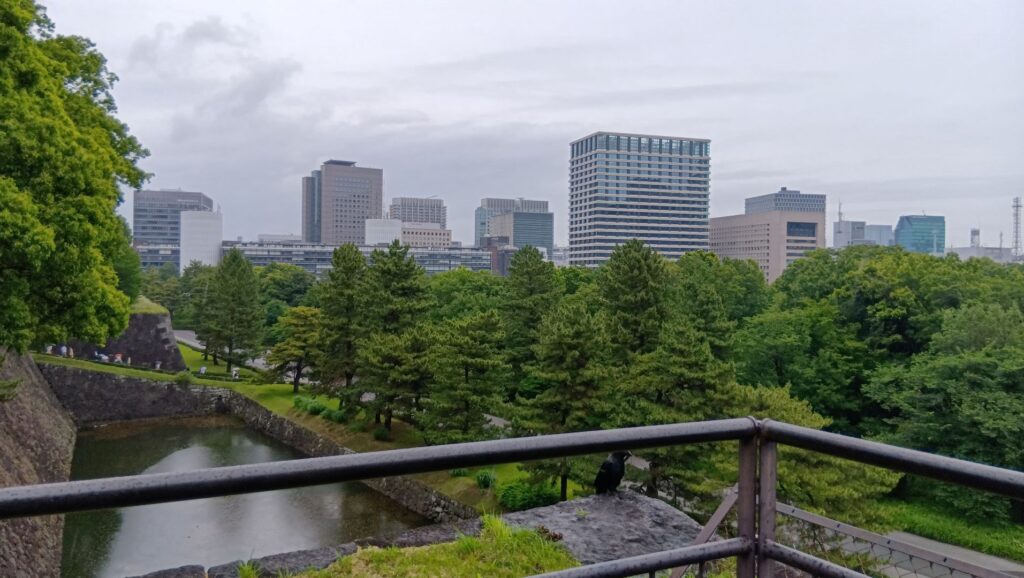
特徴、見どころ(江戸城内堀紀行)
Introduction
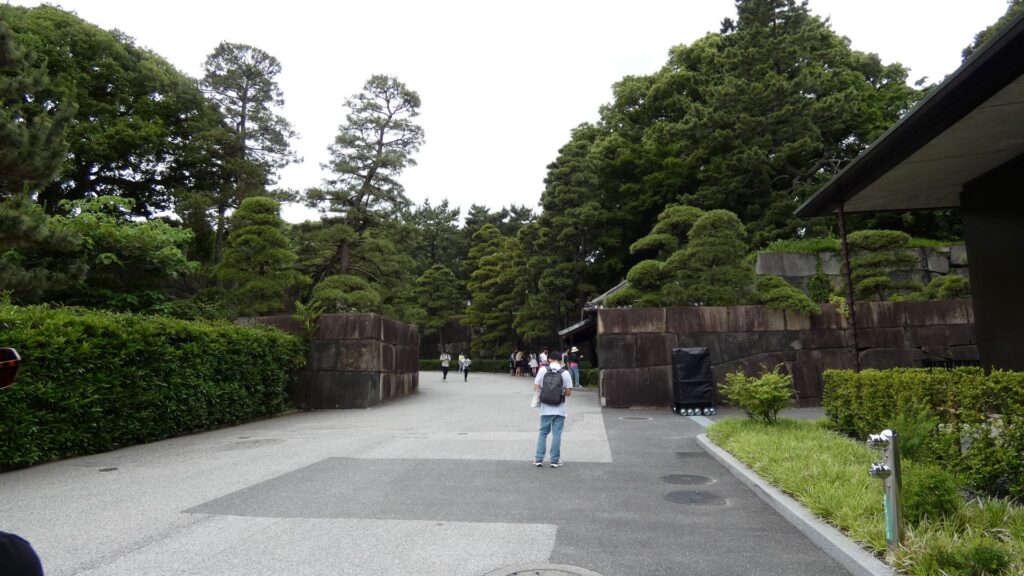
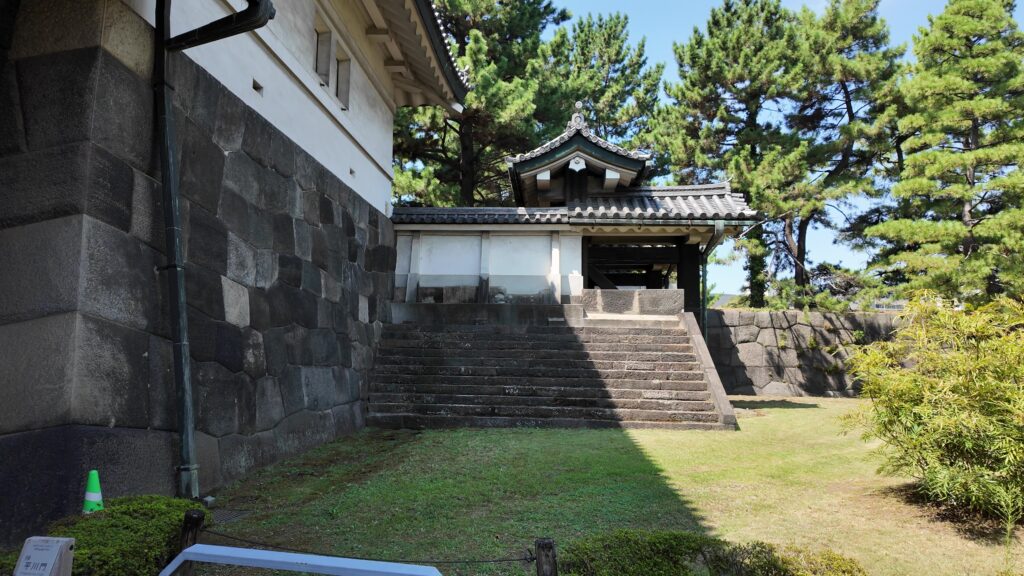
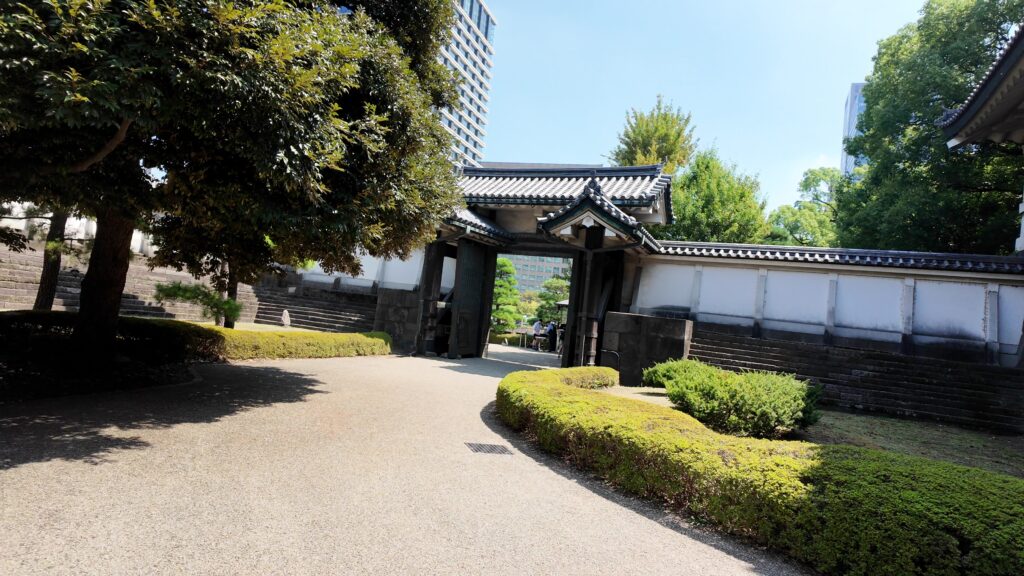
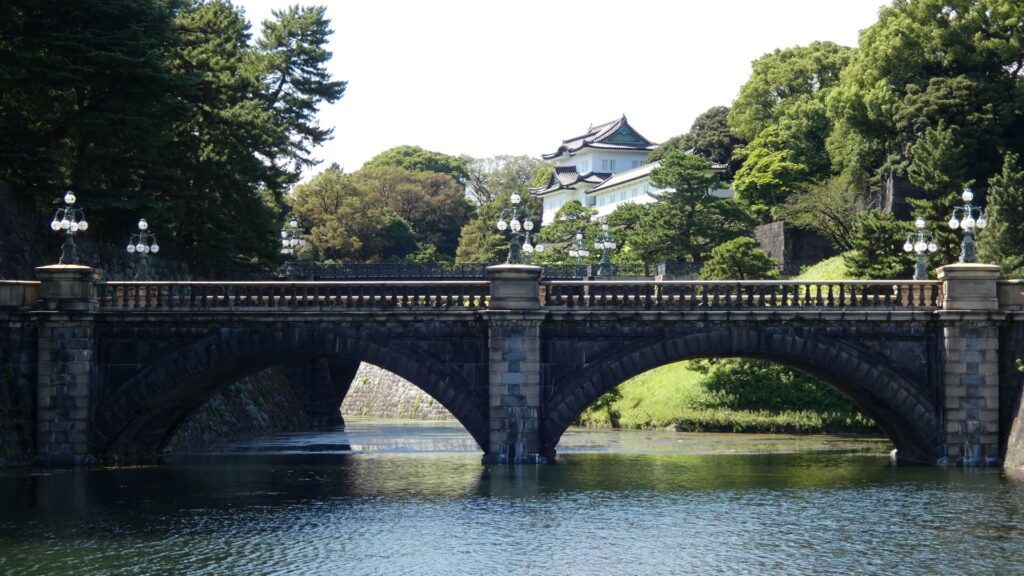
ここは江戸城平川門の前、平川橋のところです。江戸城跡の中心部を見学したときのゴール地点でした。今回は、江戸城内郭をめぐろうと思いますが、内堀のラインをずっと歩くことにします。江戸城の内堀全周は約8kmもあって、その範囲だけでも日本の城で有数の規模ですが、皇居など、普段入れないところも多いので、基本、内堀沿いを巣進みます。それでも、結構変化に富んでいて、おもしろいと思います。それでは、江戸城内堀紀行として出発しましょう。

今回の内容を趣向を変えて、Youtube にも投稿しています。よろしかったらご覧ください。
すごいぞ清水門・田安門
平川橋から内堀に沿って進みましょう。竹橋の前を折れて、北の丸に向かいます。
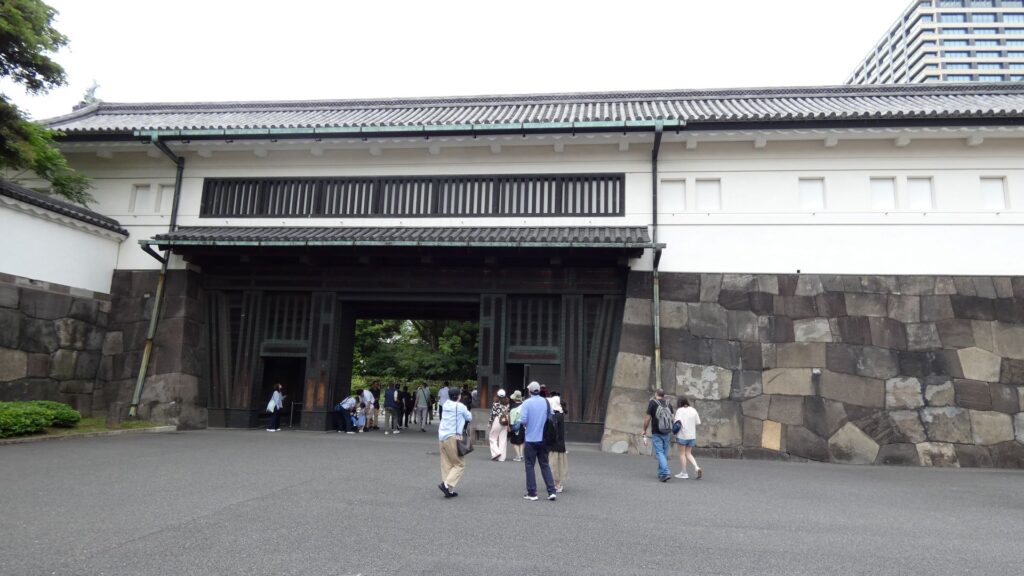
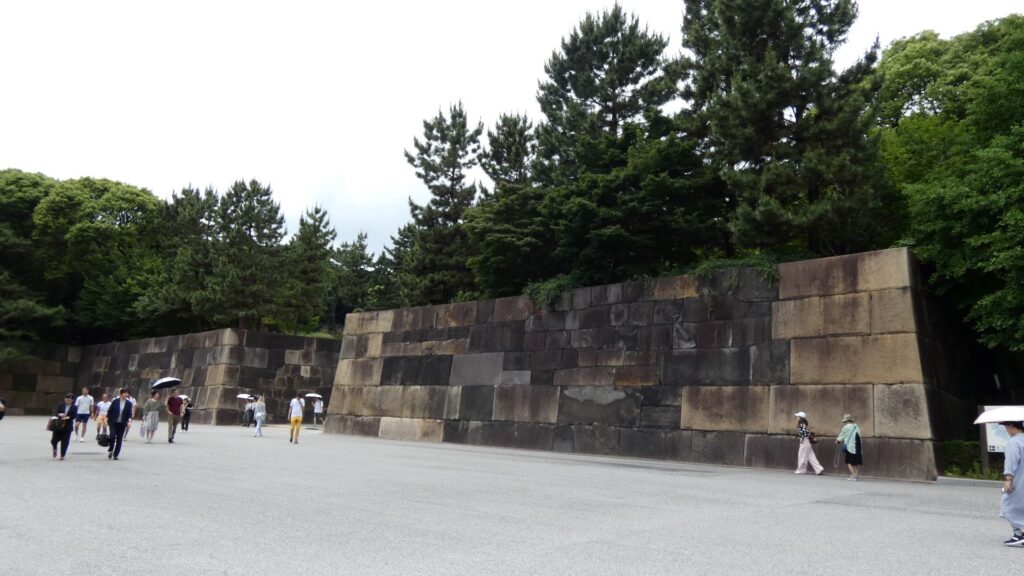
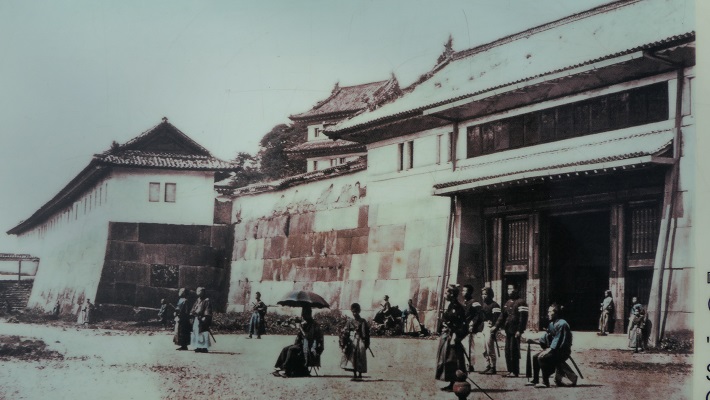
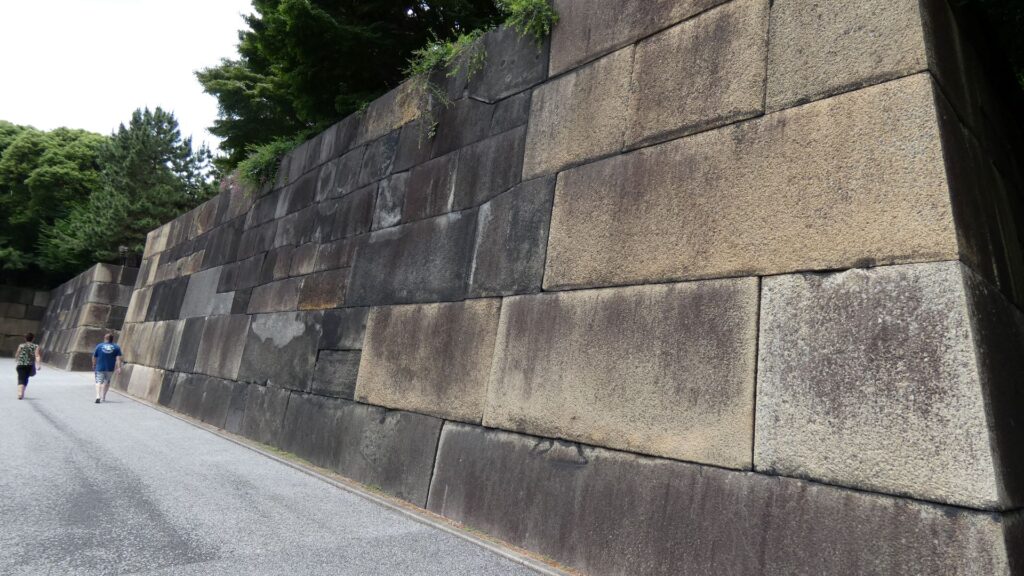
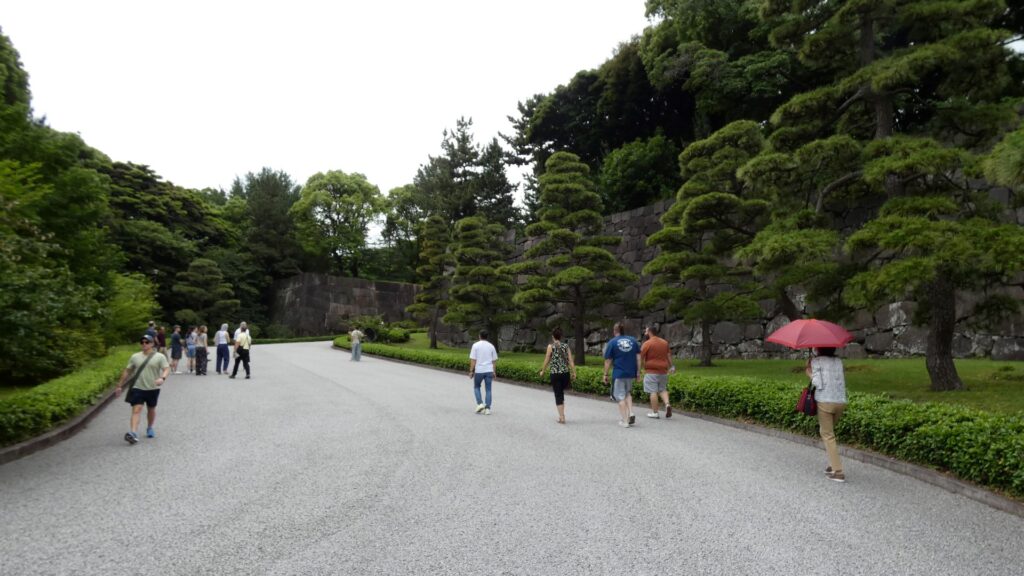
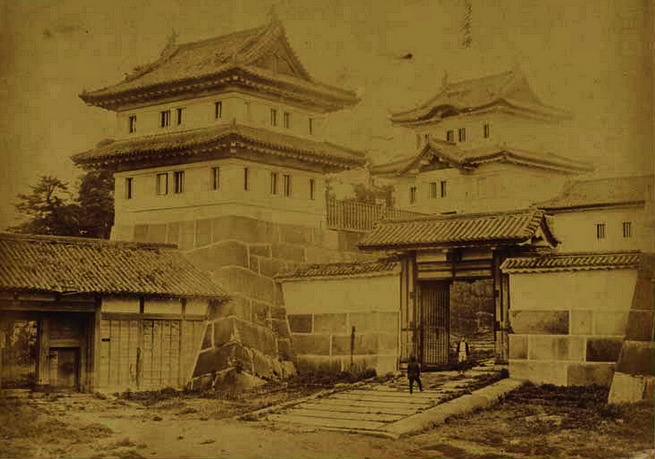
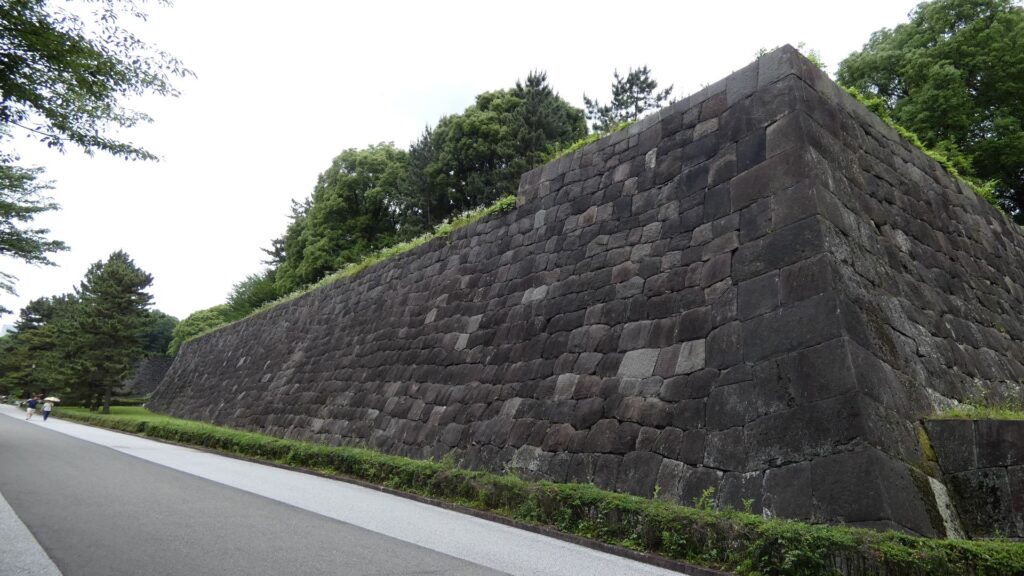
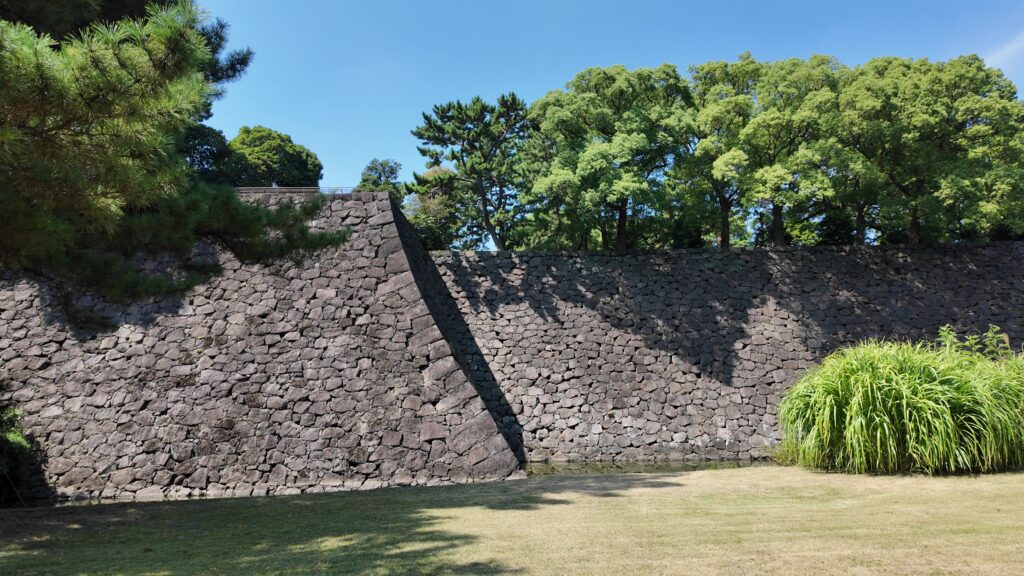
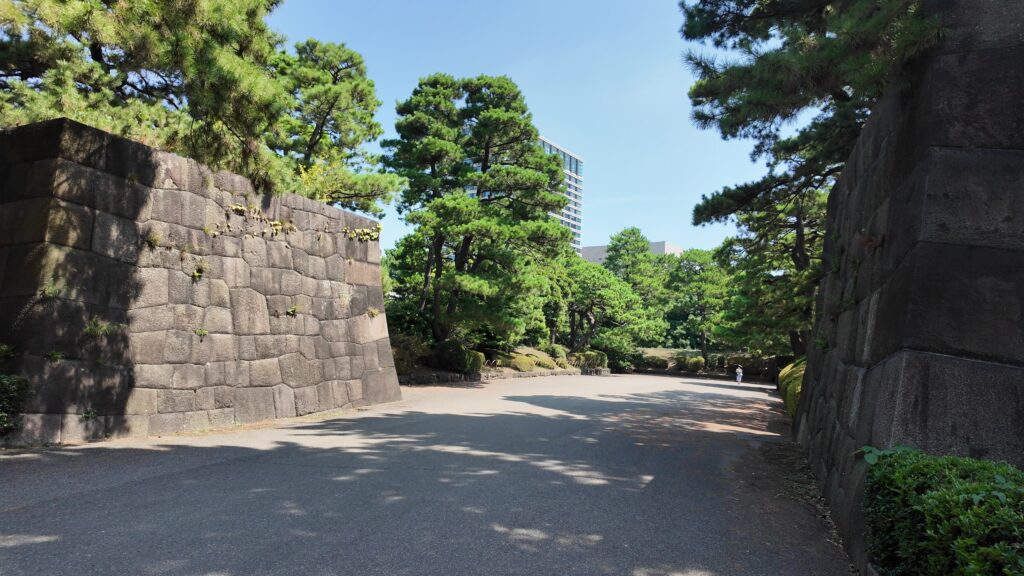
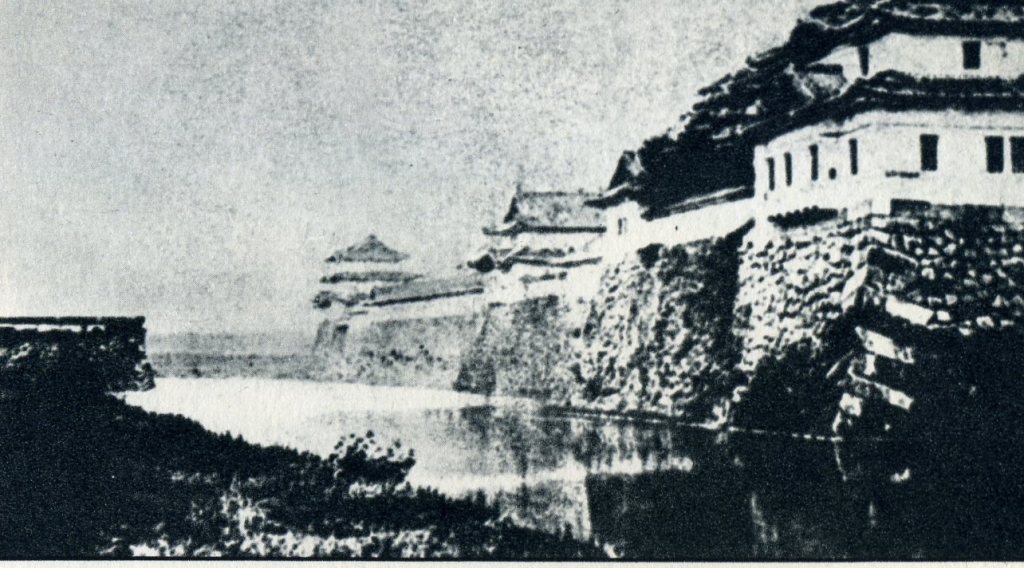
北の丸の航空写真門が見えてきました。清水門です。この門は、江戸時代初期から存在し、現在残る建物は、明暦の大火の後に再建されたものです。国の重要文化財に指定されています。右側は、家康時代に飲料水確保のため、せき止めて作った牛ヶ淵です。それだけでも長い歴史を感じます。


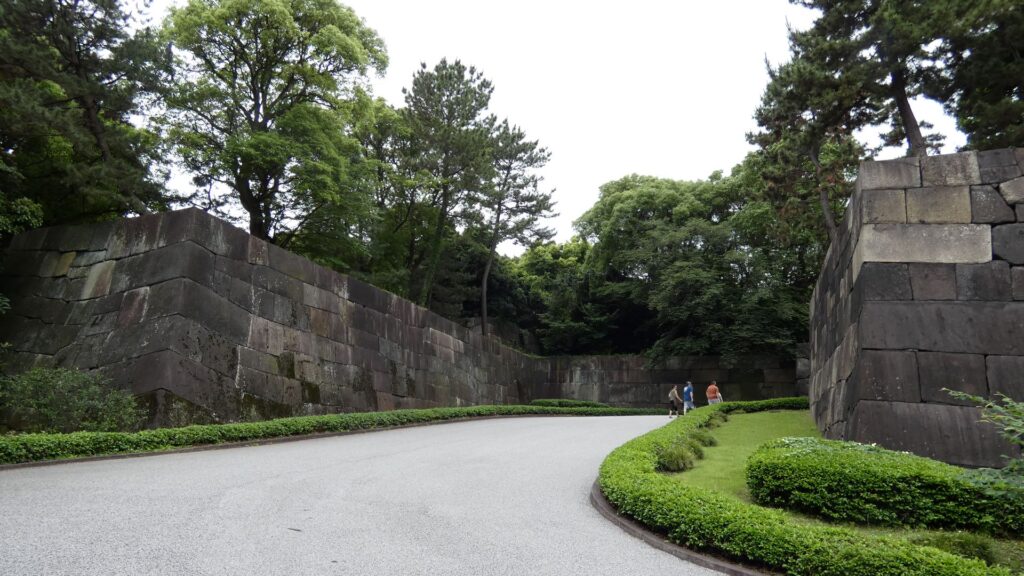
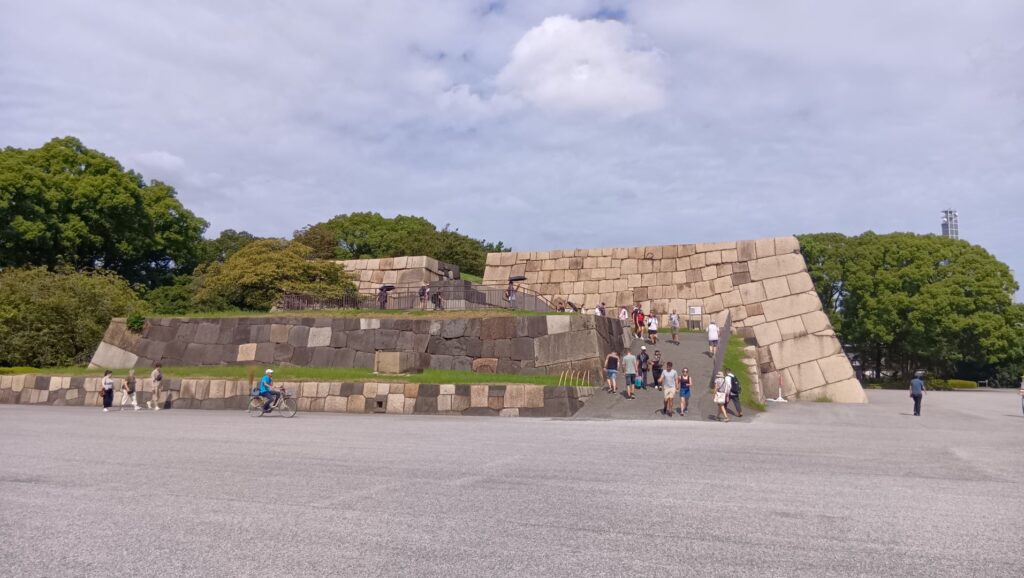
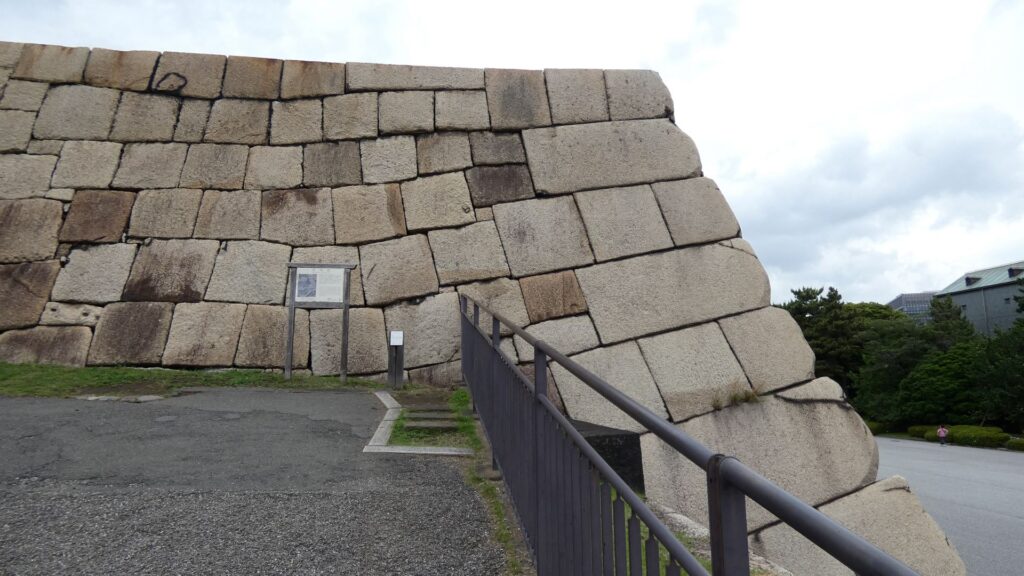
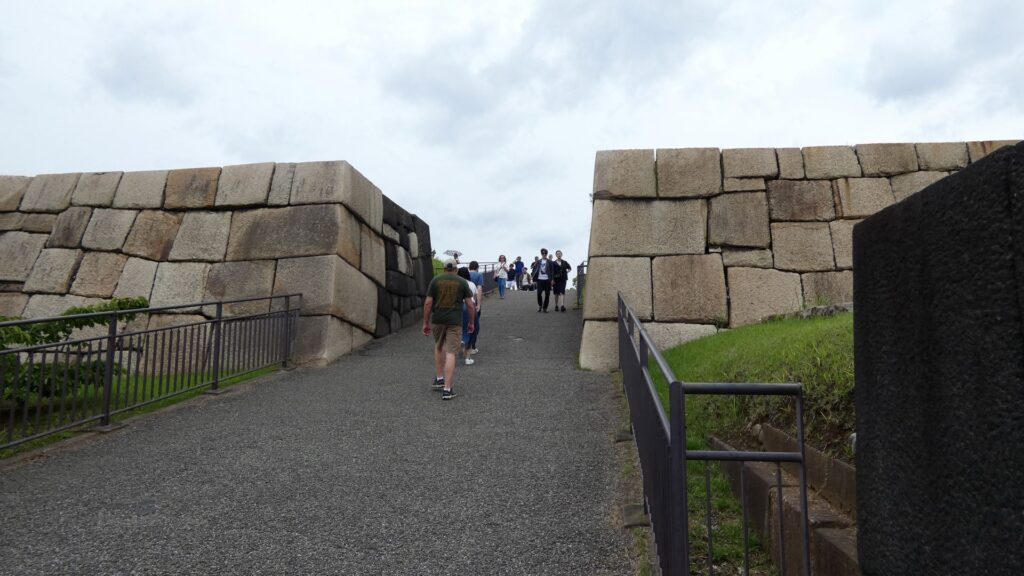
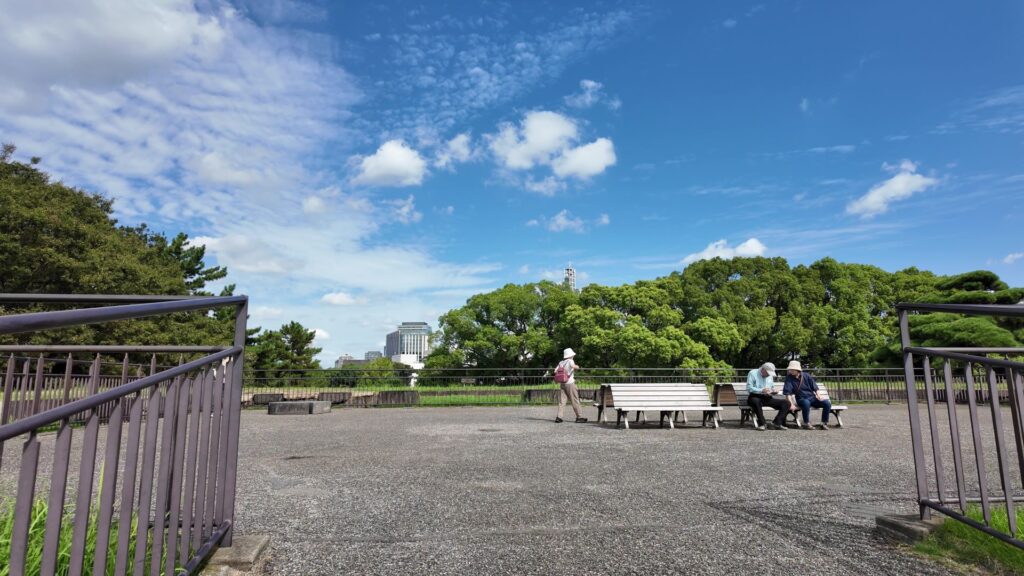
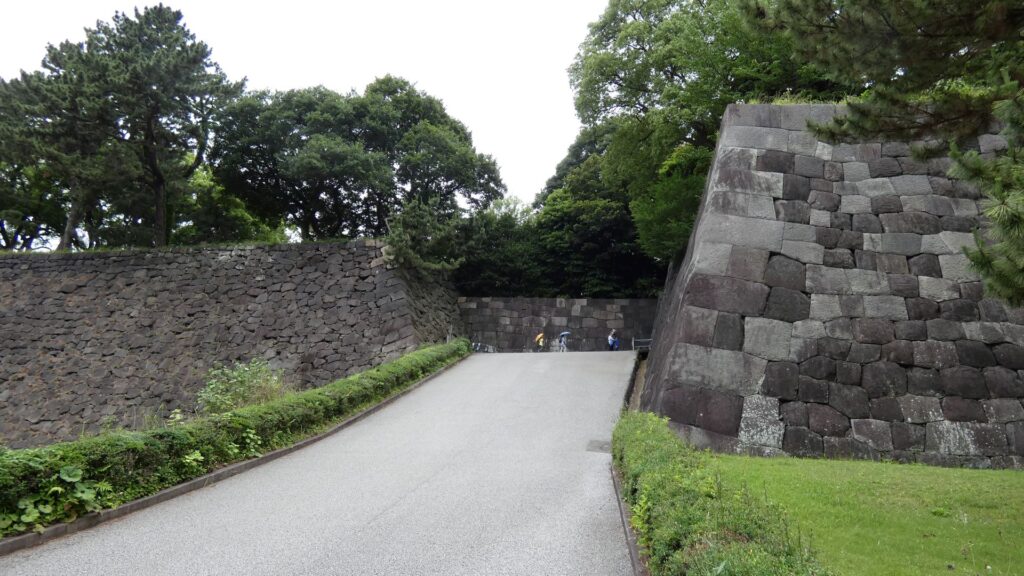
土橋から、石橋を渡り歩きます。高麗門をくぐって、枡形に入ります。そして、櫓門から枡形を出ます。出たところも枡形になっています。二重枡形になっているのです。
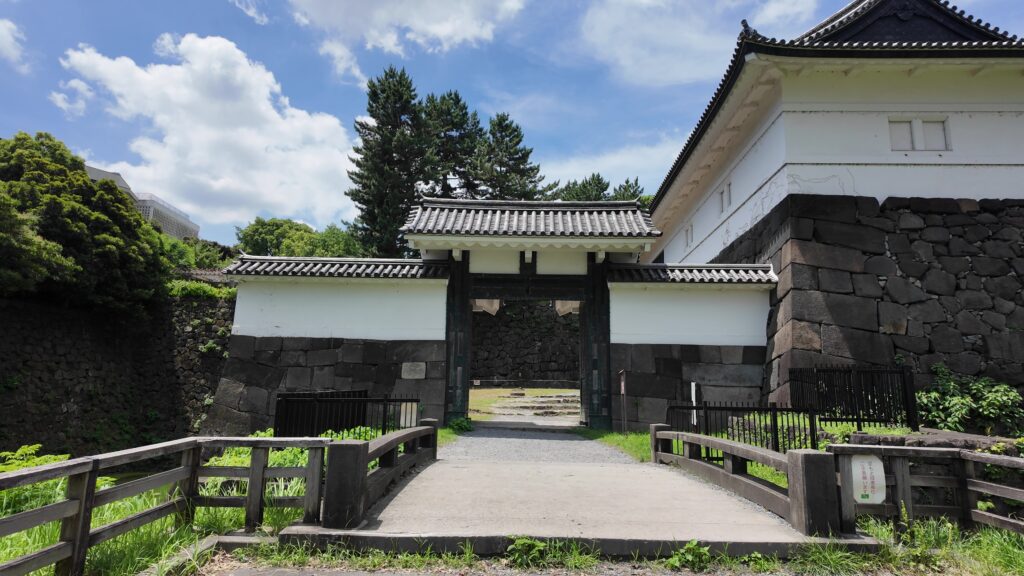
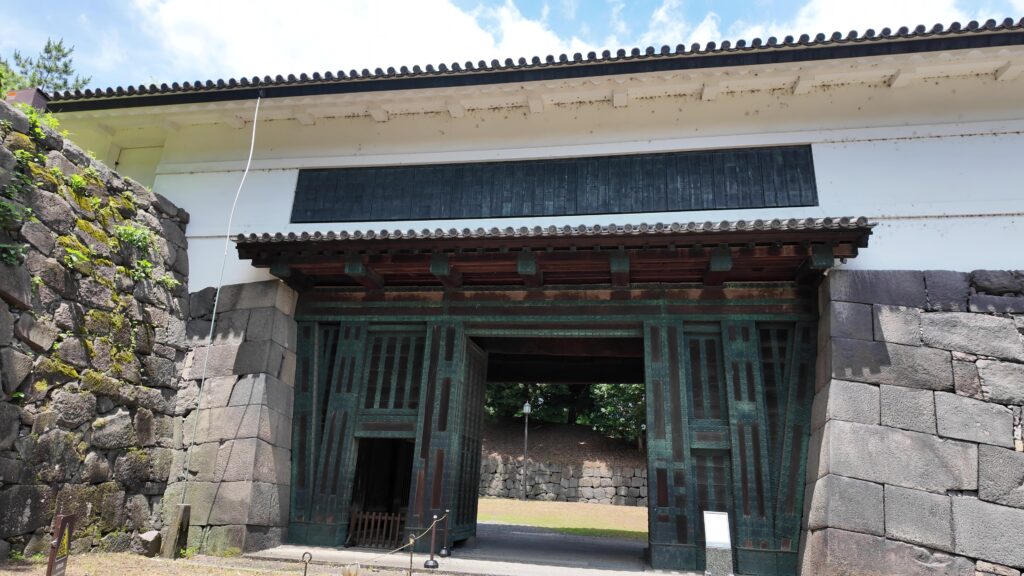
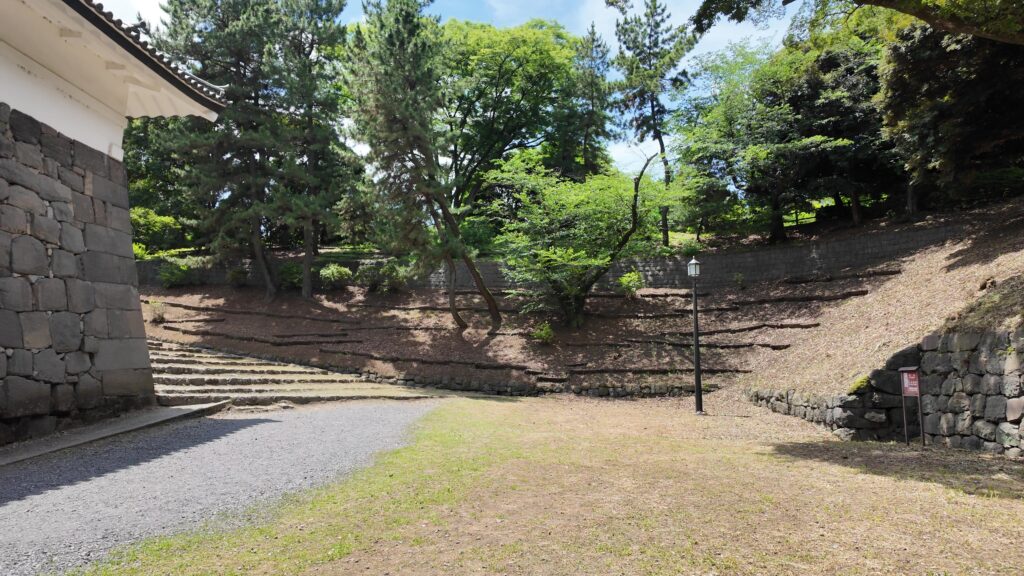



雁木を登って、門の前を見渡しましょう。ここまで通ってきた通路がお見通しです。振り返ると、二重枡形の形もばっちり見えるスポットです。
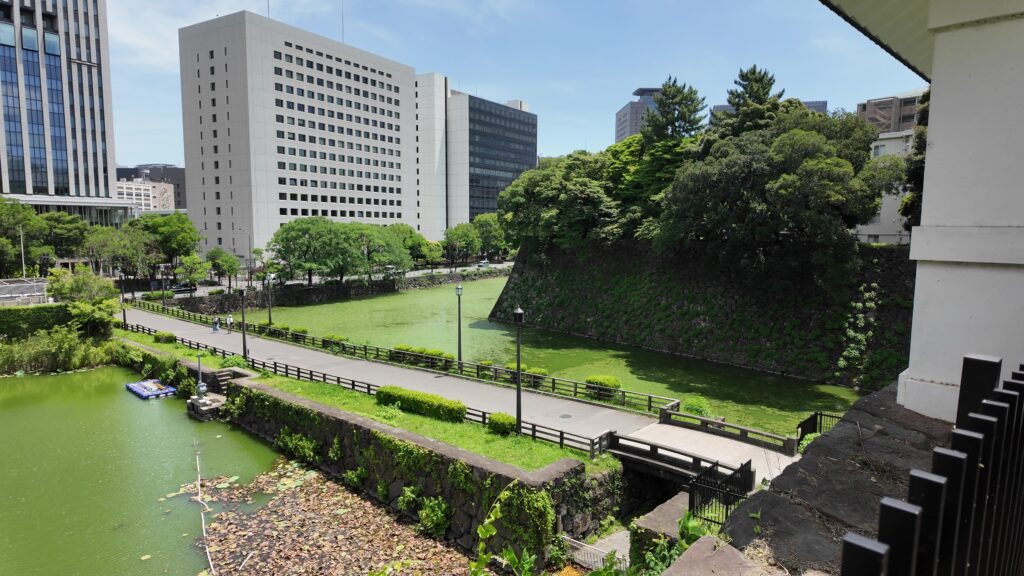
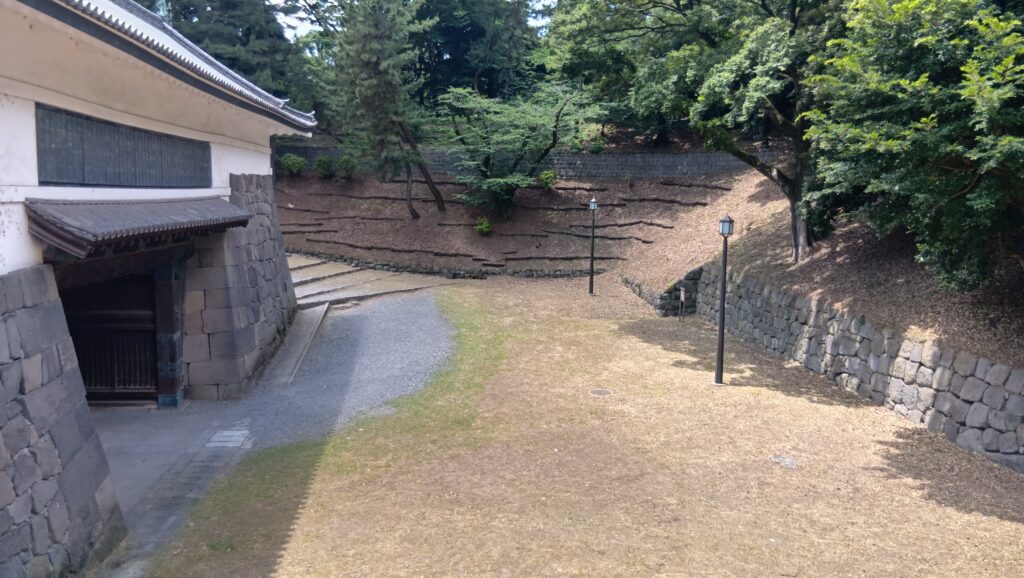


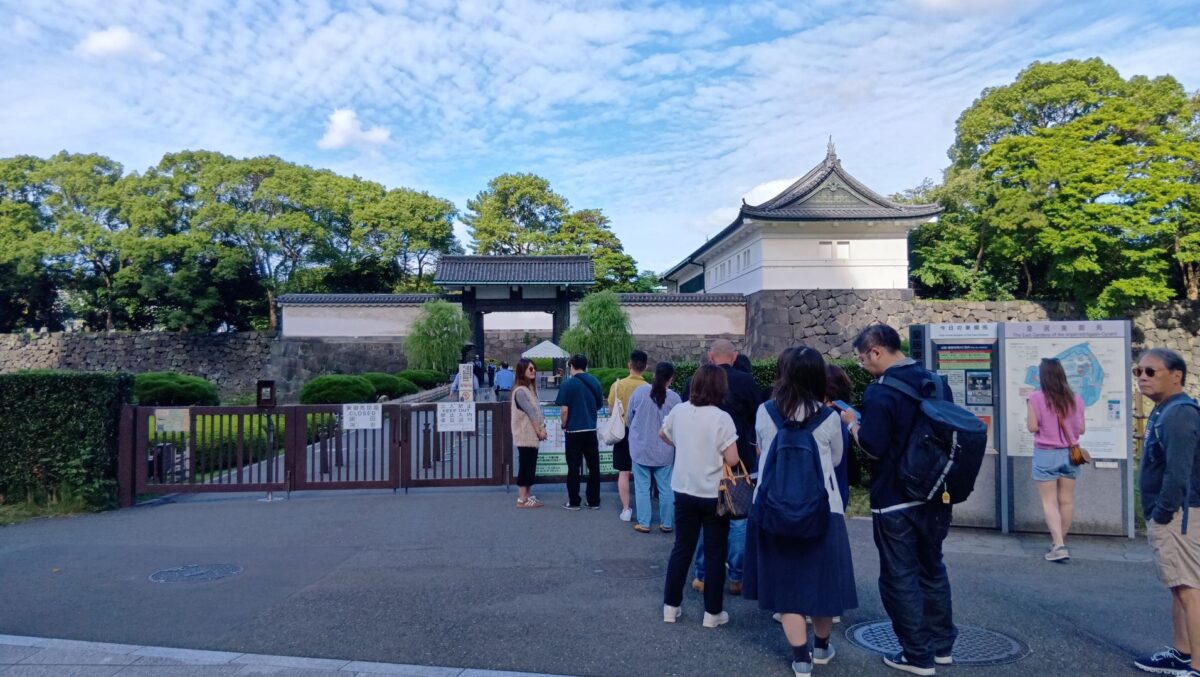
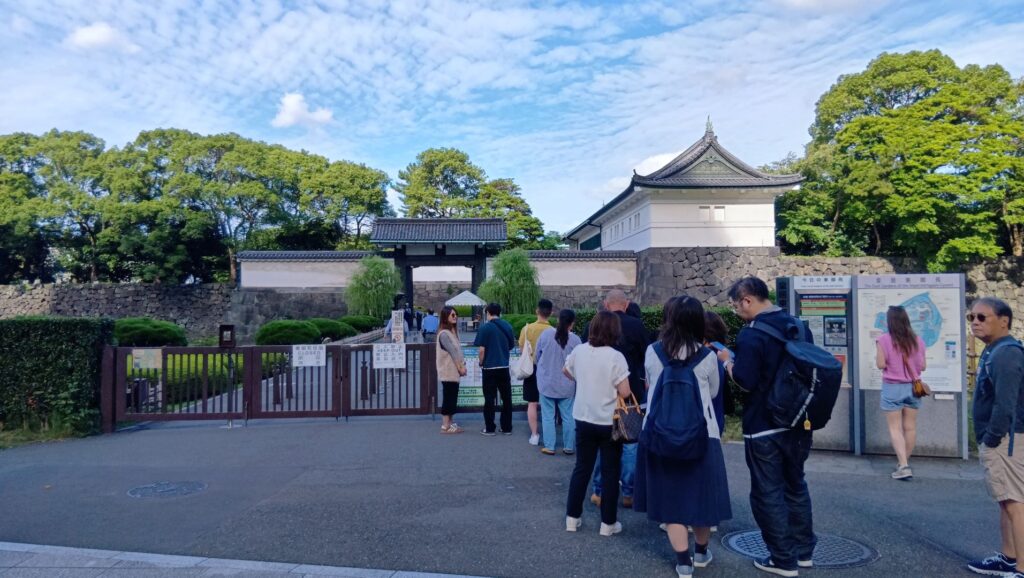
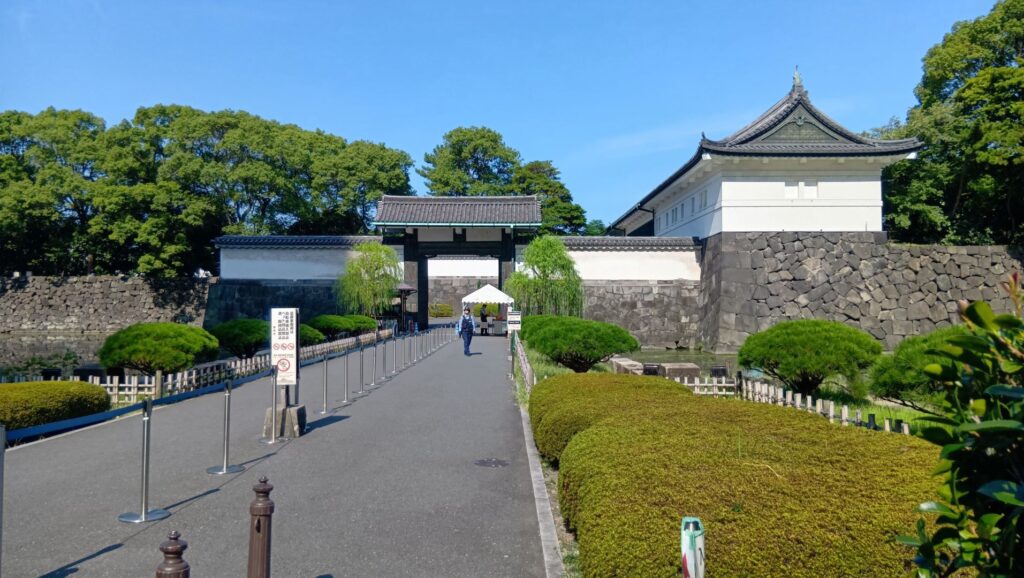
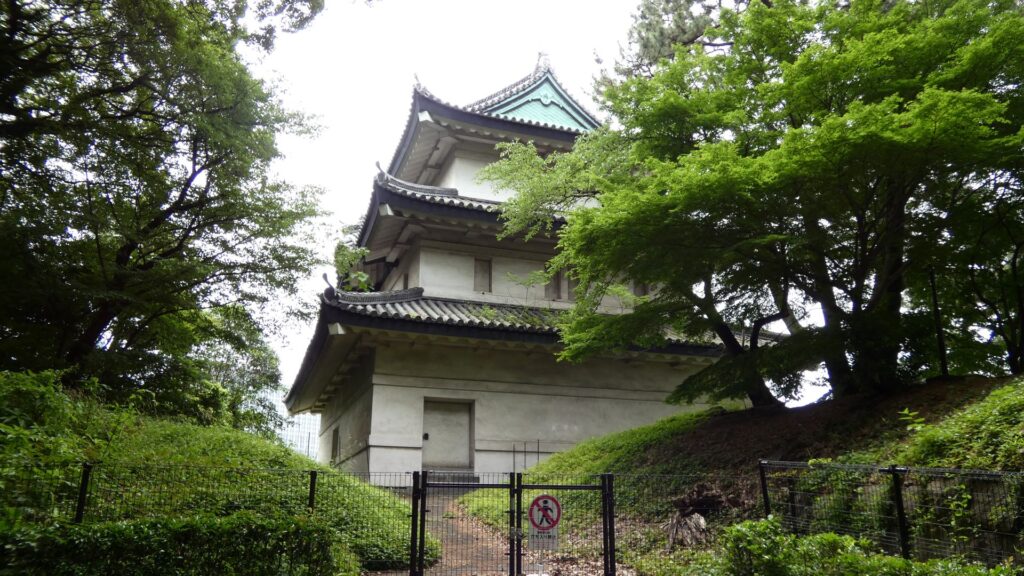
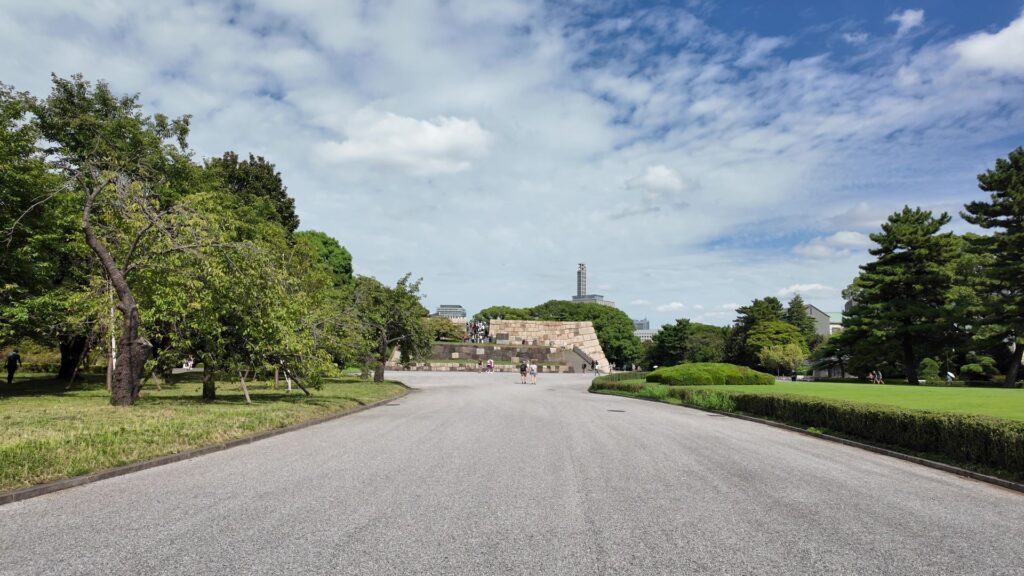
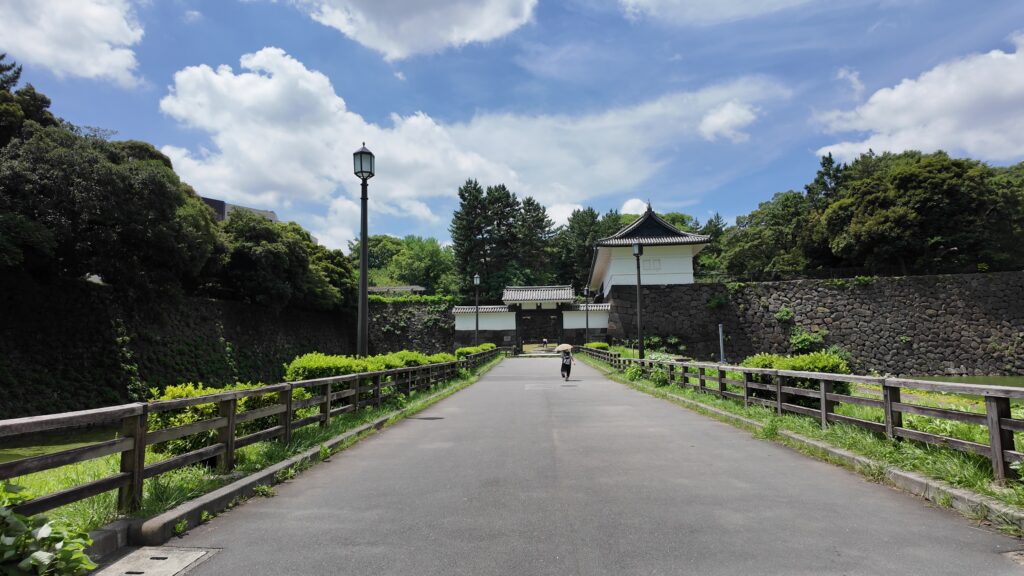
次は、九段坂を登って、田安門に向かいます。牛ヶ淵を見ると、水が流れ込んでいるのがわかります。田安門に通じる土橋が、右側の千鳥ヶ淵と、左側の牛ヶ淵の水位調整を行う仕切りになっているのです。田安門も、現存する重要文化財の建物です。正面に武道館が見えます。かつては、清水門と並んで、御三卿の屋敷に通じる門でしたが、今は、武道館に行く人たちの入場門になっているのです。
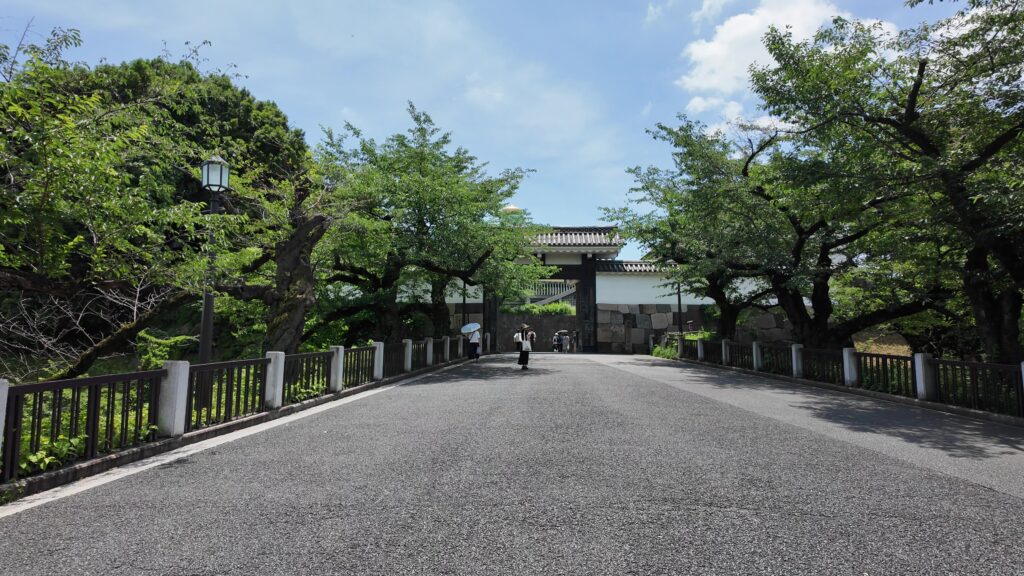
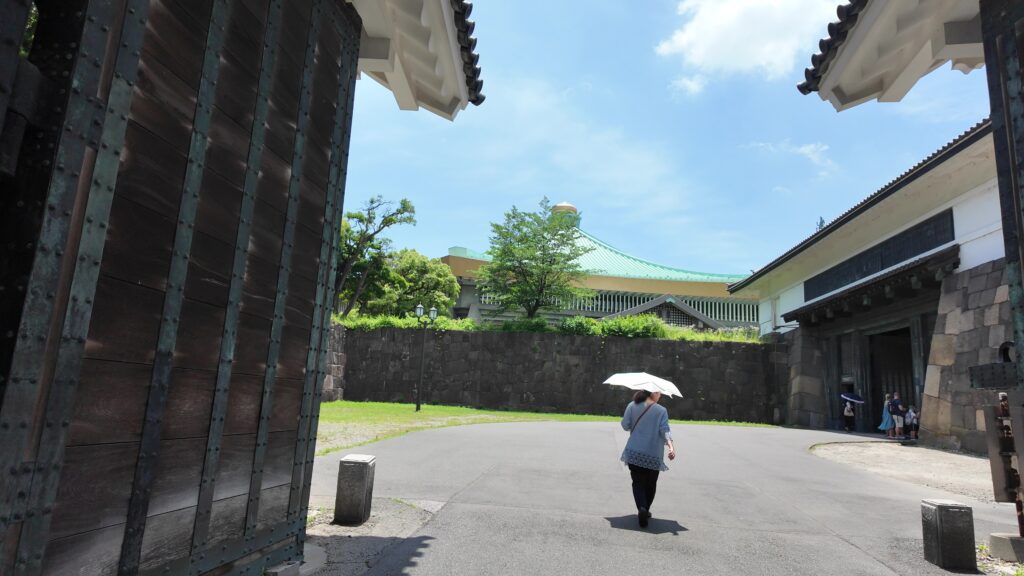




この門の内側も、しっかり枡形になっています。寛永時代の1636年に建てられ、明暦の大火も生き延びました。実は、江戸城でも最古級の建物なのです。そんな貴重な門が、今もなにげなくですが、しっかり使われているなんて、すごいと思います。
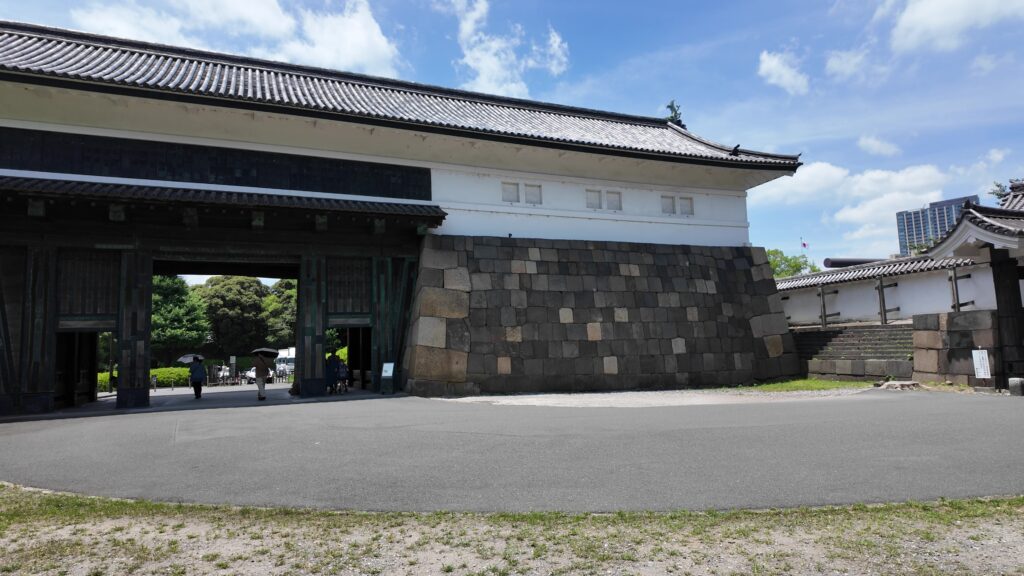


まるでダム・大河のような内堀
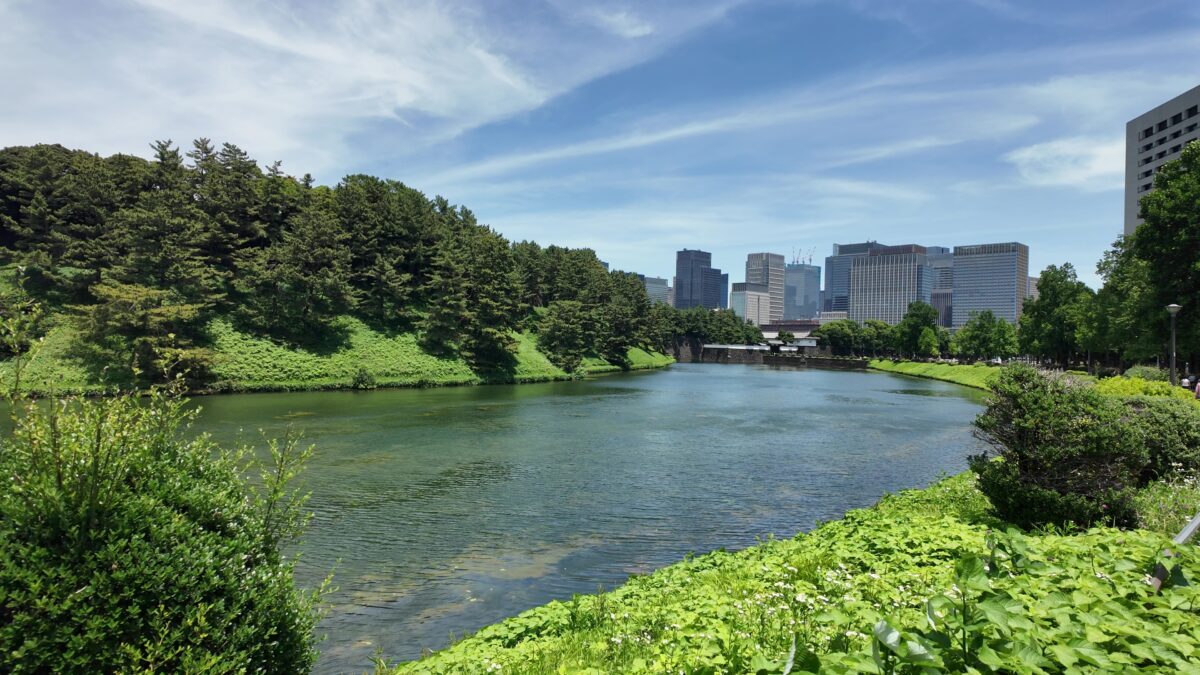
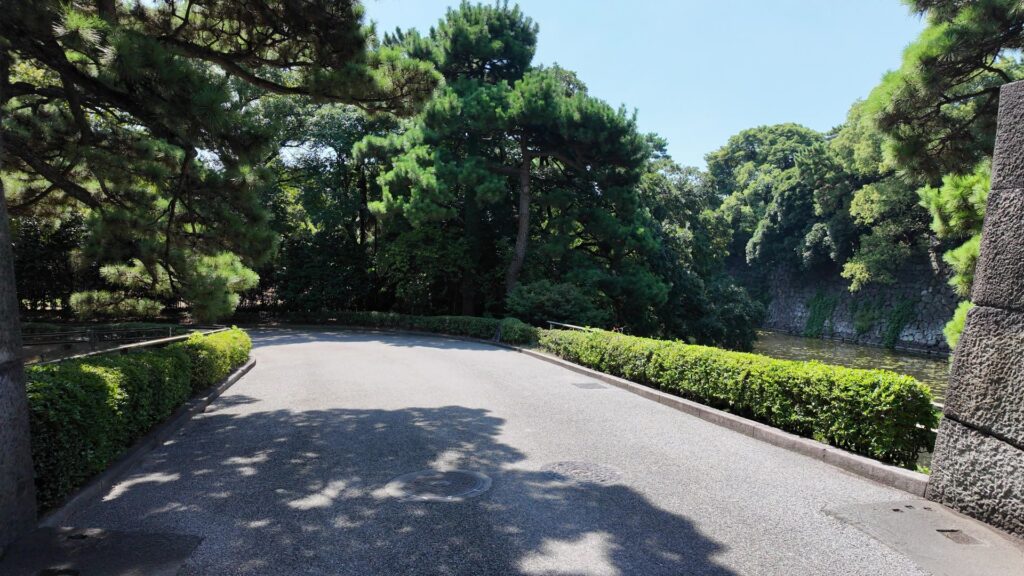
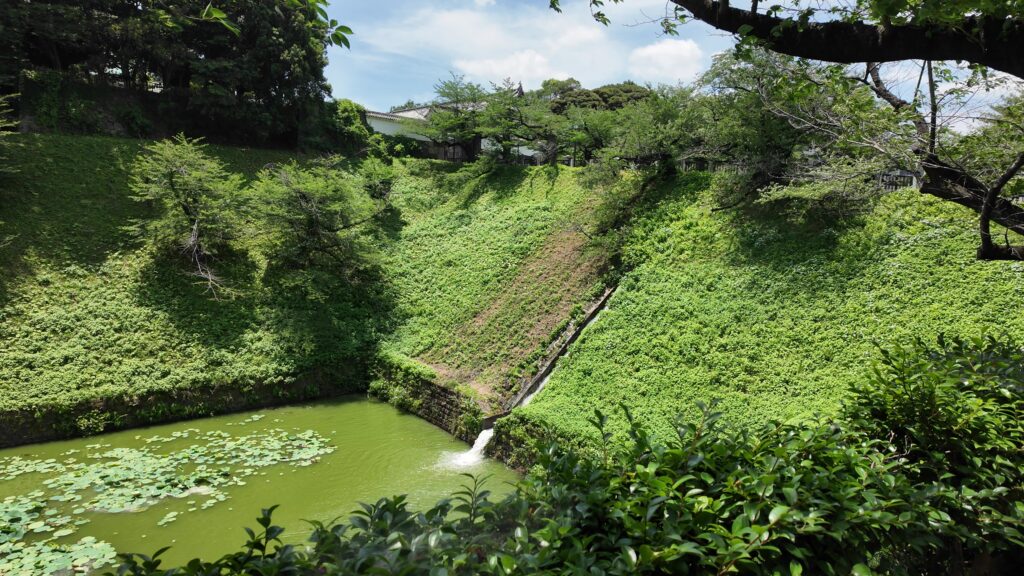
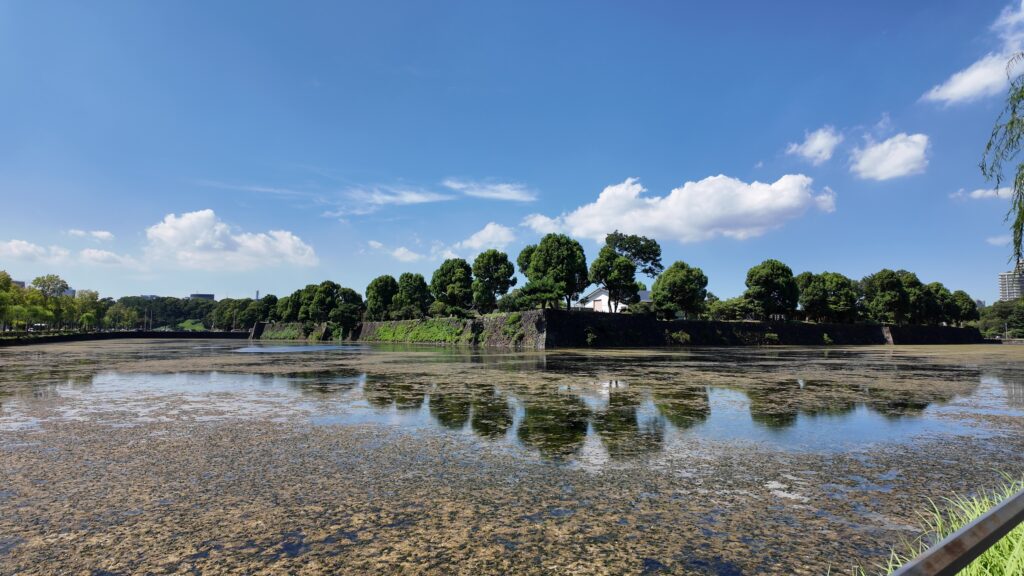
田安門から先の内堀に沿って行きましょう。今度は、千鳥ヶ淵です。桜とボートで有名なところですが、今日はボートだけです。こちらも古い堀で、牛ヶ淵同様、家康時代の飲料水確保が起源と言われています。確かにまるで貯水池のようです。内堀の中では、一番標高が高いところだそうです(約16m)。千鳥ヶ淵沿いには緑道が整備されています。散歩するにももってこいです。
内郭西側の航空写真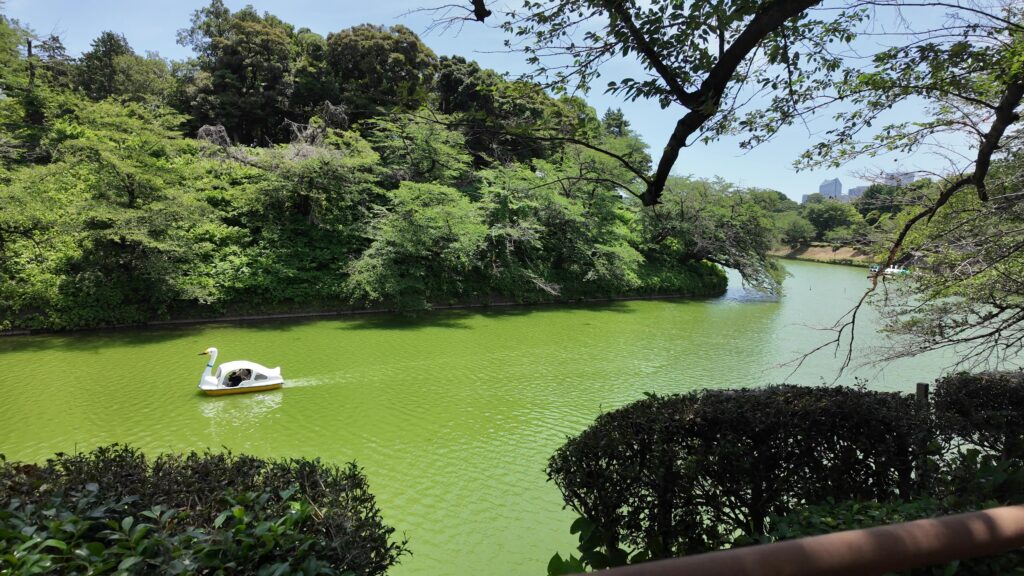
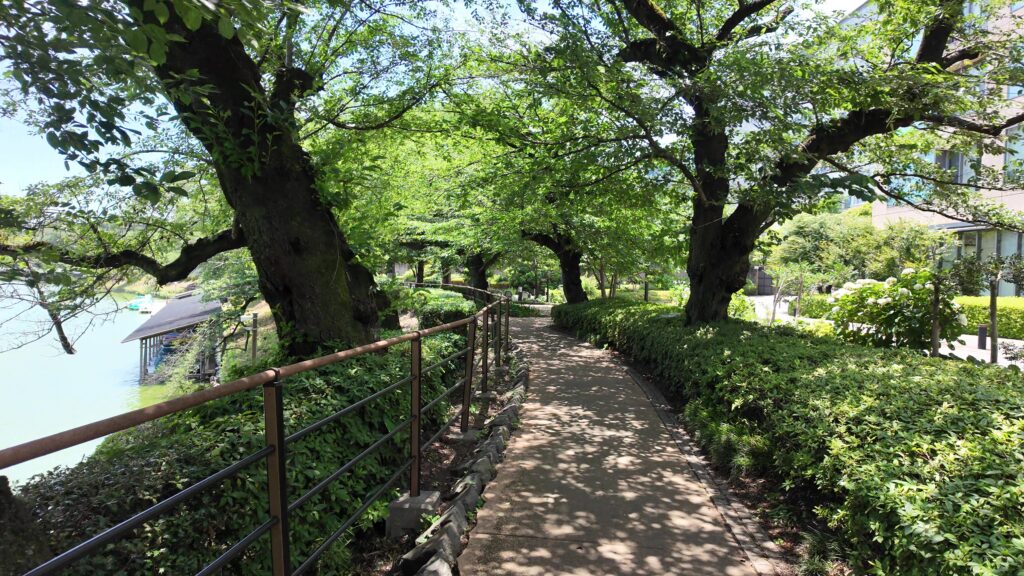

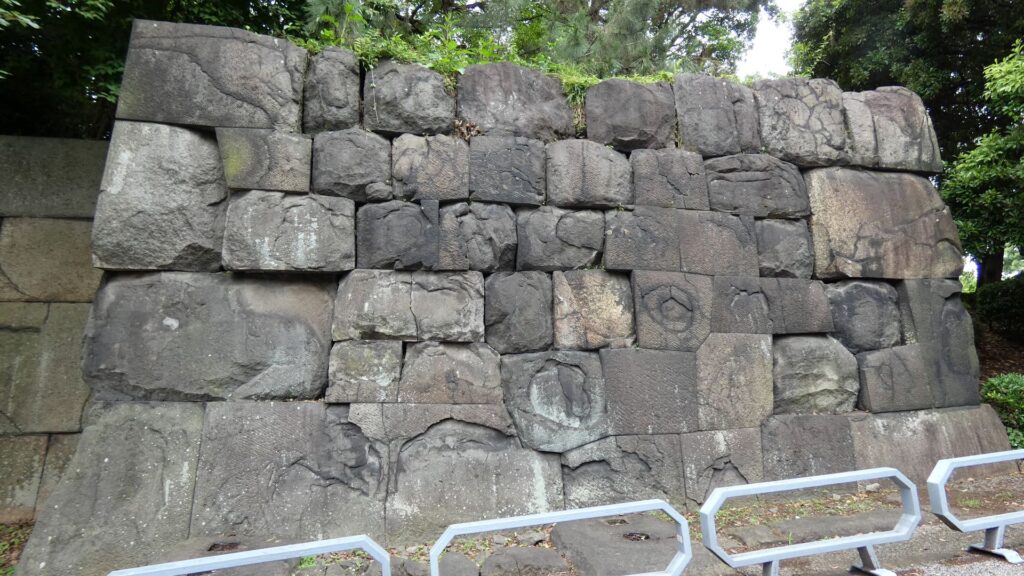
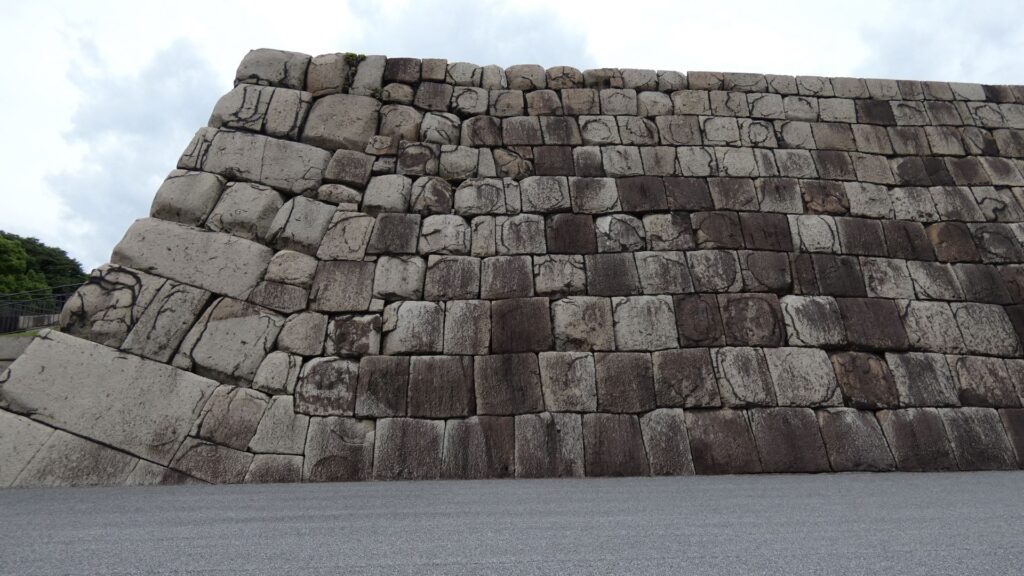
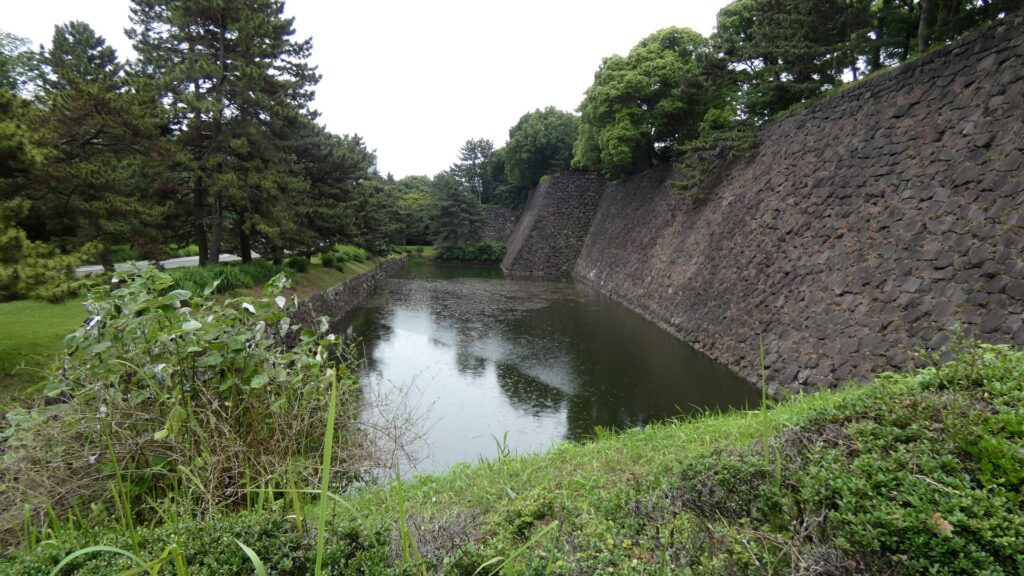
千鳥ヶ淵交差点を越えると、半蔵濠になるのですが、かつては、千鳥ヶ淵と一体だったそうです。堀の向こう側には土塁と石垣が見えます。皇居がある吹上で、土塁の上部を鉢巻石垣、下部を腰巻石垣で強化しています。似たような石垣を彦根城で見ました。どちらも天下普請で築かれた大規模なお城ですので、効率よく築城しようとしたのでしょうか。
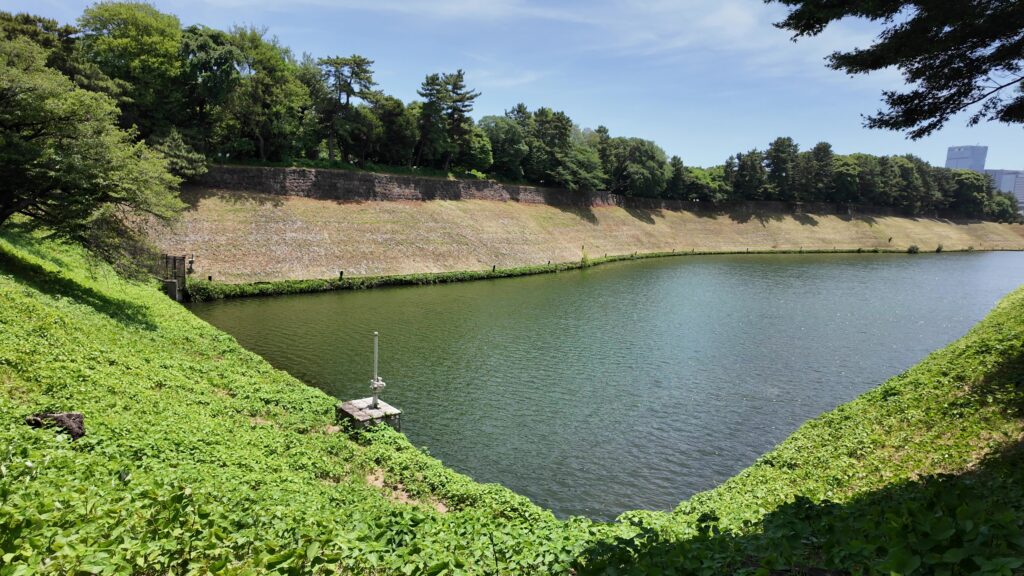
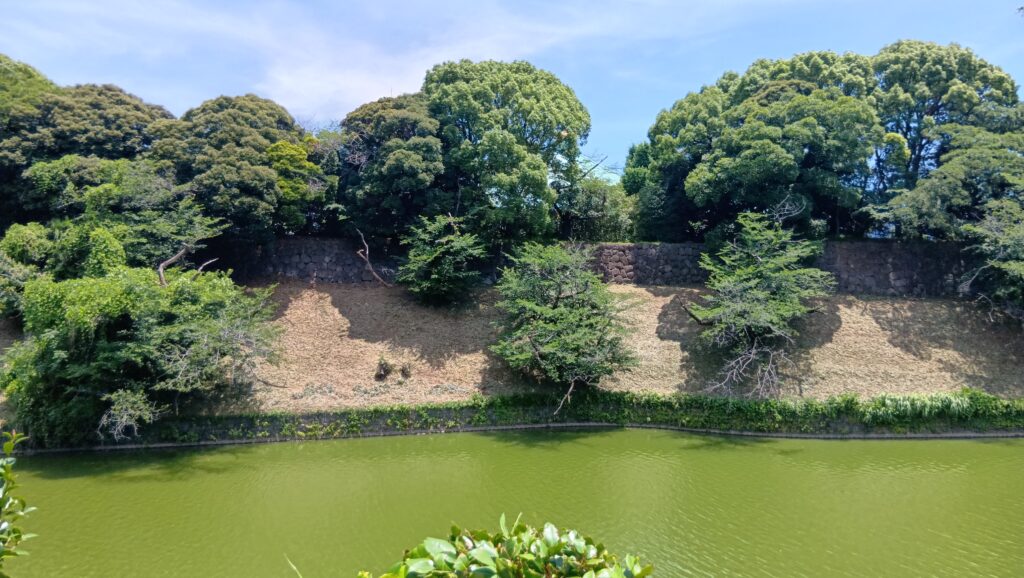



また門が見えてきました。名前はよく知られている半蔵門です。現在は、皇居の入口の一つになっているので近づけませんが、こちらも門の前の土橋がすごいのです。まるでダムのようです。右側の桜田濠が、左にある半蔵濠の下流になっているのです。
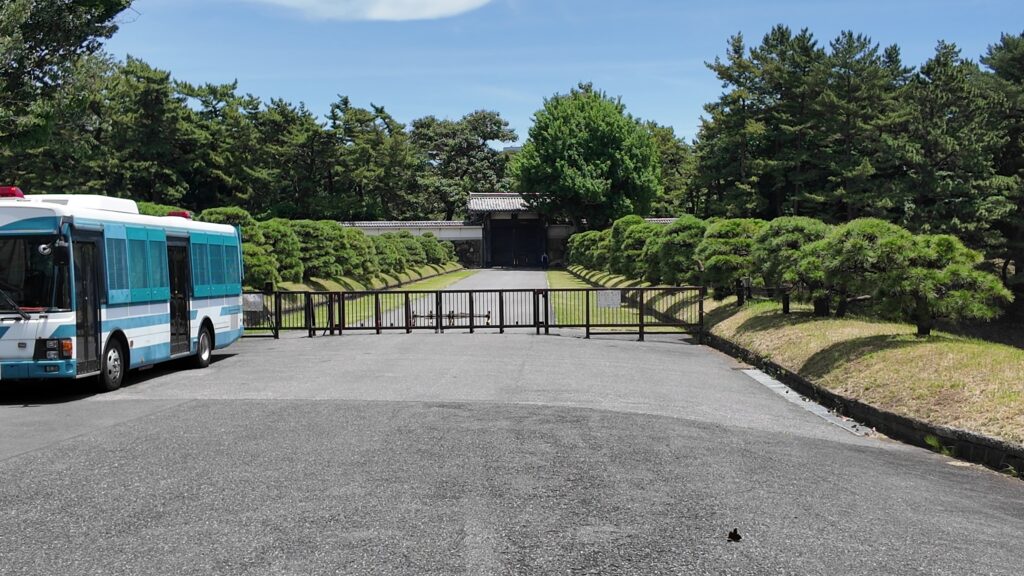
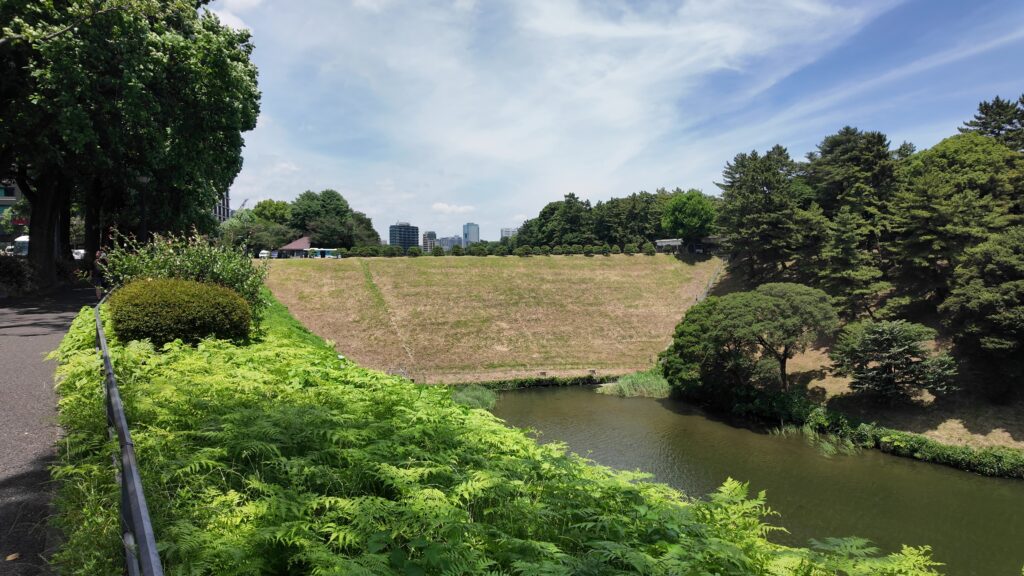


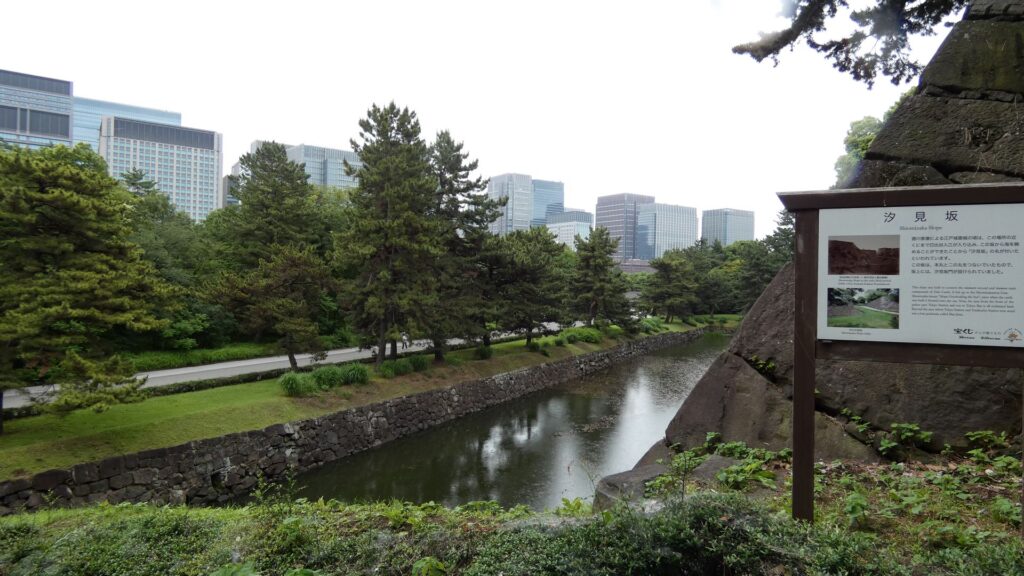
桜田濠に沿ってまた進んでいきましょう。歩道も下りになって、快調に歩けます。堀が、ダムから流れる大河のように見えます。元あった自然の谷や川を利用したのでしょうが、すごいと思います。こうやって見てみると、単なる内堀とは思えないスケールの大きさを感じます。起伏のある地形を、丸ごと城にしてしまっています。
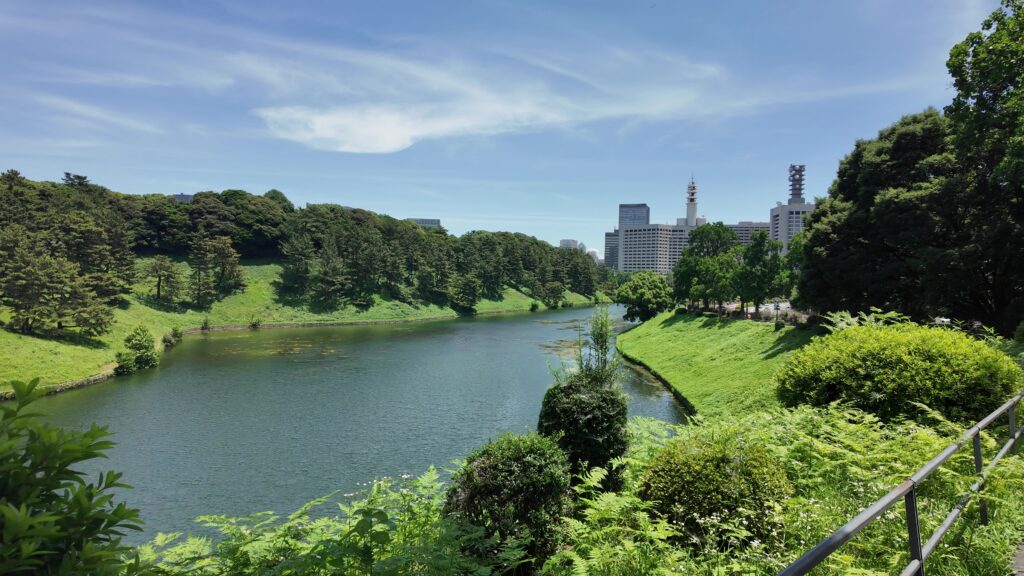
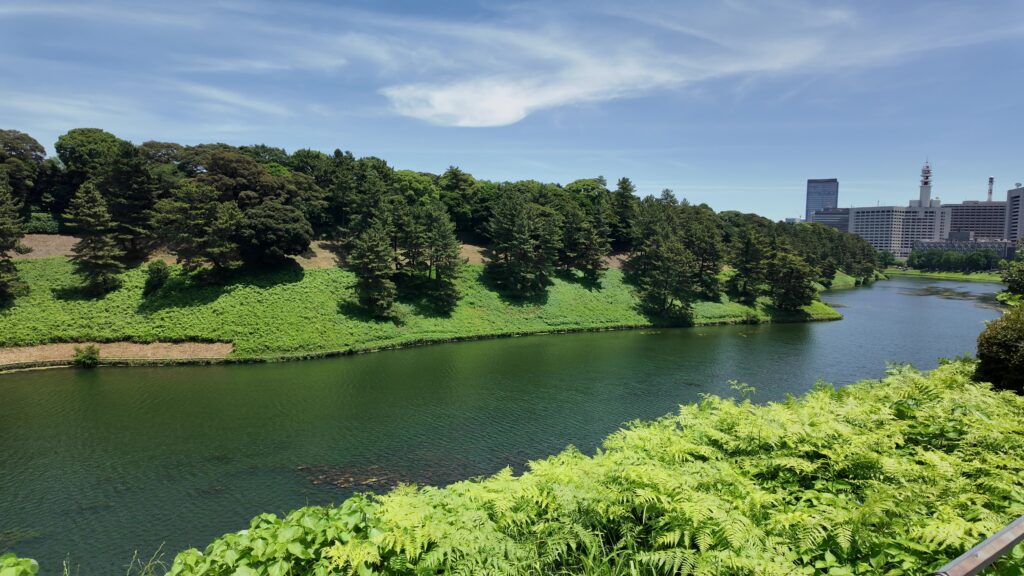


道はだんだん平らになってきました。ビル群も見えてきました。門に近づいてきましたが、桜田門です、城の中枢部分に戻ってきました。歴史の舞台になったところです。
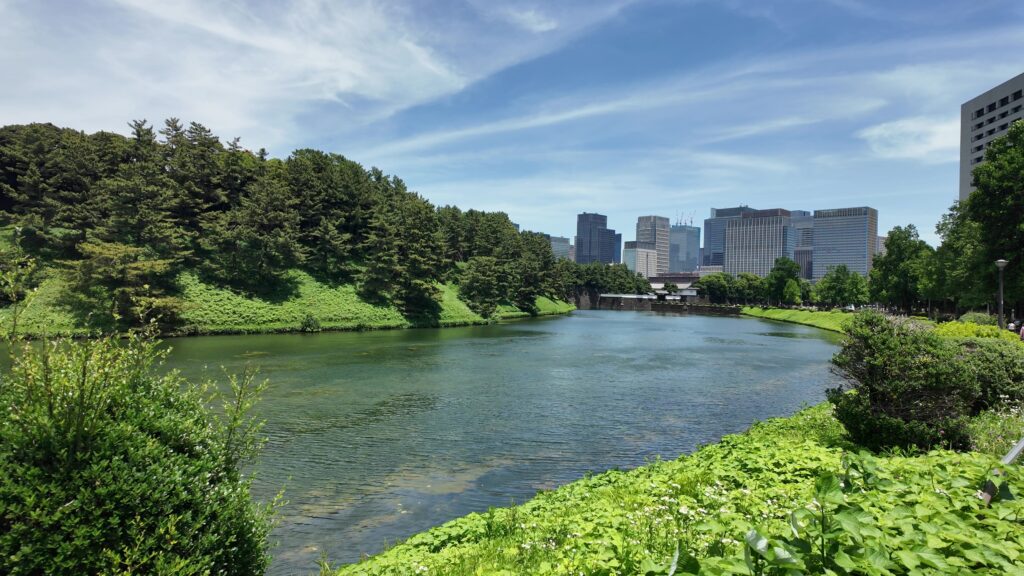
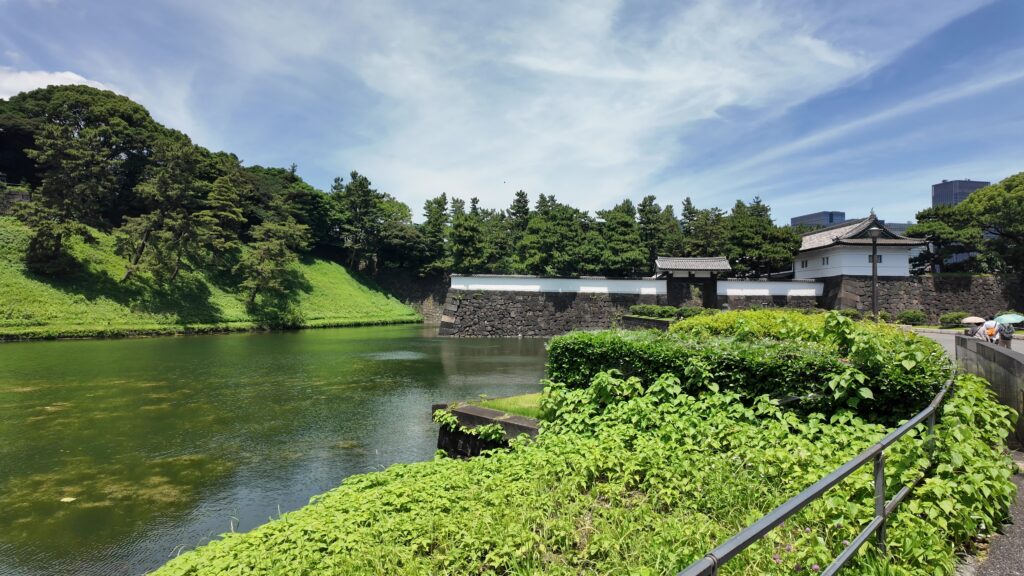


歴史の舞台、桜田門~西の丸
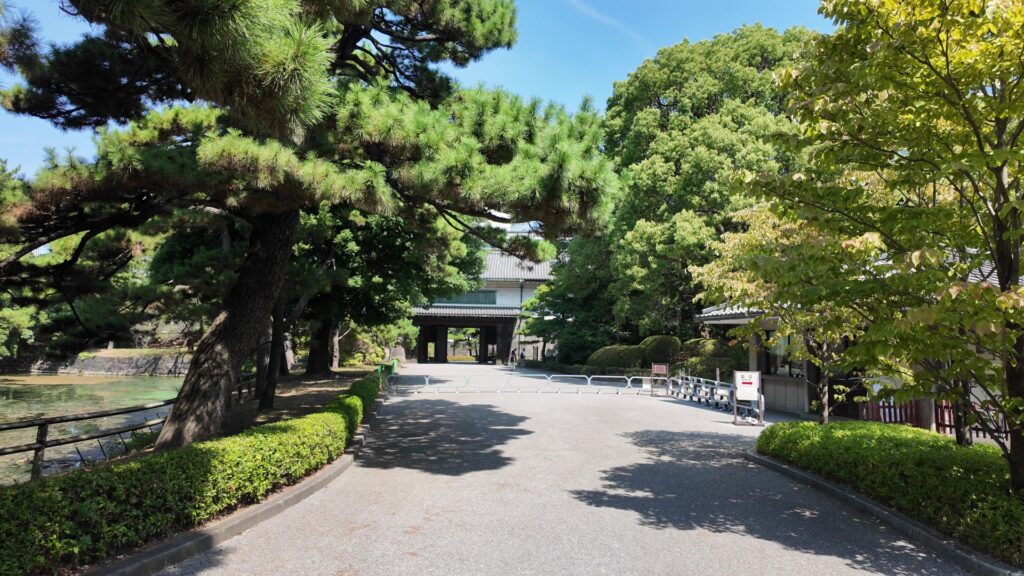
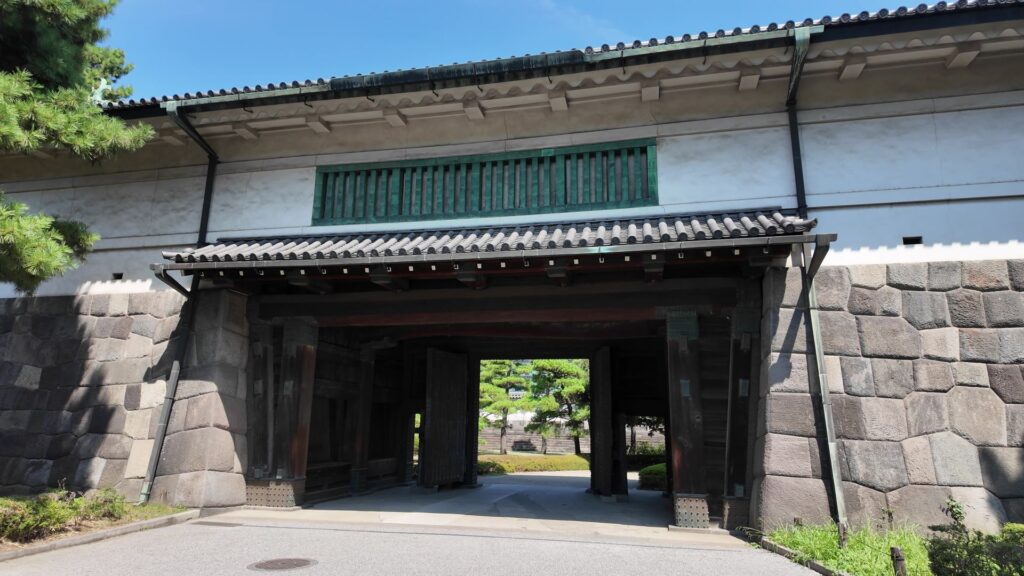
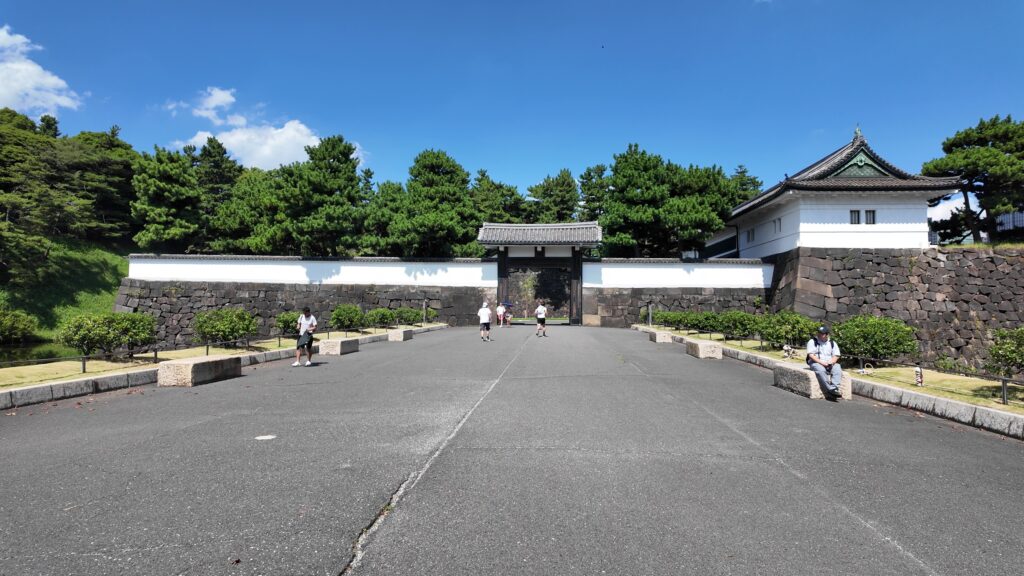
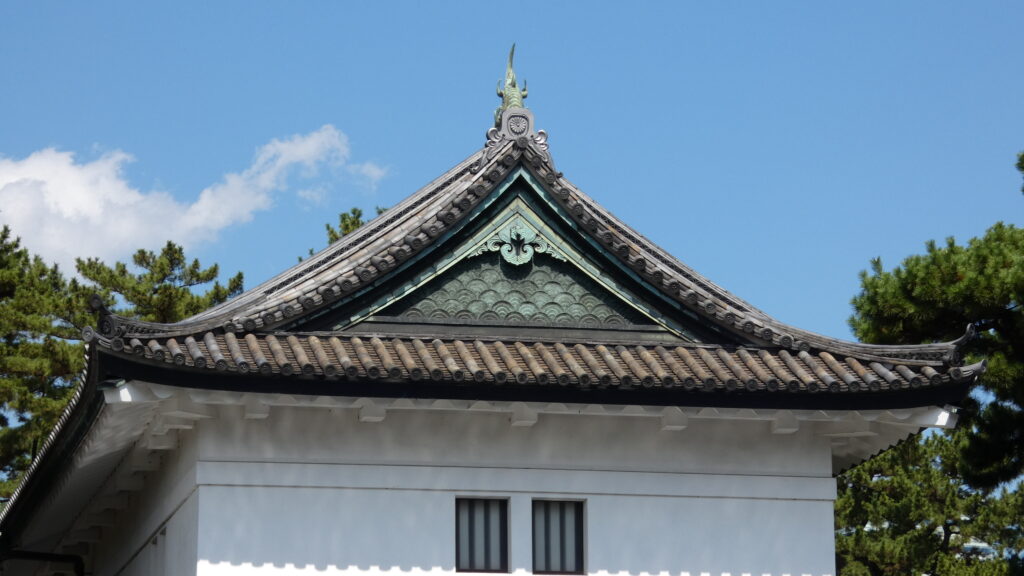
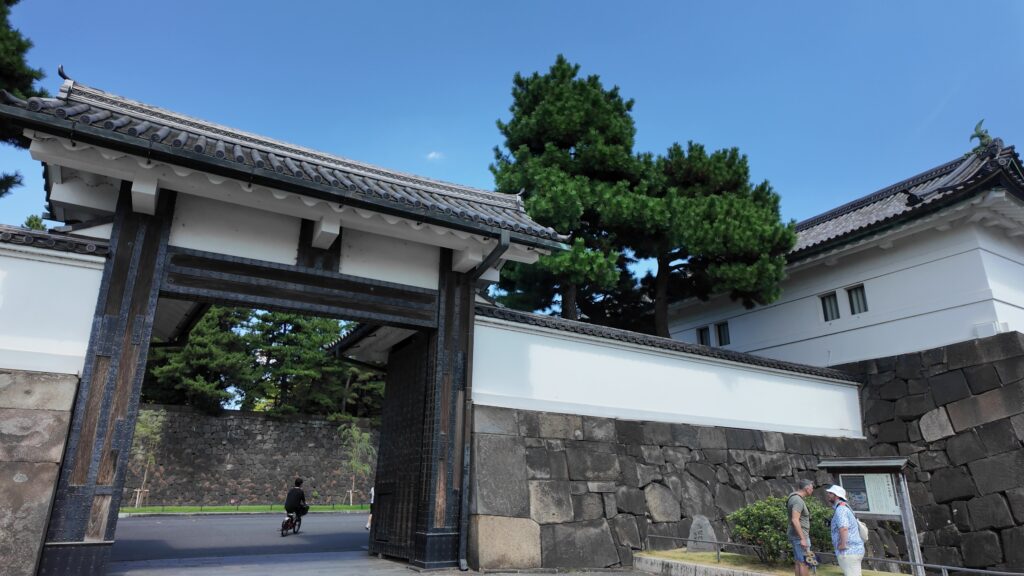
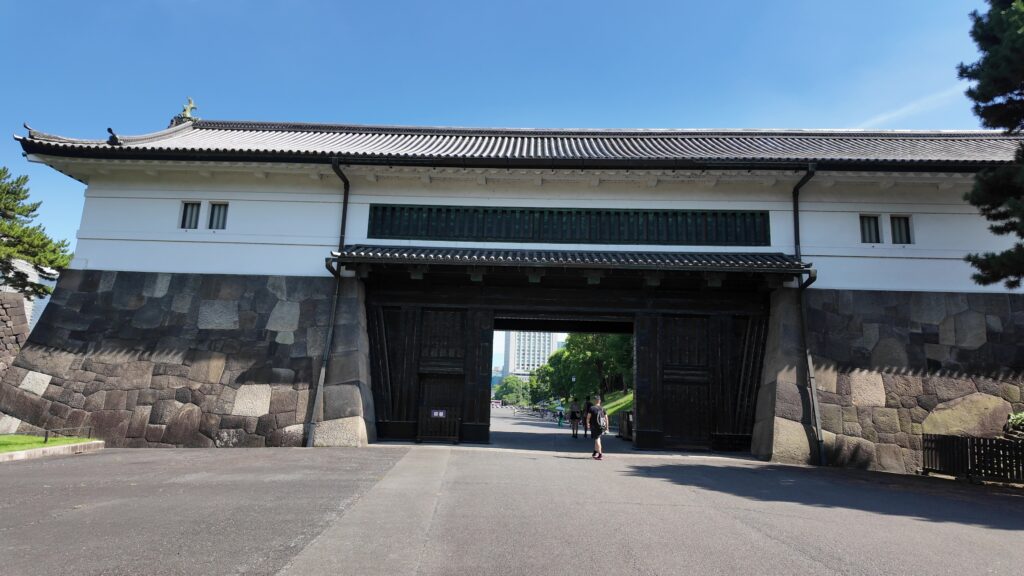
桜田門(外桜田門)は、江戸初期からあったとされていますが、現在残る建物は、明暦の大火後の1663年頃に再建されたものです。こちらも重要文化財に指定されています。外側から見ると、櫓門の妻部分の装飾がきれいです、「青海波」という模様だそうです。


桜田門外の変は、門の反対側に見える警視庁の辺りで起こったそうです。こちらも「桜田門」といわれます。

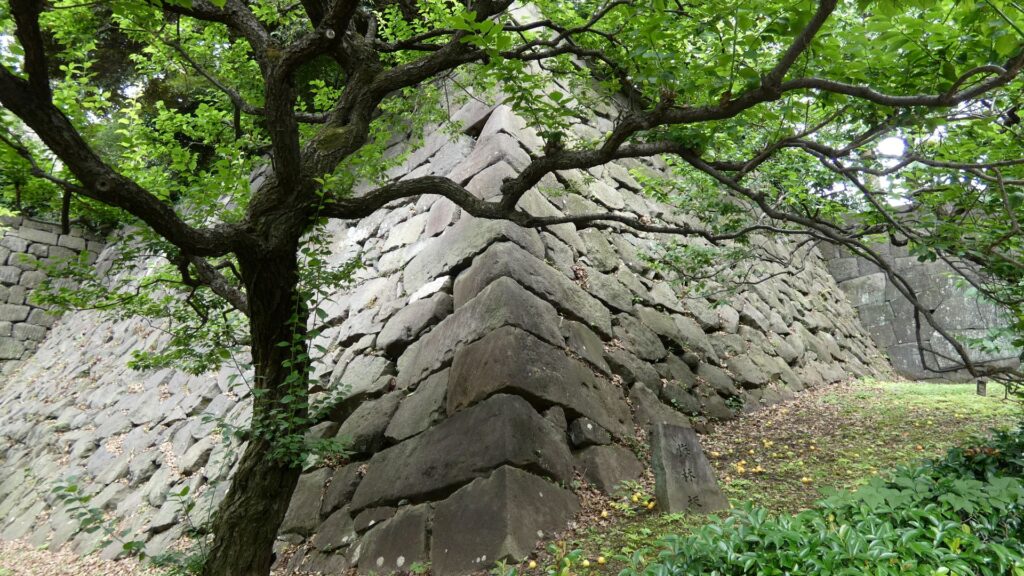
それでは、門の方に向かいましょう。高麗門から入ります。枡形の定番です。ところが、枡形に入ると、奥に石垣や塀がありません。正面から左側も一部欠けています。これは、背後の西の丸の曲輪(的場曲輪)から攻撃できるようになっているからです。枡形にもいろんな守り方があるのです。


枡形から出るときは、立派な櫓門を通ります。威風堂々としています。次の歴史の舞台に向かいます。
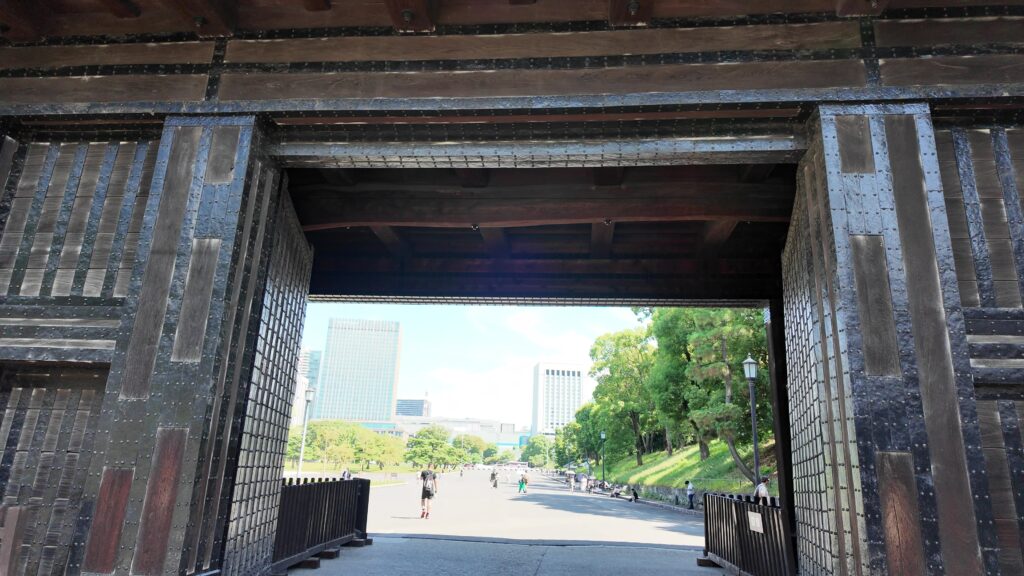


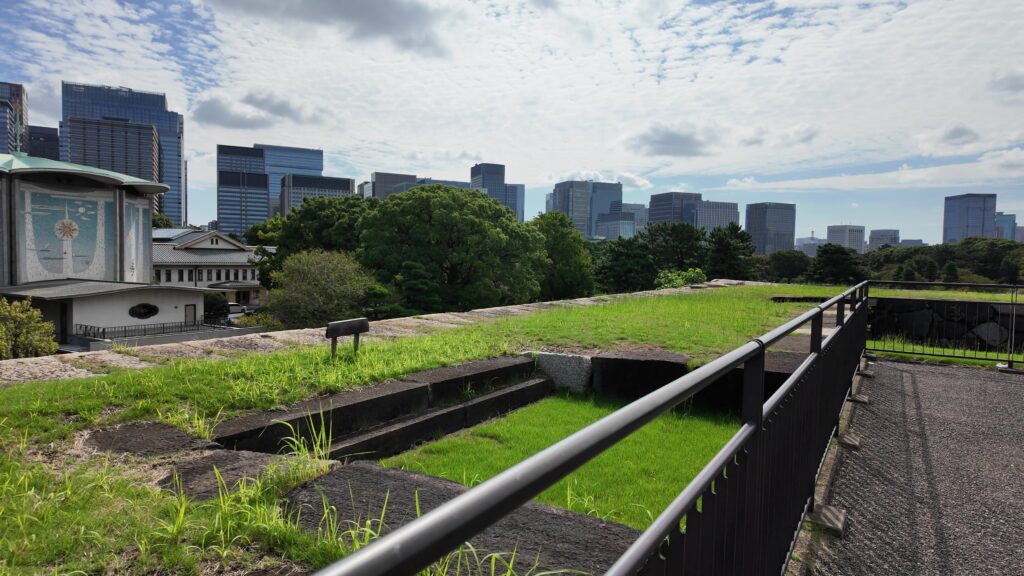
かつての西の丸下、皇居外苑に入りました。この辺は江戸城の初期、日比谷入江だったのです、信じられません。
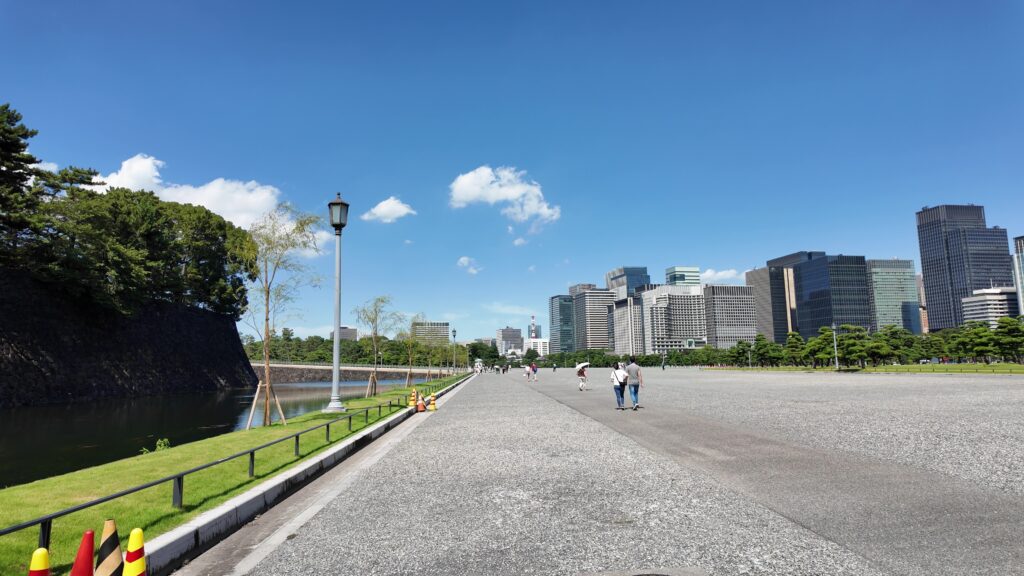

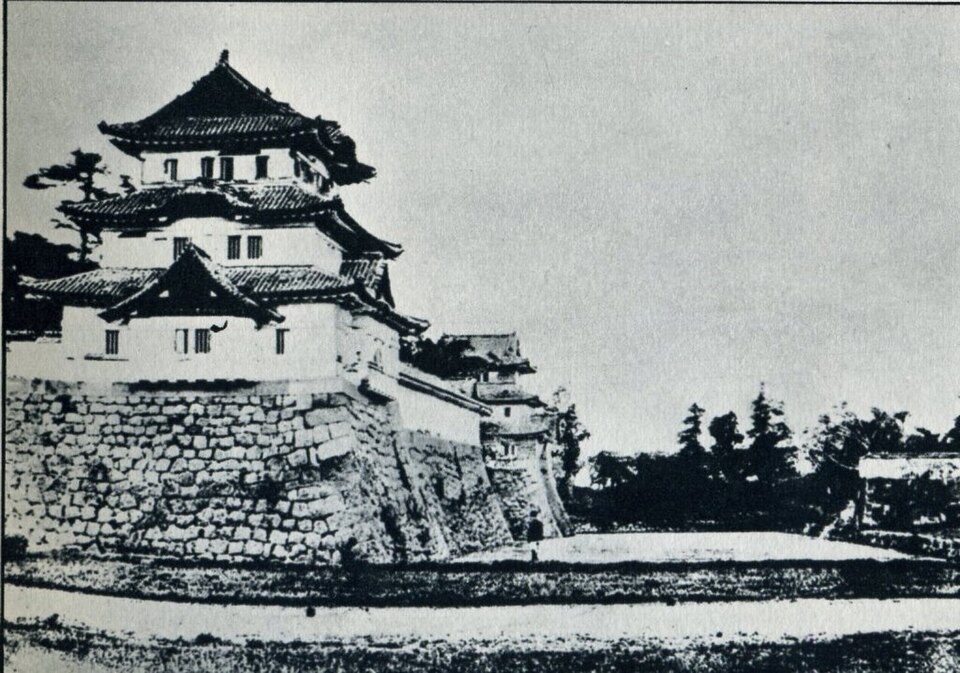
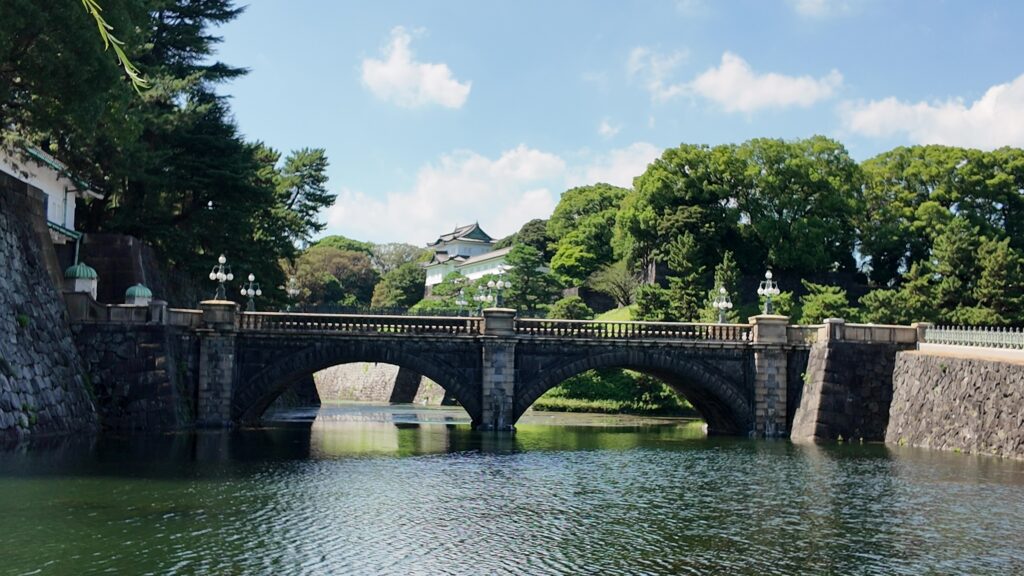
場所的には定番になりますが、おなじみの構図です。一般的には「皇居二重橋前」というのでしょうが、江戸城としては、西の丸大手門前ということになります。明治天皇が西の丸に入って以来、皇居になりました。奥に見える櫓は現存する伏見櫓です。絵になる風景です。ちなみに、正面に見えている橋は、現・皇居正門の石橋で、二重橋は、奥の方にある橋をいうそうです。西の丸に入るにも、2本の橋を渡る必要があったということです。

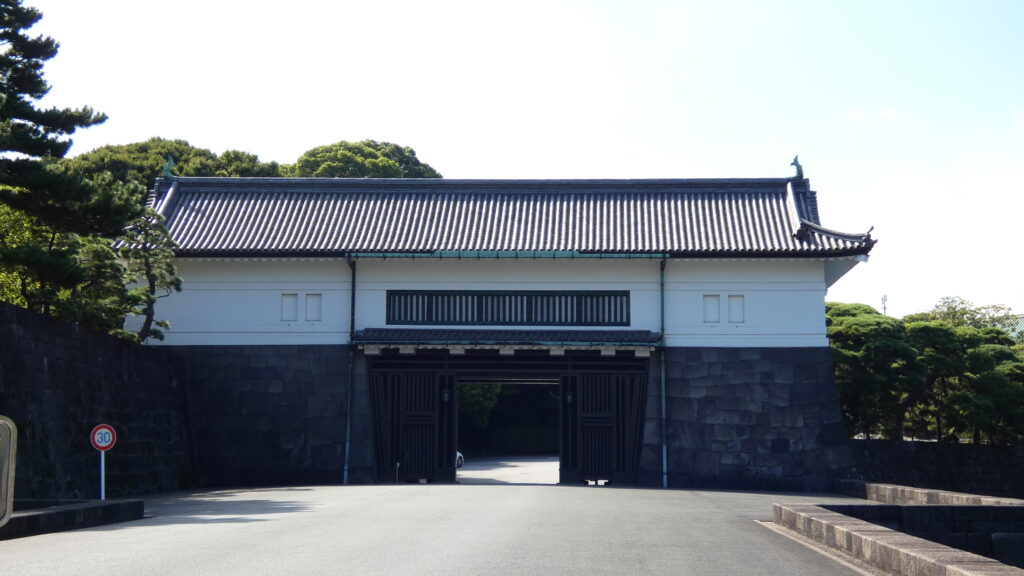
さらに先に行くと、坂下門外の変で知られる、坂下門も見ることができます。どれも激動の幕末の歴史の舞台だったのです。

元の日比谷入江を探る
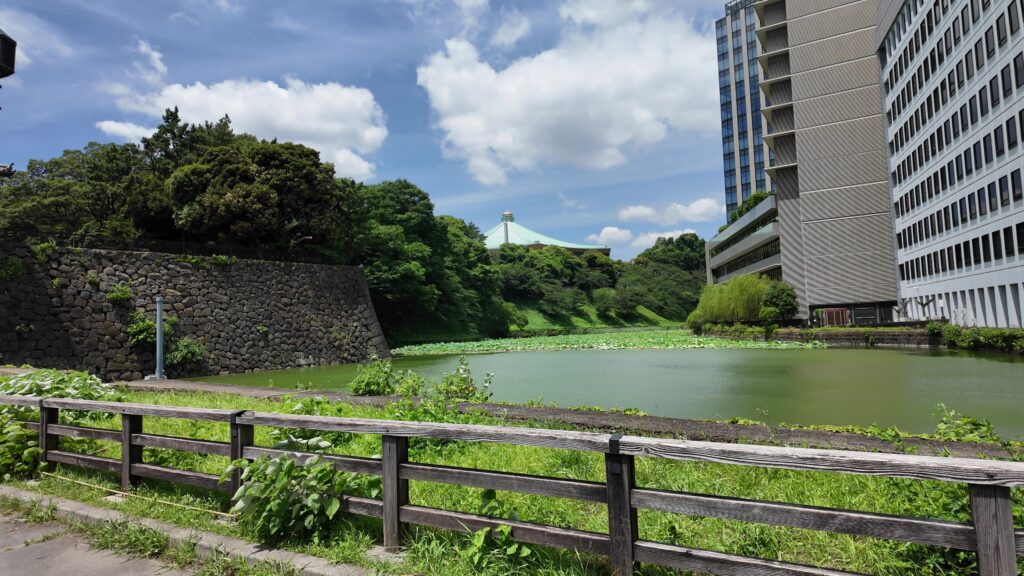
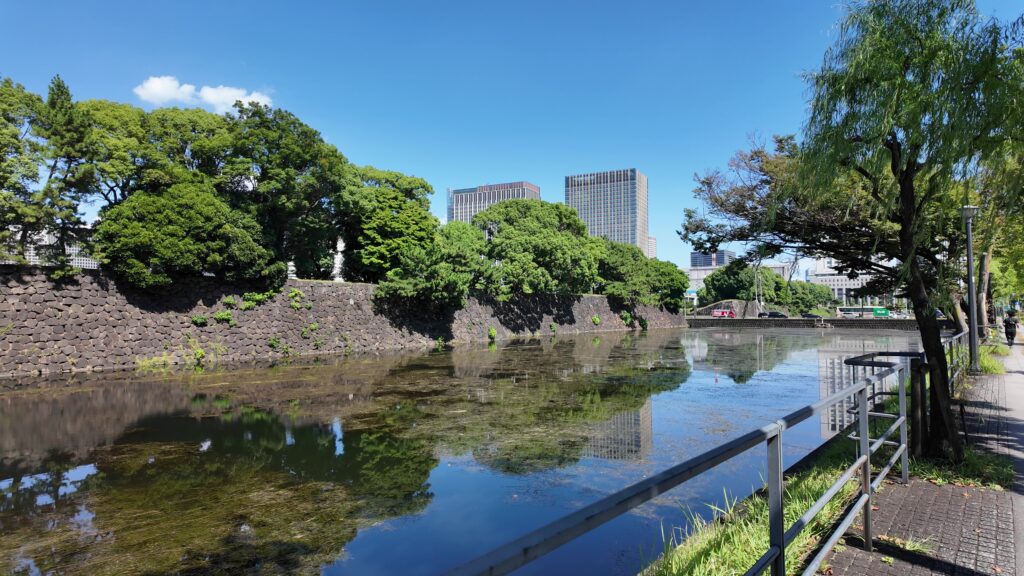
最後のセクションは、埋め立て地の西の丸下、現在の皇居外苑の周りを歩きましょう。桜田門前に戻って、内堀沿いを進んでいきます。堀は、凱旋濠から日比谷濠に移ります。先ほど歩いた桜田濠などとは全然違ってフラットです。元の地形をよく表しています。
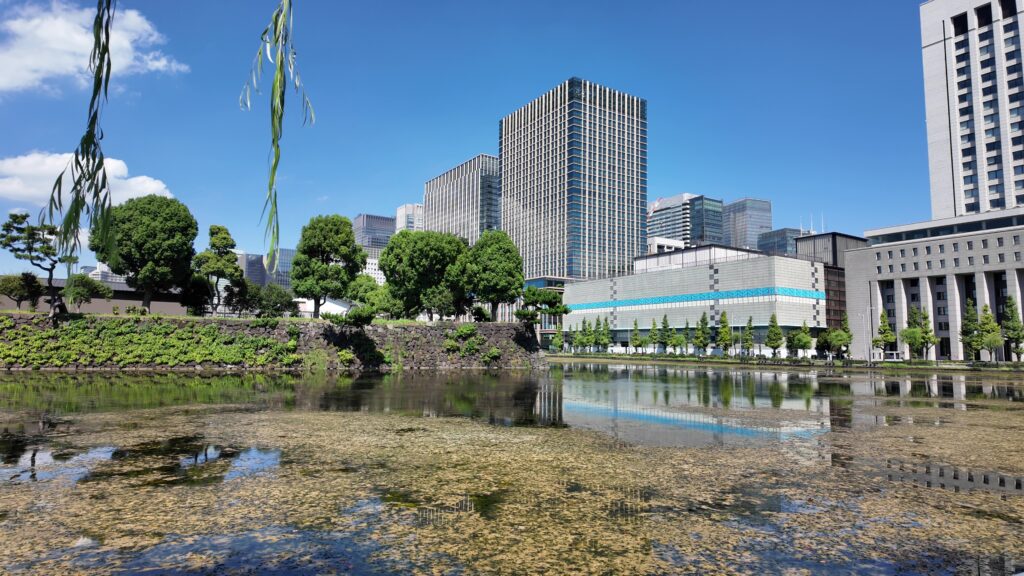


日比谷交差点のところを曲がります。現代の東京のど真ん中の場所です。今度は大きな道路と交差します。馬場先門跡です。実は日露戦争の頃まで門が残っていたそうですが、戦勝祝賀会のときに群衆が押し寄せ、枡形の中で人が亡くなる事件があり、撤去されて、今の道路になったとのことです。この近くには休憩所もあります。
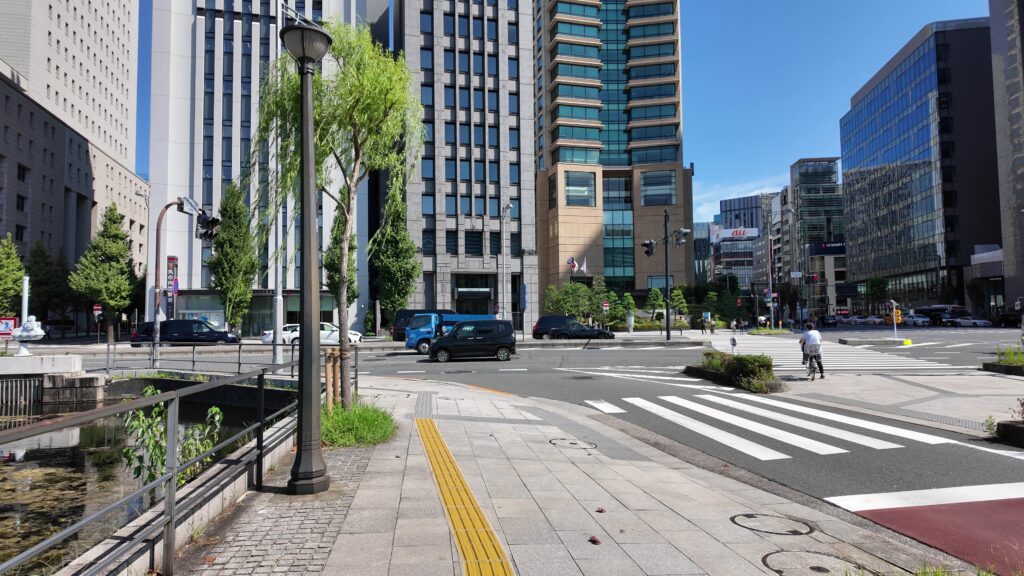




馬場先門跡から、また進んでいきましょう。これらの堀は、日比谷入江を埋め残したものといわれます。入江の大きさも想像できます。また大きな通りがあって、古い交番のような構造物も見えます。通りは大正時代にできた行幸通りで、東京駅正面から続いています。交番のようなものは、皇居の入口の守衛所として使われたそうです。
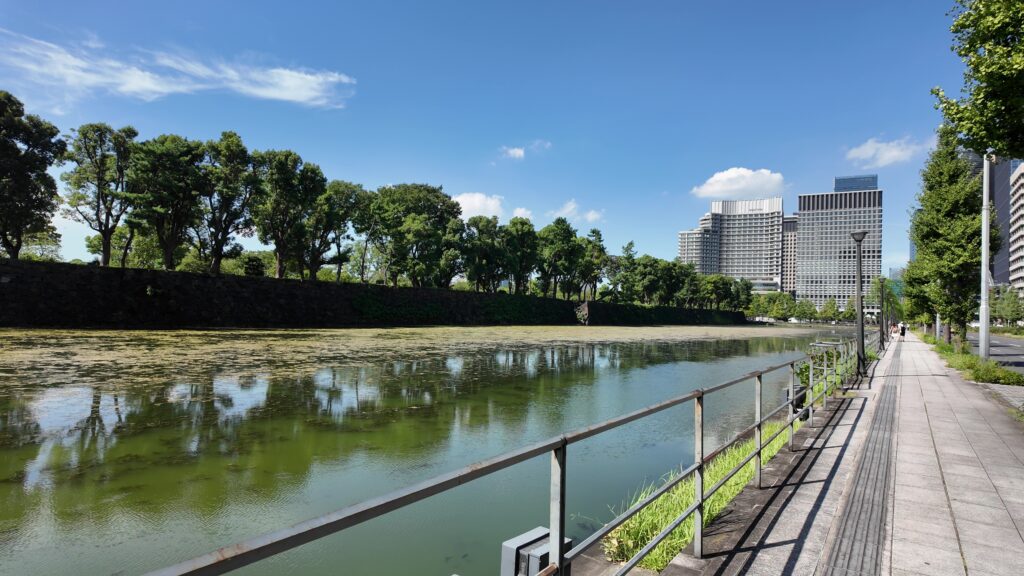
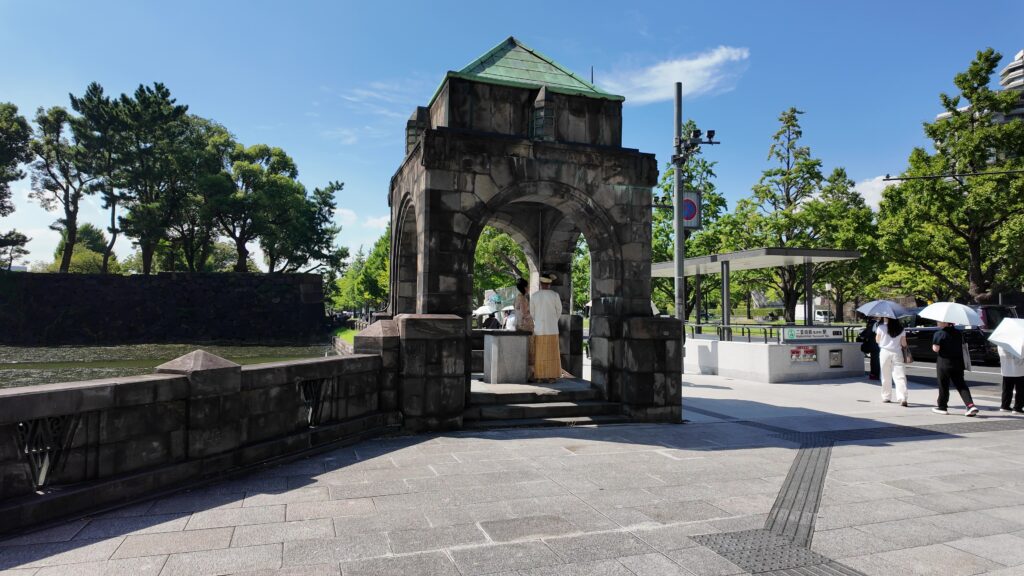


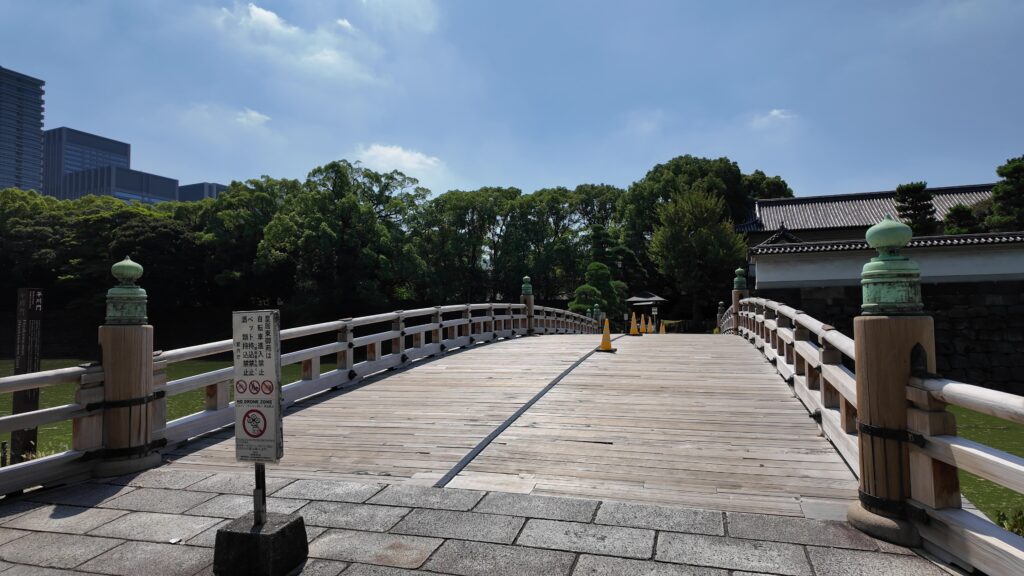
江戸城の門の跡は通りを越えた先にもあります。古風な橋が見えます。和田倉門跡です。堀を渡る橋は、平川橋とともに、江戸城にある貴重な木橋です(基礎はコンクリート造り)。柱に被さる擬宝珠は、オリジナルだそうです。橋に威厳を加えています。門の建物は、関東大震災のときまで残っていました。それでも、今も枡形の石垣があります。
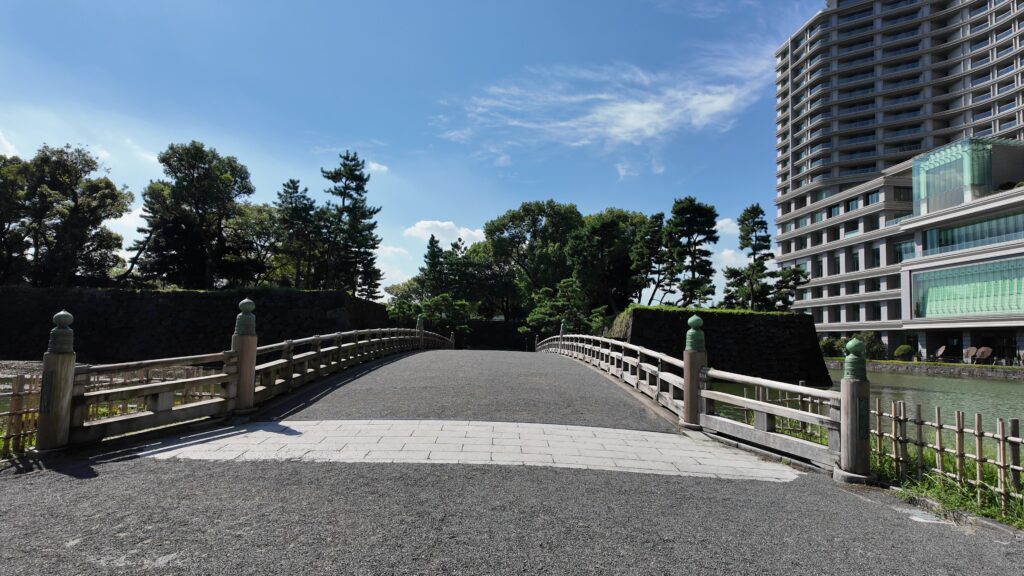
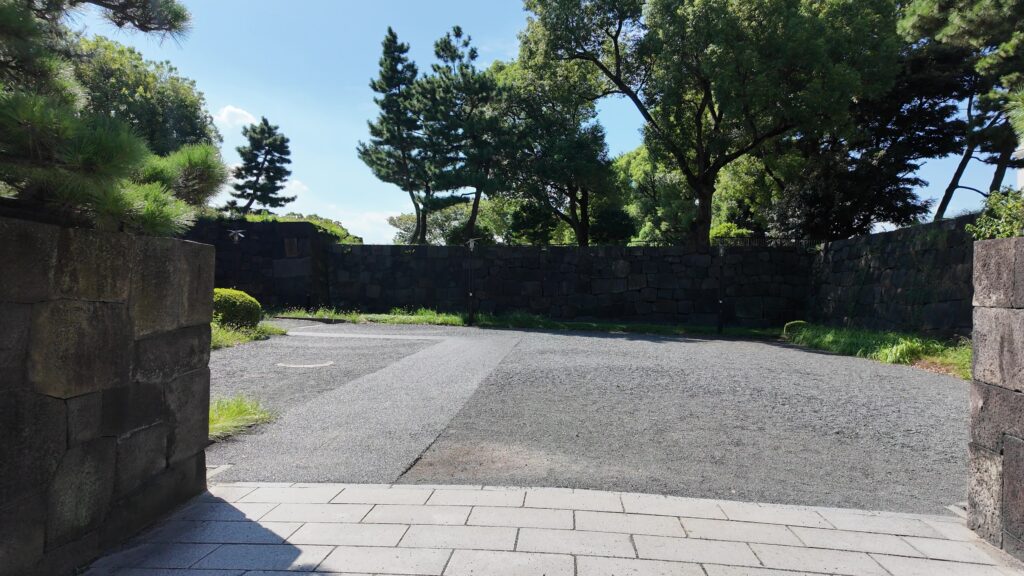


「和田倉」とは、海に臨んだ蔵という意味のようなので、当初の江戸城では、この辺りまで舟が入って、荷揚げを行っていたのでしょう。堀もここで一区切りしているので、これも入江の名残かもしれません。
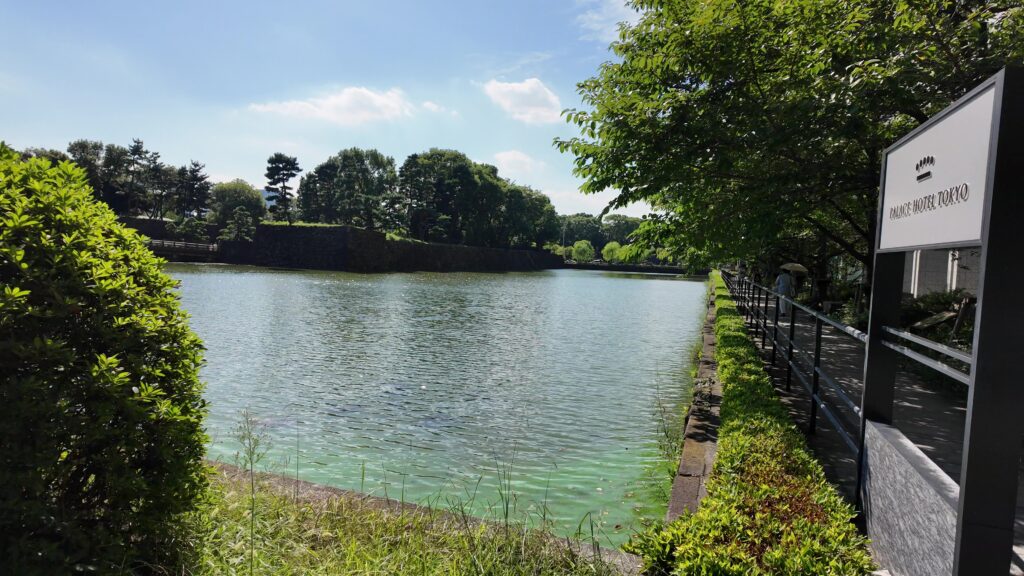

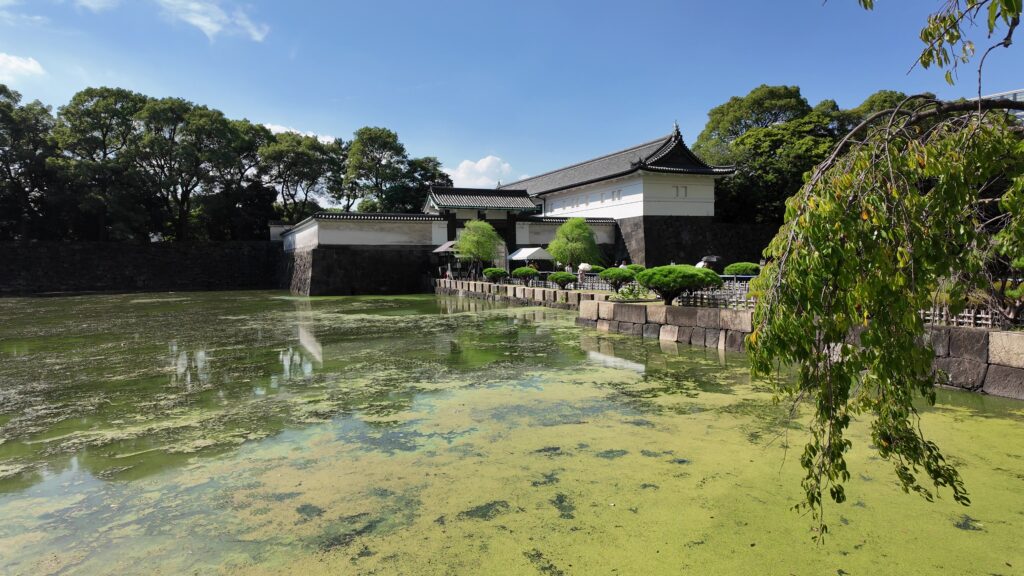
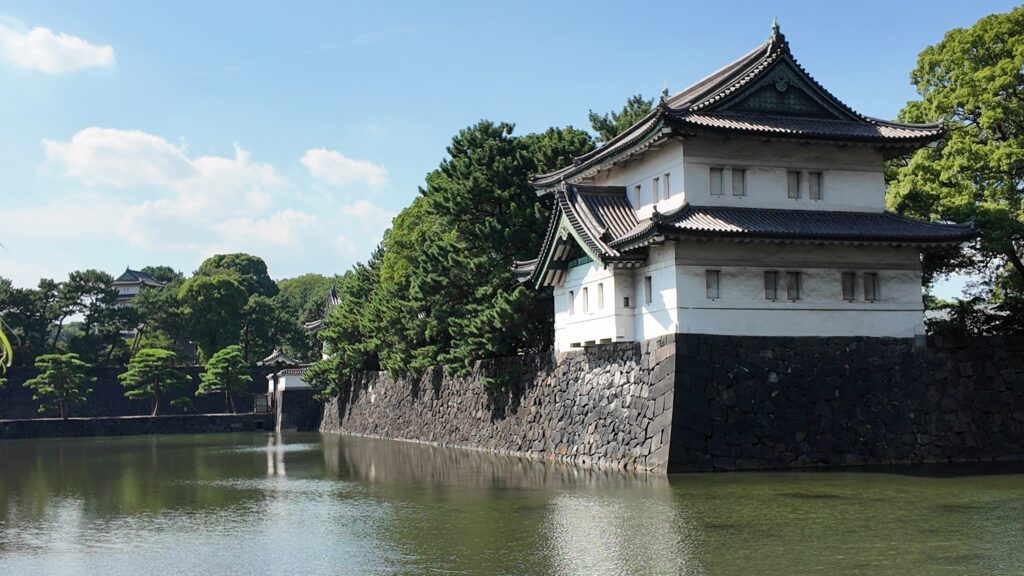
そして、近くの大手門の前に来ました。今回はここをゴールとしましょう。前回の現本丸ツアーのスタート地点でしたし、平川門とは反対側にもう一か所ご紹介したい所があるのです。これも定番になるのですが、三の丸辰巳櫓、桔梗門、富士見三重櫓がいっぺんに見れるスポットです。これも有名な景色です。


「江戸城 その1」に戻ります。
「江戸城 その2」に戻ります。
「江戸城 その3」に戻ります。
「江戸城 その5」に続きます。