Features
Introduction
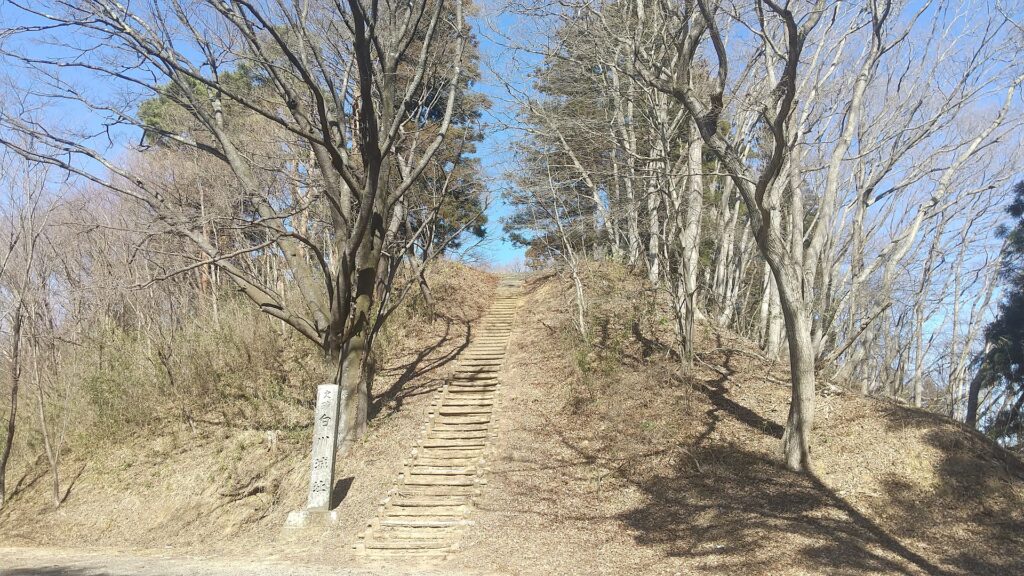
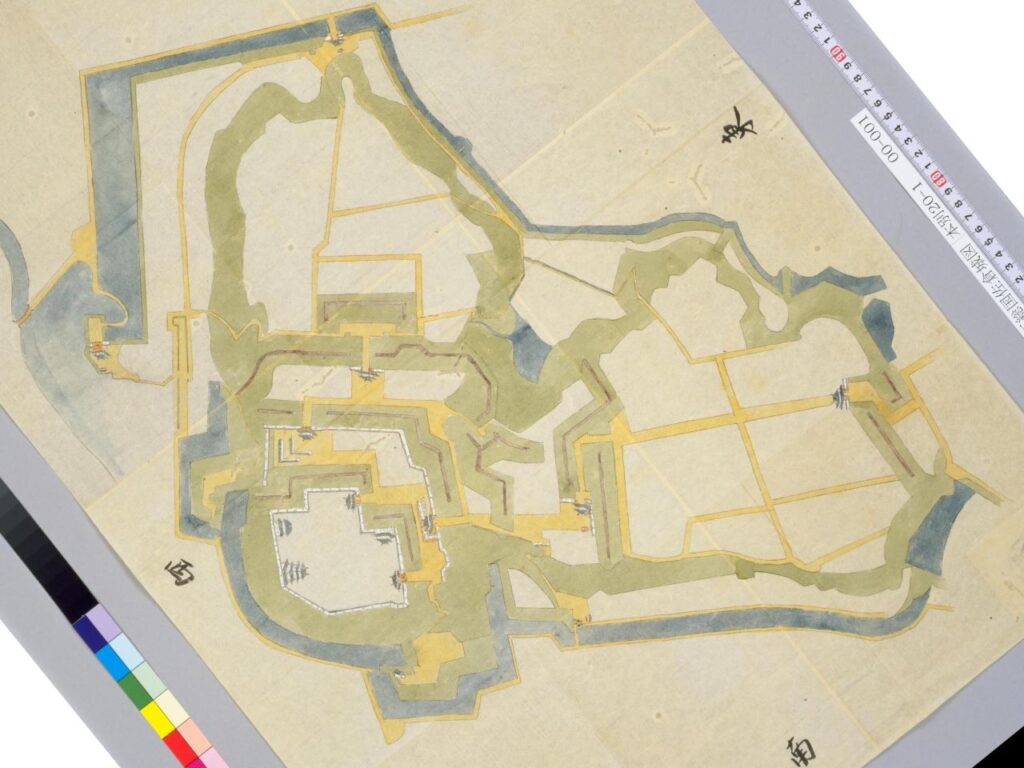
If you are at JR Sakura Station, the place, where the castle ruins are located, it may look simple at first. However, if you go there by walking up on the slopes, you will be surprised to see the spacious area on the top. Visitors coming from other places may feel the same way, too.


From Main Gate to Main Enclosure
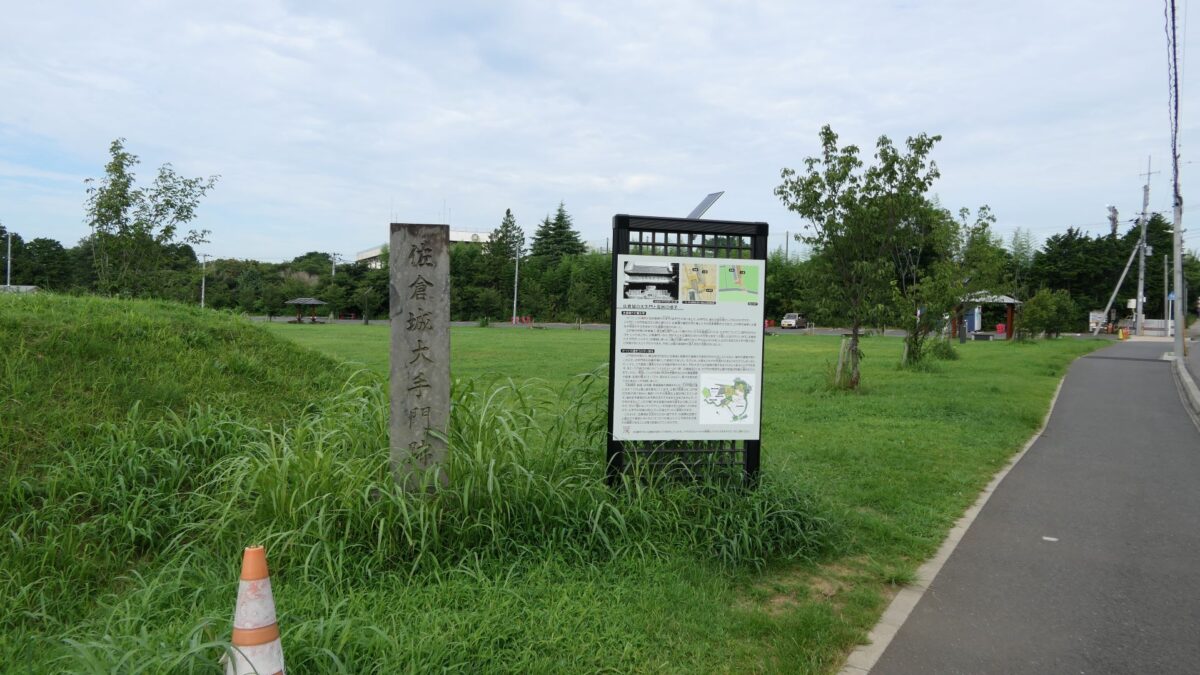
Let us go from the ruins of the main gate to the center of the castle. Unfortunately, only a part of the earthen walls remains today.
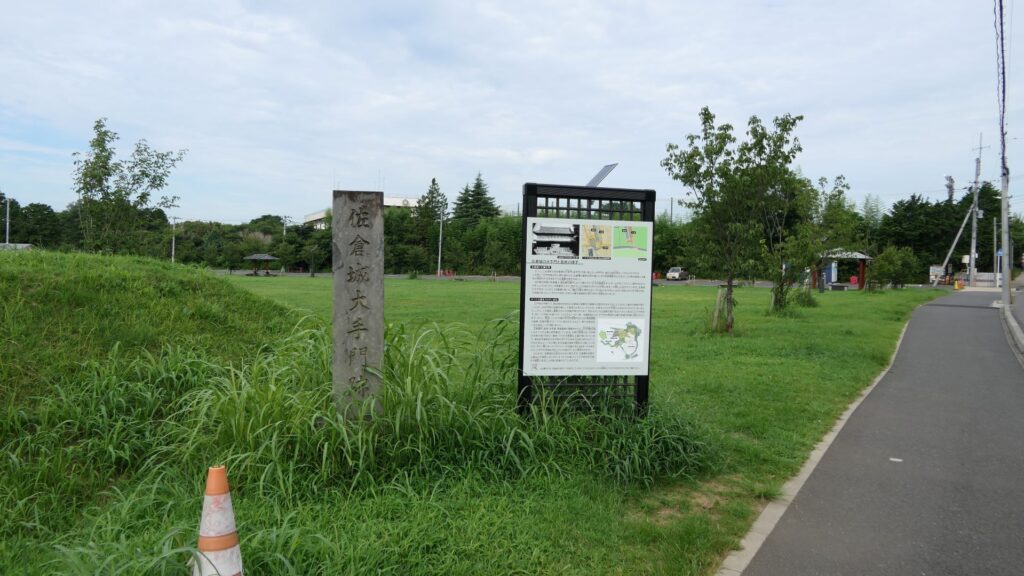
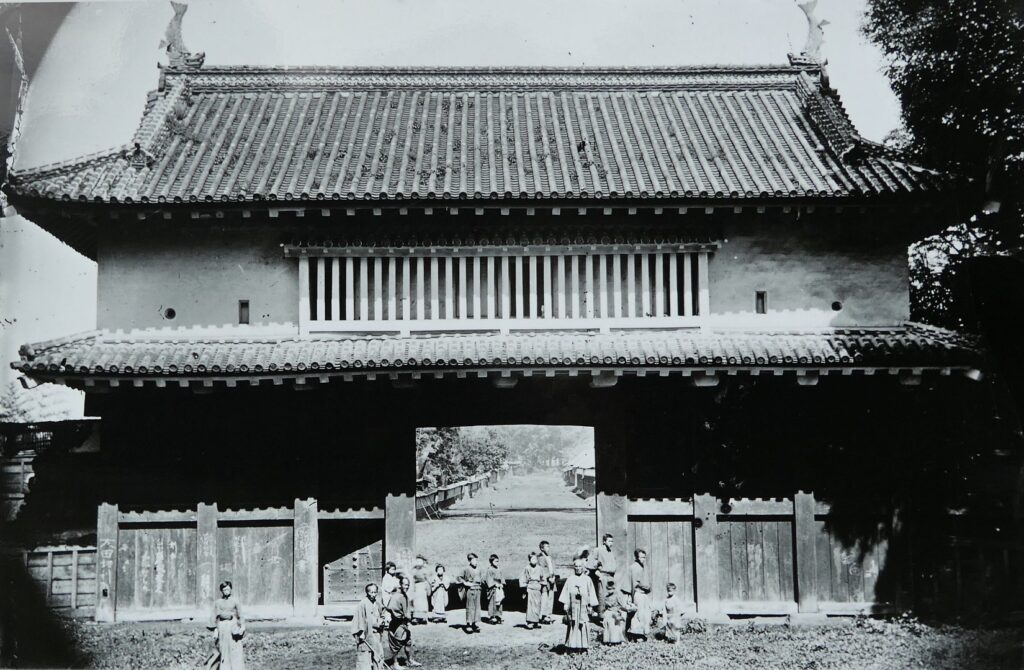



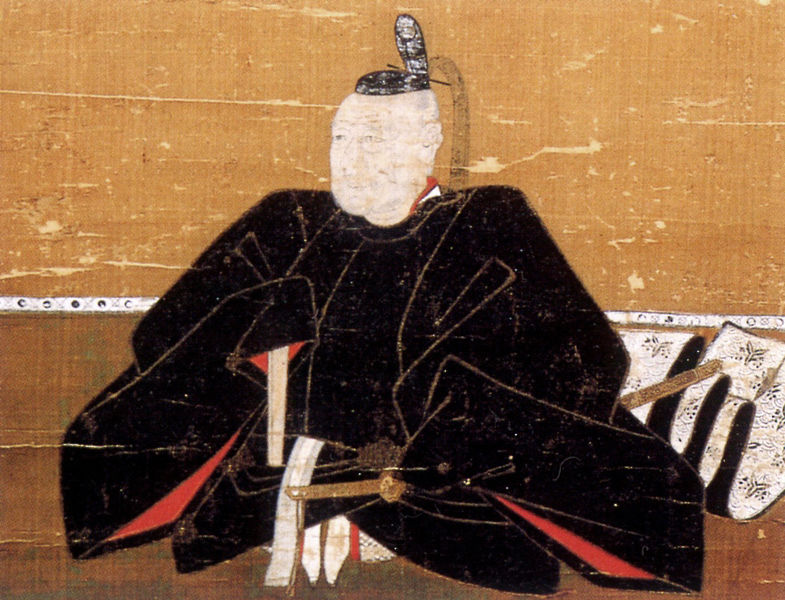
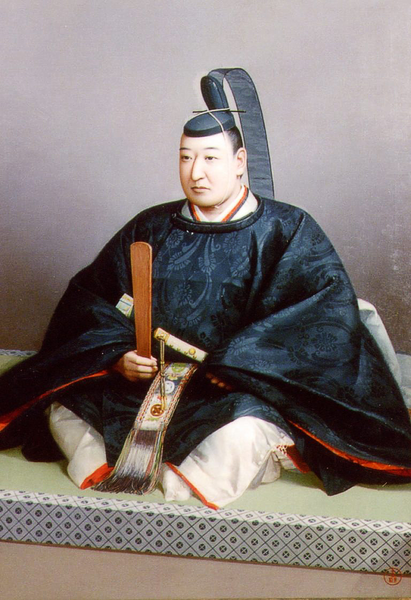
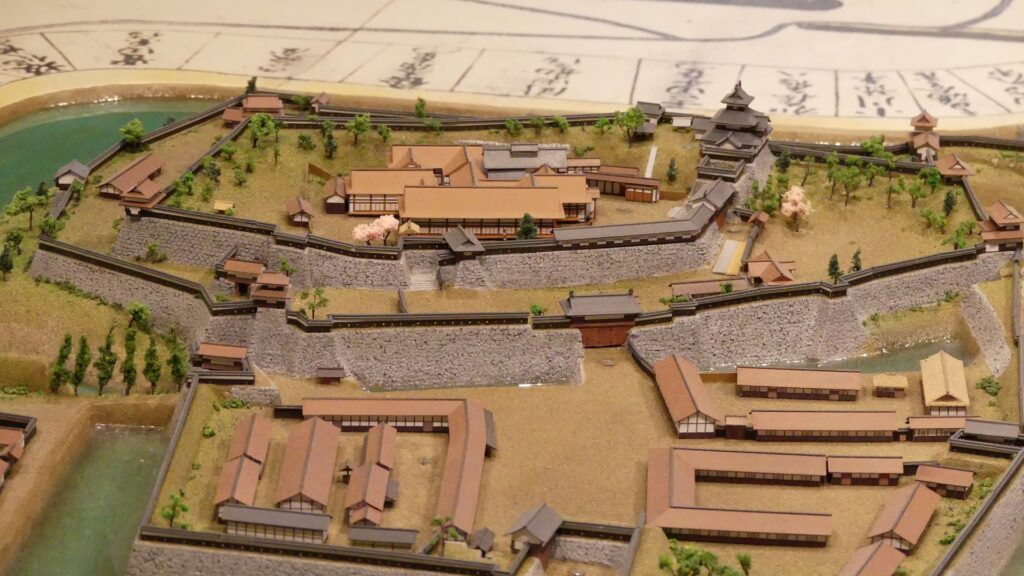
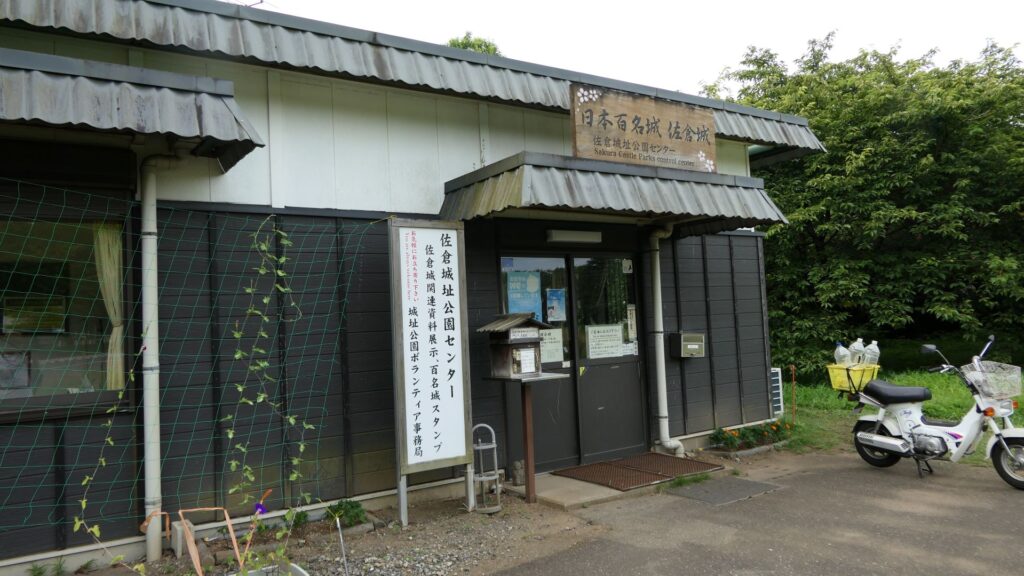
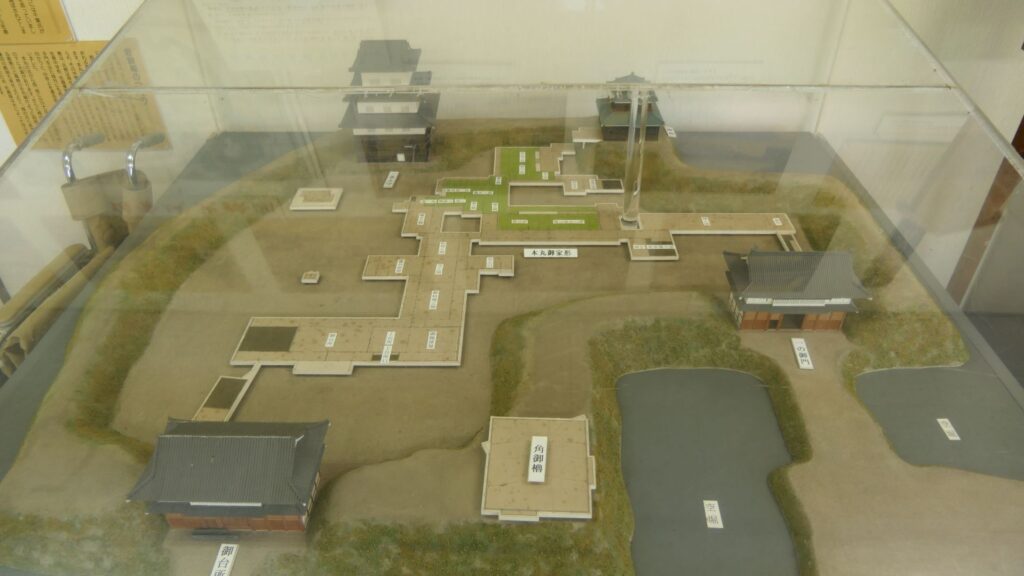
There were some large enclosures inside the gate, such as Higashi-so-kuruwa. They were turned into schools, parking lots, and a square. There is also Sakura Castle Park control center in front of the square, which shows some exhibitions of the castle. The square had the main hall for the lord and another one for the retirement residence of Masayoshi Hotta at the end of the Edo Period.


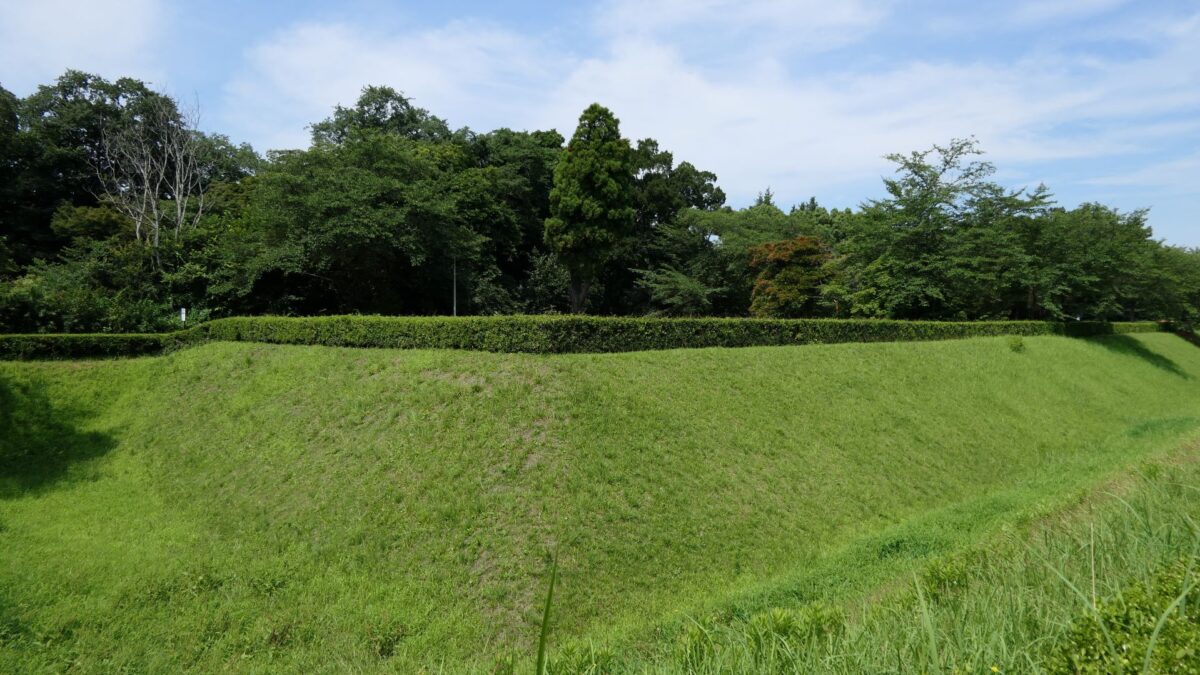
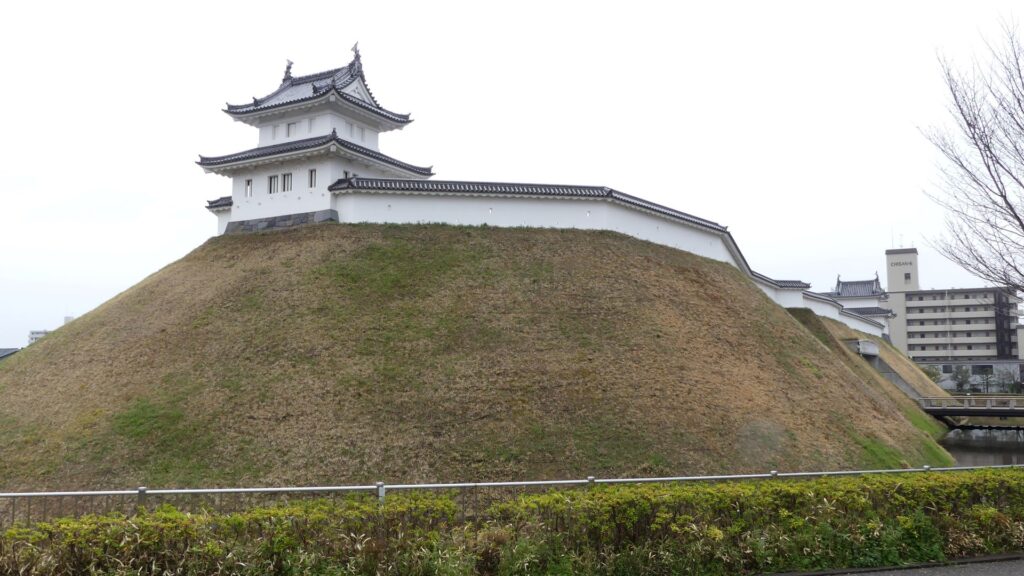
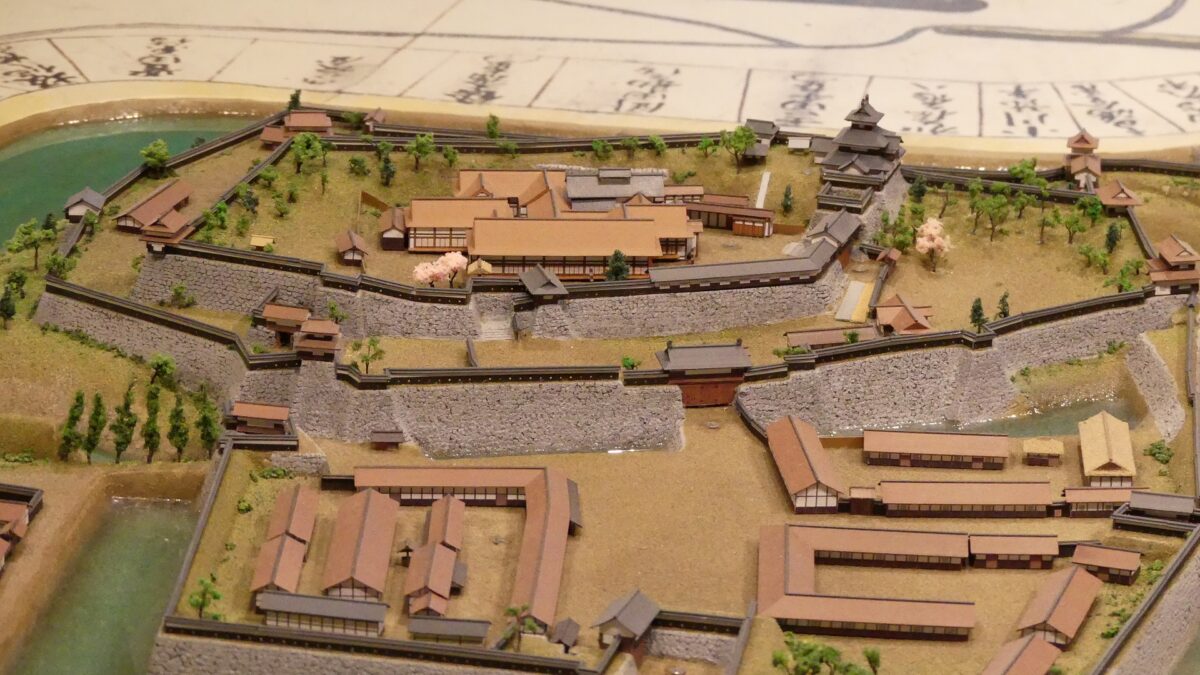
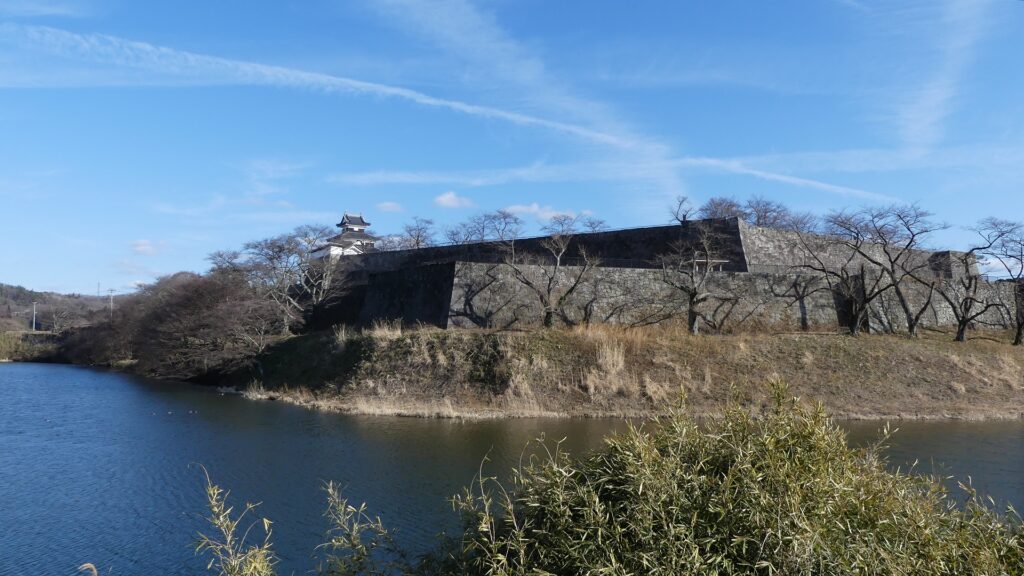
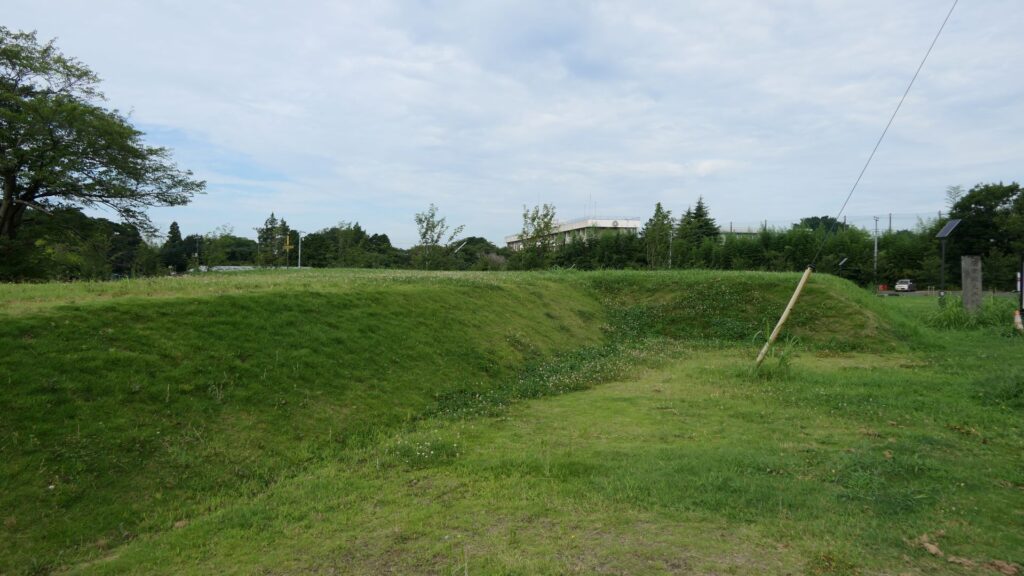
You will eventually reach the center of the castle, which has been turned into Sakura Castle Park. You will first see the remaining large dry moat. It looks beautiful, covered in grass, however, it must have been deeper and more fortified in the past.
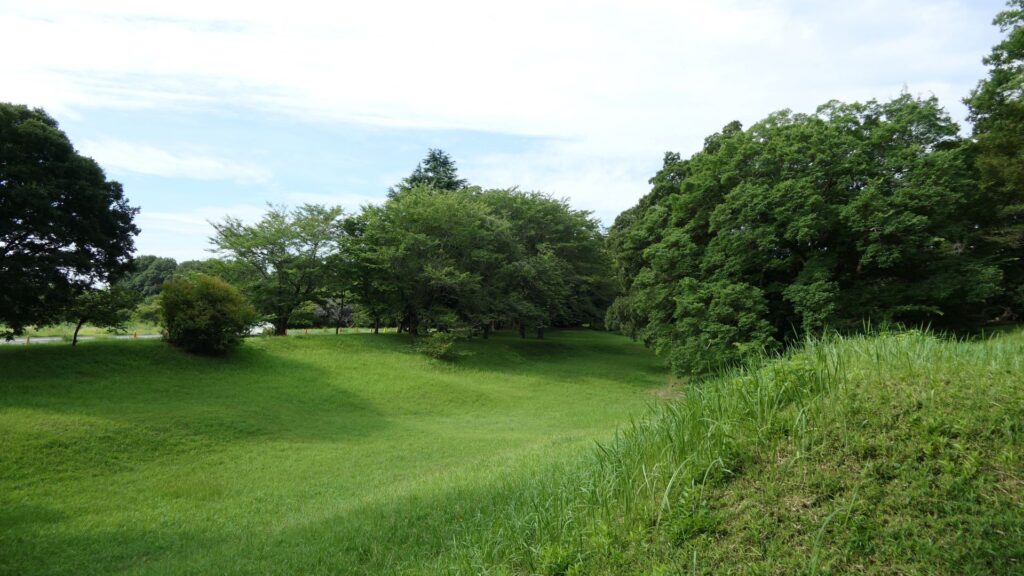


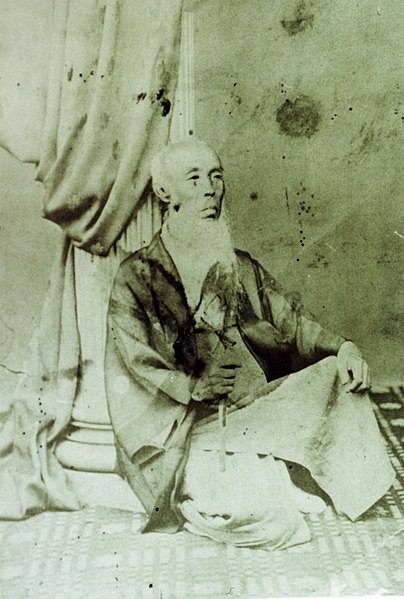
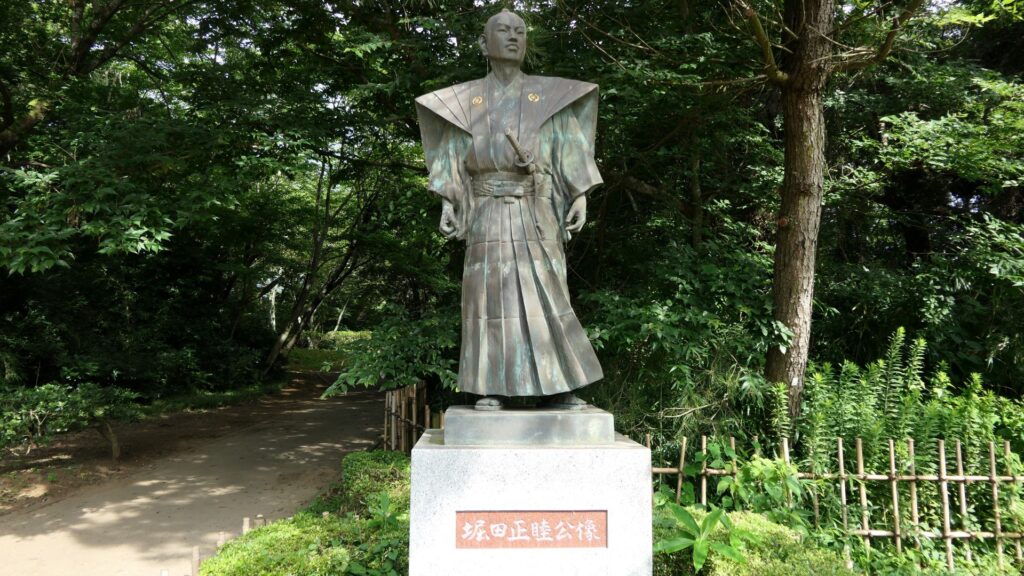
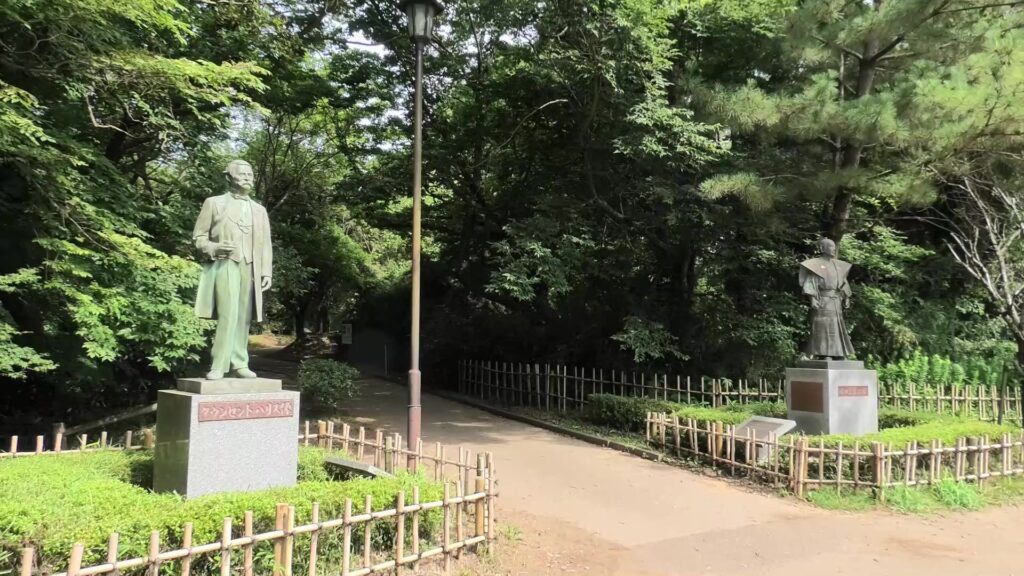
You will next reach the ruins of the third gate, which was the first gate towards the center. The third enclosure is inside of the gate, and it was the residential area for the senior vassals in the past. You will find a mini crater in the enclosure. This is the trace of another dry moat, which has been filled. If you go further, you will see the statues of Townsend Harris and Masayoshi Hotta who tried to open Japan to the rest of the world.
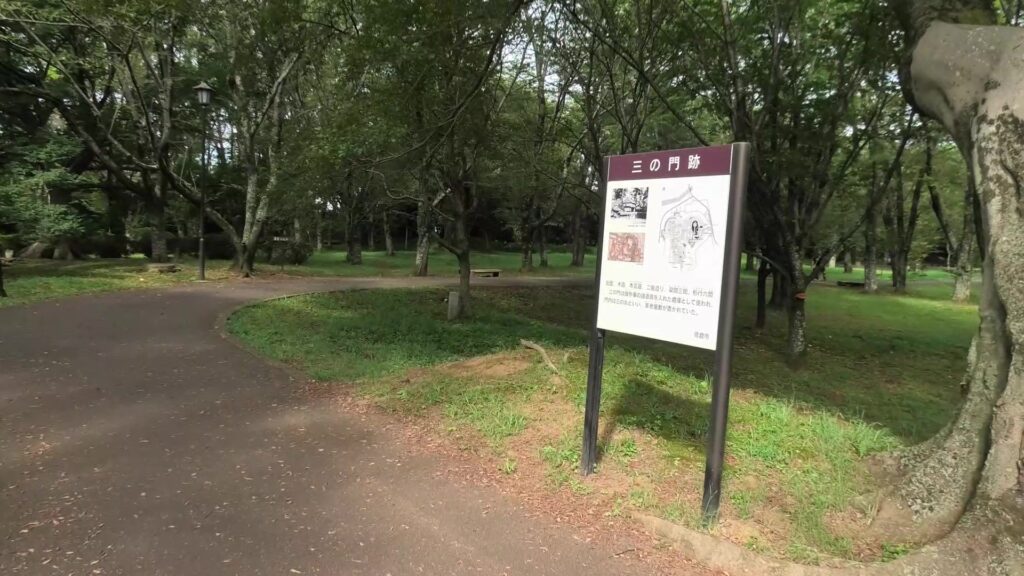
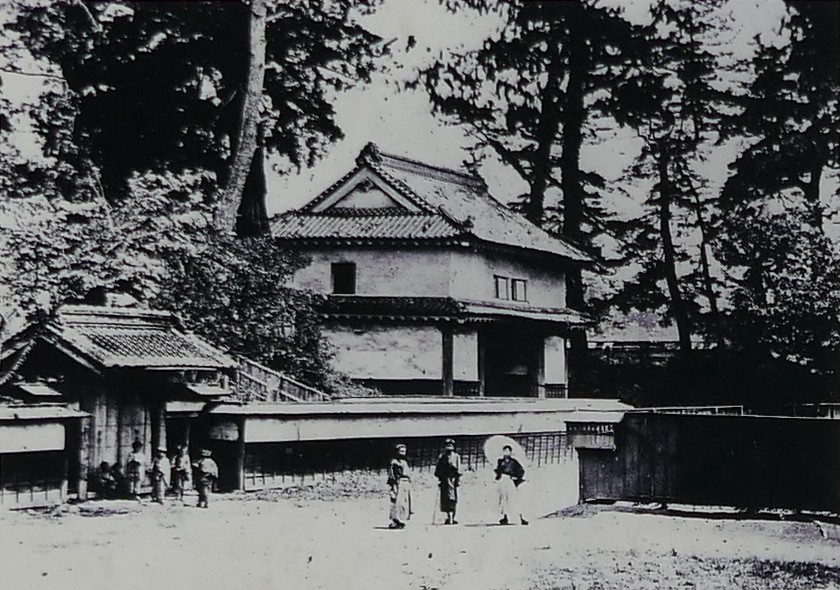




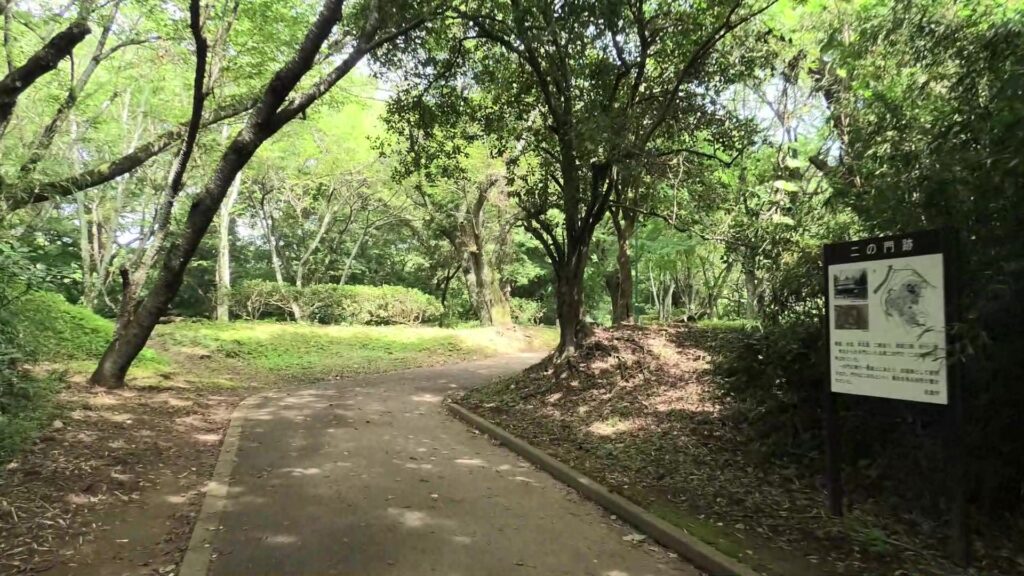
Then, you will reach the ruins of the second gate, the entrance of the second enclosure. The enclosure had had the first main hall for the lord before the one outside the third enclosure was built. There were also the rice warehouses in the back of the enclosure. You can still see its stone foundations there, too.
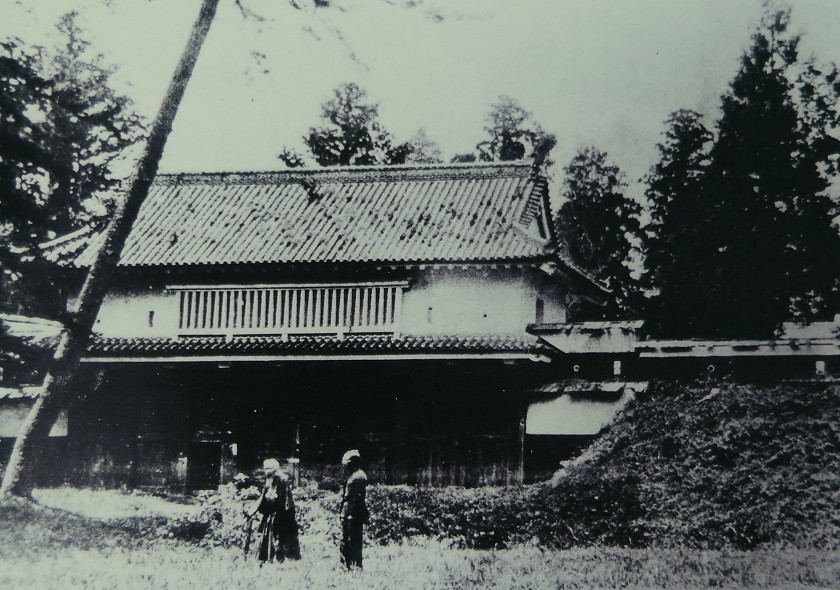
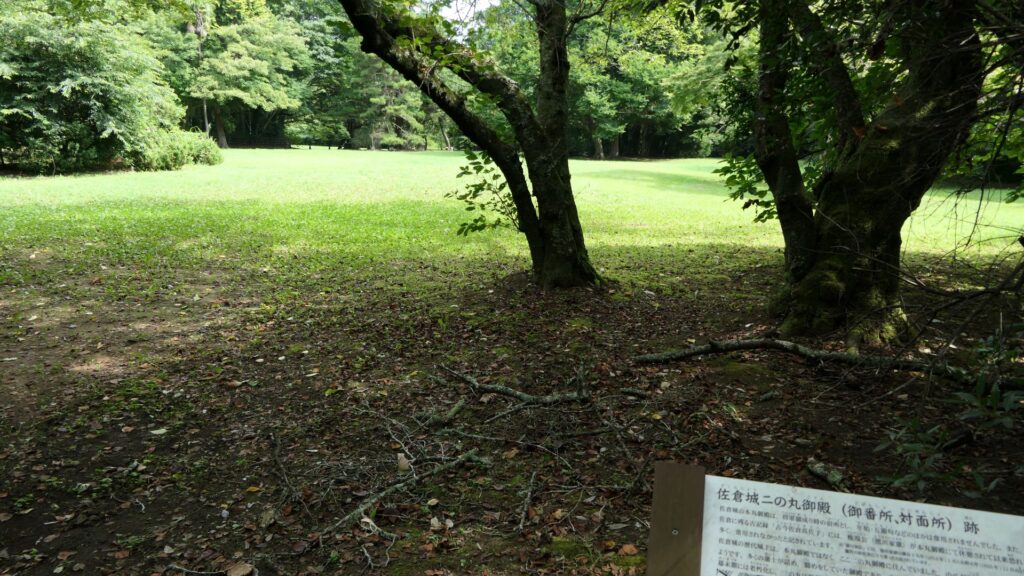
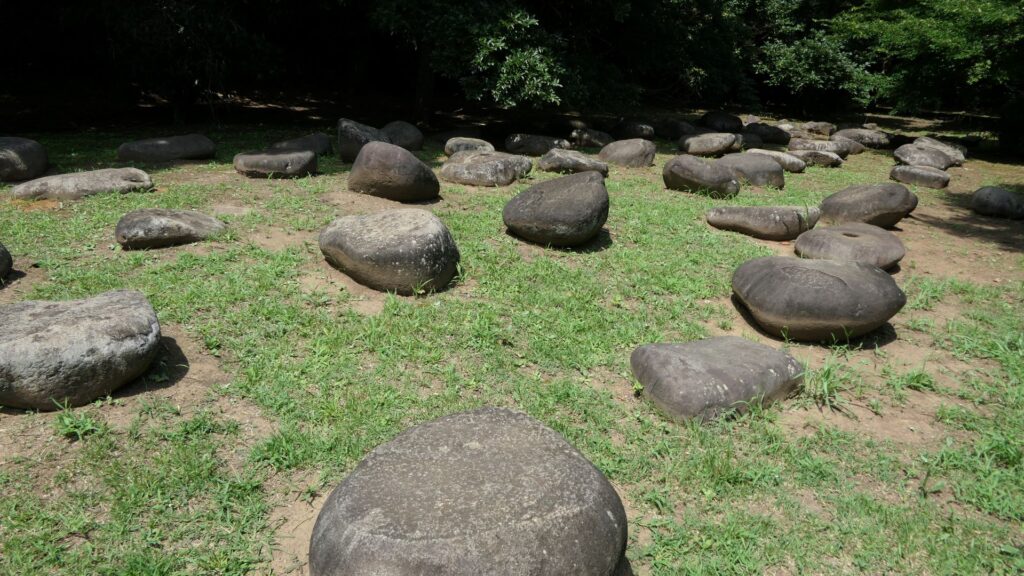




You will eventually reach the main enclosure after going across the dry moat of the enclosure. there are the ruins of the first gate.


Climbing down from Main Enclosure
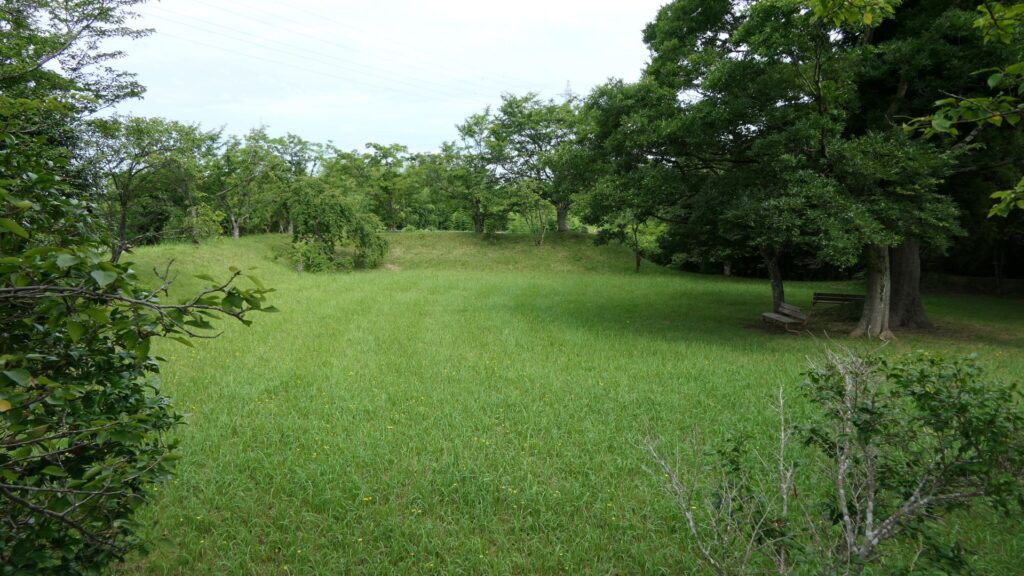
The main enclosure is all surrounded by earthen walls, so you may feel like you are being wrapped up. This area is the western edge of the plateau. There was the other main hall inside, however, it was rarely used just for ceremonies. This was because it was considered exclusive for the shoguns.


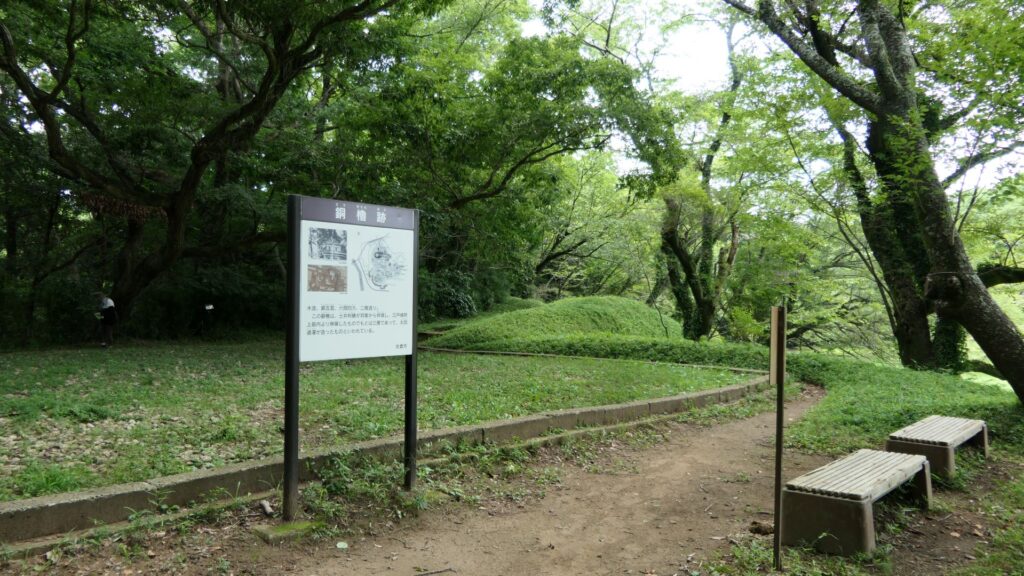
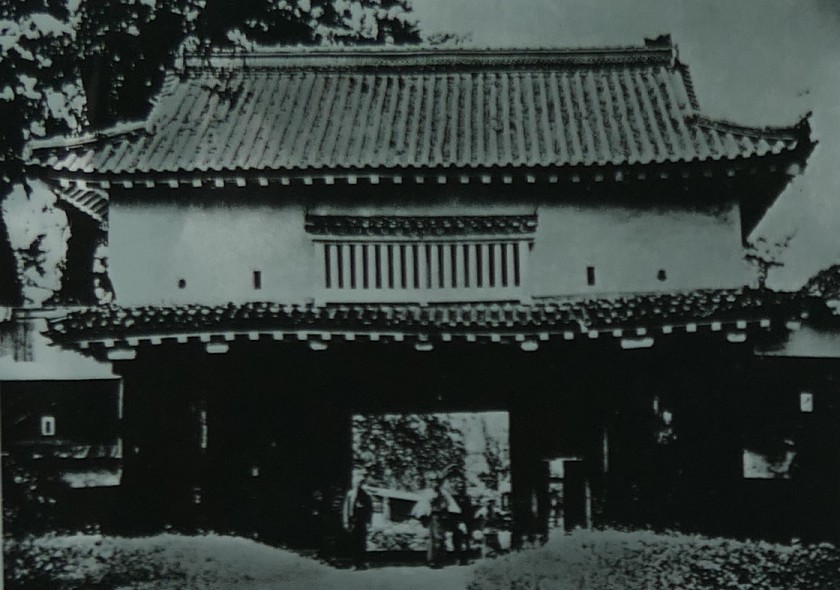
You can walk on the earthen walls around the enclosure. If you walk from the first gate ruins on the earthen walls, you will pass by the ruins of Do-yagura (the copper turret). The turret had a mysterious tradition. It says that the turret was originally built by Dokan Ota, the founder of Edo Castle, called “Shoyoken”, and moved from the castle. However, we cannot confirm whether or not the turret was moved from Edo Castle. However, if it had remained, it would have become a National Treasure of Japan.
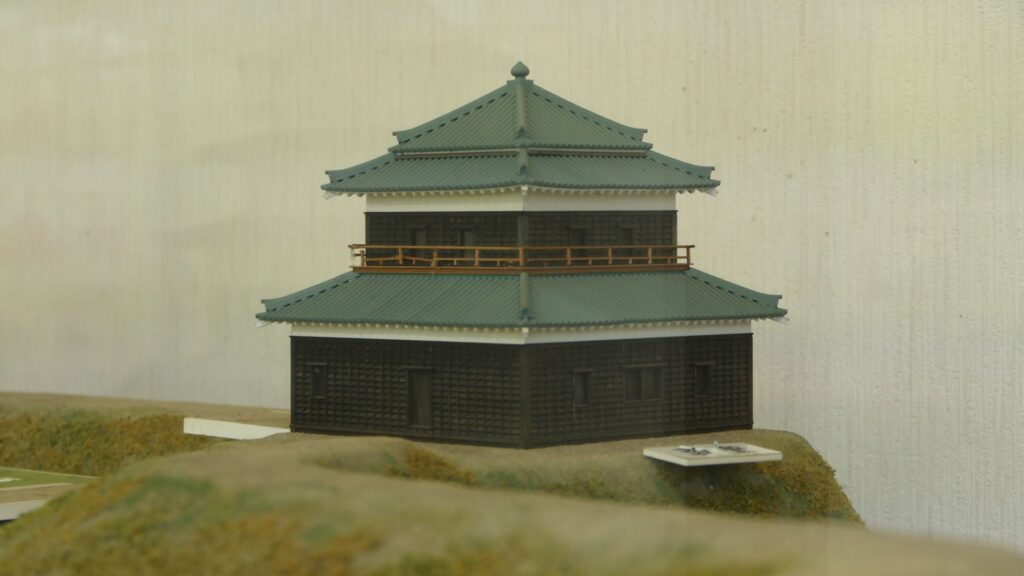

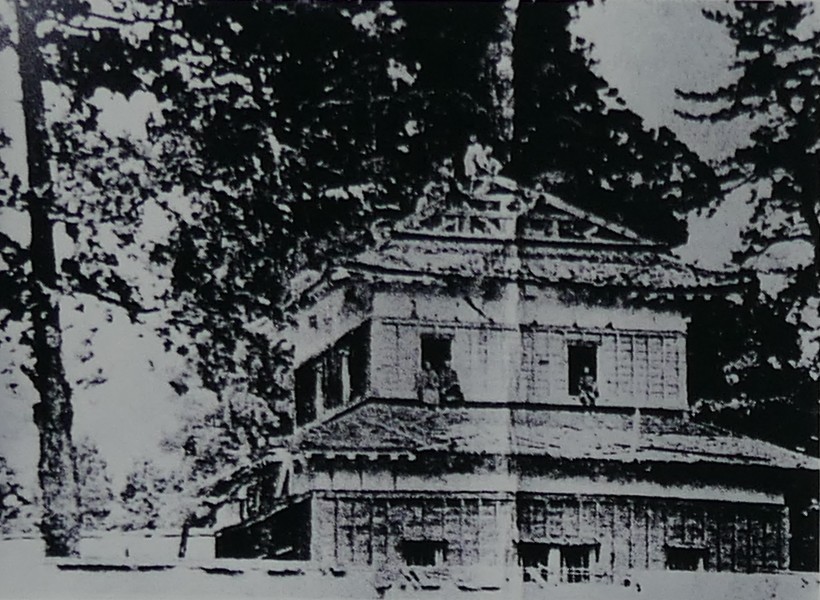

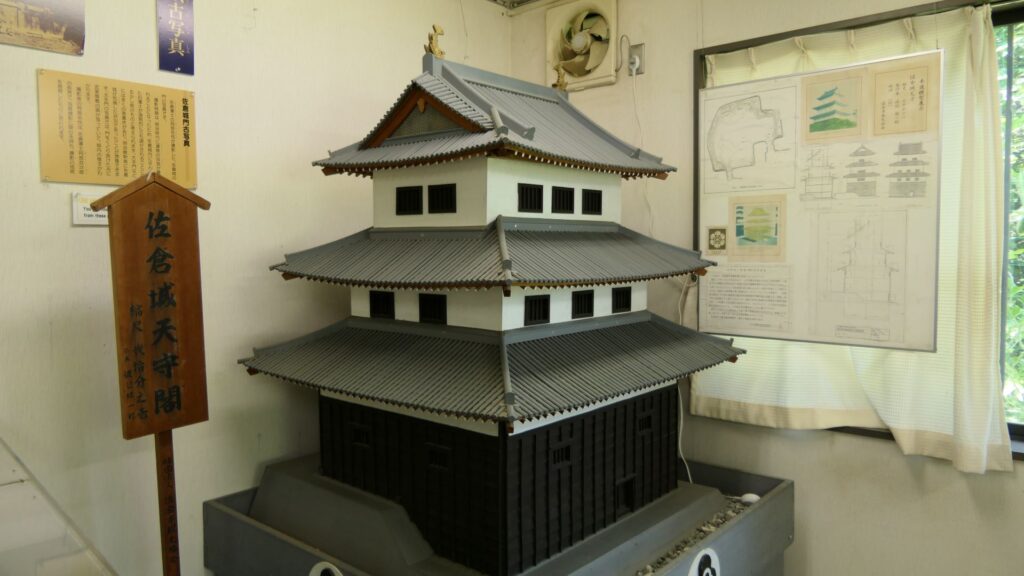
If you go further, you will eventually reach the earthen base of the main tower.
The tower was directly built on the base and its outside walls leaned on the earthen walls of the enclosure. That was why people saw the tower three-leveled from the outside but four-leveled from the inside. The tower was used as the warehouse for weapons. It was unfortunately burned down after a thief robbed it of guns and left his lantern there.
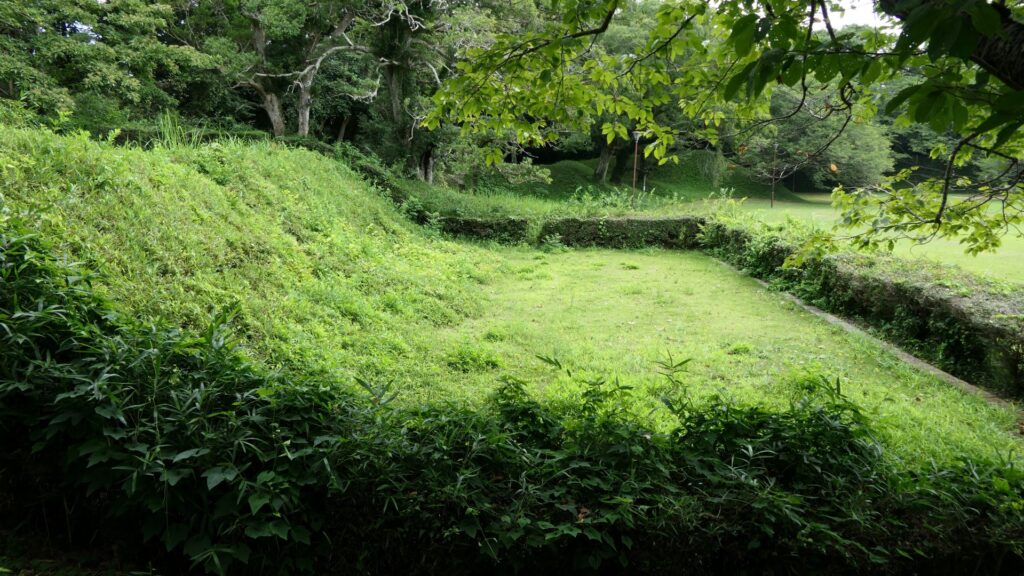


There are the other ruins of the corner turret in the enclosure. The turret also has the tradition which says it originally came from Motosakura Castle. That may have been the reason why it deteriorated sooner than the others and was renovated during the Edo Period.
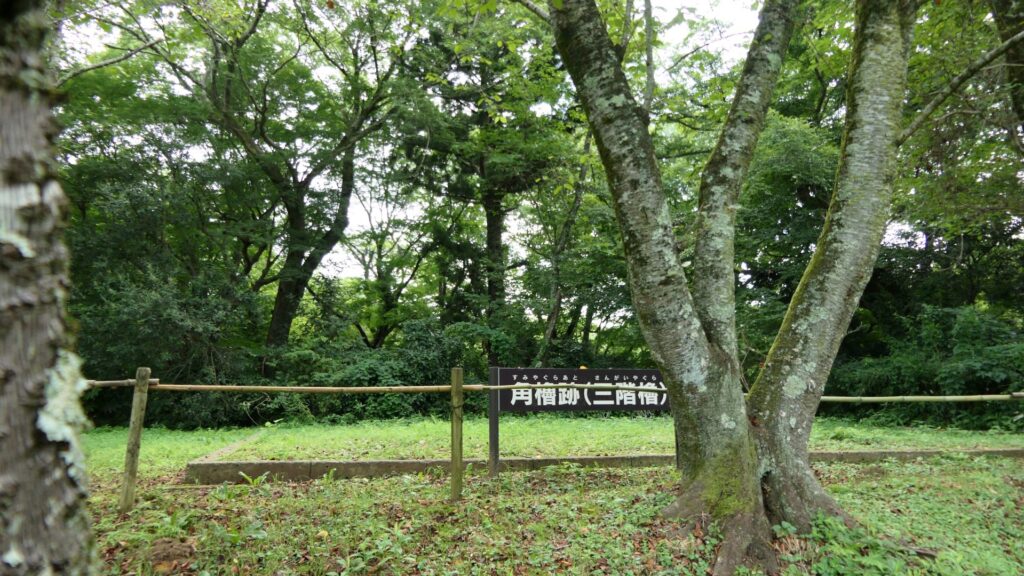

Let us next get out of the enclosure through the ruins of the back gate and climb down the slopes of the plateau. The slopes are steep which made the castle fortified. You will eventually see some trails on the mid slopes, which are the belt enclosures of the castle. The enclosures were said to have originally been dry moats and were changed to the trails by being filled naturally. If you look up the main enclosure, you will realize it is protected by the natural terrain even though it doesn’t have stone walls.
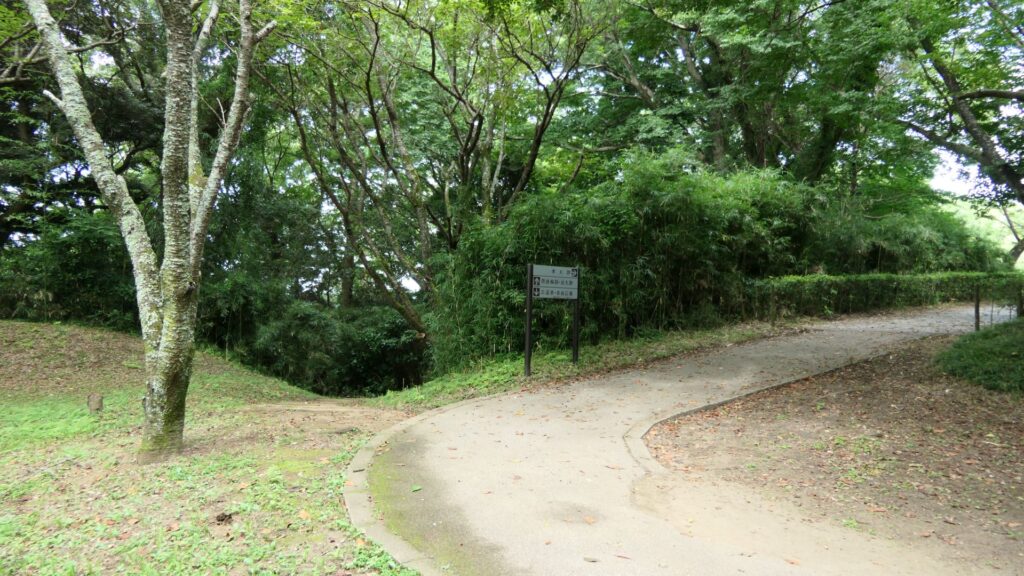
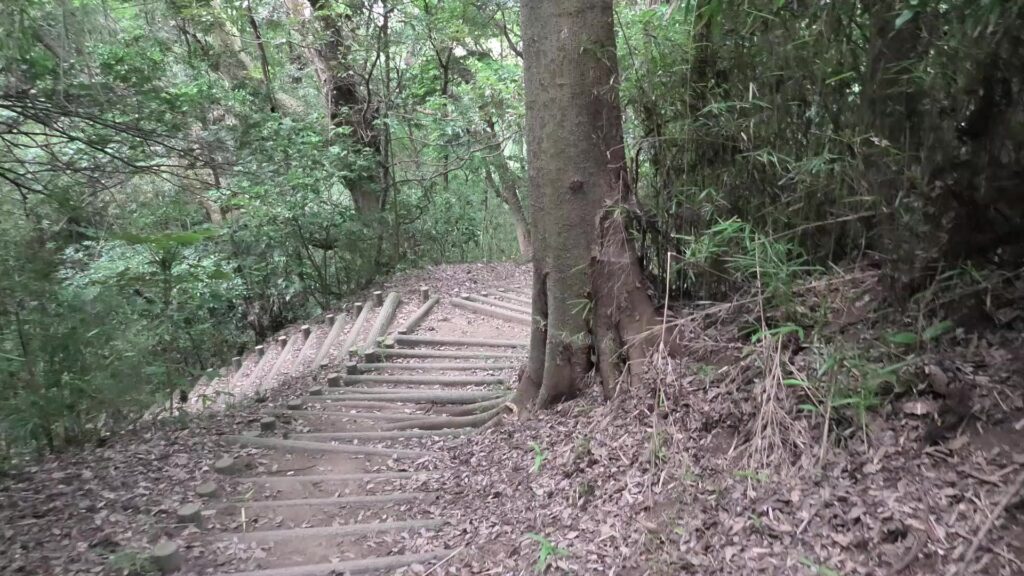





You will eventually arrive at the foot of the plateau and see the southern barbican enclosure. If you go around the enclosure, you will see it is still surrounded by water moats. It looks very defensive and cool! If you enter the enclosure as well, you will see the outside which you walked around on.
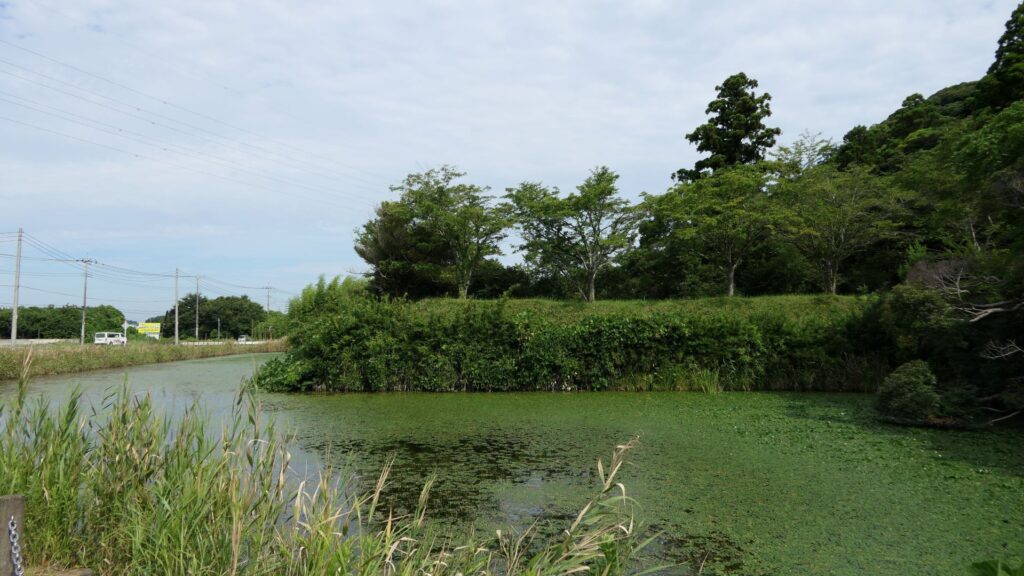



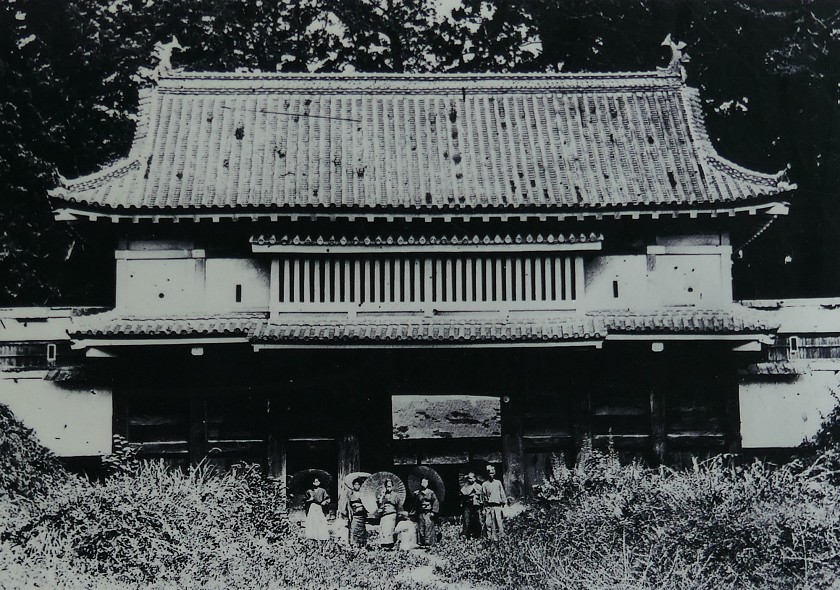
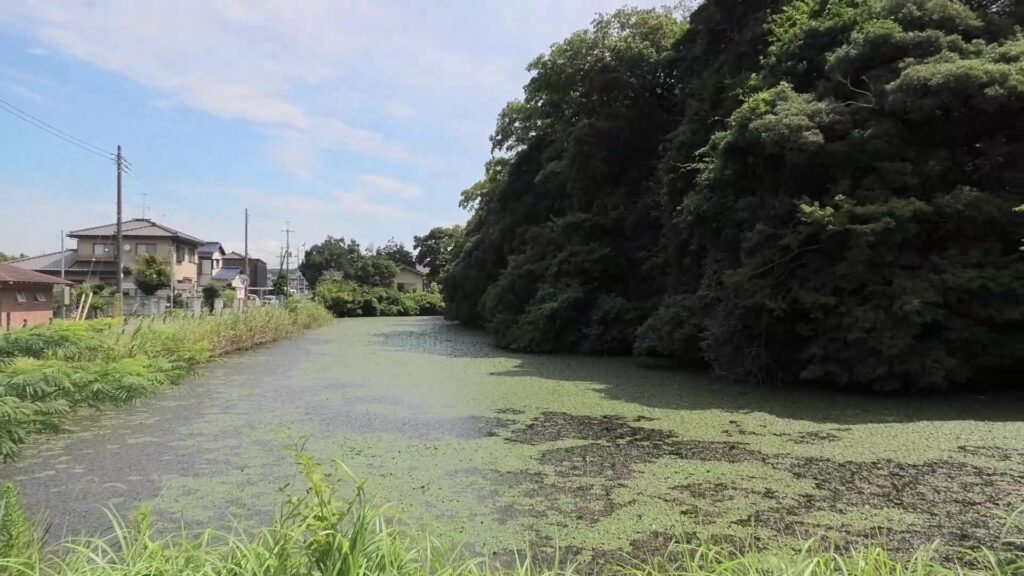
I recommend you to go back to the belt enclosure and walk on it to the other western barbican enclosure. The enclosure still has its earthen walls and water moats in good conditions. There is the only remaining building at its entrance, called Yakui-mon gate. However, No one knows for certain its original name and position, because it was moved multiple times from the current position that it is in now.
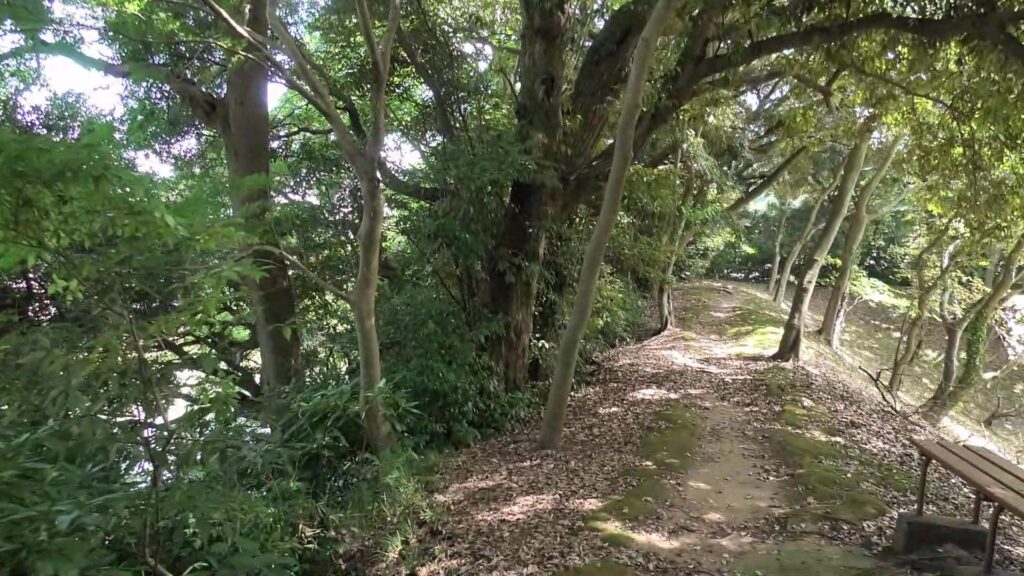



Looking at Umadashi system and Dry Moats
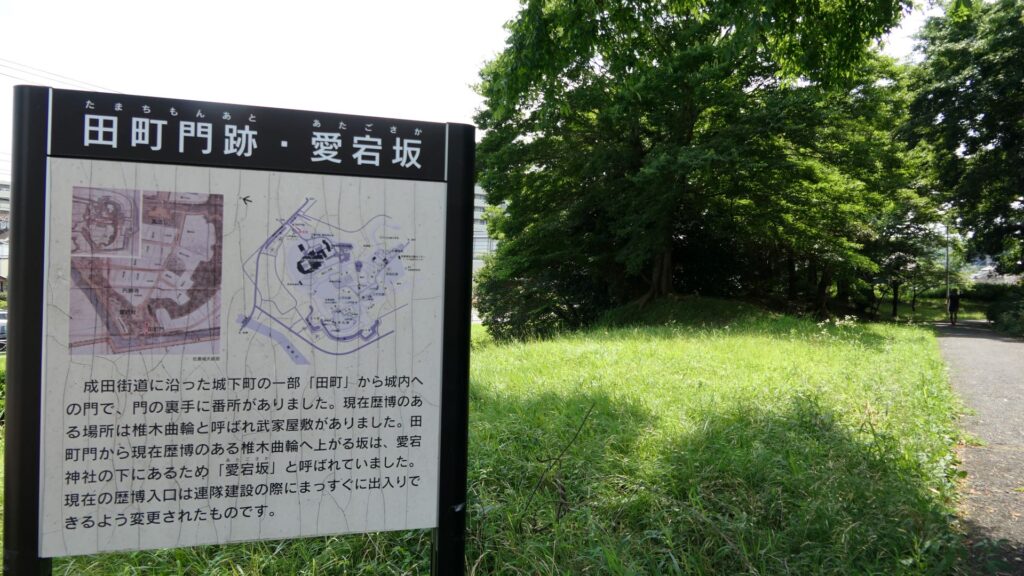
If you don’t mind, it may be better to walk around the plateau to another entrance from the north to the castle. It was called Tamachi-mon which was the back gate of the castle, on Atago slope. It is now the front gate of the National Museum of Japanese History. A large enclosure of the castle, called Shinoki-kuruwa has become the museum. The enclosure was originally used as Samurai residences and was turned into barracks for the Japanese Imperial Army before the museum. It has been used effectively because it is massive.


The floor space of the museum is about 35,000 square meters big. It exhibits the Japanese histories by classifying 5 different periods. If you want to look through all of them, you may have to spend all day long. It may be better to split up your visits to fully see everything.
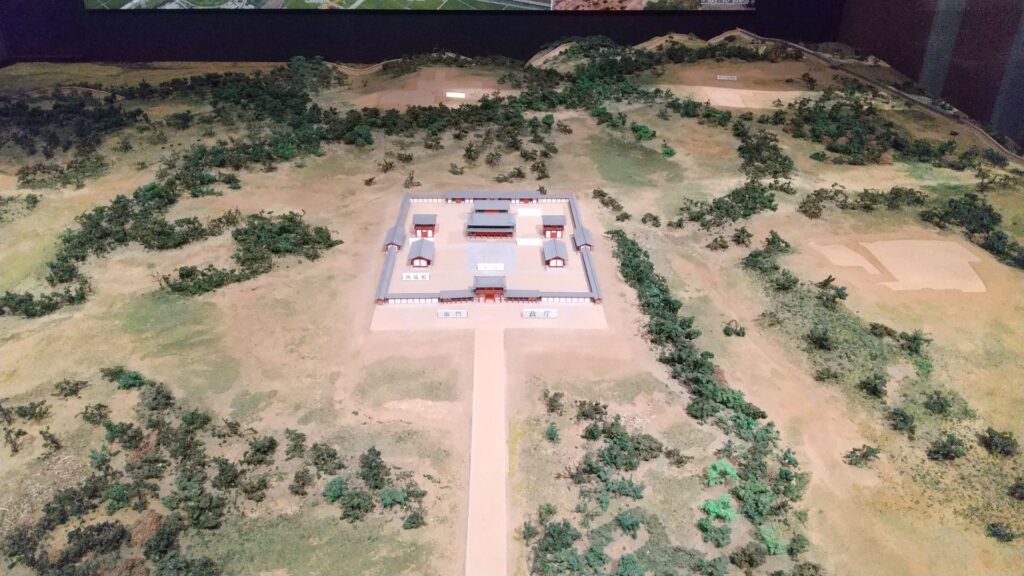



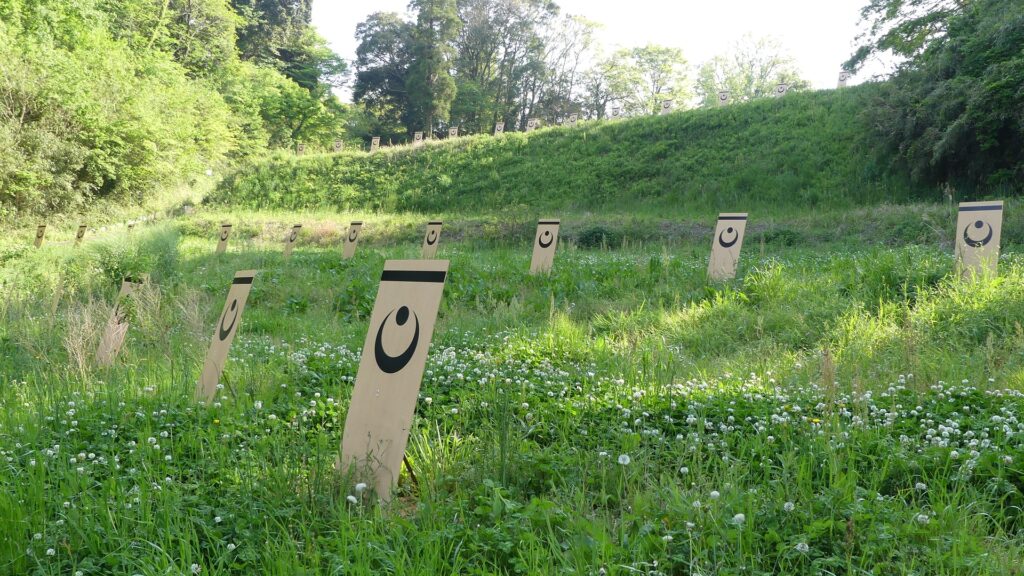
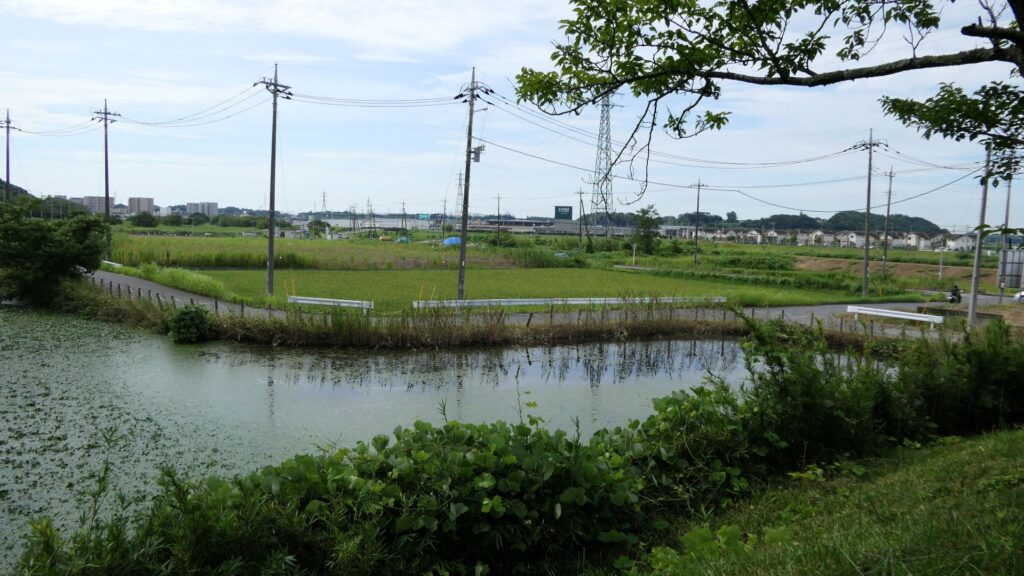
Going back to the attractions of the castle, the Umadashi system has been restored near the museum. The system was a fortified square position in front of Shinoki Gate, which was surrounded by dry moats. The long side of the square is 121m long and the short side is 40m long, same as the original. The dry moats were originally 5.6m in depth but is only 3m in depth probably for safety reasons. The system is only connected by a narrow path to the gate. It was once filled by the Japanese Imperial Army before its restoration.
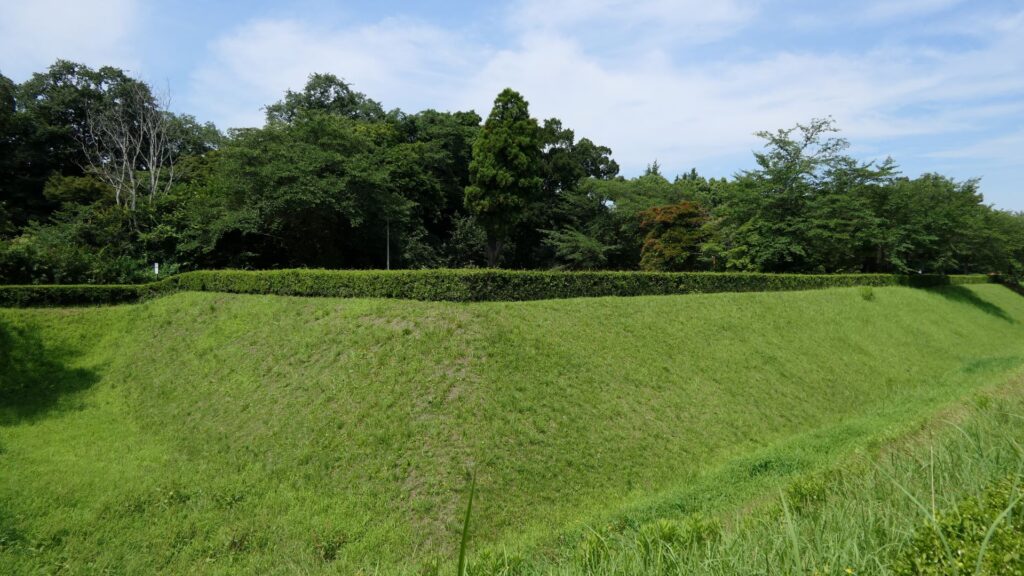

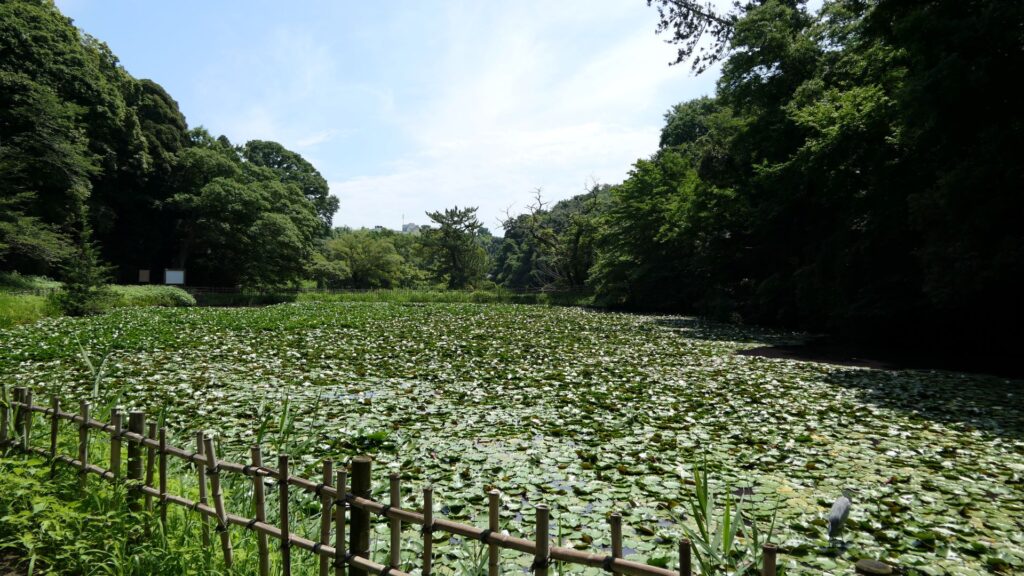
The Shinoki Gate Ruins have no buildings now, and its inside is the third enclosure. So, you can visit the second and main enclosures again. However, let us go to another place by walking down from the plateau again. It is a pond, called Uba-ga-ike, which means “The Pond of a Nursing Mother”. The name comes from a sad and unfortunate story. It says that one day, a nursing mother took the daughter of a senior vassal to the pond. However, she didn’t keep her eyes on the daughter, which lead to the daughter drowning in the pond She felt very sad and guilty about it, so, she decided to throw herself into the pond as well. For the castle, this pond divided the main gate and the back gate sides to force the defenders protect the castle quickly. It also became famous for Japanese iris and croaking sounds of frogs during the peaceful Edo Period.



You can go back from the pond to the main gate ruins by passing through a path which was another dry moat. The path has a fork which still looks like the dry moat. If you go straight, you will eventually reach the entrance of the park near the gate ruins.


Visiting Samurai Residences and Sakura Juntendo Memorial Building
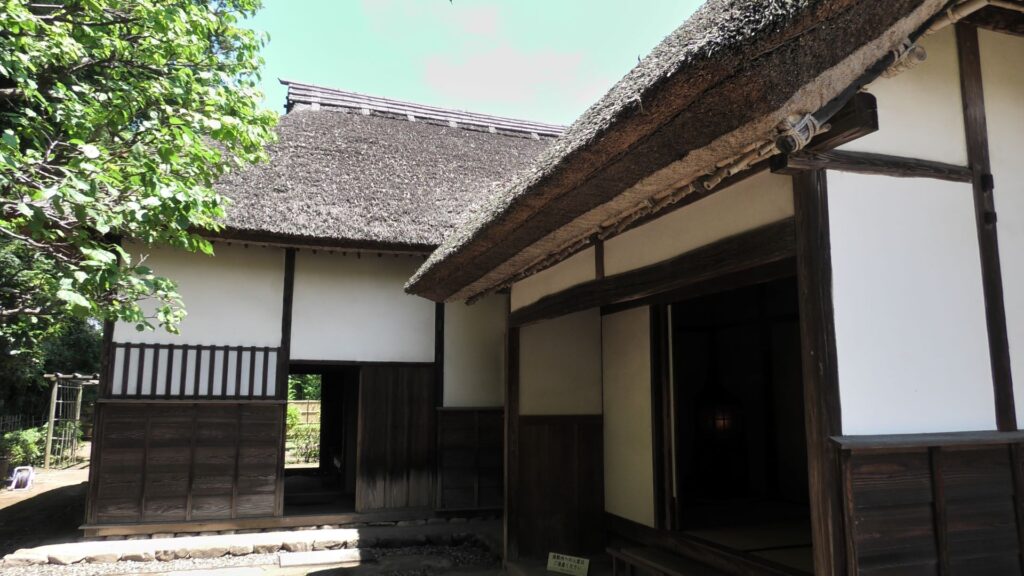
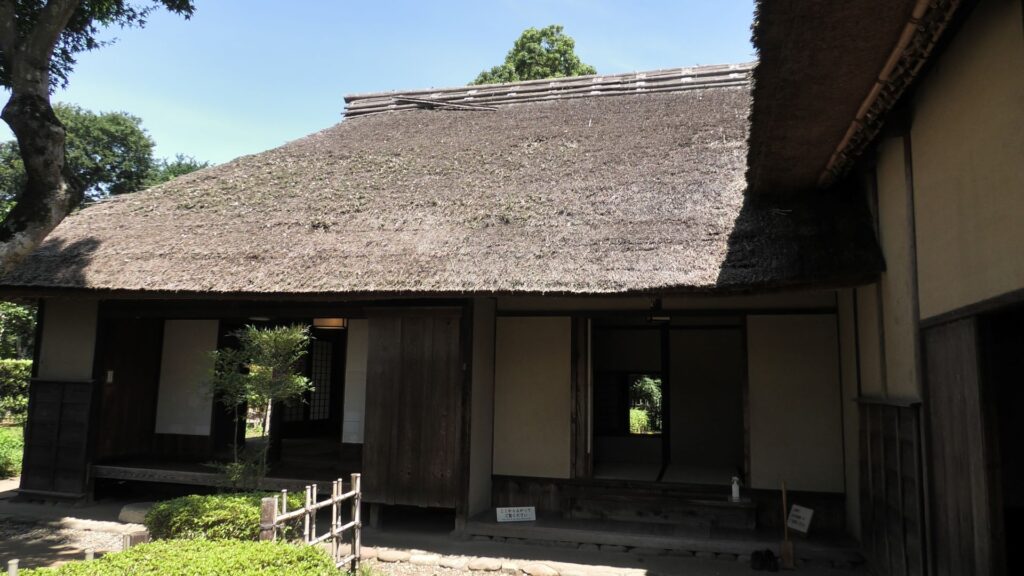
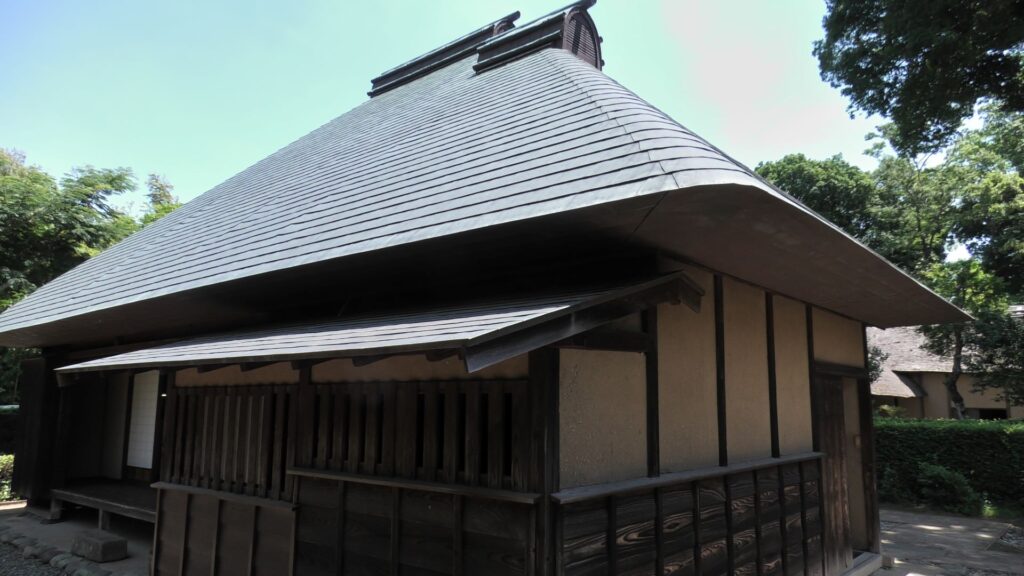
Atter visiting the castle ruins, let us go to Sakura Samurai Residences. The residence area is in Miyakoji of Sakura City, which originally had middle-class warriors’ residences. However, the current area exhibits three different residences: one of the remaining one for middle class warriors, another one form high-class warriors and finally, the other one form low-class warriors. The last two residential areas were moved from other areas, making it accessible to the public for viewing.

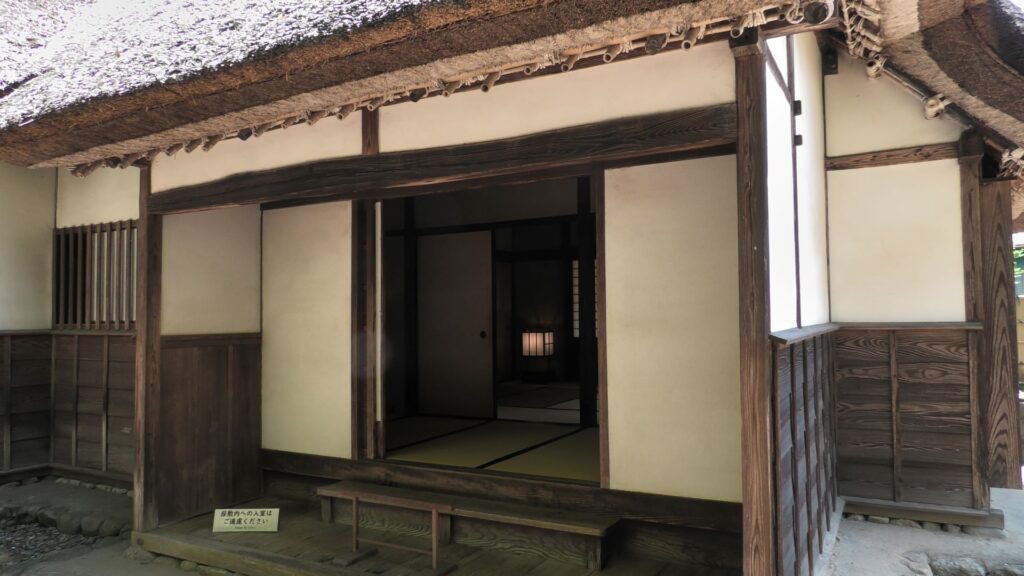
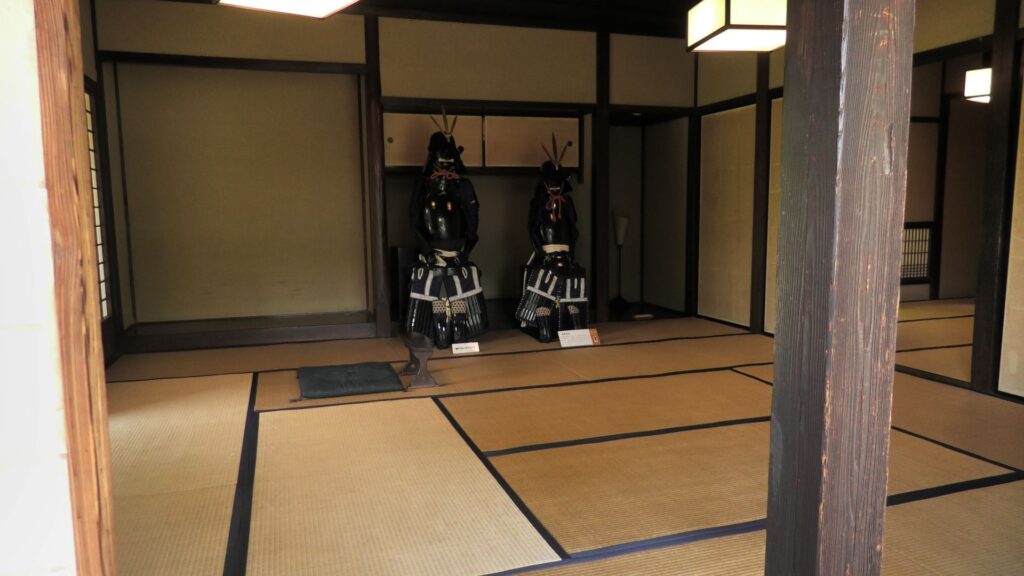
These residences were owned and maintained by the Sakura Domain like official residences. They were made differently by each warrior’s class. That was because of the class system as well as the budgetary restrictions of the domain. For example, the entrance of the high-class residence looks high in quality, but the others are simpler. The walls of the high class’s one used white plasters, while the others only used brown mud walls. The high and middle class’s ones used fine Tatami mats in their rooms, however the low class can only use simple mats without the edge decorations.






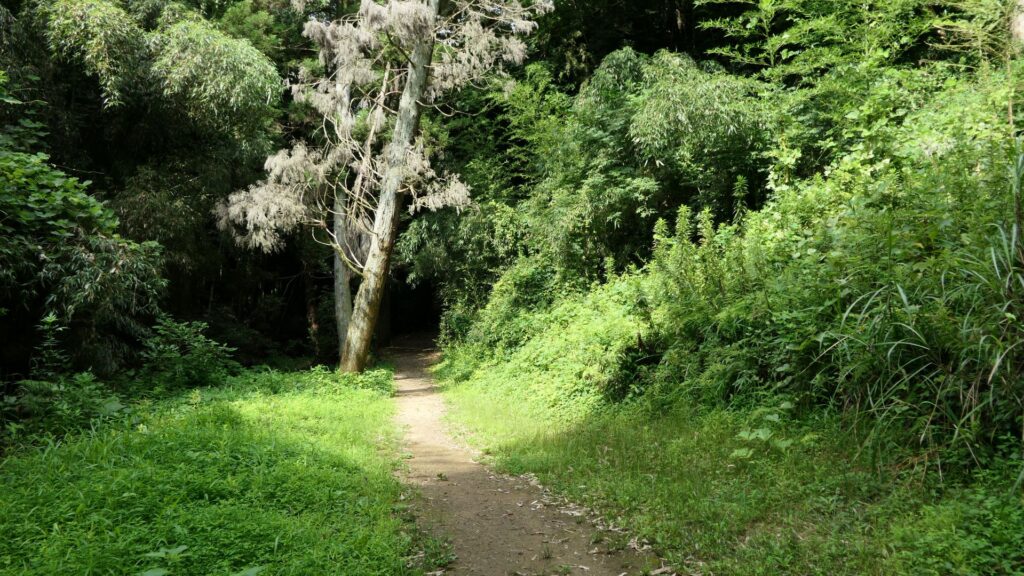
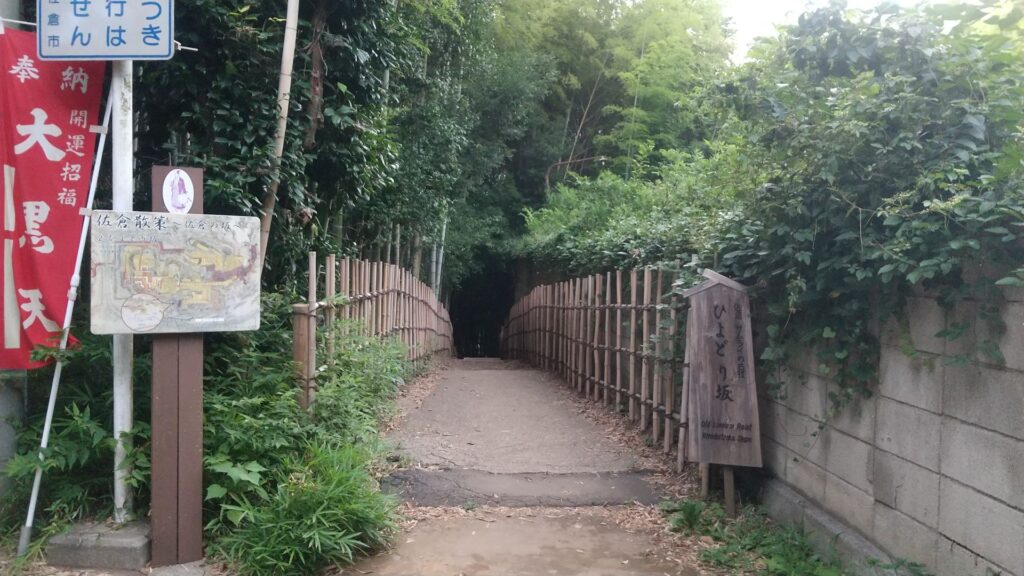
You should also try to walk along Hiyodori-zaka Slope near the residences, which was the commuting route to the castle. The route goes down on a trail, surrounded by bamboo trees, which looks exactly same as it used to.

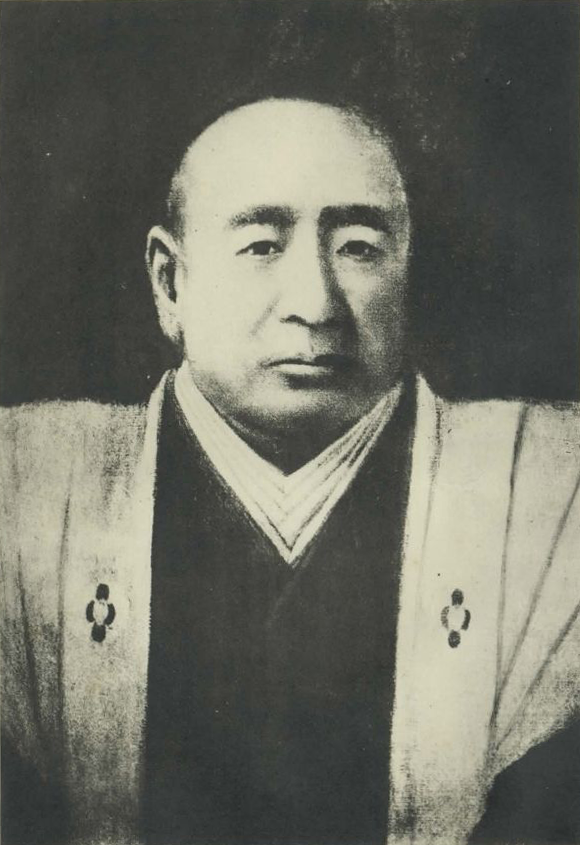
We will finally go to Sakura Juntendo Memorial Building. It was originally built by Taizen Sato as his Rangaku (Dutch studies) school and clinic. Part of it opens to the public as a museum. The museum is about 2km away from the main gate ruins of the castle and was at the edge of the castle town. This is probably because Taizen was not an official doctor of the domain. A guide of the museum suggested to me another speculation. Taizen’s father was an agent in lawsuits who was against the policies of Tadakuni Mizuno, the top of the government. Therefore, Taizen might have had difficulties in his work in Edo City. He might also have been accommodated by Masayoshi Hotta. If it’s true, Sakura Juntendo was also like a place of refuge.


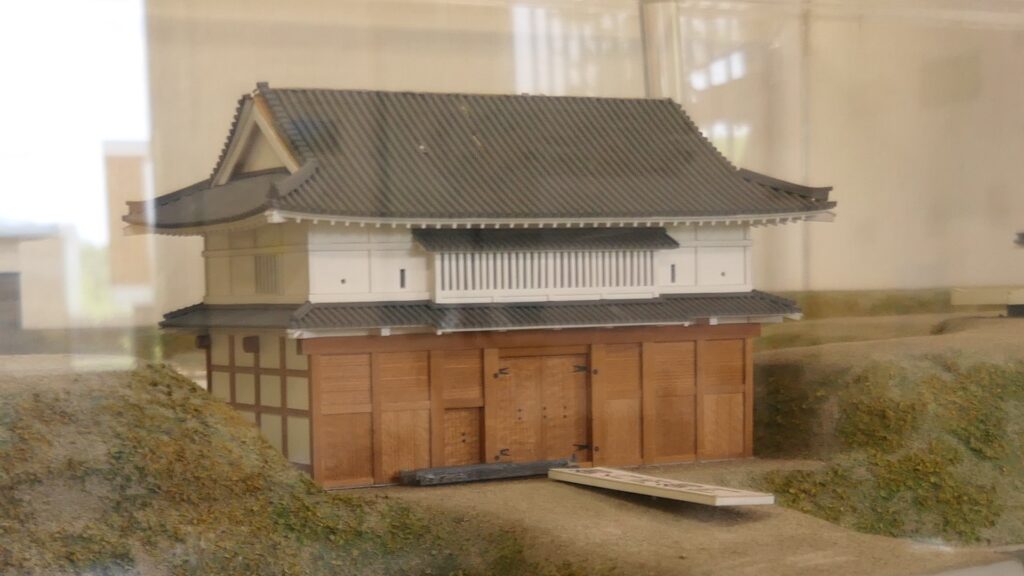
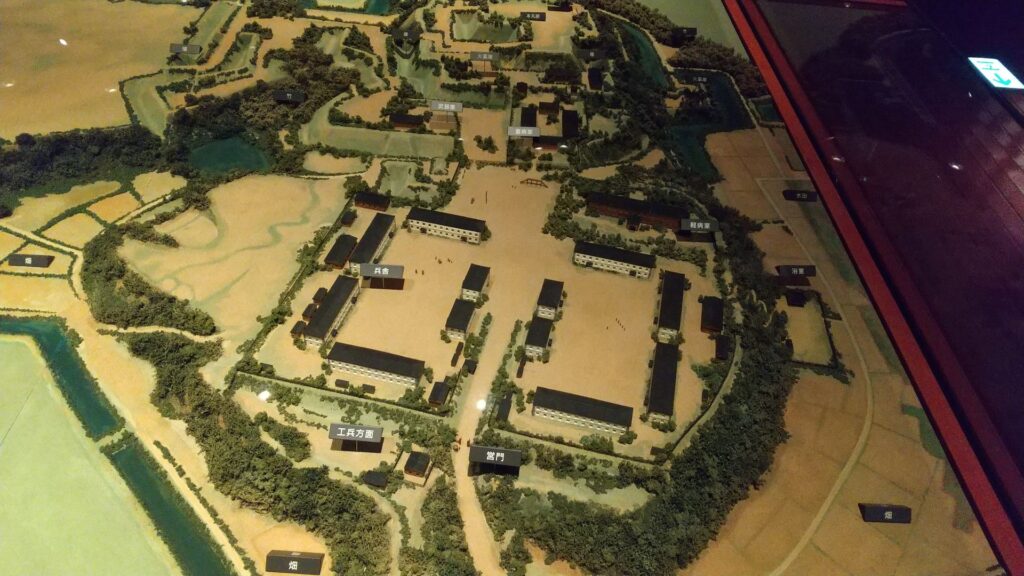
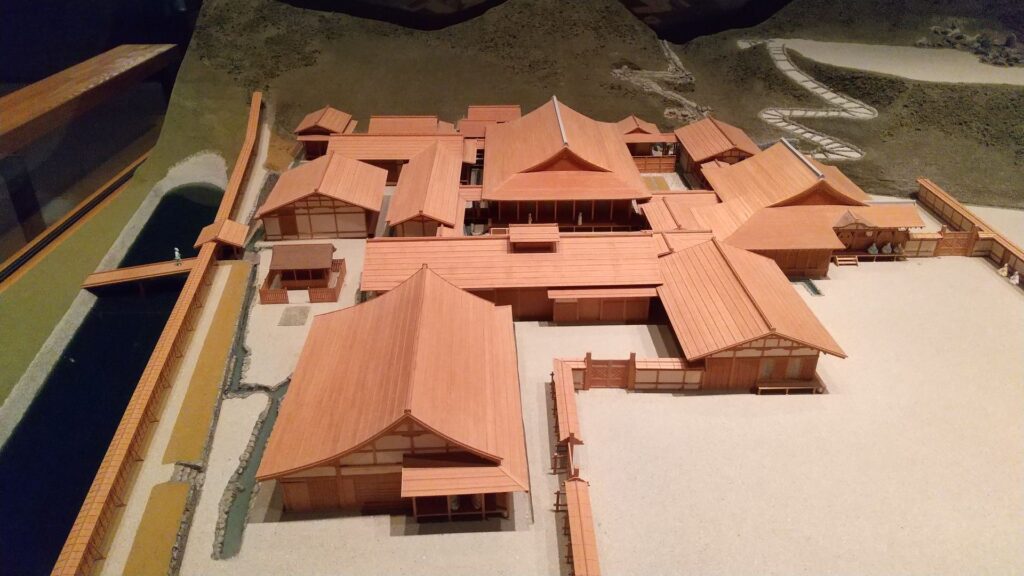
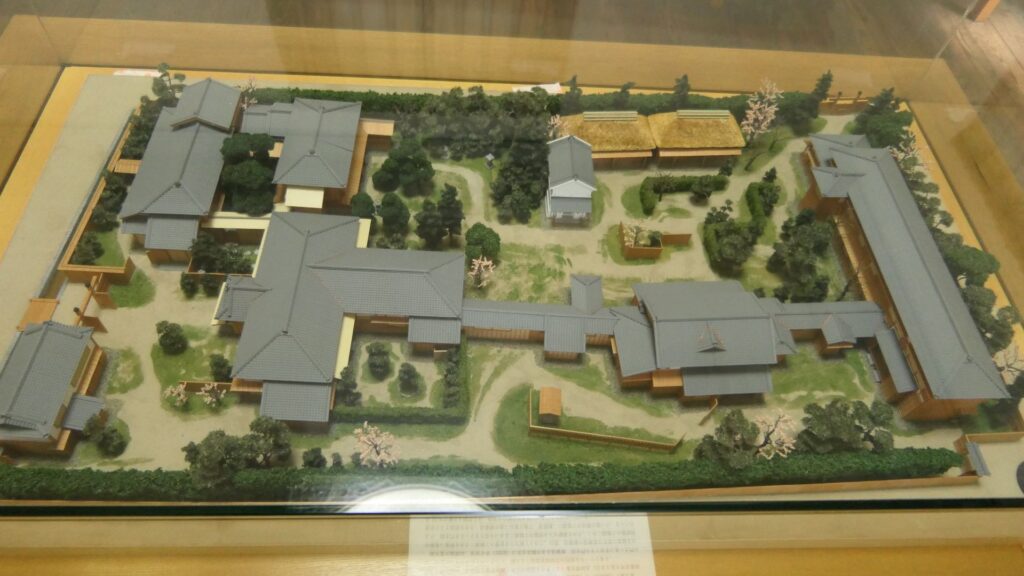
One of the exhibitions of the museum is the miniature model of the original buildings. You can see the buildings were so large. It is said that over one thousand students were there in total.

Another interesting exhibition is the original medical board which is hung on the top of the wall. The clinic mainly offered surgeries. However, the doctors didn’t use anesthesia because it was still dangerous at that time. Therefore, patients endured the pain because they wanted to get well after that.

The clinic is the origin of Juntendo University in Tokyo, one of Taizen’s successors who founded it. However, there is still the current Sakura Juntendo Clinic next to the museum. The spirits of Sakura are alive.

My Impression
Honestly, at first, I thought the castle park looked like a natural park. However, the more I looked around, the more my impressions changed. Currently it’s trendy for cities to revive castles across Japan. I think Sakura City does not need to ride the boom. This is because the city has already preserved the land of the castle as the park. The city can take enough time and be patient when developing it further. The important thing is preserving it as accurate as possible. In addition, you can still enjoy the castle ruins even without its visible buildings. So I highly recmmend you visit Sakura Catle in the future!
That’s all. Thank you.