Features
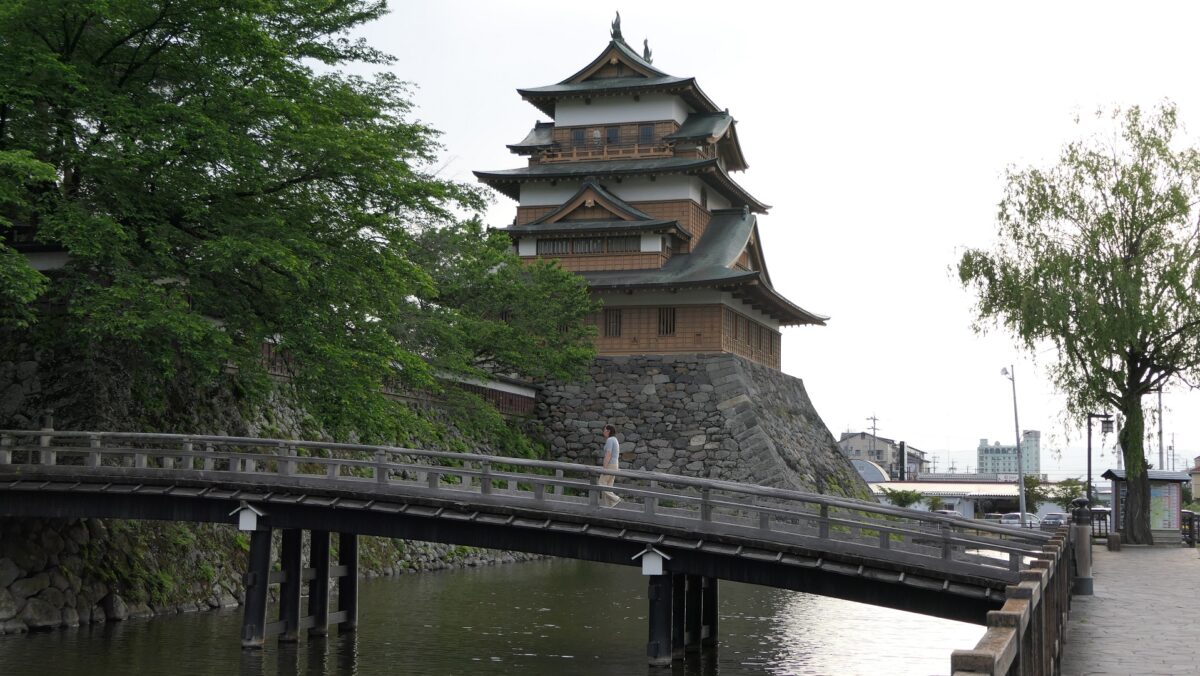
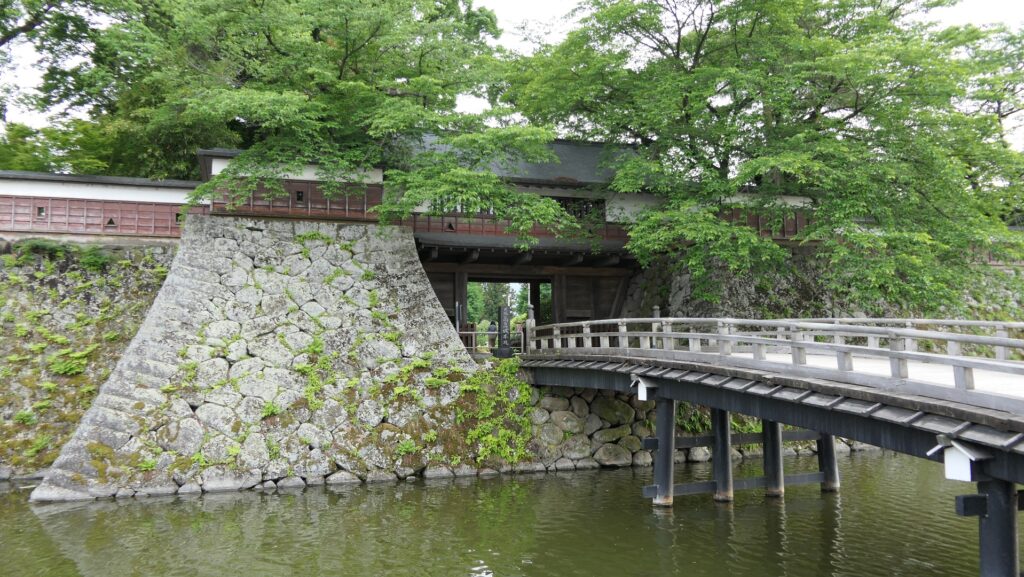
Walking outside Inner Moat after getting out of Back Gate
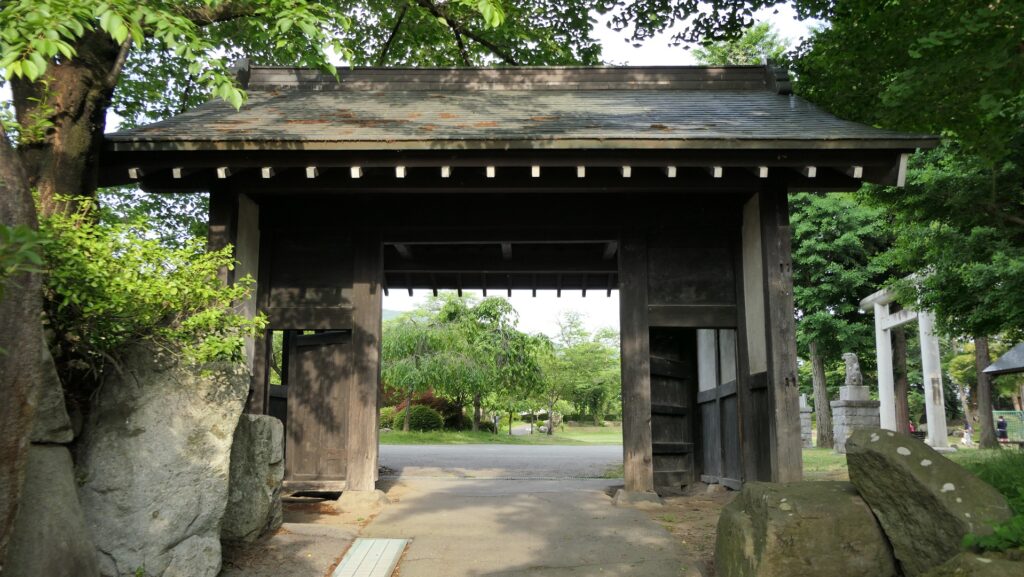
The castle park also has the back gate called Yamazato-mon which was restored in 1990. To get out of the castle area, you have to go down a few stone steps, pass another Korai-mon style gate, and go across a narrow earthen bridge. The earthen bridge was originally wooden made which would have been fallen if a battle happened. The area around the gate is sunken, on the other hand, the area over the bridge extends upward.
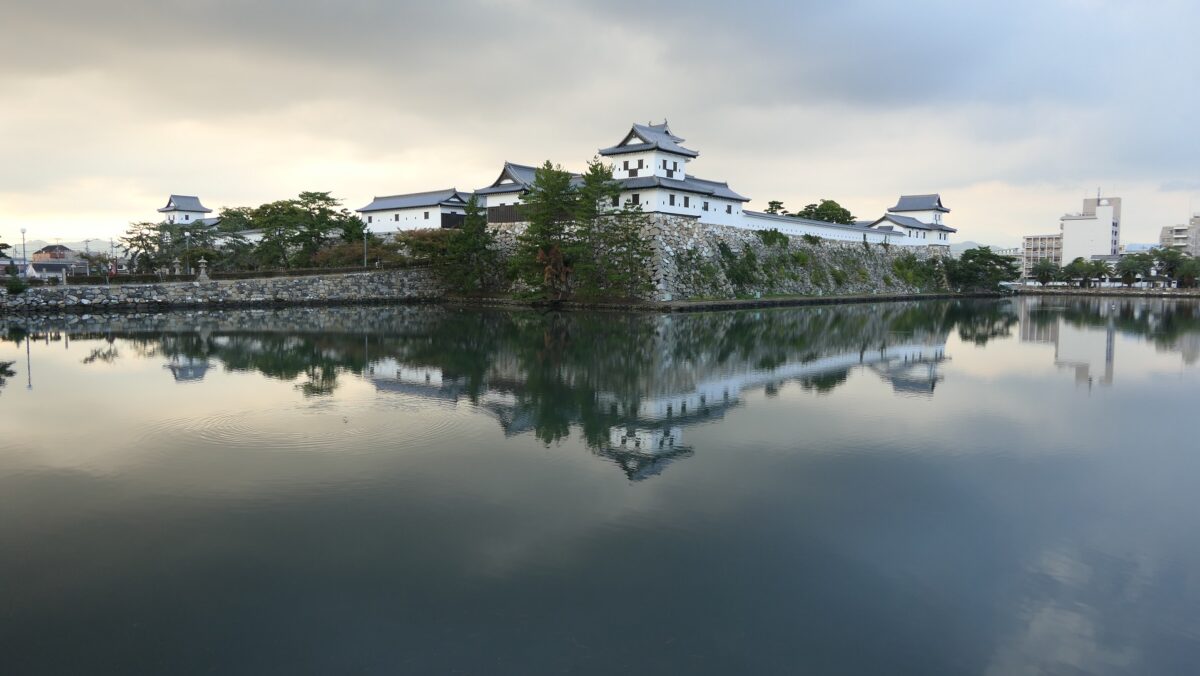
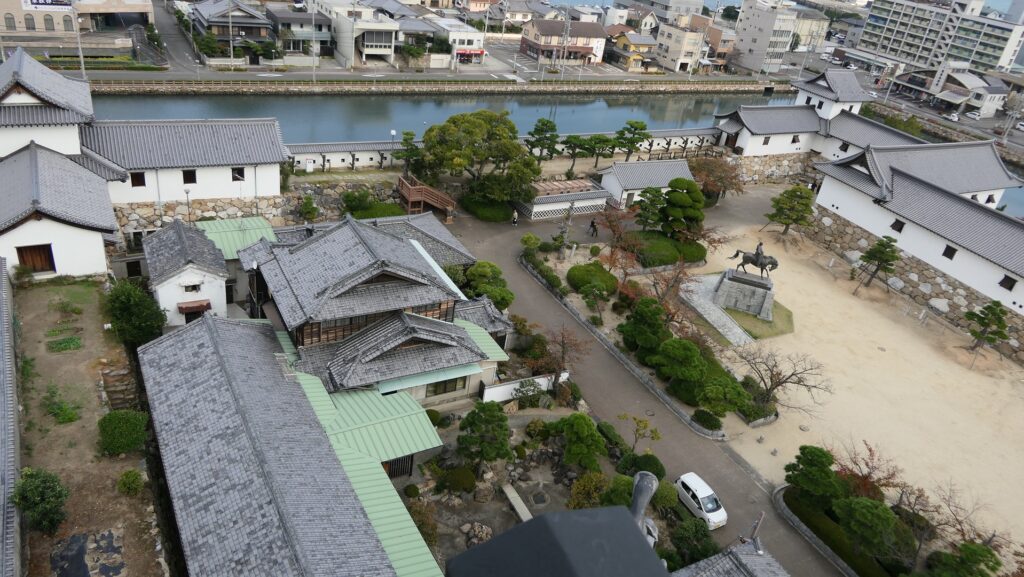
The aerial photo around the castle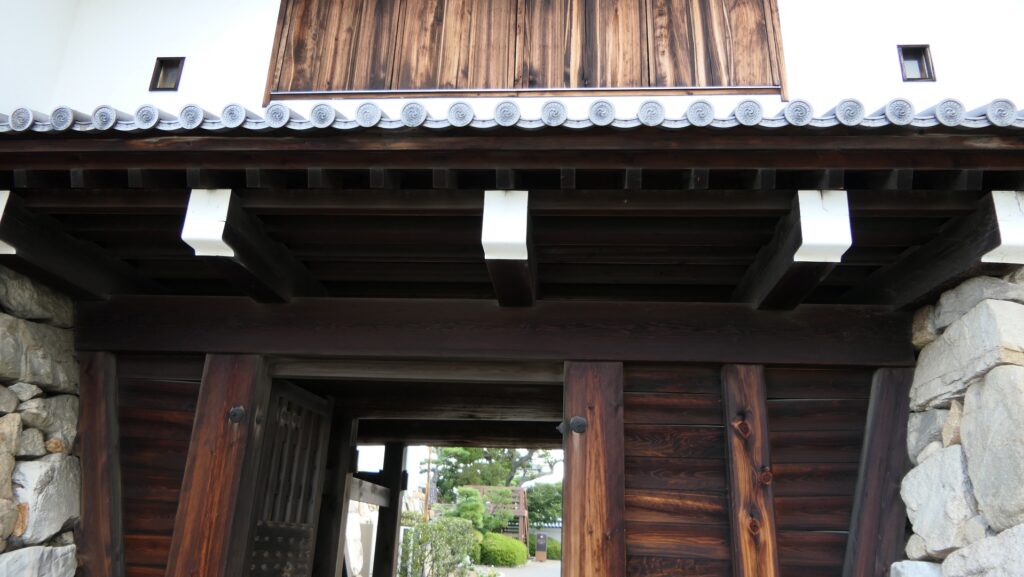
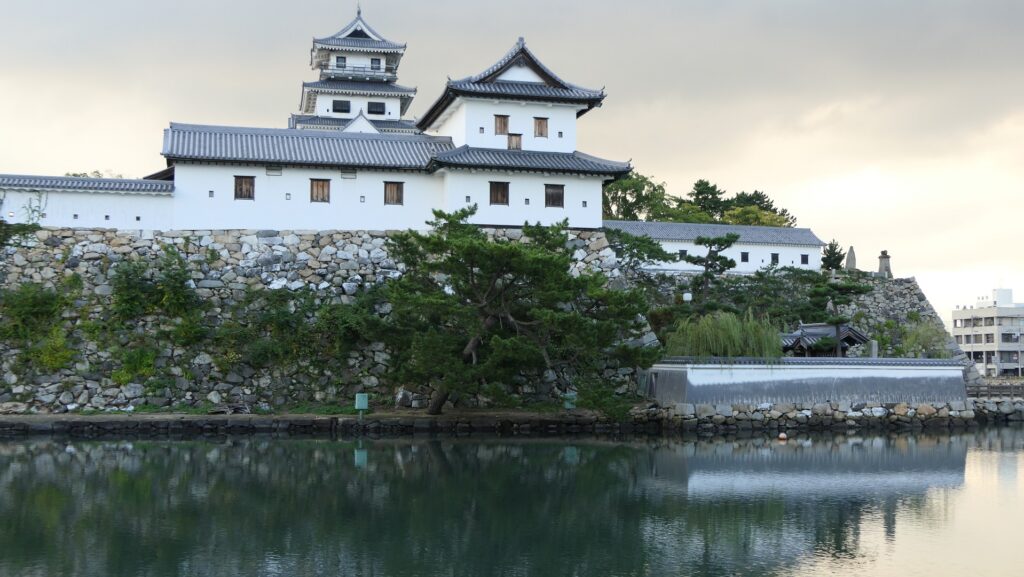
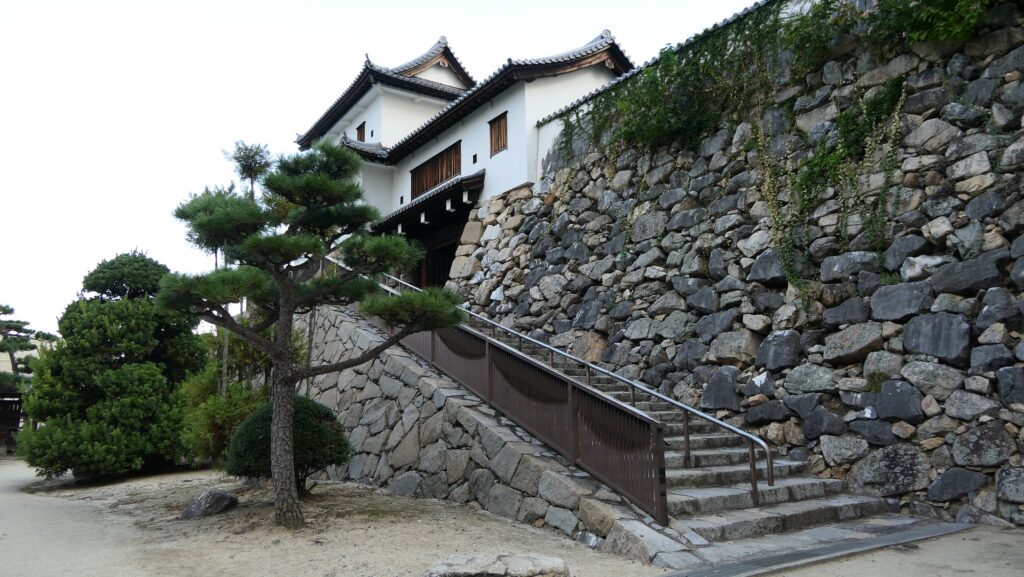
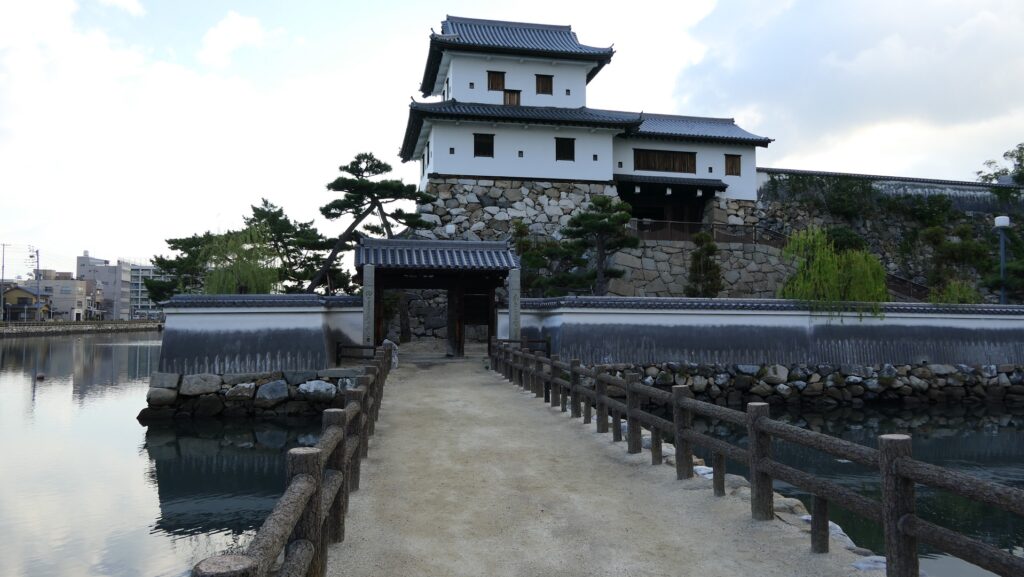
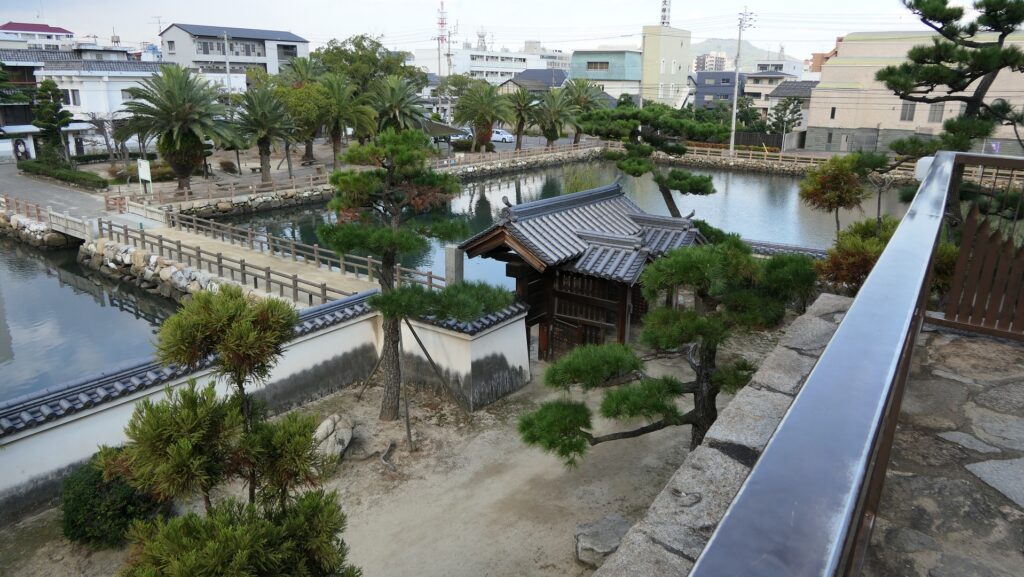




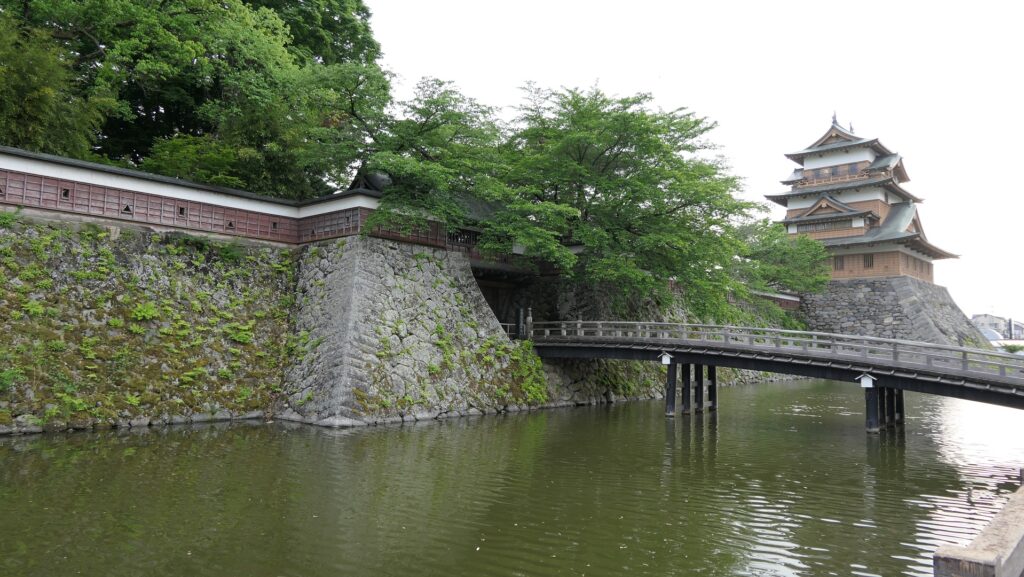
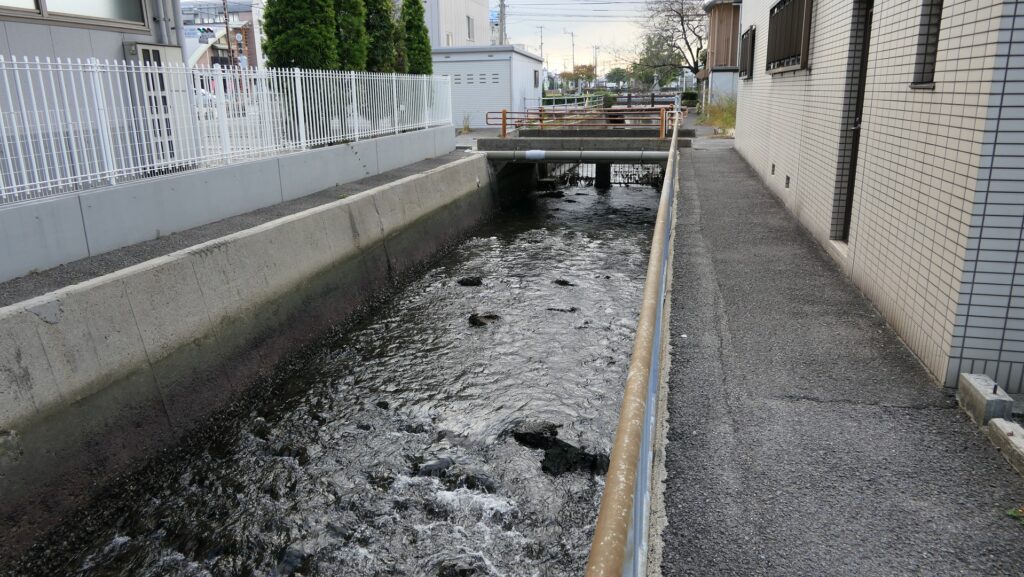
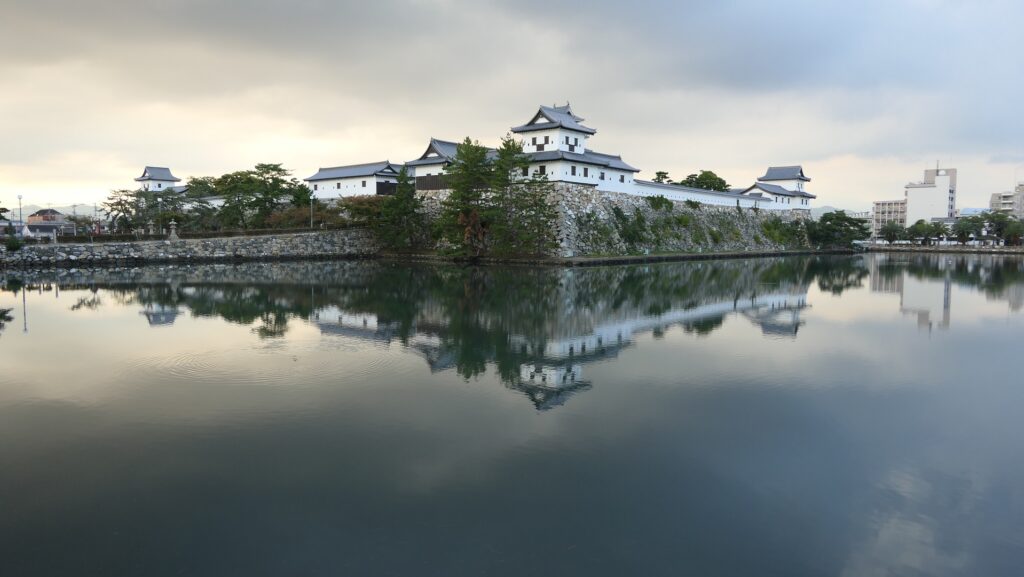
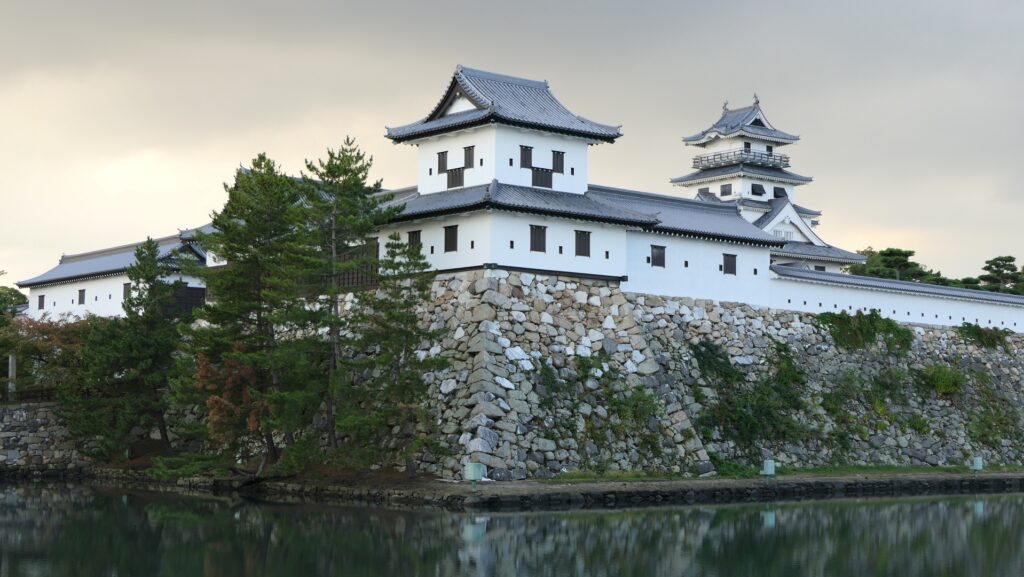
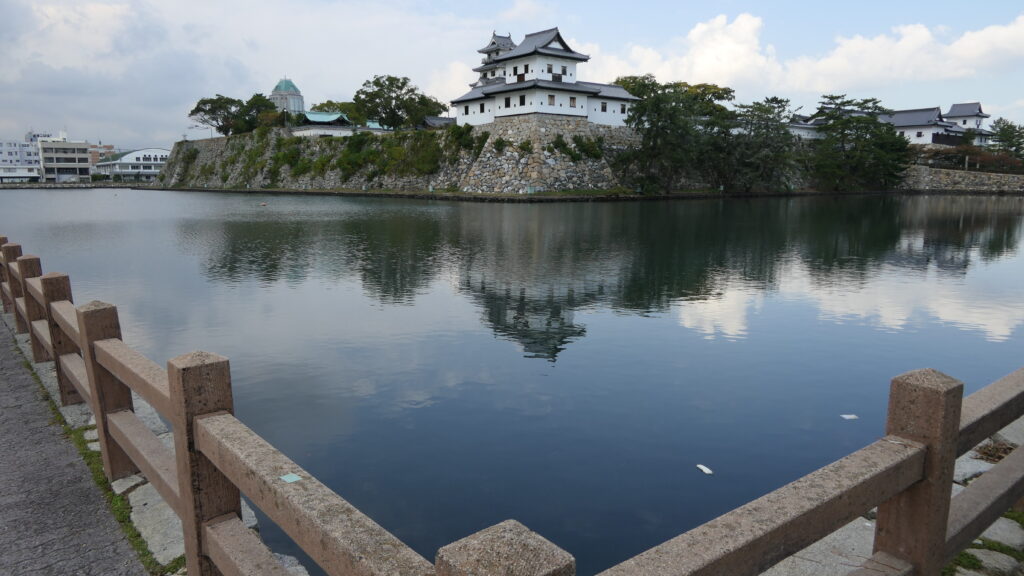
After you go out of the park, you can try walking around the Inner Moat. The moat is about 50 to 70m wide and the stone walls inside are 9 to 13m tall. They look like a floating fortress!
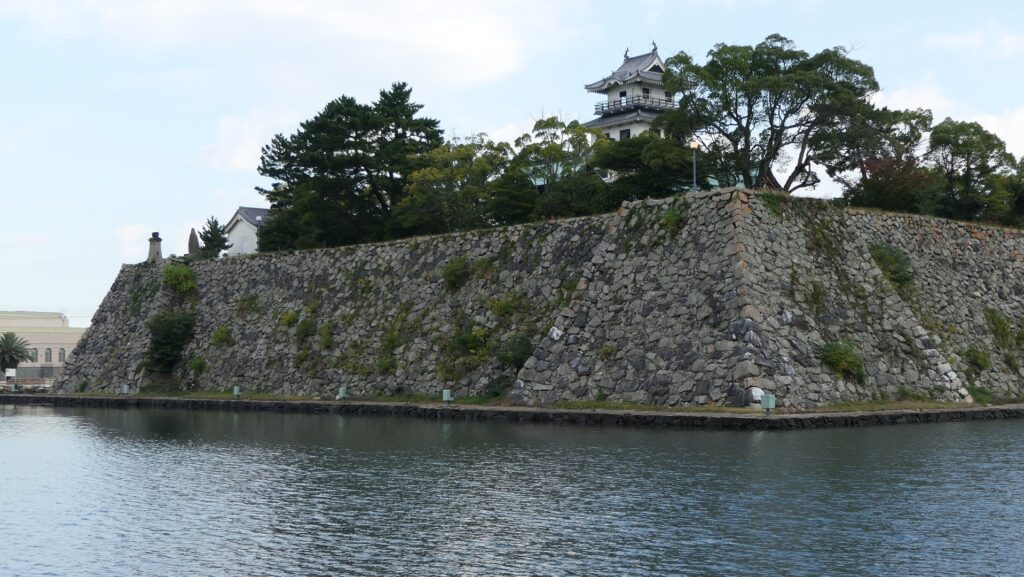
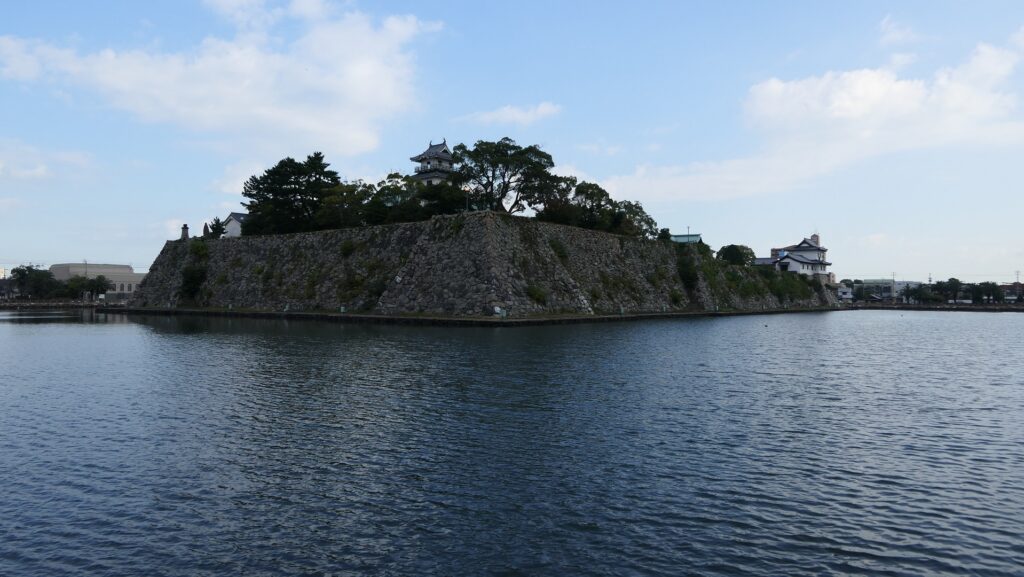
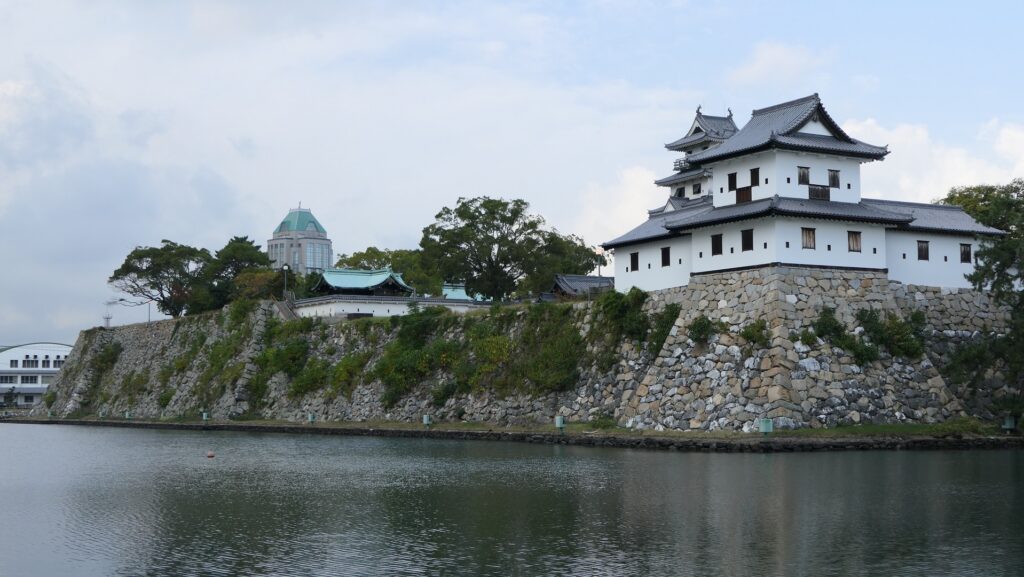



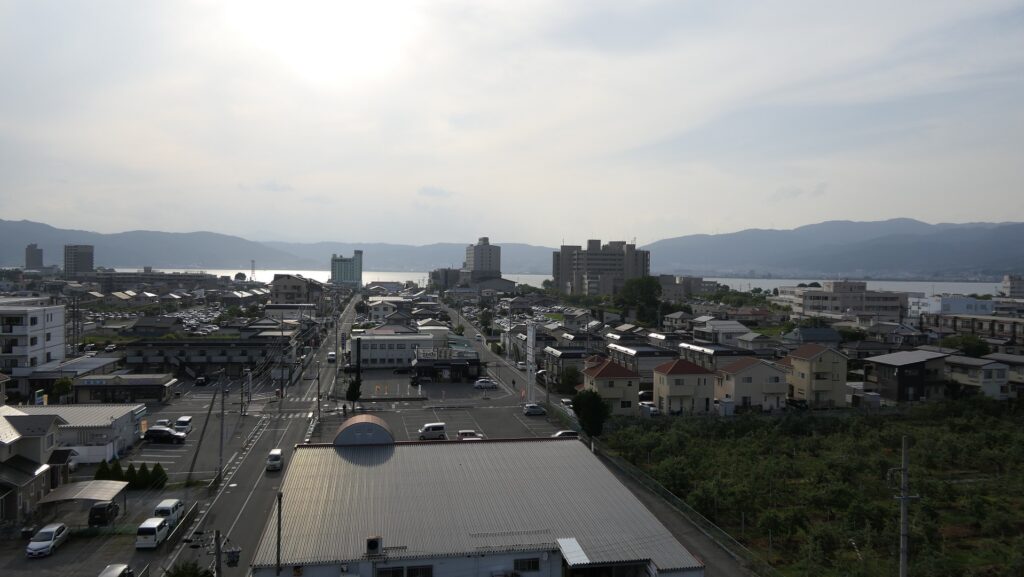
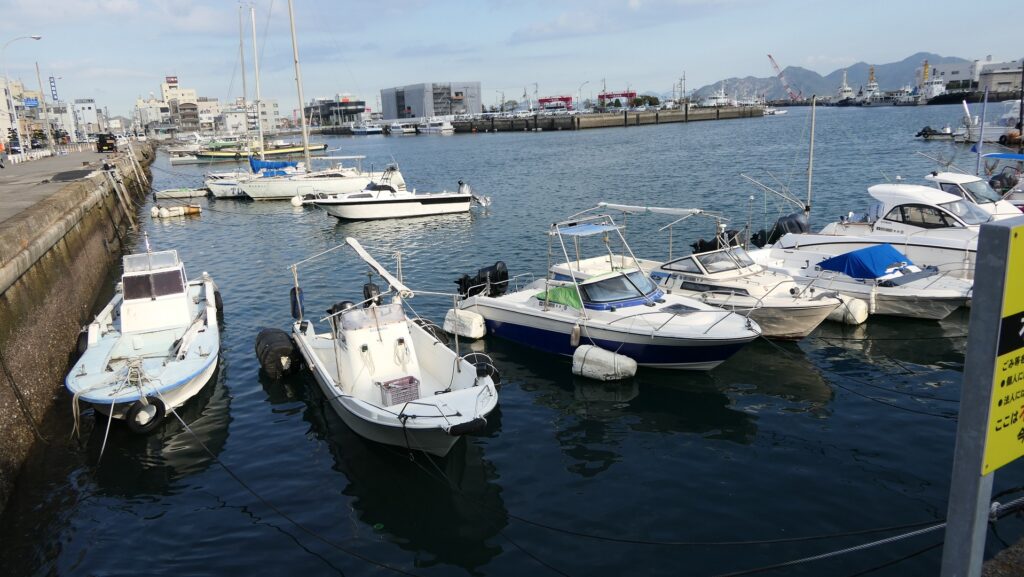
Imabari Port, Source of Inner Moat
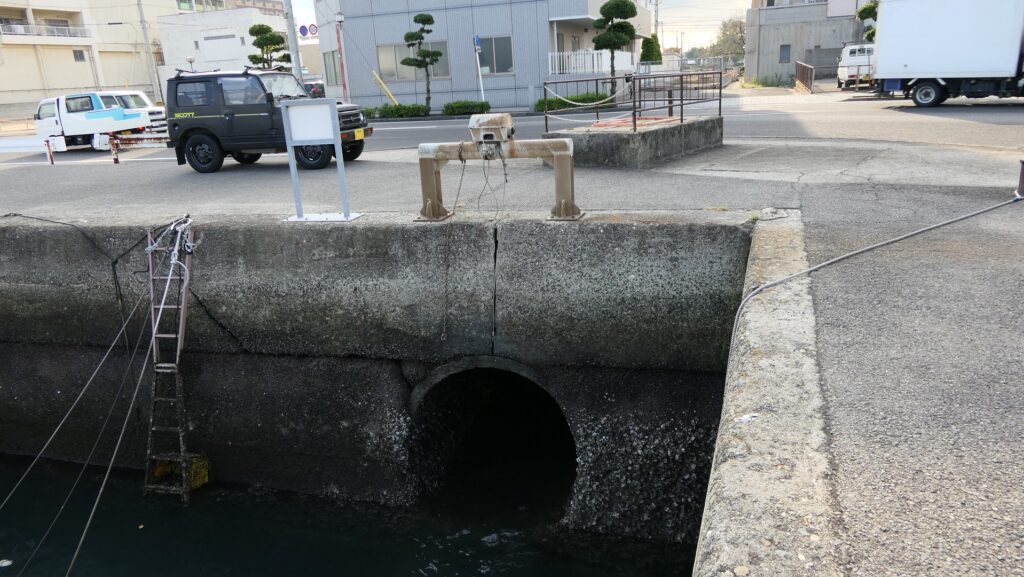
After looking around, you can check out how the sea water gets inside the Inner Moat of the castle. You can also see the water reservoir near the main entrance of the park. If you go along the waterway towards the source, you will reach the Imabari Port which was the castle port. It was located at the edge of the Middle Moat in the past. Because of that source, the surface level of the Inner Moat is changing depending on the tide.
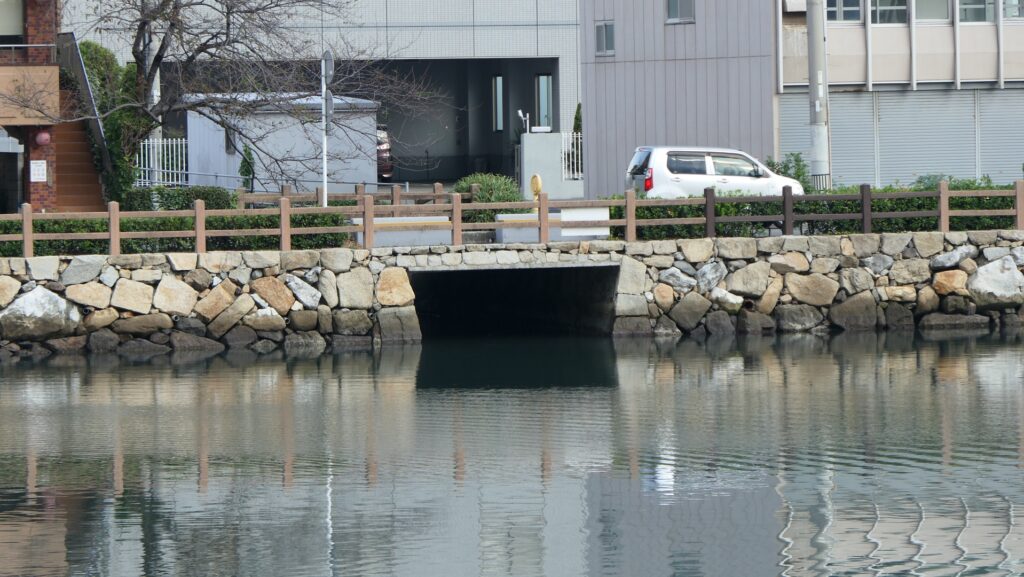




Later History
After the Meiji Restoration, Imabari Castle was abandoned and all the castle buildings were eventually demolished or burned. The Main Enclosure was turned into the Fukiage Shrine in 1872 before the Fukiage Park was established including the Second Enclosure in 1914. That’s why the main portion of the castle inside the Inner Moat still remains, while the outside of the moat was all turned into the city area. Since the castle ruins were designated as a Prefectural Historic Site of Ehime in 1953, Imabari City has been developing and restoring them as a historical park as mentioned above.


My Impression
After walking around the Inner Moat to see the great view of the moat and the high stone walls, I noticed Imabari Castle was quite practical. Why did Takatora Todo make the Inner Moat around 50m wide and the stone walls around 10m high? I speculate that the defenders on the stone walls were able to hit the attackers outside the Inner Moat effectively by guns and arrows. On the other hand, the guns and arrows from the attackers could not be useful. I think Takatora built this castle that way. Imabari Castle was beautiful as well as so strong.


How to get There
If you want to visit there by car, it is about 15 minutes from Imabari-Kita IC on the Nishi-Seto Expressway or about 20 minutes from Imabari-Yunoura IC on the Imabari-Komatsu Expressway. There is a parking lot beside the main entrance of the park.
By public transportation, you can take the Setouchi Bus bound for Imabari-Eigyosho from Imabari Station and get off at the Imabari-jo-mae bus stop or it takes about 30 minutes on foot from the station to get there.
From Tokyo or Osaka to Imabari Station: I recommend traveling by plane and when you get there you can take the bus or train to get to Imabari station.

That’s all. Thank you.
Back to “Imabari Castle Part1”
Back to “Imabari Castle Part2”