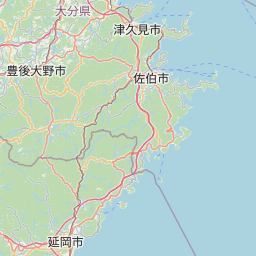
Location and History
Arima Clan builds Castle in Shimabara Peninsula
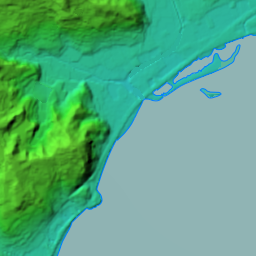
Hara Castle is known as the place where the Shimabara Rebellion was stopped in 1638. The castle was built near the edge of Shimabara Peninsula, in the western part of the Kyushu Region. The Arima Clan, one of the warlords in the region, first built the castle at the end of 15th Century. Harunobu Arima, the lord of the clan in the late 16th Century, was known as a Christian feudal lord. The Shimabara Peninsula possessed an international trade port called Kuchinotsu Port where Portuguese missionaries started to work in 1563. Christianity spread around the peninsula greatly and the area also prospered from trading. Harunobu originally lived in Hinoe Castle which the clan built many years ago. He renovated Hara Castle at the beginning of the 17th Century, probably as his new home base. However, he was punished by the Tokugawa Shogunate in 1612 before he moved to the castle. His son was also transferred to another place in 1614.



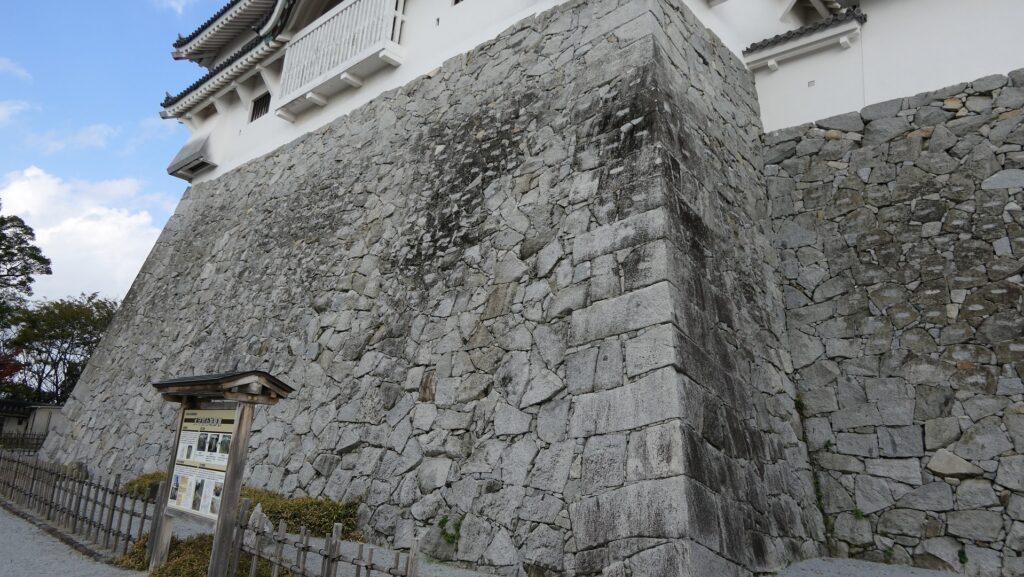
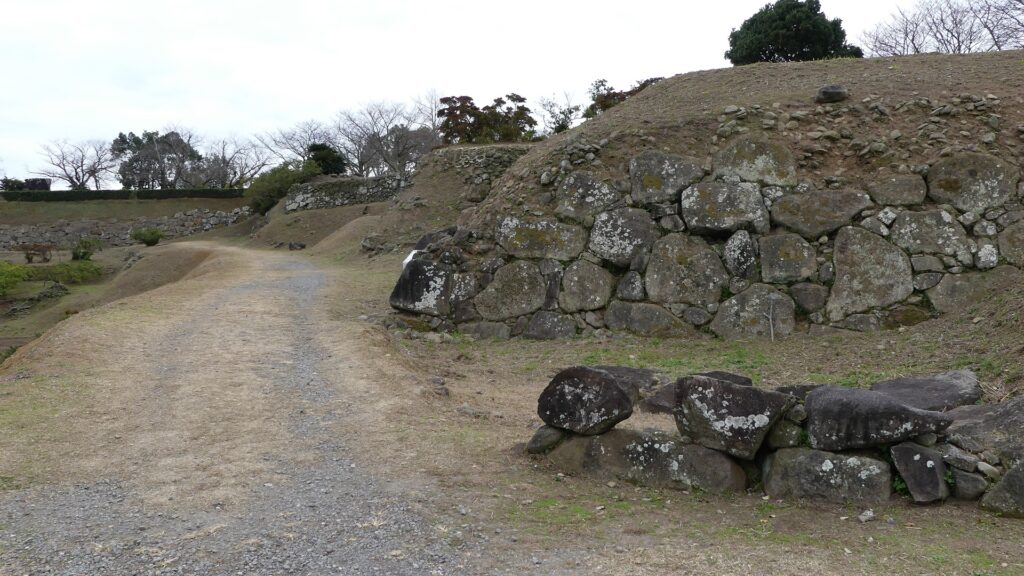
Castle uses Natural Terrain and has Great Stone Walls
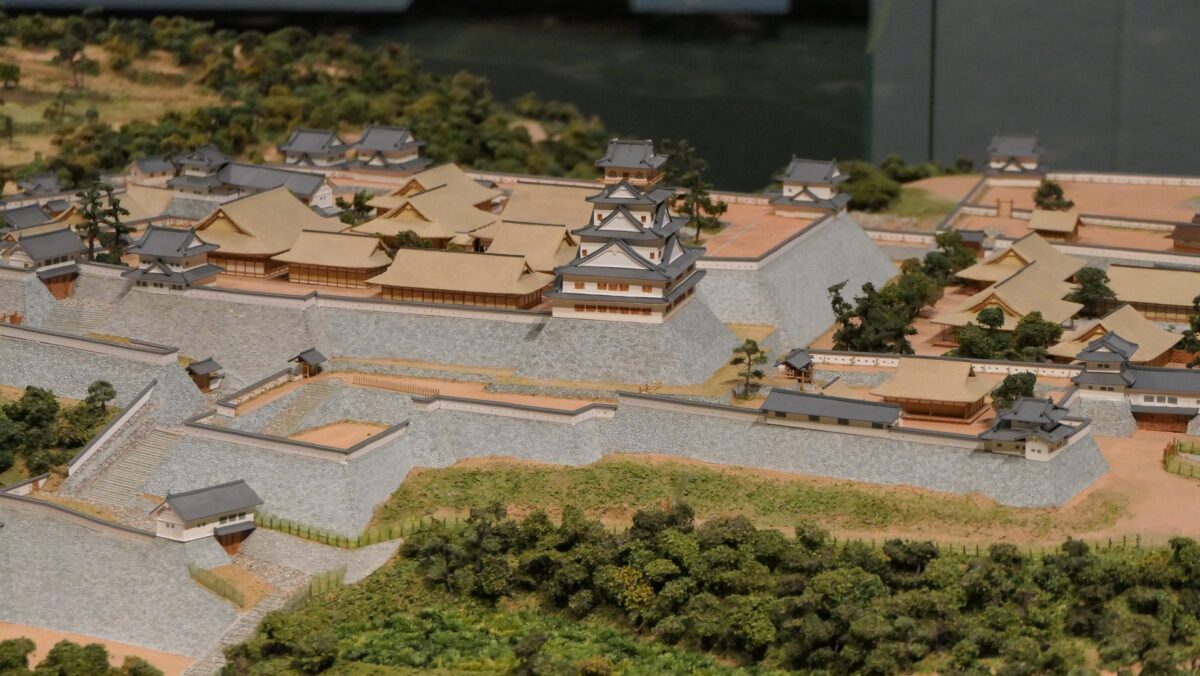
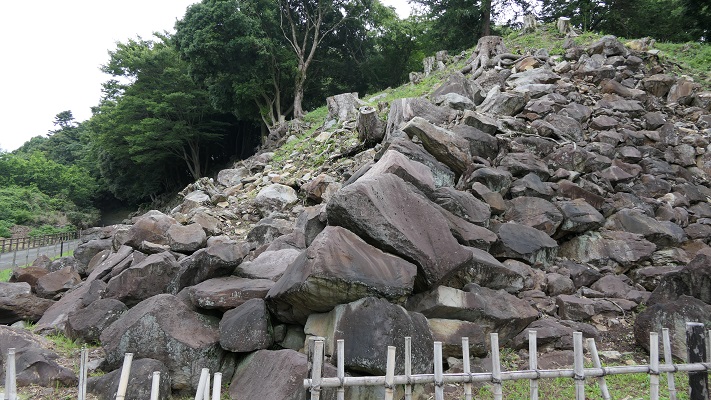
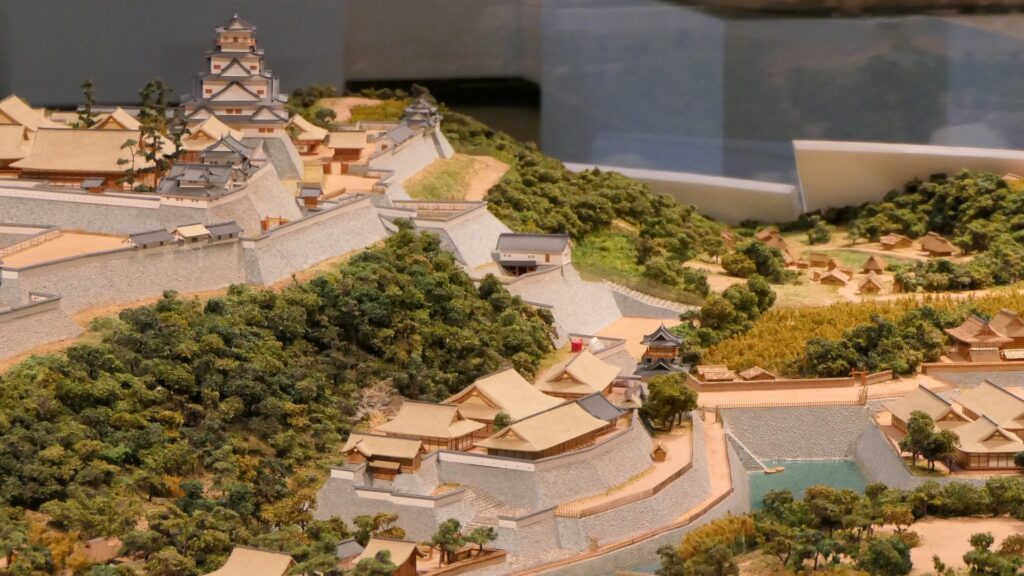
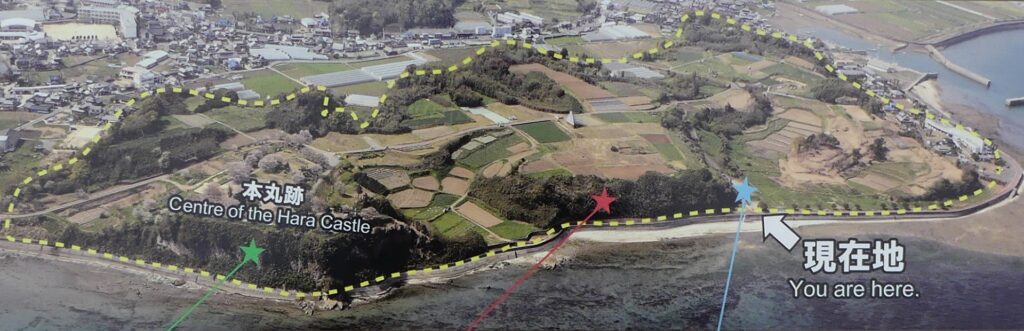
Hara Castle was built on several hills alongside Ariake Sea. The Main, Second and Third Enclosures were on different hills. These hills were by the sea with natural steep cliffs. They were divided by large and deep dry moats using the natural terrain as well. The side of the castle facing the land had a swamp. Overall, the castle could be very defensive. In particular, the Main Enclosure was all surrounded by stone walls. Its entrance, called Koguchi, was very large and had a zigzagging route using huge ornate stones. There was the Main Tower or a large turret inside the enclosure. These structures were thought to show the castle’s lord’s authority. The Second and Third Enclosures were made of soil and were probably used as warriors’ houses. The Matsukura Clan following the Arima Clan didn’t use Hara Castle and built a new castle, called Shimabara Castle, as their home base. Hara Castle was once abandoned in 1615, but at least its foundation, including the stone walls, remained.


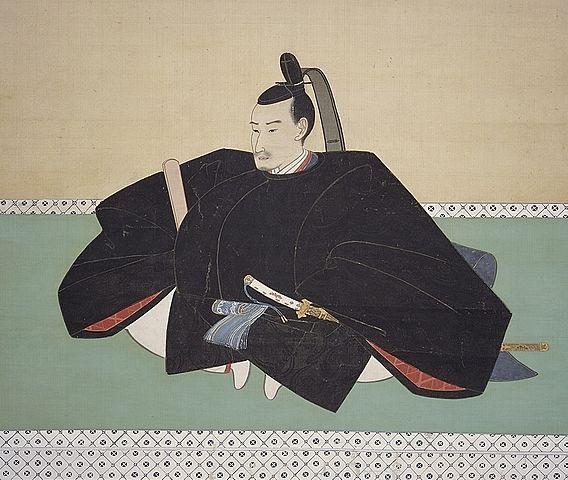
Shimabara Rebellion happens due to Matsukura Clan’s oppression
The Matsukura Clan oppressed the farmers and Christians in their territory. Being Christian had not been allowed by the Tokugawa Shogunate since 1612. 1n 1637, the people in Shimabara Peninsula, together with the people in Amakusa Islands over Ariake Sea who were in the same situation, rebelled against the Matsukura Clan and the shogunate. They were officially led by a charismatic Christian boy, Shiro Amakusa, but actually guided by the masterless warriors, called Ronin, who were former retainers of the Arima Clan and other Clans.
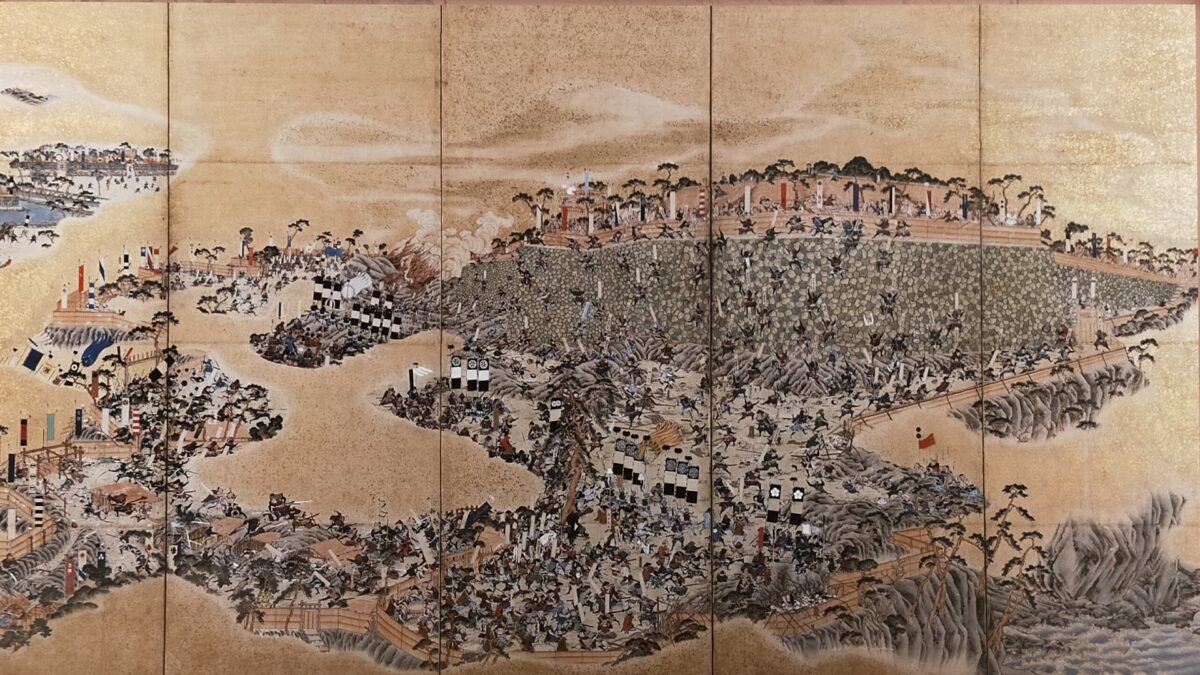
They first attacked Matsukura’s home base, Shimabara Castle, but failed. Then, they decided to be besieged in Hara Castle by themselves after they repaired it. Historians believe that they were waiting for reinforcements from Christians from other areas of Japan and Catholic countries like Portugal.


Annihilation of rebellion after 3-month siege
The siege started with about 37,000 defenders including women and children in December 1637. The troops from the shogunate first assaulted the castle but failed. Even the commander of the shogunate, Shigemasa Itakura was killed by a shot from the castle, as the counterattacks were professionally instructed and the castle was strong. The shogunate changed its tactics to encircle the castle with over 120,000 soldiers. The siege lasted for nearly 3 months, however, the reinforcements for the uprising army didn’t come. At the end of February 1638, the shogunate attacked the castle in full force when the defenders ran out of food. The castle fell and the rebellion was annihilated.
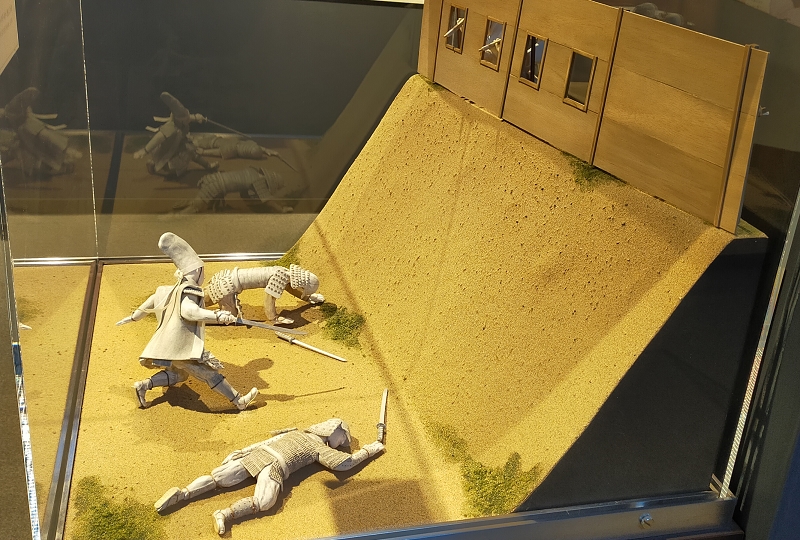


The survivors of the uprising army’s fate was extremely severe. Almost all of them, except for some runaways, were killed. It is said that many of the Christians hoped to be killed as martyrs. Hara Castle was completely destroyed and buried by the shogunate. The corpses of the executed people were also buried with the castle. The lord of the area, Katsuie Matsukura was executed due to his misgovernment. Shimabara Rebellion was one of the greatest tragedies and had a big impact on Japanese history. This incident accelerated the policy of the national isolation of Japan by the Tokugawa Shogunate.