Location and History
Introduction
Ueda Castle, which was located in the current Ueda City in Nagano Prefecture, is very famous because of the Sanada Clan. When the clan owned the castle, they repelled the invasions from the Tokugawa troops twice. However, the castle was destroyed by the Tokugawa Shogunate after the battles. After that, other clans rebuilt and maintained the castle, but they are not popular for the general people. Therefore, this article will describe not only about the Sanada Clan, but also the other clans (Sengoku and Fujii Matsudaira) regarding the castle.
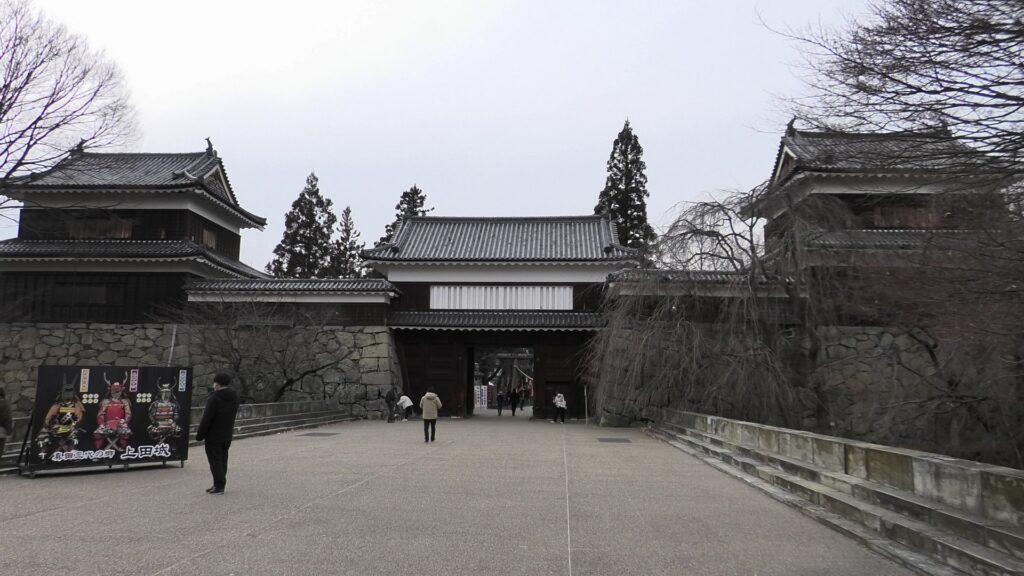

From building Ueda Castle to the First Battle of Ueda
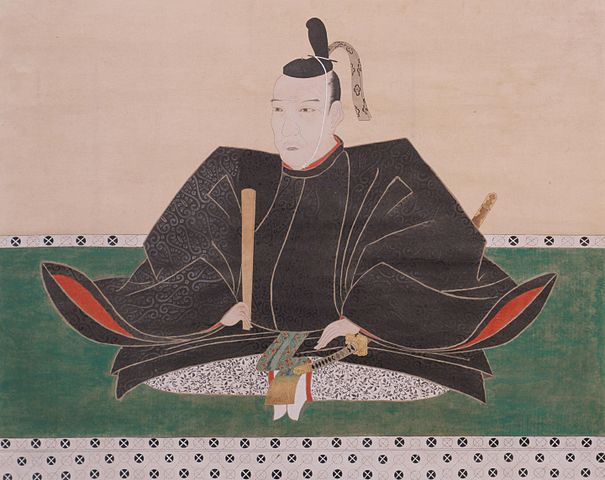
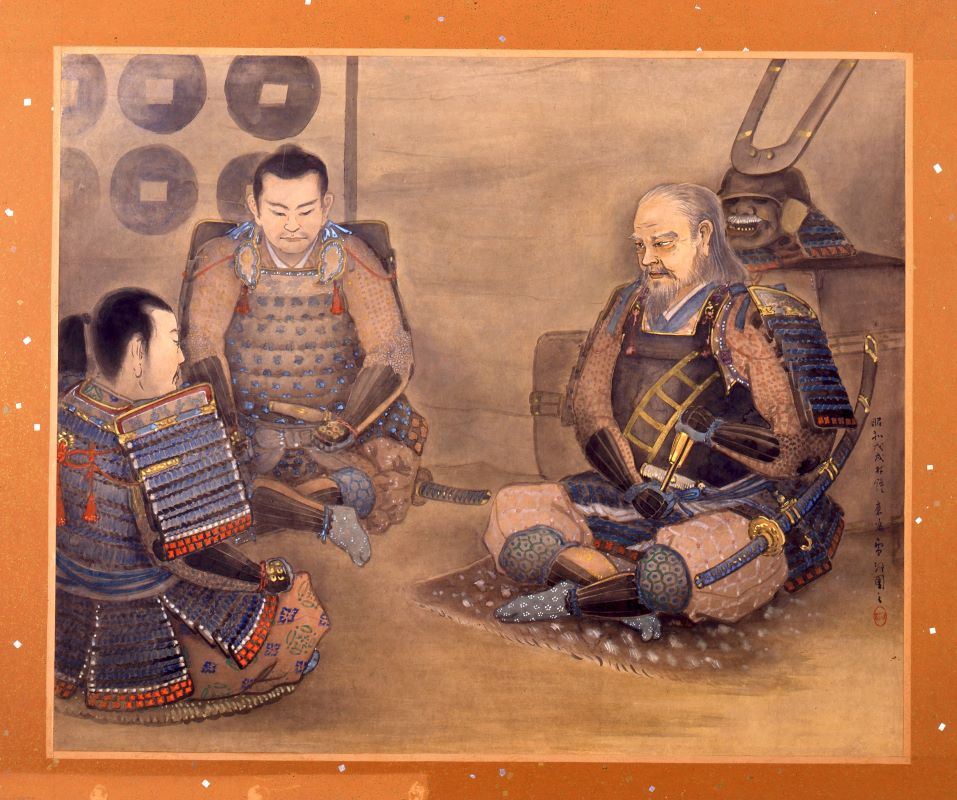
Masayuki Sanada, who first built the castle, was born in 1547 as the third son of Yukitaka Sanada. Yukitaka was a lord in Shinano Province (the current Nagano Prefecture) and became a senior vassal of Shingen Takeda, one of the greatest warlords at that time. In his later life, Yukitaka invaded the western area of the Kozuke Province (the current Gunma Prefecture). Masayuki eventually followed the invasion after he became the successor of his father. In 1579, he captured Numata Castle, one of the most important points of the province. Masayuki was still one of the Takeda’s retainers, but he behaved as if he was an independent lord.
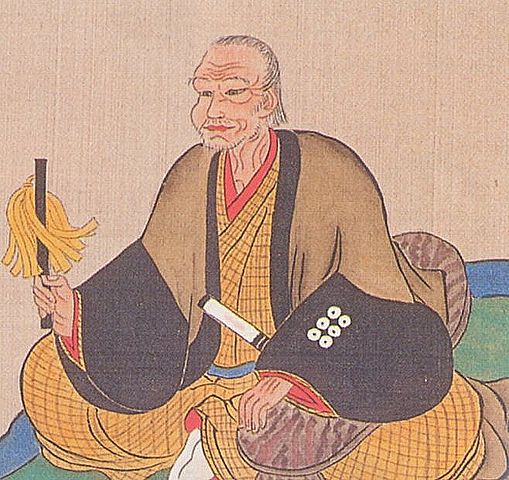

In 1582, the Takeda Clan, which was Masayuki’s master, was defeated by Nobunaga Oda, who was soon killed in the Honnoji Incident as well. That meant the large territories, which the Takeda Clan owned, became unoccupied area for other great warlords around. The Tokugawa, Hojo, and Uesugi Clans immediately started to invade the area. However, the area included Masayuki’s territories. He first allied with the Uesugi Clan but later on switched to the Hojo Clan, then finally the Tokugawa Clan in order to maintain his territories.



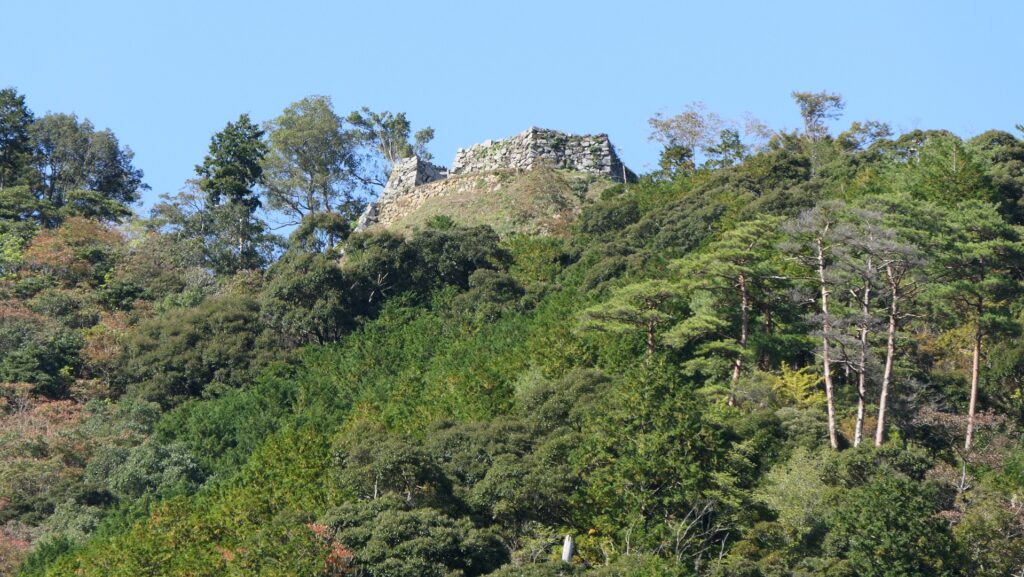
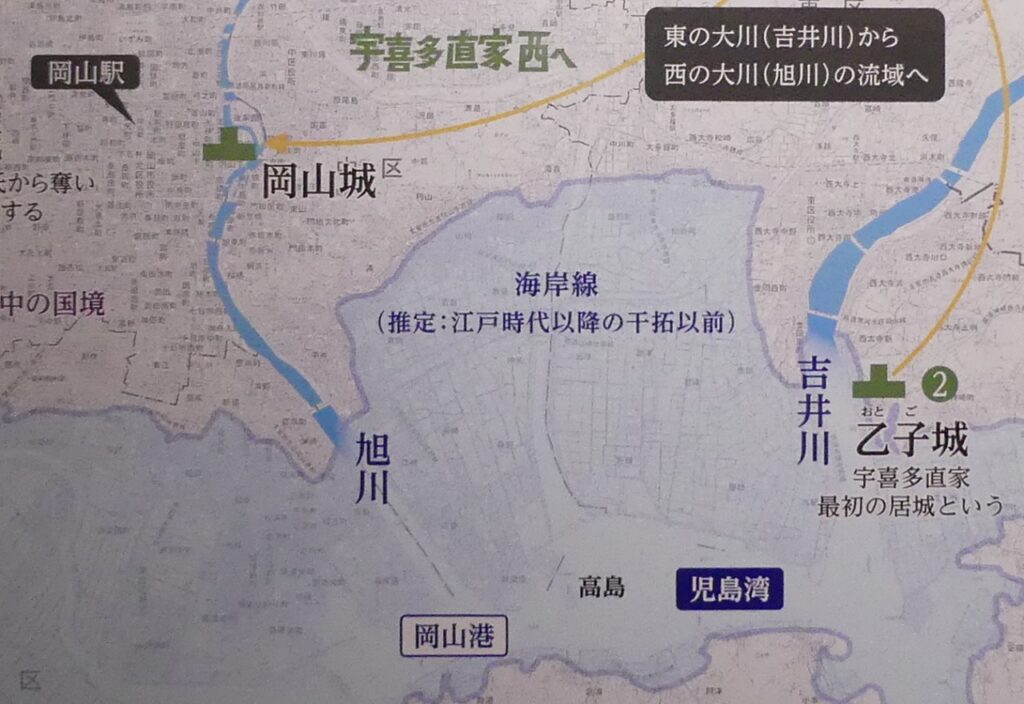
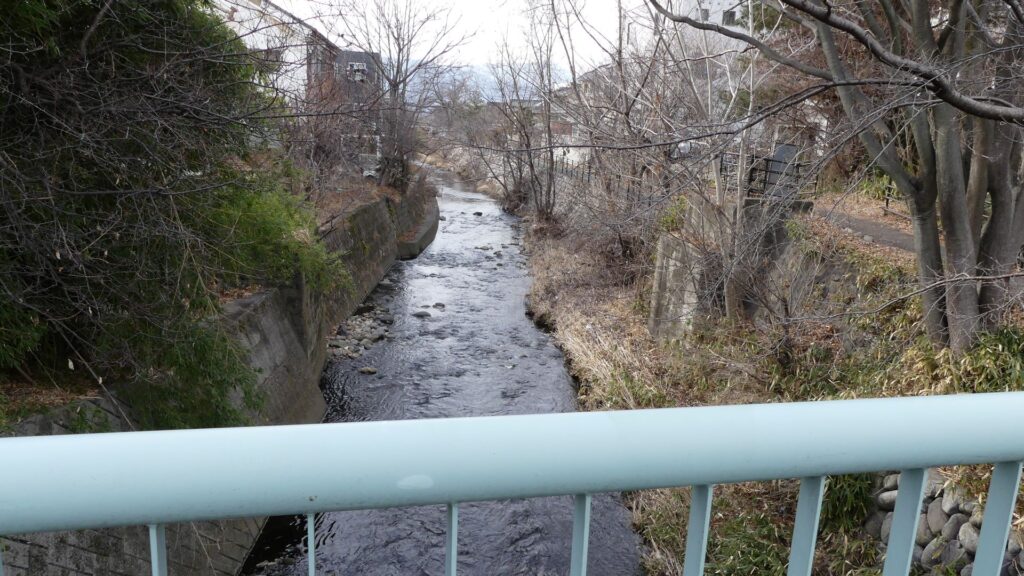
He lived in Toishi Castle which was built on a mountain at the Ueda area. Ueda Castle would be built on a plain land near the mountain castle when Masayuki was at the Tokugawa’s side. This was because this spot was very important for the intersection of roads and Chikuma River. It was also the border of the Tokugawa and the Uesugi Clans. Therefore, the castle would be the strong frontline of the Tokugawa Clan against the Uesugi Clan. Historians speculate that the construction of the castle was completely supported by the Tokugawa Clan. Kagekatsu Uesugi, who was the lord of the clan, ordered his retainers to halt the construction. The Tokugawa Clan also had to protect it.

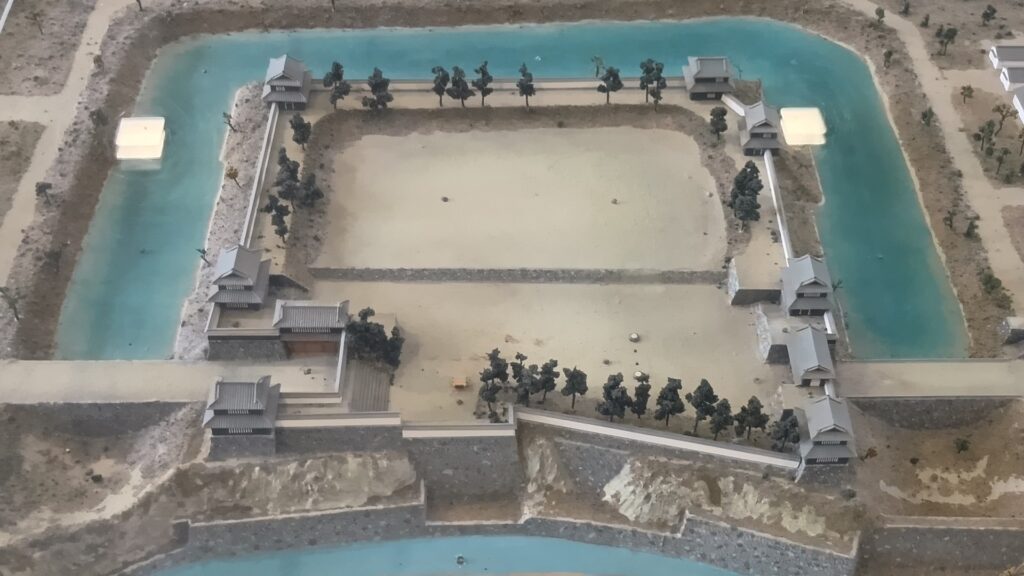
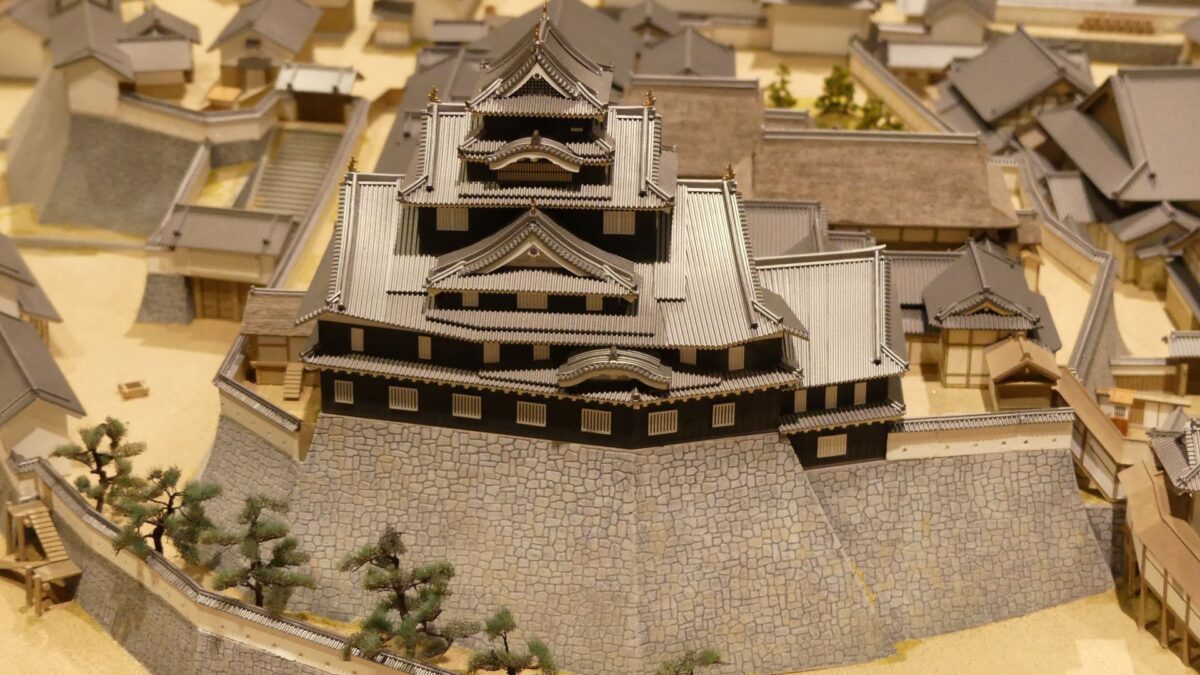
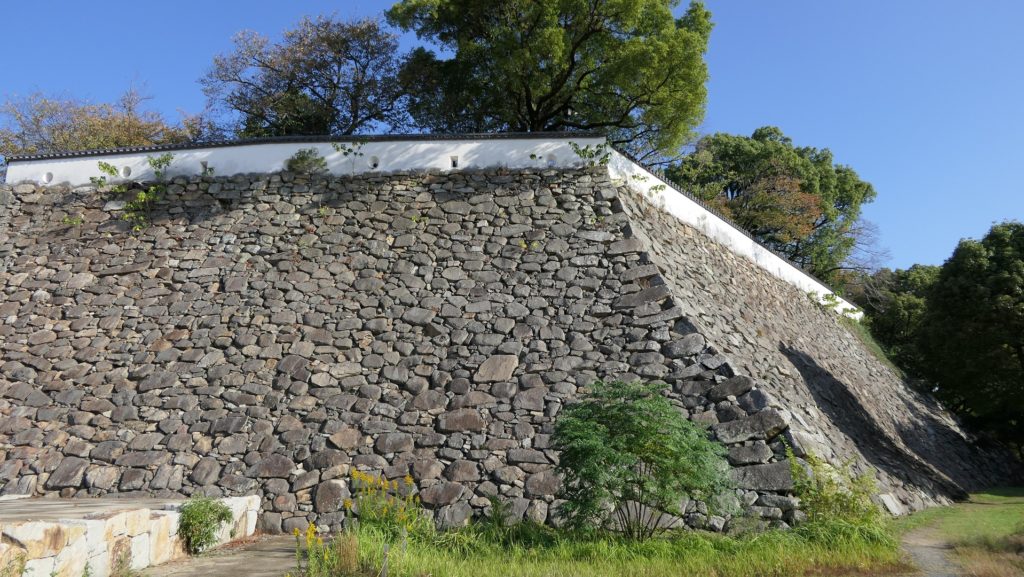
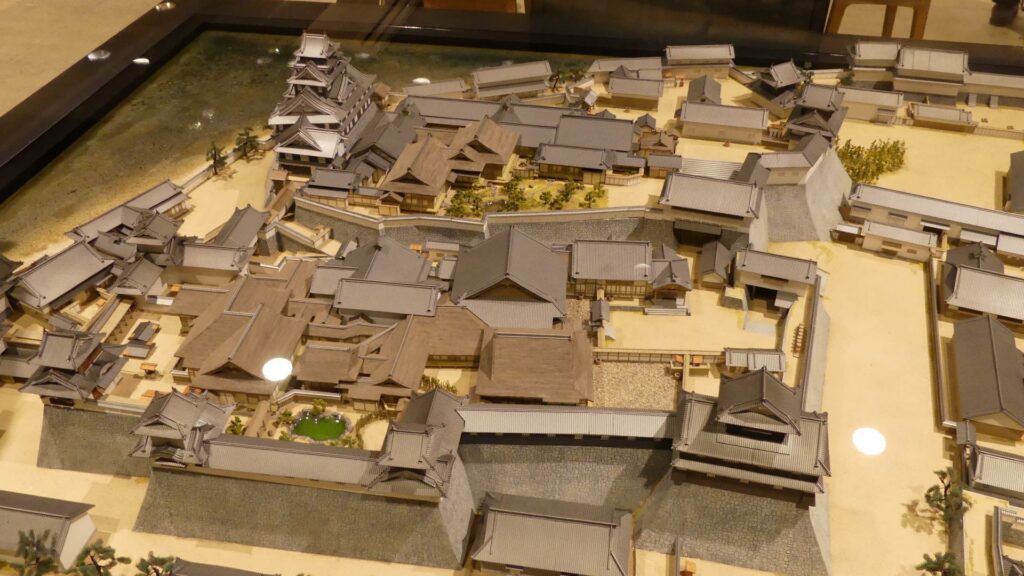
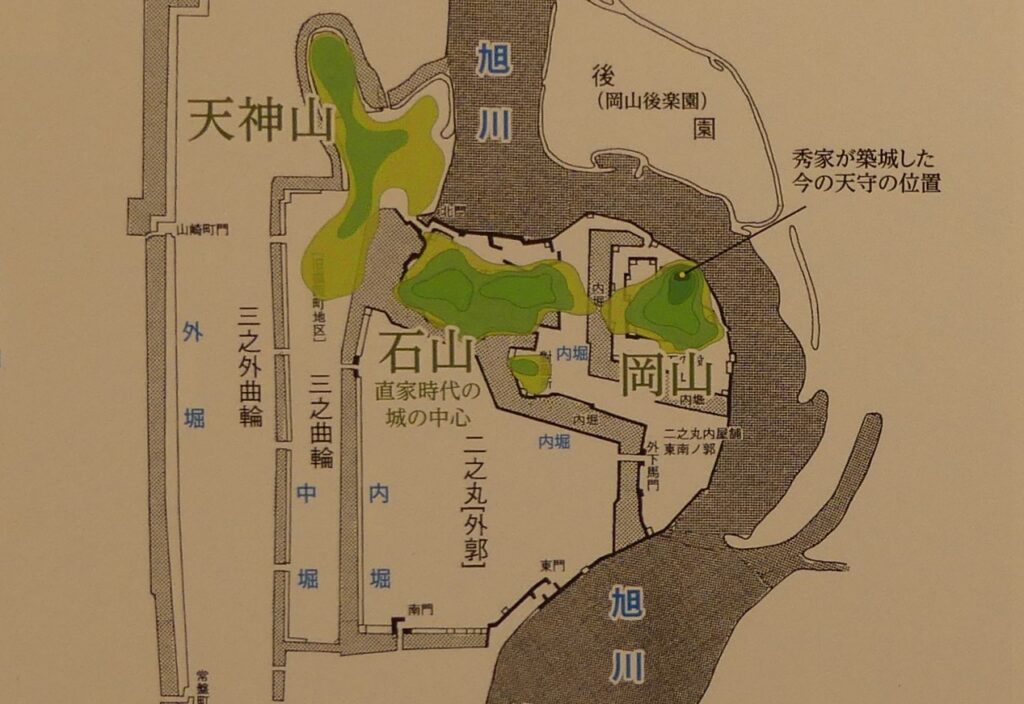
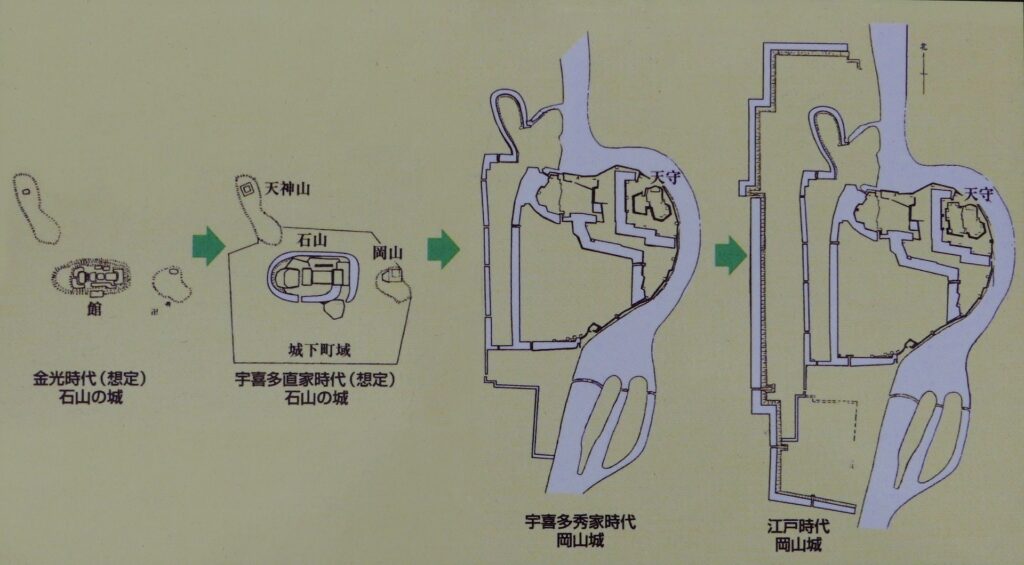
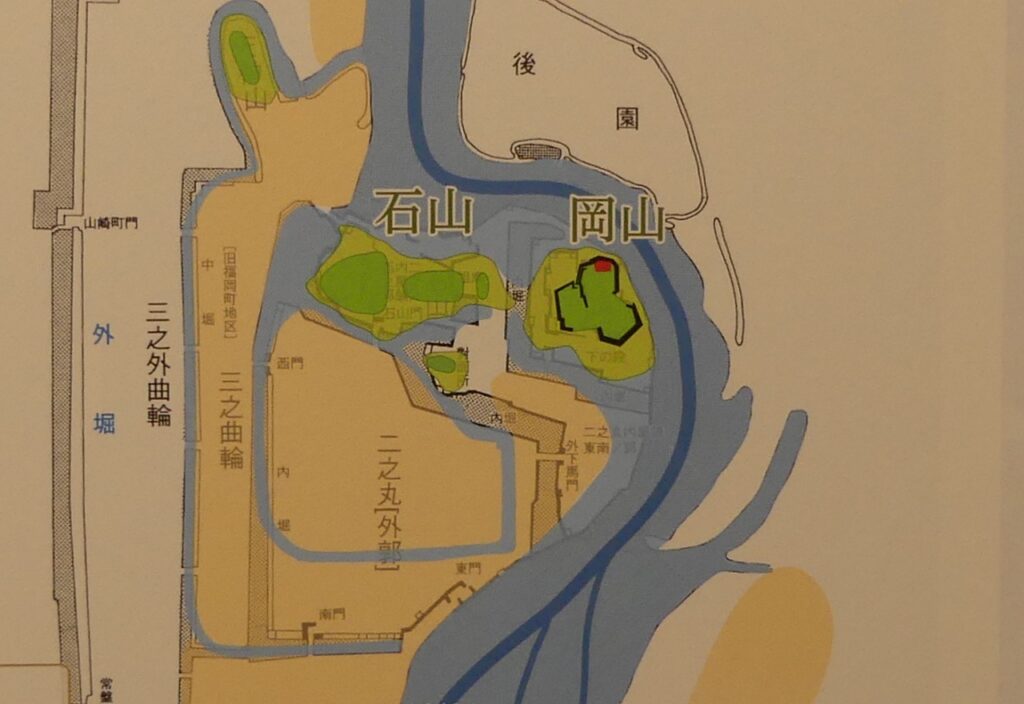
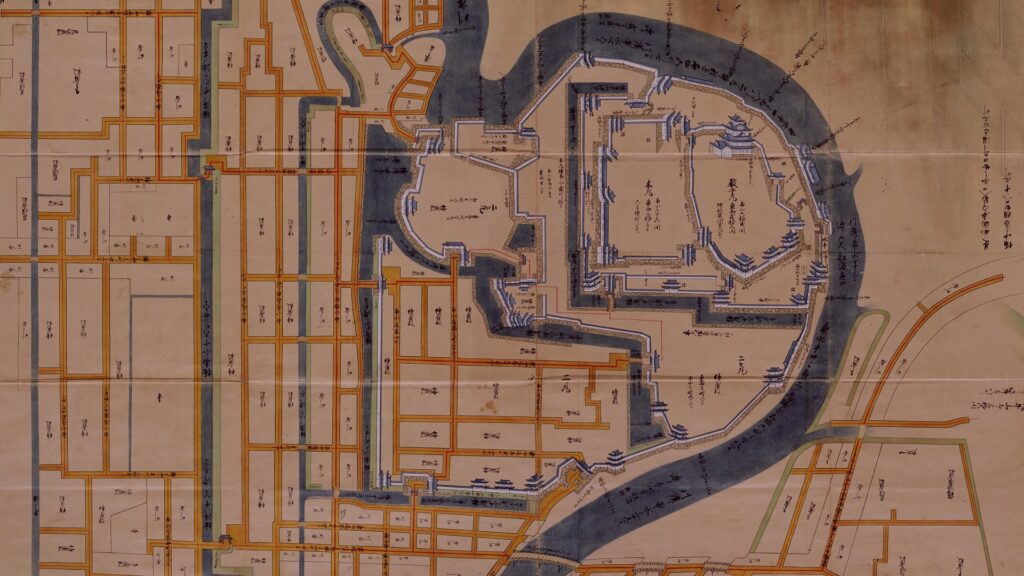
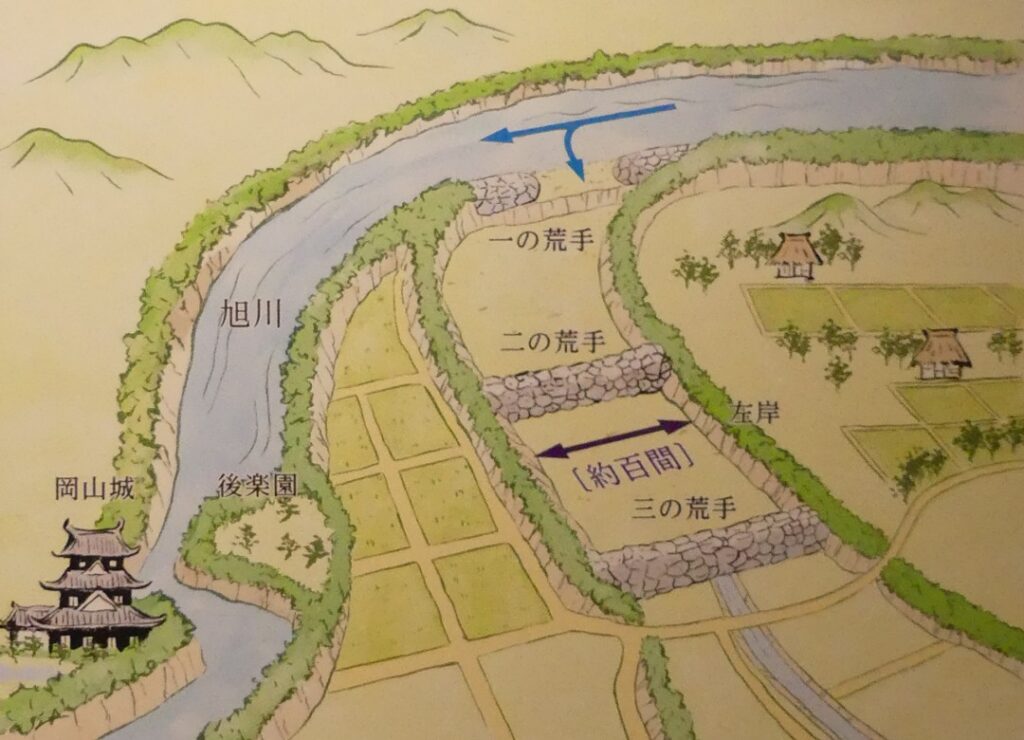
Even though the castle was built on a plain, it was protected by natural hazards. For example, it had natural steep cliffs to the south, which were created by a branch of the Chikuma River, called “Amagafuchi”. The builders also used other rivers to protect the castle. The flow of Yadesawa River was changed to build the natural outer moat to the north and the west, which faced the Uesugi’s territories. The original flow was used to make inner moats surrounding the castle. The center of the castle on a hill was turned into several enclosures, such as the main and second enclosures. The east of the castle was still waterlogged; however, it was partially used as residential areas. The construction was done between 1583 and 1585. You can see the drawing of the castle during that time, inside the Ueda City Museum.
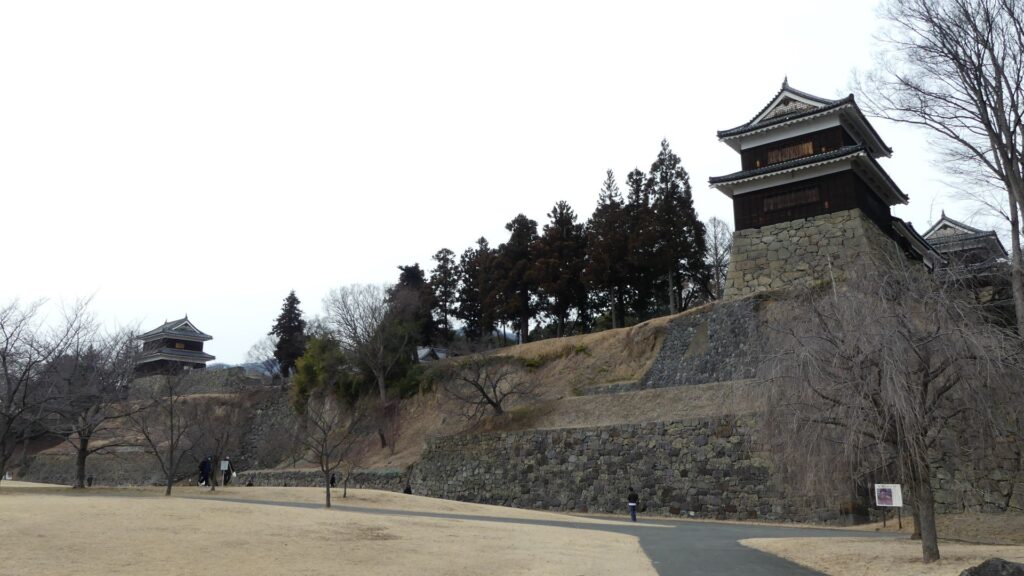



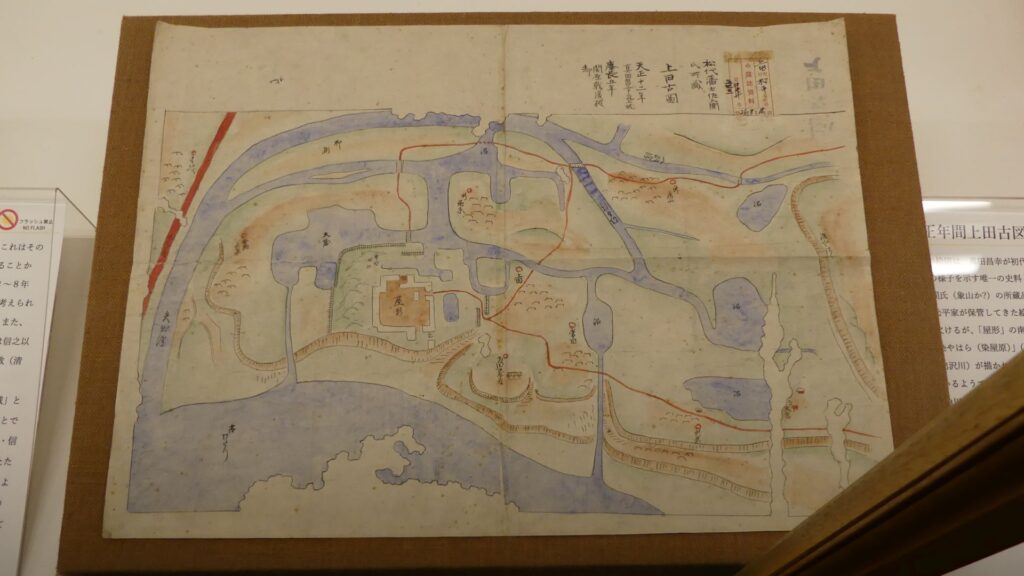
Just after the castle was completed, Masayuki switched sides from the Tokugawa to the Uesugi Clan again. This was because Ieyasu Tokugawa, who was the lord of the clan, promised to give the Hojo Clan Kozuke Province in order to make peace. That meant Masayuki would have to give up his Numata Castle in the province. He couldn’t stand giving up the castle. However, this decision caused him to fight against the two great warlords (the Tokugawa and Hojo Clans) at the same time. The Hojo Clan had been wanting to capture Numata Castle for a long time. Ieyasu was also very angry about Msayuki’s decision. Ieyasu expected Masayuki to give up Numata Castle after he had given him Ueda Castle, but this was not the case. Therefore, Ieyasu ordered his retainers to destroy the Sanada Clan, which triggered the first battle of Ueda.

The number of the Tokugawa troops was about 7,000 while that of the Sanada Clan was only 2,000. In addition, Ueda Castle was more vulnerable to the east which faced the Tokugawa’s territories, compared to the other directions. There were only protective fences facing the eastern direction. Masayuki’s plan was to divide his few soldiers between Ueda Castle and other branch castles. He also ordered them to ignore the important defensive lines to the east, Kangawa River and Someya Castle. That meant the Tokugawa troops could easily attack Ueda Castle, and they actually did it. However, many of the Tokugawa soldiers were inexperienced and overconfident. Once the Tokugawa side reached the second enclosure of the castle, the Sanada troops suddenly counterattacked. The Tokugawa Troops were very confused and withdrew but they were blocked by the fences behind them. Miraculously they managed to get to get back to Kangawa river, but the other remaining Sanada troops attacked them. Many of them were killed, which resulted in the Tokugawa’s lost.


This battle would eventually lead to the independence of the Sanada Clan with their honor. This stunt can only be done by Masayuki.
The Castle is improved under the Toyotomi Government until the 2nd Battle of Ueda
Masayuki’s choice after the 1st battle was to try to serve under Hideyoshi Toyotomi who was the new ruler of Japan. Hideyoshi called Masayuki “a man like the two sides of the same coin” and tried to defeat him. However, for some reason, Hideyoshi accepted Masayuki saying in his letter “I’ll forgive you just this time”. Masayuki had to work under Ieyasu again due to Hideyoshi’s order. Ieyasu also accepted the Sanada Clan by marrying Nobuyuki, Masayuki’s son with his adopted daughter. That meant the two biggest lords recognized the strength and threat of the Sanada Clan. This is how the clan became an independent lord family under the Toyotomi government. Numata Castle, one of the most important castles of the clan, was once given to the Hojo Clan by Hideyoshi’s order. However, the castle was soon returned to the Sanada Clan due to the Battle of Odawara, where the Hojo Clan was defeated.

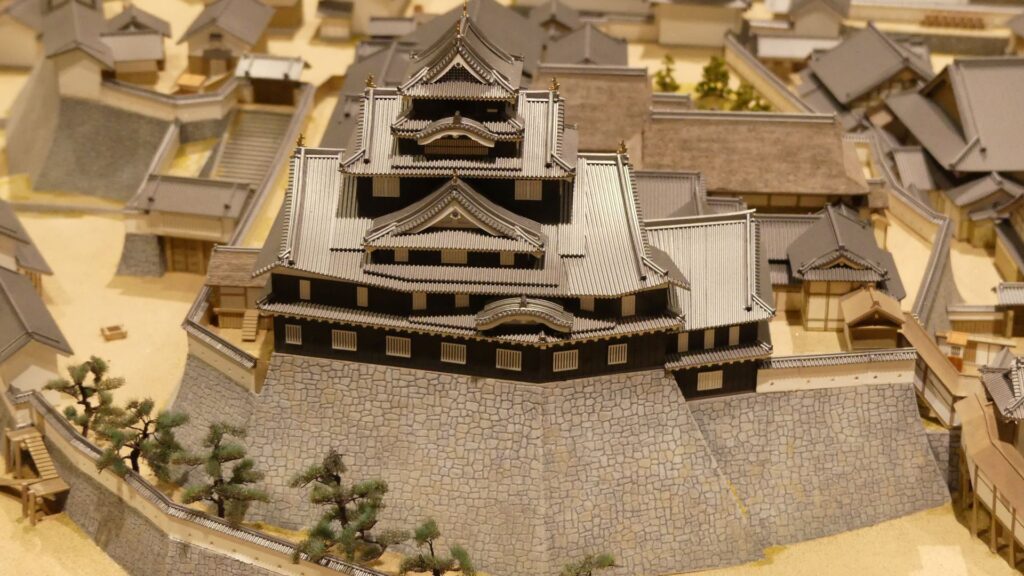
Ueda Castle was improved as one of the important castles under the Toyotomi government. Some believe that the castle had the main tower during the improvement. However, it is still uncertain as followed.
Supporting opinions:
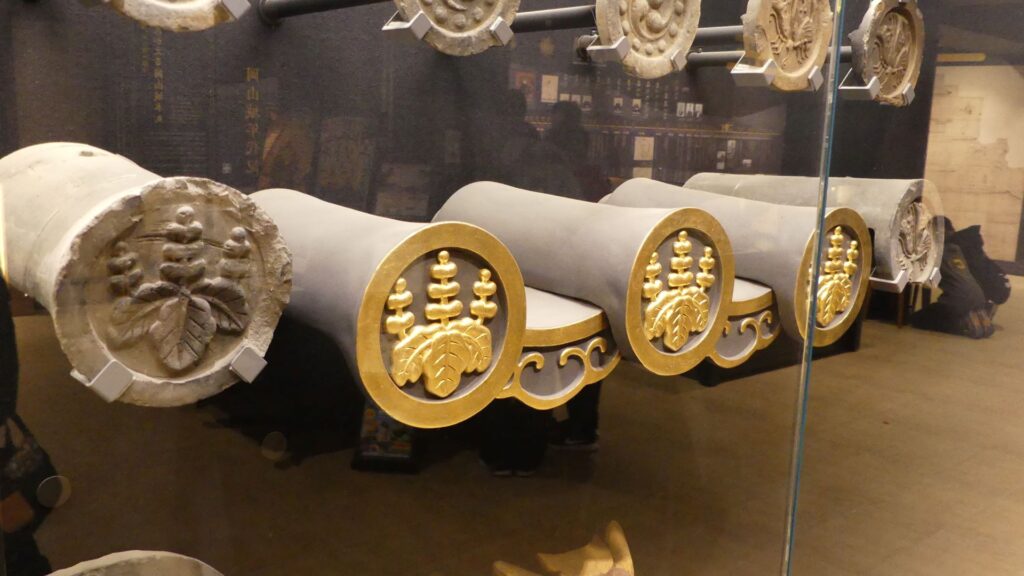
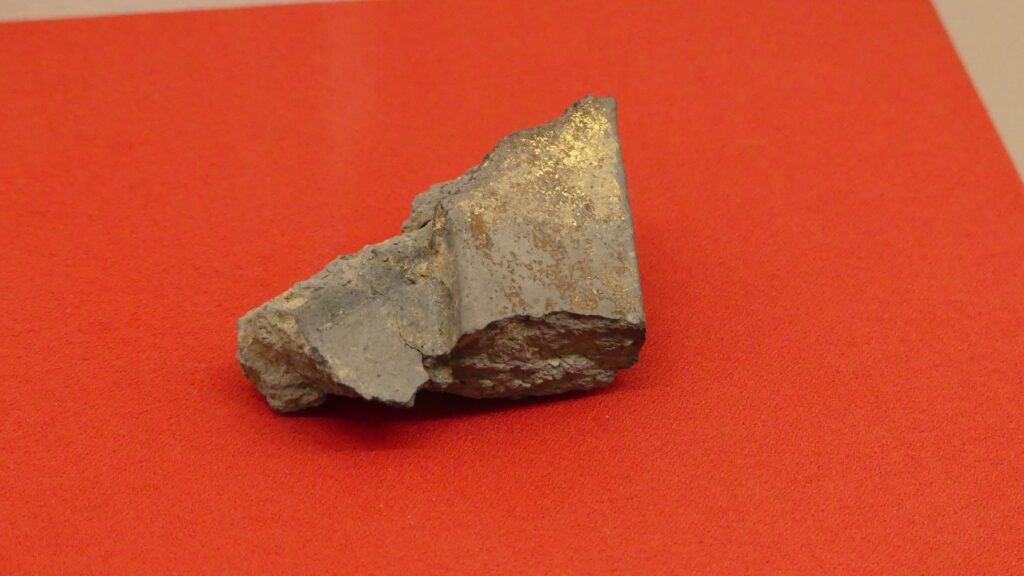
The rooftiles with golden leaf and grampus rooftiles at that time were excavated from the moats of the main enclosure. Other important castles nearby, using the same or similar rooftiles, had their main towers, such as Matsumoto, Takashima, and Komoro Castles. An old map of Ueda Castle during the Edo Period says there were the ruins of the main tower. Therefore, Ueda Castle must have had its own main tower.




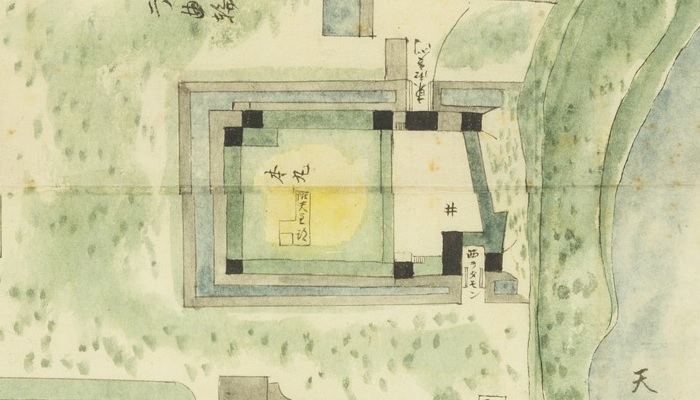
Opposing opinions:
In the case of Ueda Castle, rooftiles with golden leaf were also excavated at other enclosures aside from the main enclosure. That means main halls or other turrets might have used them. In addition, no trace of the main tower base was ever found in the main enclosure at all. The main tower of Ueda Castle did not necessarily exist.
So far, we can say the castle at least had luxurious buildings in it with these rooftiles. Historians speculate if the castle had the main tower, it was not so large that it might have only been 3 levels.
The castle was also fortified to make its eastern area more defensive. For example, the third enclosure, including the main gate, was built in the area. The castle town was also built outside the enclosure. Many temples gathered in the town because they would become the positions for soldiers when battles happened.


After Hideyoshi died, the decisive battles happened in 1600. The Sanada Clan first tried to join Ieyasu Tokugawa’s troops which would be called the Eastern Allies. They were going to the east to destroy the Uesugi Clan which was against Ieyasu. However, once the clan received the letter of impeachment to Ieyasu from the magistrates of the Western Allies, it made their decision tougher. One order was for Nobuyuki to stay with the Eastern allies,while Masayuki and Nobushige, who was Nobuyuki’s little brother, would join the Western Allies. It is thought that this decision came from Masayuki’s experiences so that some of the clan would survive no matter which allies won.

Ieyasu went back to the west to destroy the Western Allies through Tokaido Road along the seaside. He also sent about 38,000 soldiers, led by Hidetada Tokugawa, Ieyasu’s successor, through Nakasendo Road along the mountain areas. He then ordered Hidetada to capture Ueda Castle, which Masayuki and Nobushige were holding, on the way to the west. The second battle of Ueda would occur. The number of the soldiers in the castle was only about 3,000, so the plan of Masayuki this time was to delay the Eastern Army as followed.

The timeline of the 2nd battle of Ueda
September 2nd (according to the lunar calendar): Hidetada arrived at Komoro Castle, about 20 km away from Ueda Castle to the west.
September 3rd: Masayuki made an offer to surrender to Hidetada through Nobuyuki.
September 4th: Hidetada went to battle because Masayuki did not do what he had said.
Nobuyuki’s troops went to Toishi Castle which Nobushige held to capture it.
September 5th: Nobushige went back to Ueda Castle without fighting.
Their first battle was on September 6th, but its details are uncertain. This is because some records say it was a skirmish while others say Masayuki’s troops won like he used to do in the first battle of Ueda. At the very least, what I can say for sure is that Hidetada didn’t do a full-scale attack as followed.
September 8th: Hidetada received a letter from Ieyasu, telling Hidetada to immediately leave to go to the west.
September 11th: Hidetada left Komoro Castle for the battlefield to fight against the Western Allies.
As a result, Hidetada spent about 10 precious days without capturing Ueda Castle and was not able to join the battle of Sekigahara on September 15th. Masayuki’s plan was successful again. However, the Eastern Allies won on that day. Masayuki and Nobushige were eventually placed under house arrest at Kudoyama in Kii Province (the current Wakayama Prefecture). Masayuki died there after 11 years, and but Nobushige managed to escape to became famous during the sieges of Osaka Castle between 1614 and 1615.
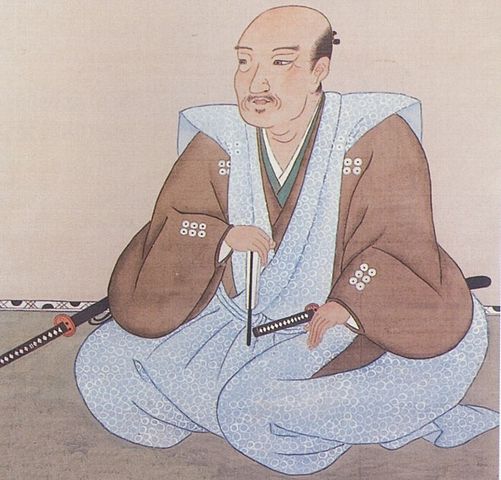

Ueda Castle finally belonged to Nobuyuki, but the center of the castle was destroyed by the Tokugawa Shogunate. Its moats were buried, and its enclosures were turned into farms. Nobuyuki stayed in his residence at the third enclosure. You can see the drawing of the castle during that time, inside the Ueda City Museum. He was eventually promoted and moved to Matsushiro Castle in 1622.
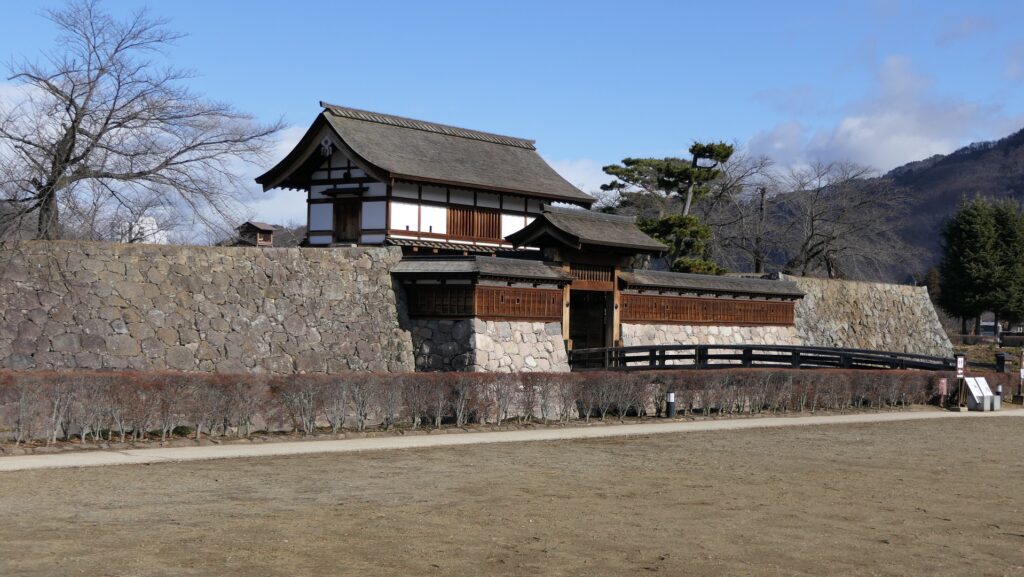

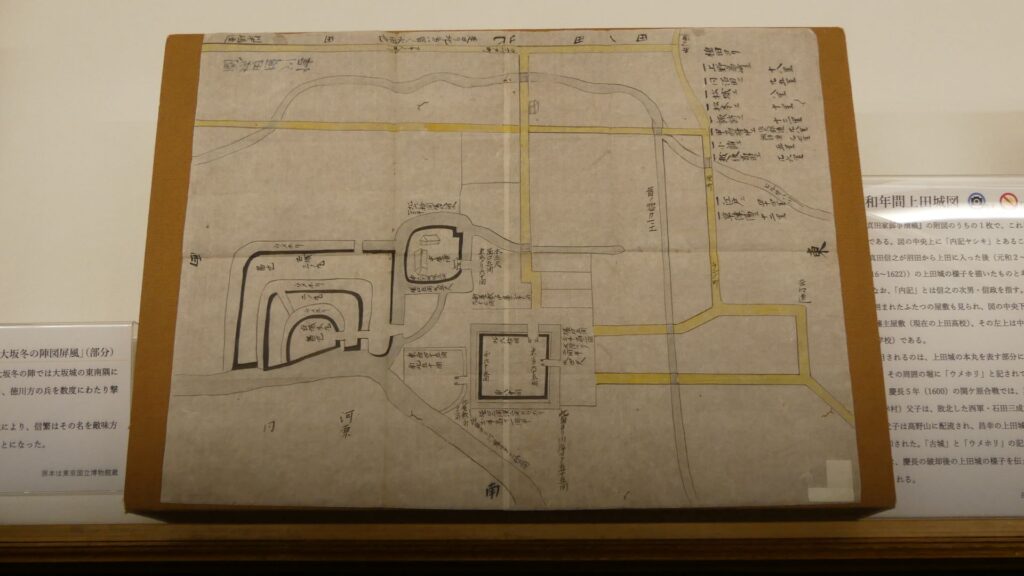
Tadamasa Sengoku reconstructs Ueda Castle
Ueda Castle was mostly abandoned before Tadamasa Sengoku came to the castle as the new lord of the Ueda Domain in 1622. He had been the lord of Komoro Castle, so he joined the second battle of Ueda as well. It was said that when he became the lord of Ueda Castle, Hidetada Tokugawa, who was the shogun at that time, told him as followed. “You may reconstruct Ueda Castle however you like as I will pay for the expenses.” Hidetada was the person who suffered from the castle during the second battle of Ueda earlier on. However, it is still a mystery why he was allowed to reconstruct the castle as well as why he was given money for the castle. The reconstruction started in 1626 after it was formally permitted by the Tokugawa Shogunate.
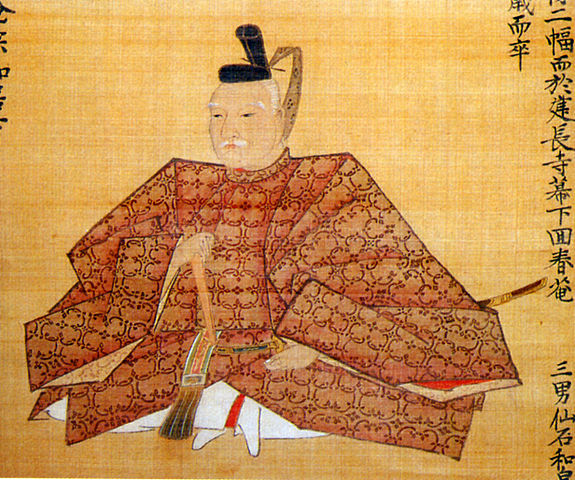
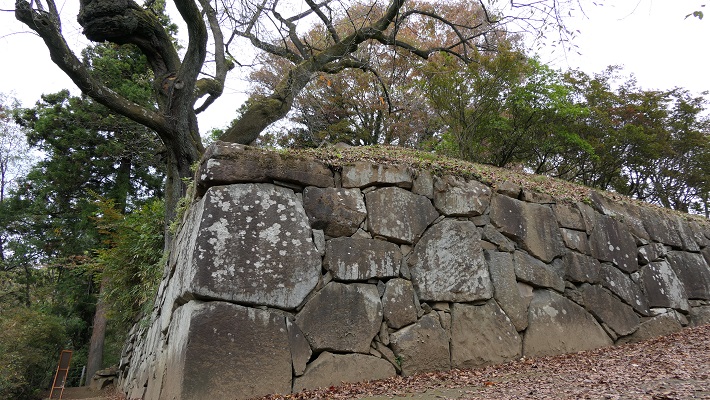
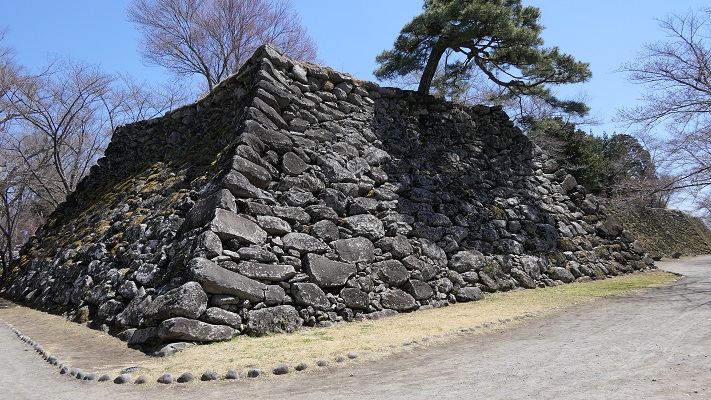
Tadamasa gave his detailed instructions to the construction builders. According to the instructions, it seemed like he tried to restore the castle during the Sanada’s period. For example, they say that if the moats of the old castle had distortions, he ordered the build to dig to widen the moats than they were in order to make them straight. That meant the layout of the castle would be similar to the old castle. However, the remaining stone walls you see now at the castle were all built by the Sengoku Clan. Part of them, which look very old, might have been built by the Sanada Clan. If so, the Sengoku Clan might also have rebuilt the stone walls by using the old stones.
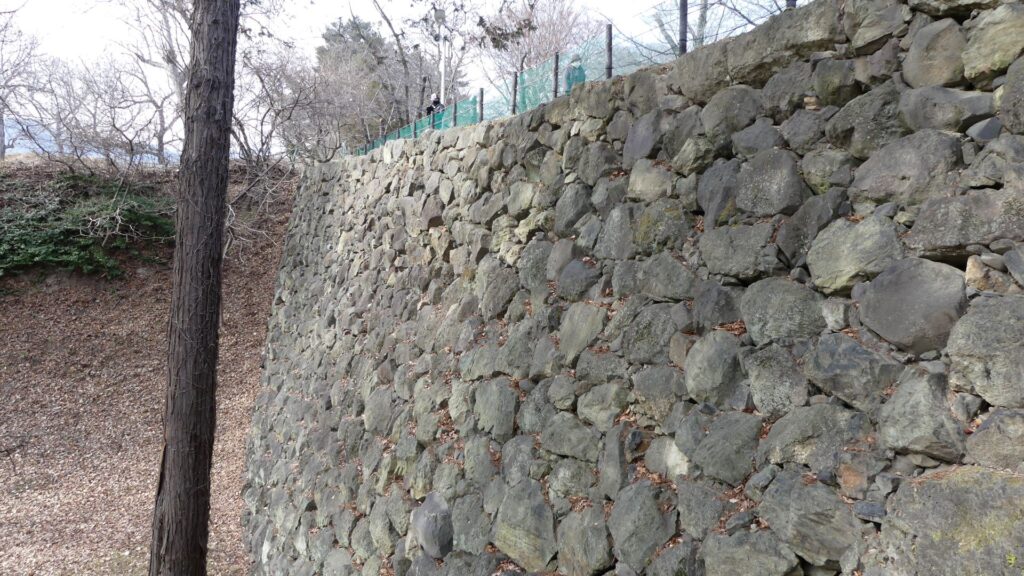


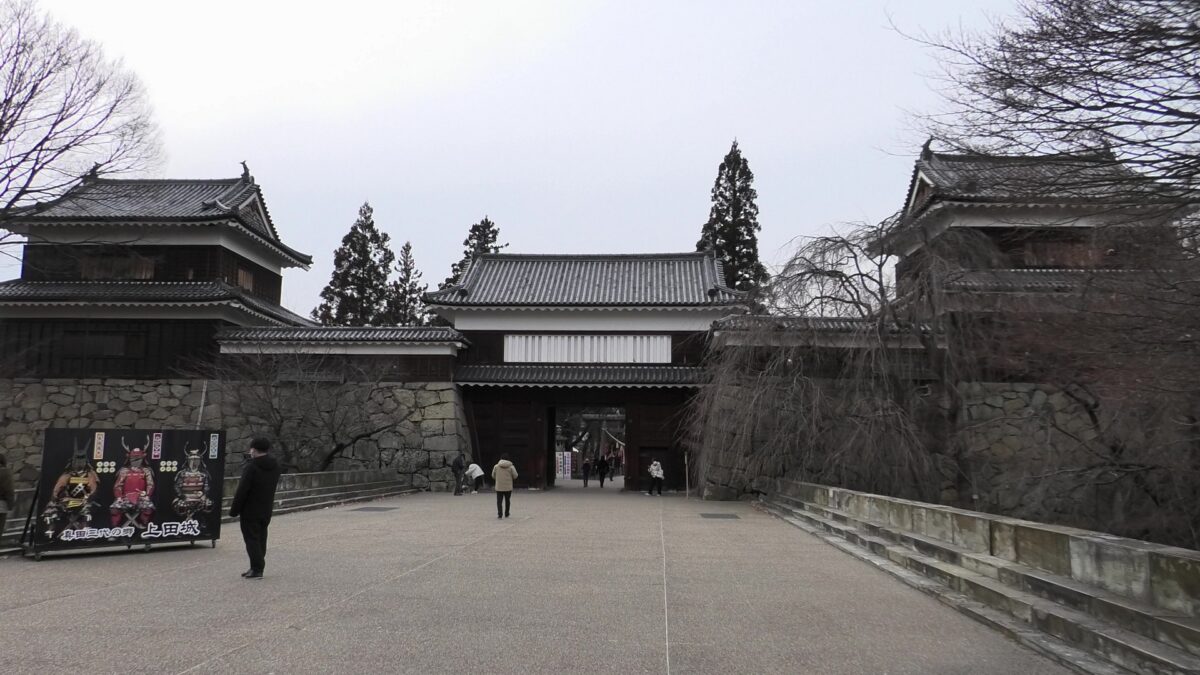
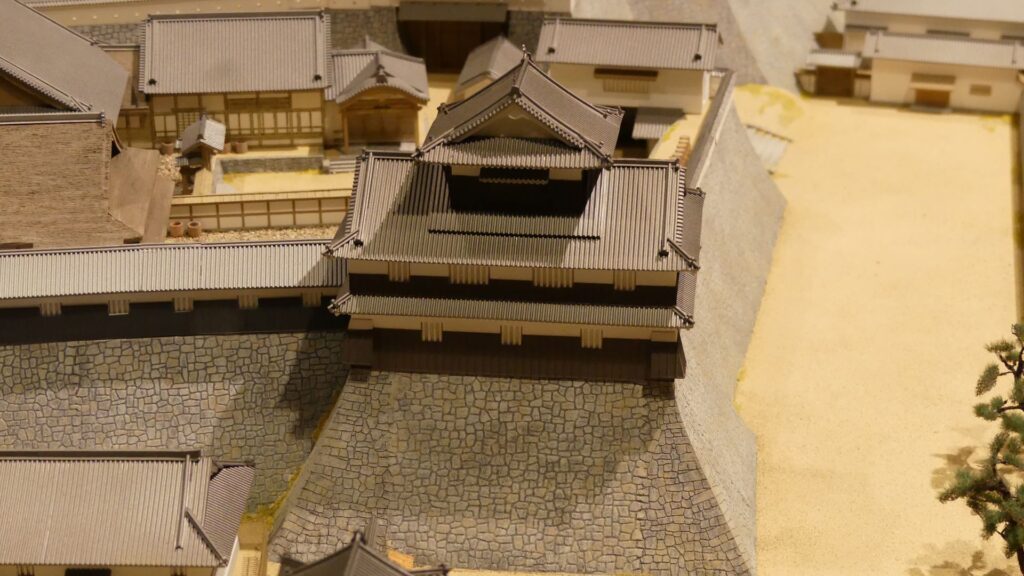
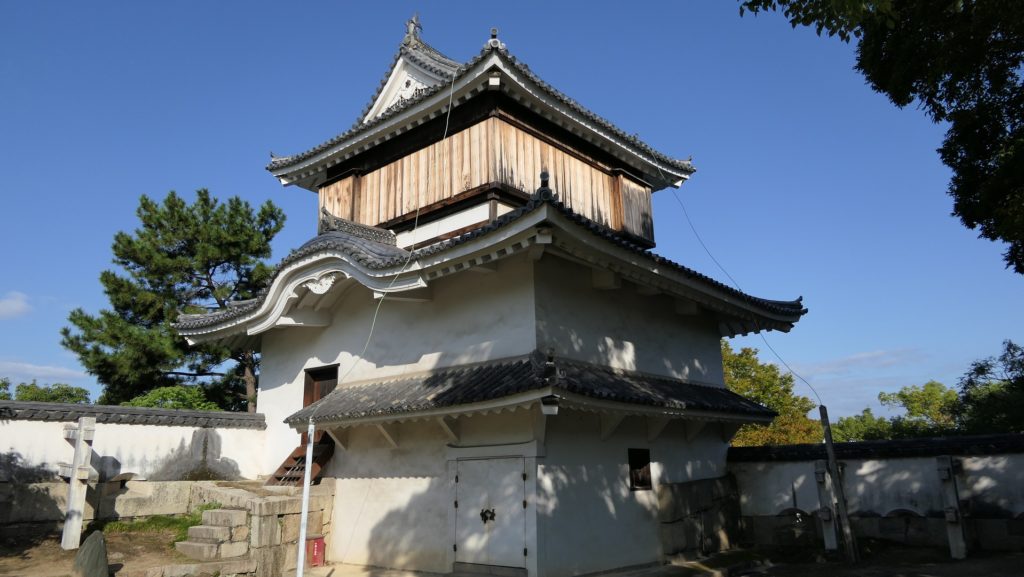
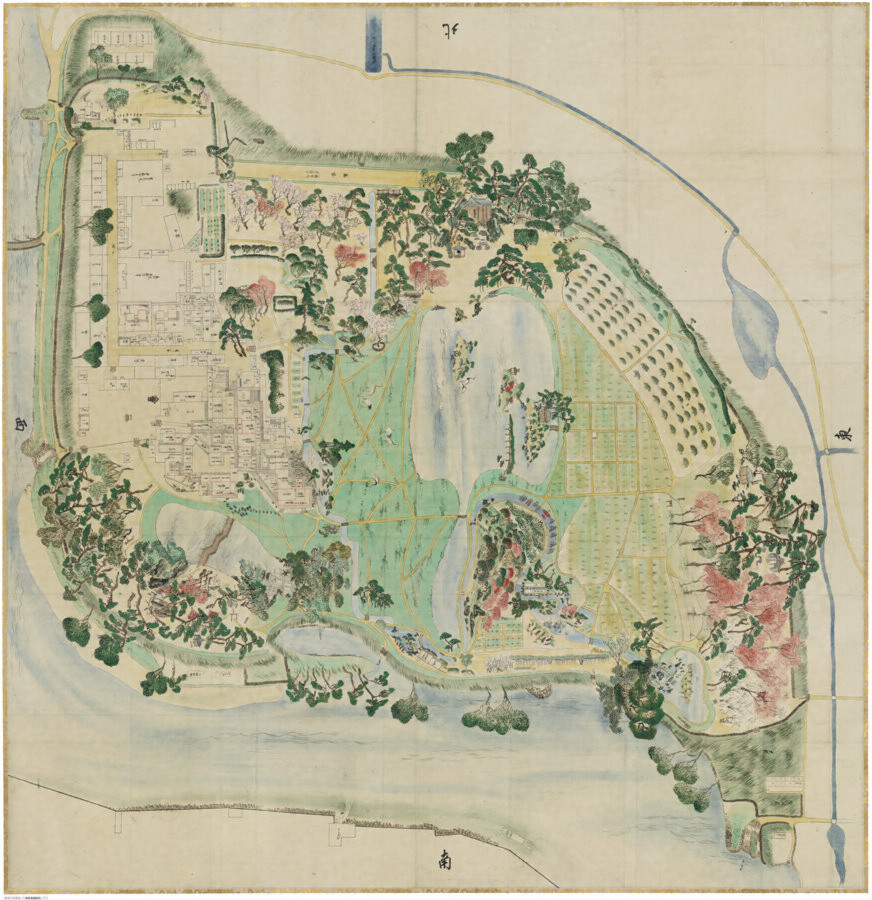
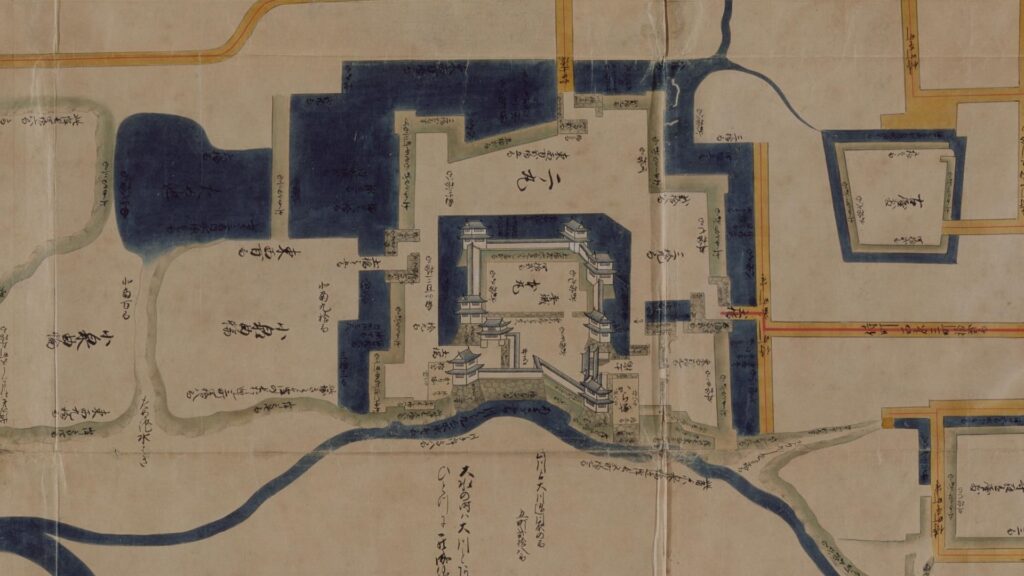
Although the main tower was not built in the main enclosure, the enclosure had seven turrets and two gates along its perimeter. However, it had no buildings in the center, like the main hall. That meant the purpose of the castle was only for reconstruction. Tadamasa planned to construct other buildings in the second enclosure, but it was canceled because of his death in 1628. The structure of the castle, built by Tadamasa, was maintained by the following lords of the Ueda Domain until the end of the Edo Period. You can see the illustration of the castle after the reconstruction, exhibited by National Archives of Japan. So, what did Tadamasa think about Ueda Castle? He might have admired the castle because of the activities of the Sanada Clan.
The Government under the Fujii Matsudaira Clan
In 1706, Tadachika Matsudaira became the lord of the Ueda Domain in place of the Sengoku Clan. His clan was sometimes referred to as the Fujii Matsudaira Clan in order to classify many Matsudaira Clans. It is one of the 18 Matsudaira which had been the relatives of the shoguns before Ieyasu Tokugawa was born. (In fact, Ieyasu himself was one of them.) The reason for the replacement would be that Tadachika was a close vassal of the 5th shogun, Tsunayoshi Tokugawa. He may have been given a closer territory than that he had had in the Izushi Domain (in the current Hyogo Province) by the shogun. The clan also maintained Ueda Castle and the government which the other clans had made.

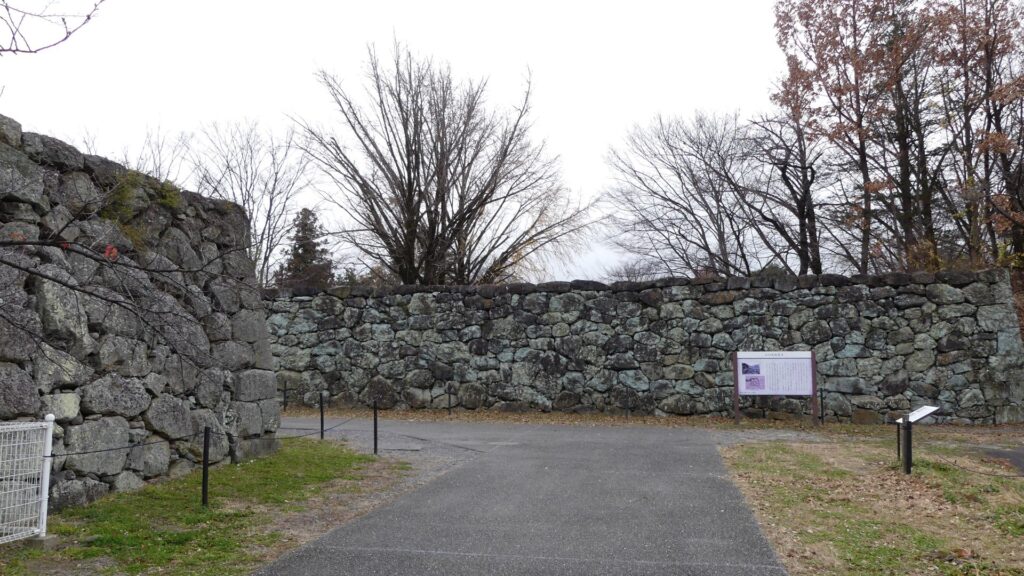
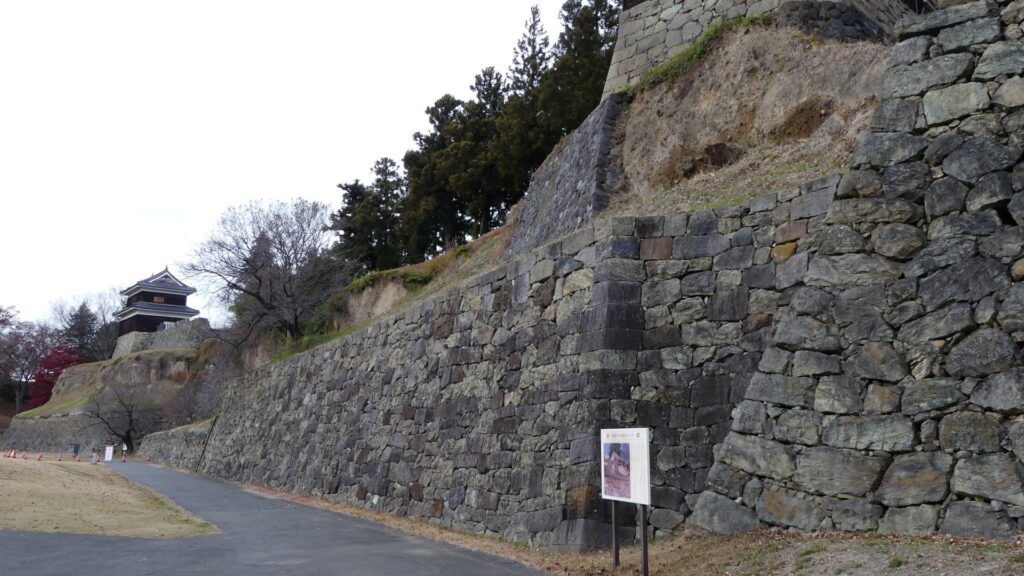
However, the most serious problems for the castle were caused by natural disasters, such as floods, earthquakes, and fires. In 1732 during Tadachika’s son, Tadazane’s period, a heavy flood from Chikuma River destroyed the cliffs of the southern side of the castle. Tadazane had to rebuild stone walls on the cliffs to protect them from the river for the next 4 years. We can still see the stone walls on the cliffs now. The clan also had to repair and maintain other stone walls of the castle many times due to harsh weathers and deteriorations.

Let me introduce Tadakata Matsudaira, the 6th lord of the Fujii-Matsudaira Clan during the end of the Edo Period. He was less popular than other politicians at that time like Masahiro Abe, Masayoshi Hotta and Naosuke Ii. However, he was one of the politicians who devoted themselves to opening the country to other western countries. When he became the lord of the Ueda Domain, the domain often suffered from famines because of the cold weathers. Therefore, he encouraged people to boost the sericultural industry (the process of breeding silkworms in order to produce silk fabrics) which was more stable. These experiences may have led his policy towards opening the country to the western countries. When the U.S. fleet led by Matthew Perry arrived at Japan in 1853, he was a member of the shogun’s council of elders. He insisted that Japan should open the country as well as allow trading with other countries. Masahiro Abe, who was the head of the members, decided to finally open the country. Ater that, Masayoshi Hotta and he negotiated with the U.S. consul, Townsend Harris about the trade treaty. Tadataka insisted again that Japan would immediately conclude the treaty despite not having the proper permission by the emperor, against Masayoshi and Naosuke Ii’s advice who thought they would need the permission. Tadataka strongly believed that the trade with foreign countries must have resulted in the national interests. After he quit the post of the members, he began selling the silk fabrics from his domain by exporting them to the countries.

Later History
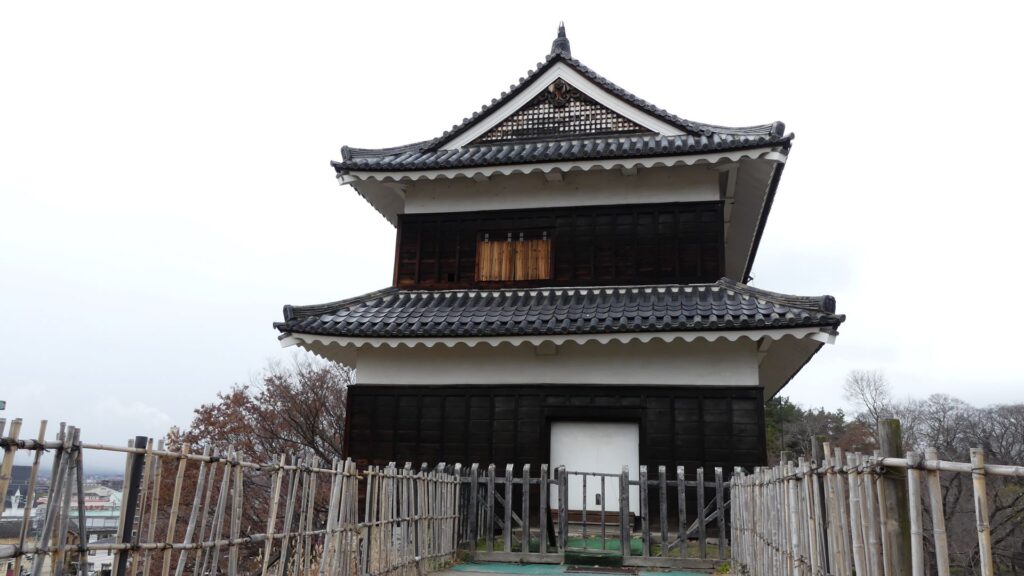
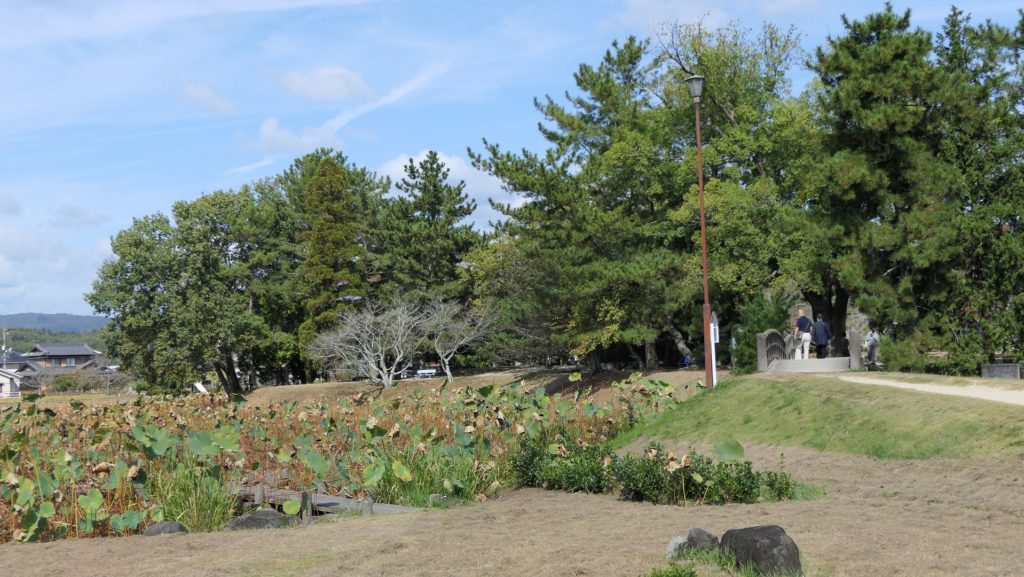
After the Meiji Restoration, Ueda Castle was eventually abandoned, and its lands and buildings were sold. As a result, the lands became farms. A rich merchant, named Heihachiro Maruyama appeared under such a situation. He earned his money by selling wooden materials and silk, maybe thanks to the policies of Tadakata Matsudaira. He bought the land of the main enclosure and donated it for the shrine which would worship the Fujii- Matsudaira Clan, the former lord family of the castle. The shrine became the current Sanada Shrine in the enclosure, which now worships the Sanada, Sengoku, and Matsudaira Clans. Then, in the second enclosure, there was once a prison and an isolation hospital before Ueda City bought the land back. The city turned the main and second enclosures into Ueda Castle Ruins Park. The park was also designated as a National Historic Site in 1934. As for the castle’s buildings, there was once the only remaining building as the western turret at the site. Other turret buildings, called the northern and southern turrets, were used in the pleasure district of Ueda. When these buildings were going to be sold again, the citizens in Ueda were worried about it. Therefore, they decided to bay the buildings and restored them back to the original positions in 1949. The gate between the turret buildings was restored as well in 1994. The city is now considering restoring the other 4 turret buildings in order to complete the 7 turrets which Tadamasa Sengoku had built for the castle.