Features
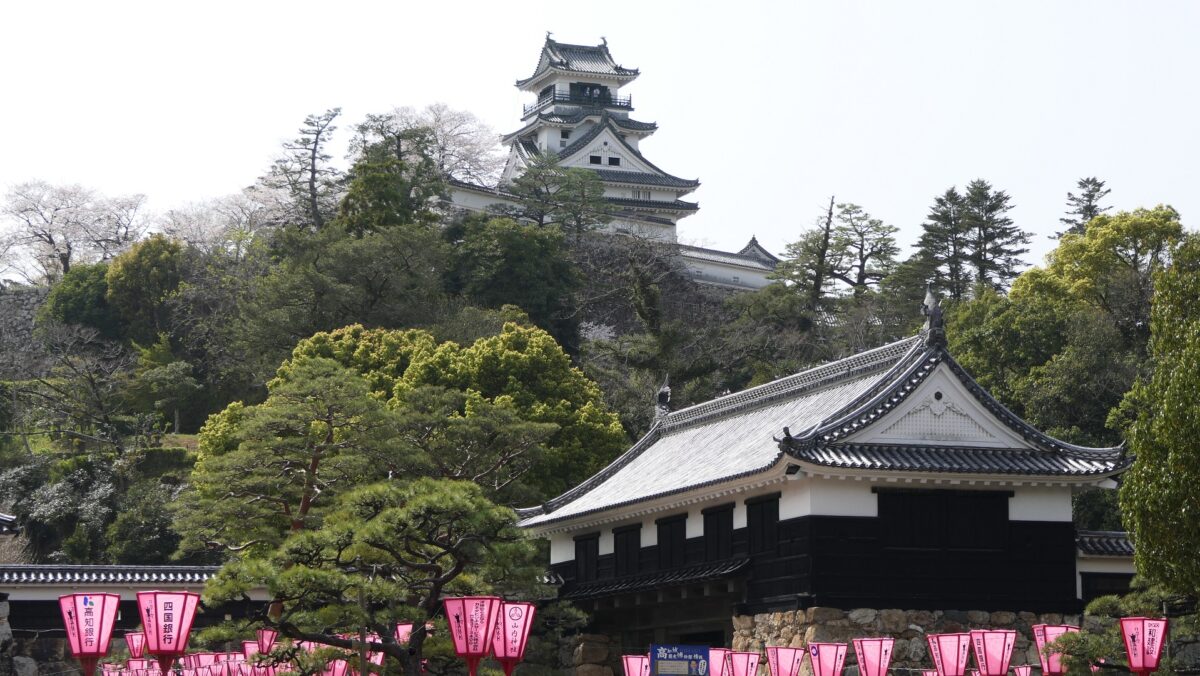
Spot for seeing both Main Tower and Main Gate
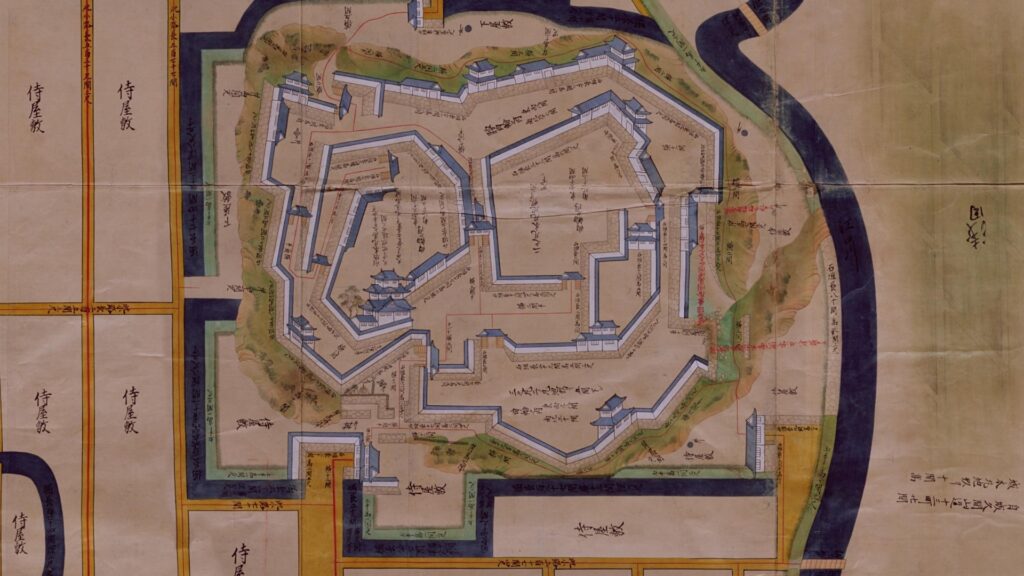
As a visitor to Kochi Castle today, you will likely enter the remaining Main Gate first, where you can also see the remaining Main Tower over there. In fact, this is a very rare spot where you can see the two kinds of remaining buildings together in Japan.
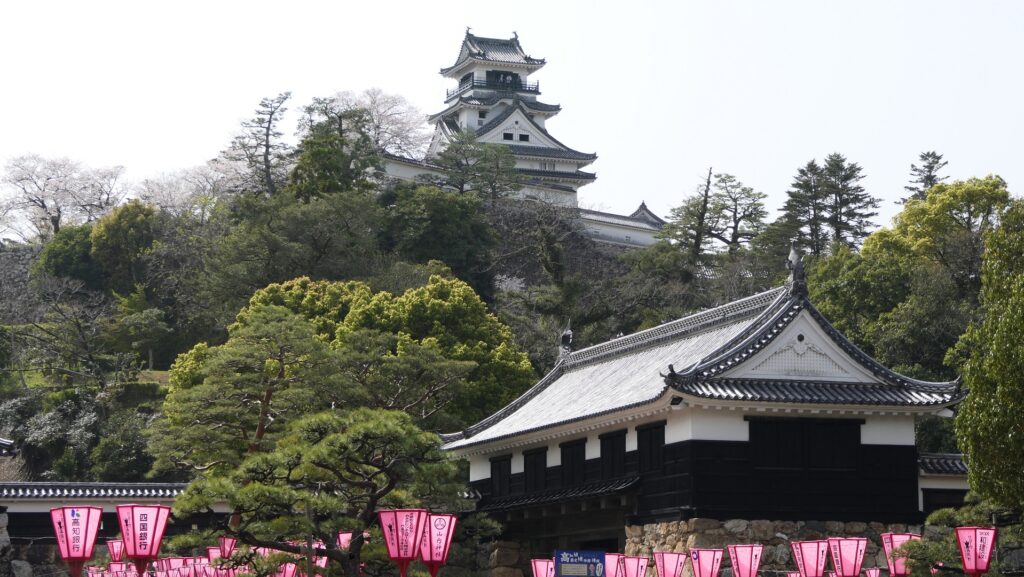
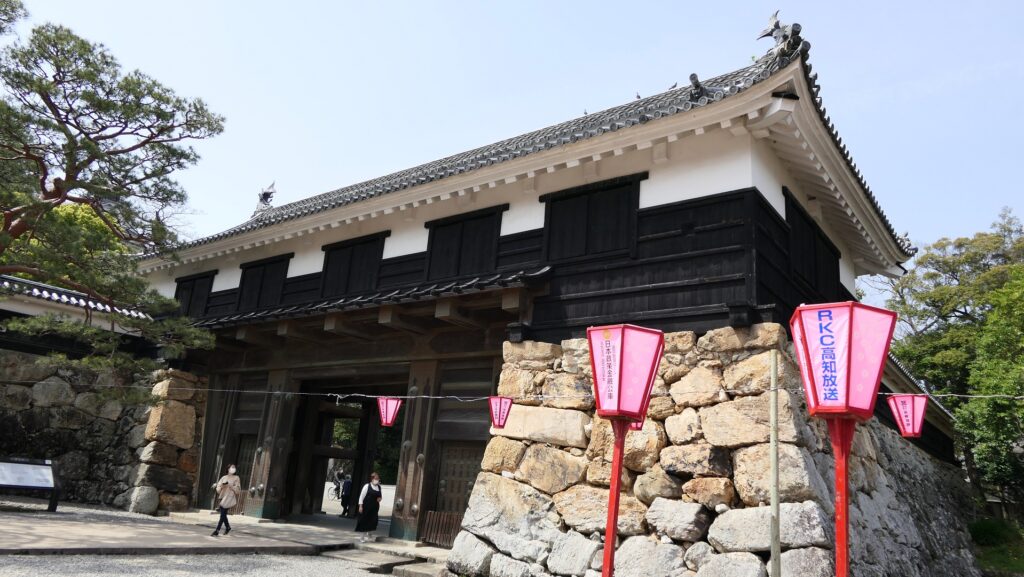


From Suginodan Enclosure to Iron Gate Ruins
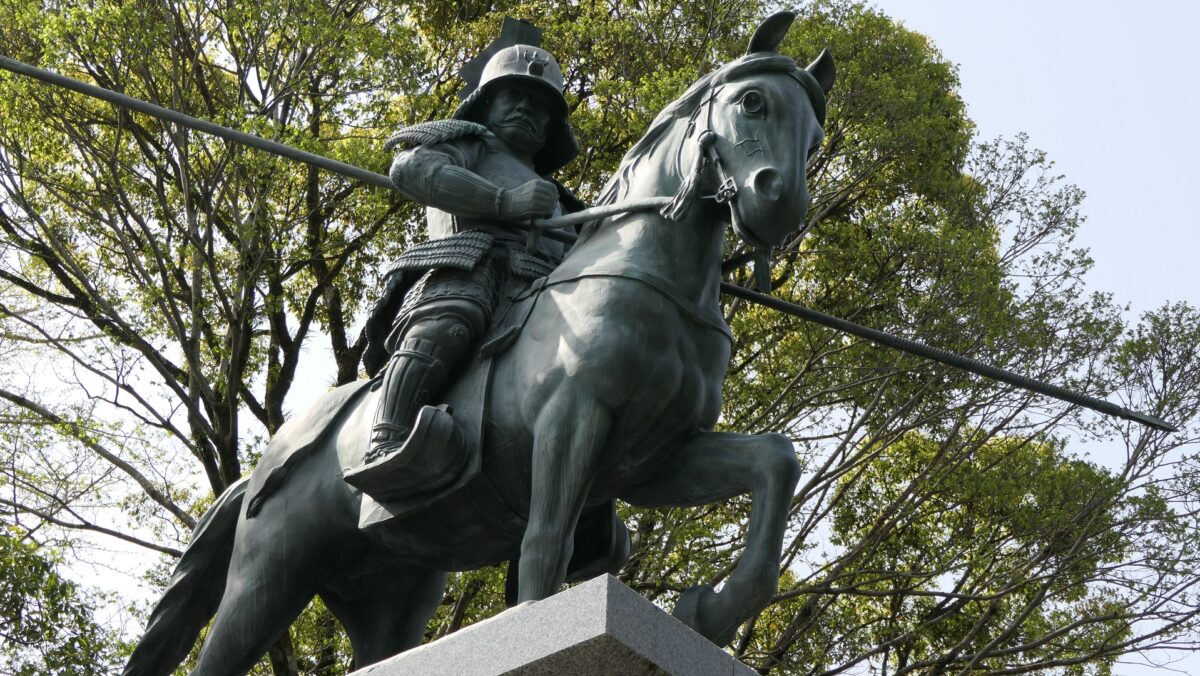
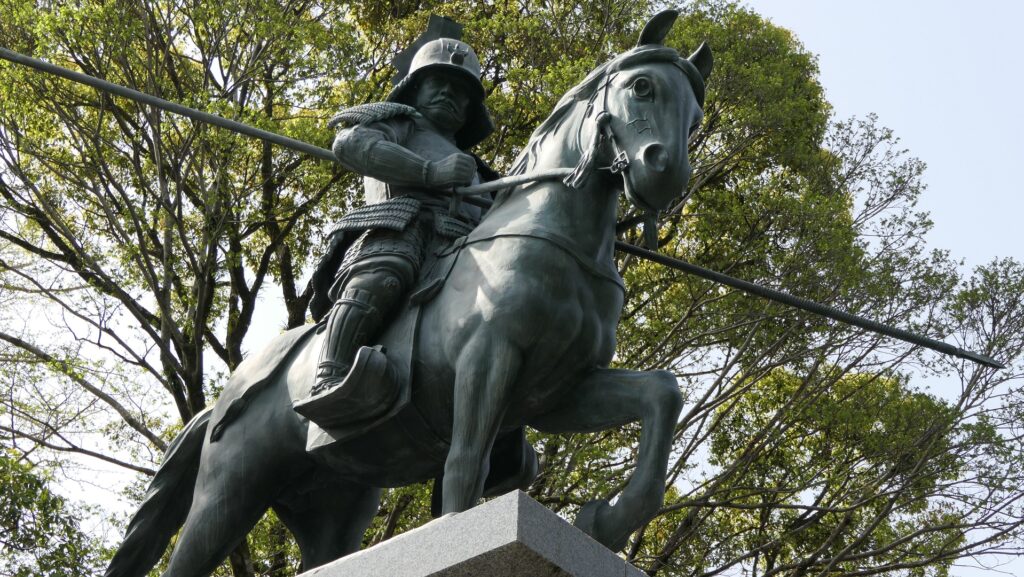
After entering the gate, you can climb on the stone steps to the Suginodan Enclosure where the statues of Kazutoyo Yamanouchi’s wife, called Chiyo, and a horse stand. These statues show that she spent her dowry to buy a fine horse for Kaszutoyo’s parade which was the chance for his promotion. You can also see the great high stone walls of the Third Enclosure above.



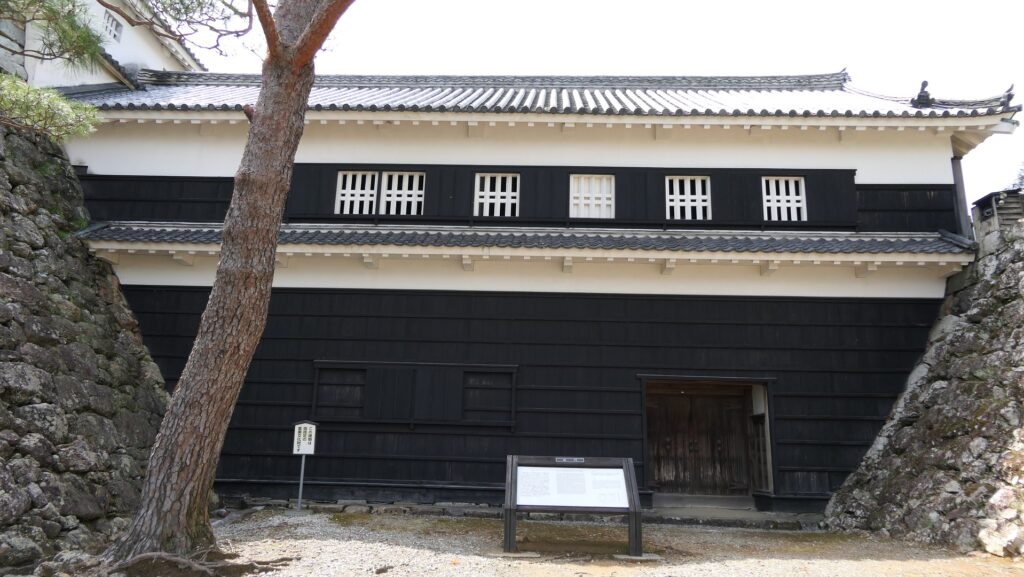
If you go further by climbing the stone steps, you will be at the ruins of the Iron Gate which was an important point for defense. The gate was next to the Third Enclosure and led to the Second Enclosure. That’s why the tricky system which could lead enemies to the false gate to the Main Tower, called Tsumemon, was built.
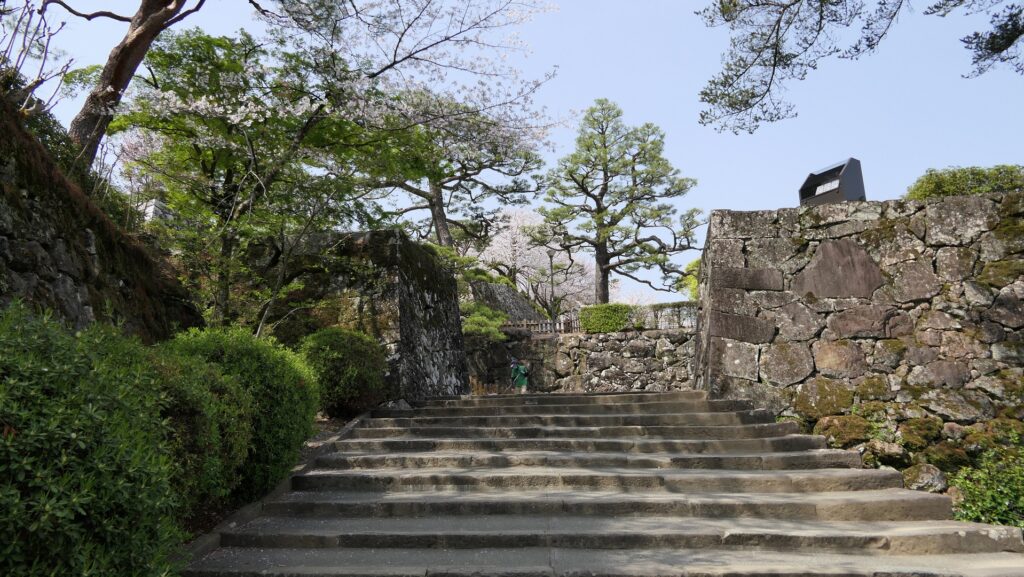


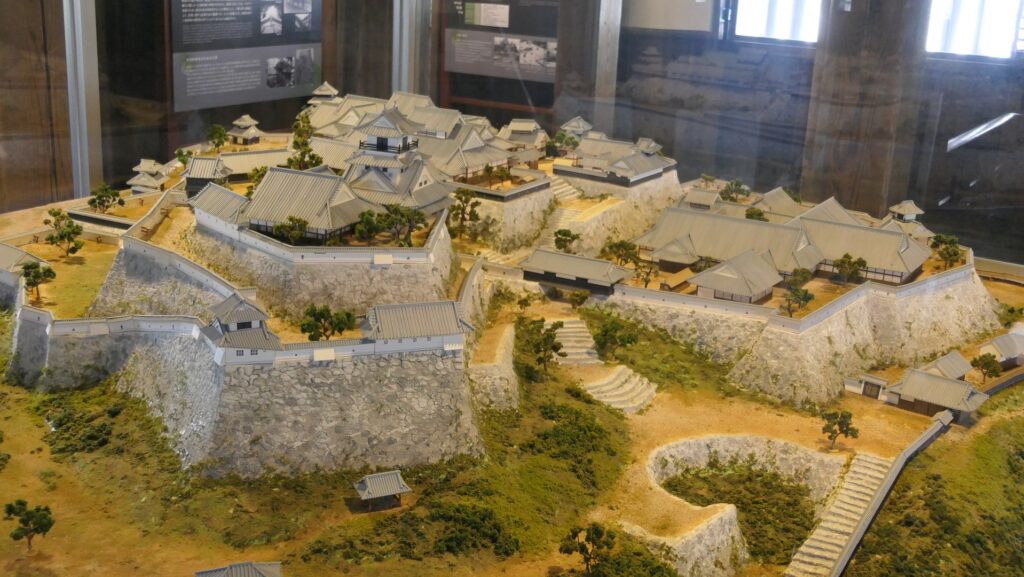
Third and Second Enclosures
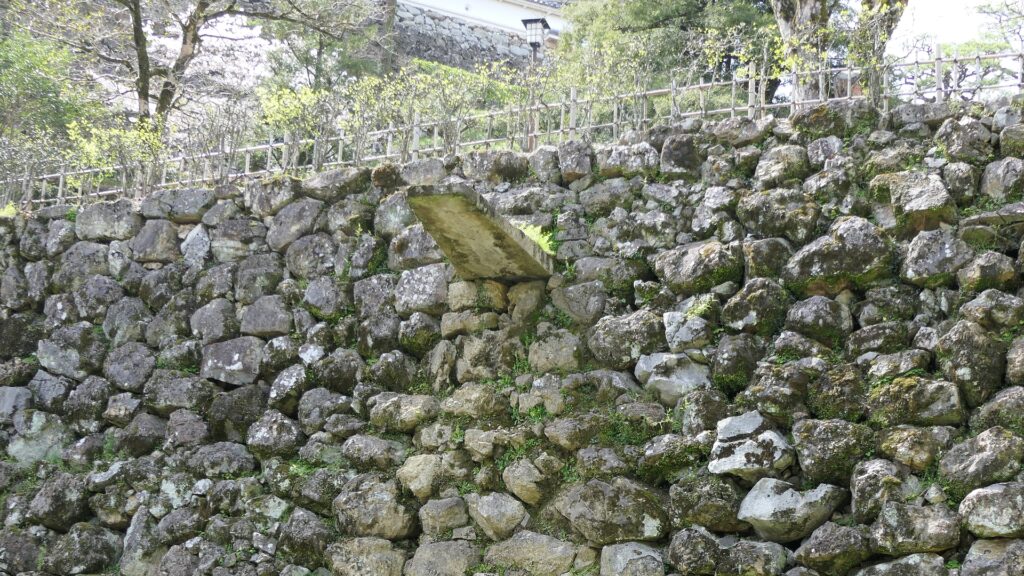
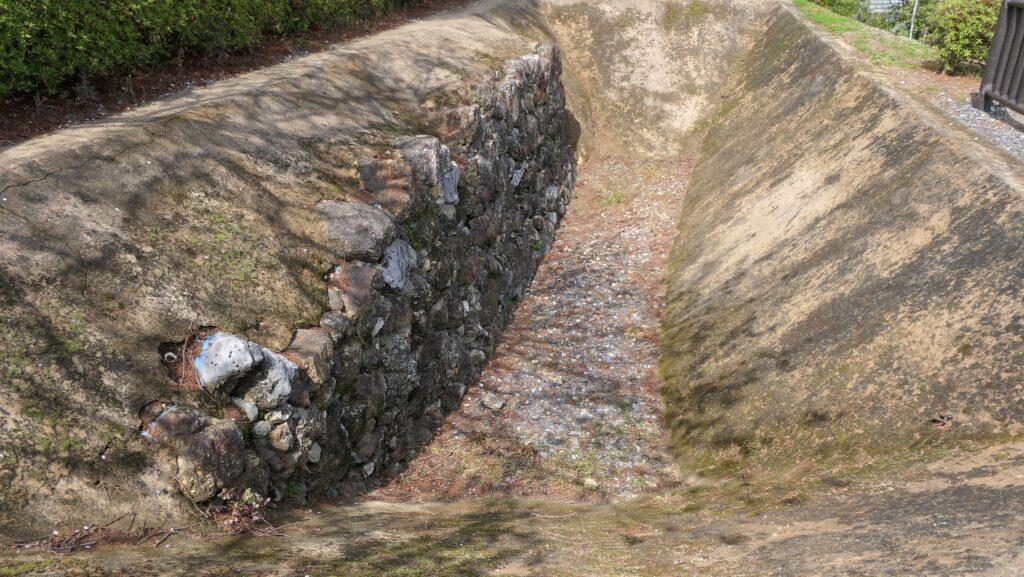
The Third Enclosure is the largest enclosure in the castle where a large building for ceremonies was in the past. In addition, the stone walls of Chosogabe’s period were found there by excavation.



The Second Enclosure had another Main Hall for the lord where he usually lived, as the hall in the Main Enclosure was too small for daily life. However, the Second Enclosure is just a square now.


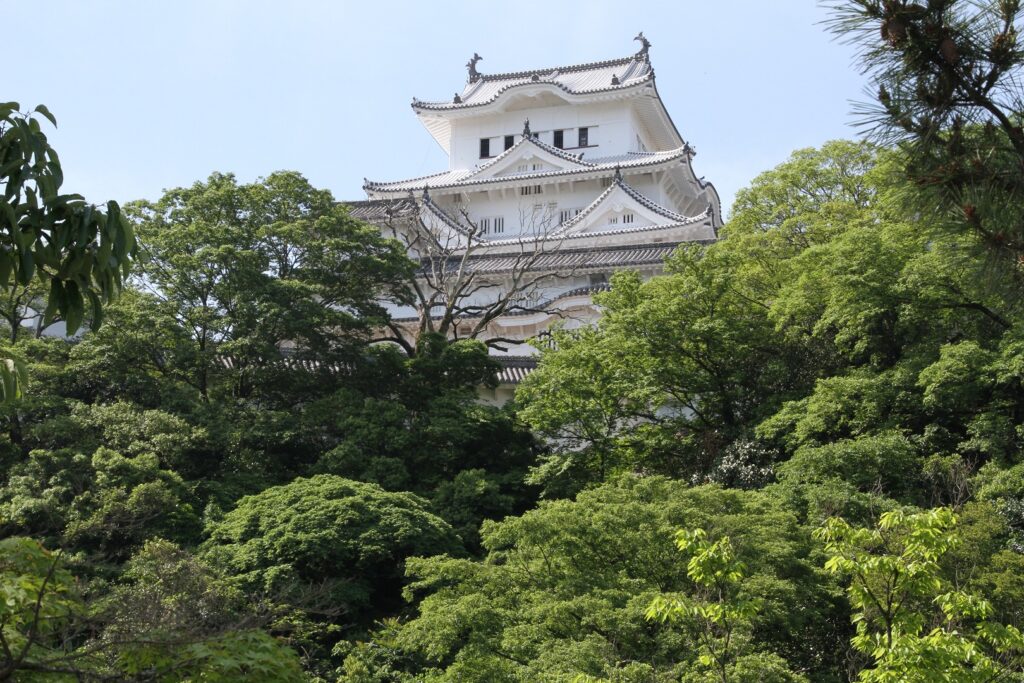
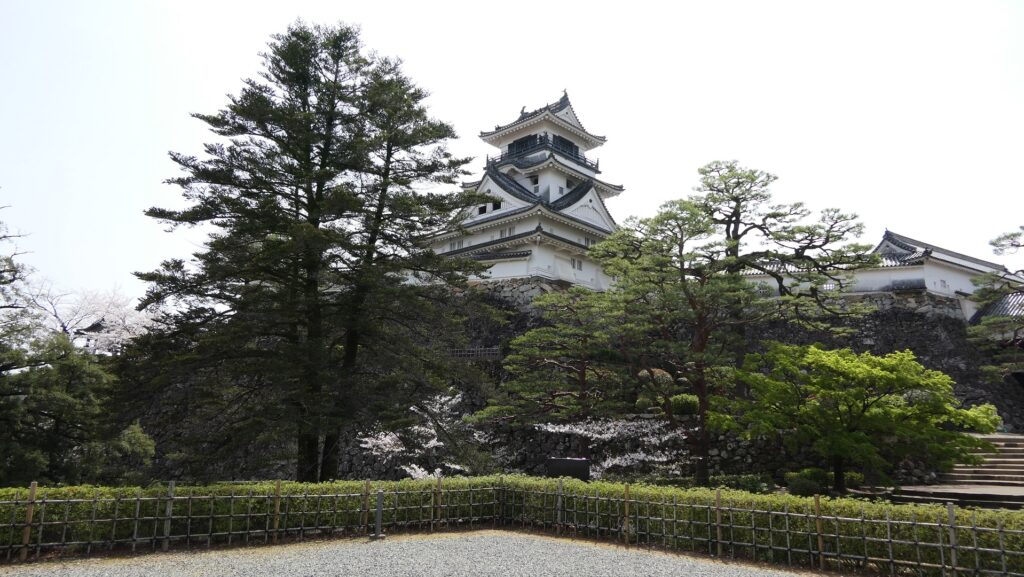
Main Enclosure, almost same condition as original
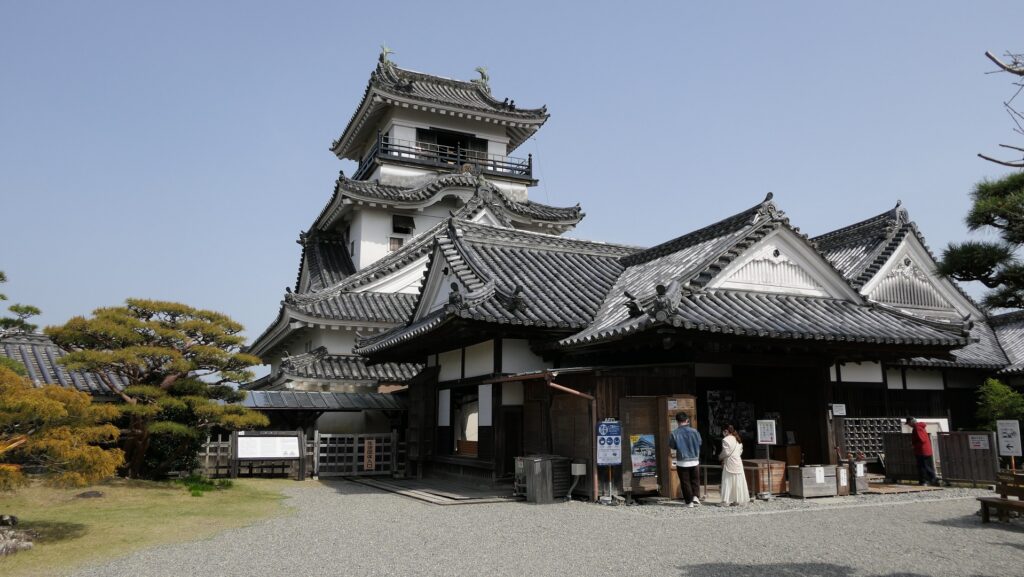
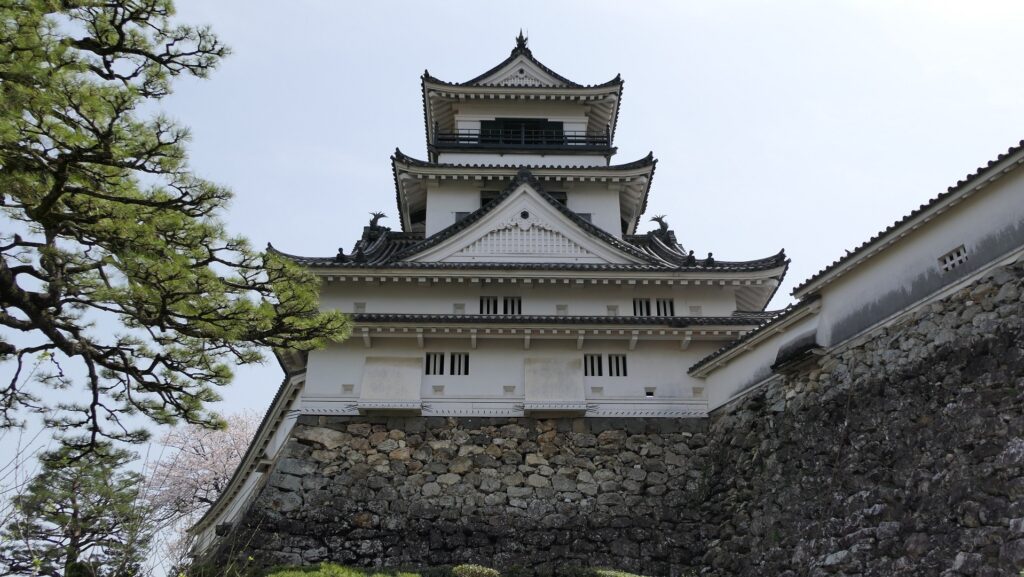
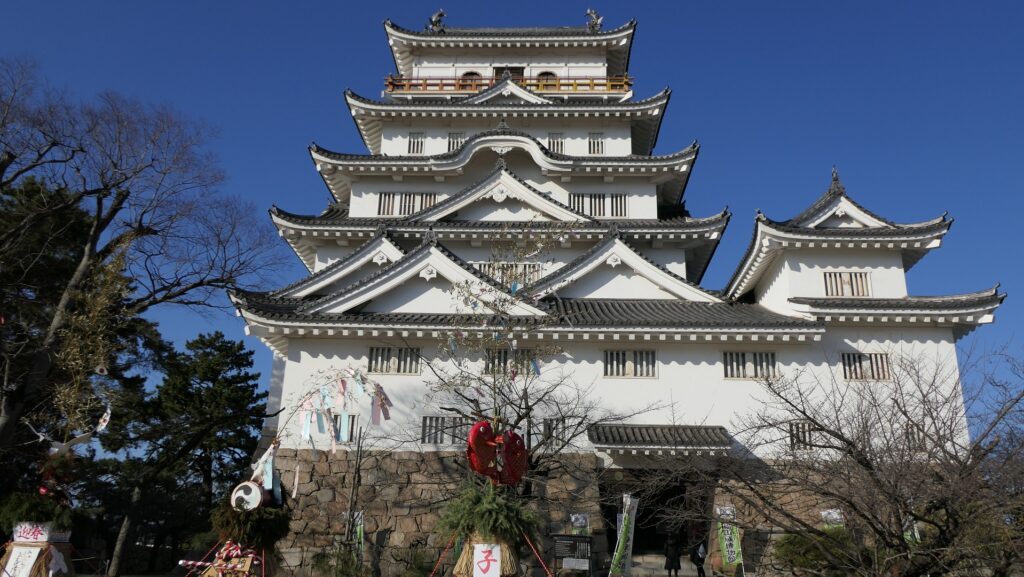
You can finally reach the Main Enclosure by crossing the remaining Tsumemon Gate from the Second Enclosure. Surprisingly, this enclosure is in almost the same condition as its original, with the 11 remaining buildings. This is also the only spot where the original Main Tower and Main Hall remain at the same place in Japan.
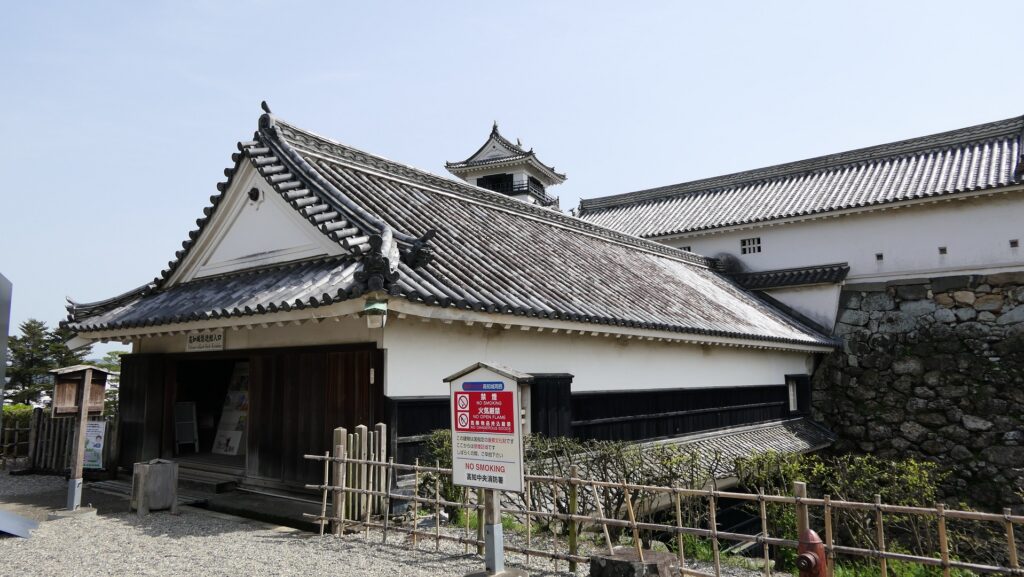
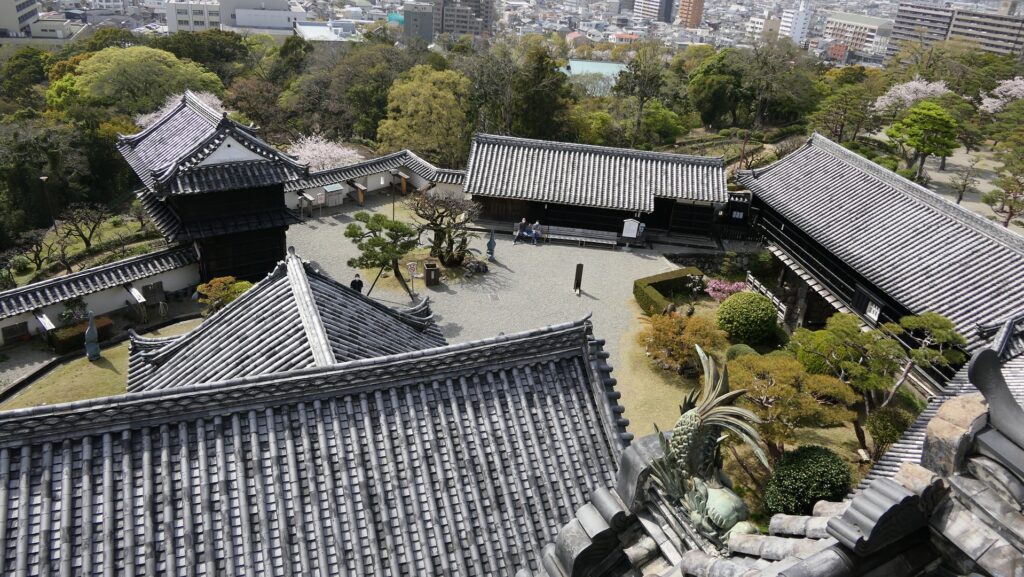


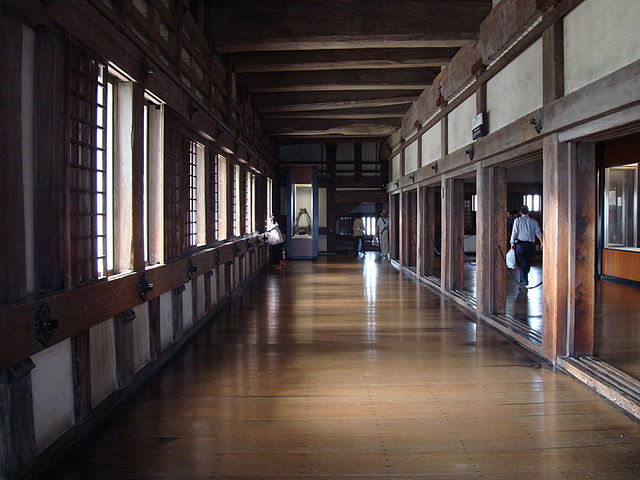
You will need to enter the Main Hall first to reach the Main Tower as they are directly connected to each other. The hall is not large because the space of the enclosure is limited, but important ceremonies for the domain were held there.


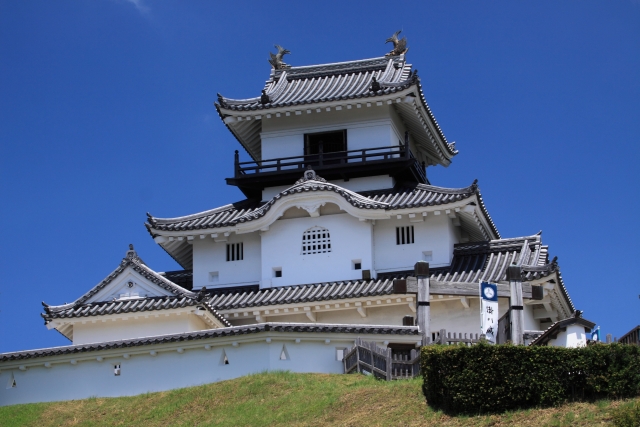
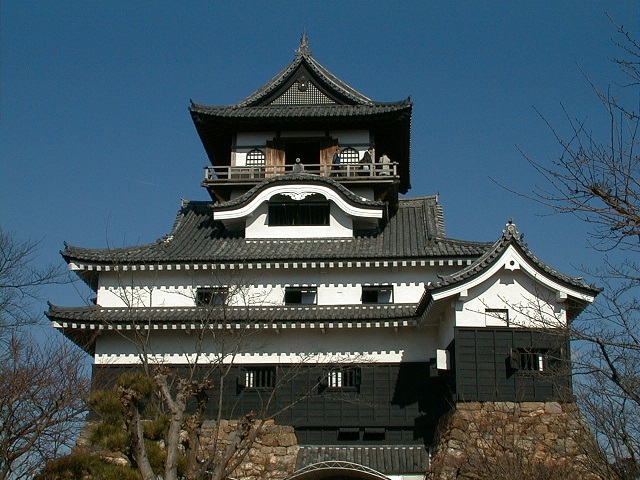
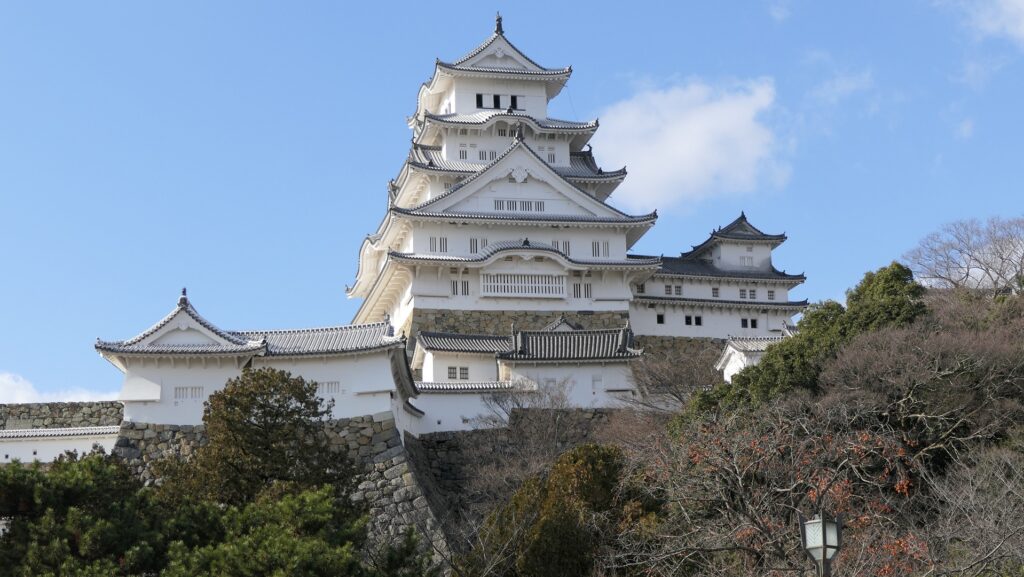
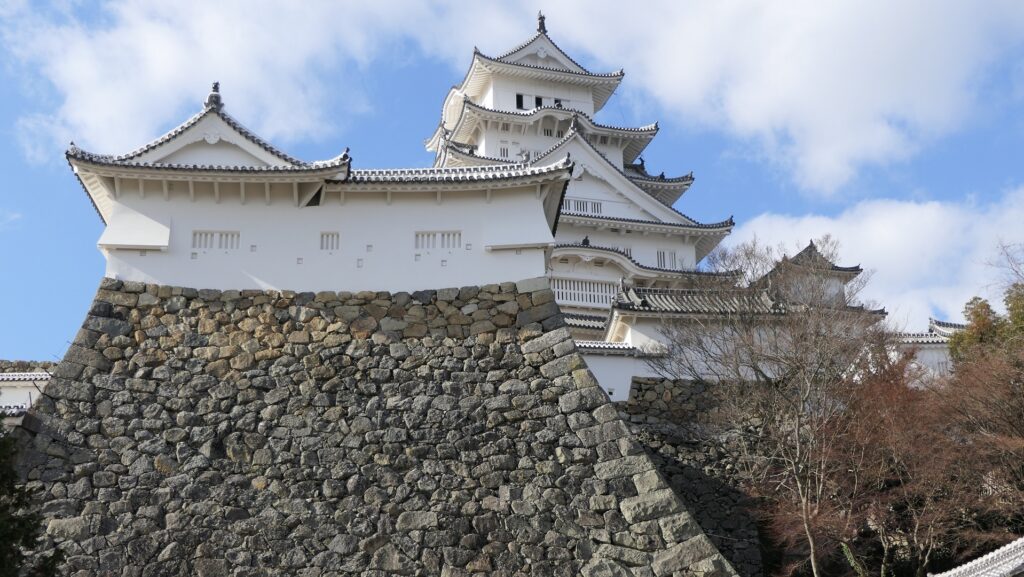
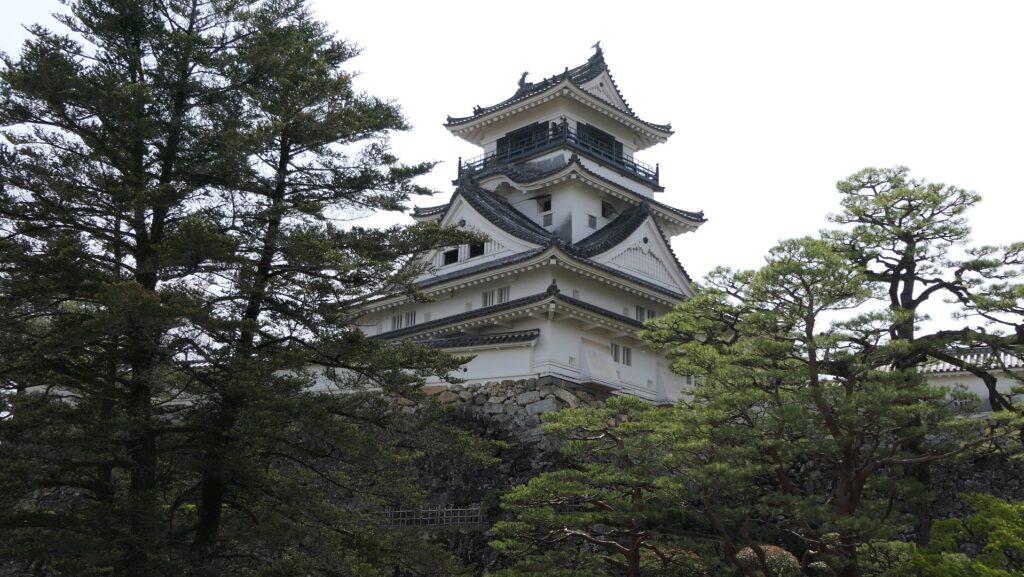
The Main Tower has four layers and six stories, that means two of the stories are attics (3F and 5F). Its style is called the lookout tower type. In the case of Kochi Castle, there is the small two-layer lookout tower on the large two-layer turret with a hip-and-gable roof. The tower also has decorations like Chinese style gables and triangular shaped gables on the roof and a veranda with the lacquered handrail at the top floor. It looks traditional and very beautiful.

To be continued in “Kochi Castle Part3”
Back to “Kochi Castle Part1”