Features
Simulation of Attack from Main Entrance to Main Enclosure
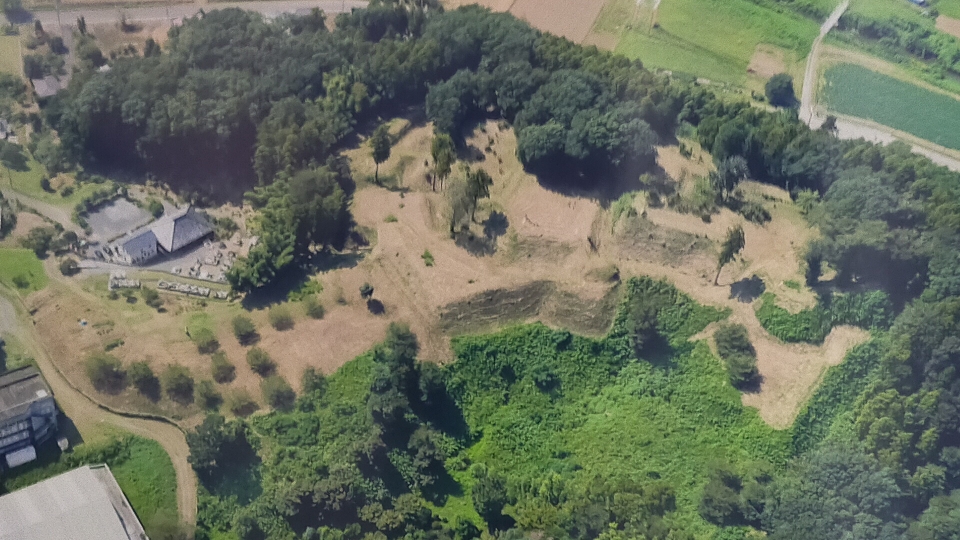
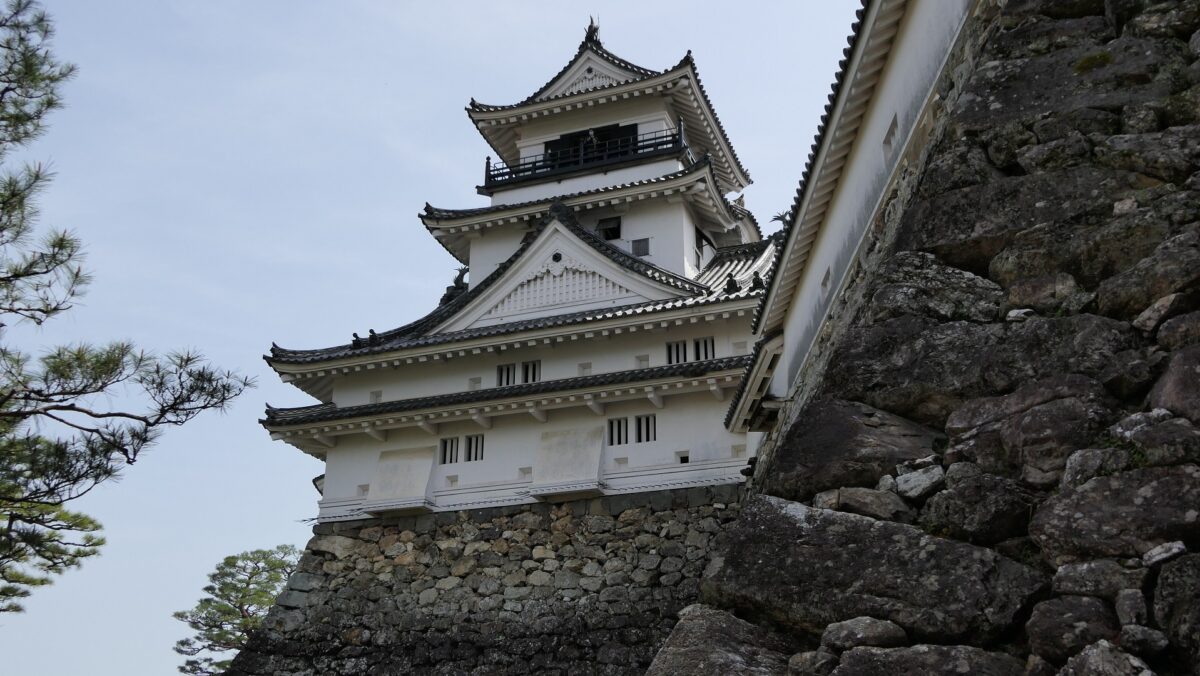
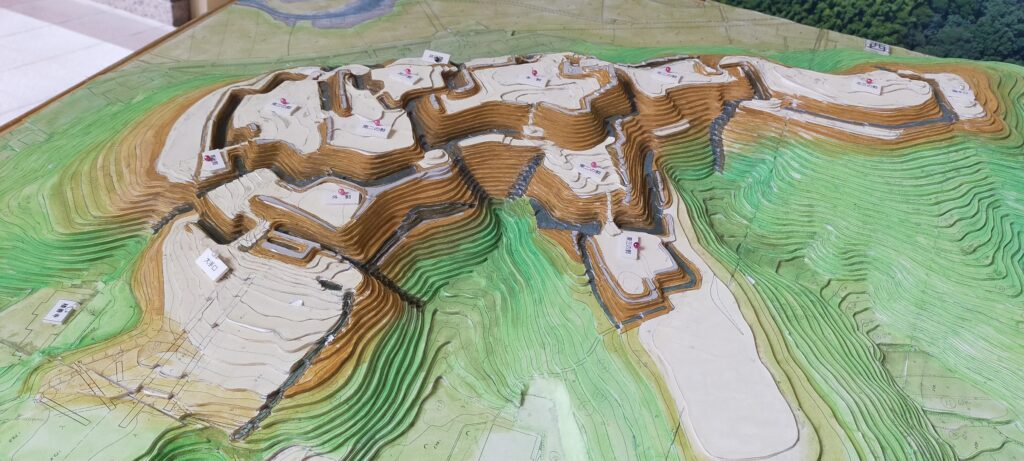
Today, the ruins of Sugiyama Castle are well-developed and maintained for visitors as a historic site. The ruins were once covered with a lot of trees and bushes, but most of them were removed. That means you can see the soil-made layout of the castle clearly. Let us simulate attacking the castle as an enemy.

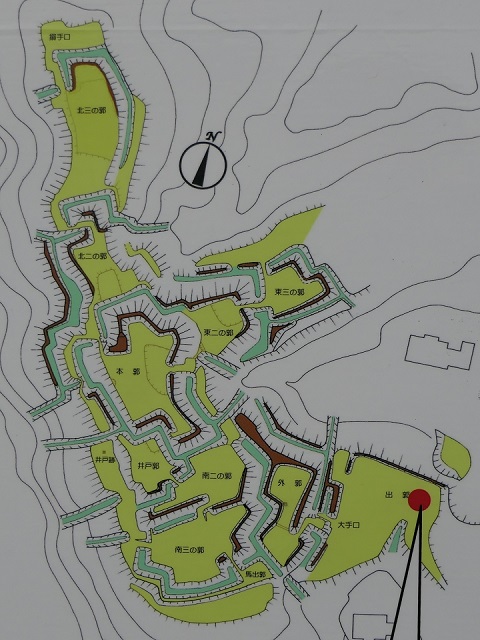
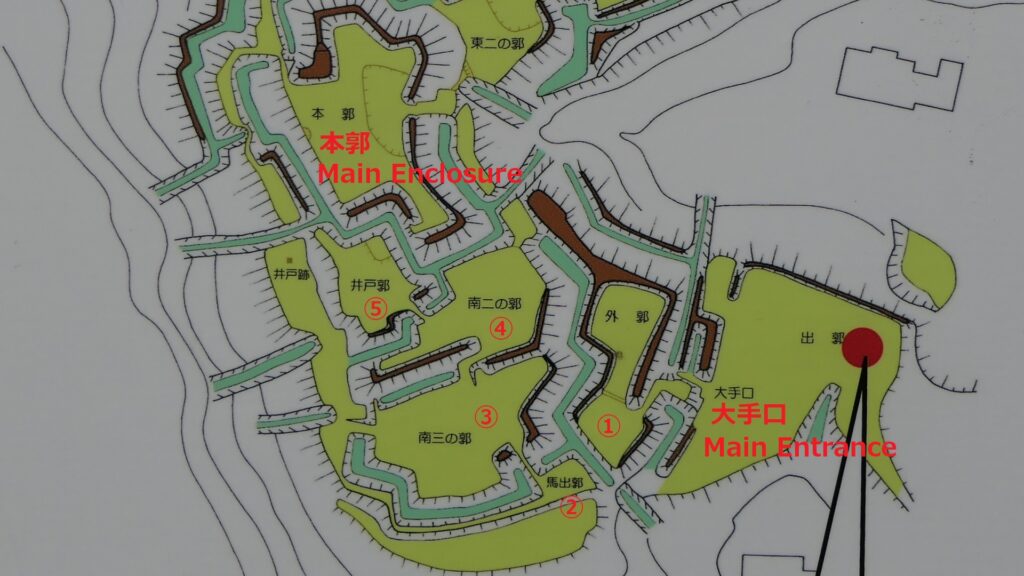
For example, if you approach the castle ruins from the south, you will first stand at the Main Entrance or Oteguchi as the starting point. In fact, you will need to pass through five enclosures to reach the Main Enclosure.
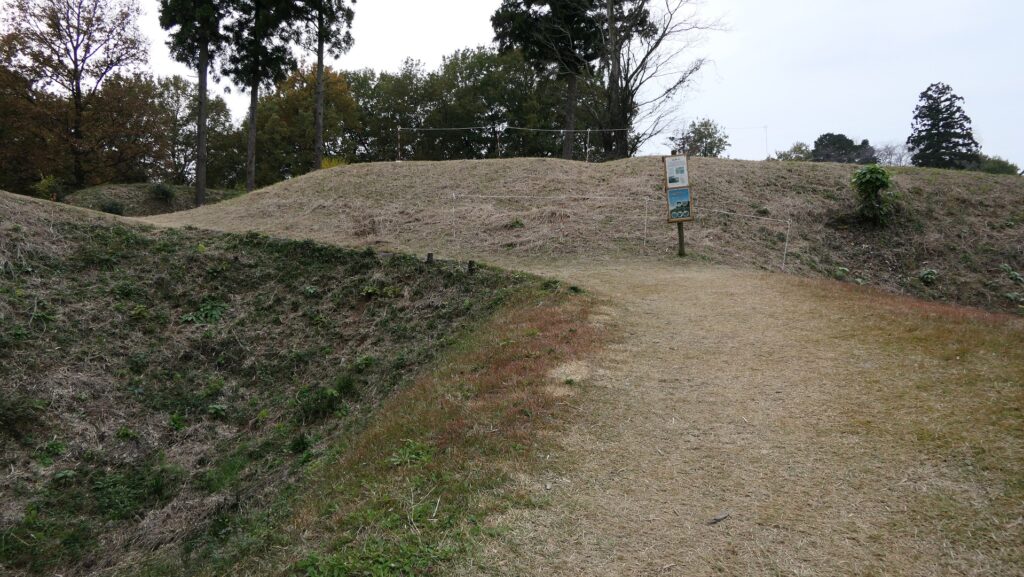

From Outer Entrance to Umadashi and Southern Third Enclosures
To enter the first enclosure called the Outer Enclosure, you will have to turn left in front of its entrance. Defenders could make a flanking attack on your left side before you turn.
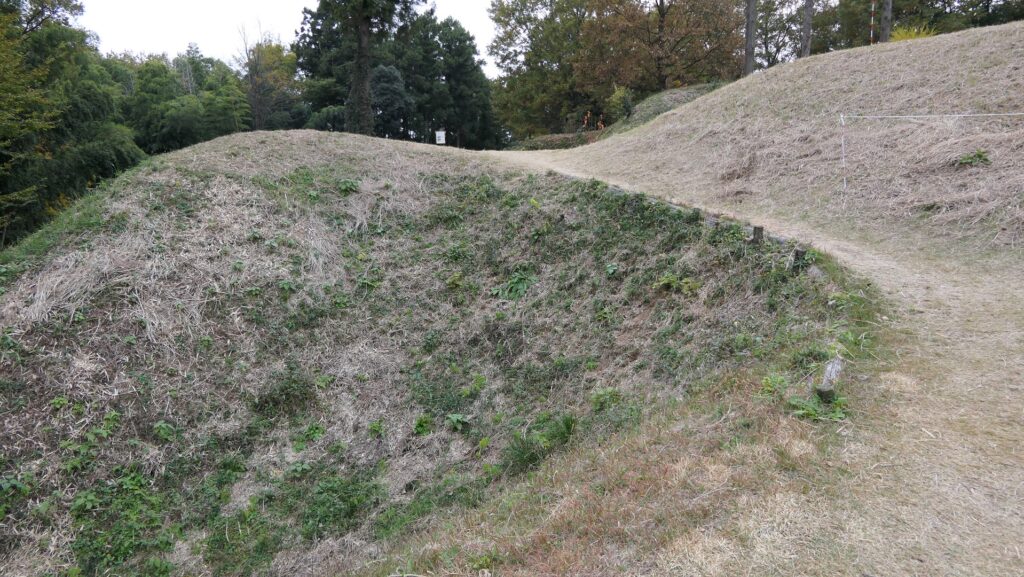
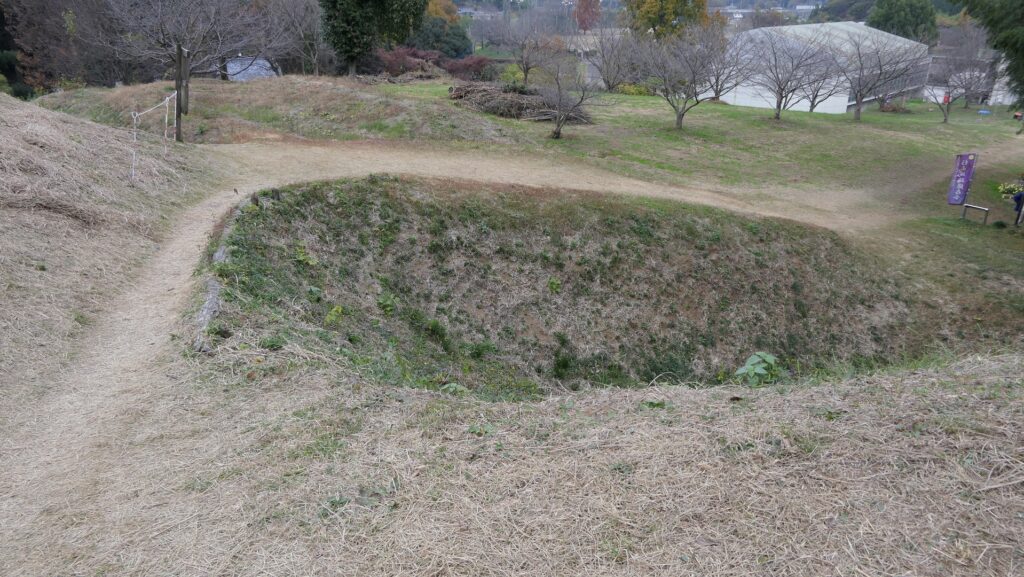


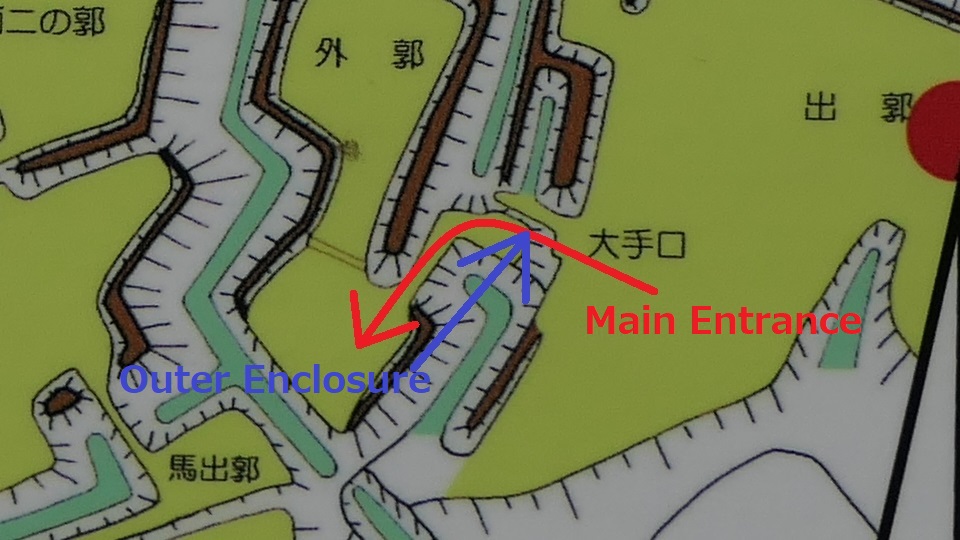
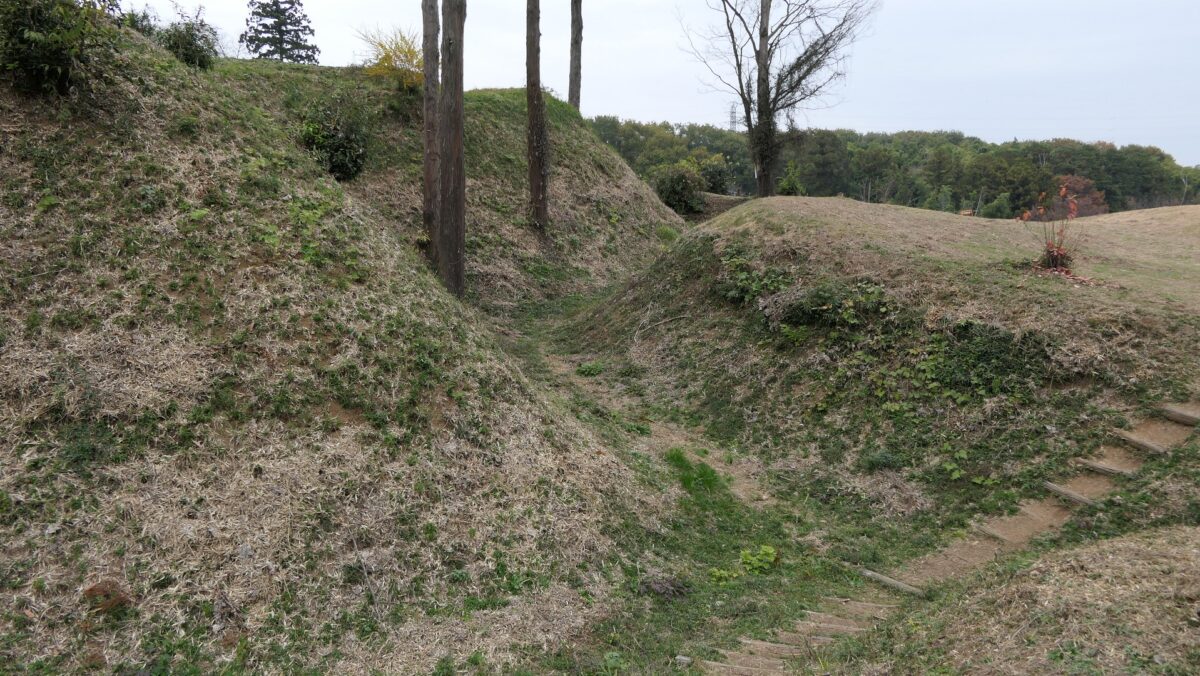
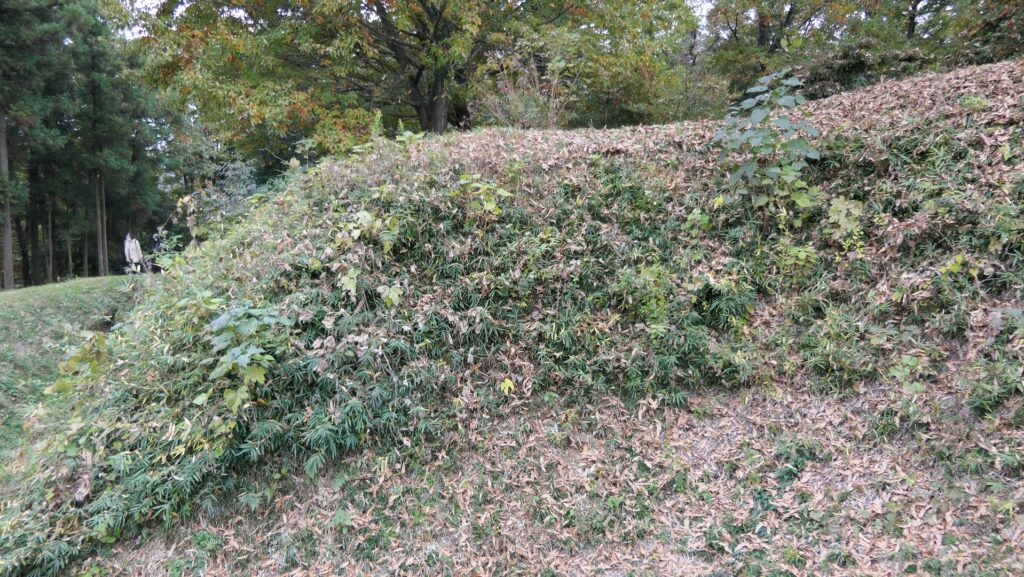
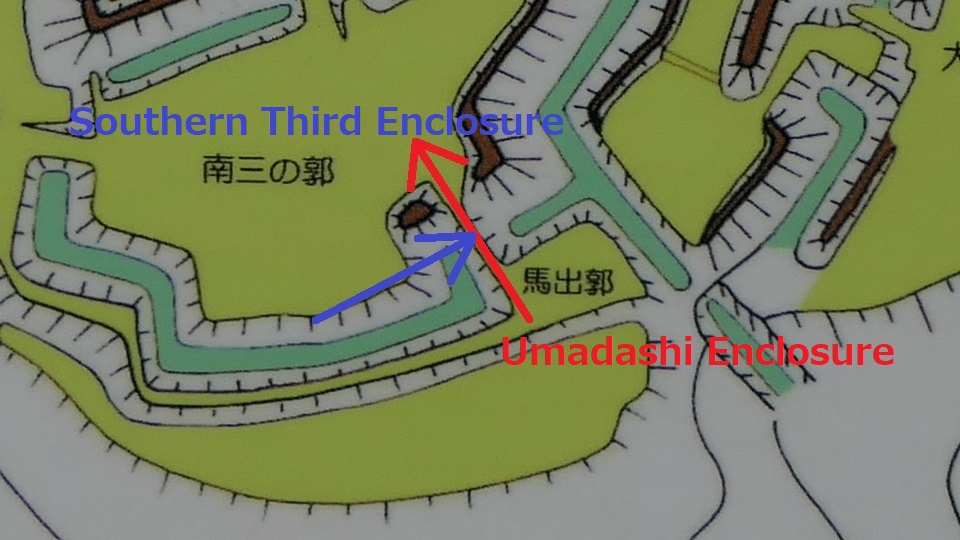
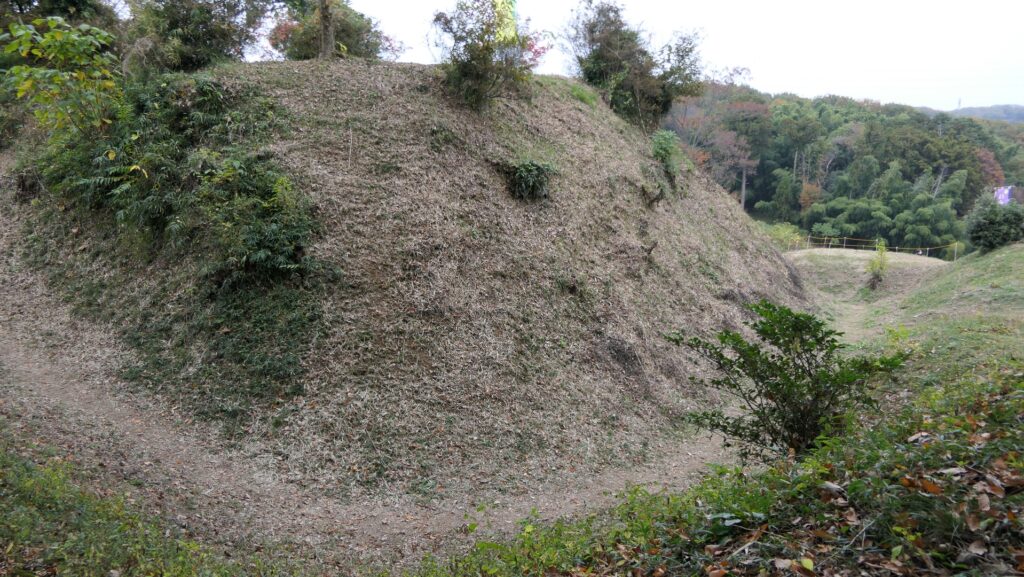
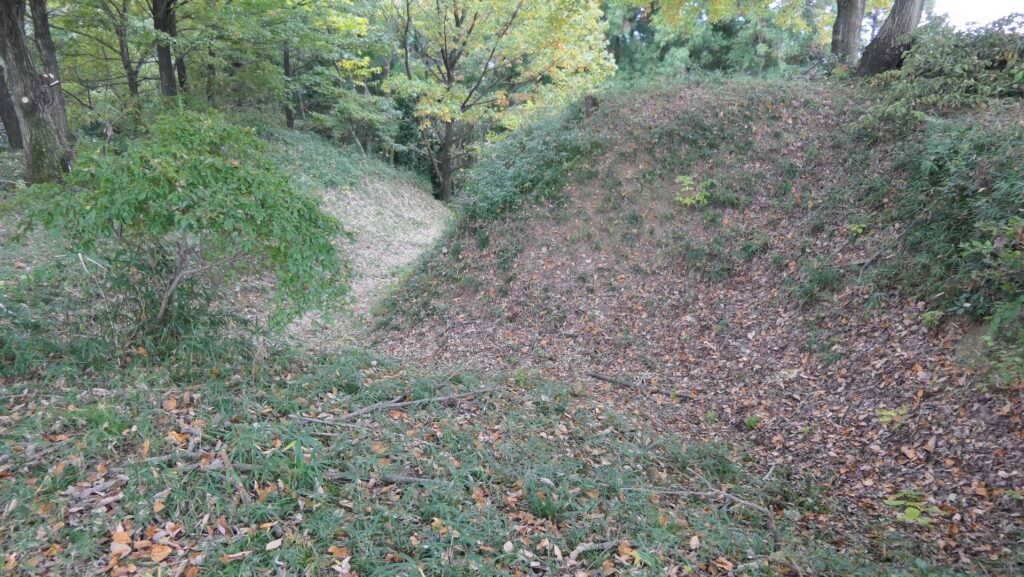
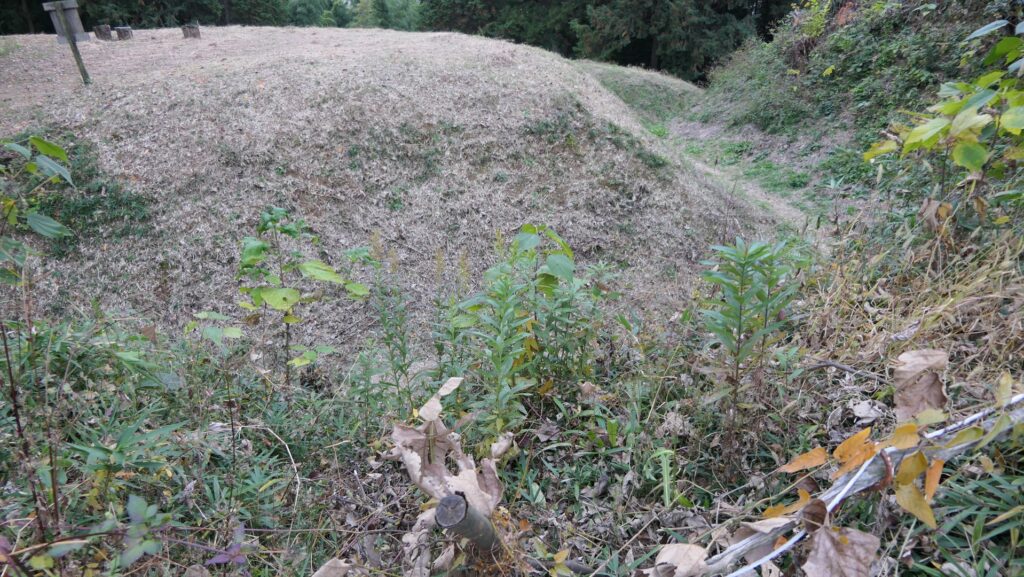
After entering the Outer Enclosure, the second one is the Umadashi Enclosure. You will need to go over the dry moat to get to the Umadashi Enclosure. A wooden bridge might have been built on it, but it would have been fallen if a battle occurred. When you cross the dry moat, you would be attacked on your right side from the L-shaped earthen walls of the Southern Third Enclosure.
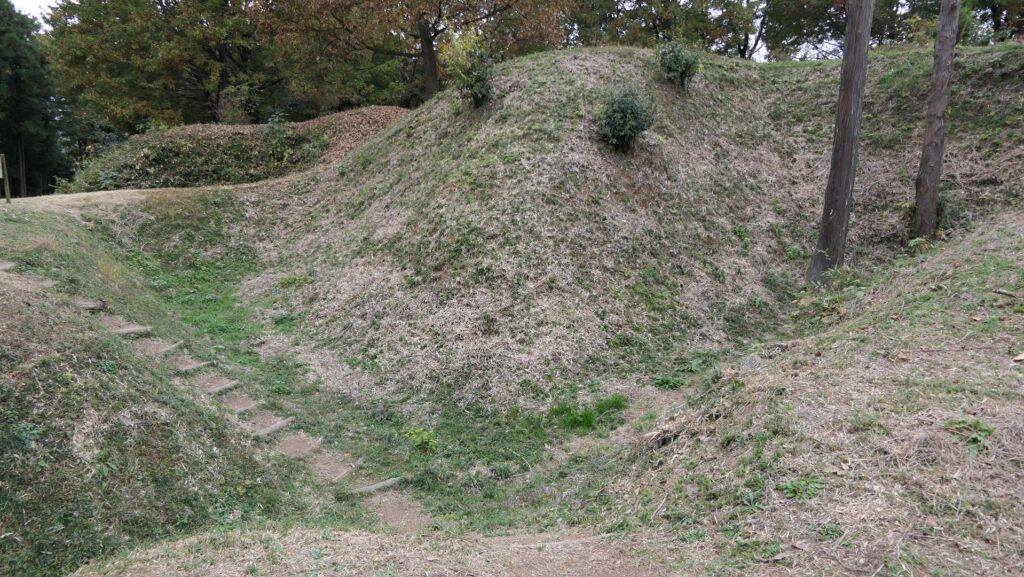
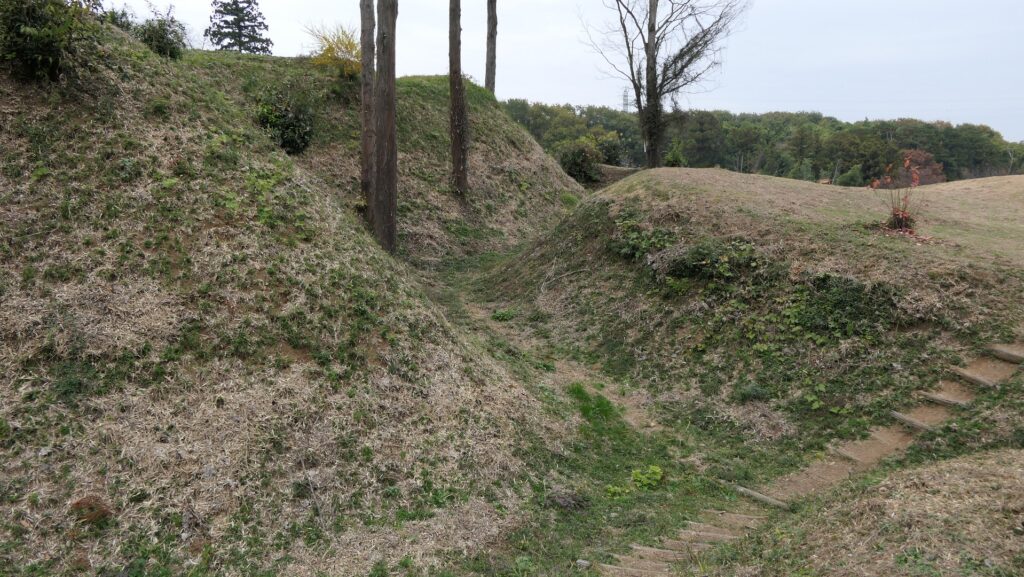
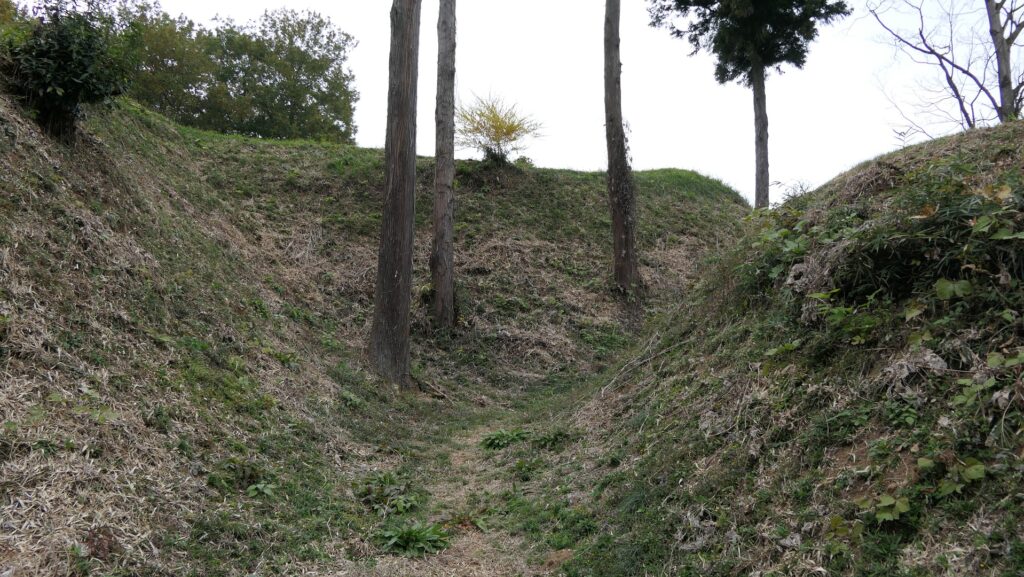
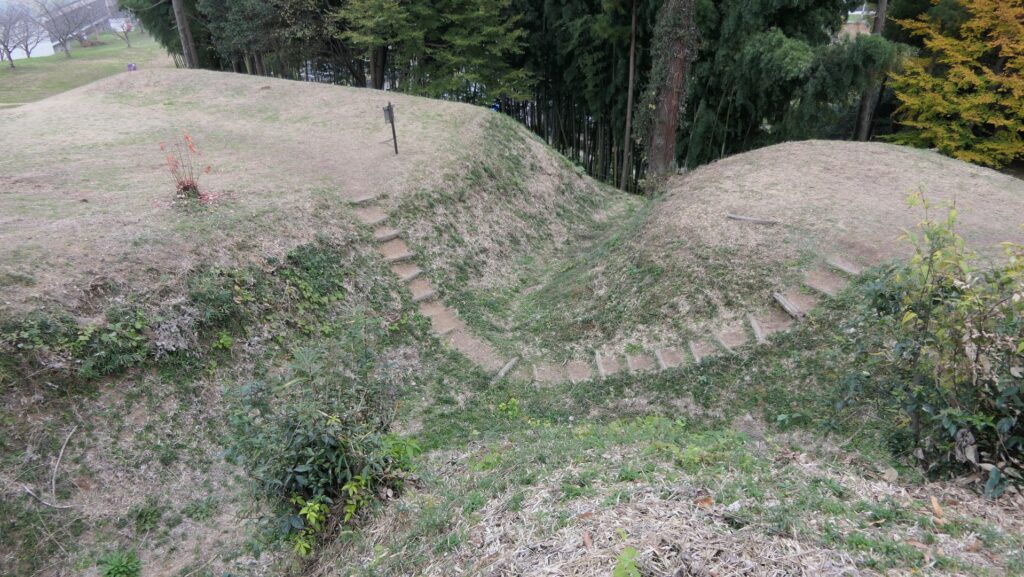




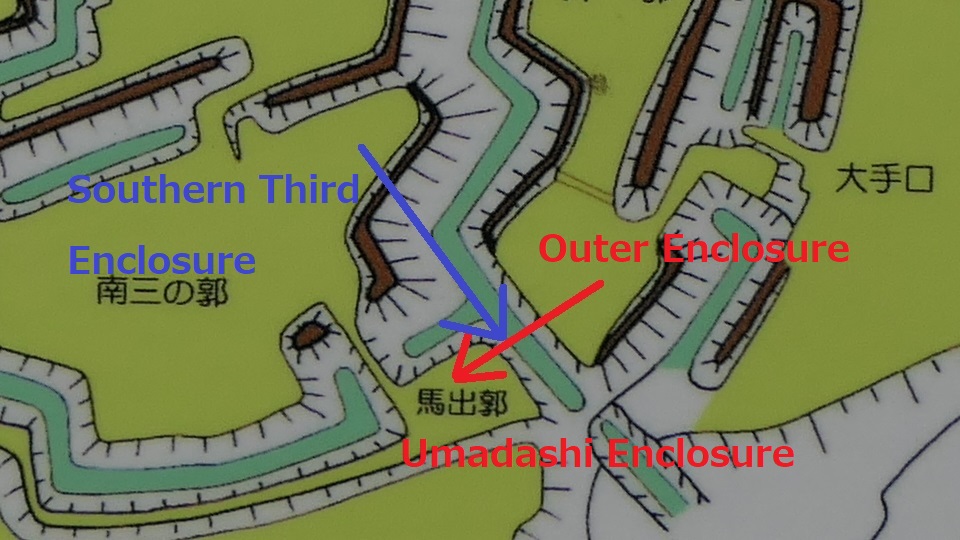
The Umadashi Enclosure is a small sticking out space from the entrance of the Southern Third Enclosure. The other L-shaped earthen walls of the Southern Third Enclosure also make it possible to defeat the enemy in this area of the castle.



Strong Defense of Main Enclosure
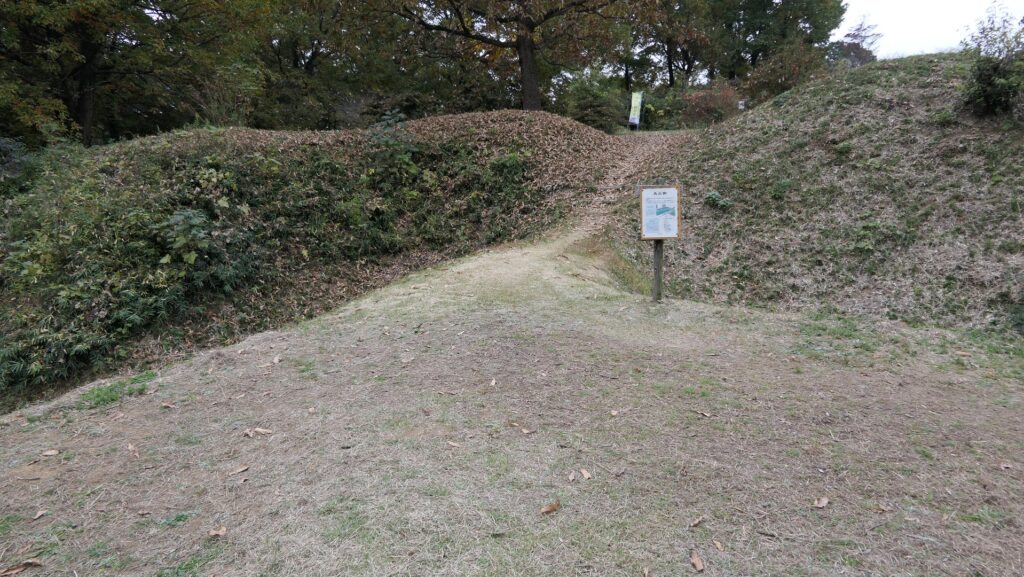
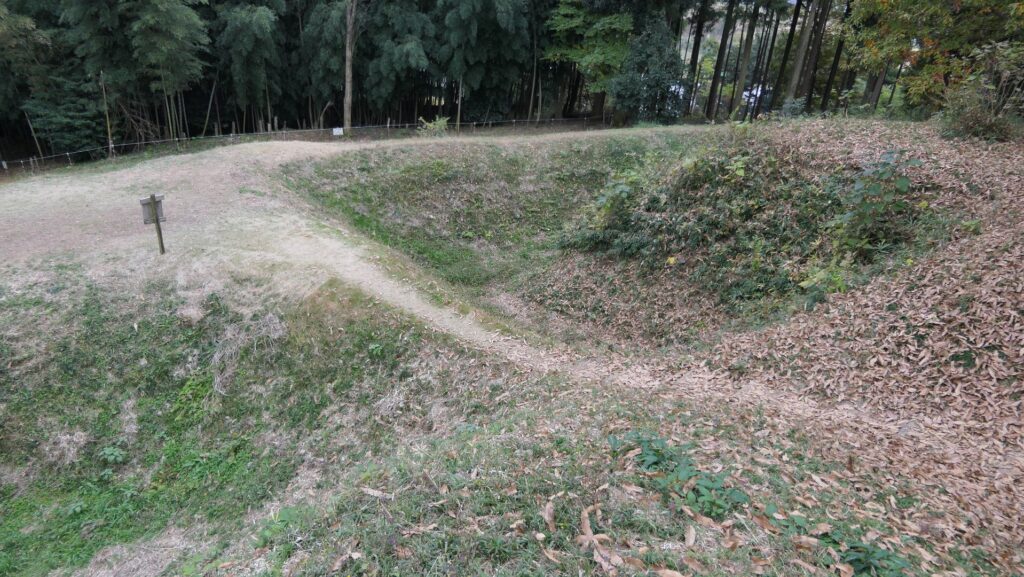
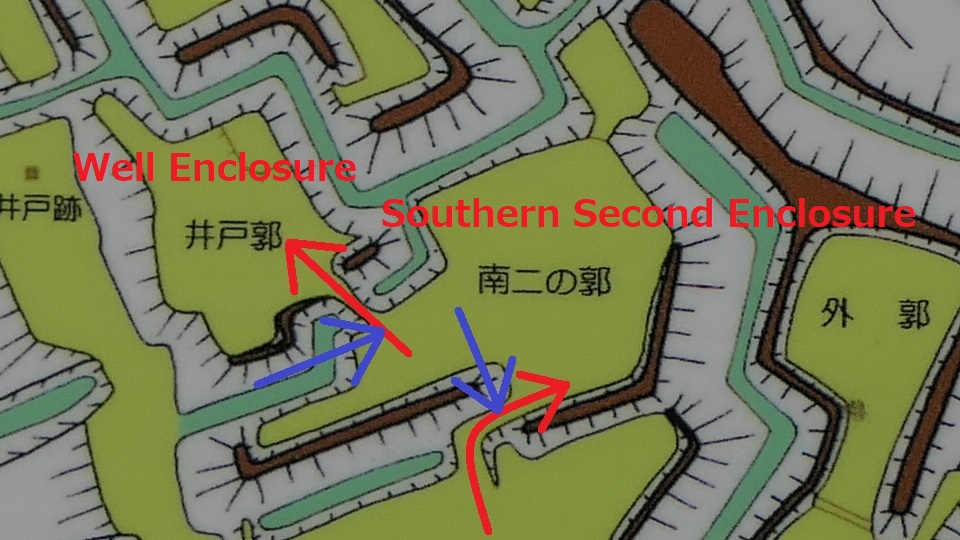
After that, if you somehow reach the Southern Second Enclosure after the Southern Third Enclosure, you will see the high earthen walls of the Main Enclosure. However, there is no direct route to the Main Enclosure, so you will have to move to the Well Enclosure on the left. (Its enclosure is guarded in a similar way to other enclosures.)
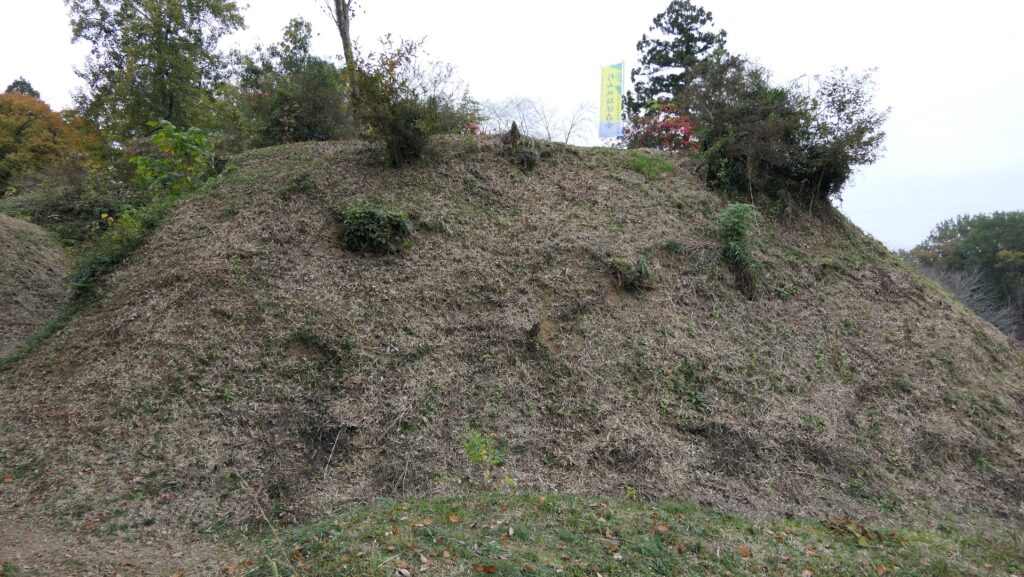
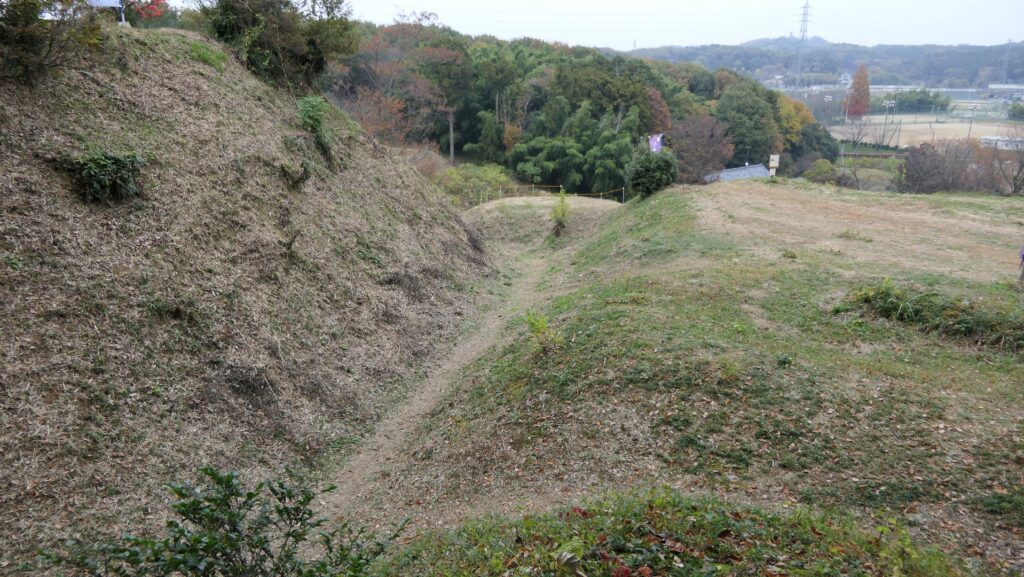
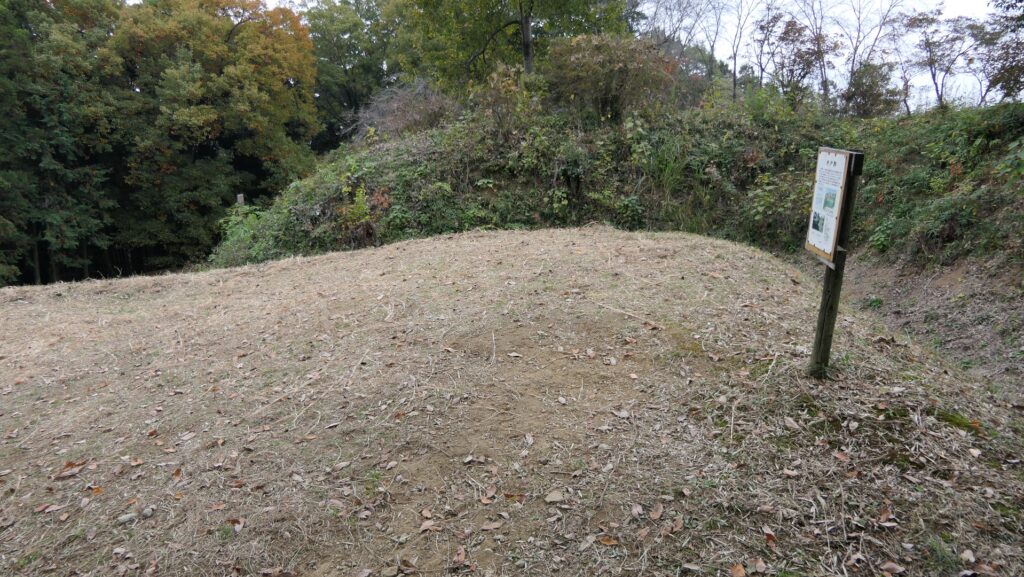




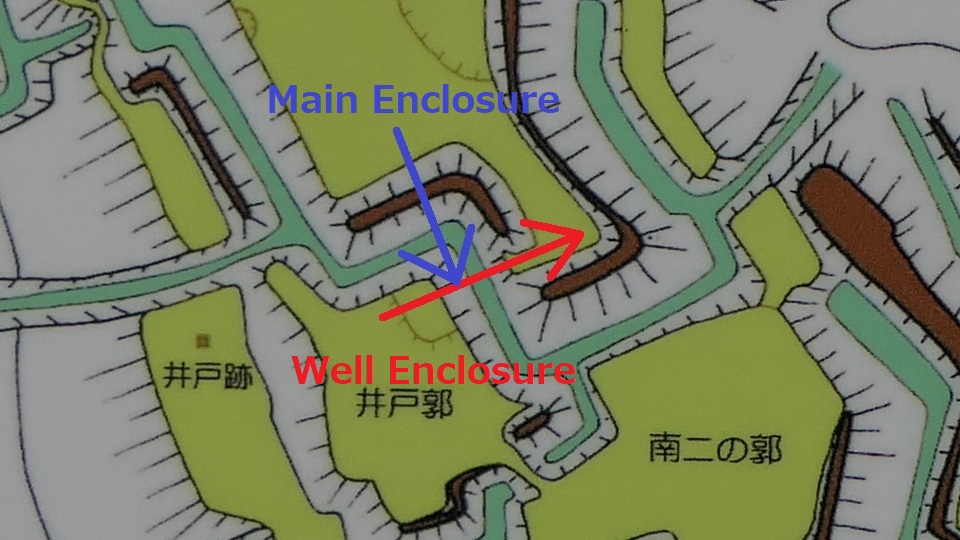
The Well Enclosure leads to the Main Enclosure, which was connected by the wooden bridge over the dry moat. However, you could be counterattacked from the front and from your left side from the Main Enclosure above. The earthen walls of the Main Enclosure are shaped to surround the attacker. Overall, you could suffer damages from the frank attacks as many as the number of the enclosures.



To be continued in “Sugiyama Castle Part3”
Back to “Sugiyama Castle Part1”