Later History
After the Meiji Restoration, Nijo Castle was used as a villa of the imperial family. For example, a party for the enthronement ceremony of the emperor Taisho was held there. The castle has become a historical site since 1934, named Former Imperial Villa Nijo-jo Castle. The site also became a World Heritage in 1994, as one of Cultural assets of the ancient capital of Kyoto.


Features
Gorgeous Second Enclosure
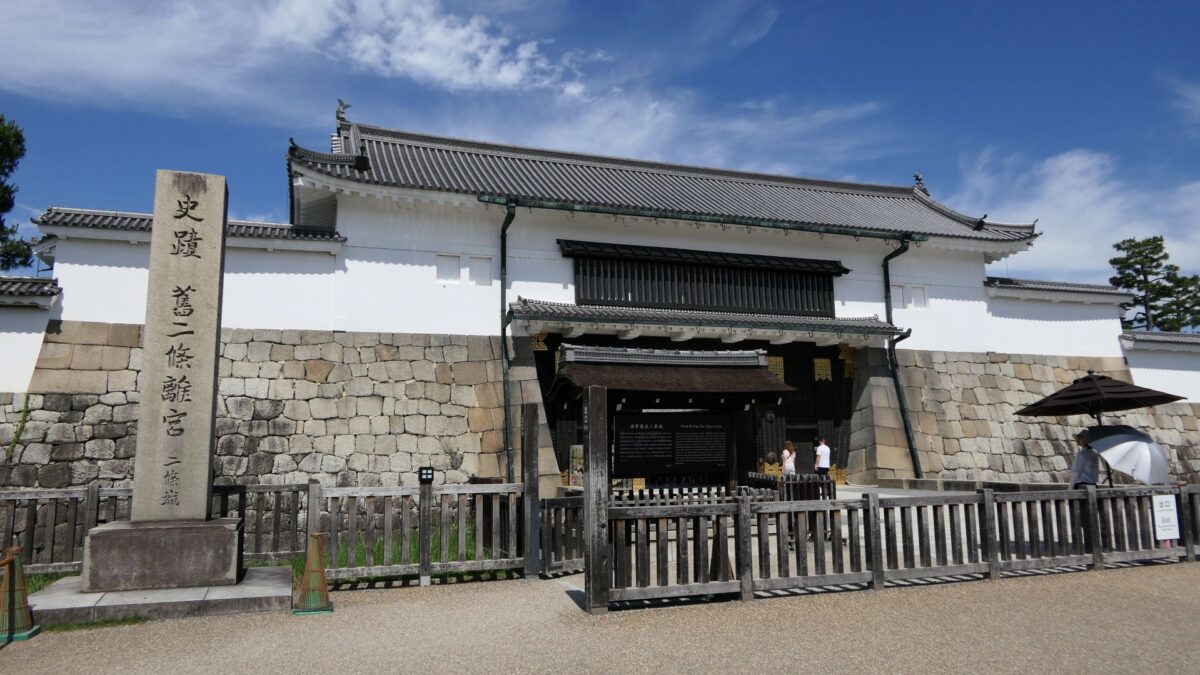
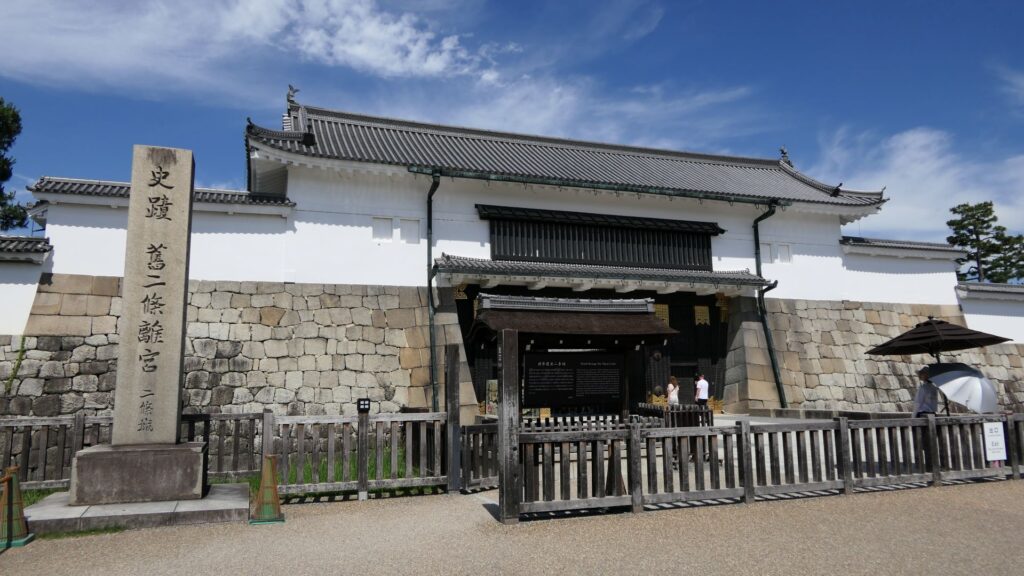
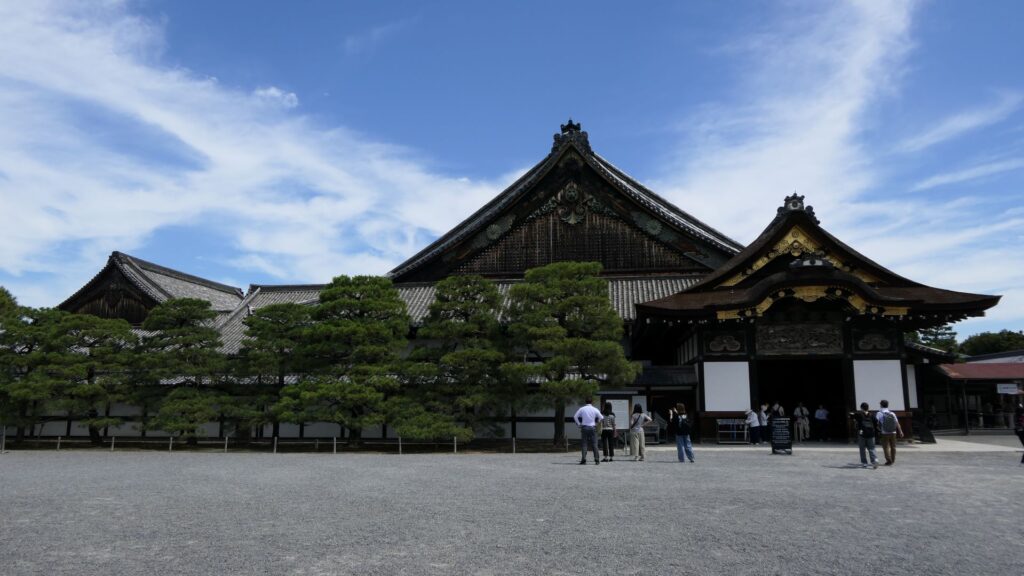
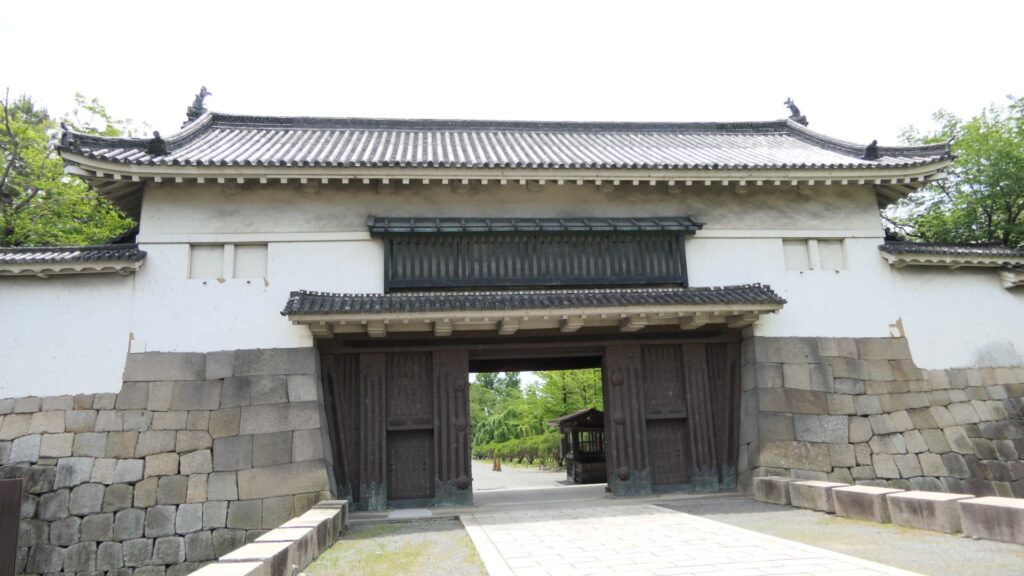
The eastern main gate is the only gate available to visitors. It looks strong on the outside, however, if you enter inside, there will be an open space with the remaining guardhouse alongside. This is probably because this gate was the front gate of the castle, which was mainly used when ceremonies were held.


If you turn right at the first corner of the tour course, you will see the Kara-mon Gate (which means Chinese-style gate). It was built with the high sophistication, as the front gate of the second enclosure main hall. It also has lots of golden decorations, which attracts many tourists, particularly those from overseas.
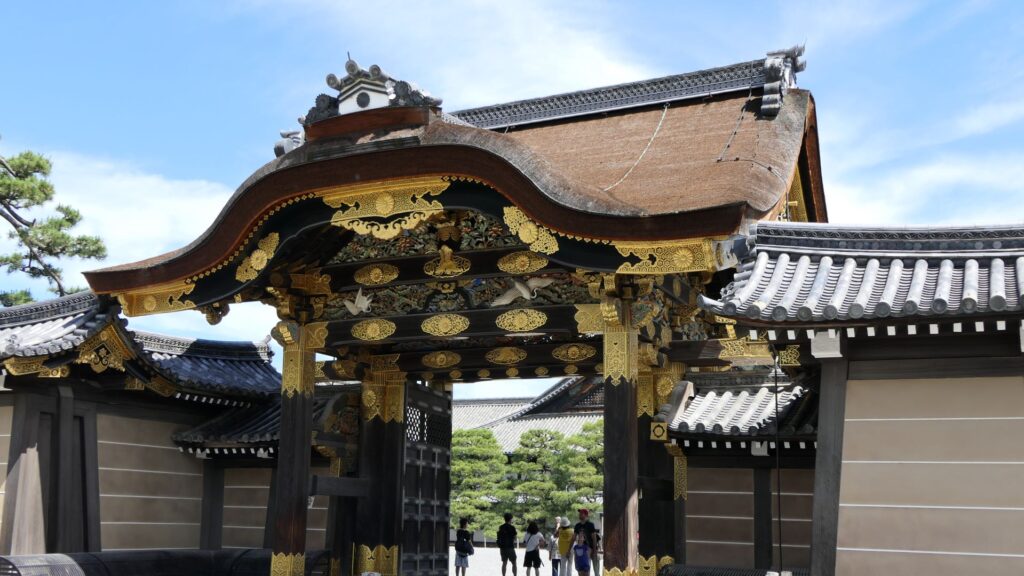

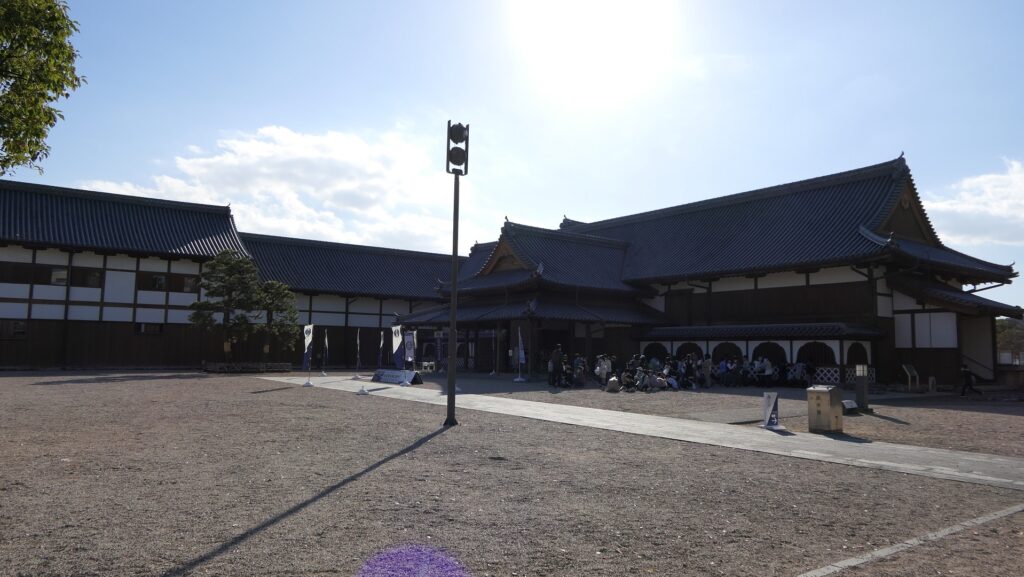
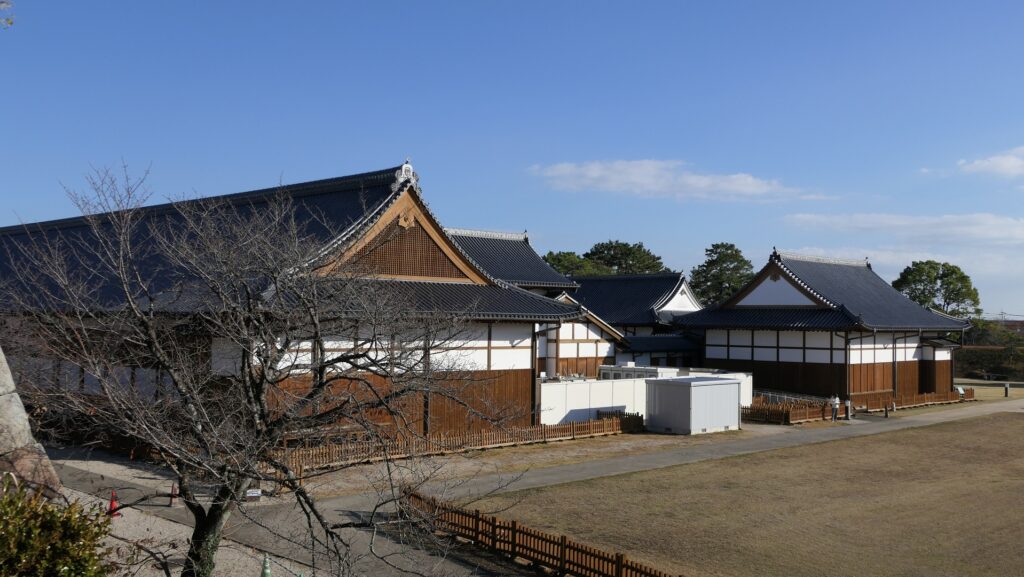
The route from the eastern main gate to the main hall through the Kara-mon Gate has been the official one since the beginning. The main hall has been intact since it was renovated for the Kanei Royal Visit in 1626. That’s why it was designated as a National Treasure in 1952, with its gorgeous pictures on its movable sliding doors inside.

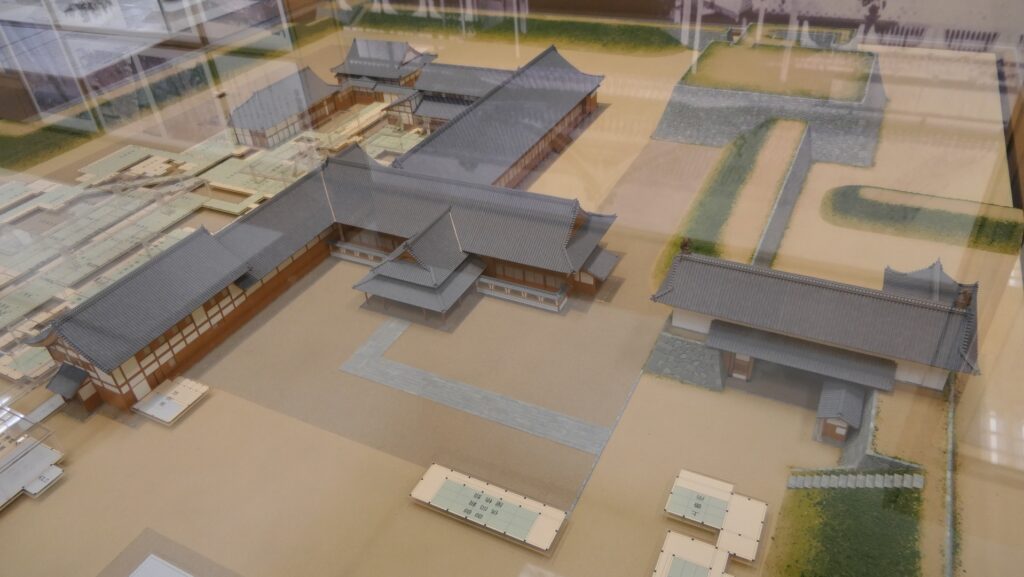
Unfortunately, we can not take pictures inside the hall. Therefore, let me explain to you about each hall while looking at the aerial pictures of the six halls. The hall basically consists of 6 buildings. The first one is the largest one (located on the bottom right of the picture), called “To-zamurai” (which means gate guardians). It was used as the entrance and the waiting rooms, including the special room for the imperial envoys in the back. The hall next to it is called “Shikidai” (which means retainers’ rooms). It was the place for the agency service between the visitors and the shogun. The service was done by Roju (the members of the shogun’s council of elders) who had their rooms in the back.
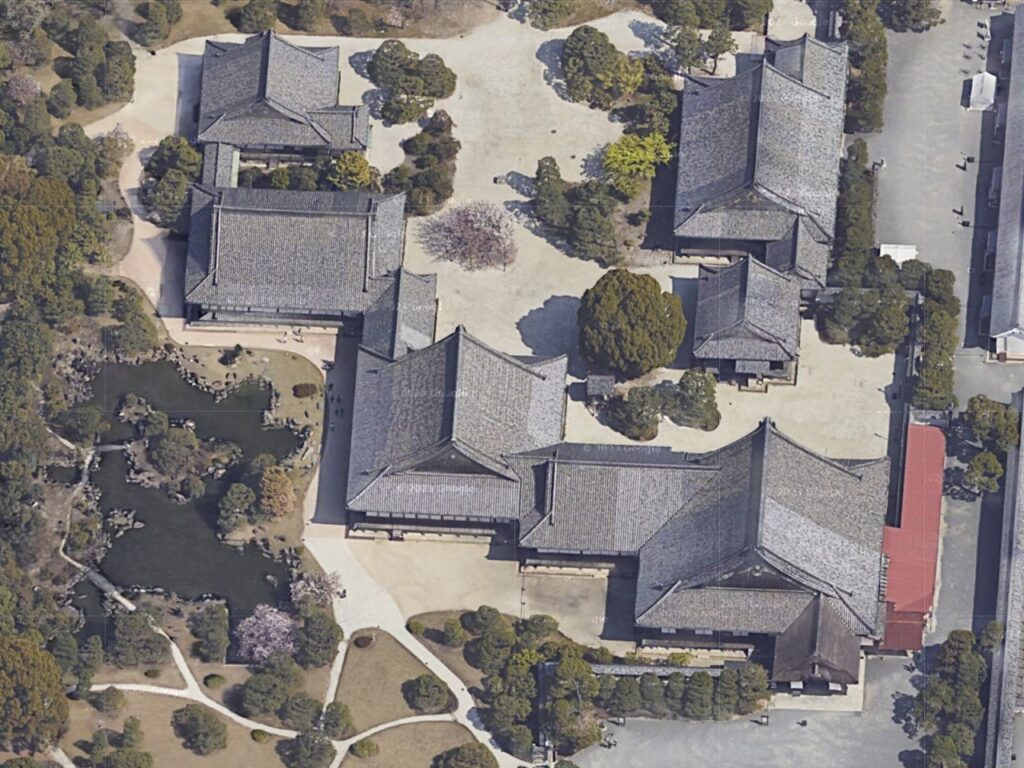
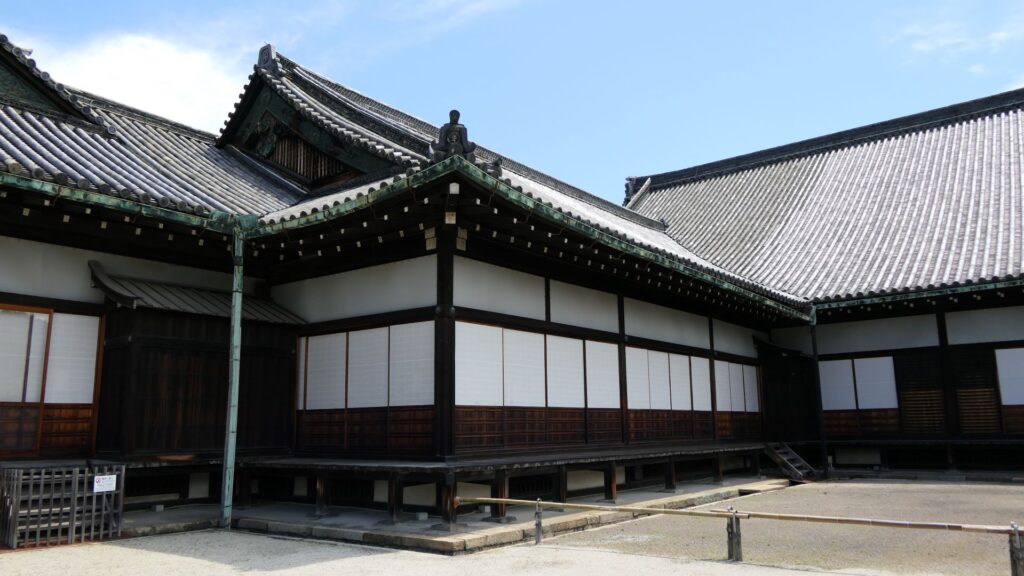


The third hall is O-hiroma (which means large hall), where the visitors officially met the shogun. In fact, The Returning of the Power to the Emperor was officially announced there in 1867. The three buildings above were like the government office. The others in the back were like the shogun’s residences.
The fourth hall, called “Sotetsu-no-ma” (which means cycad room), was the connecting hall to them. The name originates from the cycad trees, presented from the Saga Domain. They were planted outside near it. Surprisingly, the trees are still alive there today.
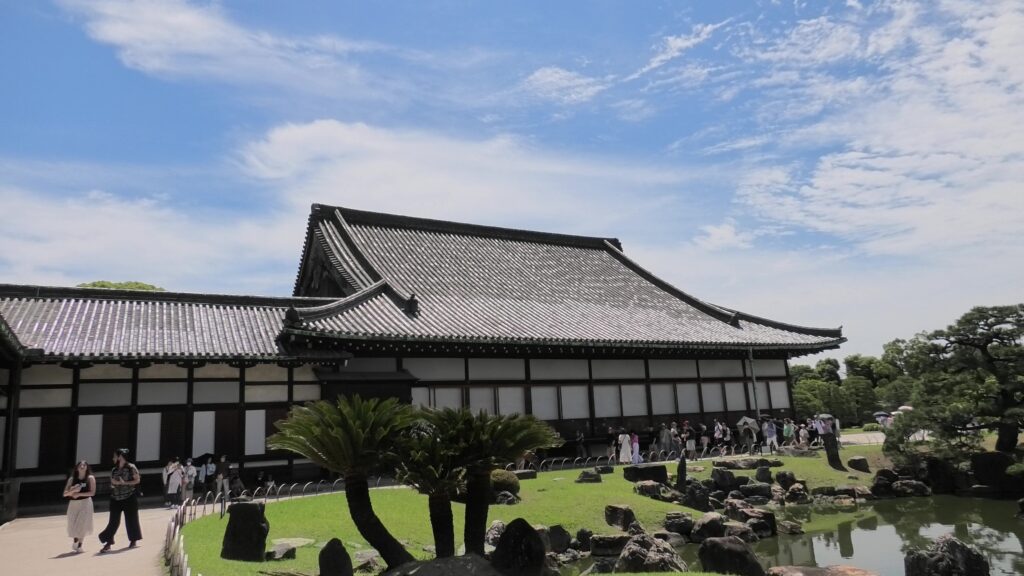

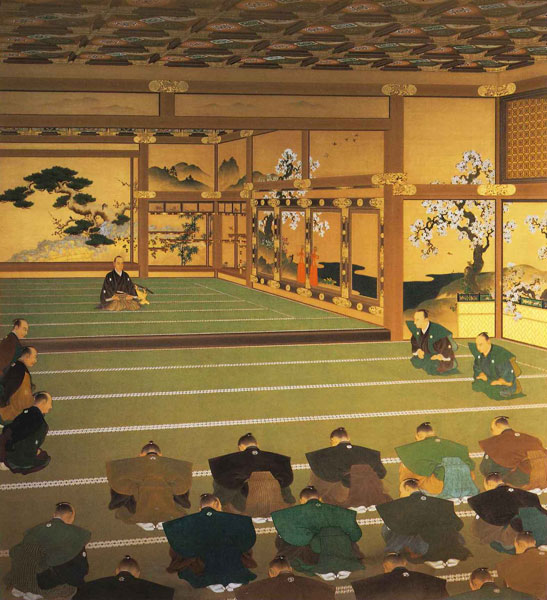
The fifth one is called Kuro-shoin (which means black library), where the shogun worked and met people in private. The famous picture of The Returning of the Power to the Emperor demonstrates the event in this room. The shogun (Yoshinobu Tokugawa) told the internal retainers about his decision in the picture.
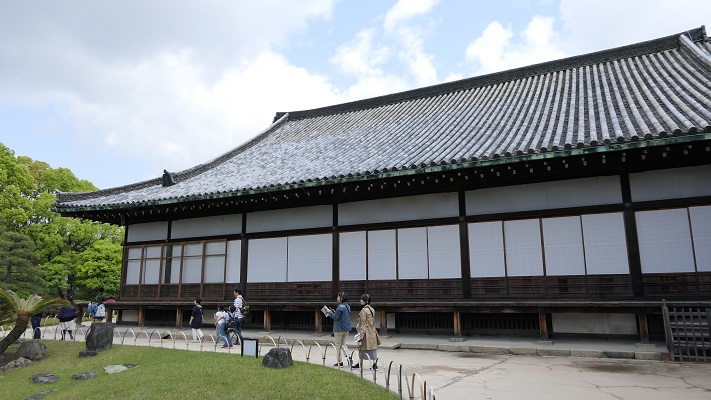


The last one is called Haku-shoin (which means white library). It was used as the shogun’s private room.

Is the Main Enclosure a Castle-like Place?
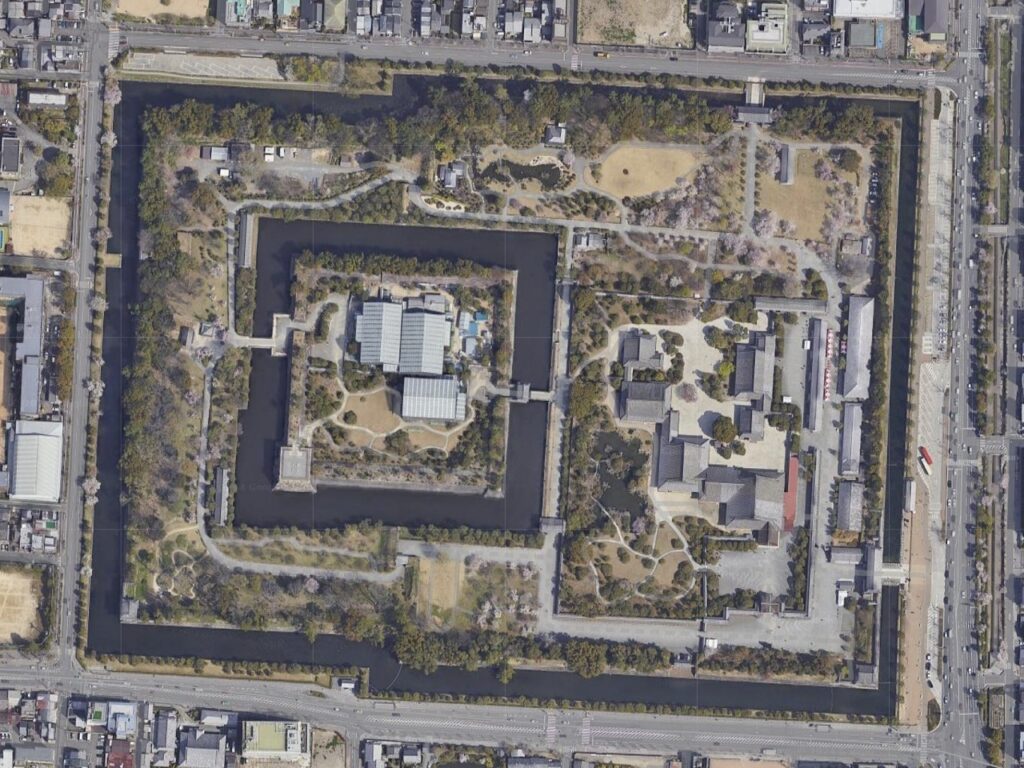
The main enclosure may be more likely a castle than the second enclosure. You can go there by crossing the bridge over the inner moat. The bridge used to have the second floor with roof overhead for the Kanei Royal Visit. The floor was demolished, but it is kept in a storage room, in case they want to restore in the future. If you go over the bridge, you will enter the remaining turret gate of the enclosure.
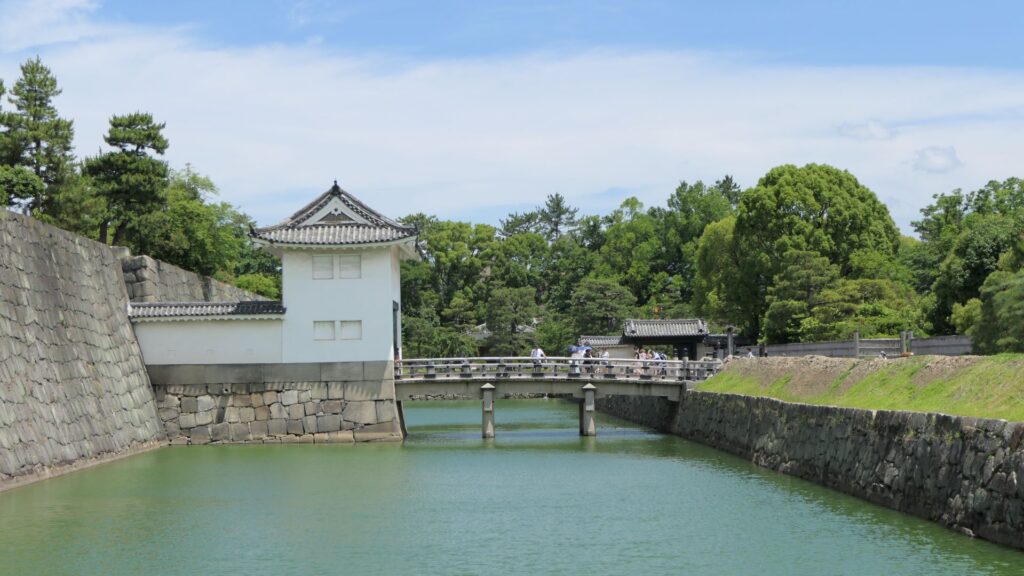

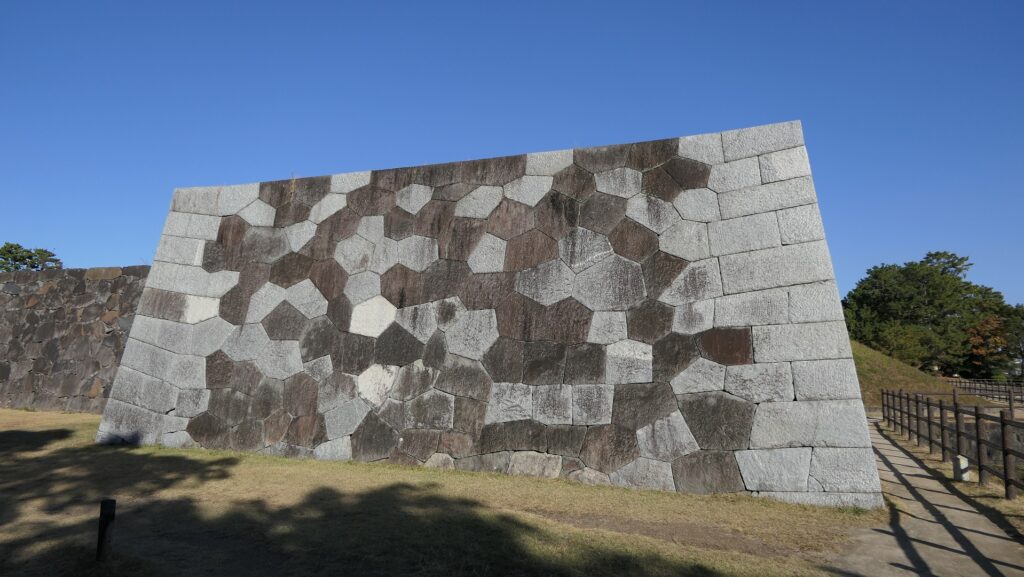
The inside of the gate is still surrounded by stone walls, which looks stronger than that of the second enclosure. The square inside the walls is one of the castle’s defense systems, called Masugata.
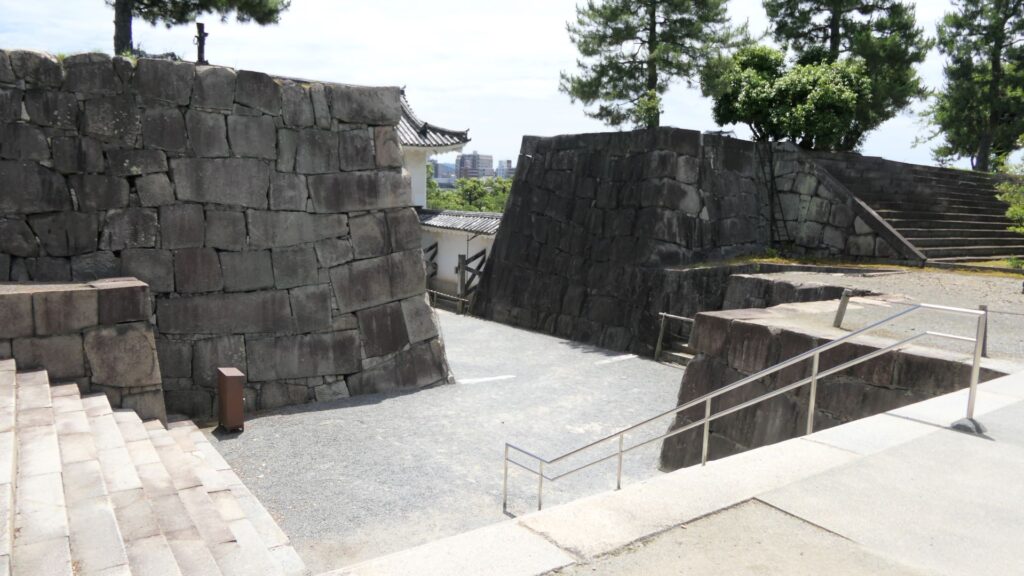

If you go to the center of the enclosure, the atmosphere around it will feel elegant. This is due to the place being developed as a garden for the former imperial villa. The remaining main hall of the enclosure is not the original of the castle but it came from the residence of the Katsura-no-miya imperial family in the Meiji Era. The emperor Taisho often stayed there when he was the prince.
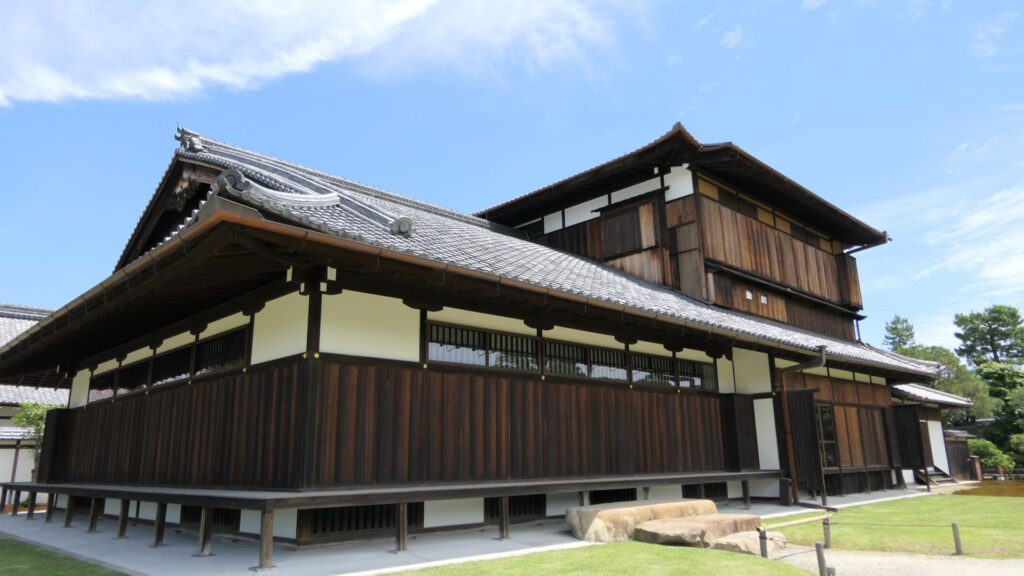

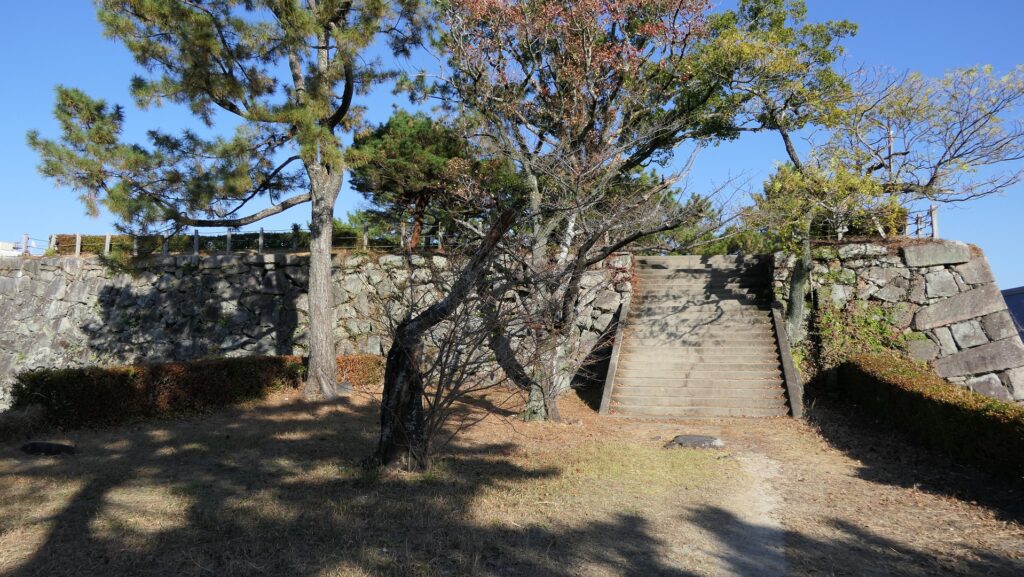
You can climb the main tower base, which had the real tower in the past. The emperor climbed the tower twice during the Kanei Royal Visit. The experts of the advisory panel for the site are now discussing how to restore the tower in the distant future.
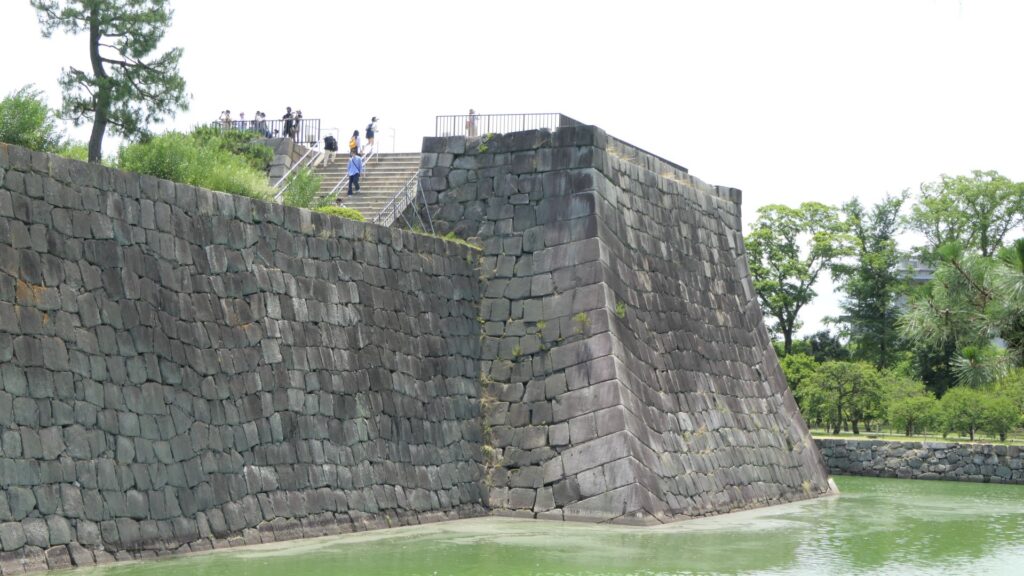

The tour course will eventually guide you to the exit of the enclosure through the western entrance which is the opposite side of the turret gate. This entrance also looks impenetrable with a square space even through it doesn’t have buildings there anymore.
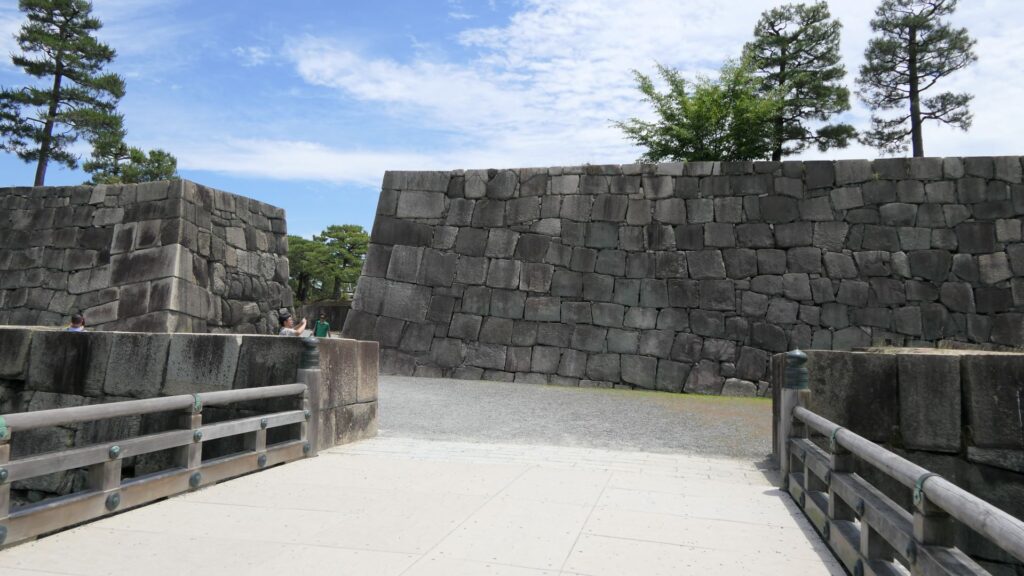

There are other defensive systems around the main enclosure. For example, the passage in front of the bridge and the gate, you first passed through, is separated by two gates, one in the north, one in the south.
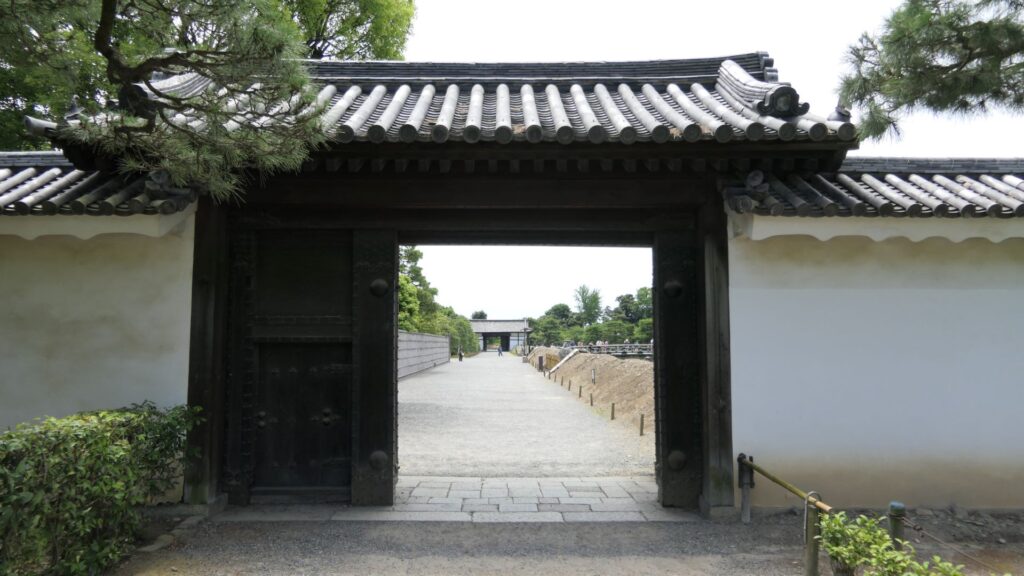
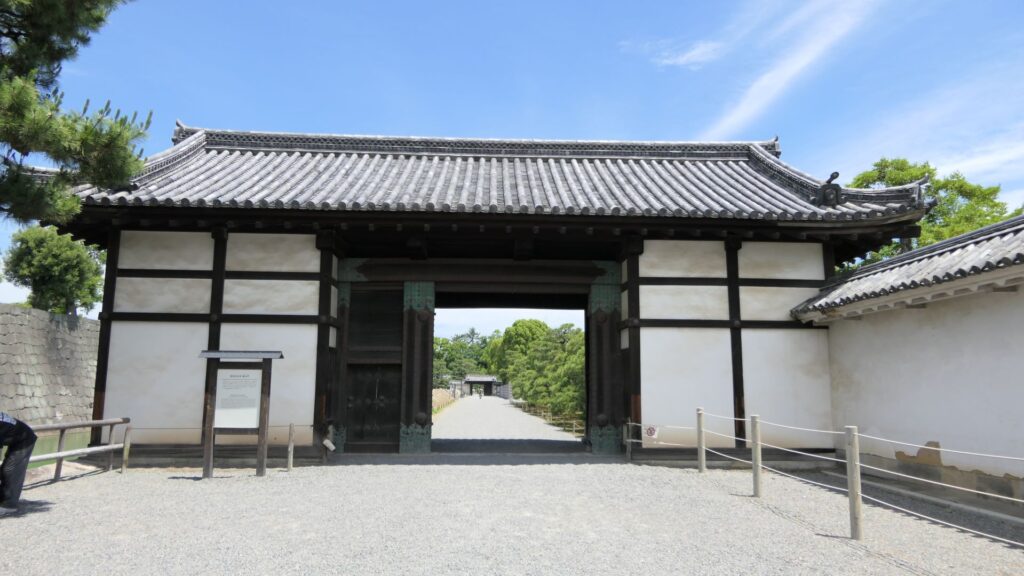


In addition to the two gates mentioned above, there are two additional gates, which were built on the northern edge of the inner moat and on the southern edge of it. These gates were used to protect the castles from enemies’ attacks and to monitor regular visitors.
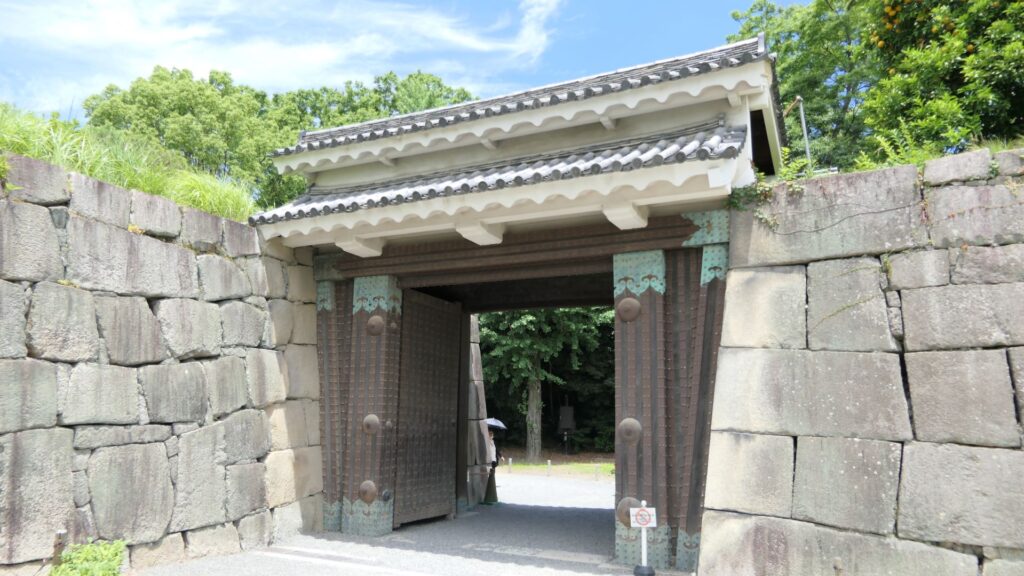
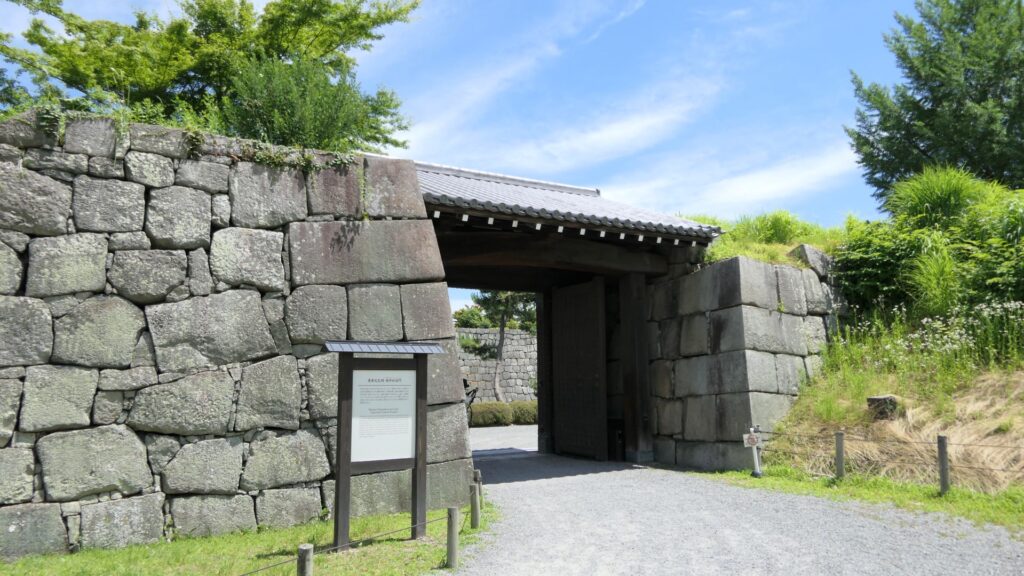


Furthermore, there are also two remaining storehouses on the western side of the enclosure. They were used to stock rice in preparation for a long siege. Three of the ten storehouses still remain in the castle today.
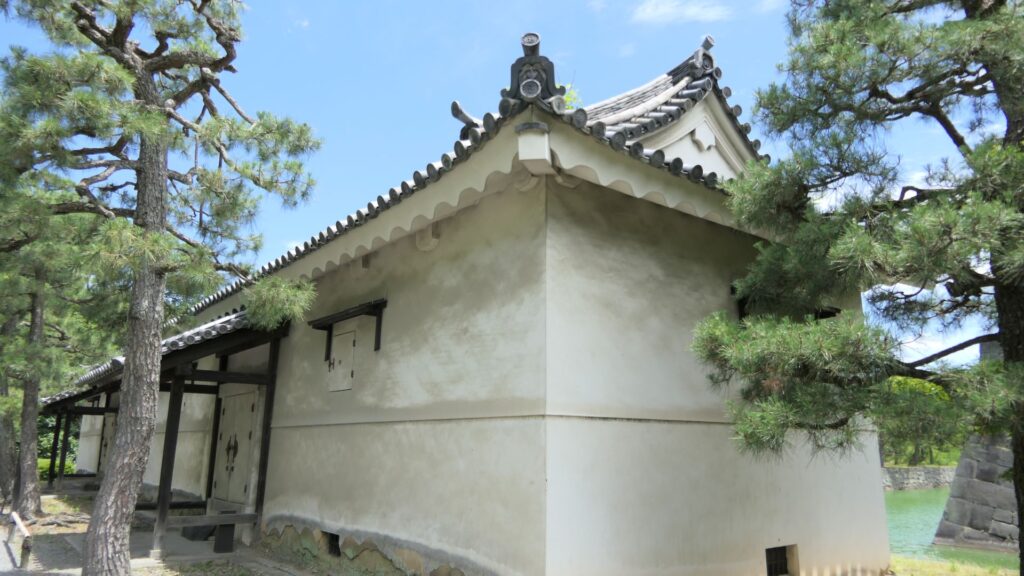
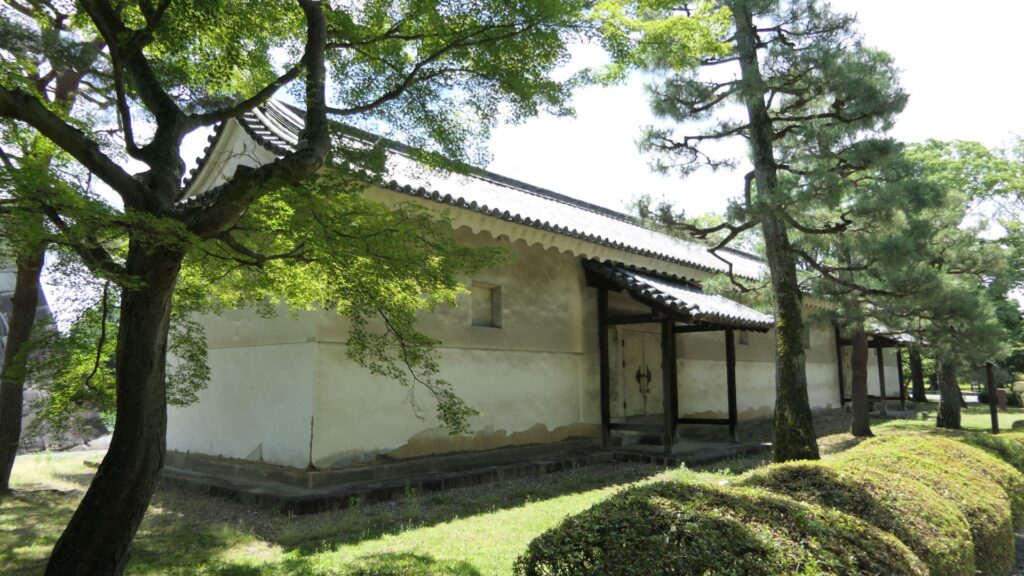


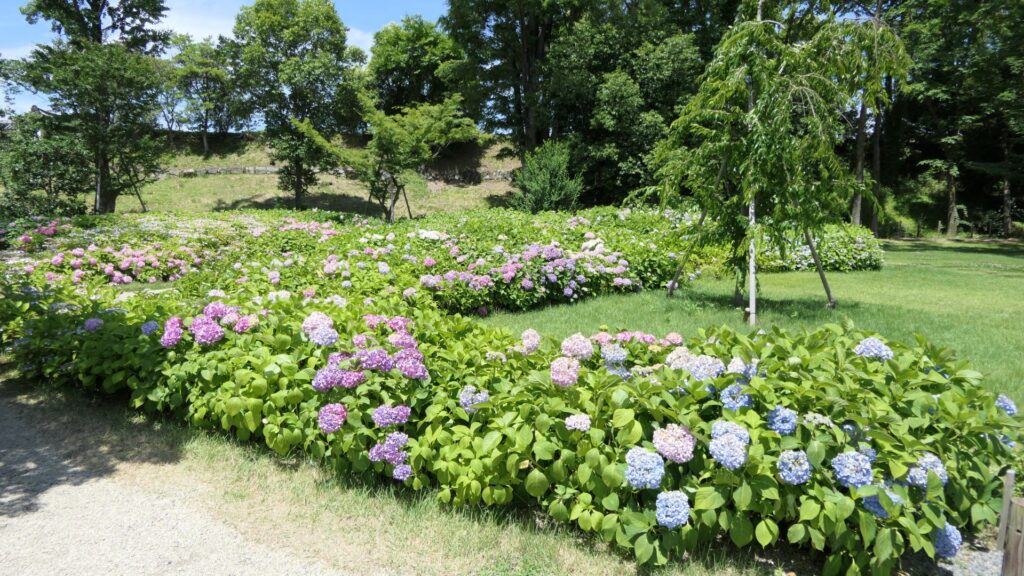
If you have time, I recommend you visit the southwestern side of the enclosure. You may enjoy seeing beautiful flowers such as plum blossoms in the spring, hydrangea flowers in the summer, etc.

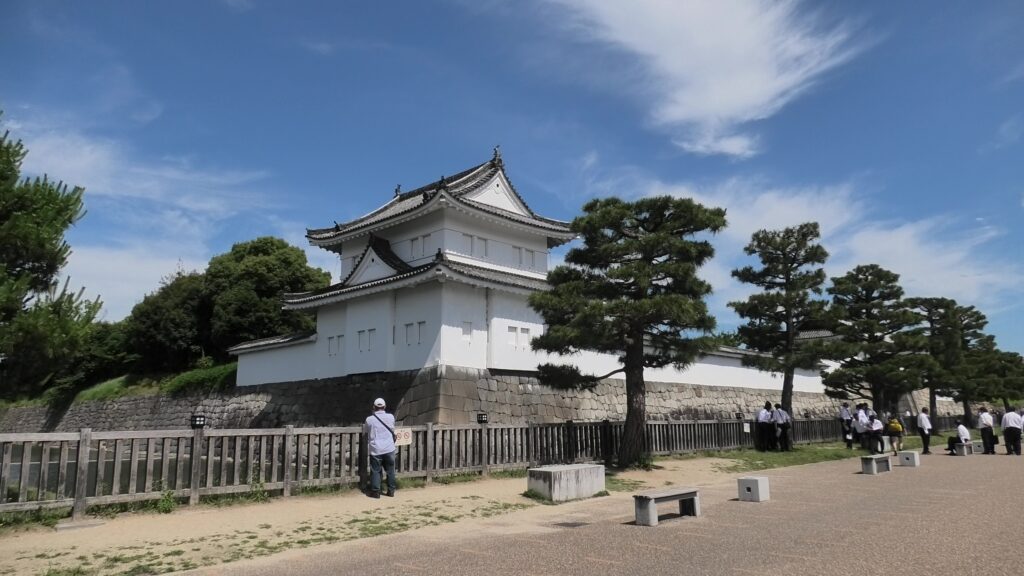
Let’s walk around Nijo Castle!
Many tourists may see only the inside of Nijo Castle. However, this article will guide you to other perspectives of the site. Let us walk around the perimeter of Nijo Castle, which is about 1.9 km long. Let’s start from the eastern side of it, where many tourists gather, finishing to the northern side.

If you walk along the northern side, you will see the northern main gate, another highly sophisticated one, following the eastern main gate. It was probably used to communicate with the shogunate government office of Kyoto, which was located across the road. In fact, it is uncertain when it was built, that means it might be the oldest building in the castle.

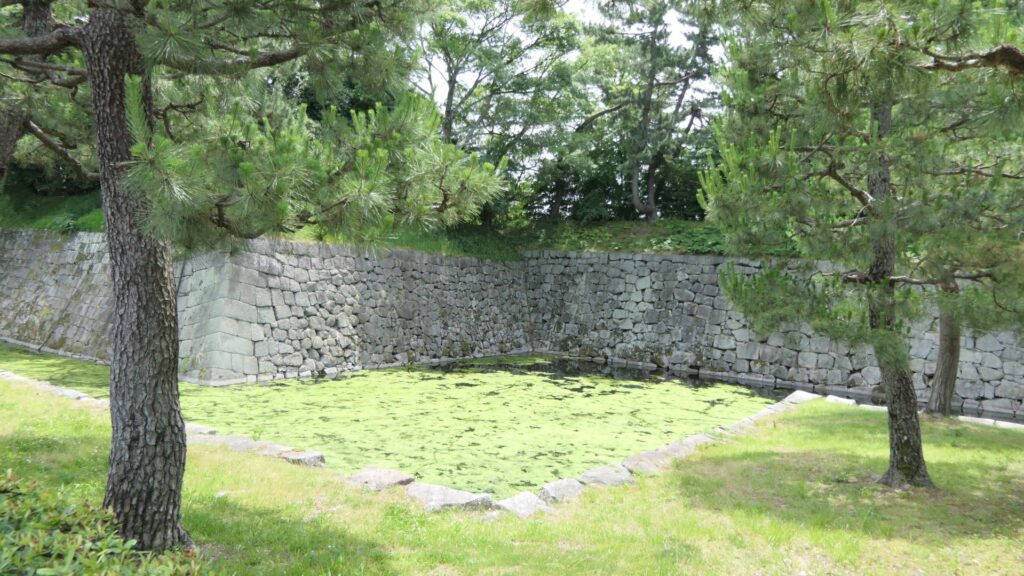
If you go further, the smaller square is attached the larger square by a protrusion shown in the picture below.

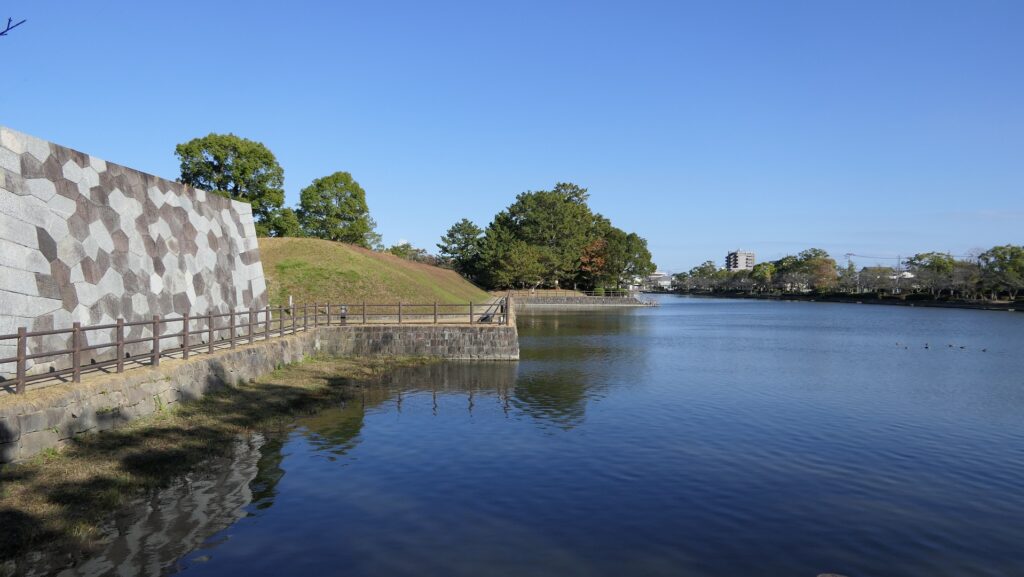
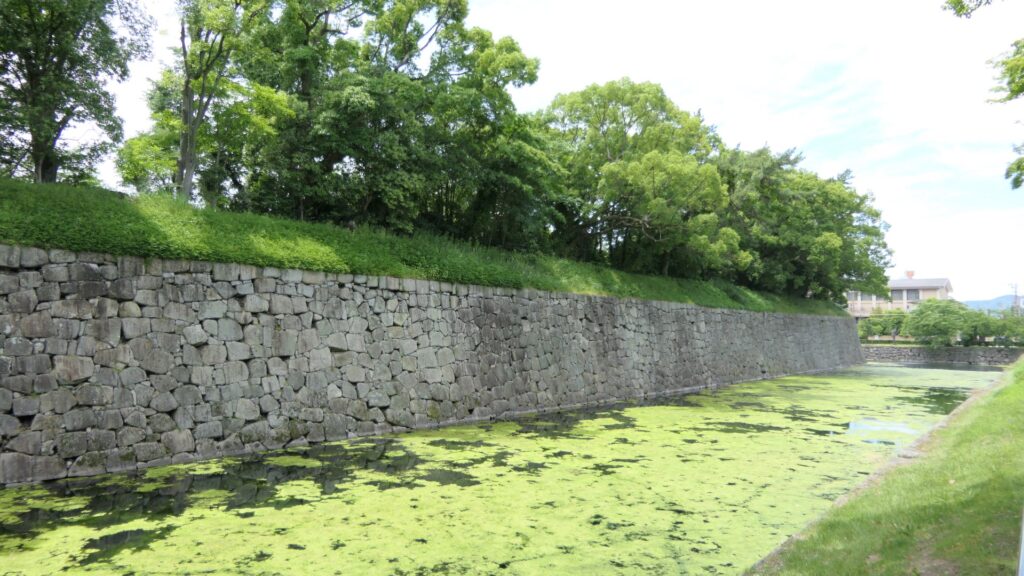
You can also walk on the special pathway, which was partially developed on this side, to see the stone walls and moats of the castle more closely.

If you go to the western side, you will see the ruins of the western gate. It was the side entrance of the castle, which people usually used, but you cannot use it now because there is no bridge over the moat. It looks smaller and more defensive than the other highly sophisticated gates of the castle. Unfortunately, you cannot get close to the gate ruins even from the inside When Yoshinobu Tokugawa, who was the last shogun, escaped from this castle, he used this same gate, not the front gate, in order to avoid confrontations.
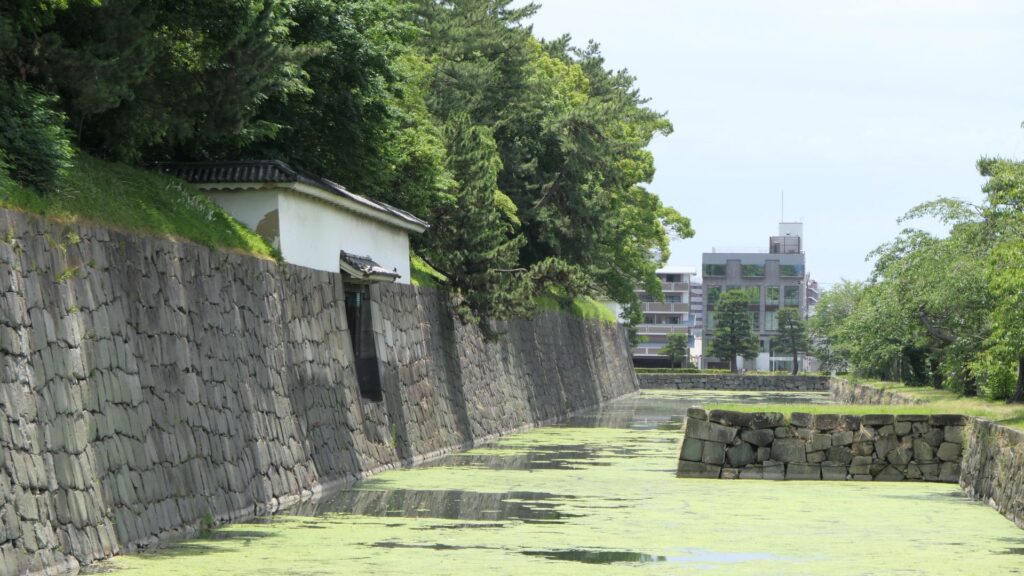

You will eventually see the other remaining “southwestern corner turret” at the corner between the western and eastern sides. It has quiet environment, compared to the southeastern corner turret.
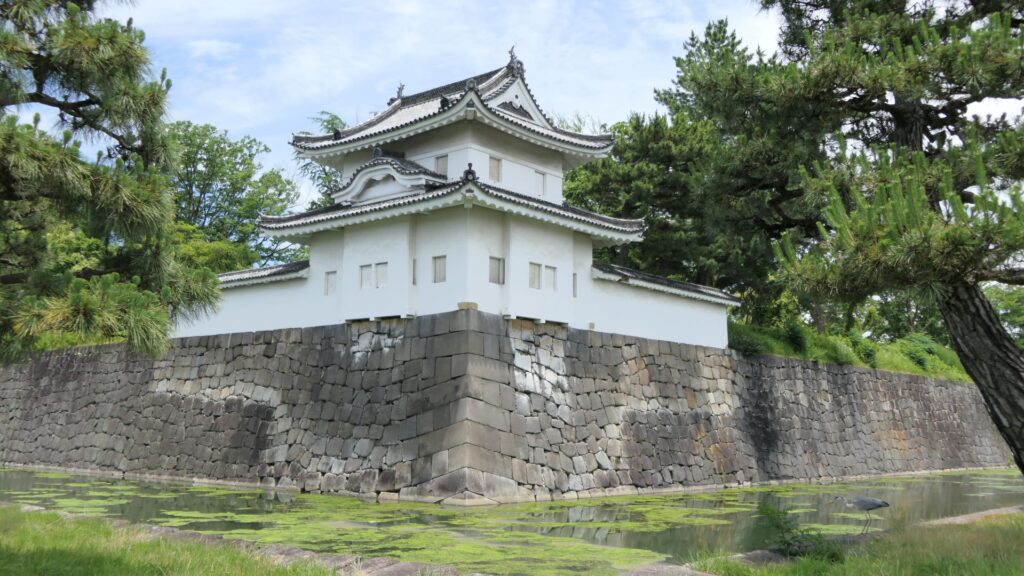

You will also see water flowing out from the moat of the eastern side. This water comes from a natural spring of this site. In fact, this site had been an ancient pond, called “Shinsenen”, before the castle was built. The current Shinsenen was downsized and is next to the castle. The castle benefits from nature of Kyoto.
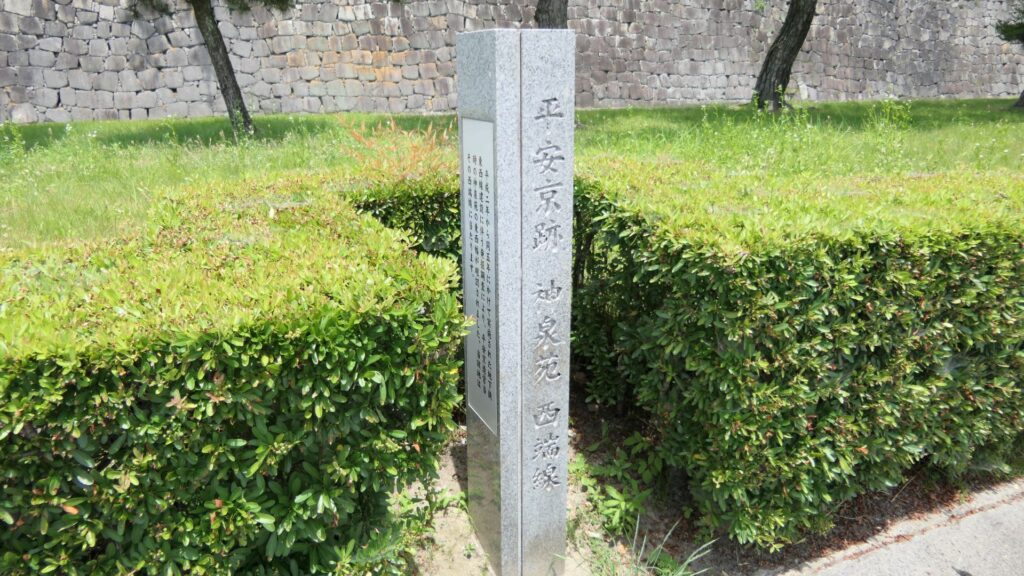


Where are the Old Nijo Castle Sites?
After walking around the current Nijo Castle, let us now go to the ruins of the old Nijo Castles. However, there are only a few of them remaining because they were all demolished. Basically, there is the only stone monument at each site.
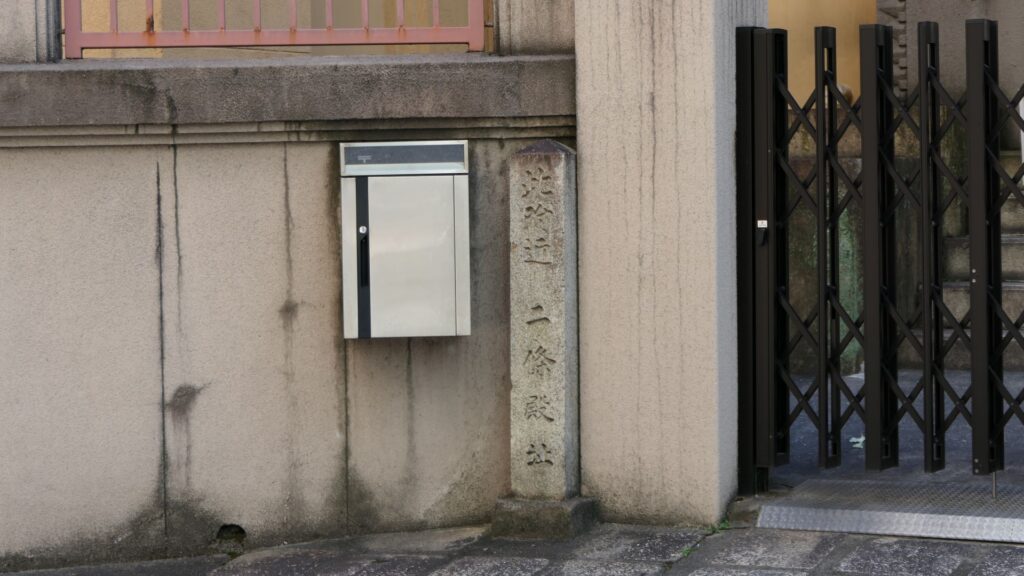


Yoshiaki’s Nijo Castle Ruins have a few other things. Some of the stone walls were excavated when the subway constructions were done. They are now exhibited on three sites. One is near Sawaragi-guchi entrance of Kyoto Gyoen National Garden, and another is in the current Nijo Castle.
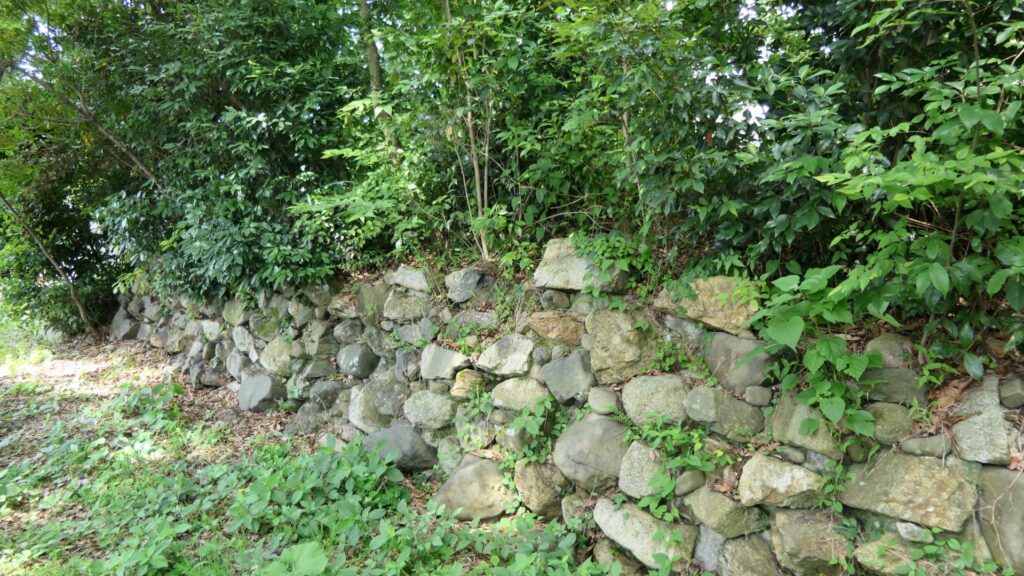
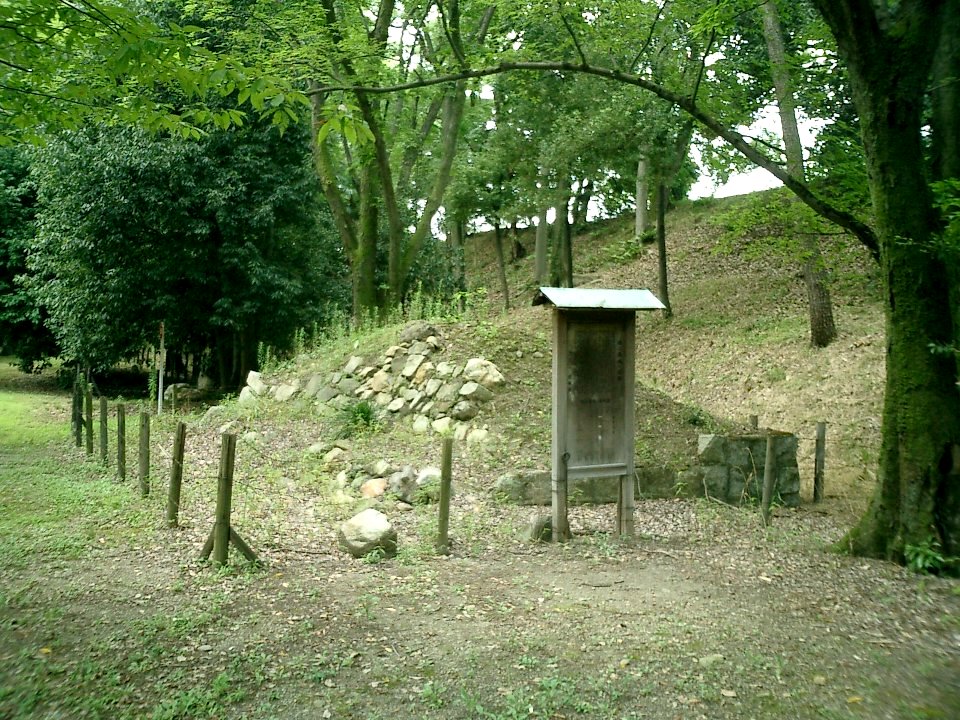


The other one is exhibited, about 10km away to the west of Nijo Castle, in Kyoto Bamboo Park. These stone walls have a distinct feature, which came from stone Buddha statues, collected by Nobunaga Oda.
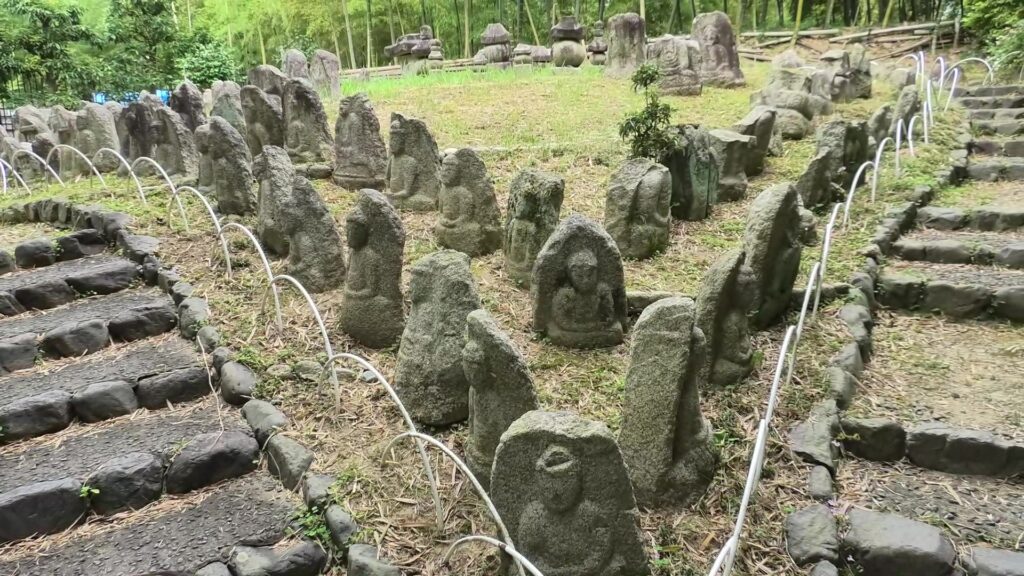

According to a Portugal missionary, Luis Frois, who was in Japan at that time, wrote that Nobunaga ordered his servants to carry these statues using ropes which made them look like prisoners. People in Kyoto were very afraid to see this because the people worshiped the Buddha statues. Some of the statues, which are exhibited in the park, were actually destroyed intentionally.
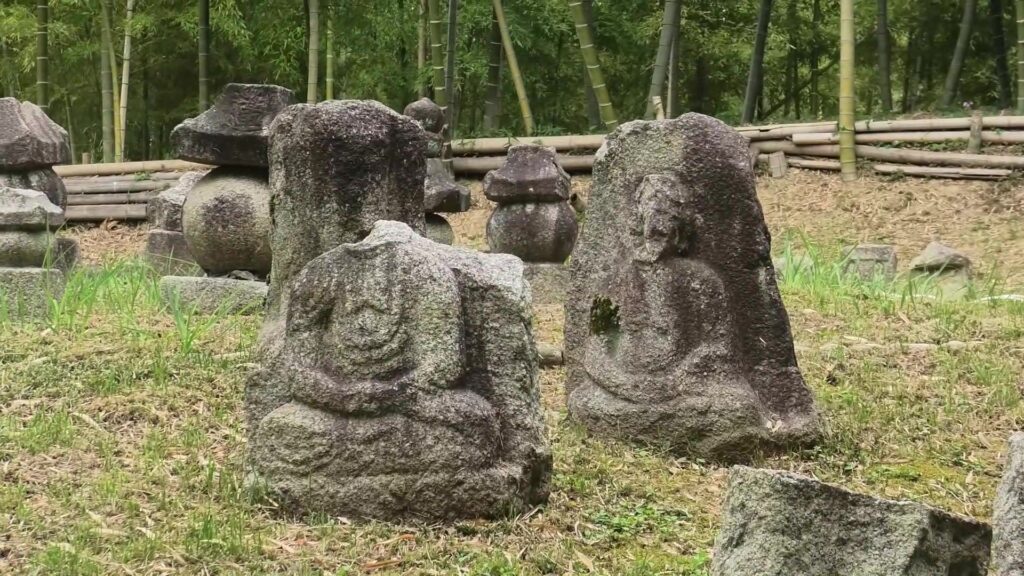

Even current Japanese people would be relieved to see that these statues survived despite the harsh treatment they were given.
My Impression
Looking at the histories of all the different Nijo Castles, there were some cases where the castles fell or their masters abandoned them. That may mean that Kyoto is easy to attack but difficult to protect. On the other hand, Kyoto must also have been an attractive place to stay for the masters. I think that the world was not built in a day and therefore, Nijo Castle was not built by one castle.

That’s all. Thank you.













