Location and History
Castle is built after Battle of Sekigahara
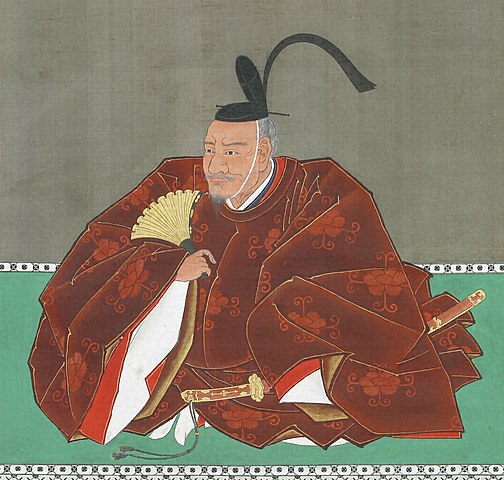
Kagoshima Castle was the home base of the Shimazu Clan during the Edo Period and is also known as the final battlefield of Seinan War which was the last civil war in Japan in 1877. The Shimazu Clan had been a great warlord in the southern part of the Kyushu Region during the Sengoku Period between the middle 15th and the late 16th Centuries. However, in the fateful Battle of Sekigahara in 1600, the West Squad including the clan was completely defeated by the East Squad, led by Ieyasu Tokugawa who would be the founder of the Tokugawa Shogunate. The Shimazu troops with about 1500 soldiers somehow escaped from the battlefield in the Chubu Region (central Japan) to their home base of Satsuma Province in the Kyushu Region. However, only 80 clan members survived.
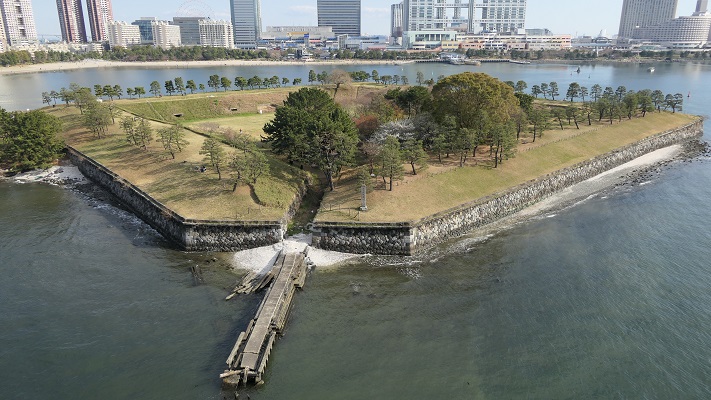
The location of the castle
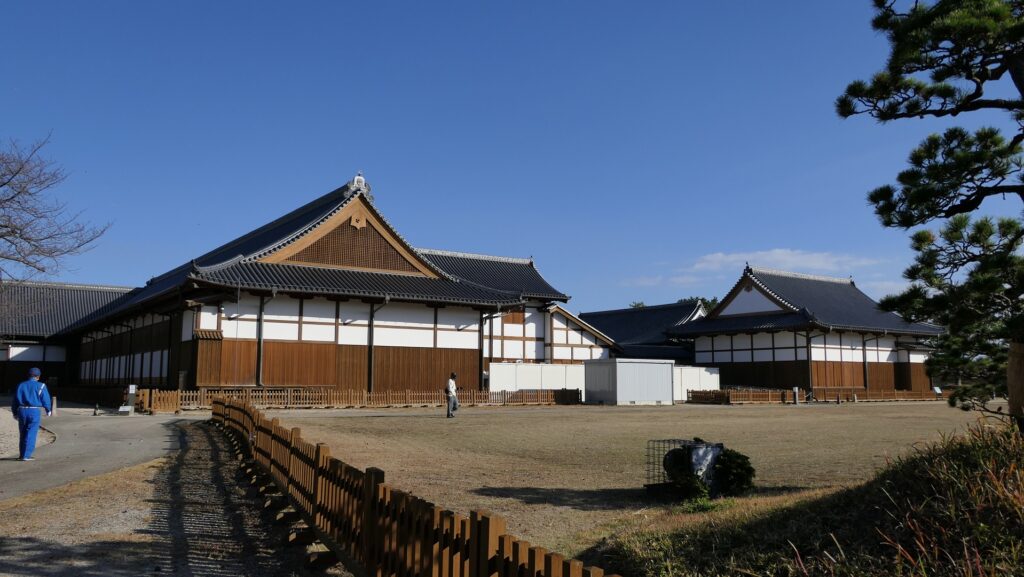
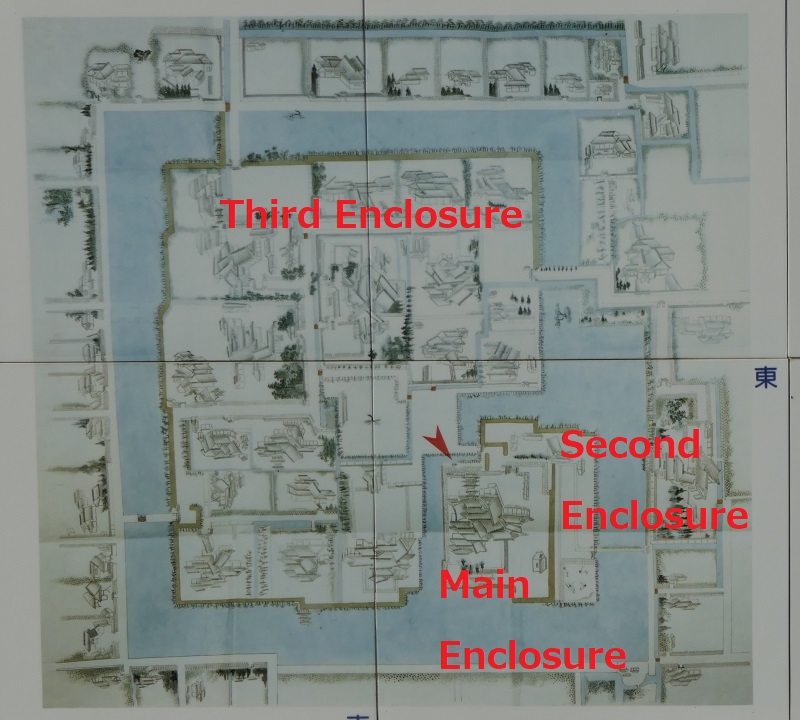
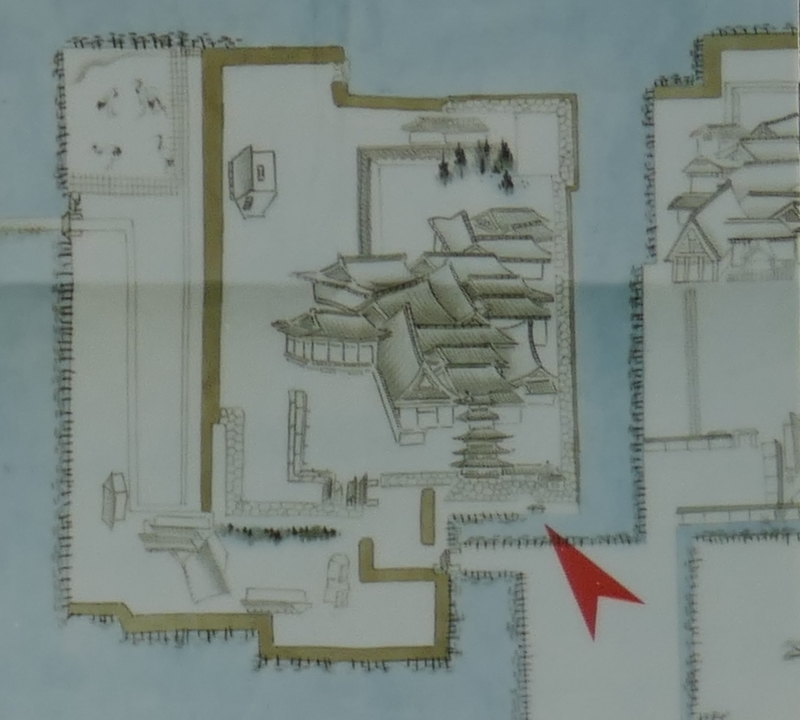
The Shimazu Clan was worried that the shogunate would attack Satsuma Province directly. Therefore, the clan decided to build a new castle as their home base, which was stronger than their previous one like a simple hall. It was built at the foot of the Shiroyama Mountain on the west, which would be used as the final place for emergencies. It had the Main and Second Enclosures which were surrounded by stone walls and water moats from the north, the east and the south. The Main Enclosure had the Main Hall for the lord inside and one of the largest castle gates in Japan, called Goro-mon. However, the defense system of the castle was still not as complex as those of other major castles in Japan, such as the Main Tower, several-level turrets, and high, elaborately bent stone walls. This was because the Satsuma Domain led by the Shimazu Clan also had a unique defense system called Tojo or the Outer Castles. It refers to the domain sending many of its retainers to their local sites and letting them govern and protect it by themselves, which was different from other domains bringing their retainers together in their home base.
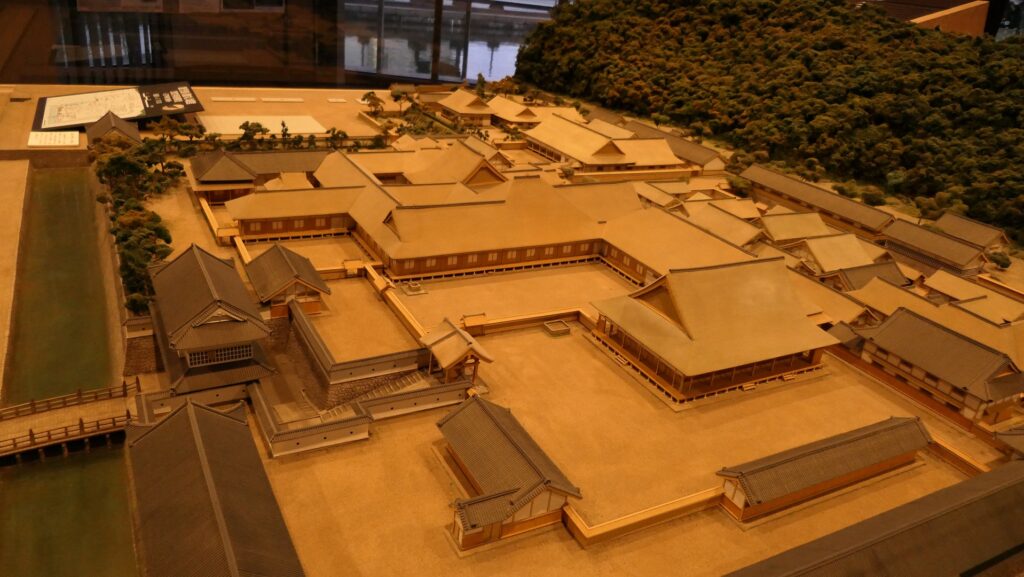
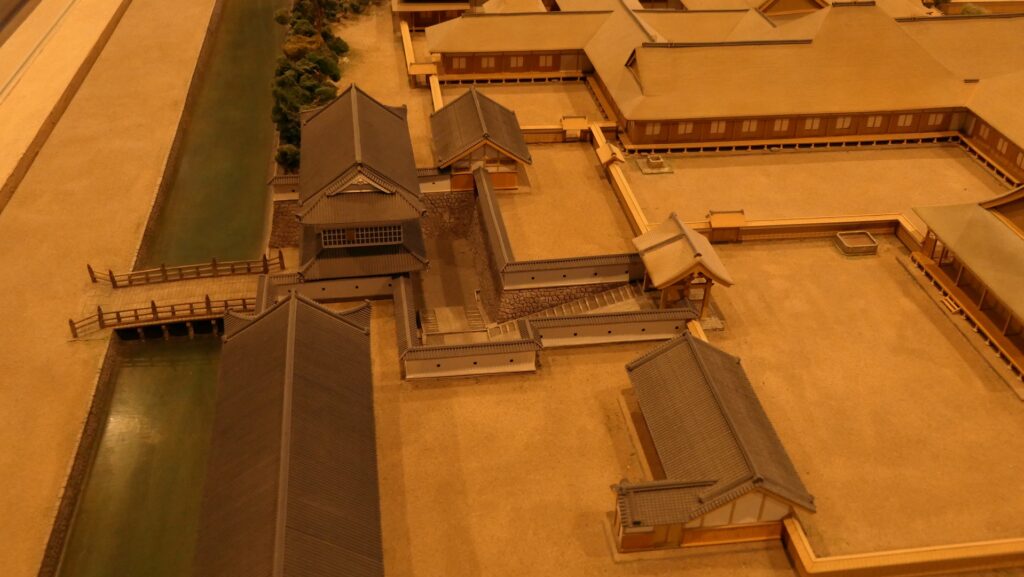
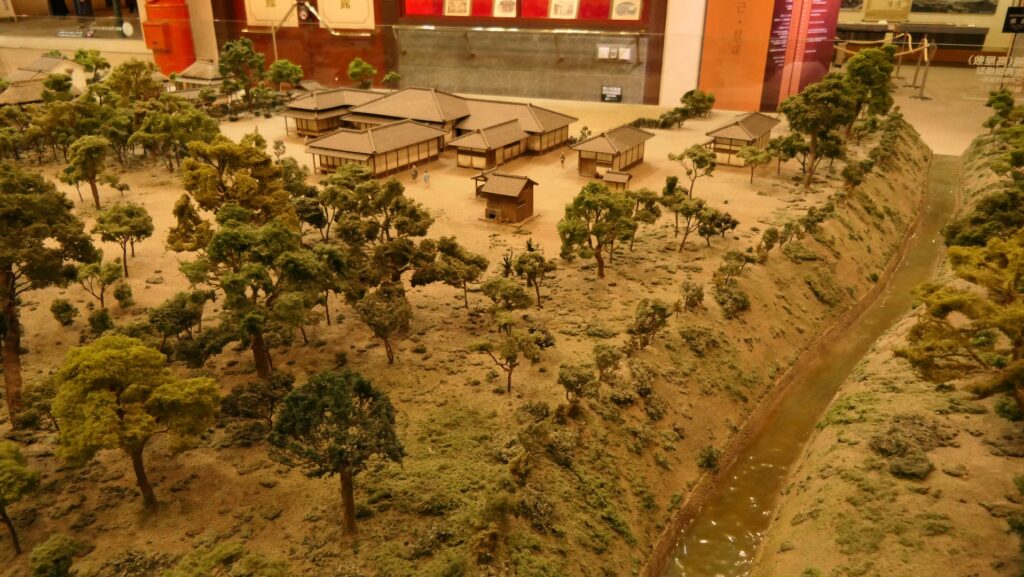



Luckily, the shogunate allowed the Satsuma Domain to continue to govern Satsuma Province until the end of the Edo Period. Even in Anglo-Satsuma War in 1863 when the English Navy battleships shot the Kagoshima city area, the castle was not targeted because it didn’t have tall buildings. After the Meiji Restoration, the castle was used as the prefectural office and as a Japanese Army base, but the buildings of the Main Enclosures were unfortunately burned down by an accidental fire in 1874.
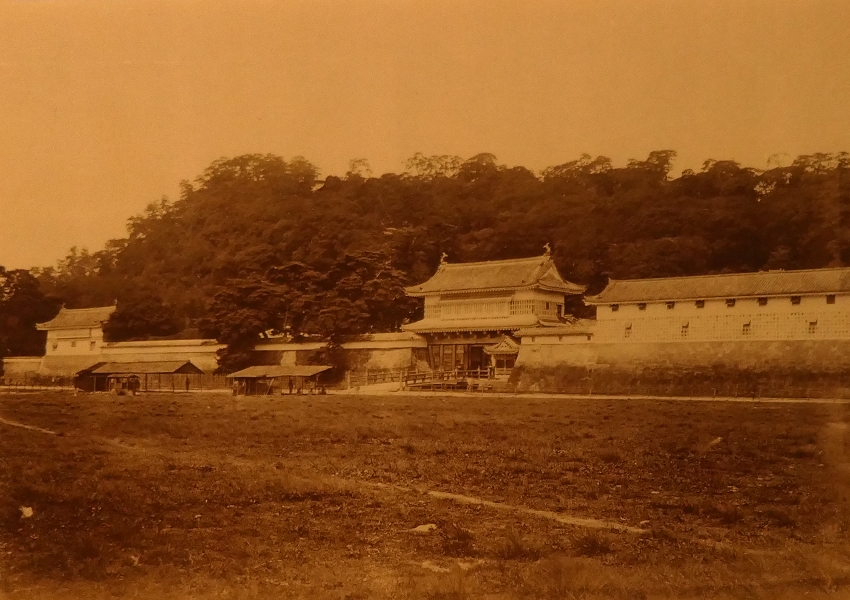

Outbreak of Seinan War
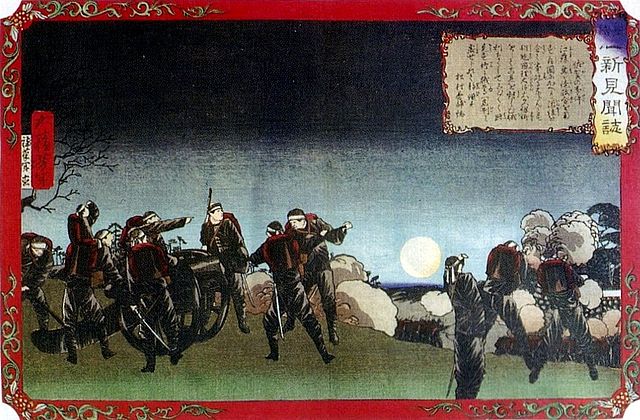
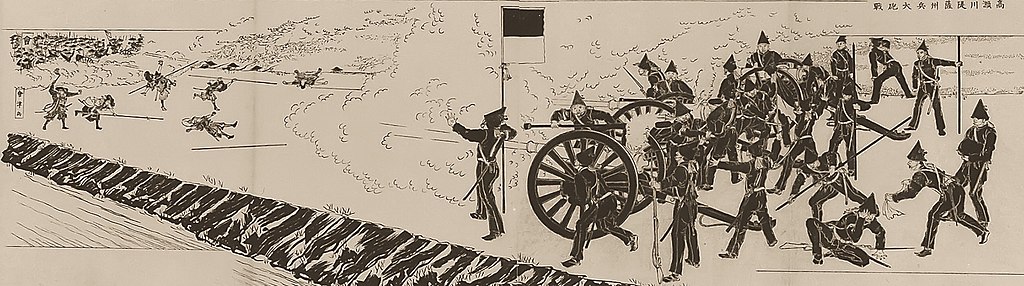
The climax event for the castle finally happened in 1877. Takamori Saigo, one of the Three Greatest Heroes of the Restoration, quit all his government posts, being against the other two, Toshimichi Okubo and Takayoshi Kido, and returned to his home of Kagoshima in 1873. He established his private school called Shigakko in the Second Enclosure of Kagoshima Castle in 1874 to educate young warriors. He tried to control the young people gently, however, as a result, he became the head of the rebellion against the government led by Okubo, which eliminated the privileges of warriors, such as having a sword, and it cut their hereditary salaries in 1876. Several rebellions happened in the same year, followed by the largest Seinan War led by Saigo, which occurred in February of 1877.


Saigo with his troops decided to go north and capture Kumamoto Castle. He and his crew were at first optimistic as they were professional warriors and accommodated supporters from other areas in the Kyushu Region, with the total of 30,000 at maximum. While the number of the defenders in the castle was only over 3,000 and many of them were drafted farmers. The Saigo troops even expected that the defenders would soon surrender because some of their leaders had come from Satsuma. However, the defenders, led by General Tani, never surrendered and Okubo sent the reinforcement to the castle. It also had many drafted soldiers, but was more well trained than Saigo expected and more equipped and supplied than the Saigo troops. The government even used advanced information technologies such as telegraph the Saigo troops never had. Saigo had to withdraw from Kumamoto Castle in April and tried to stay in other areas in the Kyushu Region, such as Hitoyoshi Castle, but all failed. He finally declared the dissolution of his troops in August. He and his close warriors of only nearly 400 wanted to have their last and desperate battle in their original home base, Kagoshima Castle.
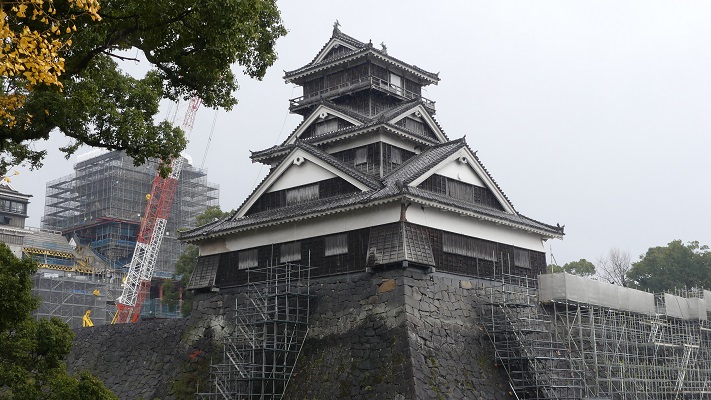


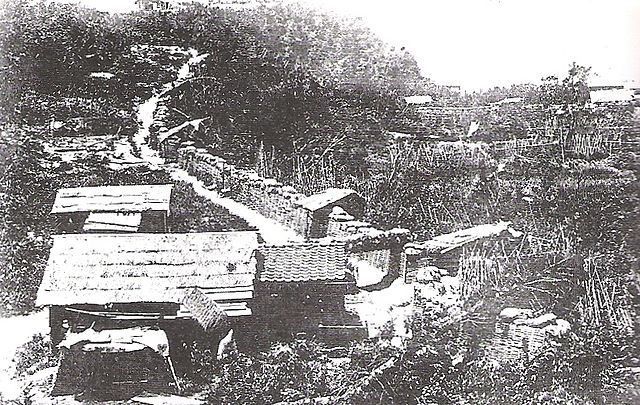
Last moment of Saigo and Castle
They somehow reached there in the first of September and allocated themselves to the foot area and Shiroyama Mountain. Of course, they were too few to prevent the government troops of as many as 50 thousands from attacking. If it had been in the Sengoku Period, Saigo would have set his stronghold on the mountain, but it was impossible because it could be targeted by cannons. Therefore, he had to stay in the caves in a valley between the mountain and the foot, which would be called the Saigo Caves later on. The government troops completely besieged the Satsuma rebels so that no one could escape. Their full scale attack was done on 24th of September. Saigo was assaulted from his cave, but was shot, and finally killed himself by performing the Harakiri.