Location and History
Matsudaira Clans are Shogun’s Relatives
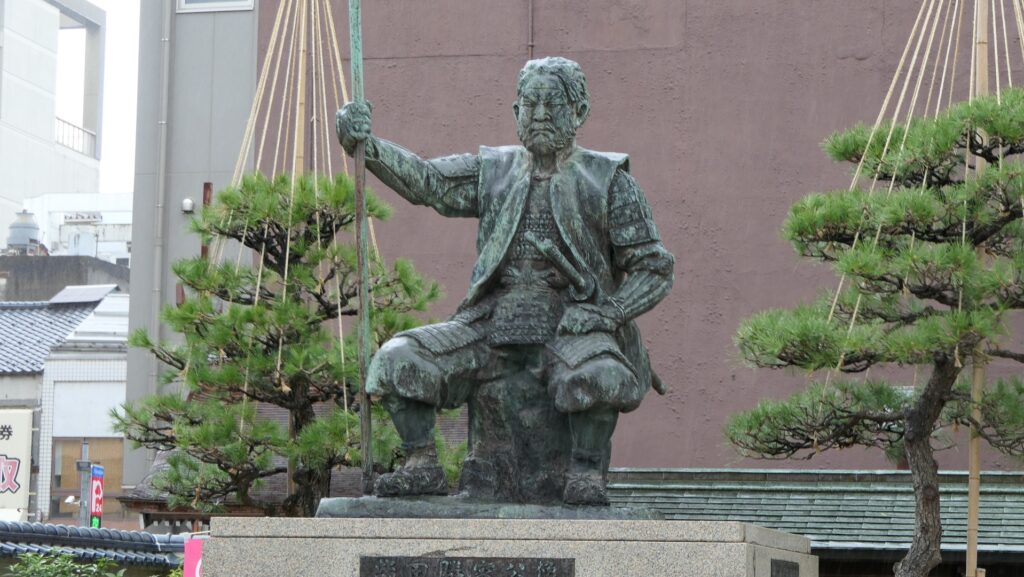
Tatsuoka Castle was located in Shinao Province which is modern day Nagano Prefecture. It was built at the end of the Edo Period and it is one of the two Pentagonal Style Forts in Japan, with Goryokaku in Hokkaido. The builder of the castle was Norikata Matsudaira, who was the lord of the Tatsuoka Domain. In fact, there were so many Matsudaira Clans at that time, which were the relatives of the Tokugawa families in the shogunate. The family name “Tokugawa” was only allowed to be used with the few core family members who could be the Shogun. The other Tokugawa’s relatives used “Matsudaira” as their family name which had been their original before the first Shogun, Ieyasu started to use Tokugawa.

The Matsudaira Clans can roughly be categorized into three groups. The first group is those which originated from Ieyasu or other Shogun’s children, such as the Echizen Matsudaira Clan at Fukui Castle and the Aizu Matsudaira Clan at Wakamatsu Castle. They were very reliable to the Shogunate, so they often had large territories and castles. The second group is those which had existed before Ieyasu was born, and are sometimes called the Eighteen Matsudaira Clans. In fact, Ieyasu came from one of them, called the Anjo Matsudaira Clan. They were also certainly Ieyasu’s relatives, but he trusted them less than the first group because they could be a competitor to him. As a result, they often had smaller territories which sometimes weren’t allowed to have their own castles because of the area criterion. The last group is those who didn’t have any blood relation with Ieyasu or other Shoguns, but were allowed to use Matsudaira for special reasons.


Norikata from Matsdaira Clans builds Castle
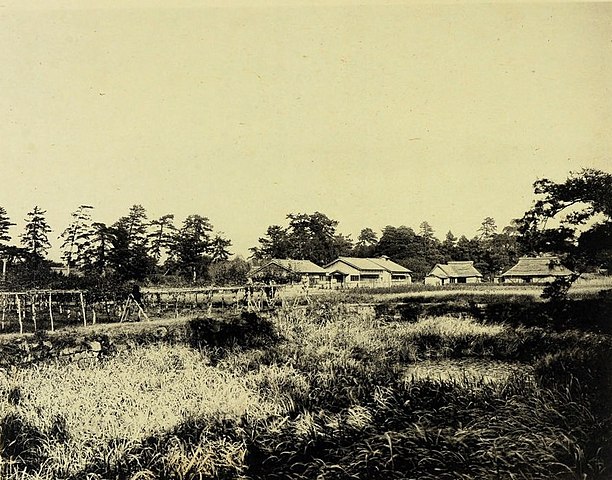
Norikata Matsudaira belonged to the Second group and his clan was also called the Ogyu Matsudaira Clan. Ogyu was the name of their original territory and has been used to identify them among many other Matsudaira Clans. In fact, the clan itself had several branch families because of its long history. Norikata was the lord of the Okutono Domain with an earning of only 16 thousand koku of rice, which meant he was not allowed to have a castle. In addition, his territory was divided into the smaller Okutono in Mikawa Province (now part of Aichi Pref.) and the larger Tatsuoka. His domain had been based in Okutono, so called the Okutono Domain, and the lords had lived in a hall, called the Okutono Camp.

The situation changed after Japan opened the country to several Western countries in 1854. The shogunate relaxed the restrictions for the lords against the threats from these countries. Norikata was an excellent politician and he learned a lot about the Western items. He thought it was a good chance to do something using his knowledge to follow the government’s new policies. One of them was to move his home base to the larger Tatsuoka, and another was to build his own castle, called Tatsuoka Castle.
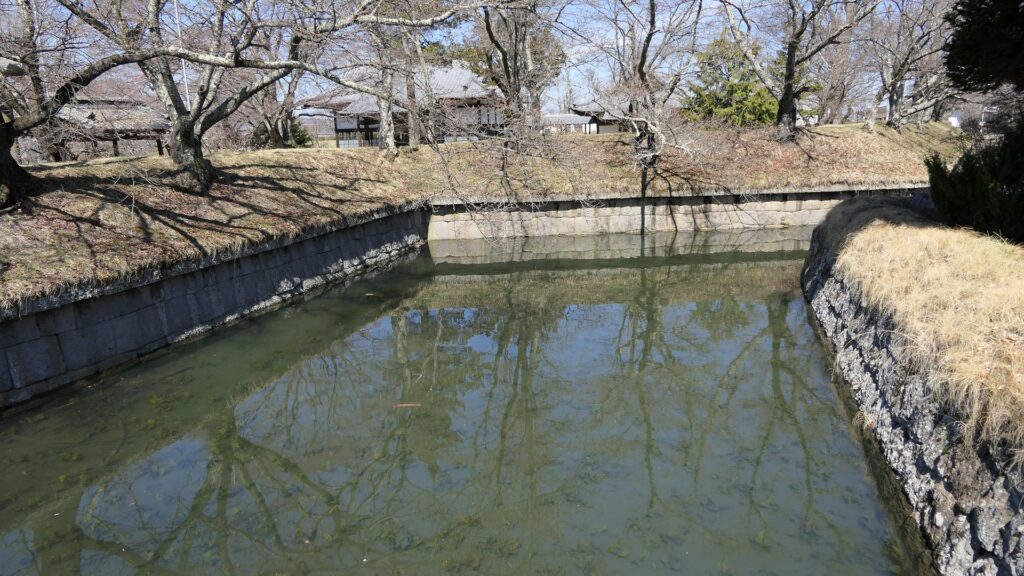
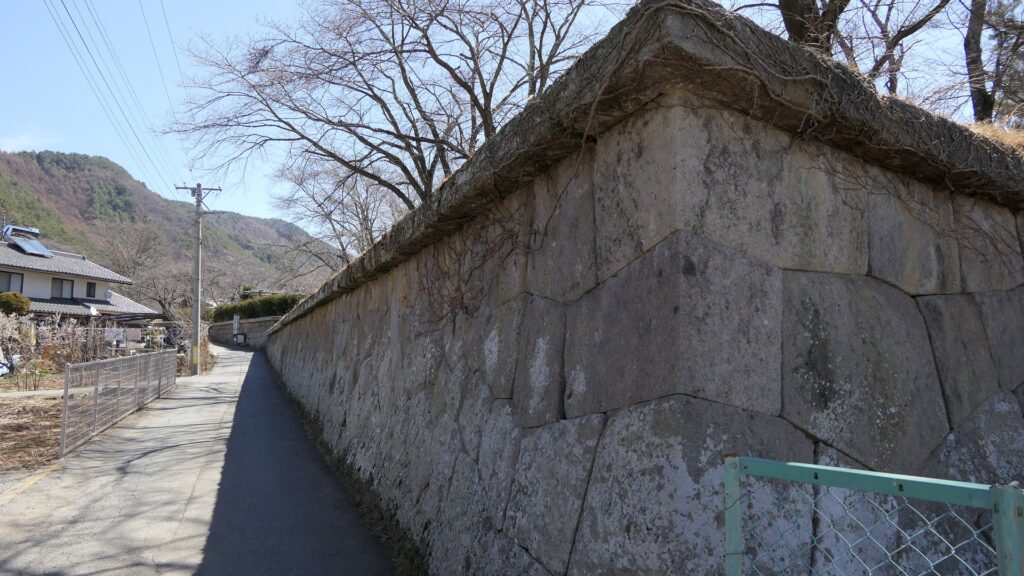
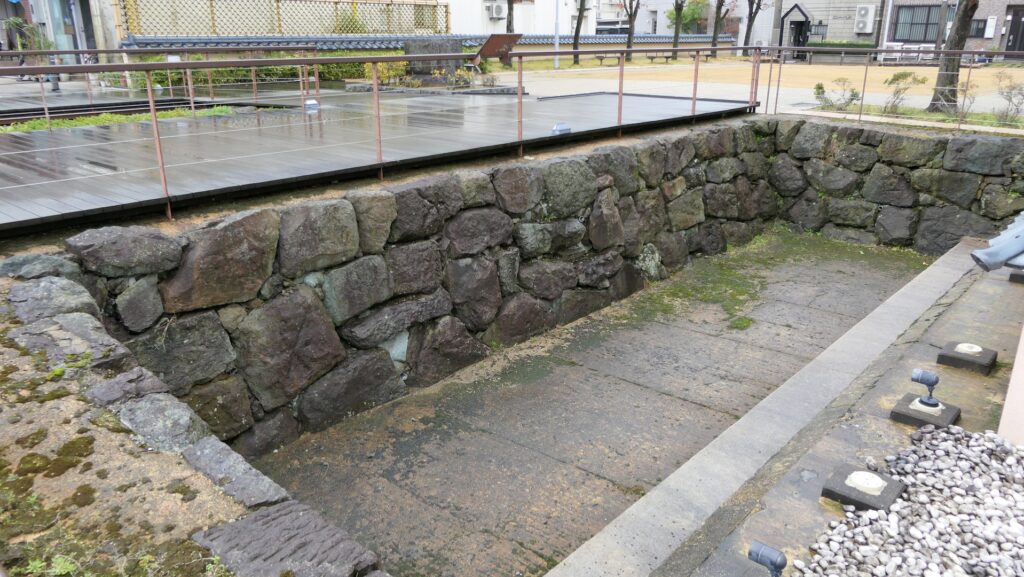
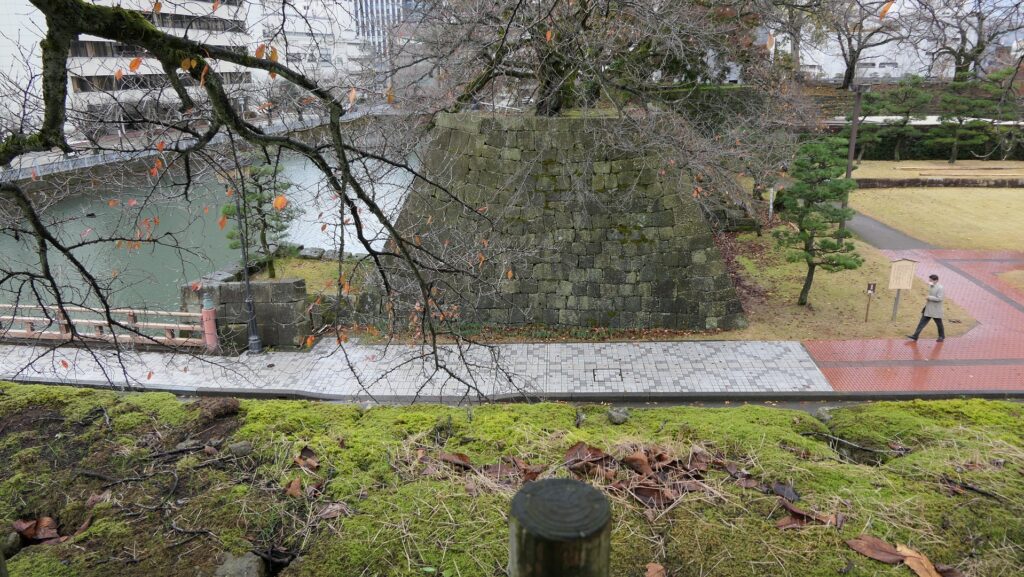
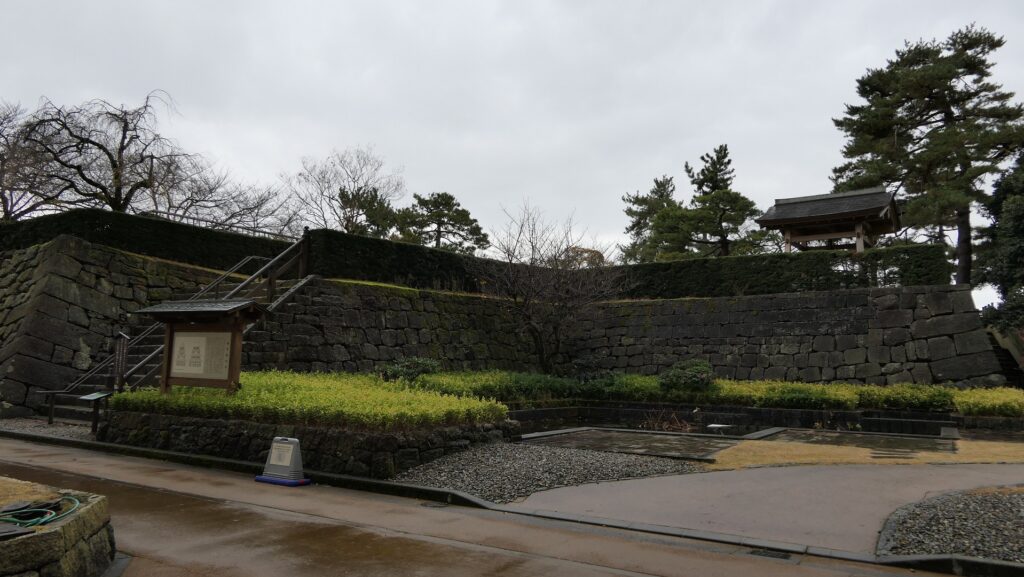
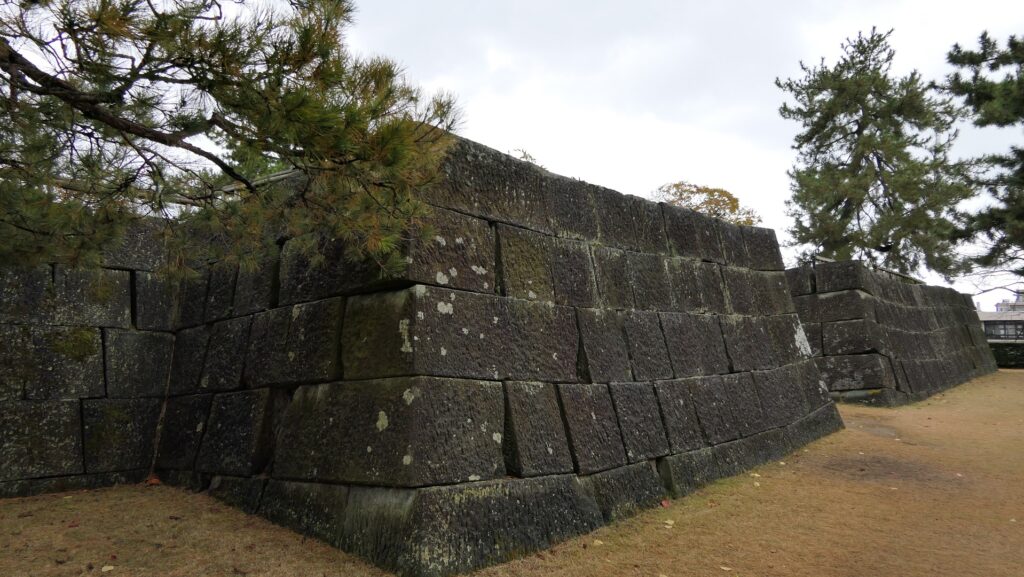
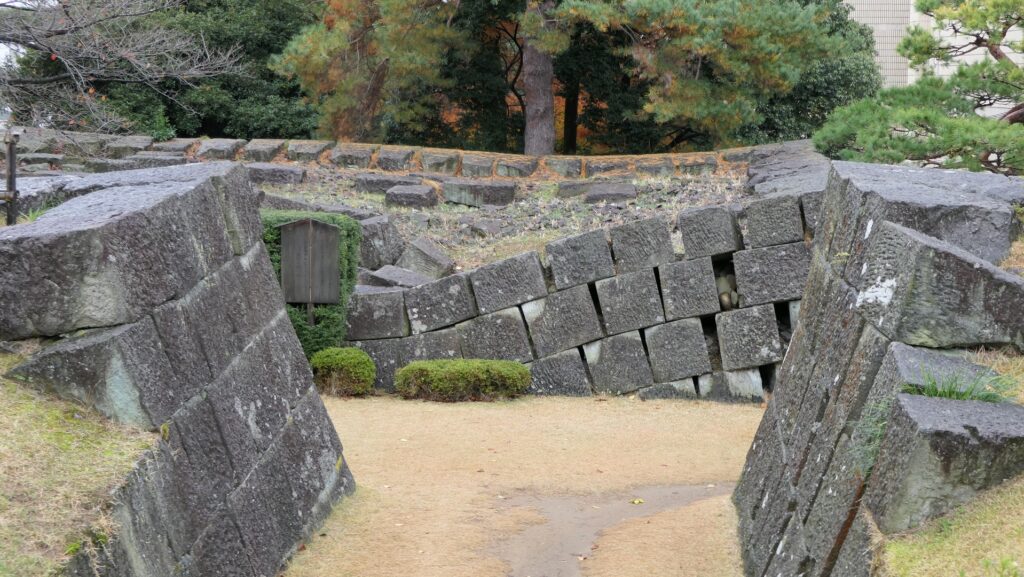
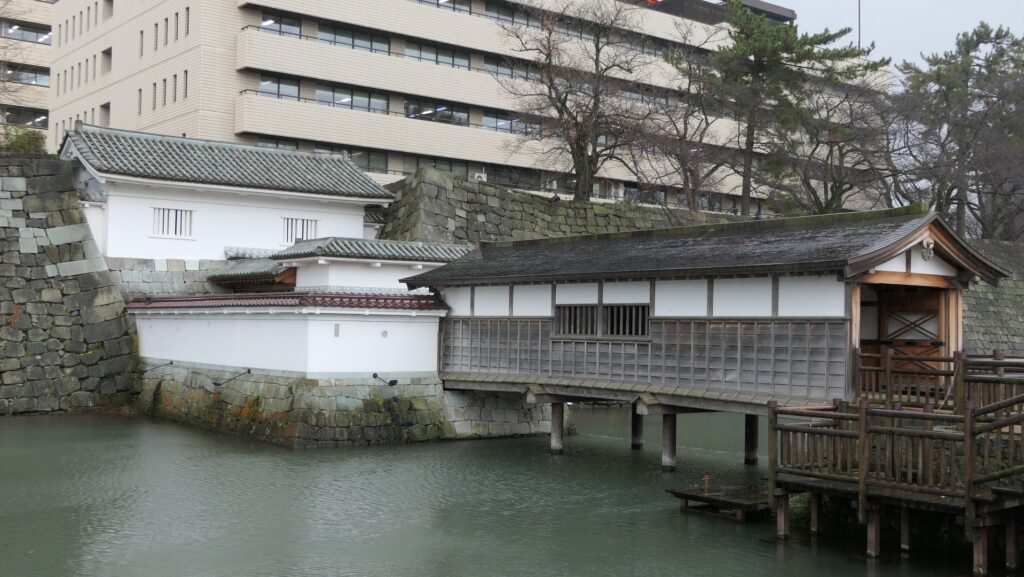
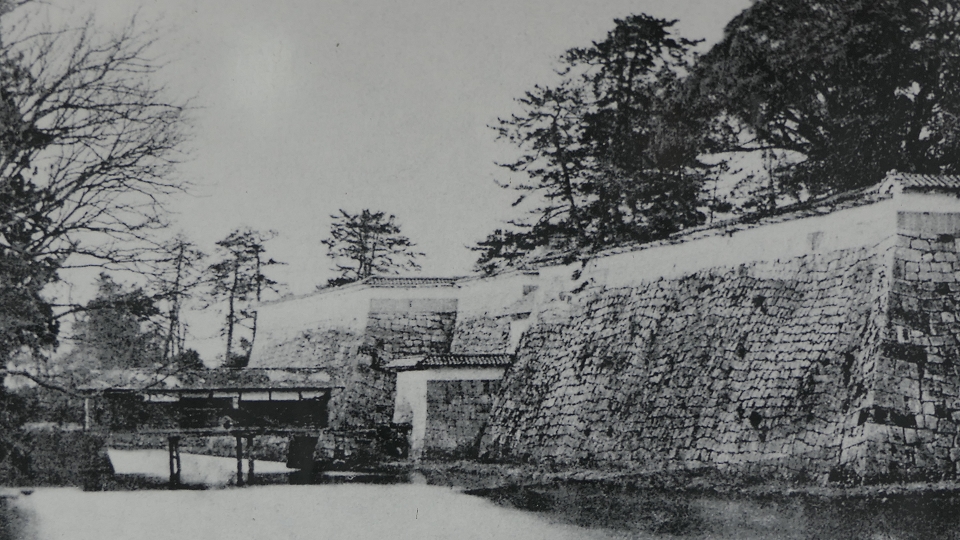
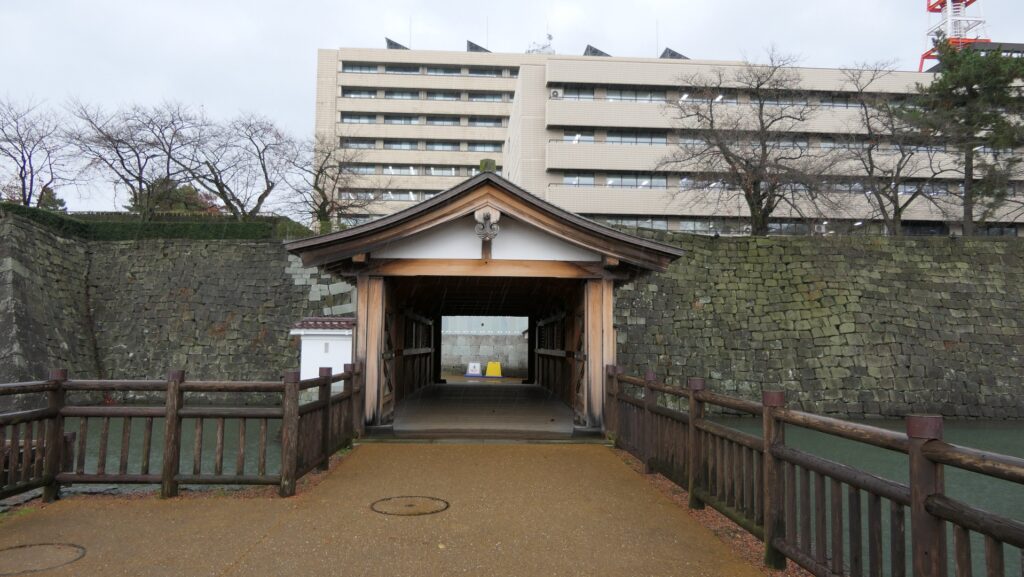
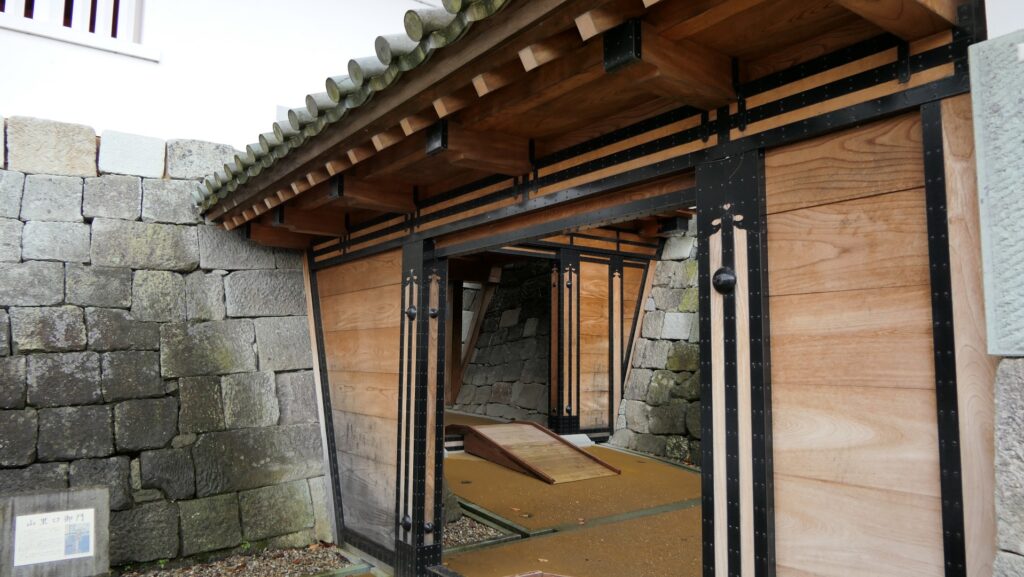
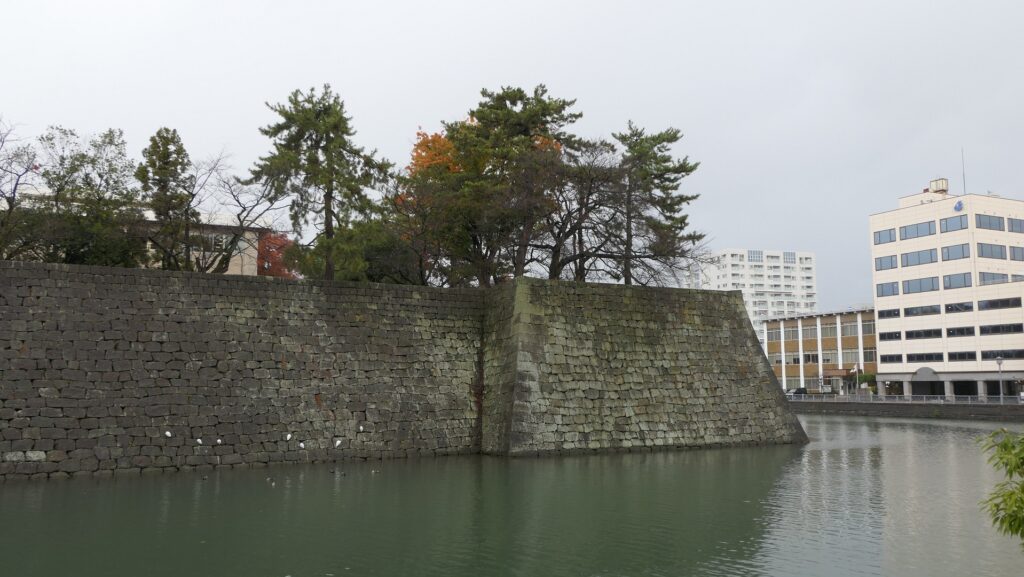
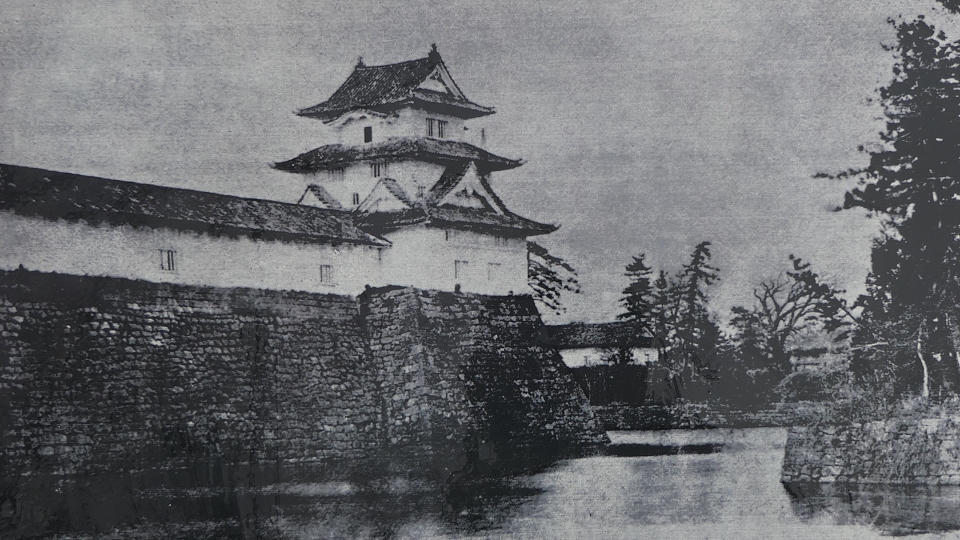
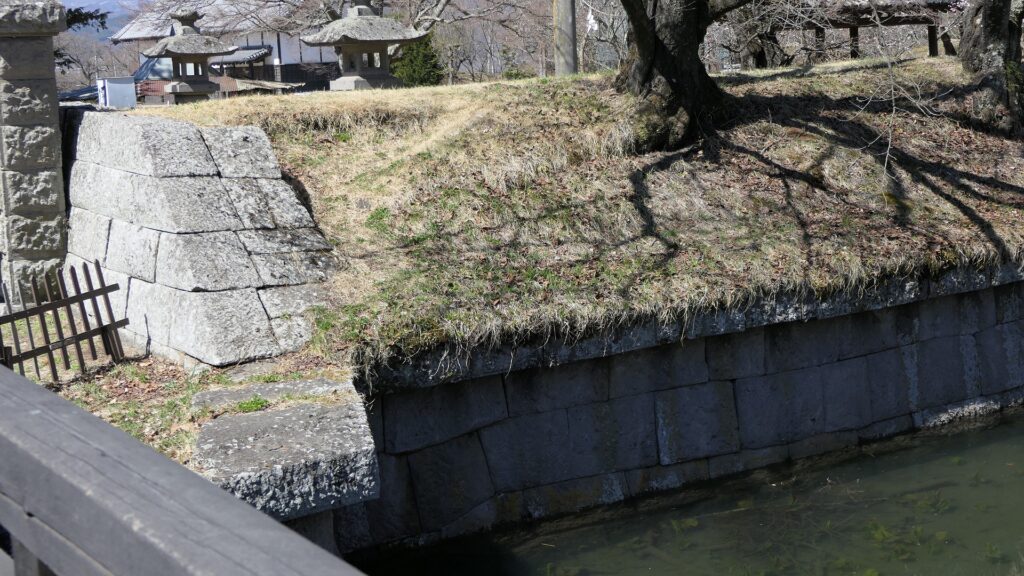
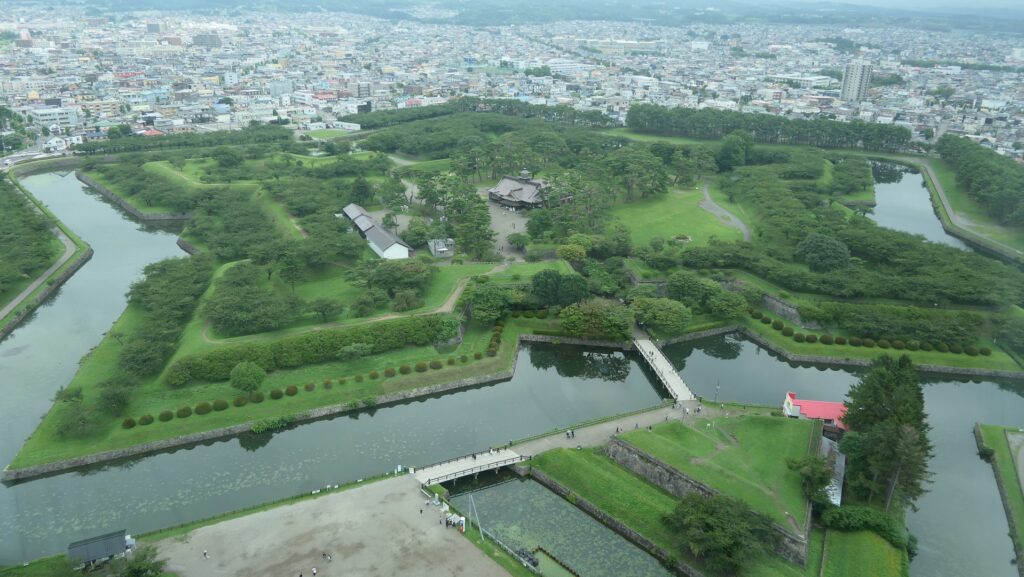
The location of the castleNorikata’s attempts were allowed by the shogunate and the construction of the castle (officially it was still called a camp) started in 1864. The castle was designed to be a European style fort which had five bastions like a star. It came from Norikata’s ideas and was thought to be an effective way to protect it from enemies’ attacks from any directions. The five pointed star shape was all surrounded by advanced stone walls like the Tortoise Shell style and Hanedashi style (in which all the stones in the top row are so layered to prevent enemies from invading). It was expected that water moats were dug all around the castle and canons were placed inside all the bastions. There were the Main Hall for the lord and a parade ground inside. The castle was finally completed in 1866, following the first Pentagonal Style Fort known as Goryokaku in Hokkaido, which was completed back in 1864. Norikata was very pleased to see it, inviting local people to show it, then his domain would be re-considered the Tatsuoka Domain.
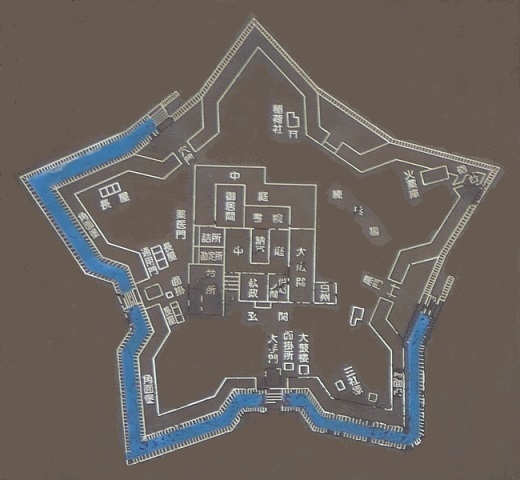


Castle for Experiment
However, in fact, there were some disadvantages for the castle. First, Tatsuoka Castle was much smaller than Goryokaku. It was about 150m long, about half of Goryokaku at about 300m, so in terms of size, it was about one forth the size. The stone walls were 3.5m high and the moats were about 10m wide at most, which would be insufficient even in the Sengoku Period. The moats actually covered two thirds of the perimeter and only one bastion had a cannon. Moreover, the castle could be easily targeted by a cannon from a mountain, at about 500m away from it. What did the facts mean for the castle? Norikata probably meant the castle to not be used for a battle, but for authority of his government and an experiment of new technologies instead. The life of the castle only lasted a few years because of the Meiji Restoration.


































