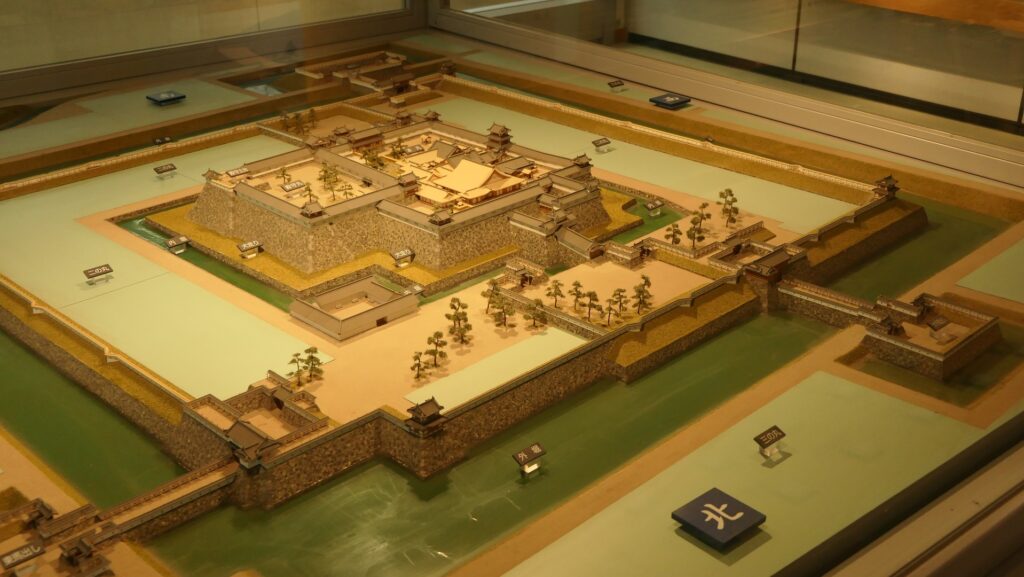
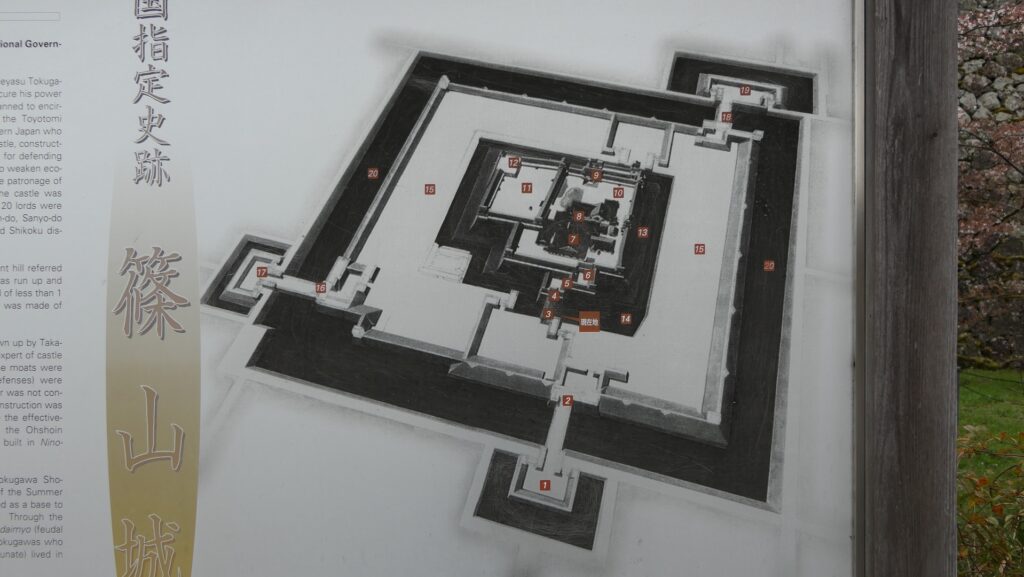
Features
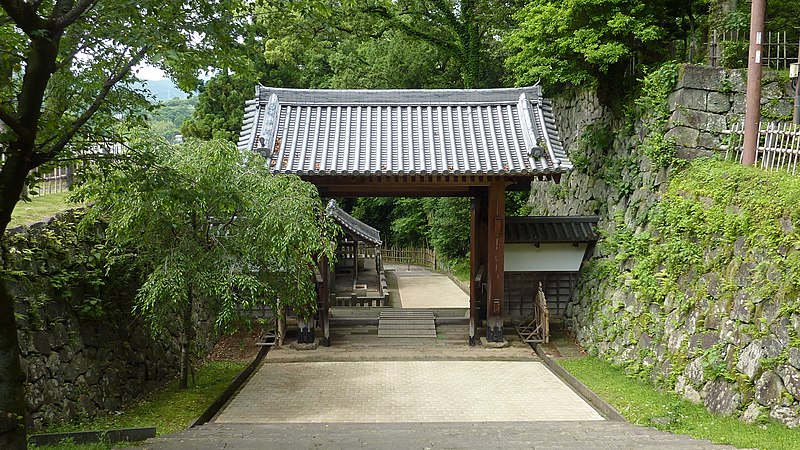
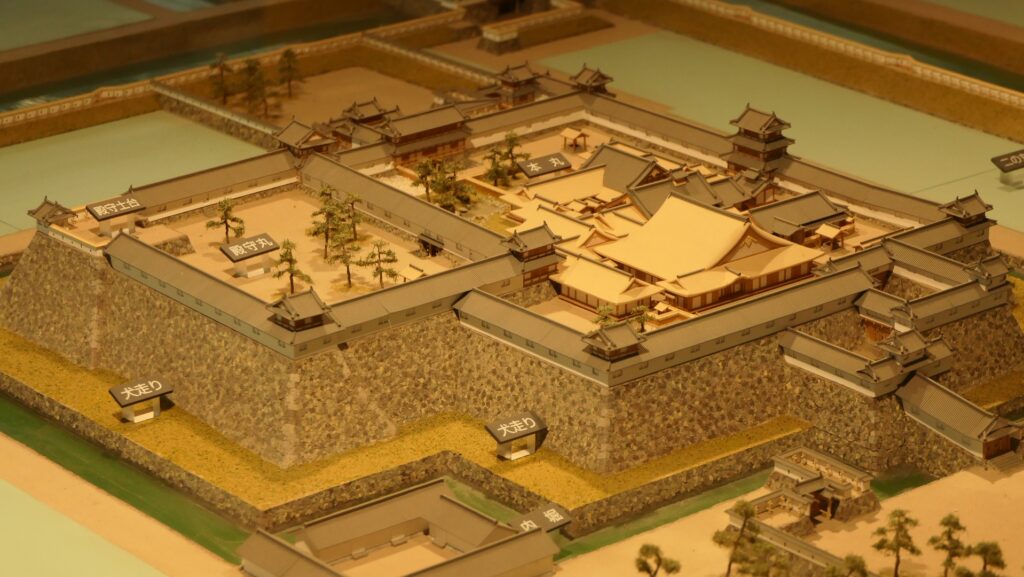
Outside of Main Enclosure
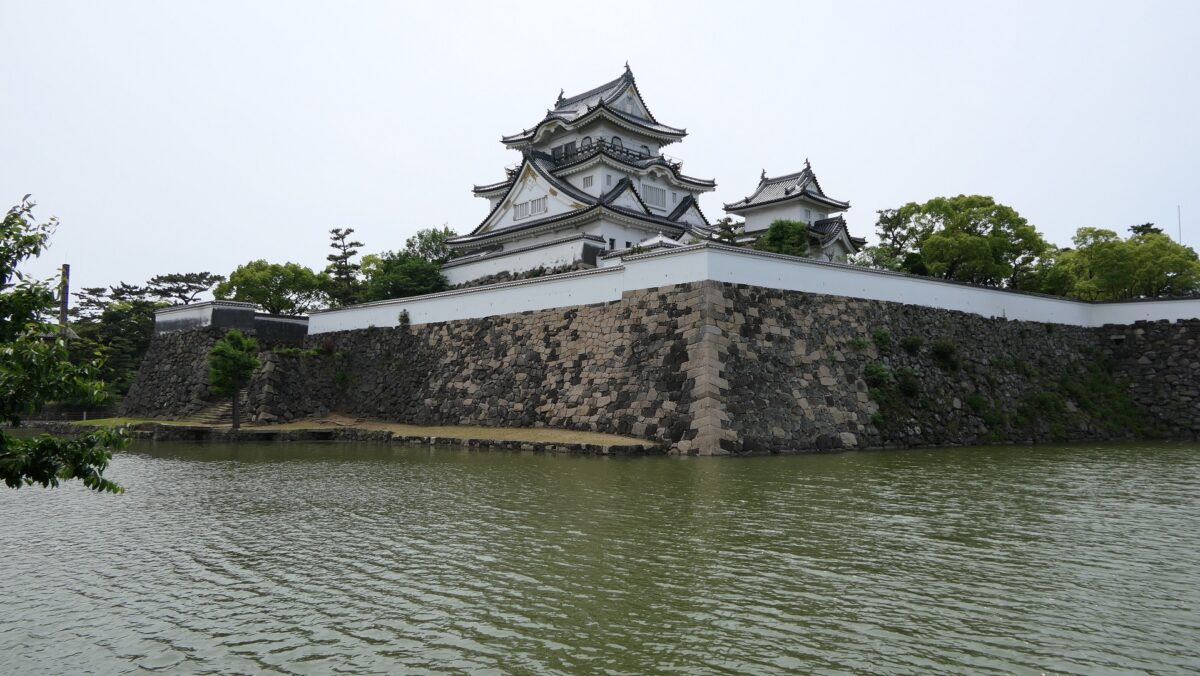
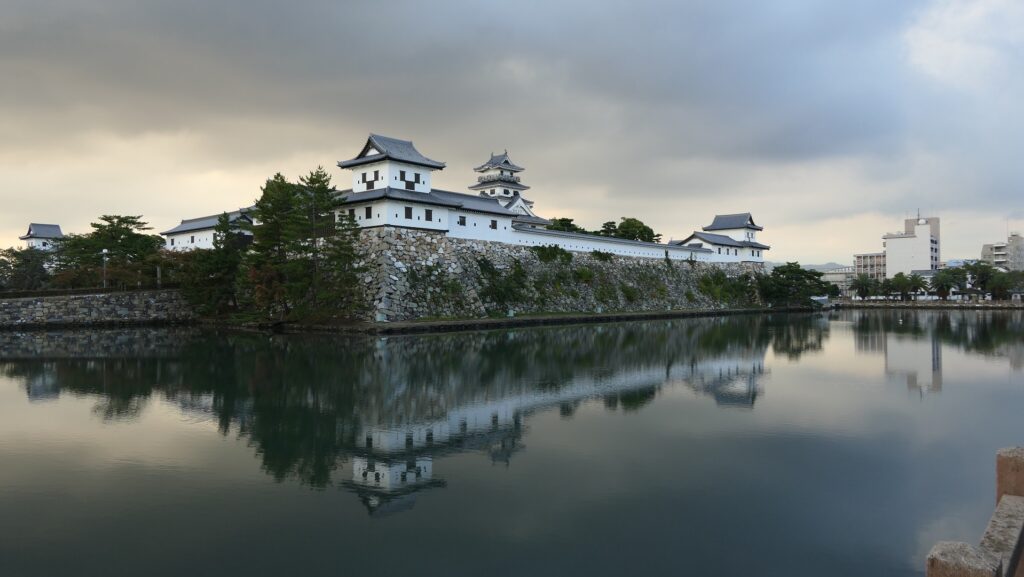
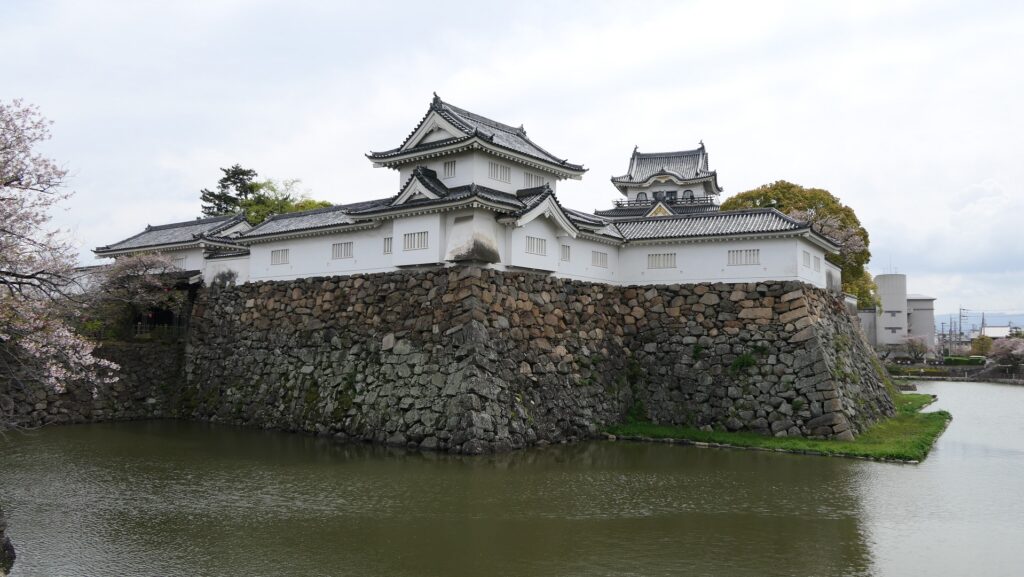
The Main Enclosure is only connected to the Second Enclosure by the earthen bridge which is the same as the past. It looks like a castle island floating on the moat which must have had a defensive design.
The aerial photo around the castle
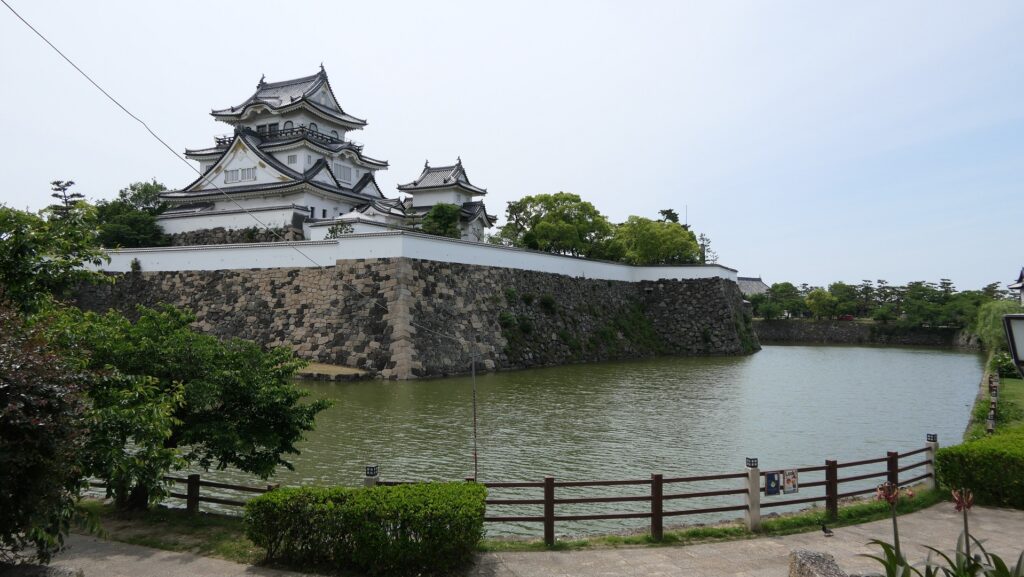

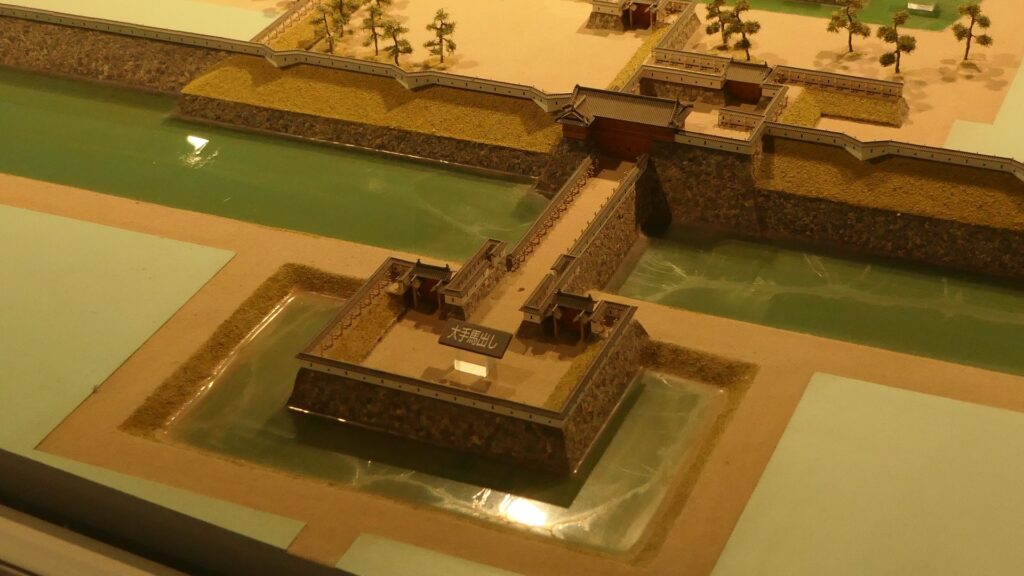
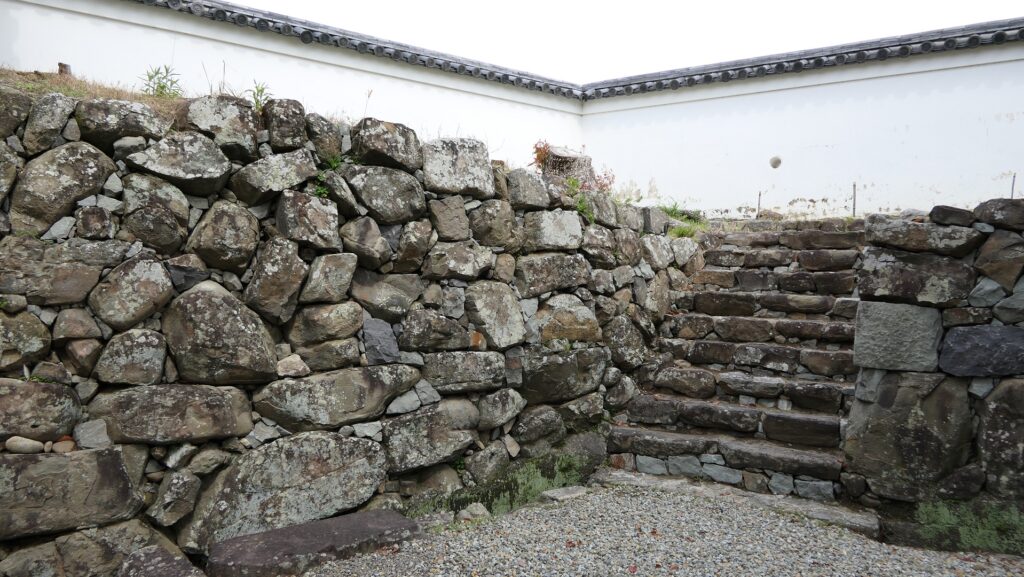
However, if you go around the back side, you will find its back entrance ruins with stone steps, where a bridge to the outside was built. The bridge can not be seen in the drawing of the castle submitted to the shogunate. The reason for it could be that it was built after the drawing had been submitted or it was removed from the drawing intentionally.
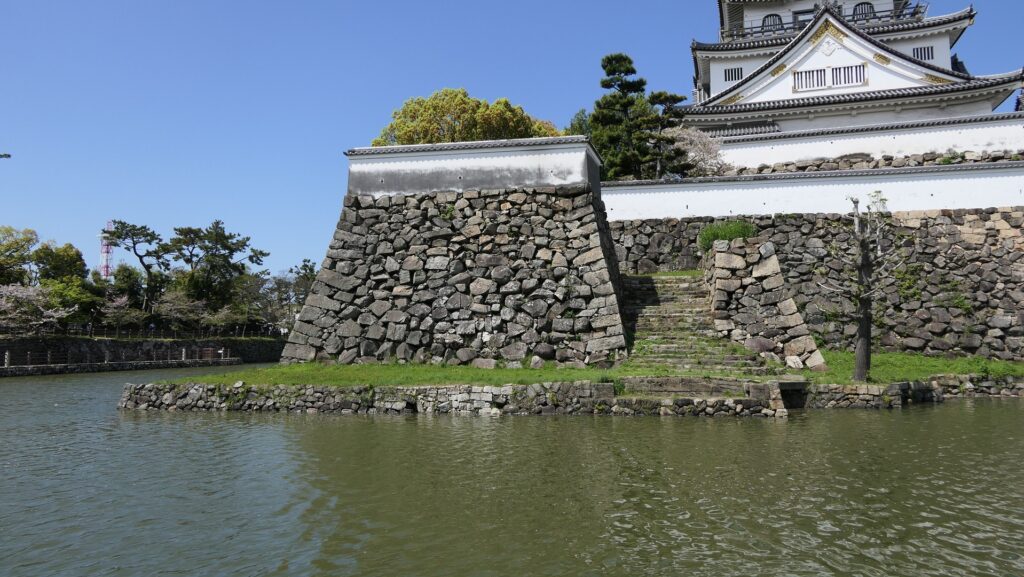

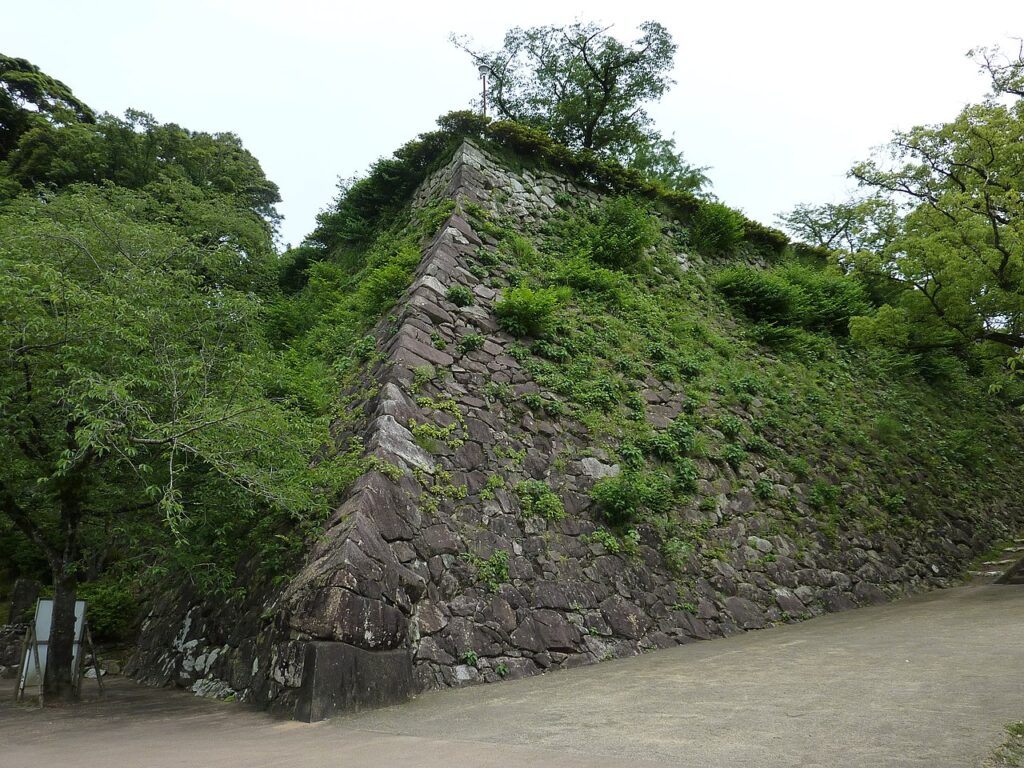
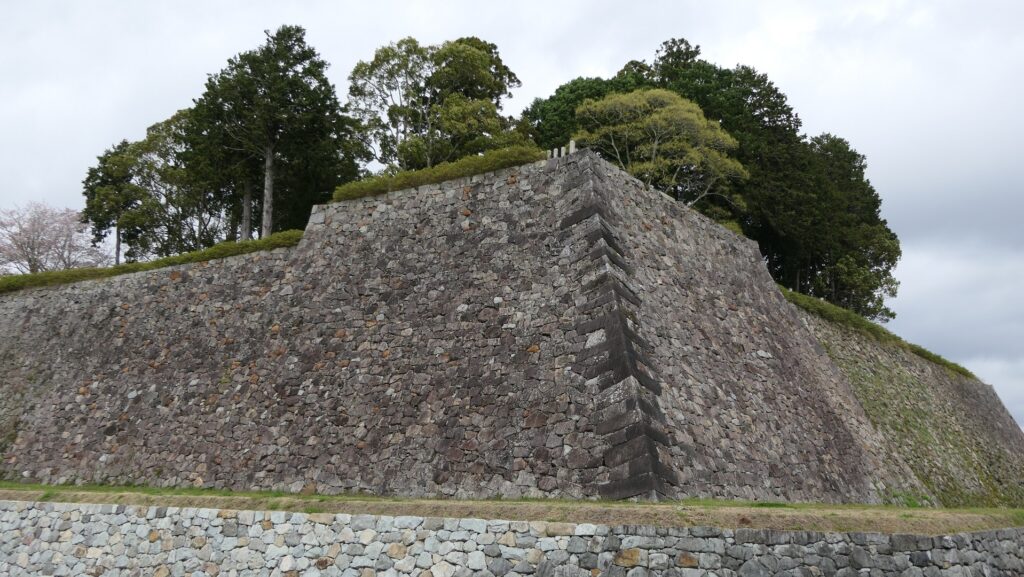
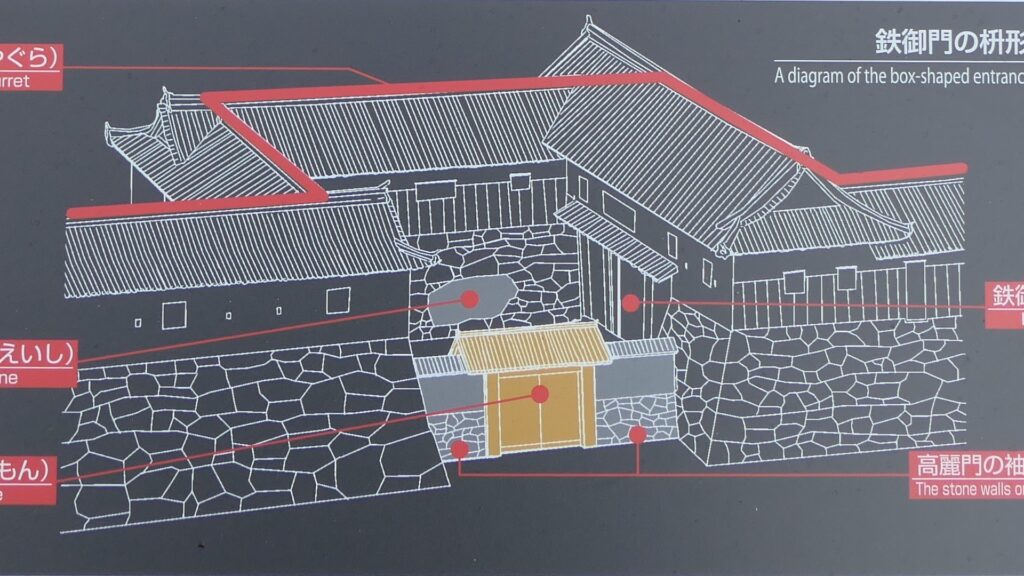
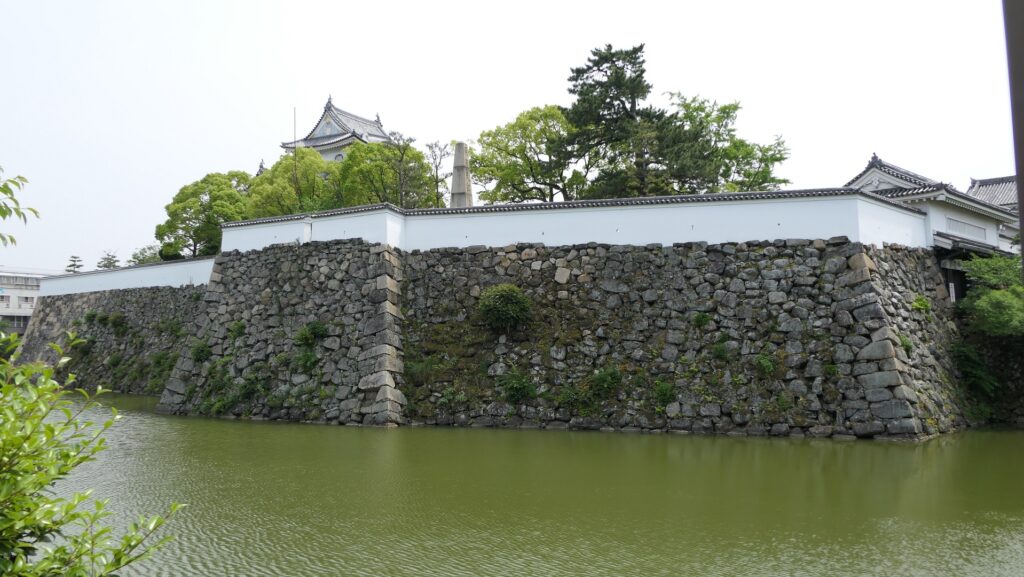
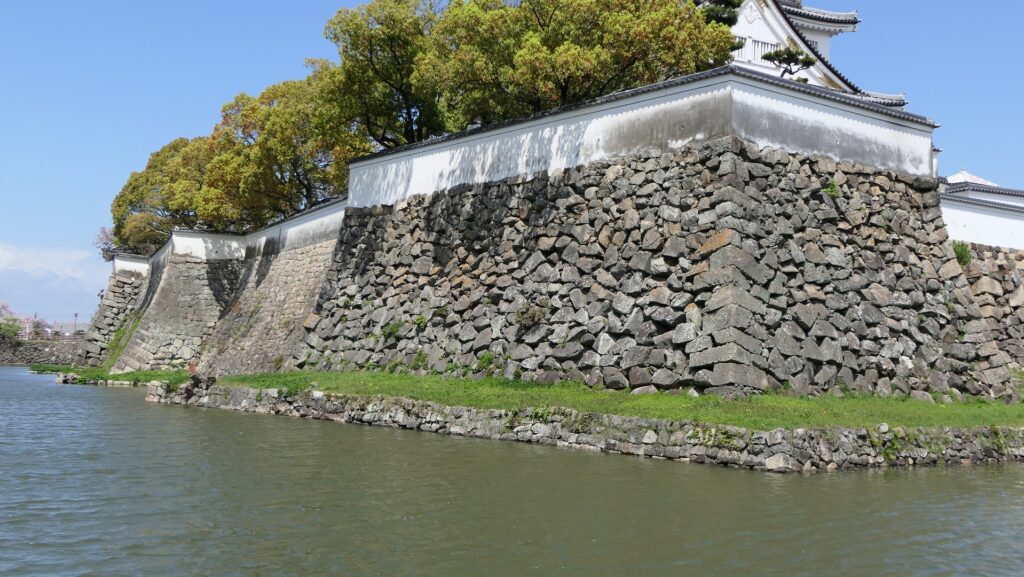
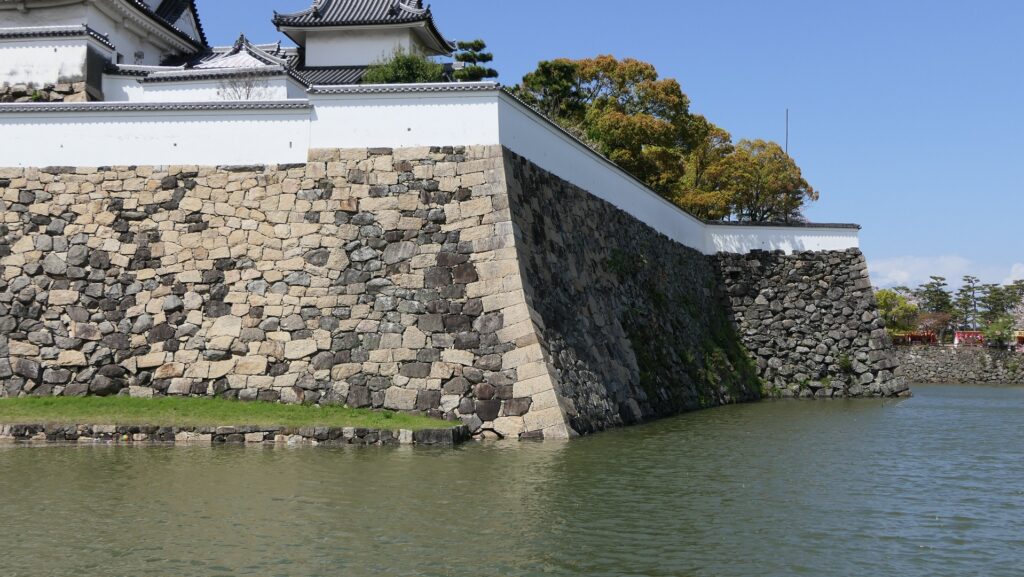
The high stone walls surrounding it also look technical as they are curved elaborately to counterattack the enemies’ sides. They also use the lips as their base which is a rare case in Japanese castles. Some historians think that the reason may be to support the sandstones used for the walls which are weaker than the other types of stones. That’s why the stone walls were partially repaired in the present time, using granite to make them durable.



Inside of Main Enclosure
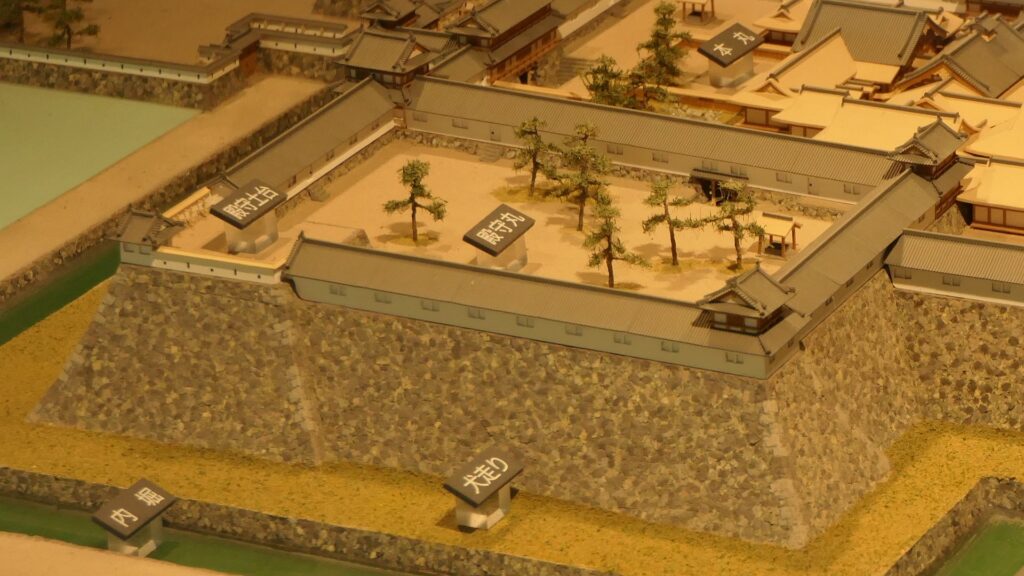
The inside of the Main Enclosure has the reconstructed Main Tower, a gate, a corner turret and white walls. They have different designs from the original ones compared with those in the drawing. For example, the current Main Tower has three levels with many decorations while the original one had five levels with a simple roofing. In case like the current Main Tower of Kishiwada Castle, which was rebuilt but has a different design, should be called “reconstructed”. The enclosure also has a modern Japanese dry garden, called Hachijin-no-Niwa or the Garden of Eight Battle Formation, which was built in the same period as the current Main Tower and was designated as a National Scenic Beauty in 2014. The builders might also have created the Main Tower freely without its original design as a modern building.
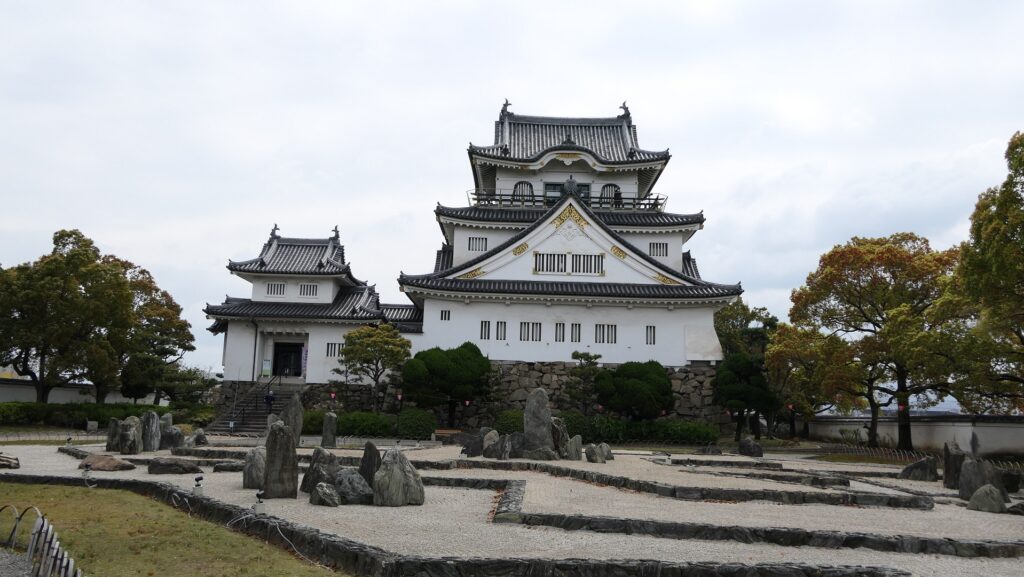
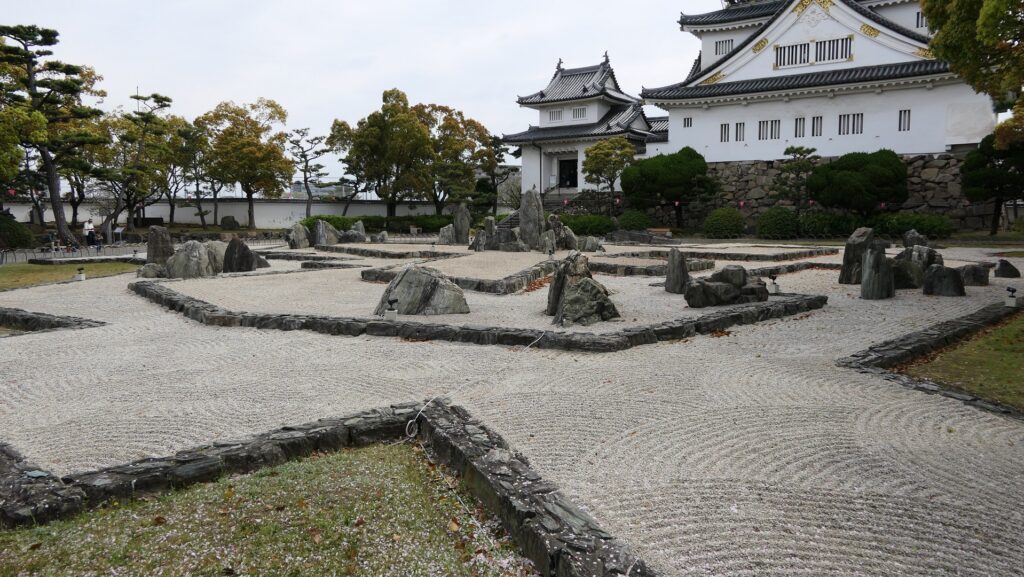



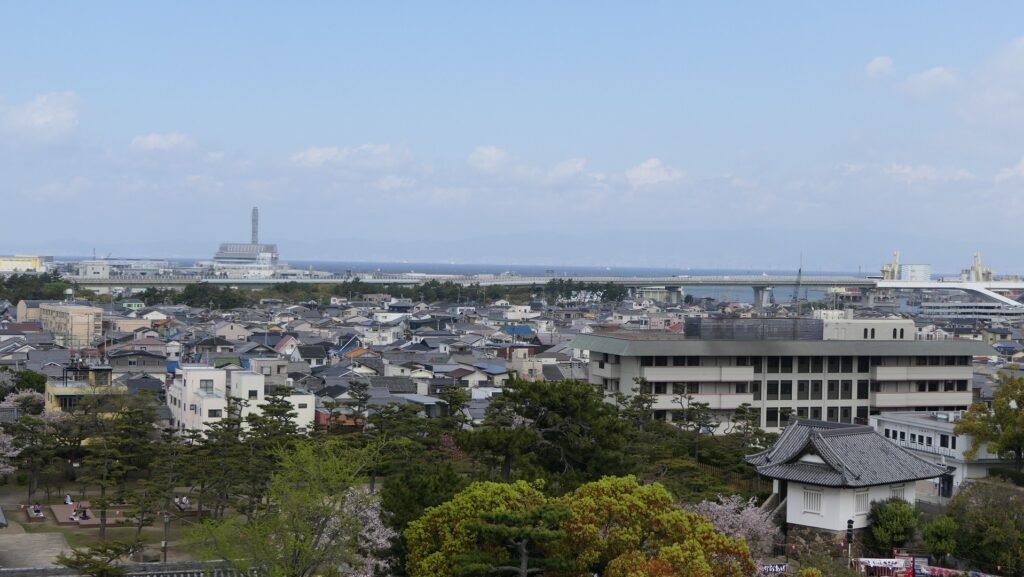
The tower is used as a historical museum inside and an observation platform on the top floor. The floor has a good viewing spot where you can enjoy the scenery of the area around including Osaka Bay. However, you can’t see anything on the outside from the enclosure except for the platform due to the high white walls on the top of the stone walls.


Later History
After the Meiji Restoration, Kishiwada Castle was abandoned and all the castle buildings were demolished. The castle land excluding the Main and Second Enclosures was turned into the city area. There was probably no other way to use it, other than modernizing the city of Kishiwada. After a long time, people in Kishiwada wanted to rebuild the Main Tower of the castle though they needed donations for it. As a result, it was finally completed in 1954 as the three-level Main Tower, but actually a modern concrete building has become a symbol of the city. Some people had argued that it should have been a five-level wooden one which was the same as the original tower, but there was a budget problem and the former lord, the Okabe Clan supported the original reconstruction plan. Kishiwada City is currently struggling to consider the earthquake-resistance measures of the reconstructed Main Tower due to its old age and the stricter regulations than before. It is also continuing to repair the remaining stone walls by replacing collapsed sandstones with new granite stones.

My Impression
I think the more you visit the current Kishiwada Castle, the more you will be interested in its history. The castle started out as a small one facing the sea, and it developed into the only one in Izumi Province, and finally became the symbol of the city. However, the only thing I would ask the city to improve on the castle would be to open the views from the Main and Second Enclosures. Currently, visitors can’t see the views below from them because of the walls or hedges probably for the safety reasons. I think the city will be able to replace them with other fences which can provide the views so that visitors can fully understand how the castle was developed more.


That’s all. Thank you.
Back to “Kishiwada Castle Part1”
Back to “Kishiwada Castle Part2”