Location and History
Yoshitaka works hard for Unification of Japan with Hideyoshi Toyotomi
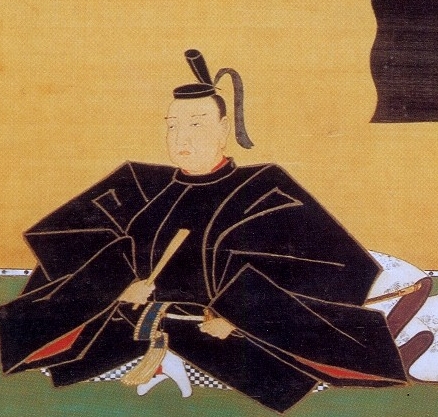
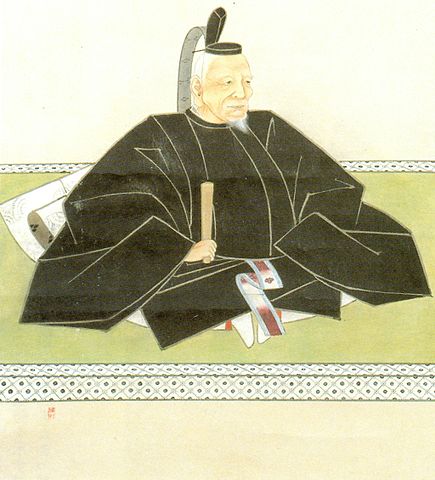
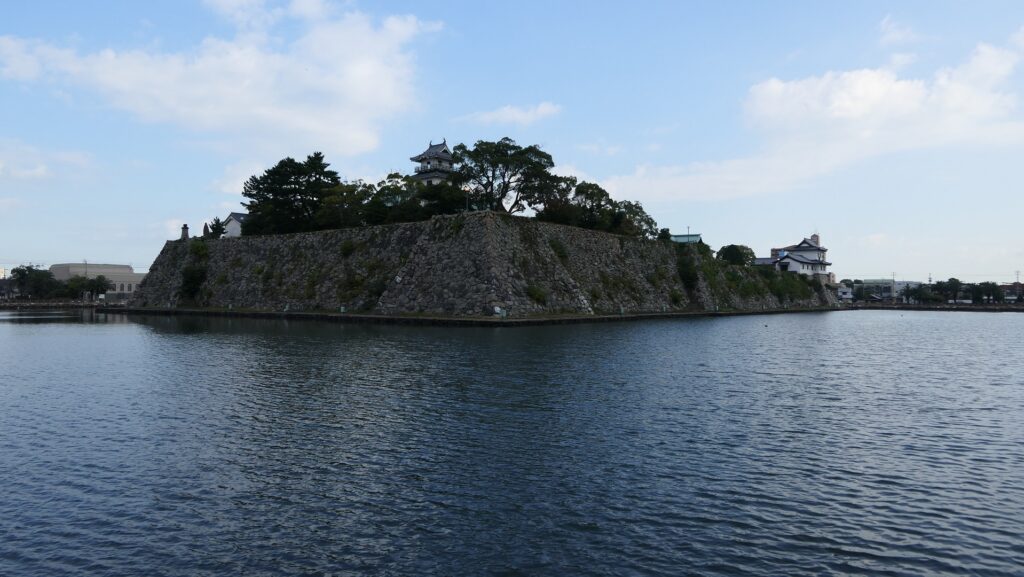
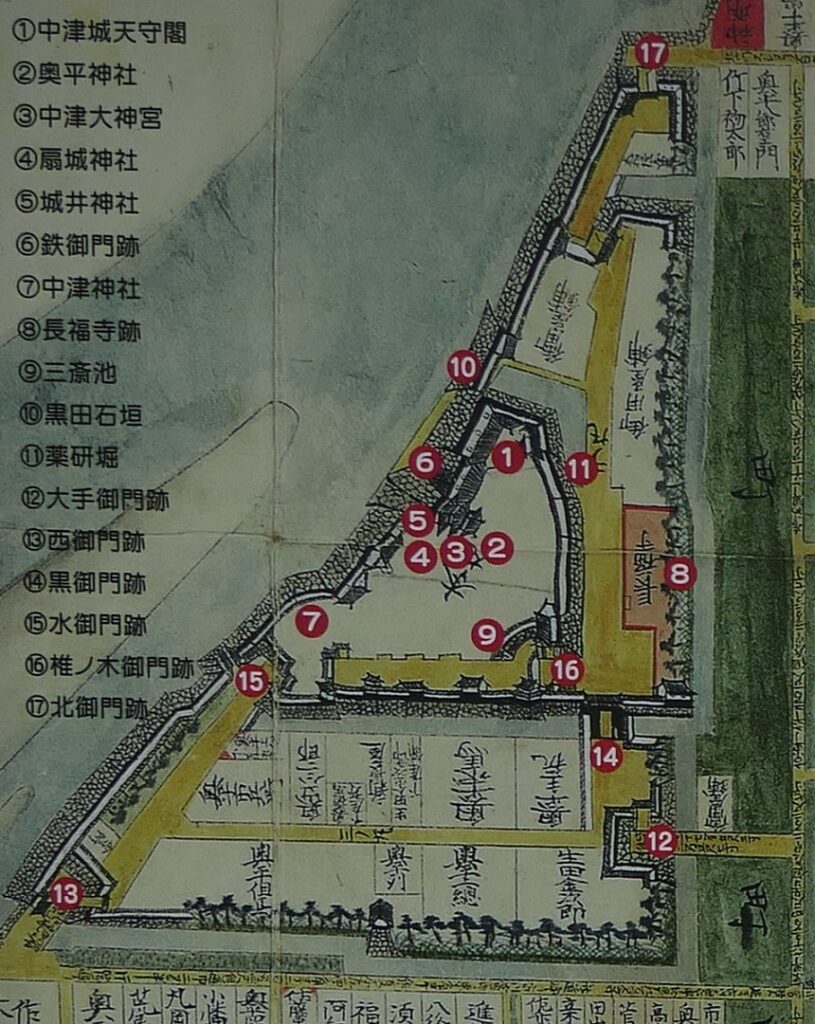
Nakatsu Castle was located in Buzen Province which is equivalent to the eastern part of Fukuoka Prefecture and the northwestern part of Oita Prefecture. The province was also the northernmost part of Kyushu Island which was connected with the Main Island of Japan through Kanmon Straits. The castle was built on a delta in the estuary of Nakatsu River flowing into Buzen Sea, in the central part of the province, by Yoshitaka Kuroda (he is more often known as Kanbe Kuroda or Josui Kuroda after he retired). He is known to many Japanese people as Gunshi or the military strategist of Hideyoshi Toyotomi who was the ruler of Japan in the end of the 16th Century. However, the degree was given by later people like historians, critics, and novelists, he was actually a working general and a secretary under Hideyoshi.
The range of Buzen Province and the location of the castle
Yoshitaka was originally a senior vassal of a local lord, the Kodera Clan in Harima Province (now the southern part of Hyogo Province). When Hideyoshi invaded the Chugoku Region, which included the province, as a general under Nobunaga Oda, Yoshitaka supported Hideyoshi by providing his own Himeji Castle to Hideyoshi. After that, he did his best to help complete the unification of Japan by Hideyoshi. A famous story about him in the early stage is that he was confined for about one and a half years in Arioka Castle when he visited to persuade Murashige Araki who had decided to be against Nobunaga. While Hideyoshi had become the ruler after Nobunaga was killed by Mitsuhide Akechi, Yoshitaka worked at Hideyoshi’s beck and call. For example, he negotiated with the Mori Clan in the Chugoku Region to divide territories into each other without battles. When the invasion of Kyushu happened in 1587, Yoshitaka set the stage for Hideyoshi’s arrival by fighting against local lords or making them surrender.


Yoshitaka builds Castle in his territory in Bungo Province
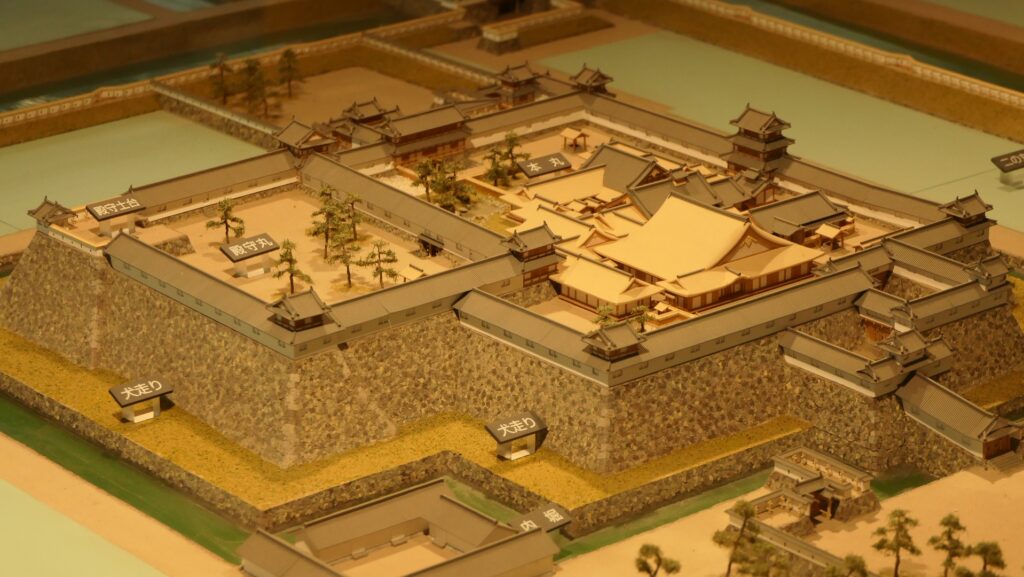
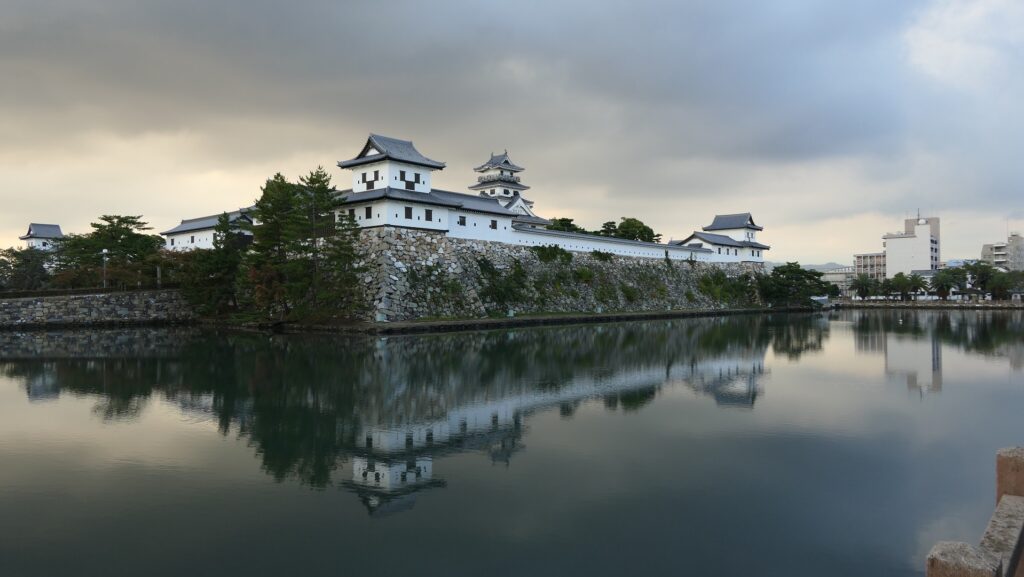
After the invasion, Yoshitaka was given part of Buzen Province by Hideyoshi. His territory was small for his contribution so far, because, it has been said it was because Hideyoshi feared Yoshitaka’s potential power. However, some suggest that it could have been because Yoshitaka was a Christian which Hideyoshi had banned from spreading just after the invasion. Yoshitaka at first lived in Umagadake Castle, one of mountain castles which were common then, but launched the construction of Nakatsu Castle in 1588, which would be considered one of the Three Great Sea Castles in Japan, together with Imabari and Takamatsu Castles. Its location was decided by Yoshitaka for the convenience of the government and transportation, but probably also instructed by Hideyoshi. Hideyoshi’s other retainers also built sea castles in their new territories in the Kyushu Region during the same period, such as Kokura, Oita-Funai, and Yatsushiro Castles, which were used for the preparation for the invasion of Korea planned by Hideyoshi as well.
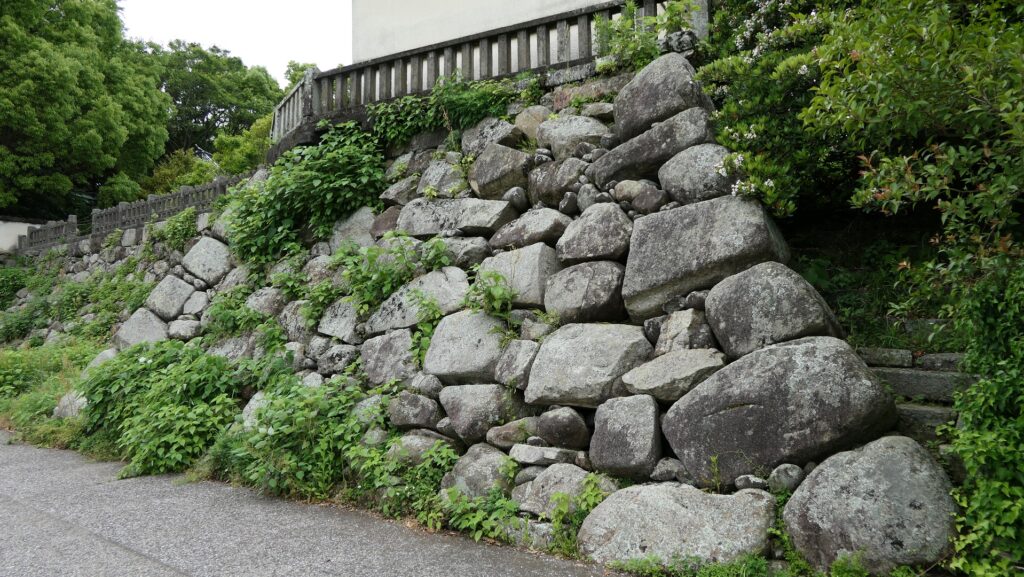
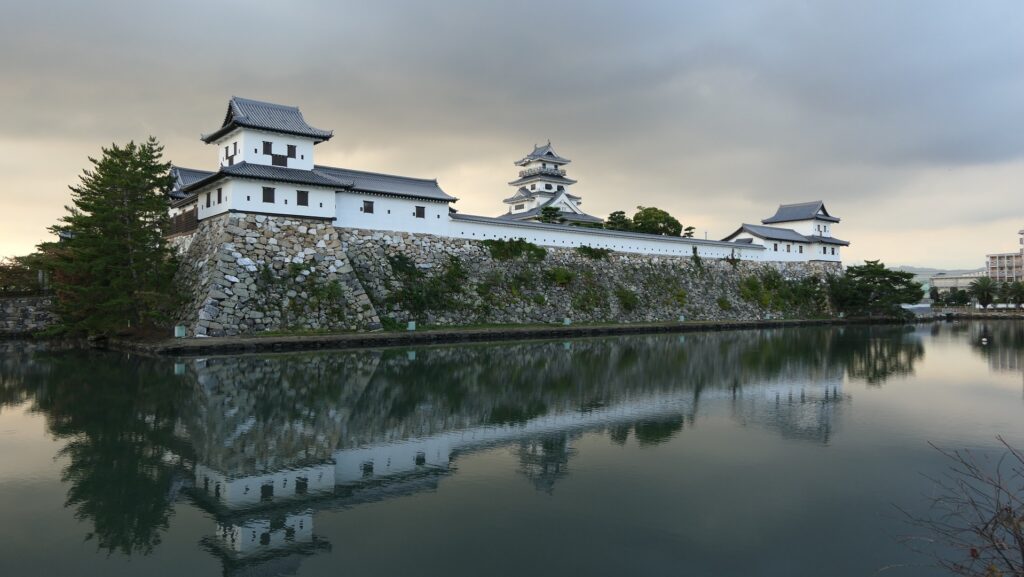
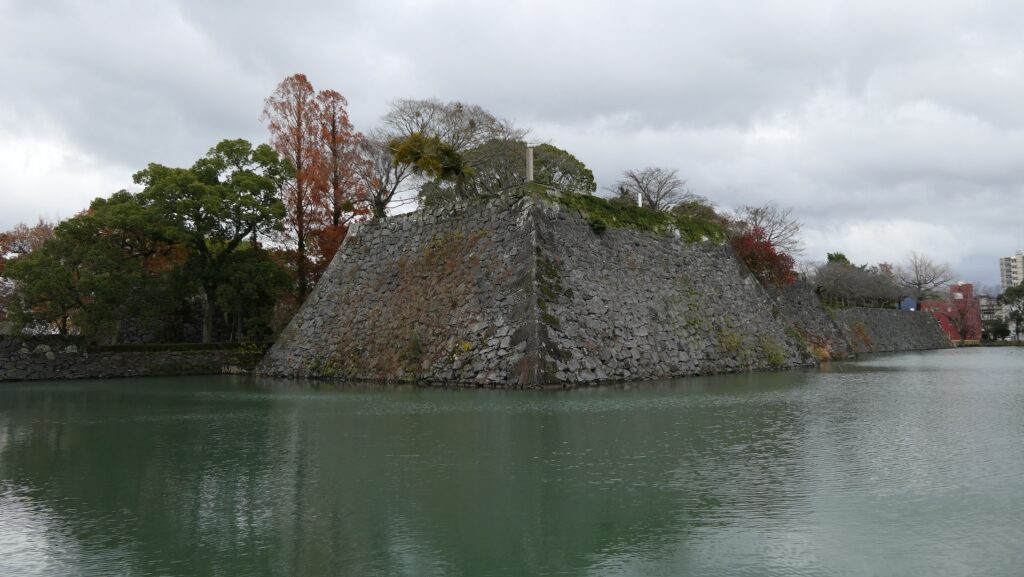




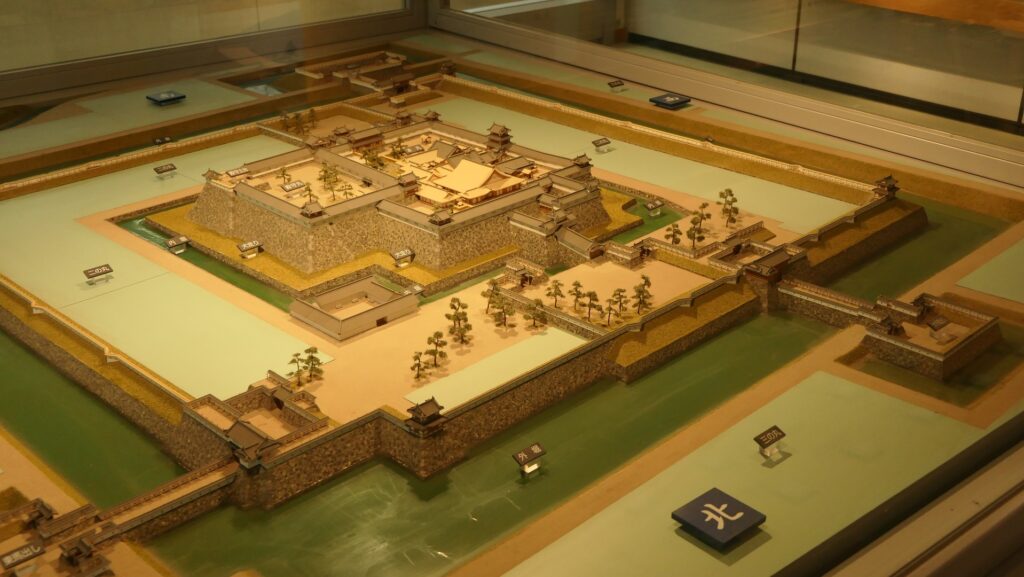
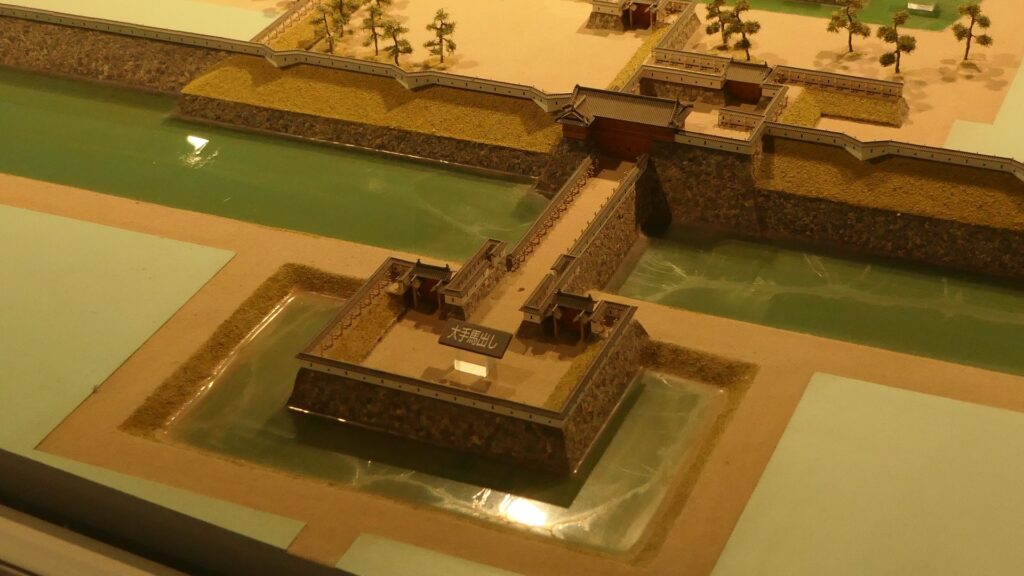
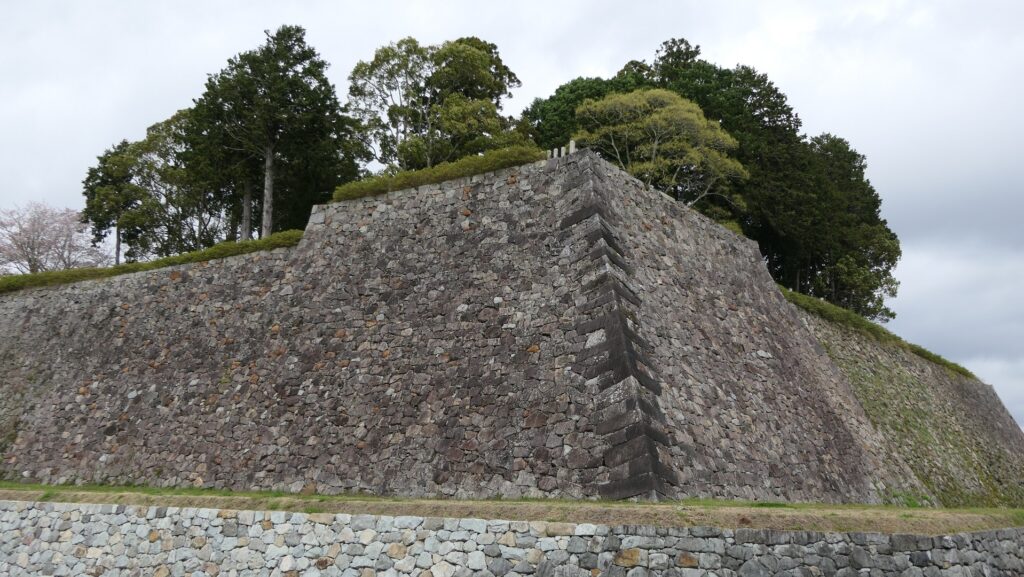
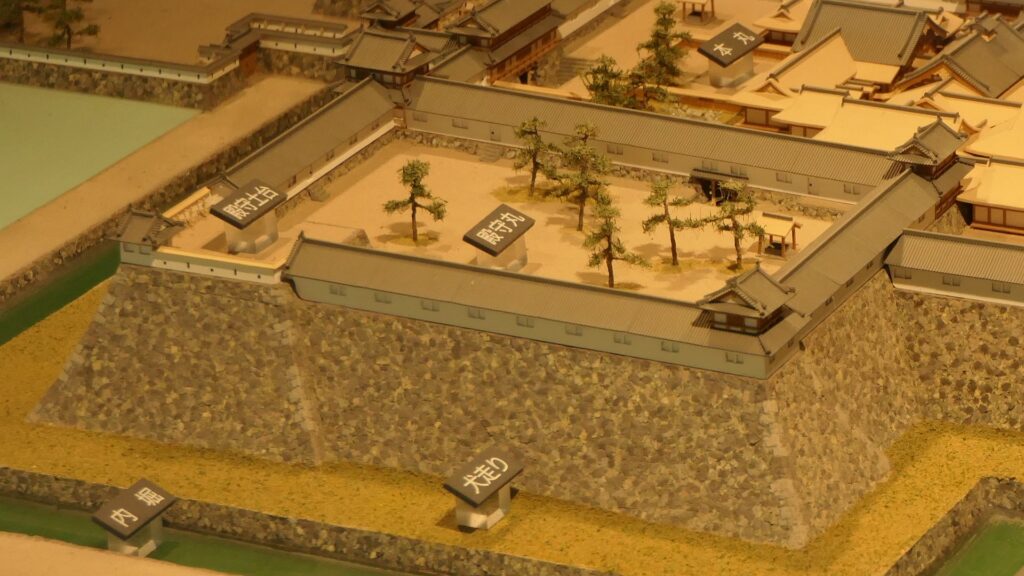
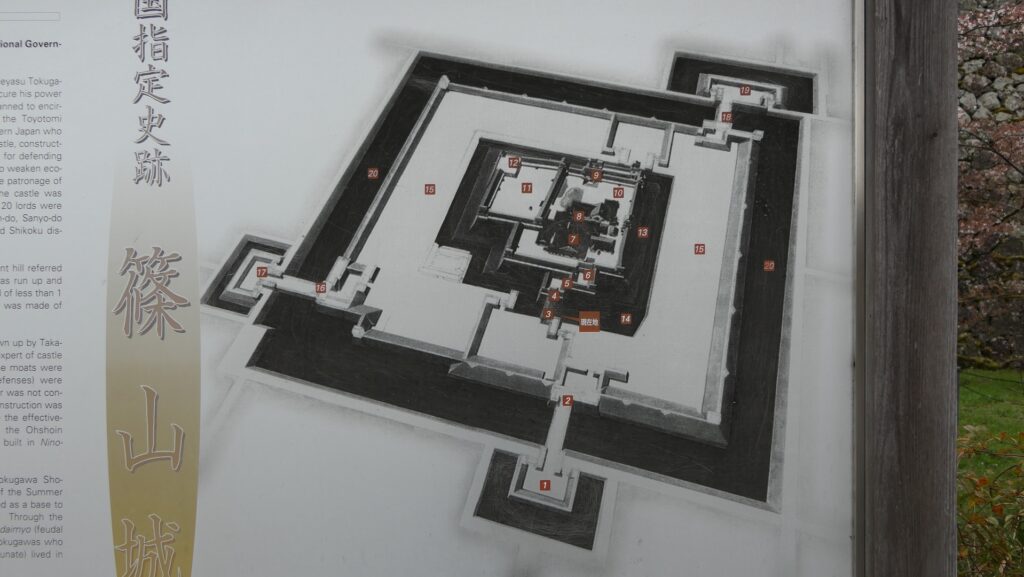
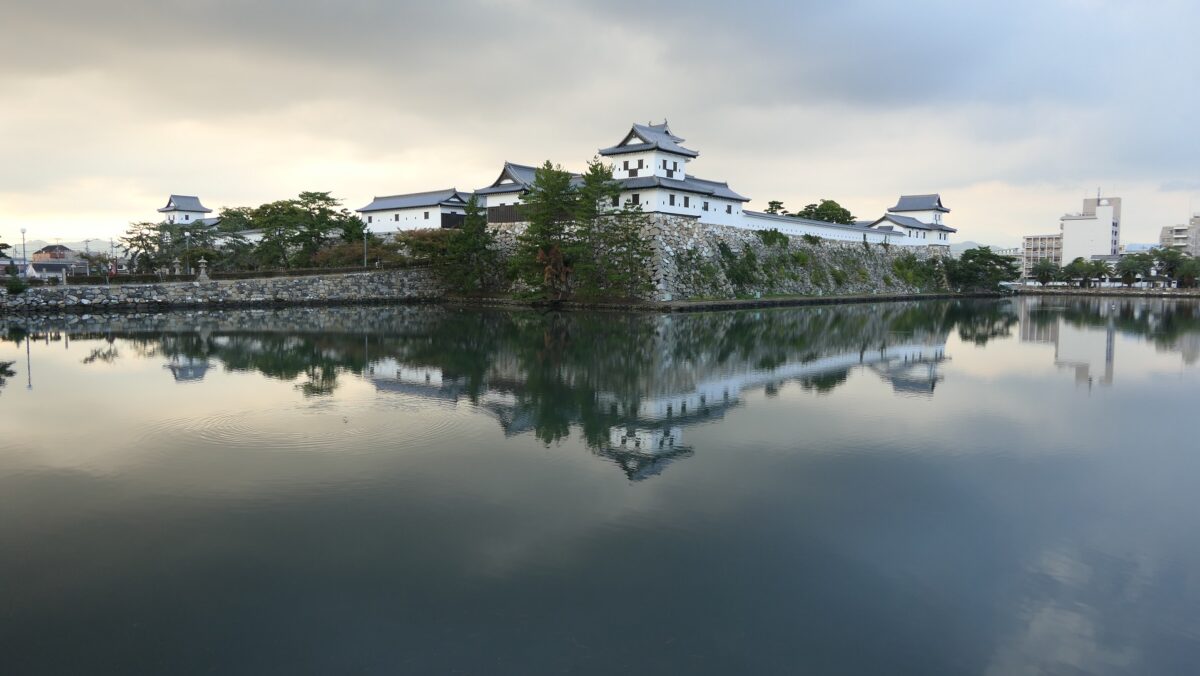
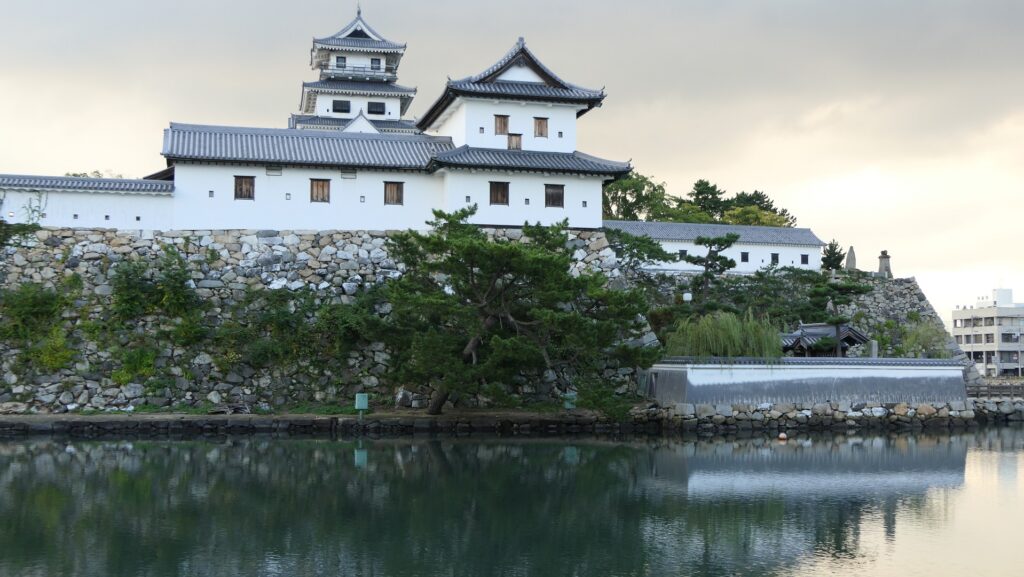
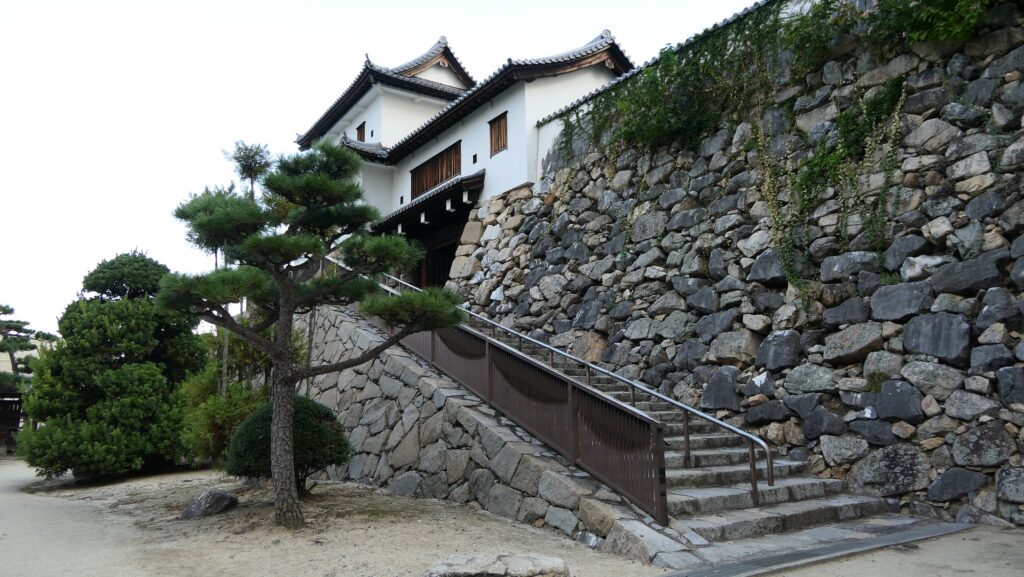
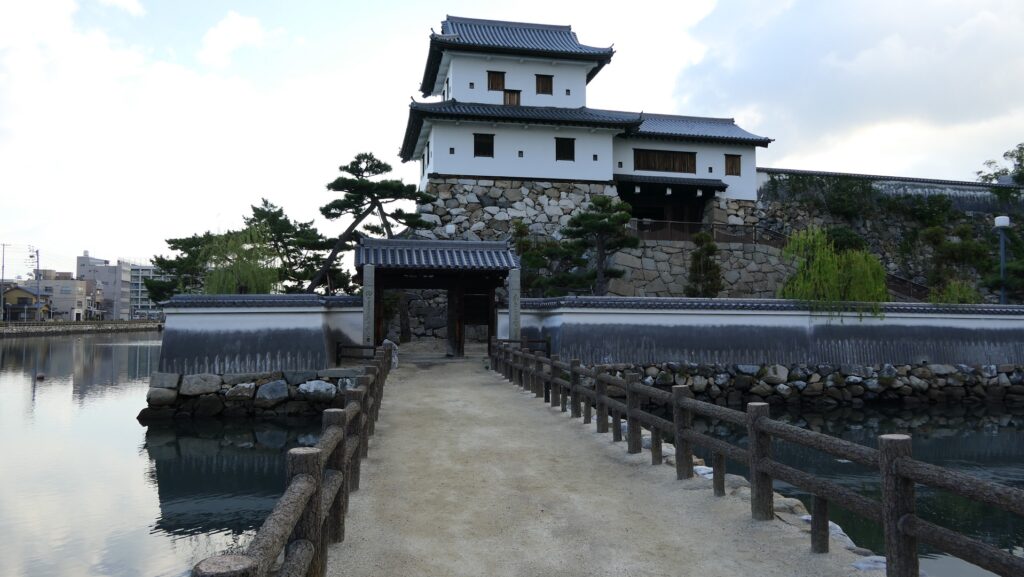
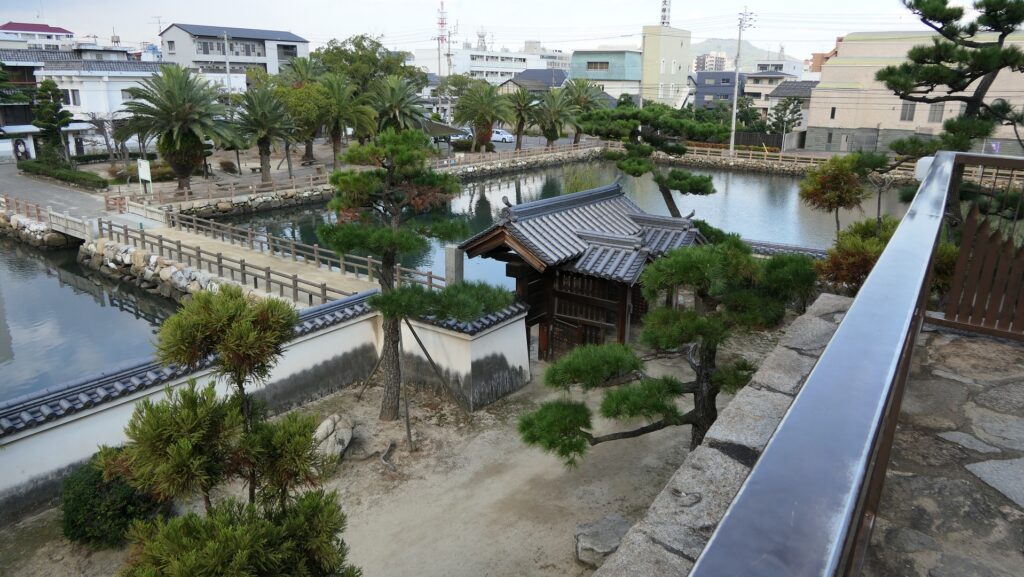
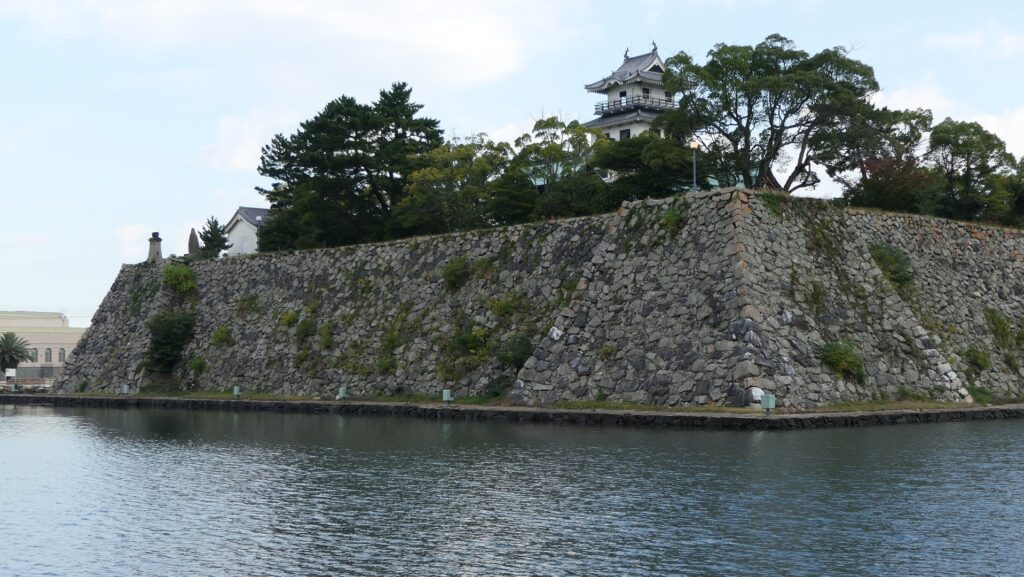
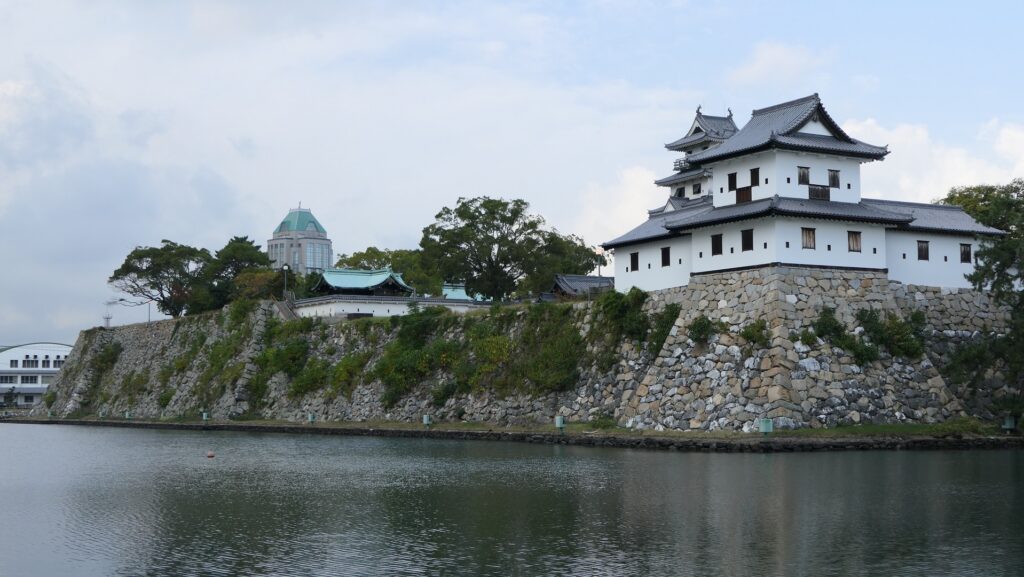
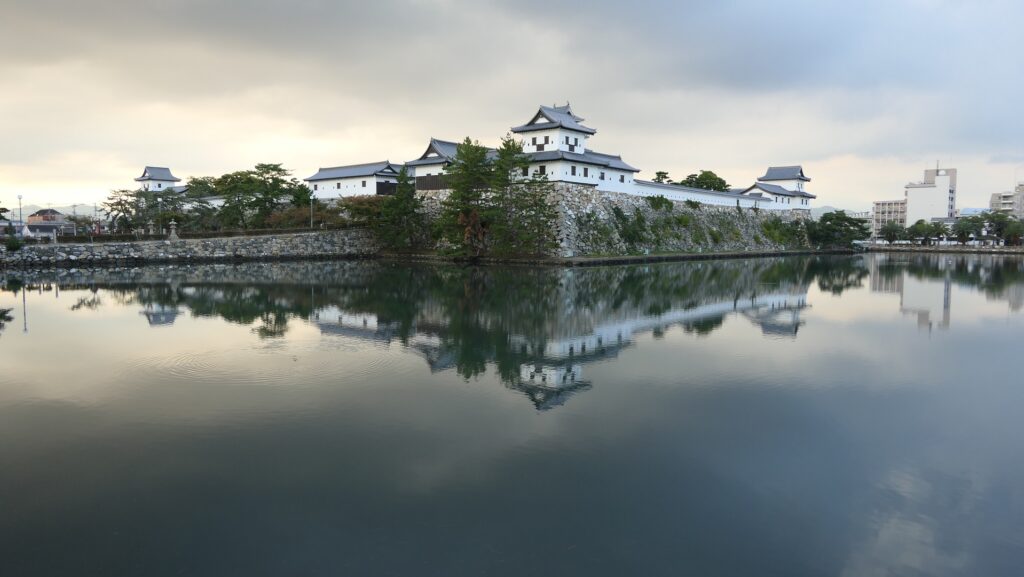
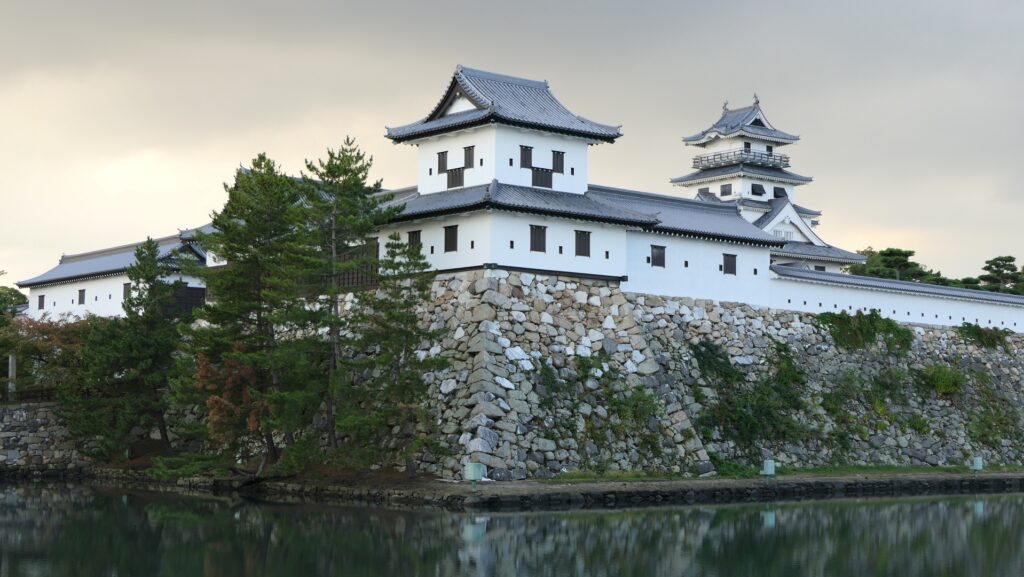
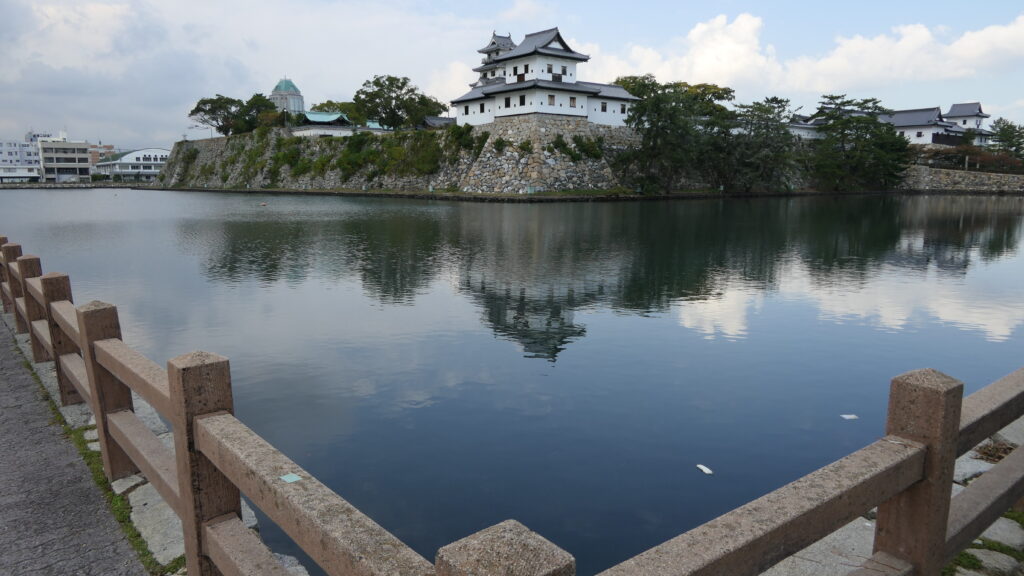
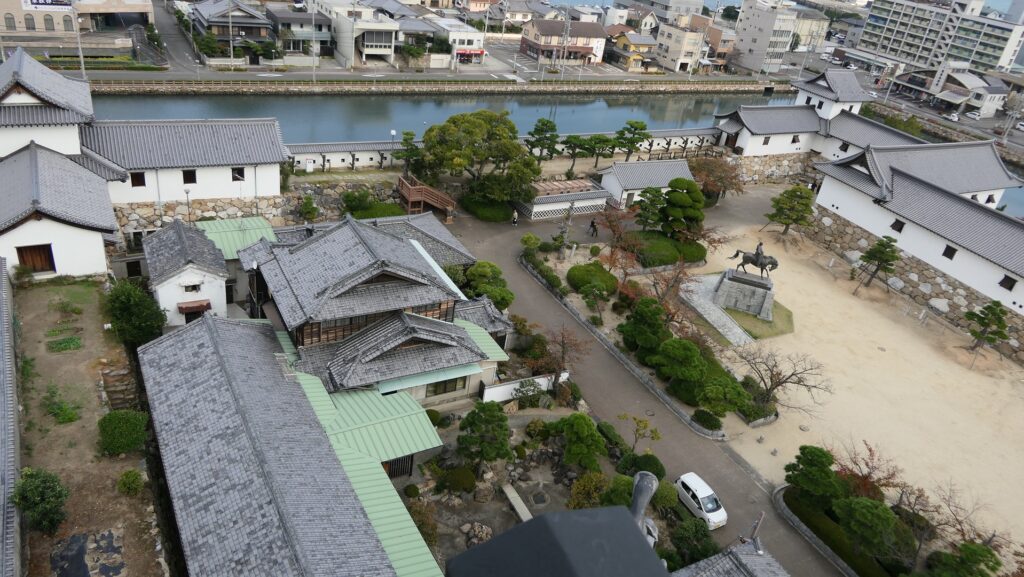
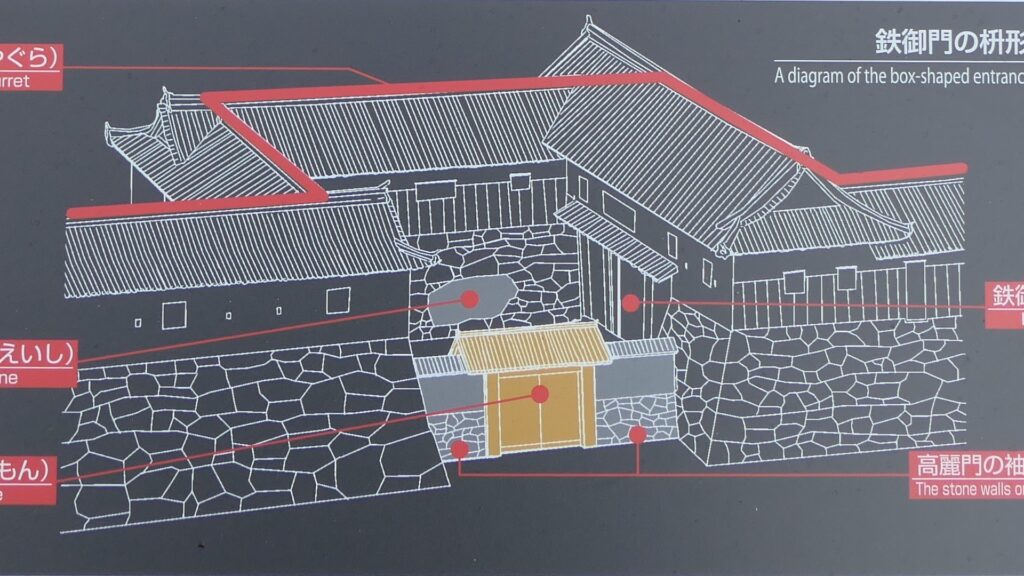
Nakatsu Castle was also one of the earliest modernized castles with turrets and stone walls in the region. The Main Enclosure was in the center but along the estuary and had a gate directly to it, which is a rare case in Japanese castles. The Second Enclosure was in the front of the sea and the Third Enclosure was in the back. All of them were on the delta which looked like a folding fan. The number of the turrets was 22 at its peak, but the Main Tower was not built for some reason.
Did Yoshitaka want to be Ruler?
The highlight of Yoshitaka’s life came when the decisive battle happened in 1600 between the East Quad led by Ieyasu Tokugawa and the West Quad by Mitsunari Ishida after Hideyoshi died. Yoshitaka joined the East Squad with his son Nagamasa, who fought with Ieyasu against Mitsunari in the Battle of Sekigawara in central Japan. Yoshitaka himself stayed at Nakatsu Castle, and after he left, he captured castles in Kyushu, which other lords in the West Squad owned, one by one. The Battle of Sekigahara, where Ieyasu defeated Mitsunari, ended in only one day on the 15th of September. However, Yoshitaka continued to invade the region for about two more months until Ieyasu stopped him. Yoshitaka had already captured all the Kyushu Region with his allies except for the territory of the Shimazu Clan in southern Kyushu. This made people later speculate that Yoshitaka would have liked to be the ruler, but only he knew the answer. The Kuroda Clan was promoted to be the lord of much larger territory of Fukuoka Domain including Fukuoka Castle before Yoshitaka died in 1604.



Castle is followed by Nakatsu Domain which promotes learning Western sciences
Nakatsu Castle was followed by the Hosokawa Clan as their branch castle. The castle survived even after the Law of One Castle per Province, issued by the Tokugawa Shogunate in 1615. It is said this was because Sansai Hosokawa, the father of the lord used it as his retreat. The castle was finally governed by the Okudaira Clan as the Nakatsu Domain until the end of the Edo Period. A remarkable event during the period was that the lords promoted learning about the Western sciences through Dutch language, called Rangaku. Japanese people were usually not allowed to learn them because trading the Western items and communicating with the Western people were strictly limited. Only the trading with Dutch at the Dejima trading house in Nagasaki and visiting Edo by the head of the house every four year were allowed. However, the third lord, Masashika Okudaira started to promote it after seeing his mother’s broken bones were mended by Western medicine. Ryotaku Maeno, who first translated a book of Western medicine with his colleagues such as Genpaku Sugita, was the domain’s doctor. Yukichi Fukuzawa, who was a great philosopher and educator in the Meiji Era, came from lower class samurais of the domain but started in life by learning Rangaku.