Location and History
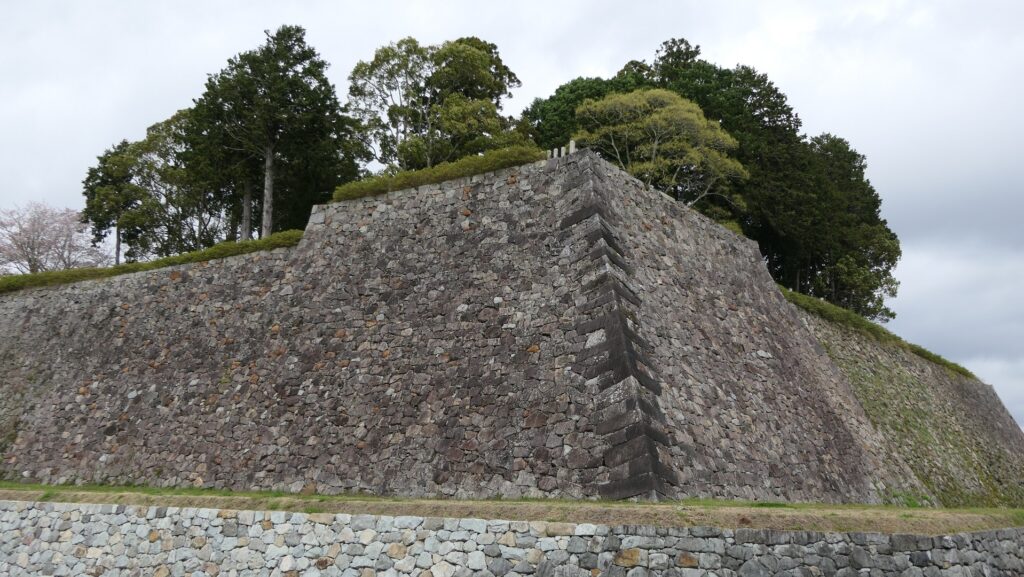
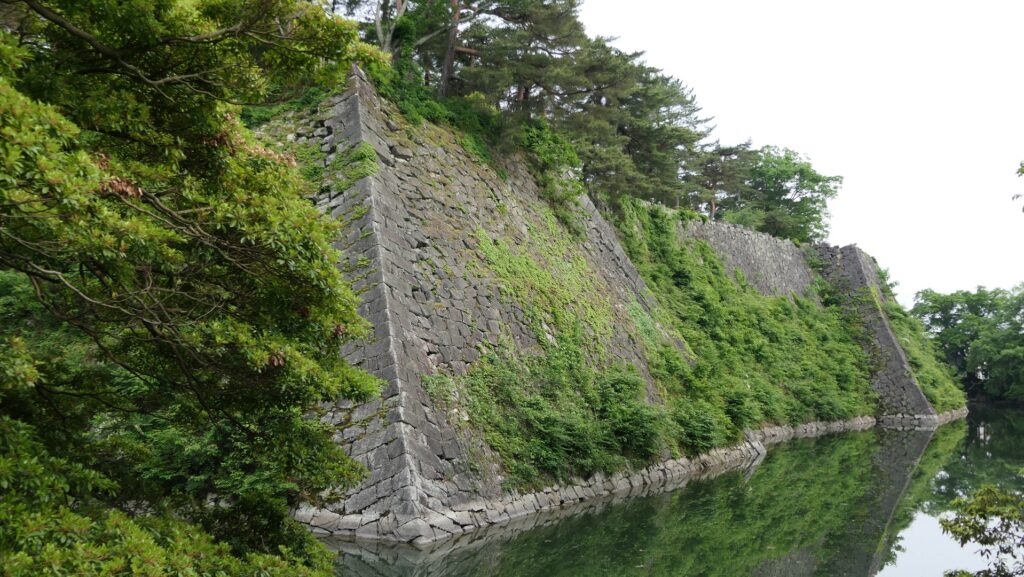
Castle is built using Natural Hazzard
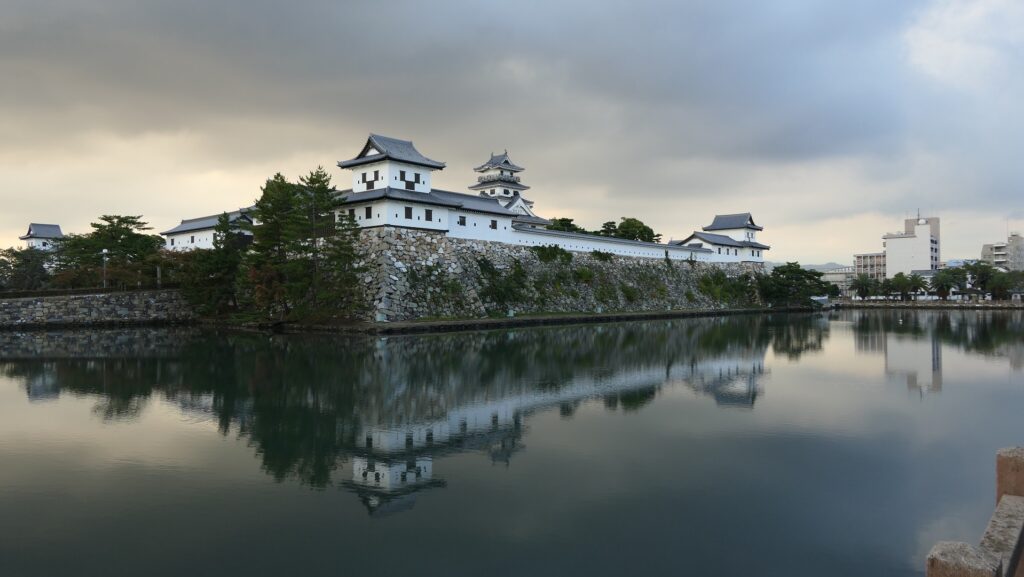
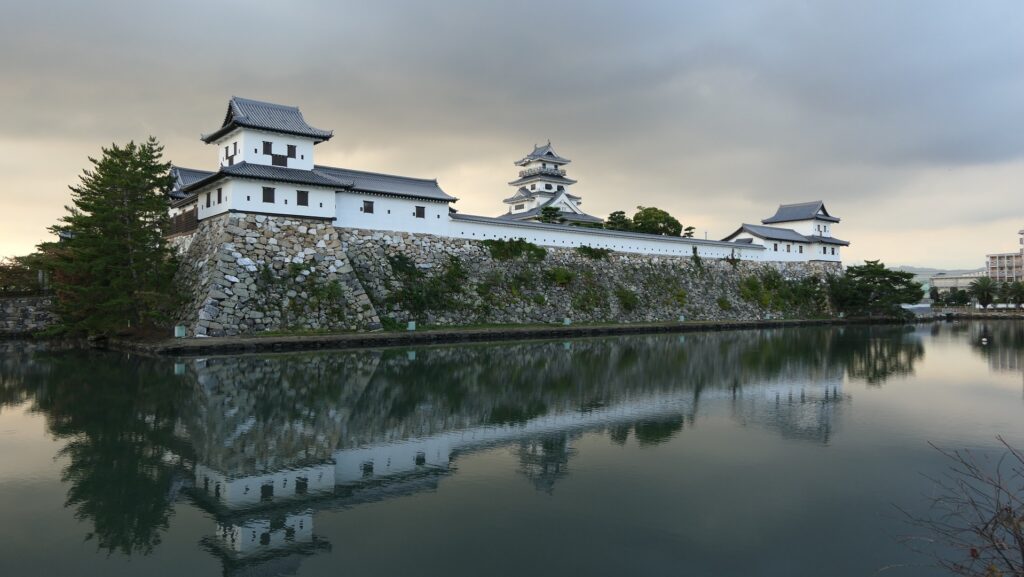
Mito Castle was located in the modern day Mito City which is the capital of Ibaraki Prefecture. The castle became the home base of the Mito-Tokugawa Clan, one of the three branches of the Tokugawa Shogun family. However, the castle looked very different from those of the other branches, Nagoya and Wakayama Castles, and the shogun’s Edo Castle.
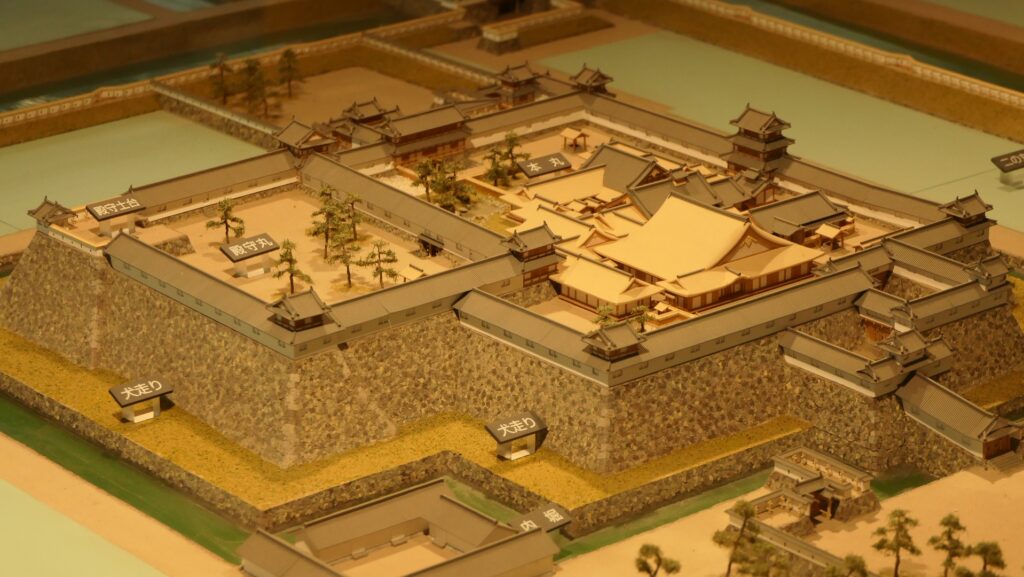
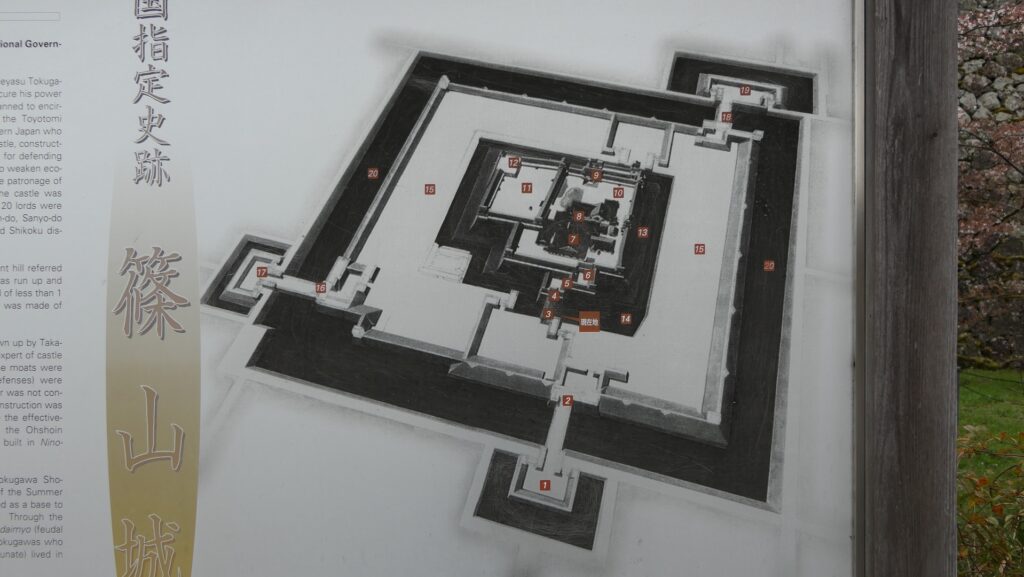
The range of Mito City and the location of the castleIt was said that the castle was first built by a local lord, the Baba Clan sometime in the early Middle Ages. It was built on a diluvium plateau sandwiched between Nakagawa River in the north and Senba Lake in the south. Its original location was defensive due to the natural hazard, so it could be easy for the lord to build the castle on it. However, it was thought that the early stage of the castle was still small probably with only the lord’s residence on the eastern edge of the plateau.
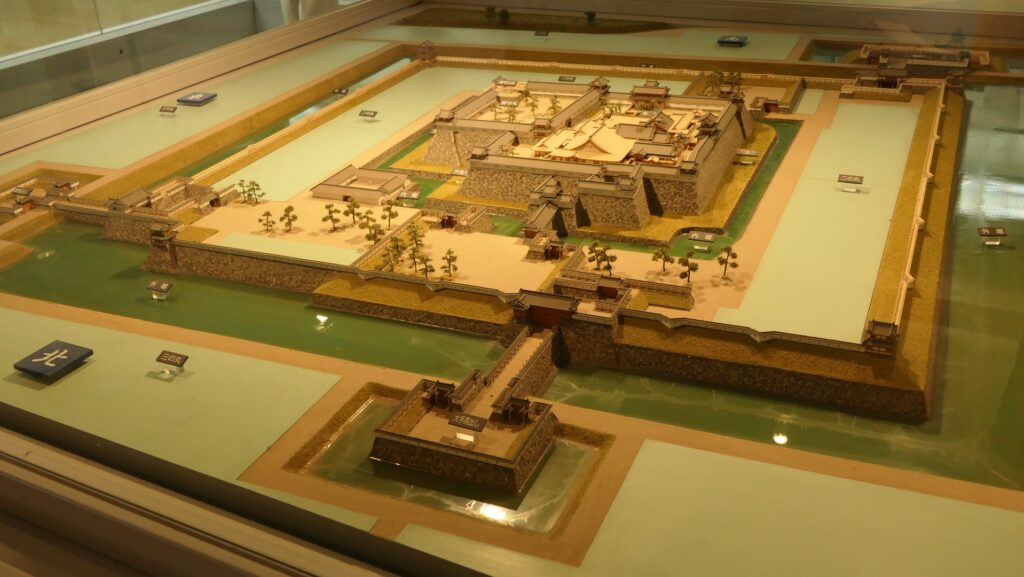
The relief map around the castleAs time passed by, the castle was followed by greater lords, the Edo and Satake Clans, and was developed larger and larger. The Satake Clan was one of the greatest warlords in the Kanto Region during the 16th Century in the Sengoku Period. The clan completed the basic structures of the castle, establishing the Main, Second and Third Enclosures in a straight line from the east to the west on the plateau. These enclosures were made of soil and divided by deep dry moats, which were typical methods for building castles at that time in eastern Japan. However, the clan was transferred to the Tohoku Region (they would build Kubota Castle there) in 1602 by Ieyasu Tokugawa, the founder of the Tokugawa Shogunate, since they didn’t support Ieyasu in the decisive battle in 1600.

Home Base of one of Three Tokugawa Branches
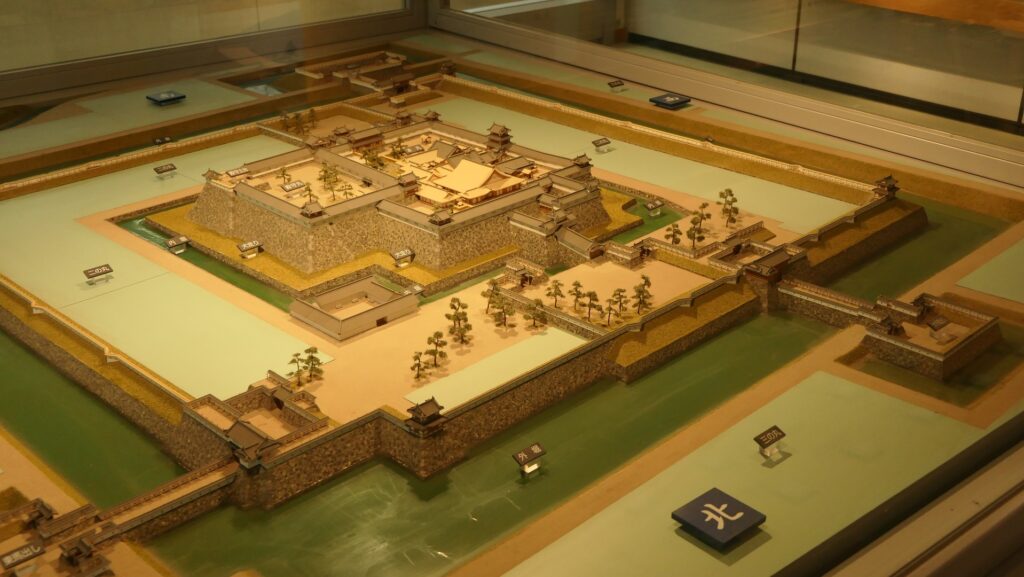
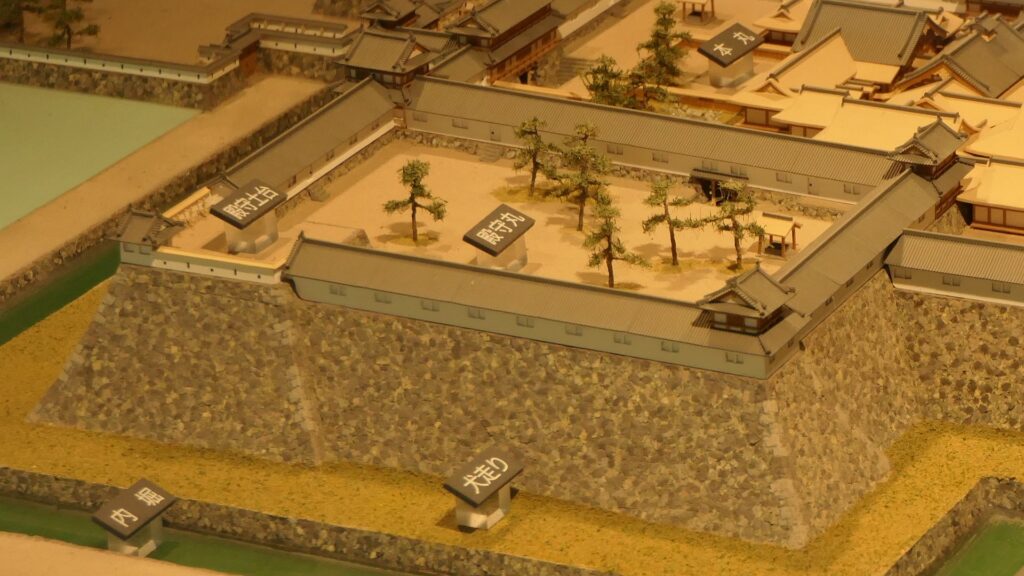
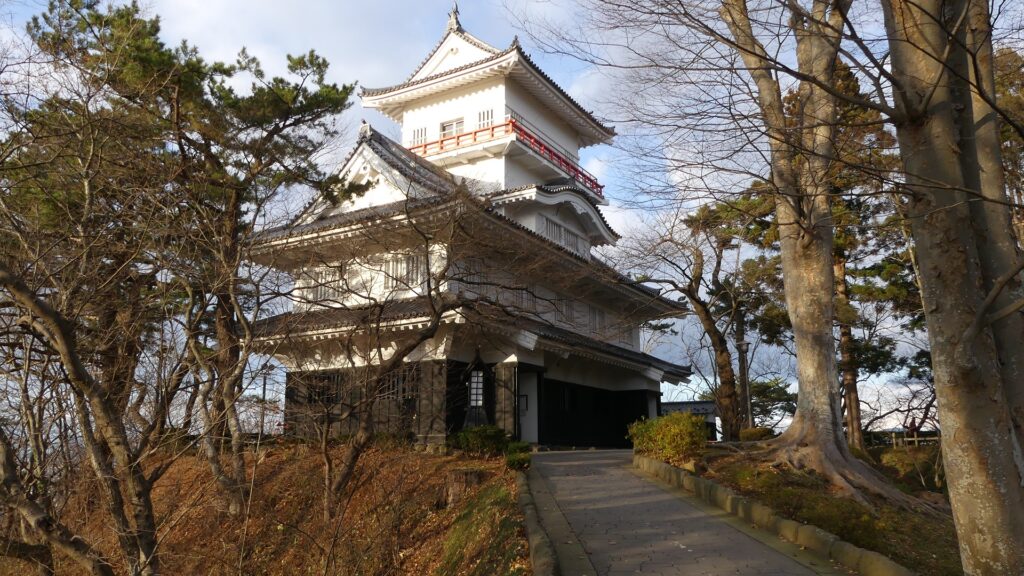
Ieyasu sent his sons to Mito Castle as it would be an important northern strongpoint to defend Edo Castle, the home base of the shogun. His youngest son, Yorifusa finally became the lord of the castle as the founder of the Mito Domain in 1609. Since then, the domain governed the castle and the area around it until the end of the Edo Period as one of the three branches of the Tokugawa Shogun family. The castle was also developed further, for example, the Main and the Second Enclosures were combined to make a new Main Enclosure, the Third Enclosure was renamed the new Second Enclosure, and the new Third Enclosure was built outside the others in the west.


However, unlike Nagoya, Wakayama and Edo Castles other Tokugawa relatives built using advanced items, such as Main Towers and high stone walls, Mito Castle was still made of soil using conventional technologies from eastern Japan. The reason for it could be that the lords of the Mito Domain usually lived in the Main Hall near the shogun in Edo, or there was no need to improve it more after the government of the shogunate became more stable. However, the most likely reason is that Mito Castle was strong enough without stone walls.




Mito Domain creates Imperialism and Exclusionism
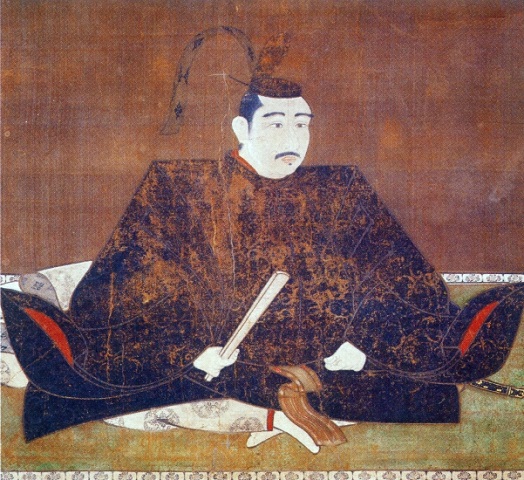
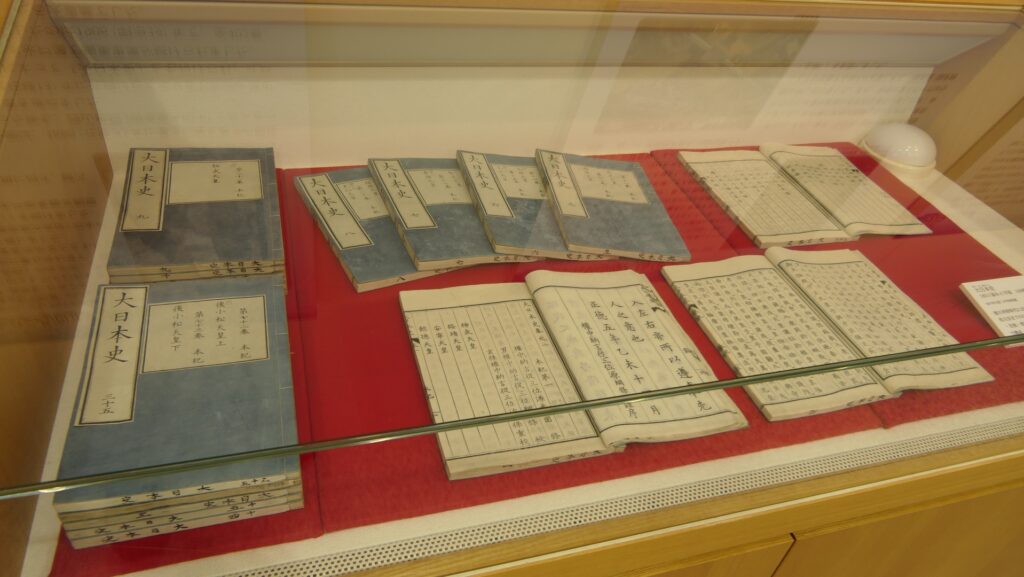
The second lord, Mitsukuni Tokugawa, known as Mito-Komon in several historical plays, promoted arts and started to edit Dainihonshi or the History of Great Japan at the Shokokan institute in Edo, which would later be moved to the Second Enclosure of Mito Castle. This activity uniquely resulted in the idea of Imperialism although the domain was a relative of the shogunate which had taken the power from the Imperial Court.
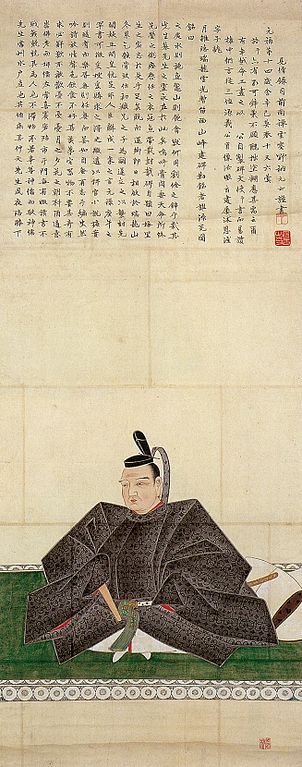


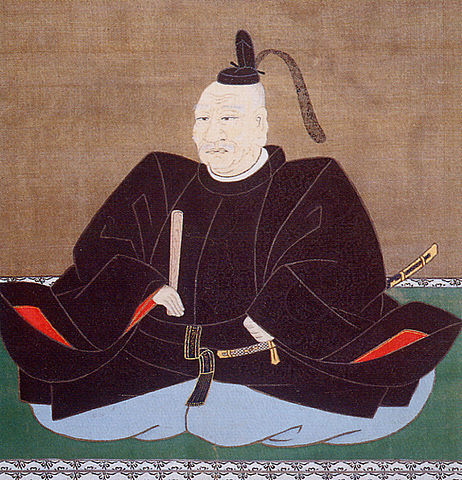
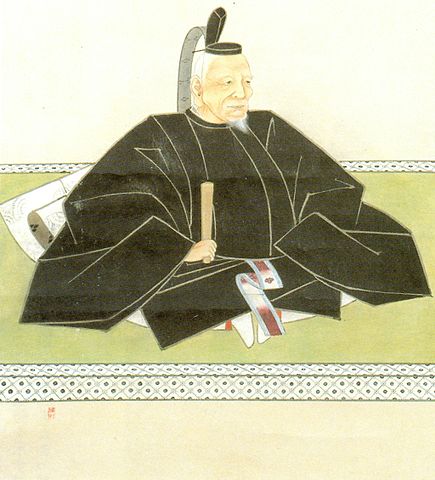
The ninth lord, Nariaki Tokugawa, during the end of the Edo Period, established the domain school called Kodokan in the Third Enclosure of the castle in order to educate the retainers and open Kairakuen Garden to all the people. While the Western foreign ships were often seen around Japan, he opposed the policy of the shogunate to open the country to foreigners. As a result, the Imperialism of the Mito Domain led many other domains’ retainers to the movement for Imperialism and Exclusionism over the country, which finally caused overthrowing the shogunate, which was later called the Meiji Restoration. However, in the domain, the retainers were divided into Tengu Party (believing the movement) and Shosei Party (supporting the shogunate), which would bring into a serious tragedy.


Sad Killing each other by Mito Domain at Mito Castle
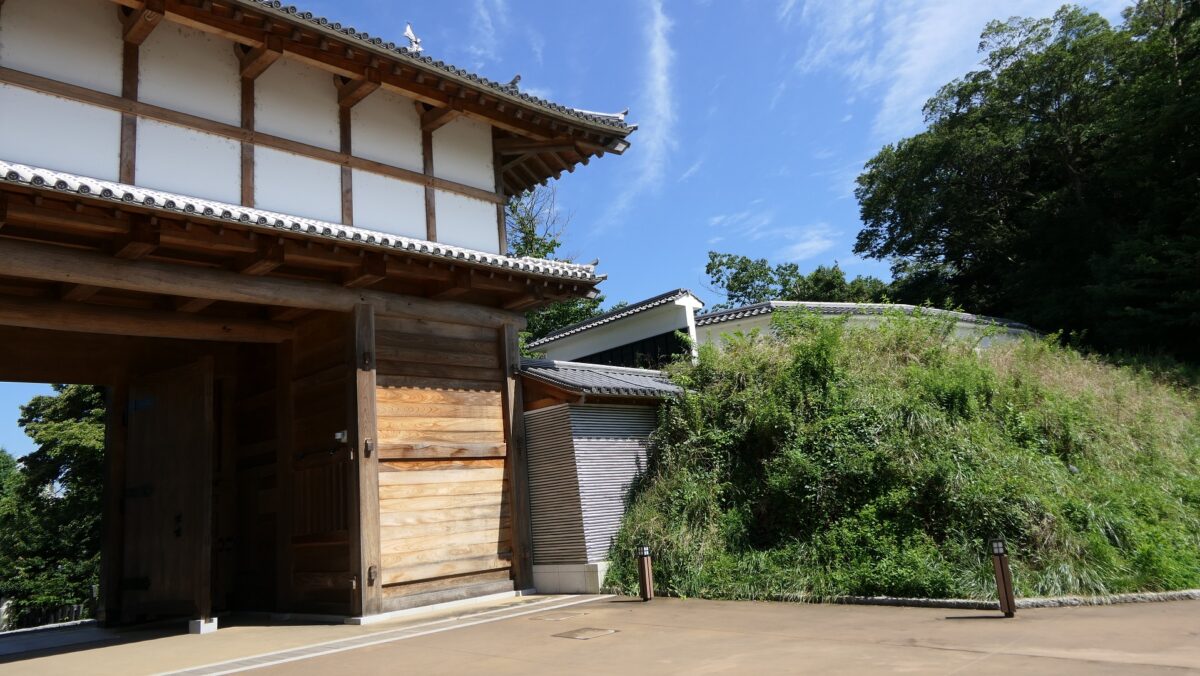
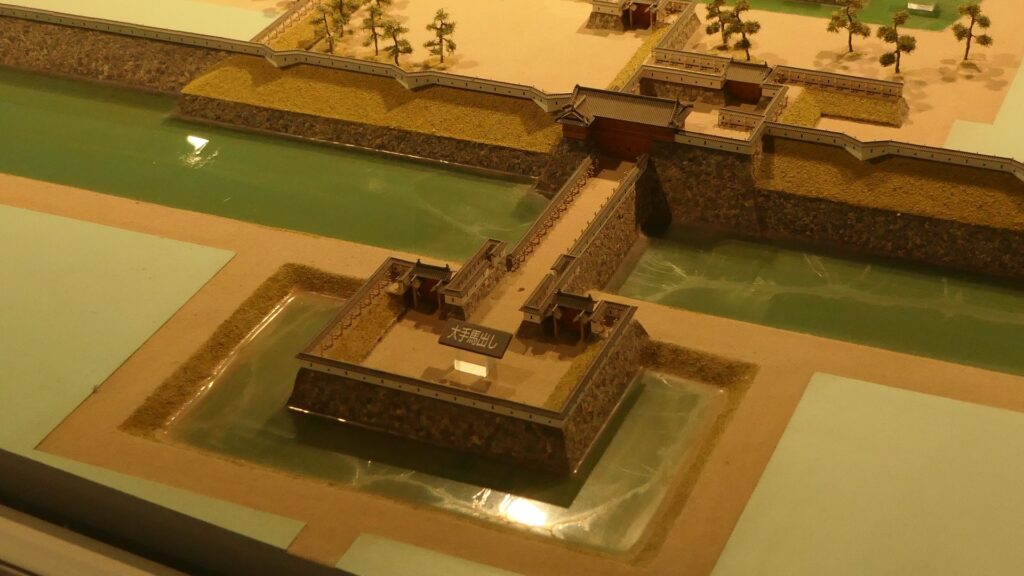
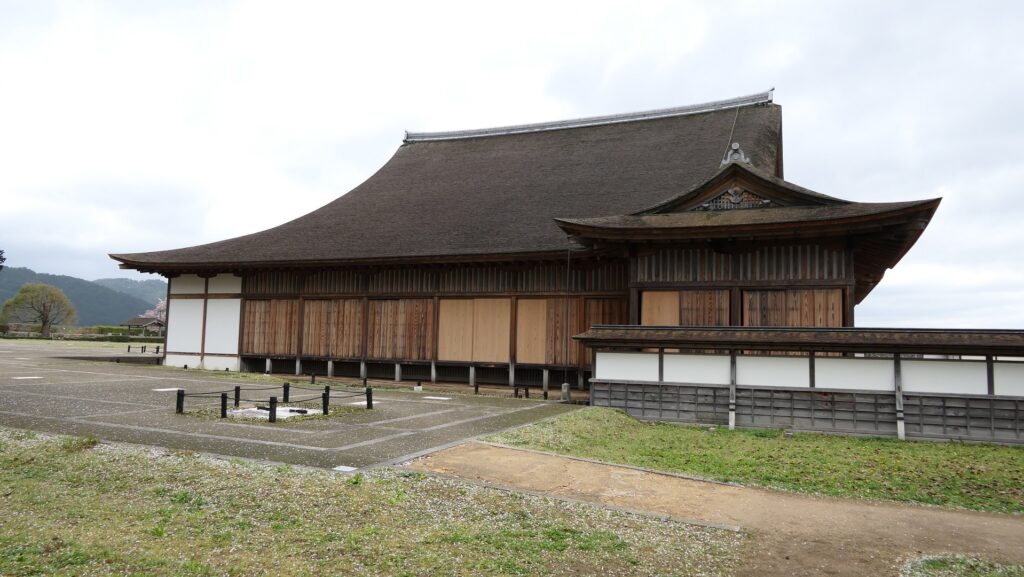
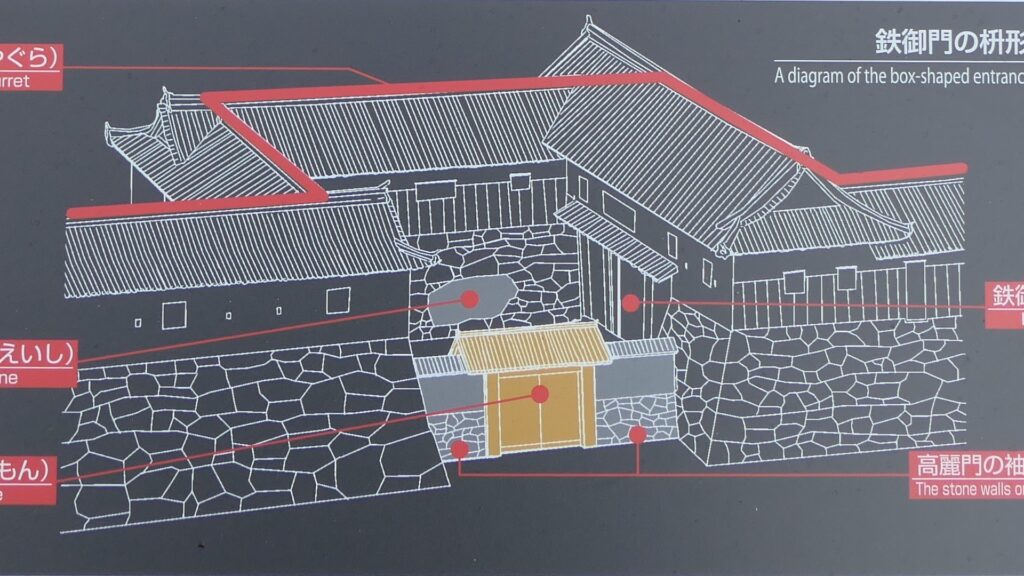
The final version of Mito Castle was like that the largest Second Enclosure became the center of the castle. It had the Main Gate, the Main Hall (also used as the government office), the Shokokan institute, the Corner Turret, and the Three-level Turret. In particular, the Three-level Turret was built as a substitute for a Main Tower. It was about 22m tall, which was too high for a three-story building, in fact, it had five floors inside.
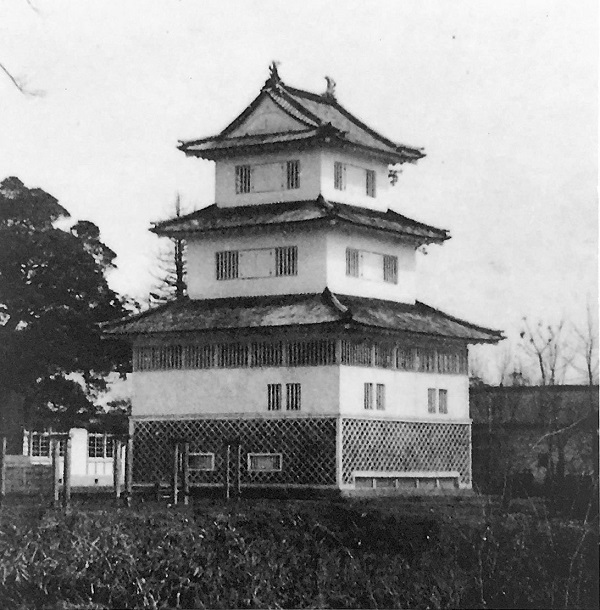


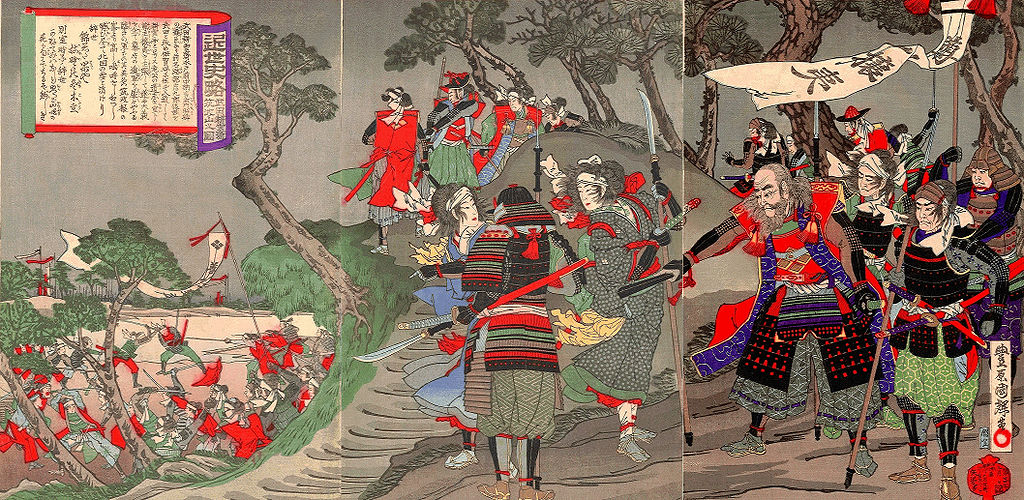
The Tengu Party started a rebellion to ask the shogunate to stop trading with foreigners and to exclude them in 1864. In this war, the Tengu Party attacked Mito Castle the Shosei Party resided in, but failed. They eventually went west to ask Yoshinobu Hitotsubashi in Kyoto, who was a son of Nariaki and would become the last shogun, for what they wanted. However, they were arrested by Yoshinobu’s instructions and many of them were executed. The Shosei party also killed or persecuted the families in Mito of the Tengu Party. After that, the situation dramatically changed that the New Government was established and the shogunate was defeated in 1868. The survivors of the Tengu Party returned to Mito Castle and avenged against the Shosei Party. Some of the Shosei Party, who were on the run, attacked the castle the Tengu Party were resided in this time, but failed again. The strength of the castle was ironically proven by the tragedy between the retainers of the owner domain. Records say the number of the retainers was reduced from 3,449 to 892 during the internal conflict, which meant competent personnel from the domain ran out to modernize Japan.