Location and History
Nagoya Castle revived
There was another Nagoya Castle which had the same name and was built at the same place as the present Nagoya Castle in the middle 16th century during the Sengoku Period. It is said that the famous warlord Nobunaga Oda was born at the old Nagoya Castle. Nobunaga eventually moved his home base to Kiyosu Castle before the old Nagoya Castle was abandoned. Since then, Kiyosu Castle (about 10km away from Nagoya Castle on the northeast) had been the center of Owari Province (what is now the western part of Aichi Prefecture). In 1609, the Tokugawa Shogunate decided to build a new castle in place of Kiyosu Castle which often suffered from floods. They needed a stronger castle for their relatives to prepare for a battle with the Toyotomi Clan at Osaka Castle. The castle was named Nagoya Castle once again.
The location of Nagoya Castle and Kiyosu Castle
Simple but Strong Castle with one of Largest Main Tower
The area of the castle was very large but built simply and strongly. The center of the castle, the Main Enclosure, was protected on all directions by other enclosures such as the West Enclosure. The Second Enclosure was added on the southeast of the Main Enclosure, which had the Ninomaru Main Hall for the lord of the castle. The largest Third Enclosure was on the south of all other enclosures, which was used as the senior vassals’ houses.
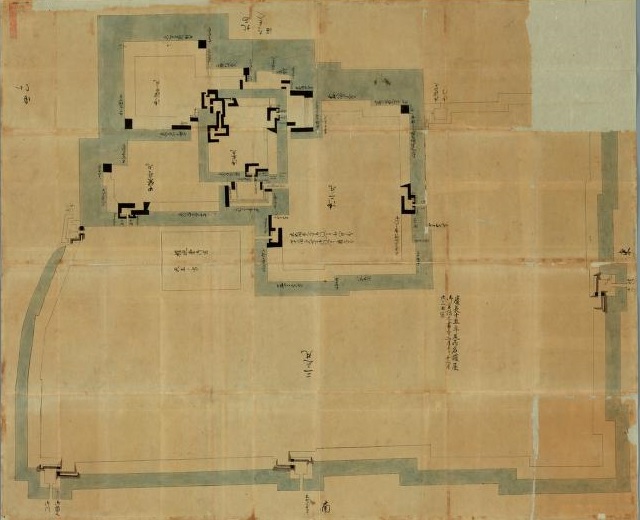
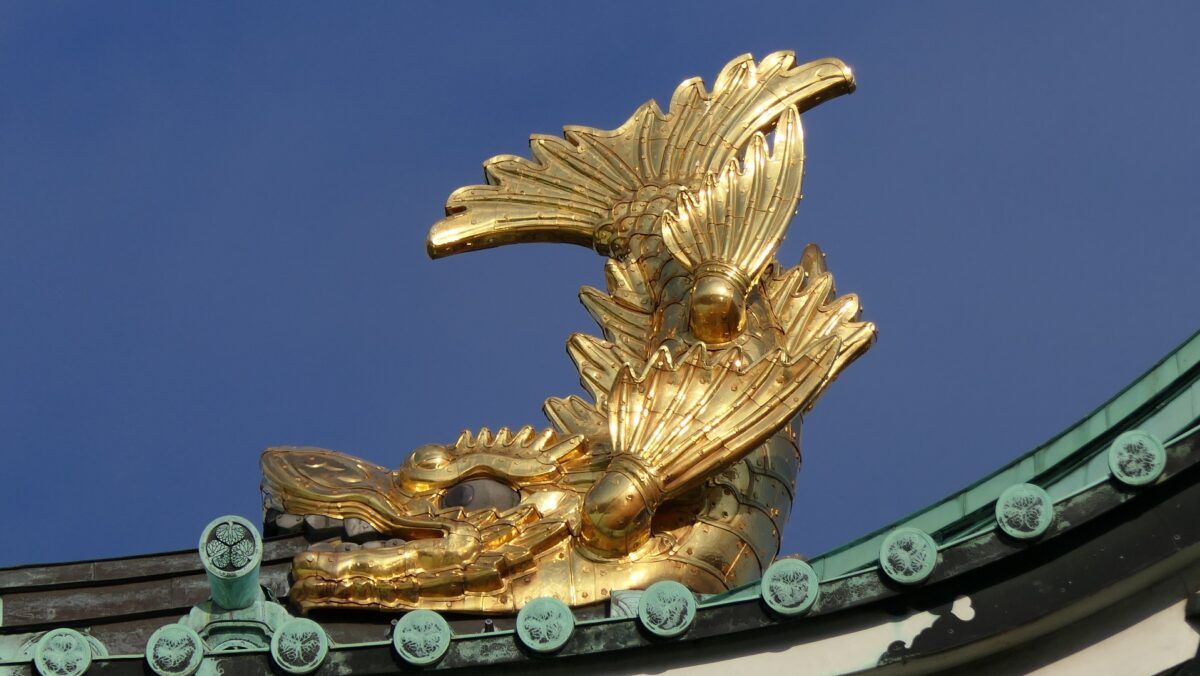
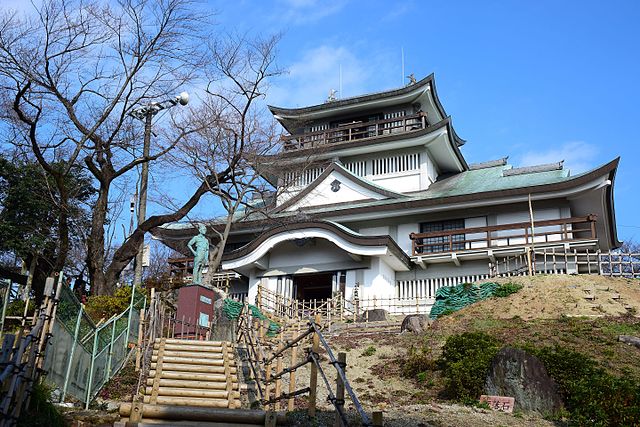
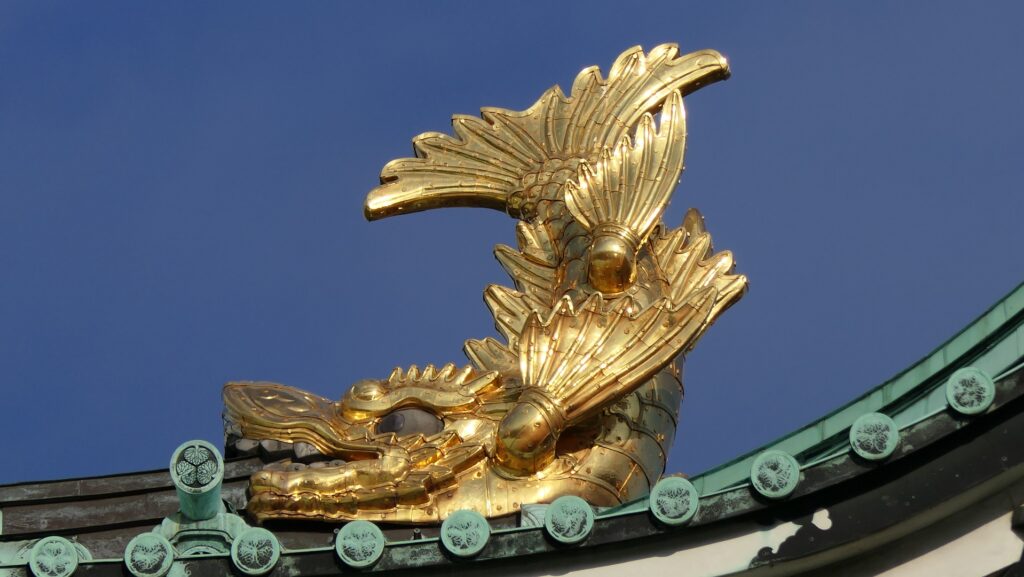
The Main Enclosure had the five-layer Main Tower, one of the largest main towers on record. The two golden grampuses on the top were particularly popular among people. It is said the first generator of them used 215 kilograms of gold. The enclosure also had the Honmaru Main Hall, but it was only for the Shogun’s stay. Actually, just three Shoguns used it. People have been saying that “The castle makes Nagoya what it is.”.

Destruction and Revival
After the Meiji Restoration, the large enclosures such as the Second and Third Enclosures were turned into a Japanese Army base. However, the government decided to maintain around the Main Enclosure as a castle. Many traditional buildings including the Main Tower and the Honmaru Main Hall remained as they were. They were designated as the first National Treasure for a castle in 1930. It is regrettable to say this, but almost all of them were burned down in 1945. Only three turrets and three gates remain now.
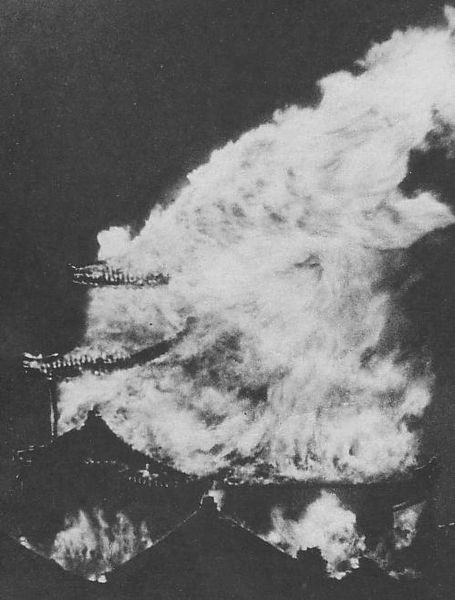
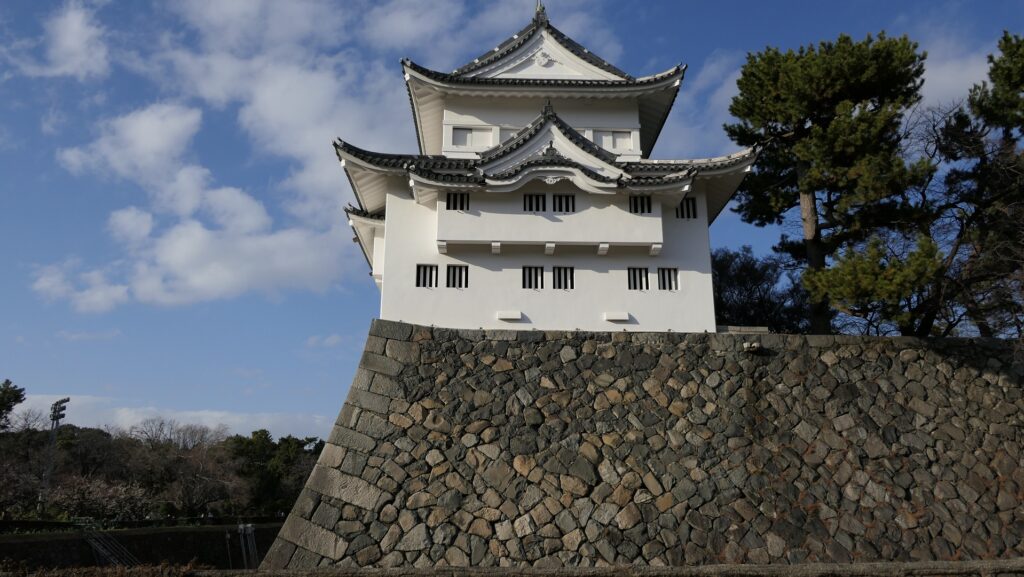
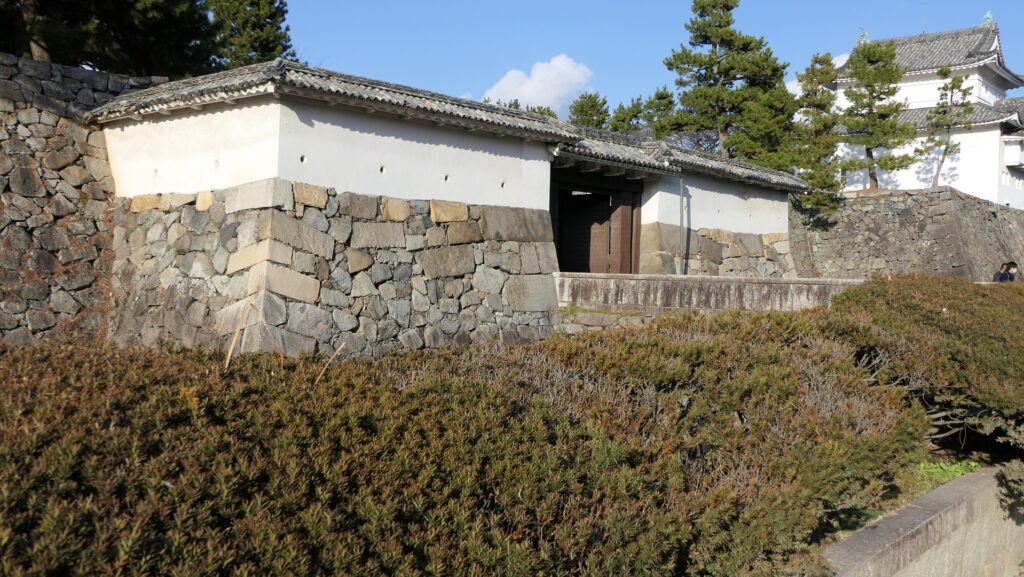



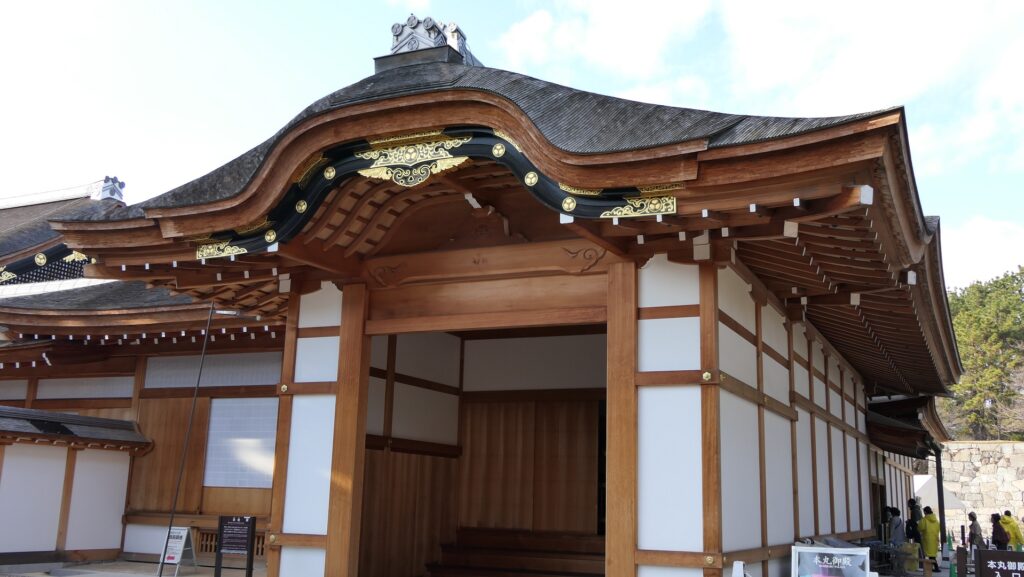
After 14 years from the tragedy, people in Nagoya rebuilt the Main Tower which we now see. One third of the fund for rebuilding it came from the citizens’ donation. The appearance of the tower is almost the same as the original one, but it is a modern concrete building on a huge caisson inside the original stone wall base. The original golden grampuses, which were also burned in 1945, were restored at the same time. The present ones include 88 kilograms of gold. In 2018, the Honmaru Main Hall in the Main Enclosure was restored using the original methods. The enclosure is returning to its former appearance.



To be continued in “Nagoya Castle Part3”
Back to “Nagoya Castle Part1”



















