Location and History
From Home of Ninja to Site for protecting Osaka
Iga-Ueno Castle was located in Iga Province which is now the western part of Mie Prefecture. Iga is probably more well known for being the home of Ninja than for the castle. Actually, before the castle was built in 1585, the province was divided among many small local lords. They gained special knowledge and techniques so that they could protect themselves. They were also often hired by larger warlords in other provinces as spies or Special Forces we now call Ninja. Unfortunately, they were conquered by Nobunaga Oda in 1581. When Nobunaga’s successor, Hideyoshi Toyotomi was organizing his unification of Japan, he sent Sadatsugu Tsutsui to the province as the lord.
The range of Iga Province and the location of the castle
Hideyoshi was based in Osaka Castle, so Iga Province was on the direct route from Osaka to eastern Japan. That’s why he sent Sadatsugu who first built Iga-Ueno Castle in 1585. Therefore, the castle was supposed to prevent enemies from attacking from the east. The three-level Main Tower of the castle was also built in the eastern part of it. Sadatsugu somehow survived when Ieyasu Tokugawa became the final ruler at the beginning of the 17th Century after Hideyoshi died. However, he was fired by the Tokugawa Shogunate in 1608 due to a claim of misgovernment from his retainers. Historians speculate that the shogunate, in fact, wanted to remove Sadatsugu who was doubly loyal to both the shogunate and the Toyotomi Clan still at Osaka Castle.


Takatora Todo renovated Castle for attacking Osaka
Instead, the shogunate transferred Takatora Todo from Imabari Castle in Shikoku Island to Iga province. Takatora was not a hereditary feudal lord, which meant he didn’t work under Ieyasu Tokugawa, who was the founder of the shogunate, for a long time. However, he was a well-known master of castle construction through having build Uwajima, Ozu and Imabari Castles. He also helped the shogunate build its famous castles such as Edo, Nagoya, and Nijo in Kyoto. That’s why he was trusted by the shogunate. They expected Takatora to build a strong castle to stand against the Toyotomi Clan at Osaka Castle in the west. Takatora accomplished this by renovating Iga-Ueno Castle. He thought that if the shogunate were to be beaten at Osaka Castle, he could accommodate Ieyasu in Iga-Ueno Castle.
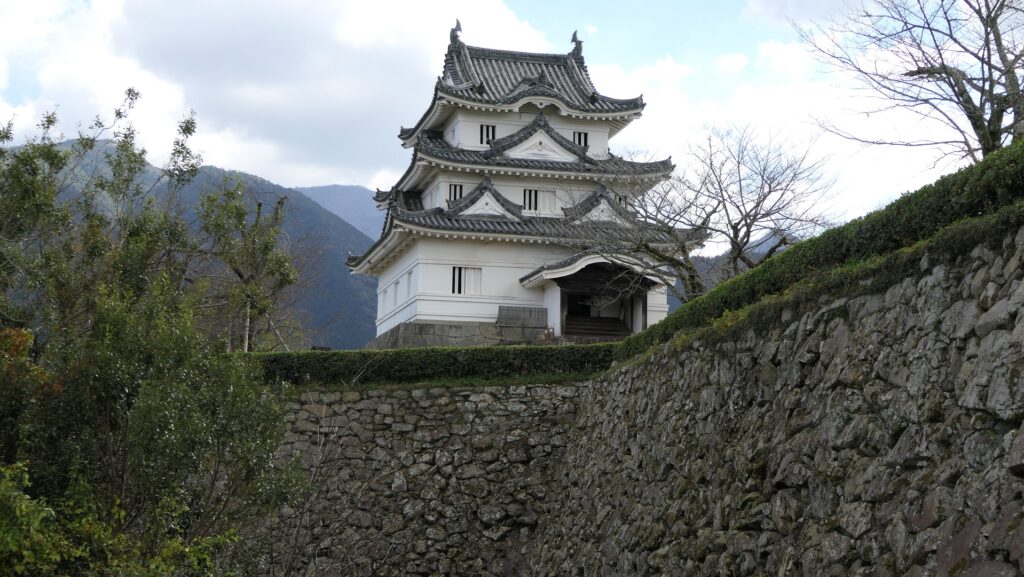



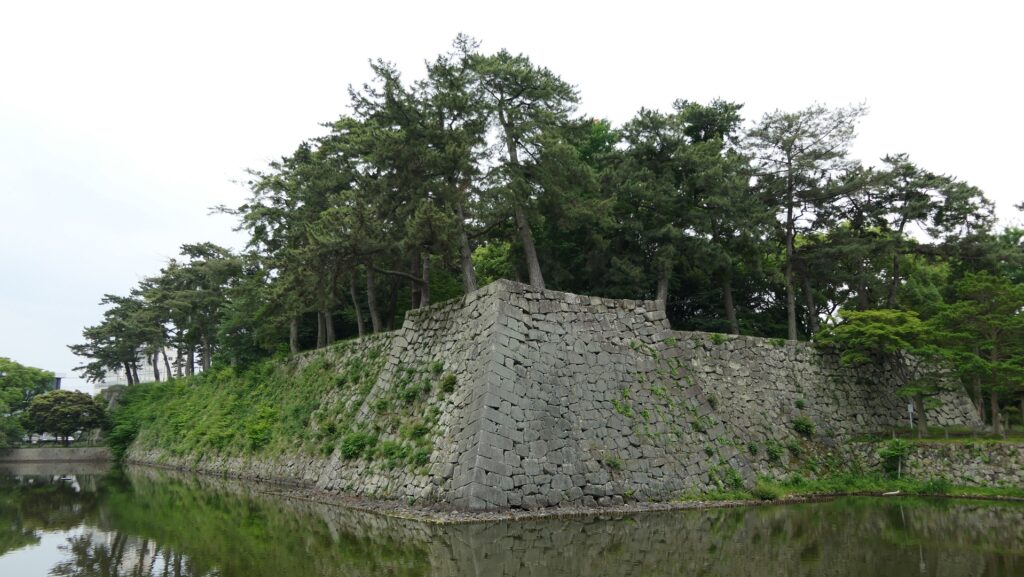
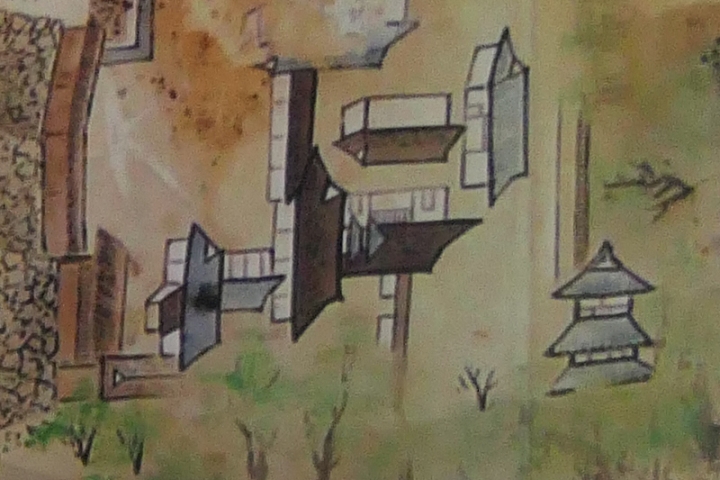
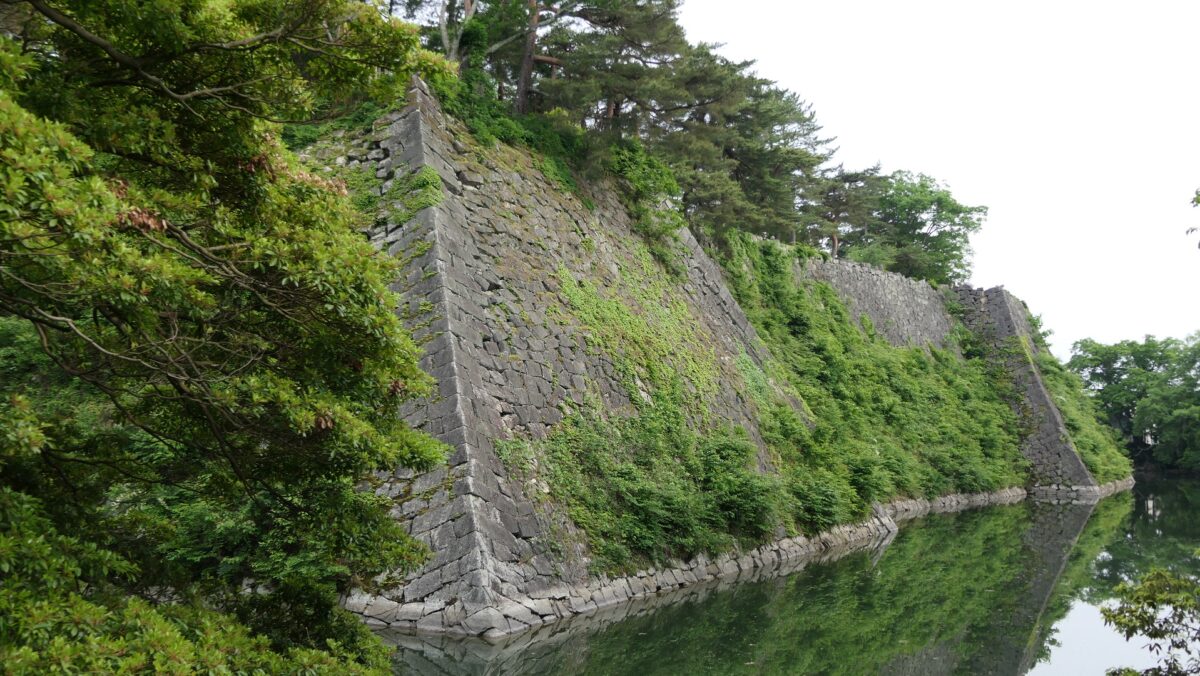
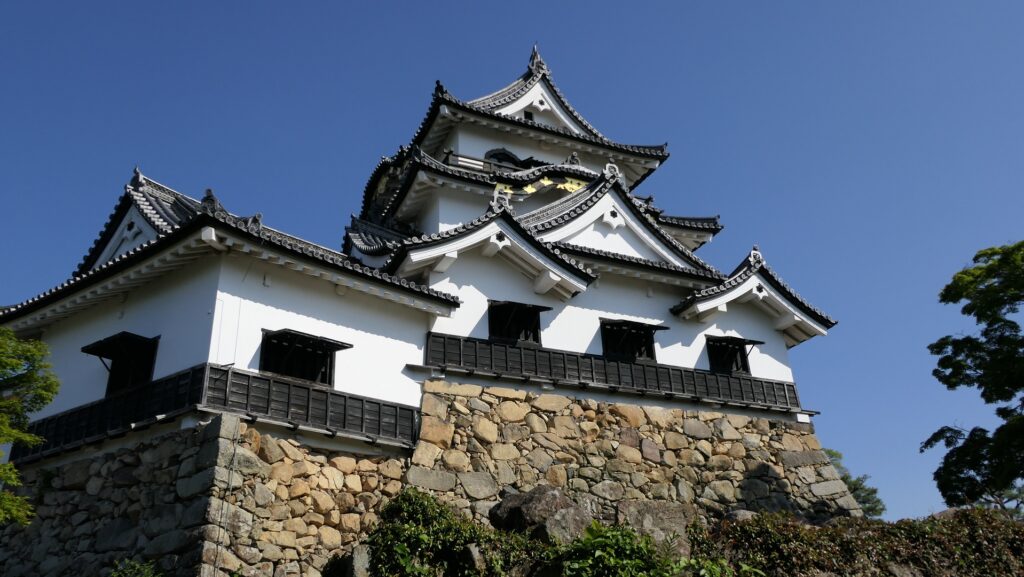
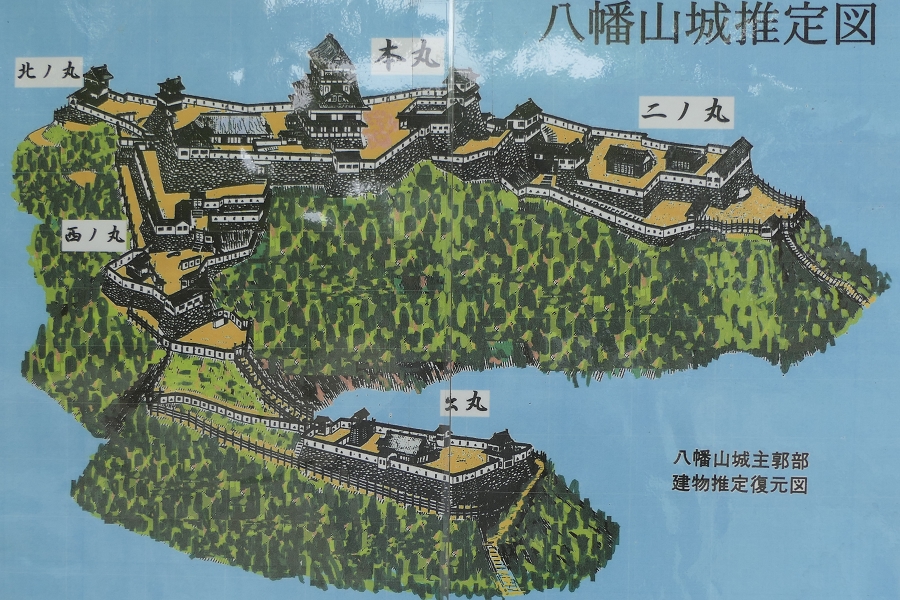
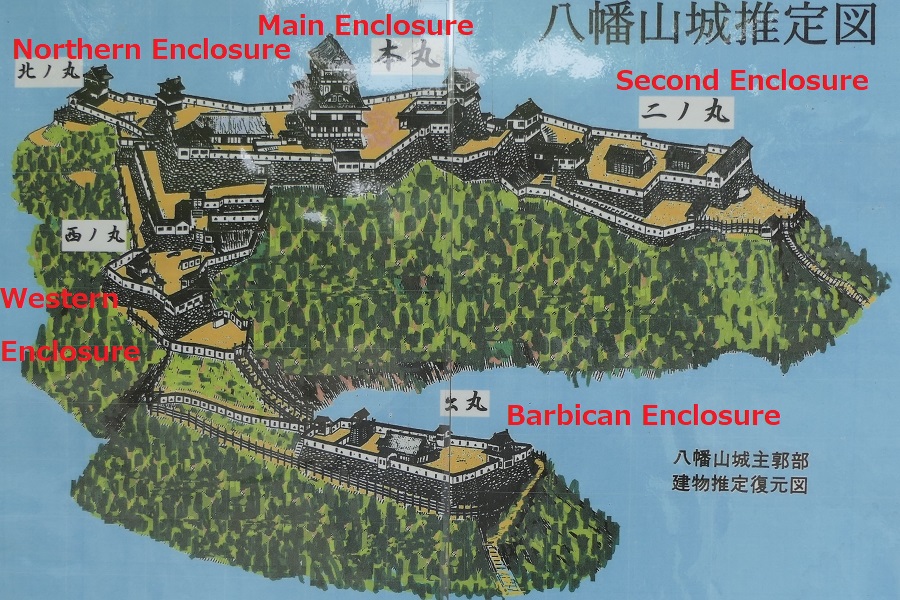
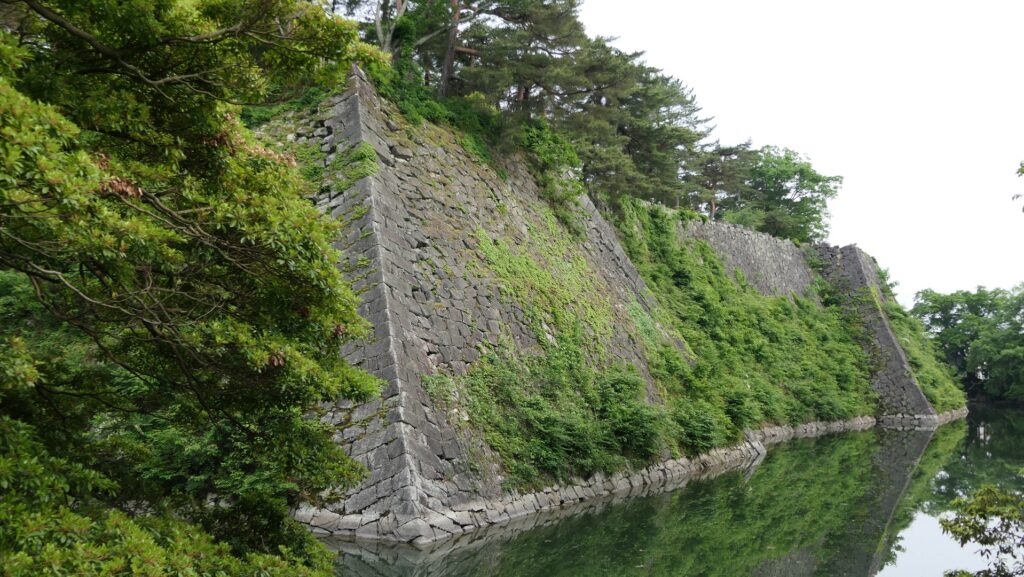
Takatora extended the Main Enclosure, the center of the castle on a hill to the west, towards Osaka Castle. He invited a guild of craftsmen called Ano-shu to build the highest stone walls (at that time) at the western side of the enclosure. It was completed- Takatora’s biography praises him, saying the stone walls were greater then those of Osaka Castle. Takatora also started to build the five-level Main Tower behind the stone walls, however, the tower collapsed due to a windstorm in 1612. The Second Enclosure was built beside the hill in the south, which was used as warriors’ housing. It had two large Main Gates in its western and eastern parts. The construction was ongoing when the battles between the shogunate and the Toyotomi Clan happened in 1614. however, it halted after the shogunate beat the Toyotomi Clan in 1615.


Homebase for Wartime
Takatora gave his younger brother Iga-Ueno Castle as his branch castle, and set Tsu Castle as his home base. Tsu Castle was located in a plains area near the sea in Ise Province which was another territory of his. He said that Tsu Castle would be his home base for peacetime while Iga-Ueno Castle would be the other one for wartime. After that, the senior vassals of the Todo Clan governed the castle and Iga Province in the peacetime of the Edo Period. They lived in the official residence where Sadatsugu Tsutsui originally lived. The first Main Tower, which Sadatsugu built, also remained for a while, but it is thought to have collapsed due to another windstorm in 1633 as well.