Location and History
Mitsuyasu Kato might have developed it greatly
Kofu Castle was located in Kai Province (what is now Yamanashi Prefecture). Kai Province was owned by the Takeda Clan for a long time until 1582 when the clan was defeated by Nobunaga Oda. Since then the Oda clan governed the province but immediately followed by the Tokugawa, Toyotomi, and the Tokugawa clan again. Kofu City, which is the prefectural capital of the prefecture, had already been the castle town for the Takeda Clan Hall. It is said that the Tokugawa Clan first built Kofu Castle at the south of the town in 1583 of their first governance, but it is uncertain. In 1590, Toyotomi’s servant, Mitsuyasu Kato was given Kai Province. He improved Kofu Castle greatly, probably with building the large scale stone walls. This is because Toyotomi had the craftsmen who were able to build stone walls called Ano-shu, which Tokugawa didn’t have. It is thought that the basic structure of the castle was completed at the same time.
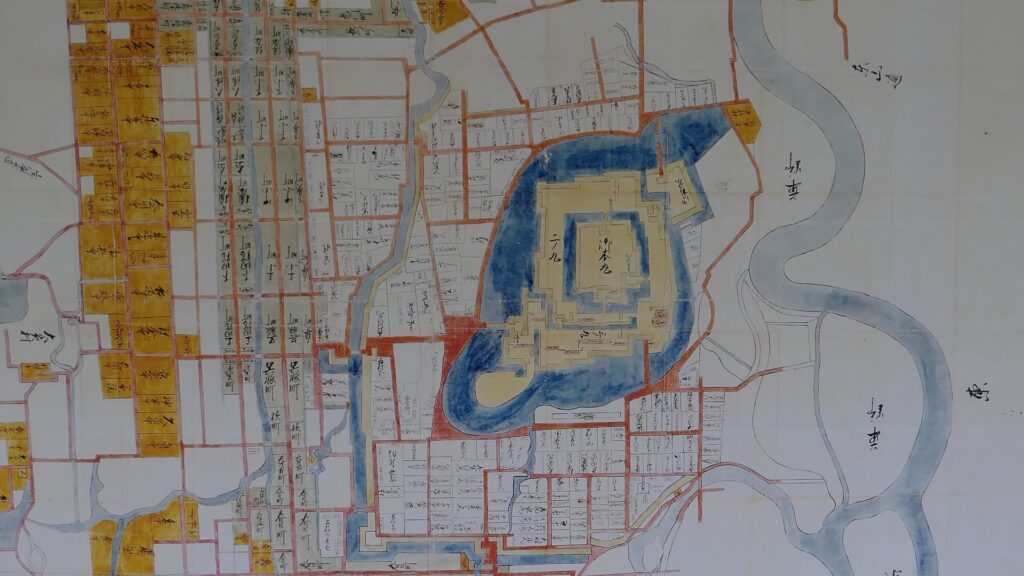
The location of the castle
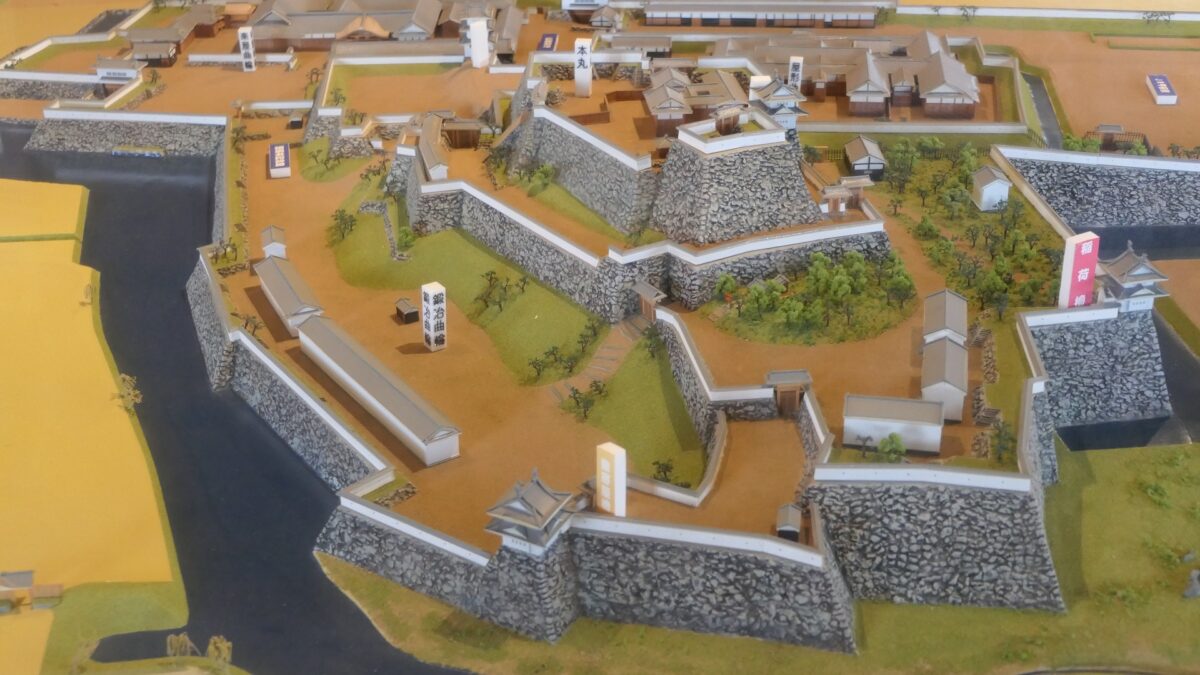
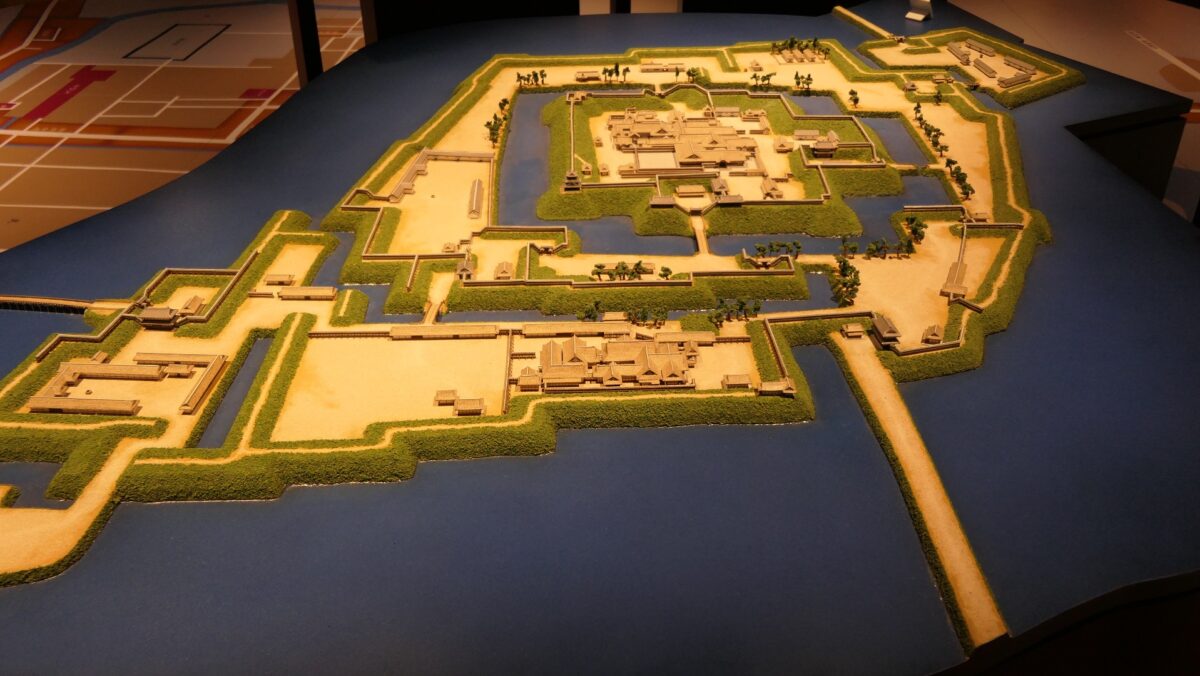
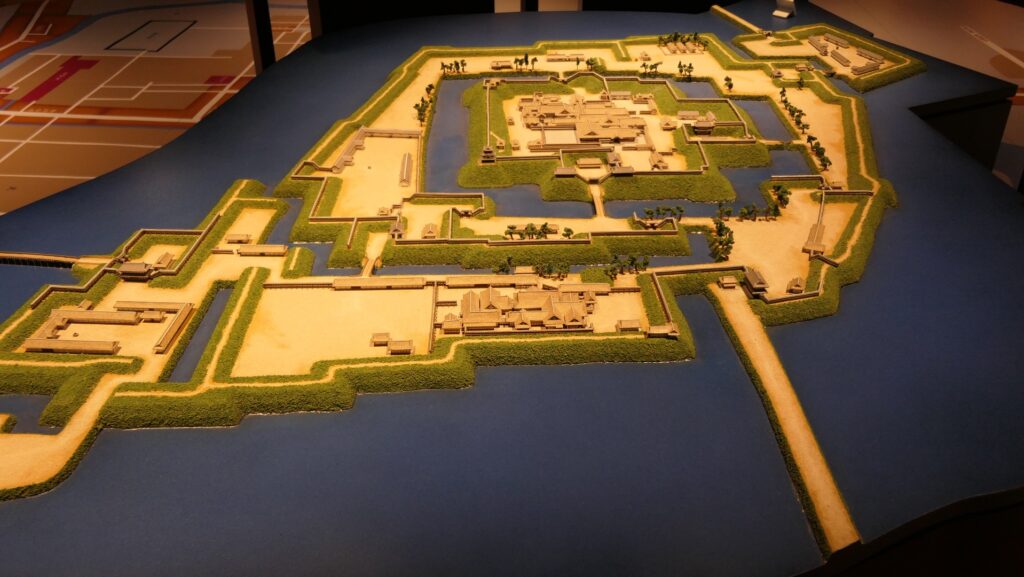
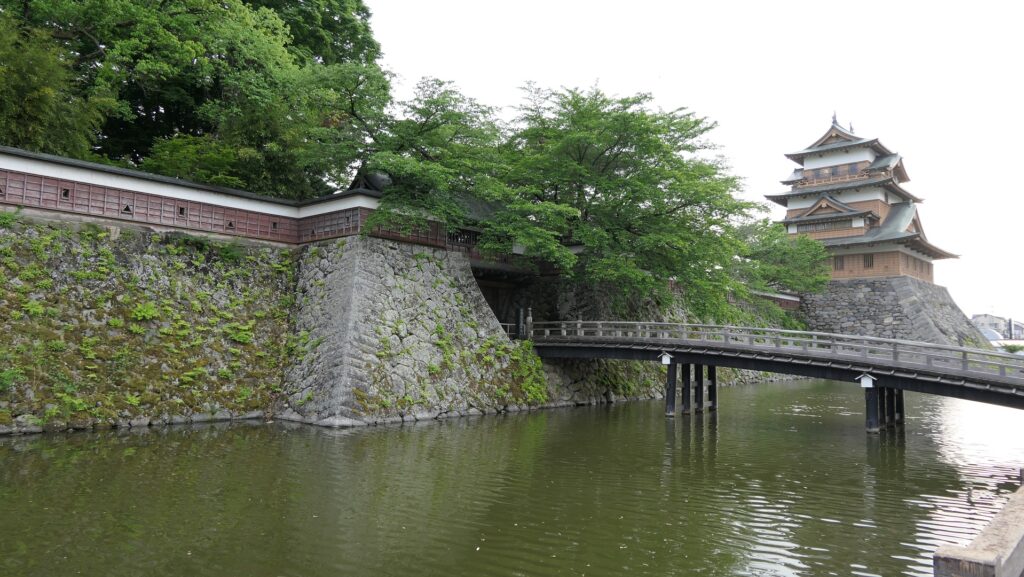
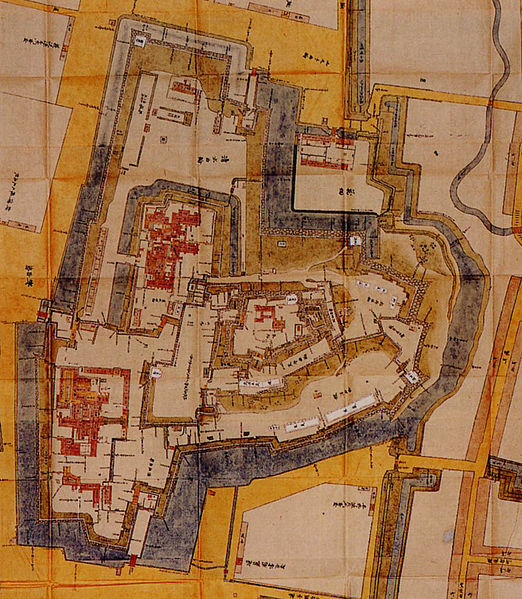
Protected by High Stone Walls and Tripled Moats
The castle consisted of three parts. The main portion is called Uchi-shiro, it includes the Main Enclosure, the base for the Main Tower and other enclosures. It was surrounded by stone walls and the Inner Moat. It was also on a hill called Ichijo-koyama, and had three entrances – the Main Gate on the south, the Yamanote-mon Gate on the north, and the Yanagi-mon Gate on the west. The eastern part of the main portion is protected strictly by the high stone walls. Secondly, the ground for the warriors’ houses called Naikaku was around the main portion, surrounded by the Second Moat. Lastly, the ground for the castle town was around Naikaku, also surrounded by the Third Moat.
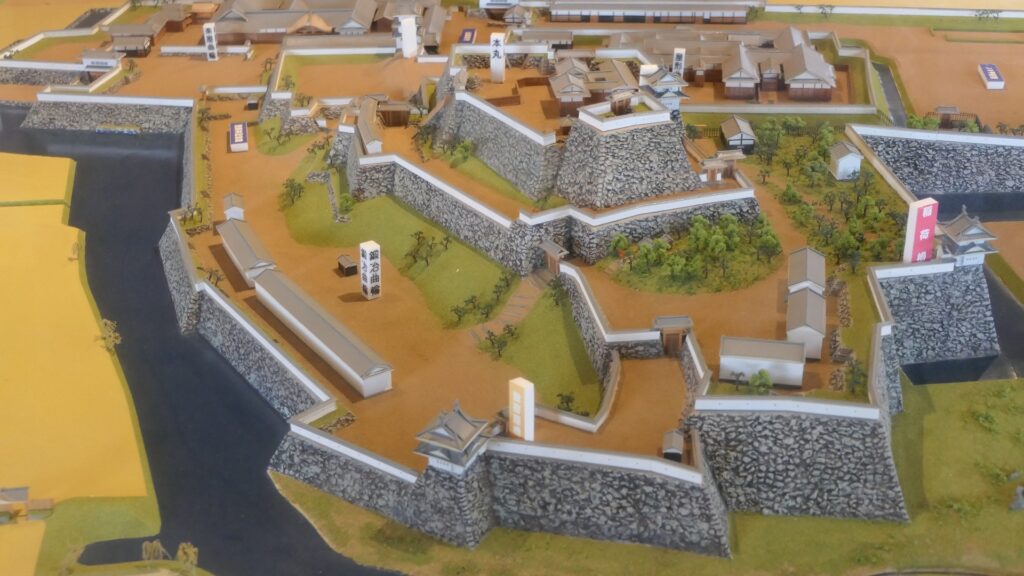

Important Strongpoint for protecting Edo
In the Edo Period from the 17th Century, Kofu Castle became a very important spot. The Tokugawa Shogunate set the Five Major Roads including the Kofu Road passing through Kofu town. Kofu was regarded as the western strongpoint to protect Edo (what is now Tokyo), the Shogun’s home base. For this reason, the Shogunate basically governed the castle directly. For example, the Shogun’s relative Tsunatoyo Tokugawa lived in the castle, who became the sixth Shogun Ienobu later. Yoshiyasu Yanagisawa was the first lord of the castle out of non-Shogun’s relatives in 1705, who was a senior vassal of the Shogunate. His son, Yoshiyasu was transferred to Yamato-Koriyama Castle in 1724, then Kofu Castle was Shogunate-owned again.
The positional relation between Kofu and Edo
In 1868 during the Meiji Restoration, the battle between the New Government and the Shogunate happened. Taisuke Itagaki, one of the leaders of the New Government Army thought they needed to capture Kofu Castle faster than the Shogunate. The Shogunate also sent the famous warrior party called the Shinsen-gumi led by Isami Kondo to Kofu Castle. Itagaki rushed and succeeded to enter the castle by a narrow margin, so that he could defeat the Shinsen-gumi.