この城は、伝説と現実の間(はざま)にあります。
This castle is between legend and reality.

Location and History
「菅谷館」という名前には少し説明が必要です。「館」という用語は、この場合には「中世初期の武士の館」を指します。通常は、平地の上に土塁か柵を伴う館が堀で囲まれている構成でした。例としては足利氏館が挙げられるでしょう。
The name “Sugaya Hall” needs a small explanation. The term “hall” means ”warrior’s hall in the early Middle Ages” in this case. It usually consists of a hall with earthen walls or fences, and a surrounding moat on a plain, for example, like the Ashikaga clan hall.

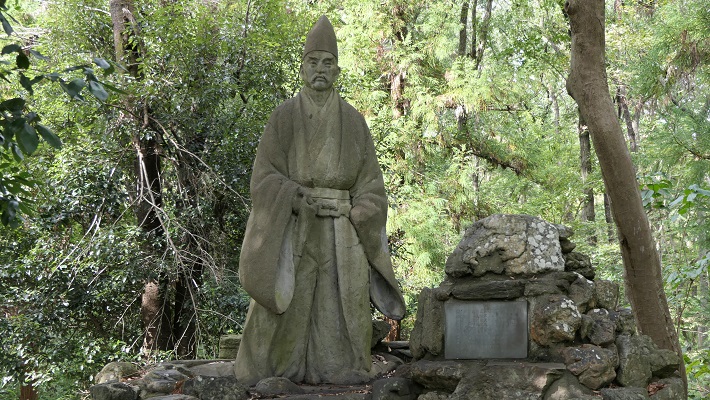
菅谷館には、鎌倉幕府の重臣であった畠山重忠について、当時ここに住んでいたという地元の言い伝えがあります。古い記録である「吾妻鏡」にも彼が菅谷館に住んでいたという記載があります。そのためこの遺跡が菅谷「館」と呼ばれ、ここに重忠の像が立っているのです。
Sugaya Hall has a local tale about Shigetada Hatakeyama, a senior vassal of the Kamakura Shogunate, living there at that time. An old document called “Aduma-Kagami” also says he lived in Sugaya Hall. That’s why these ruins are called Sugaya “Hall” and the statue of Hatakeyama is standing on the ruins.

しかしながら、この遺跡の外観はそのような説明と違っています。明らかに戦国時代の城跡に見えるのです。その時代の古書もまたこの城を「館」ではなく、菅谷「城」と記しています。加えて、発掘の結果からも戦国時代の1500年前後に使われたことが判明しています。つまるところ、「菅谷館」という名前は、行政側による伝説と現実との間での妥協の産物のようなのです。
However, the appearance of the ruins is different from such descriptions. They look like the ruins of a castle in the Warring States Period obviously. Old documents in the period also call them Sugaya “Castle”, not “Hall”. In addition, the result of excavation says the castle was used around 1500 in the Warring States Period. Overall, the name “Sugaya Hall” seems to come from a kind of compromise between legend and reality by the officials.

いずれにせよ、この城は1488年の「須賀谷原の戦い」のような戦国大名が戦いを繰り広げた重要な地域にありました。戦国大名の一つ、扇谷上杉氏がその戦いのため菅谷古城を再興したこと、しかし敗れてその城に幽閉されたことが記録されています。他の文書にはその約100年後には北条氏がこの城を使っていたとあります。つまり、この城は何度か使われたり放棄されたりしたようなのです。
Anyway, the castle was in the important area where warlords battled each other such as “The battle of Sugayahara” in 1488. Records say that one of the warlords, the Ogigayatsu Uesugi clan, restored the old Sugaya Castle for the battle, but they were defeated and kept under arrest in the castle. Another document says that the Hojo clan used the castle about 100 years later. After all, the castle seemed to be used and abandoned several times.
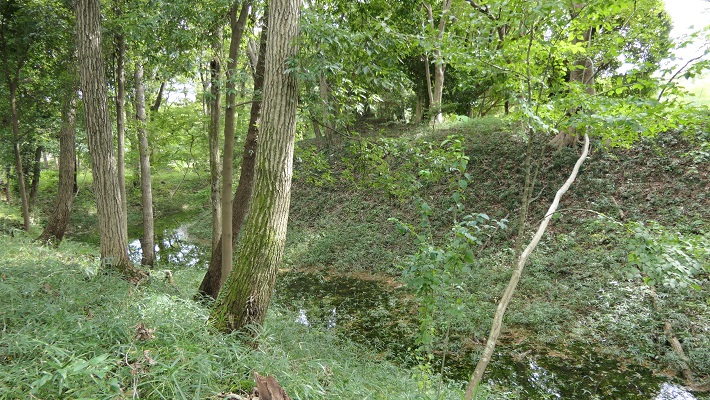

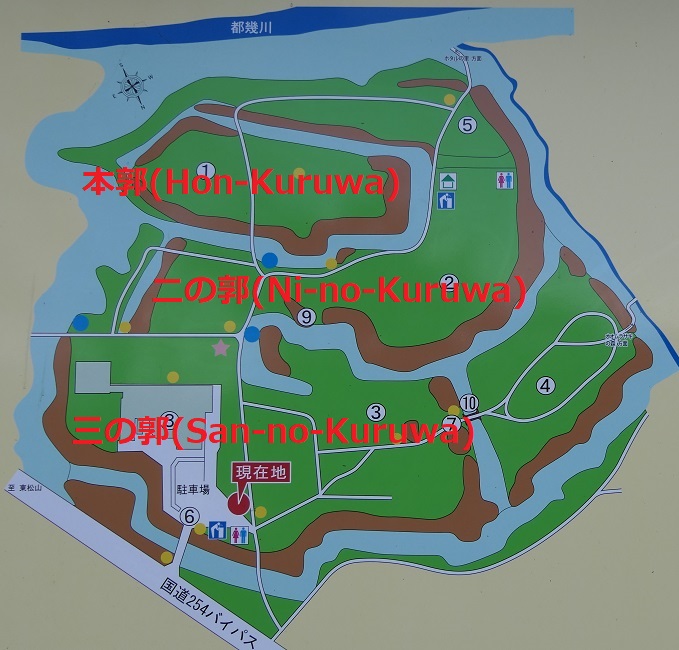
菅谷城は現在の埼玉県西部にあたる場所の低台地上にあり、近くには中世の主要街道である鎌倉街道が通っていました。中心の本郭は、背後を都幾川に、両側を自然の渓谷により守られていました。本郭の入り口は厳重に防御され、二の郭、三の郭などいくつかの郭が本郭の前に広がっていました。
Sugaya Castle is located on a low plateau in what is now the western part of Saitama pref. where the Kamakura road, a main road in the Middle Ages was passing nearby. The main enclosure, “Hon-Kuruwa”, was protected by the Tokigawa river behind it and natural valleys both sides. The entrance of Hon-Kuruwa is strictly guarded and several enclosures including “Ni-no-Kuruwa” and “San-no-Kuruwa” spread out in front of Hon-Kuruwa.
Features
菅谷館跡には建物はありませんが、基礎は残っており、よい状態で保存されています。基礎は全て土造りであり、戦国時代の東国においてはそれが一般的な方法でした。
The ruins of Sugaya Castle retain their foundation but with no buildings. The foundation is well preserved, and is all made from soil which is a typical method of building castles in eastern Japan in the Warring States Period.
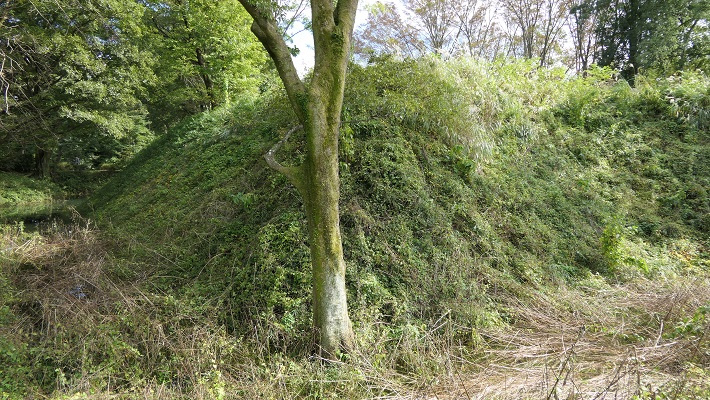

一例として、本郭を見てみましょう。この郭は、重忠の館があったと考えられています。それが事実なら、後から城の中心部分として強化されたはずです。
Let’s look at Hon-Kuruwa for instance. This enclosure is thought to be Hatakeyama’s hall. If it’s true, it must have been strengthened as the center of the castle later.

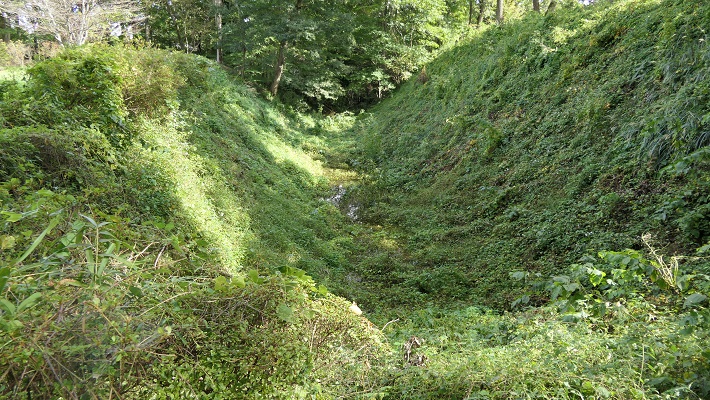
本郭は、高い土塁と深い空堀に囲まれています。これにより、防御側は敵の攻撃から守りやすくなります。「虎口」と呼ばれる入り口は狭くなっており、そこに至る進路はジグザグに作られていて、敵がまっすぐ内部に入れないようになっています。
Hon-Kuruwa is surrounded by a high earthen wall and deep dry moat. That makes it easier for defenders to protect them from an enemy’s attack. Its entrance, called “Koguchi”, is narrow and the route to it is made zigzagged so that attackers are unable to enter inside directly.


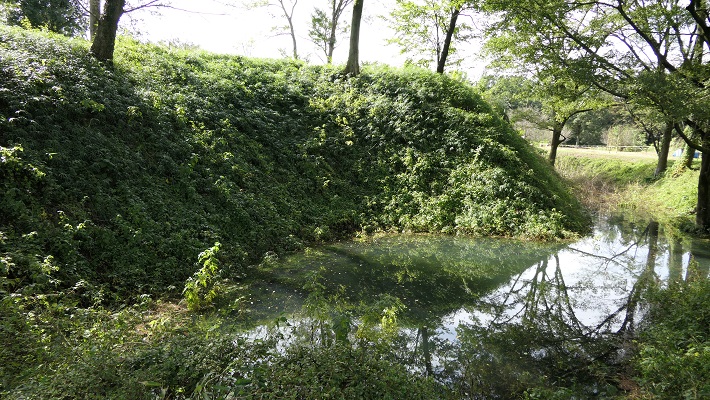
更には、この土塁は部分的に意図的に突き出ています。これにより防御側はその部分から敵の正面と側面両方を攻撃することができます。このような構造は「出桝型土塁」と言われます。これは戦国時代においては、他の構造と組み合わせることで、高度な城の防御システムとなりました。よって一部の歴史家は、北条氏が城を改修したのだろうと推定しています。
In addition, the wall is partly stuck out on purpose. This allows defenders to attack from the sticking point to an enemy’s front and sides. Such a structure is called a “Dematsu” shaped earthen wall. It is an advanced system when combined with other defensive features for castles in the Warring States Period. So some historians speculate Hojo might have improved the castle.



Later Life
この城は戦国時代の終り頃から長い間放置されていたようです。それ以来、城跡は民間の所有となり、畠山重忠の遺産であると思われてきました。約100年前の大正時代に初めてここが調査されたとき、重忠の像が建てられます。1973年になって遺跡が国の史跡に指定され、2008年には「比企城館跡群」の一つに改めて指定されました。
The castle seemed to be abandoned for a long time since sometime at the end of the Warring States Period. Since then, the ruins were private owned and thought of as Hatakeyama’s heritage. His statue was built when the ruins were first investigated in the Taisho Era about 100 years ago. In 1973, the ruins were designated as a National Historic Site, then were newly designated one of the “Hiki Castles Ruins” in 2008.
My Impression
関東地方の戦国大名は必要な数だけ城を作りました。その城がいらなくなったときは、速やかに廃城としました。一方、廃城となった城を再利用したいときは、その城を再建または増築しました。結果として城を廃城とするときは、完全には破壊しませんでした。代わりに一部を壊すか、建物だけを撤去しました。恐らくそれが効率的で、且つ再利用しやすかったからでしょう。それで菅谷館(城)の基礎がよく残ったと思うのです。
Warlords in the Kanto region built castles as many as they needed. When they didn’t need the castles, they immediately abandoned the castles. On the other hand, when warlords wanted to reuse abandoned castles, they restored or improved the castles. As a result, when warlords abandoned castles, they didn’t completely destroy the castles. Instead, they often destroyed part of the castles, or just remove their buildings. Probably it could be because it is more efficient and easy to reuse. I think that’s why the foundation of Sugaya Hall (Castle) remains well.

今、城跡の三の郭には嵐山史跡の博物館があります。そこでは比企城館跡群(菅谷館、杉山城、松山城、小倉城)の歴史や出土品を展示しています。そこで歴史を学んでまず菅谷館に行ってみましょう。その他の内、杉山城はここからわずか5キロのところにあります。両方行ってみるのもよいでしょう。
There is the Ranzan Historical Museum on San-no-Kuruwa of the ruins now. It shows the exhibition of history and the excavation about Hiki Castle Ruins including Sugaya Hall, Sugiyama, Matsuyama and Ogura Castles. Let’s look into their history and visit Sugaya Hall first. Out of the others, Sugiyama Castle ruins is only about 5 km from there. So, how about visit the set of them.

比企城館跡群の4つの城(The four castles of Hiki Castle Ruins)
How to get There
車を使う場合、遺跡は関越自動車道の嵐山小川ICの近くです。嵐山史跡の博物館に駐車場があります。
電車を使う場合は、東武東上線の武蔵嵐山駅から歩いて約15分です。
東京から武蔵嵐山駅まで:池袋駅から東武東上線に乗ってください。
When using car, the ruins is near Ranzan-Ogawa IC on Kan-Etsu Expressway. Ranzan Historical Museum offers a parking lot.
When using train, it takes about 15 minutes on foot from Musashi-Ranzan Station on Tobu Tojo line.
From Tokyo to Musashi-Ranzan Station: Take the train on Tobu Tojo line from Ikebukuro Station.
