Features
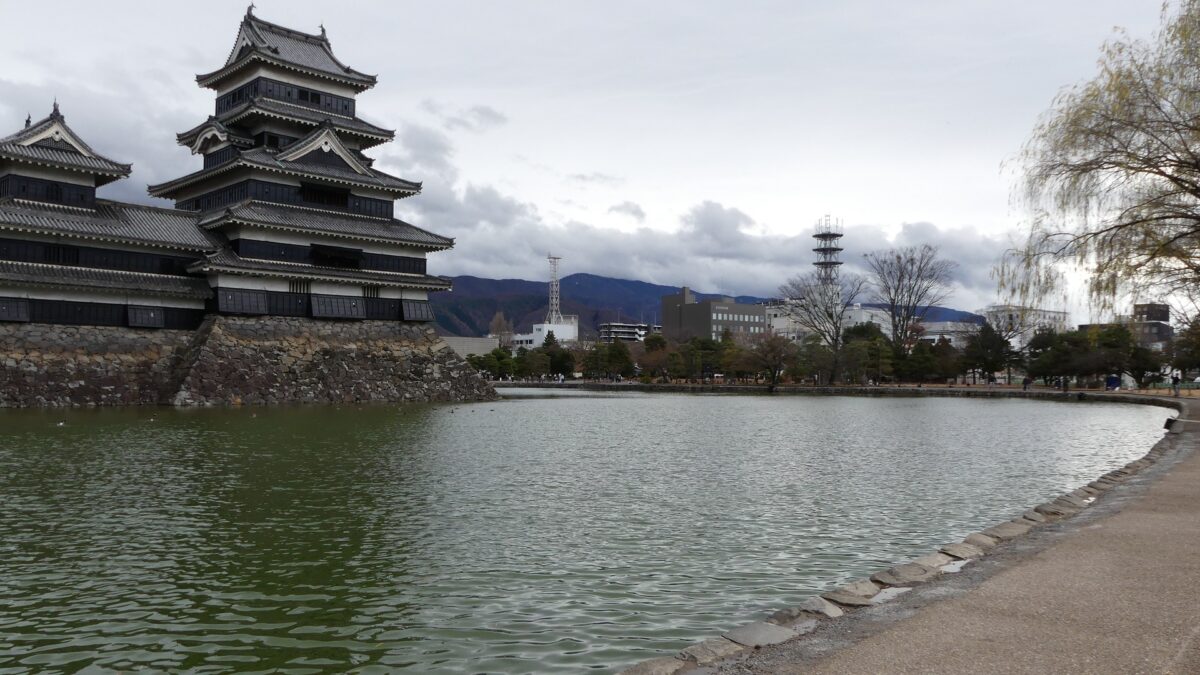
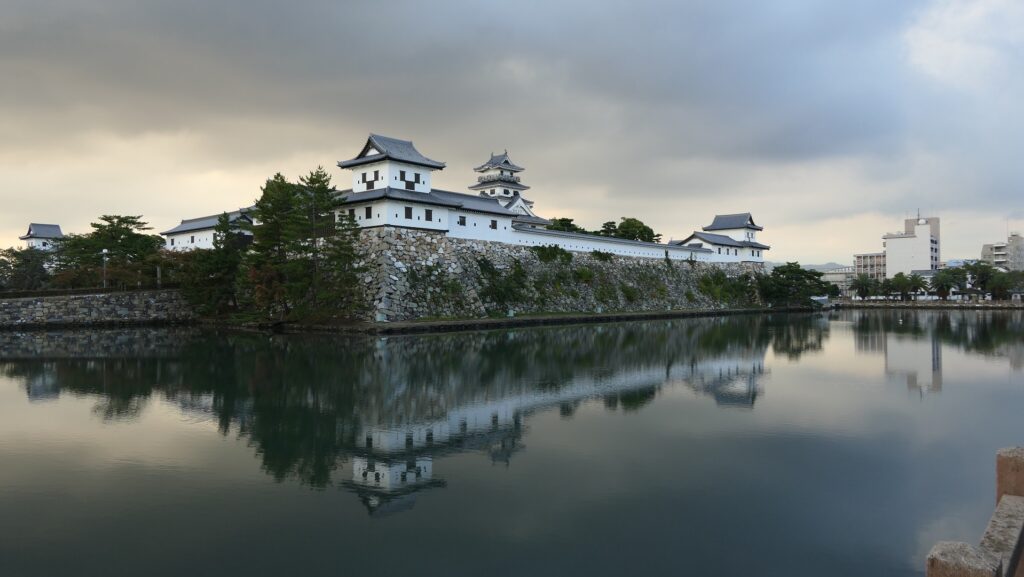
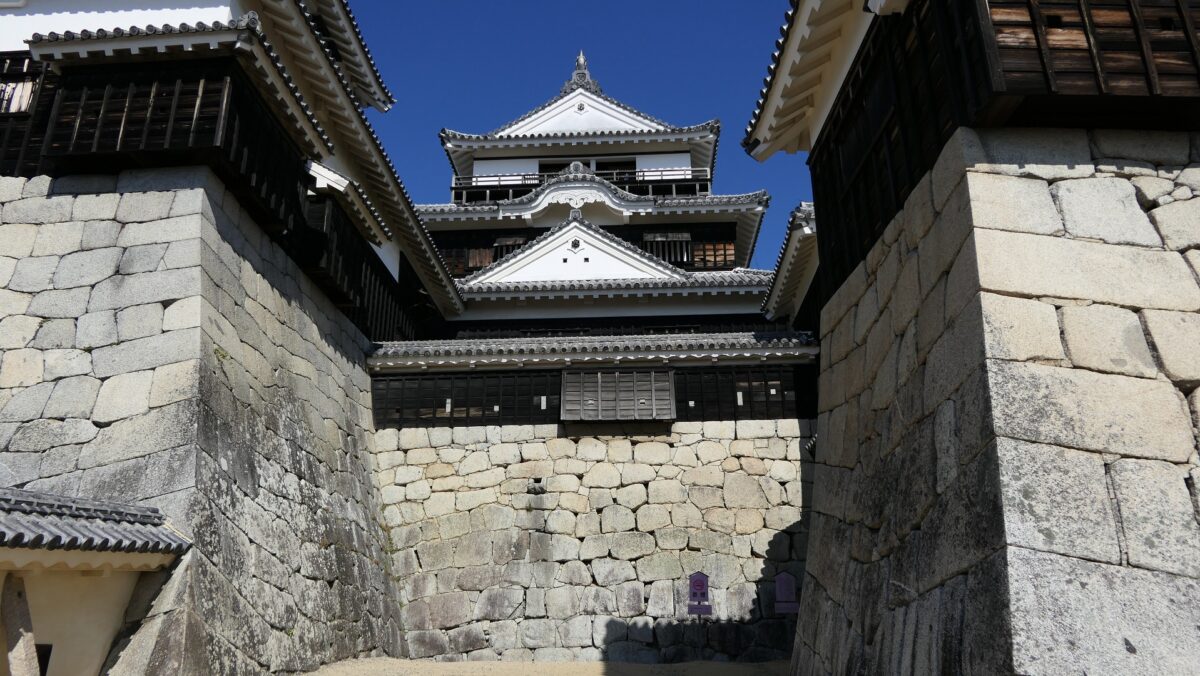
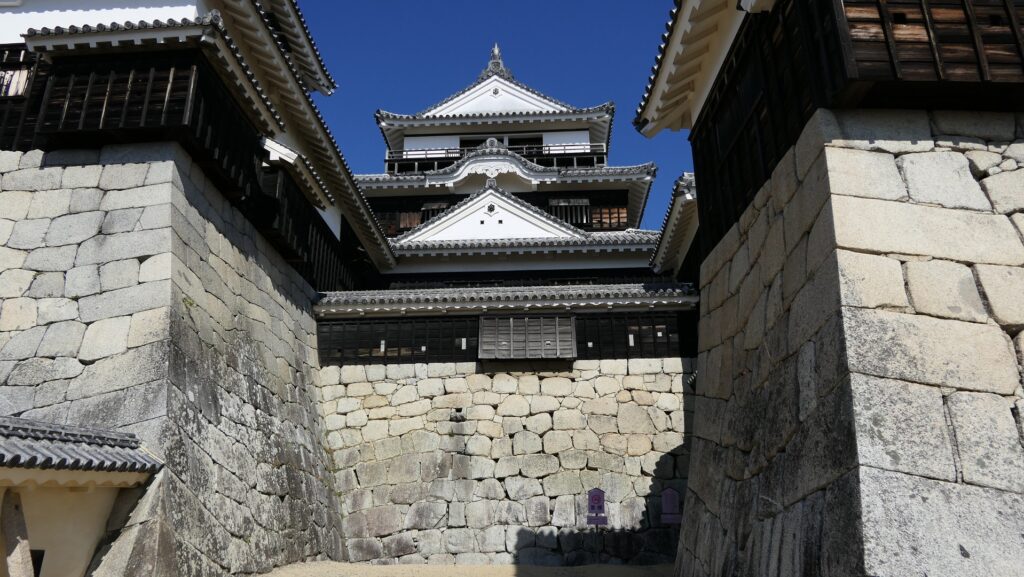
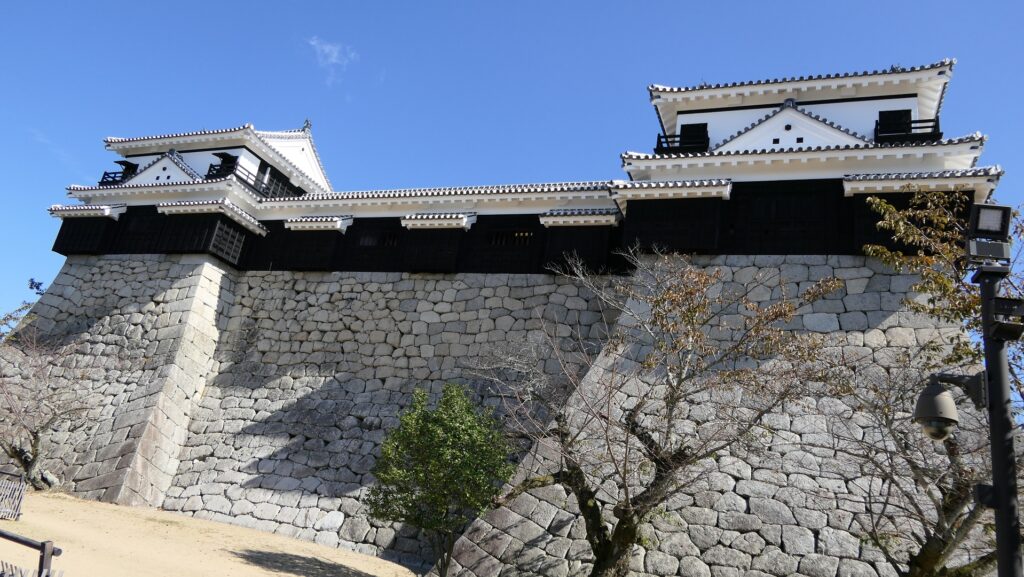
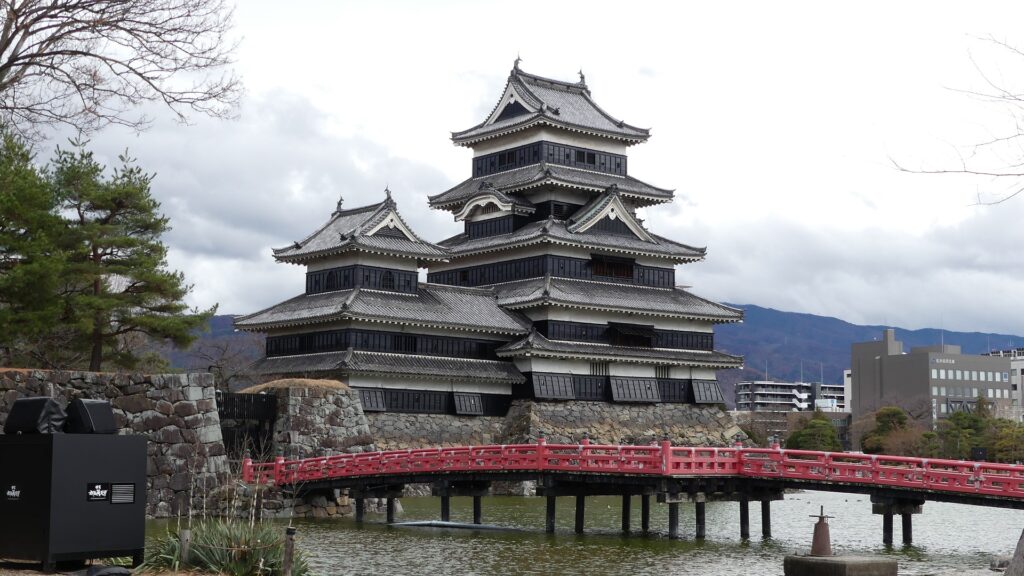
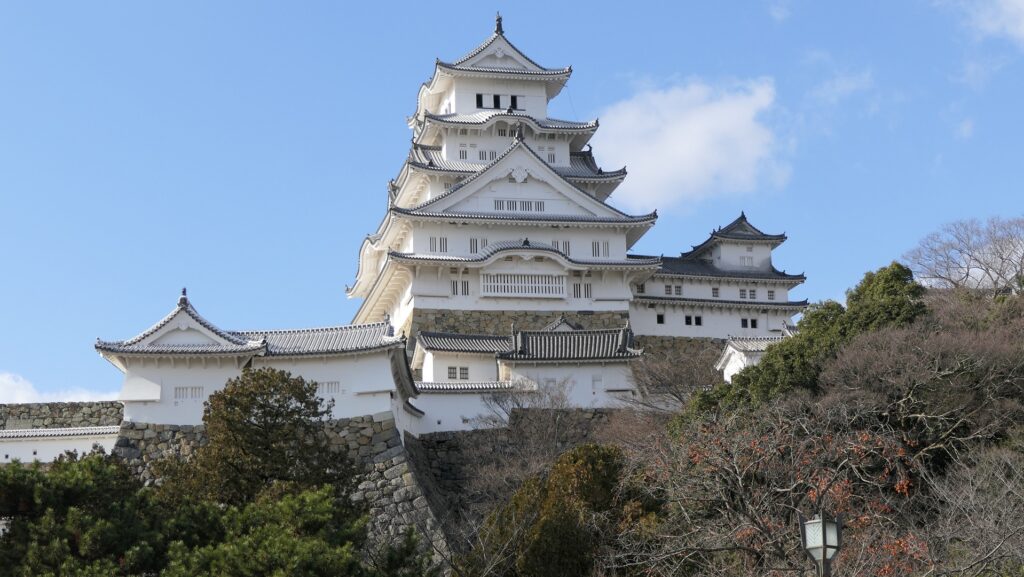
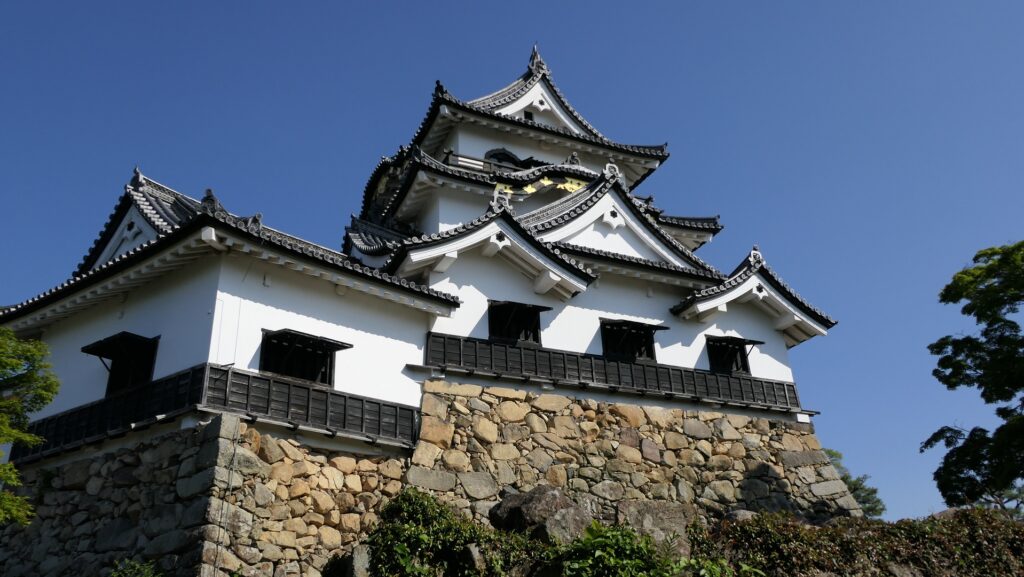
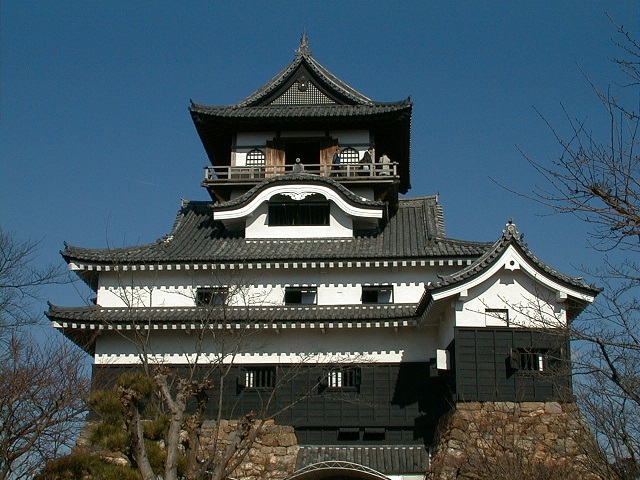
When you arrive at Matsumoto Castle, in the present time, the first thing you have to do is to enjoy its Main Tower. It is one of the only two remaining five-level Main Towers, followed by Himeji Castle, one of the five Main Towers of Japan’s National Treasures (the previous two plus Hikone, Inuyama and Matsue Castles), and one of the twelve remaining Main Towers.





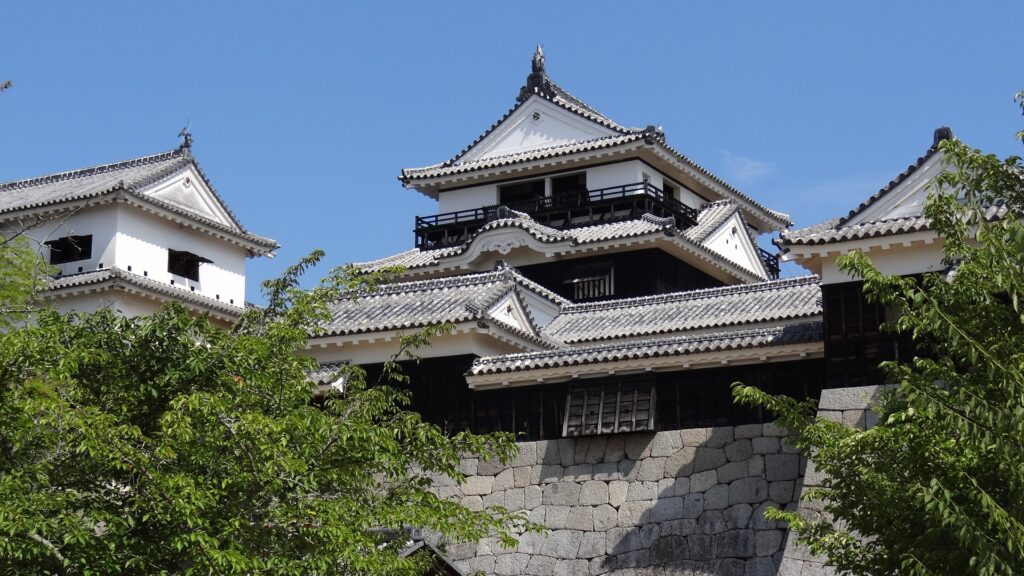
Beautiful but Strong Main Tower
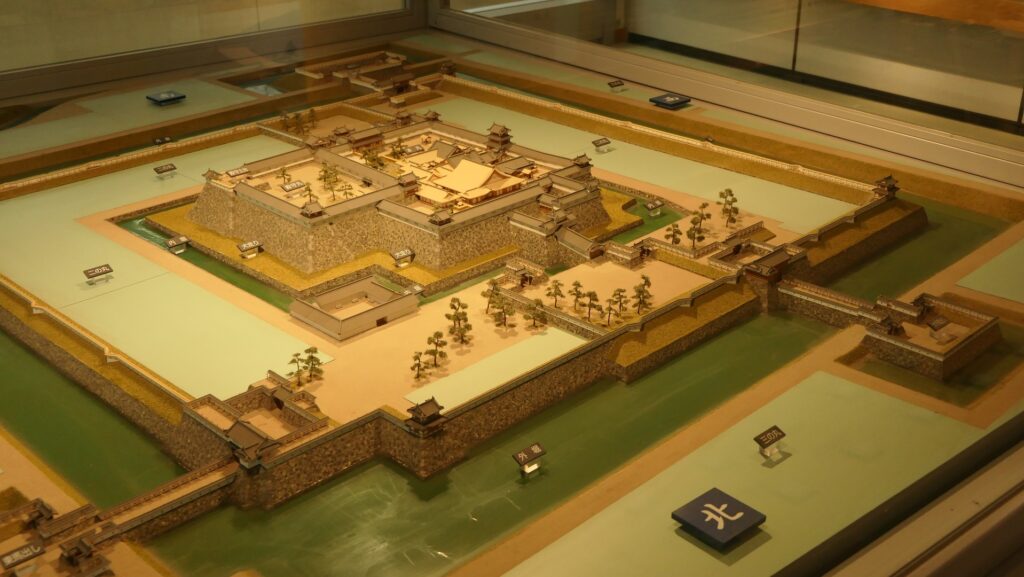
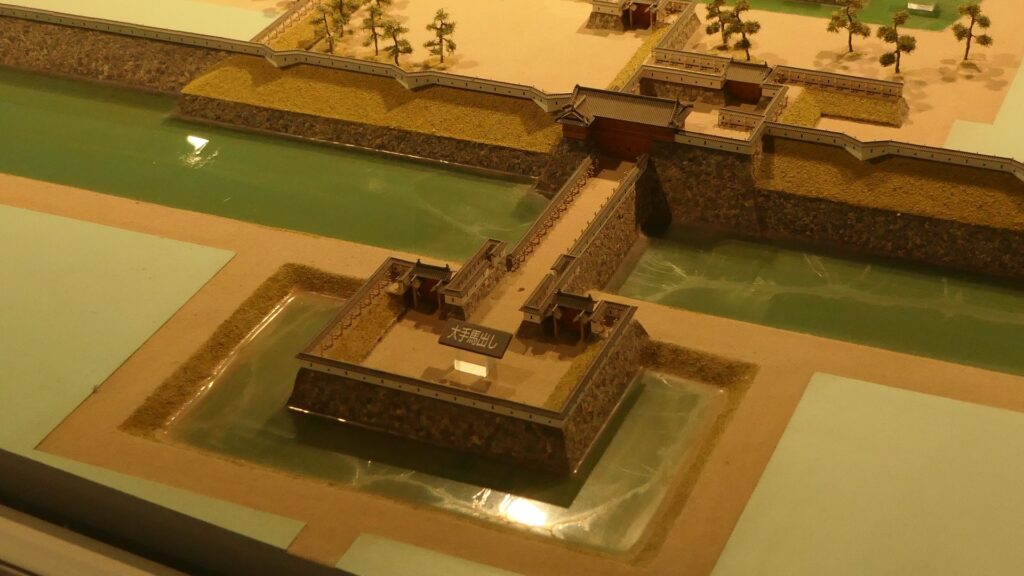
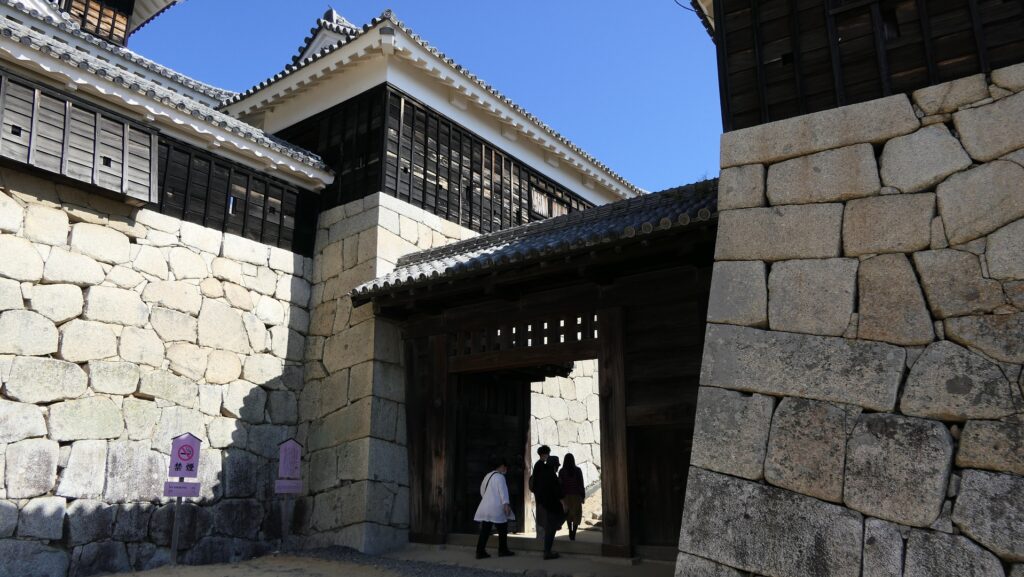
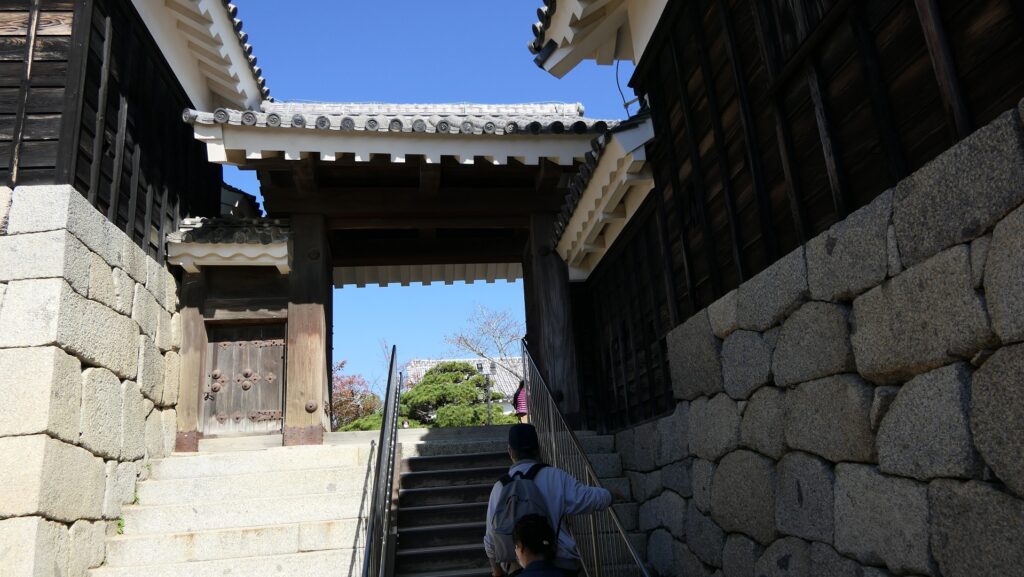
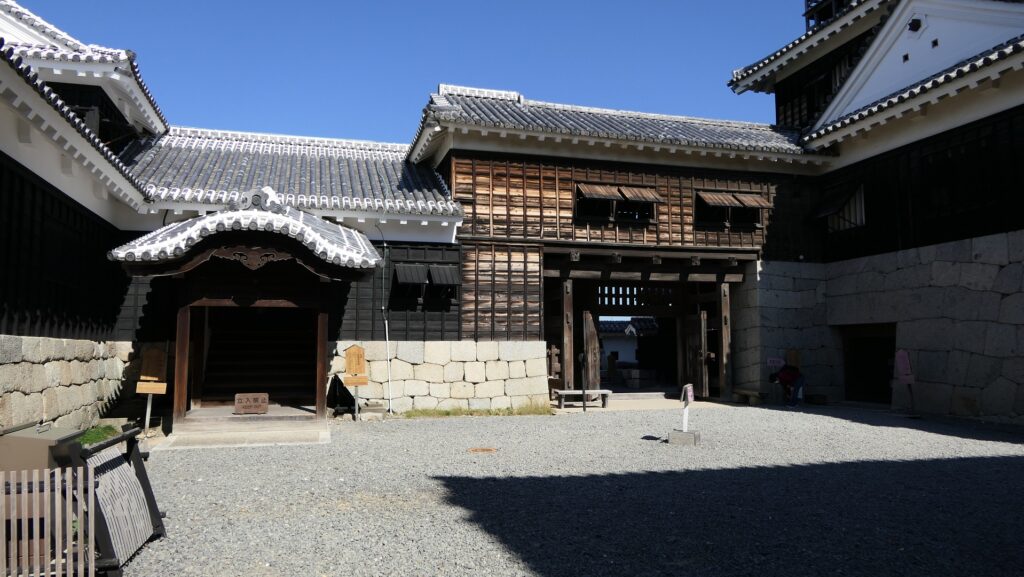
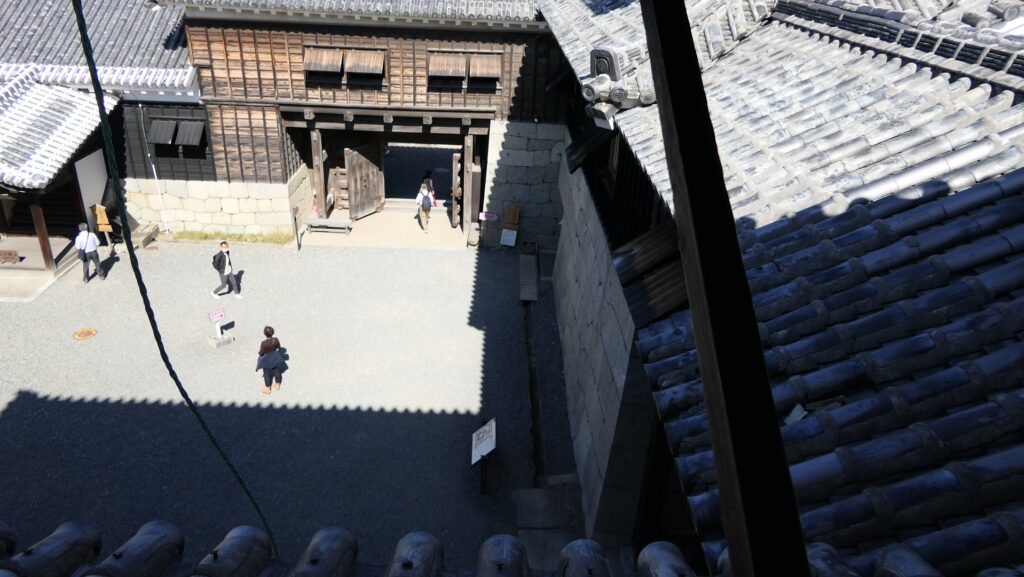
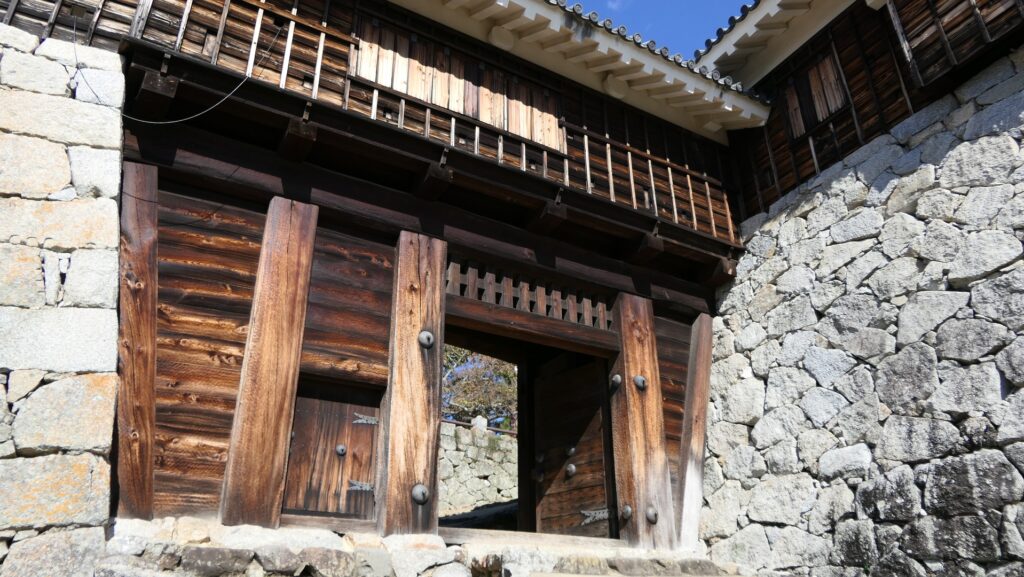
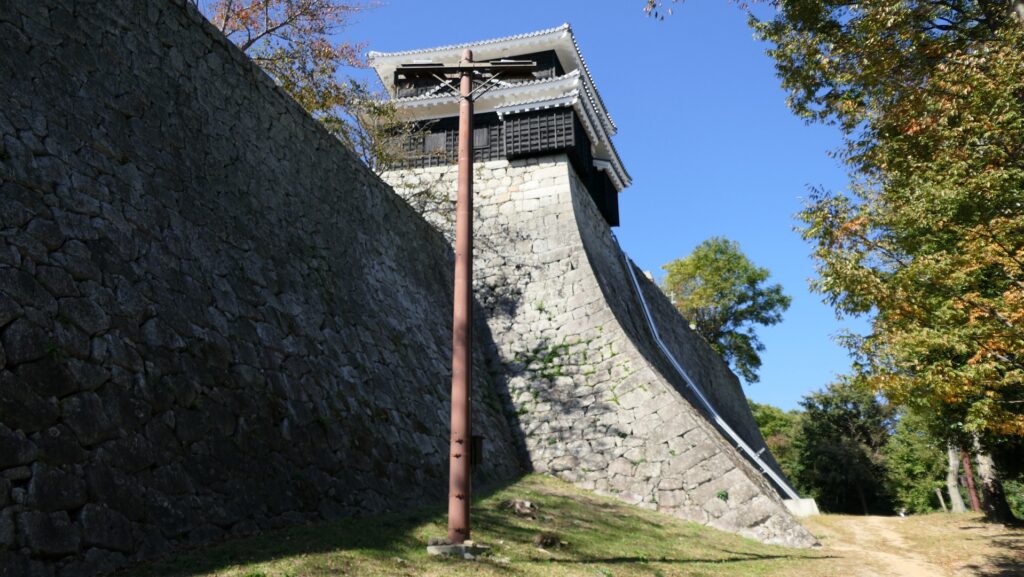
It may be a good idea to walk around the inner moat surrounding the main enclosure to enjoy a beautiful view of the tower before entering it. The width of the moat in front of the tower is about 60m. It would make enemies shooting up from the side ineffective but defenders shooting down from the tower more effective at that time. In addition, if the enemies could swim across the moat to the tower, they would be heavily counterattacked by the defenders through its defense systems such as machicolations and loopholes.
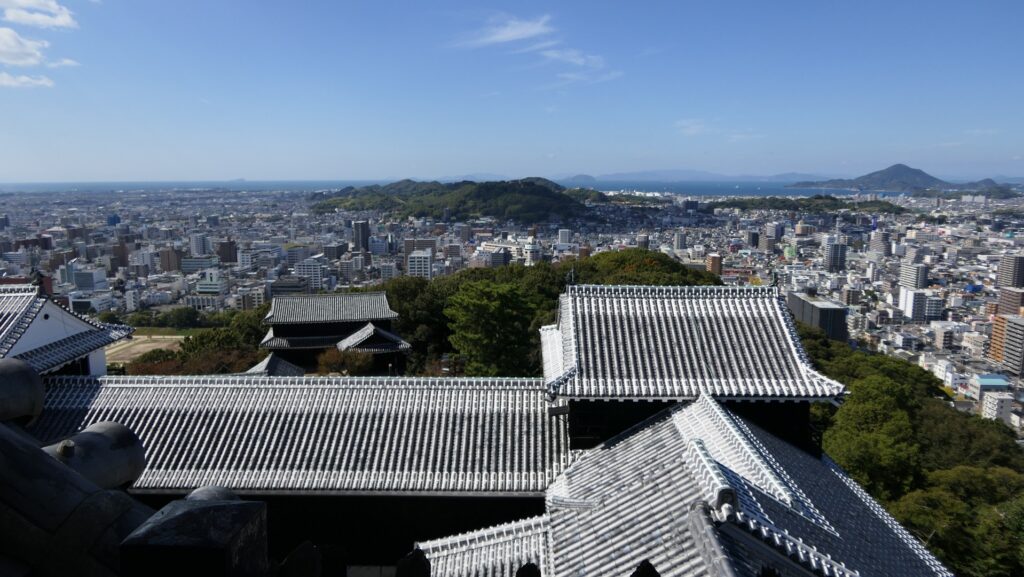
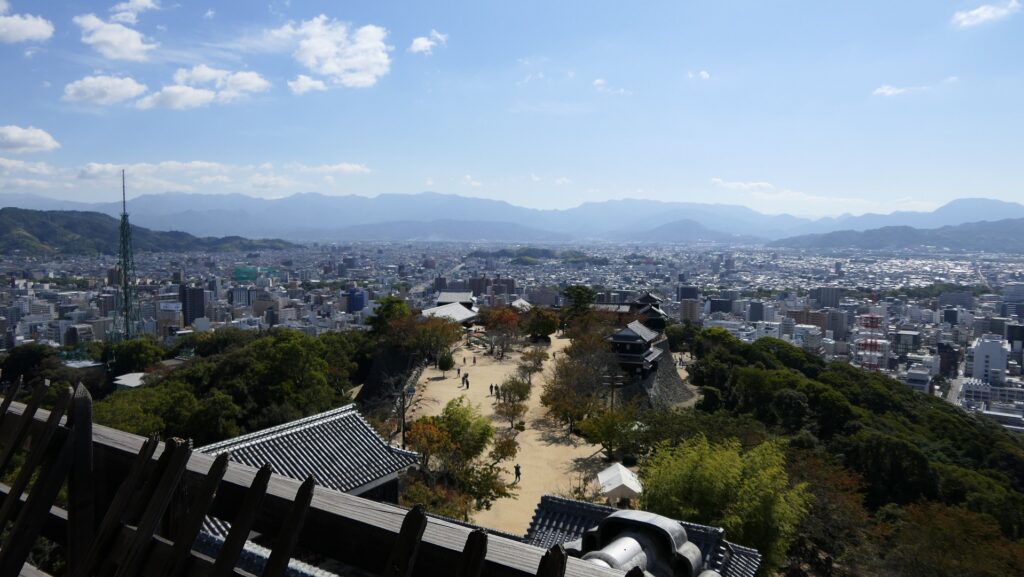
The aerial photo around the castle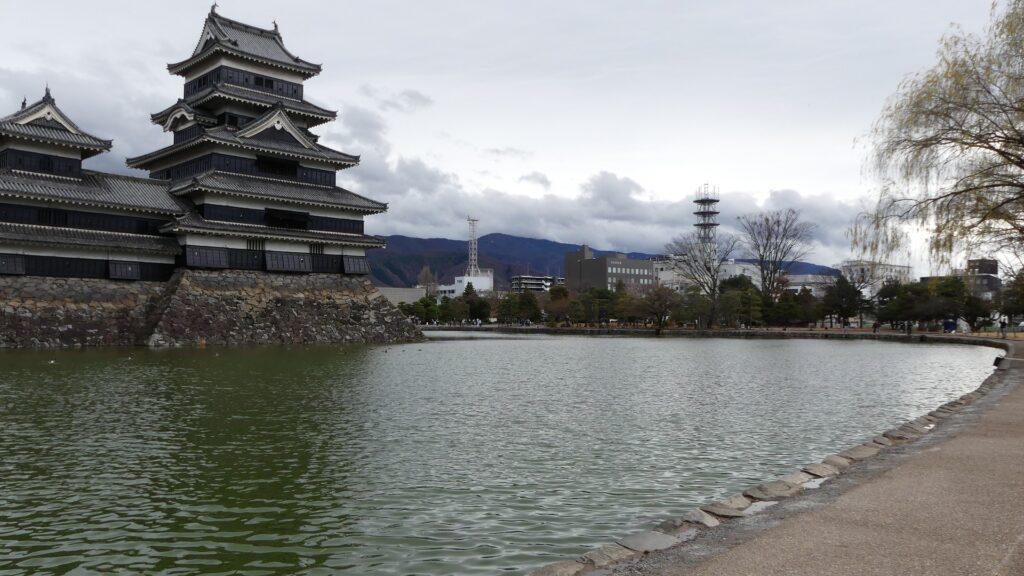

Reasons for Black Main Tower
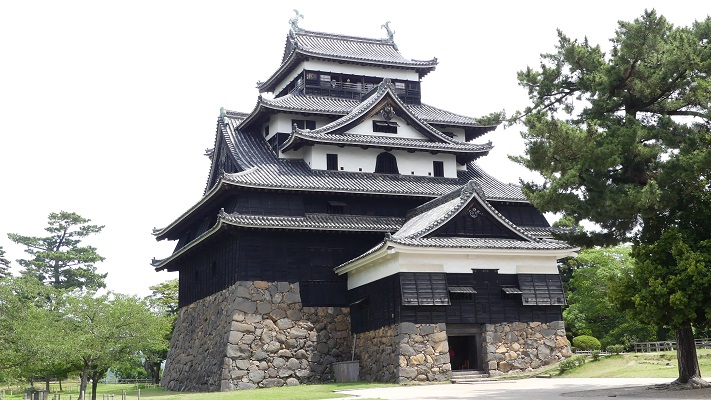
The black-looking Main Tower of Matsumoto Castle (sometimes called “Crow Castle”) is often compared with the Himeji castle’s painted white clearly by contrast. Its black appearance comes from its wooden side walls covered with special Japanese lacquer, which could withstand harsh weathers. Himeji Castle is covered in plaster, which make it look white, and it is newer than Matsumoto Castle. It is said that using plaster on all walls of a castle would not effectively protect against the rain when Matsumoto Castle was built. That meant the improvements in wall painting techniques occurred between the building of the two castles. Another possible reason for the using the black walls is that wooden walls are stronger than plaster walls against the cold winter of inland area like the Matsumoto Basin.
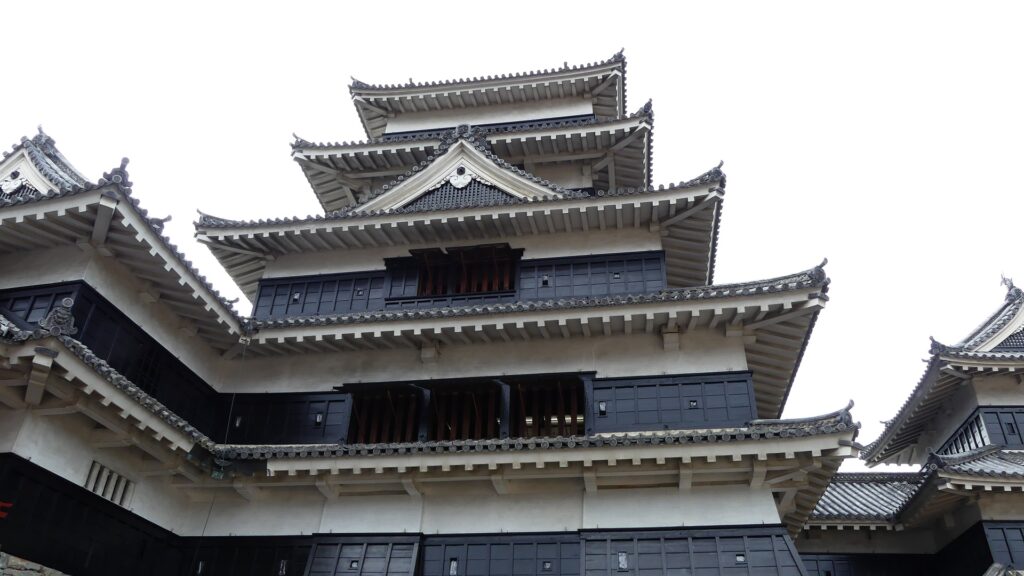
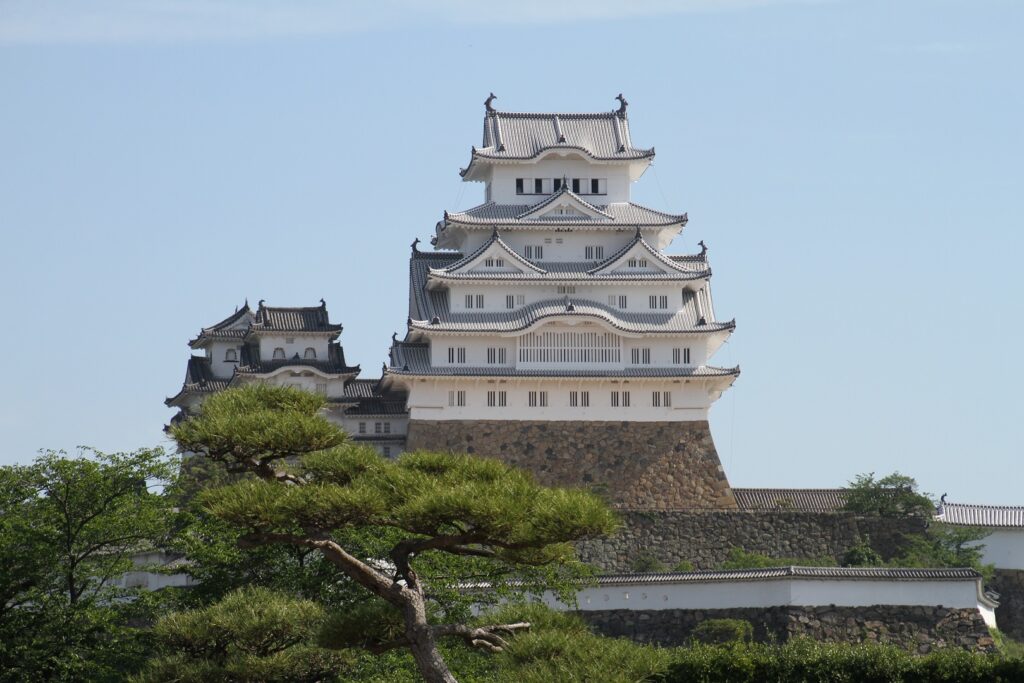


Some also say black was a favorite color of Hideyoshi Toyotomi, while white was the color which Ieyasu Tokugawa often used for his castles when Himeji Castle was built. Anyway, these speculations are enjoyable to see the contrast.


Unique Lookout Tower
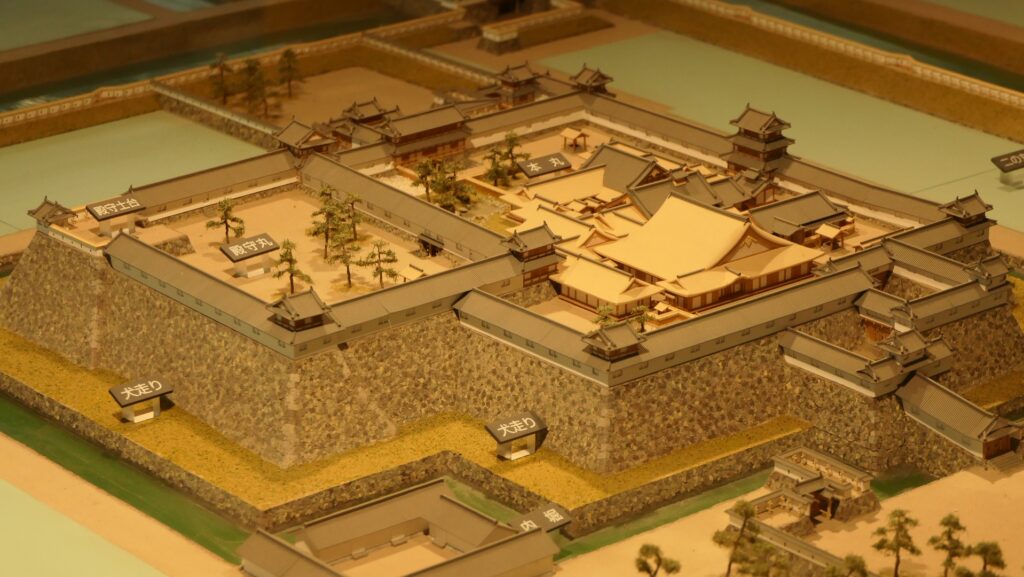
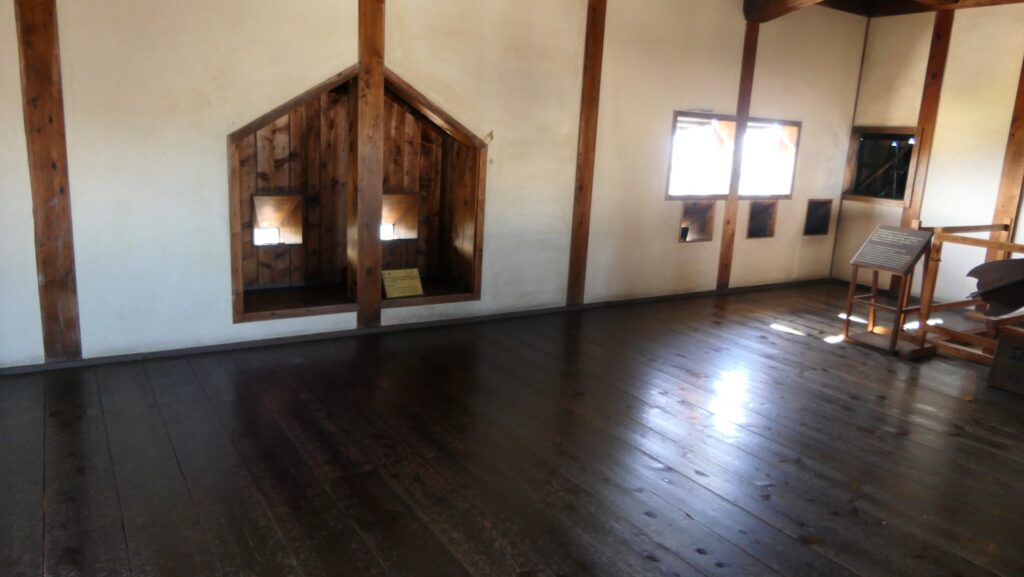
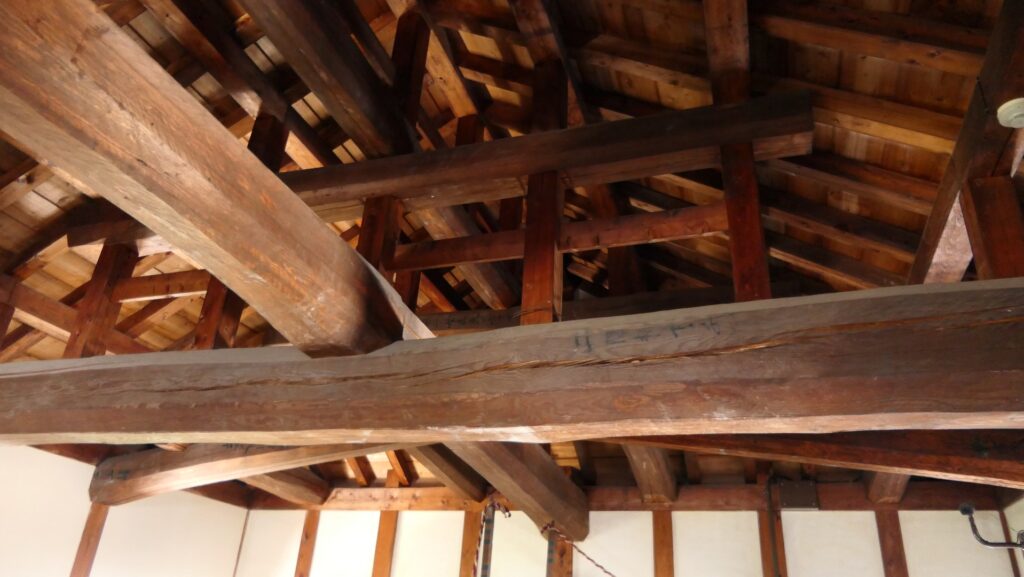
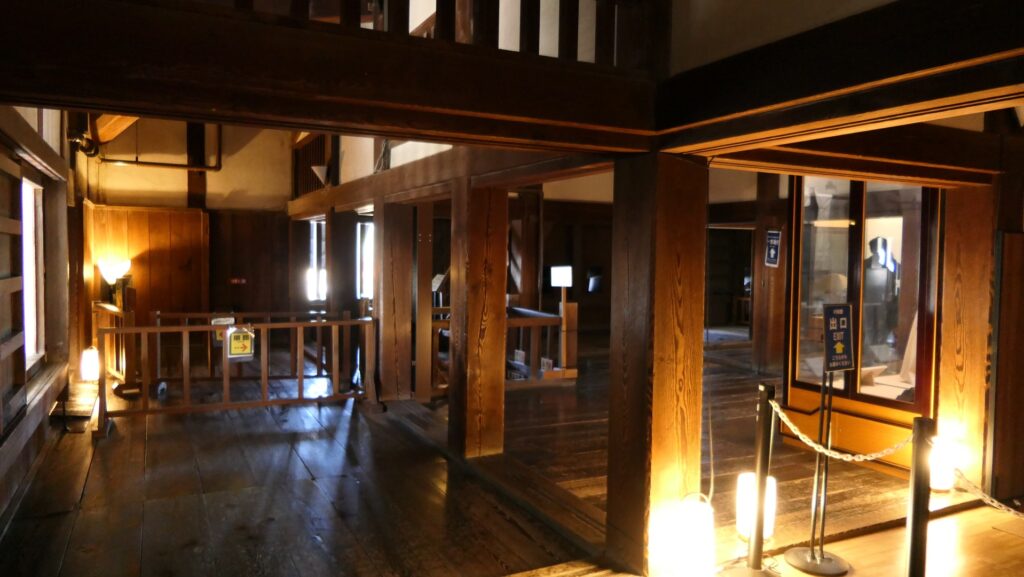
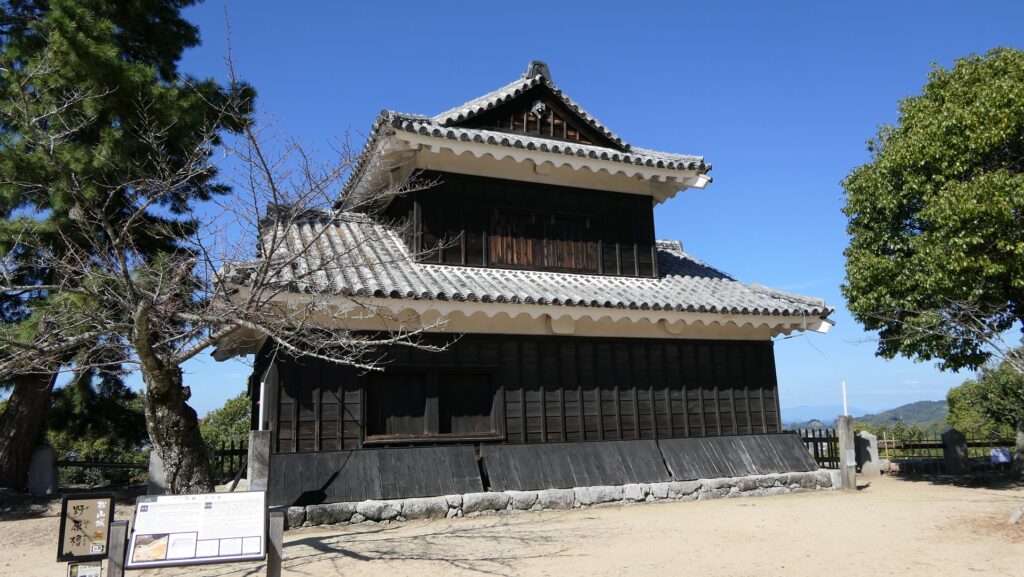
The Main Tower of Matsumoto Castle actually consists of the large main tower, the Inui small main tower, and three turrets (Watari Yagura, Tatsumi-Tsuke Yagura and Tsukimi Yagura) which are connected to each other. This is called “multiple attached style”. The large one is generally considered “the Main Tower”. The tower has five levels but six floors inside. This type of the tower is called the lookout tower type, which refers to a small lookout tower on a large turret. In the case of Matsumoto Castle, the turret part is the first and second floors and the fifth and top floors is the tower part, binding the middle part of the third and fourth floors. However, the third floor is built as the attic of the turret part, with no roof. That’s why the numbers of its levels and floors are different.
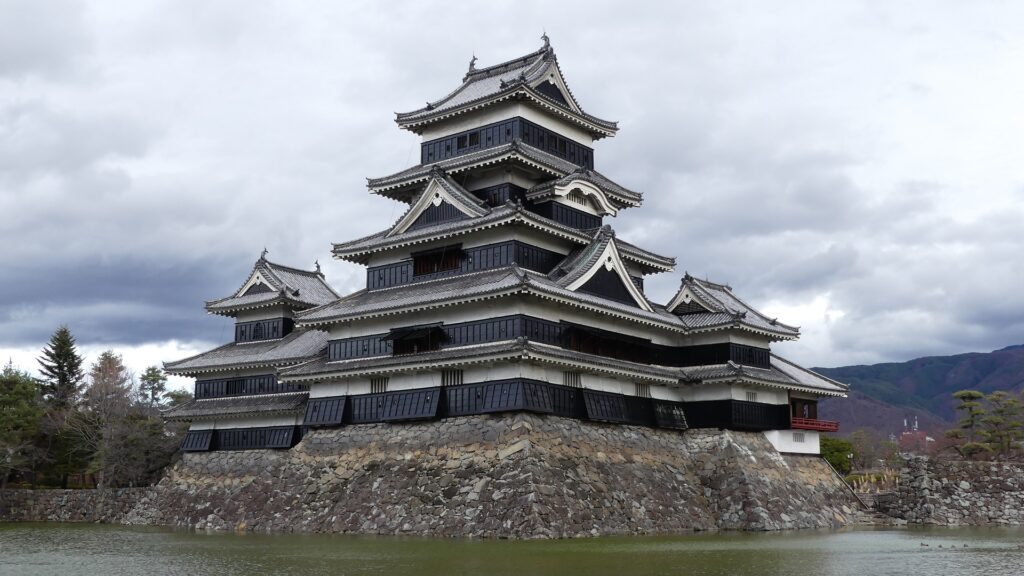

In addition, the Main Tower has a striking appearance for a lookout tower. One of the reasons for this is that the top floor doesn’t have a veranda, which lookout towers usually had, and is covered with walls. The fact is that it had been first planned to have a veranda, but was changed to its current state during construction. As a result, the tower looks a little top-heavy.

To be continued in “Matsumoto Castle Part3”
Back to “Matsumoto Castle Part1”