Location and History
Sakura Castle was located at the current Sakura City of Chiba Prefecture. The castle was built as the home of the Sakura Domain during the Edo Period, which is the origin of the city. The areas around the city had many other castles until the Sengoku Period and some of which were very important. For example, there was Usui Castle in the western part of the city, where the battle of Usui Castle happened back in 1566. Kenshin Uesugi, who tried to rule the whole Kanto Region, attacked the castle but failed. There was also Motosakura Castle in the eastern part, which was the home of the Chiba Clan. Usui Castle was a branch of the clan. Cuttently, this castle is called “Motosakura” but back then, it was called “Sakura Castle”. So therefore, Sakura Castle was the former name of Motosakura Castle. This article will explain the formative years of Sakura Castle including the formation of Motosakura Castle, which should make it easier for people to better understand the history.


Formative Years of Sakura Castle
The Chiba Clan had owned Shimosa Province, which was the northern part of Chiba Prefecture, since the end of the ancient times. The most famous person of the clan would be Tsunetane Chiba who supported the launch of the Kamakura Shogunate at the end of the 12th Century. Their home, Inohana Castle, was located at the current Chiba City for a long time. However, the castle was destroyed when many battles occurred in the 15th Century during the Sengoku Period. The clan decided to rebuild their new home in another location, which would be called Motosakura Castle. The castle was on the Shimosa plateau and was surrounded by Inbanuma Lake and other waterlogged areas. Its location was much more fortified than before and more convenient for water transportation. The lake was also much larger than now, where people could easily access Kasumigaura Lake and other great rivers. The wide water area was even called Katori-no-umi, which means the Katori inland sea.


The situation changed during the 16th Century. The Hojo Clan was invading the Kanto Region from the west. On the other hand, the Satomi Clan also got the power from the south (Boso peninsula). The Chiba Clan wondered what to do and they eventually allied with the Hojo Clan. That’s why Kenshin Uesugi, who would help the Satomi Clan, decided to attack Usui Castle, a branch of the Chiba Clan. The victory of the clan was partially due to the Hojo Clan’s help. As a result, the Hojo became more effective to the Chiba Clan. As for the home of the clan, Chikatane Chiba, who was the lord of the clan before the battle, originally planned to move his home from Motosakura to another. The new land for his new home later became Sakura Castle, which was called Kashima Castle then. Mysteriously, he died in 1533, which ultimately canceled his plans of moving the castle.
The location of the castle, Notice the smaller Inbanuma Lake on the left next to Usui Castle. This important river used to span much larger that what the current map is showing. It used to be part of a much larger body of water.

The Hojo Clan interfered in the internal affairs of the Chiba Clan at the end of the 16th Century. For instance, Ujimasa Hojo married his daughter to Kunitane Chiba, the lord of the clan. The Hojo Clan allowed Kunitane to resume the construction of Kashima Castle but failed to do so because the lord was killed again. Ujimasa next married his son to Kunitane’s daughter, in order to be the successor of the clan. It was said that Kashima Castle was finally finished for the new home of the couple.

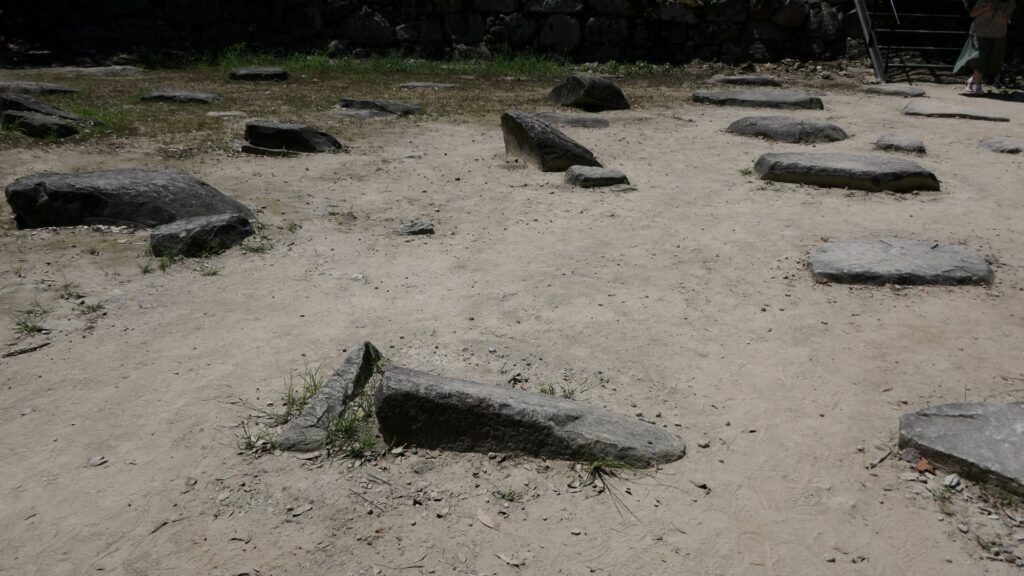
However, it is difficult to confirm whether these records are the factual, as Sakura Castle was built on the old Kashima Castle. The few discovered old dry moats at the site proved that they were at least trying to build the castle there. So, why did the Chiba and Hojo Clans want to move there again and again? One of the reasons would be that the land for the new castle was much larger than the old one. For the Hojo Clan, another possible reason may have been to protect their territories from the potential invasions by Hideyoshi Toyotomi from the west. The plateau, where the new castle was built on, had steep slopes and was surrounded by rivers towards the direction. That would have had a very defensive fort against the invasion. However, the Chiba Clan was eventually fired by Hideyoshi, after their master, the Hojo Clan was defeated at the battle of Odawara Castle in 1590.


Toshikatsu Doi builds Sakura Castle
After the Battle of Odawara Castle, several lords were assigned one after another by Ieyasu Tokugawa who was the founder of the Tokugawa Shogunate. In 1610, Ieyasu ordered his retainer, Toshikatsu Doi to stay in Motosakura Castle and to build a new home at the former location of Kashima Castle, which would eventually be called, Sakura Castle. The new castle was supposed to support Edo Castle, the home of the shogunate. If Edo Castle was attacked by enemies from the west, the shogun could escape from his home to Sakura Castle towards the east. Sakura Castlewas situated in a great location that had very strong natural defense.
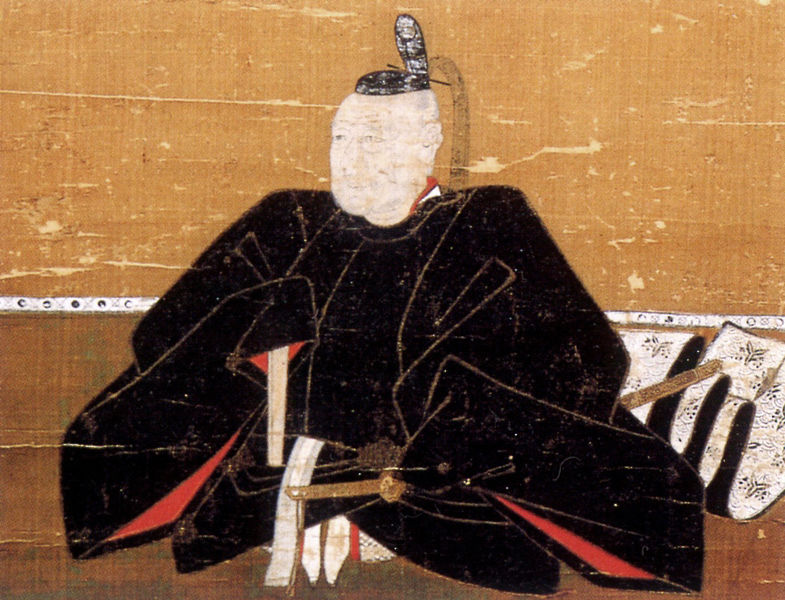

Toshikatsu served three generations of the shoguns: Ieyasu, Hidetada, and Iemitsu. He was one of the most important senior vassals for them and established the system of the government. He was born in 1573 when Ieyasu was only a warlord during the Seongoku Period. There are some theories about who his father was.
The first one is that Toshimasa Doi was his father, according to the official family trees by the shogunate.
The second one claims that he was a son of Nobumoto Mizuno who was a brother of Odai, Ieyasu’s mother, according to the official history books of the shogunate. Odai originally came from the Mizuno Clan.
The last theory is the most surprising theory, it was said that Toshikatsu was an illegitimate son of Ieyasu, according to the official trees of the Doi Clan.
Each theory has substantial evidence, however only one theory can be true. Why were there different theories?

Recent studies believe the followings. Toshikatsu has a short sword where the family crest of the Mizuno Clan was engraved. It was passed down from Odai to Ieyasu who gave it to Toshikatsu. That meant Toshikatsu was Ieyasu’s son. However, it was a very know fact, which was not recorded officially. That’s why the official family trees simply say Toshikatsu was a biological son of the Doi Clan (in fact, adopted). After that, Toshimasu Doi, who was a grandson of Toshikatsu, was worried about the declining reputation of his clan. He thought that he should settle the mystery of his grandfather to gain a stable position for the clan. His decision was that he would announce that Toshikatsu was a son of the Mizuno Clan by using its family crest on the sword. The writers of the official history books probably heard about it. Finally, Toshisato Doi, the 8th lord of the clan, was asked as to who Toshikatsu’s mother was by the shogunate. Toshisato decided that he would answer by telling the truth and put it on his clan’s official trees. However, the shogunate couldn’t accept it because the matters of Ieyasu were too serious to change for them. As a result, the three theories certainly unchanged today. As for Toshikatsu himself, he became a close vassal of Hidetada, who was the successor of Ieyasu, when Toshikatsu was only 7 years old. No matter who his father was, it’s no mystery that he was a very talented person.

When Ieyasu established the shogunate, his most influential retainers were the Honda and the Okubo Clans. However, they often had internal conflicts with each other. As a result, Masazumi Honda survived when Hidetada became the 2nd shogun. Hidetada didn’t want to let Masazumi have more power. He and his close vassals, including Toshikatsu Doi, decided to trick Masazumi. When Masazumi went on a business trip from his home, Utsunomiya Castle, to another castle where he was told about his replacement. That’s the reason Masazumi would not be able to raise a rebellion. In fact, that’s the same way Masazumi excluded the Okubo Clan earlier on. Toshikatsu must have joined the careful planning of the strategy. He continued to serve the shoguns, including the third shogun, Iemitsu, for a long time. He also contributed to the shogunate by building the group guidance system of the shogunate. The system would avoid relying on individual abilities and having internal conflicts so much like the shogunate had used to.


In reality, Toshikatsu survived these internal conflicts. Therefore, people sometimes viewed him as a Machiavellian. On the other hand, he was a well-informed and kind person whom the shoguns, his colleagues, and even foreign merchants often relied on. That may be one of the reasons for his longevity. He was also the founder of the Sakura Domain and built Sakura Castle in over 7 years, which was eventually completed in 1616.
Features of Sakura Castle
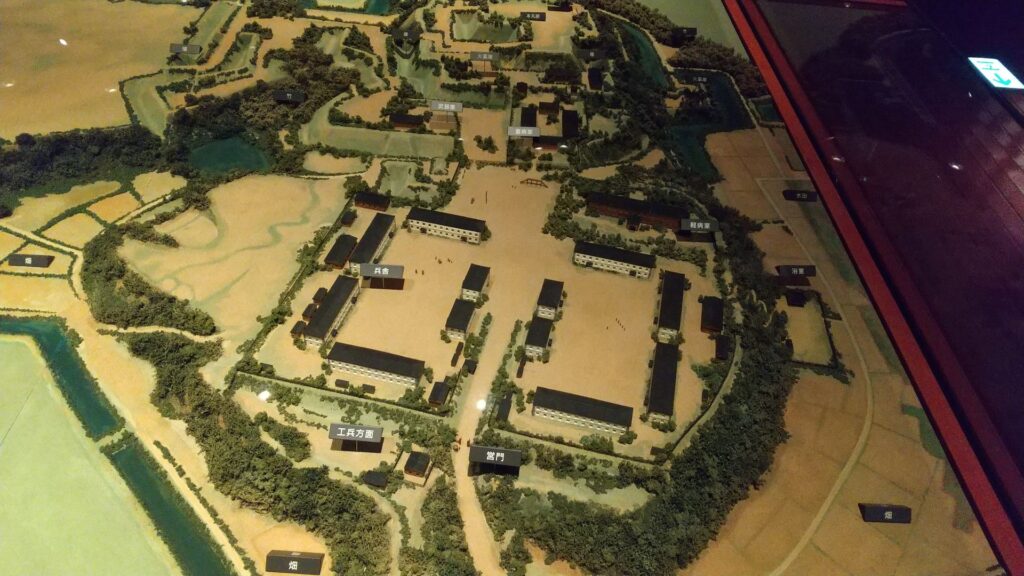
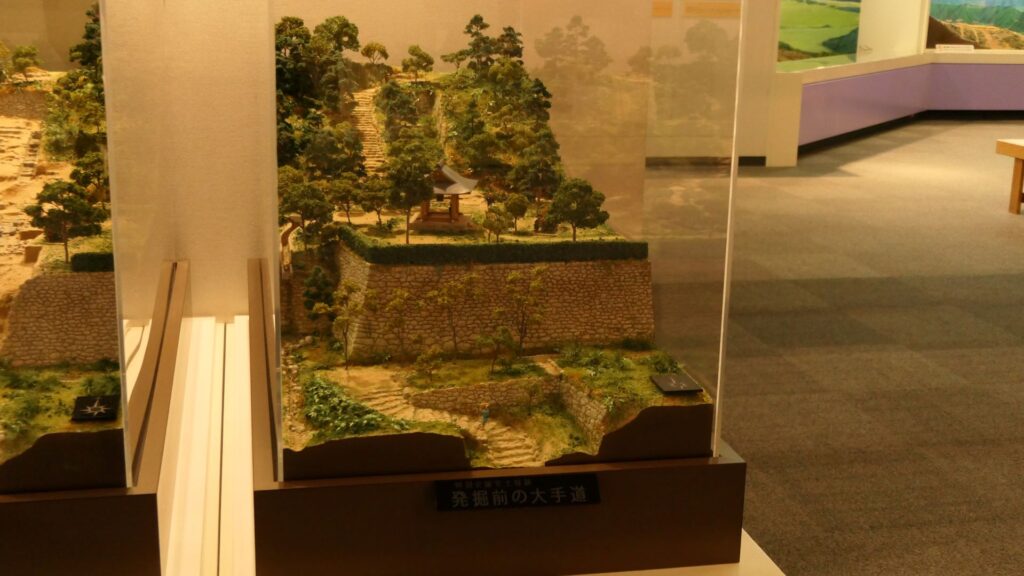
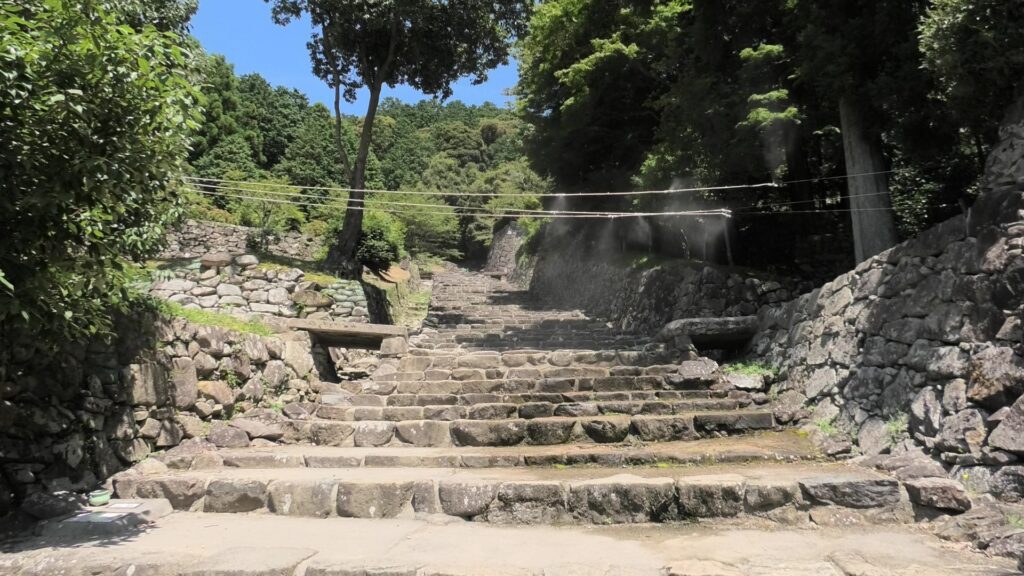
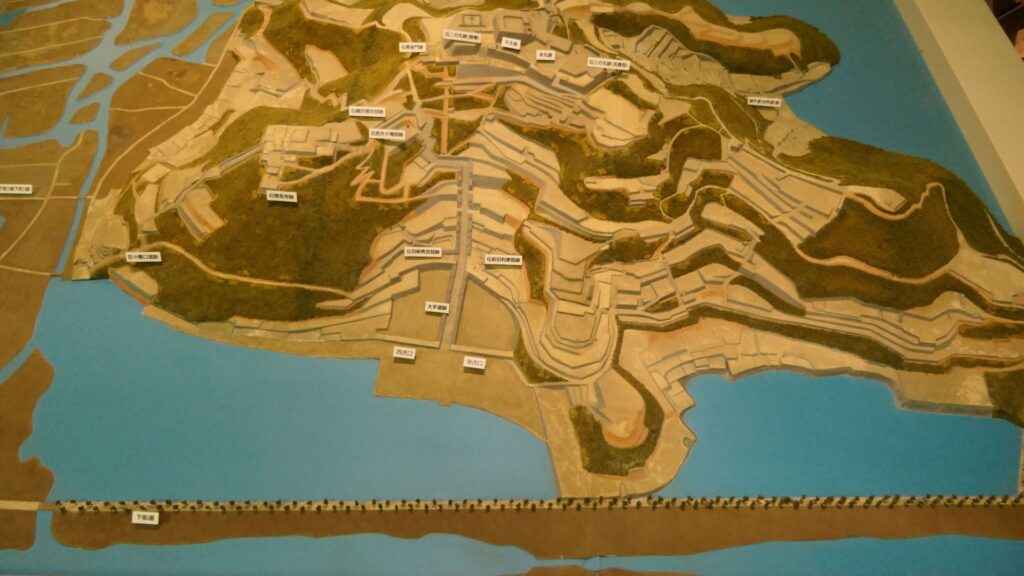
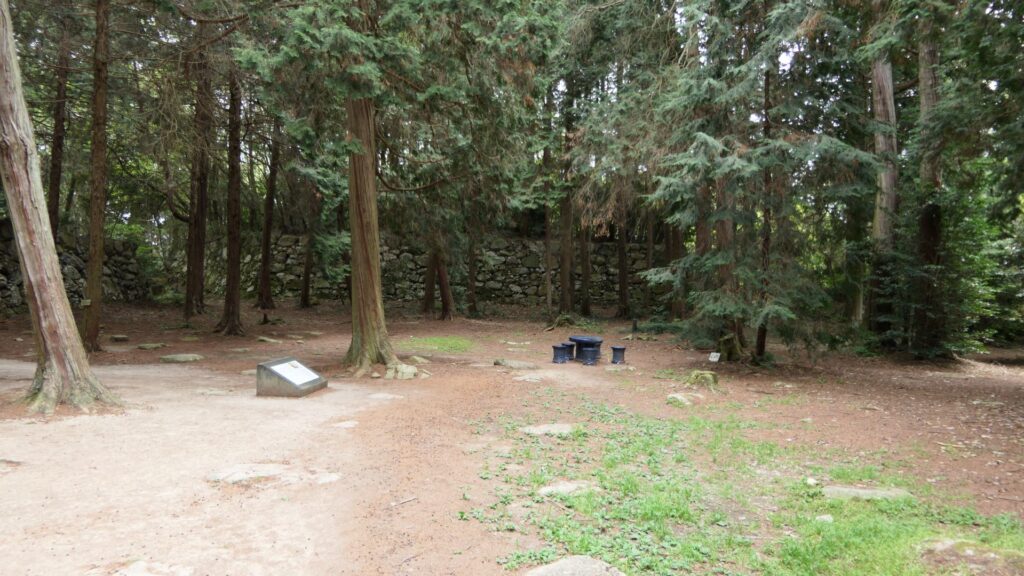
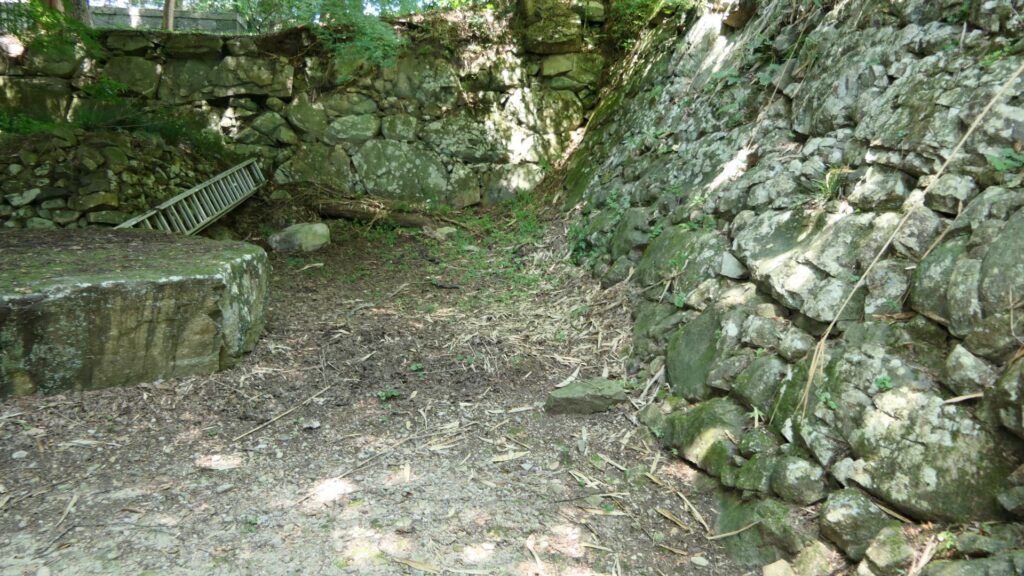
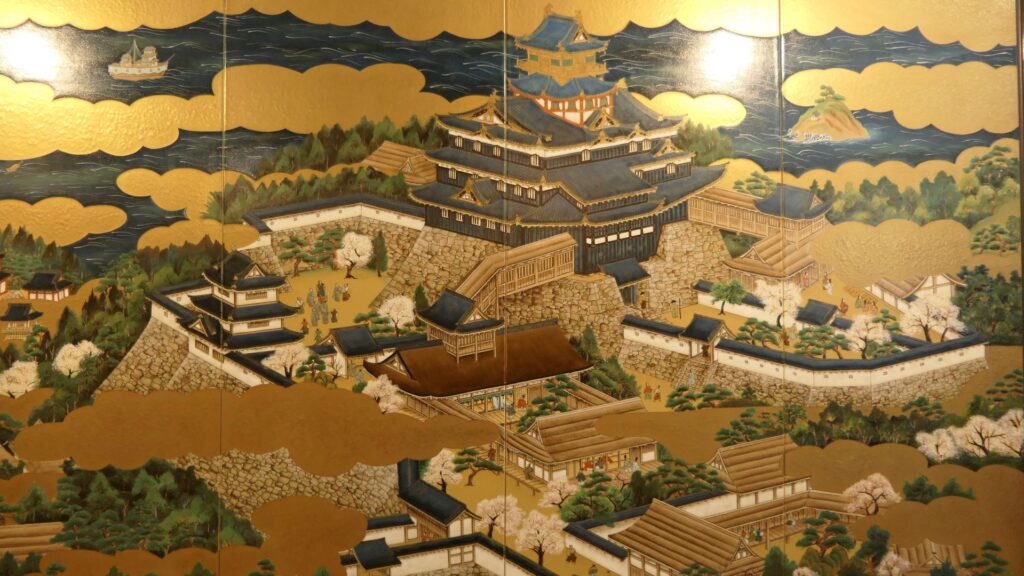
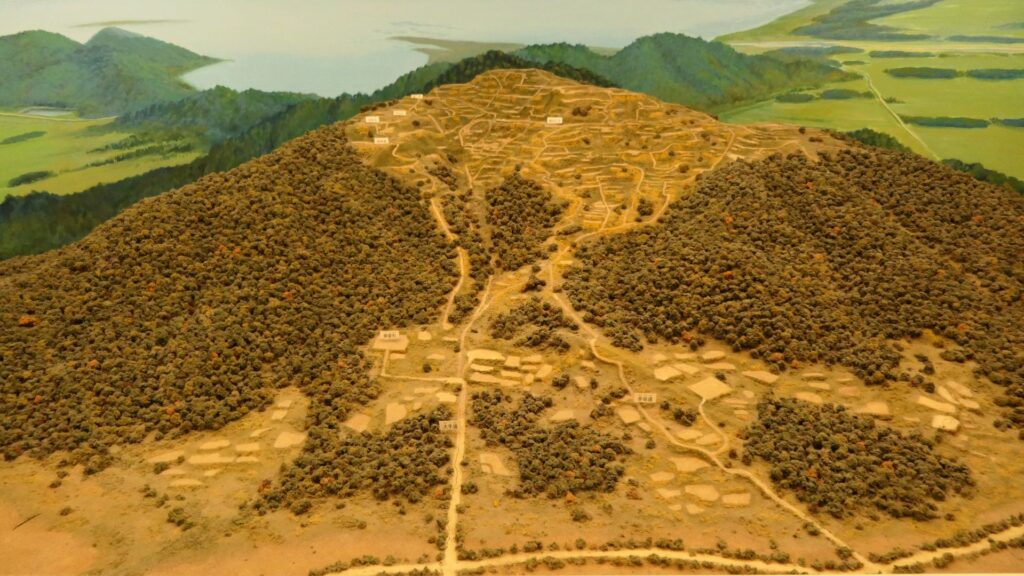
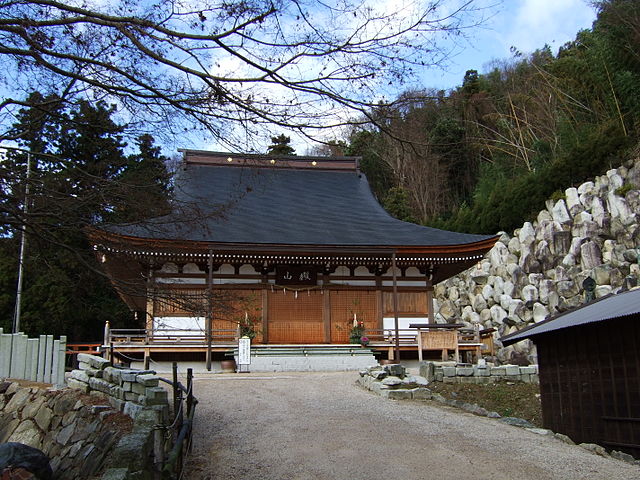
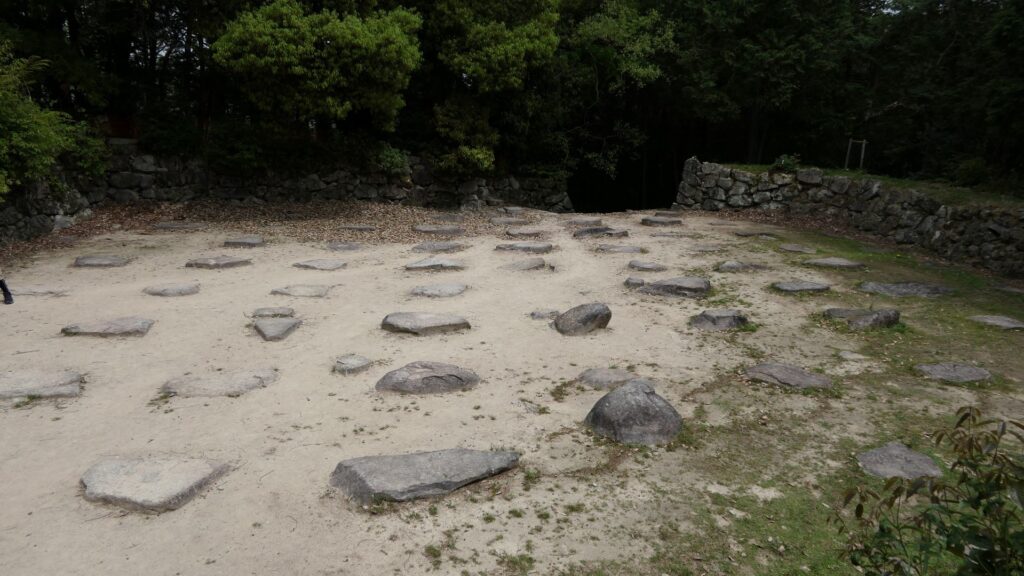
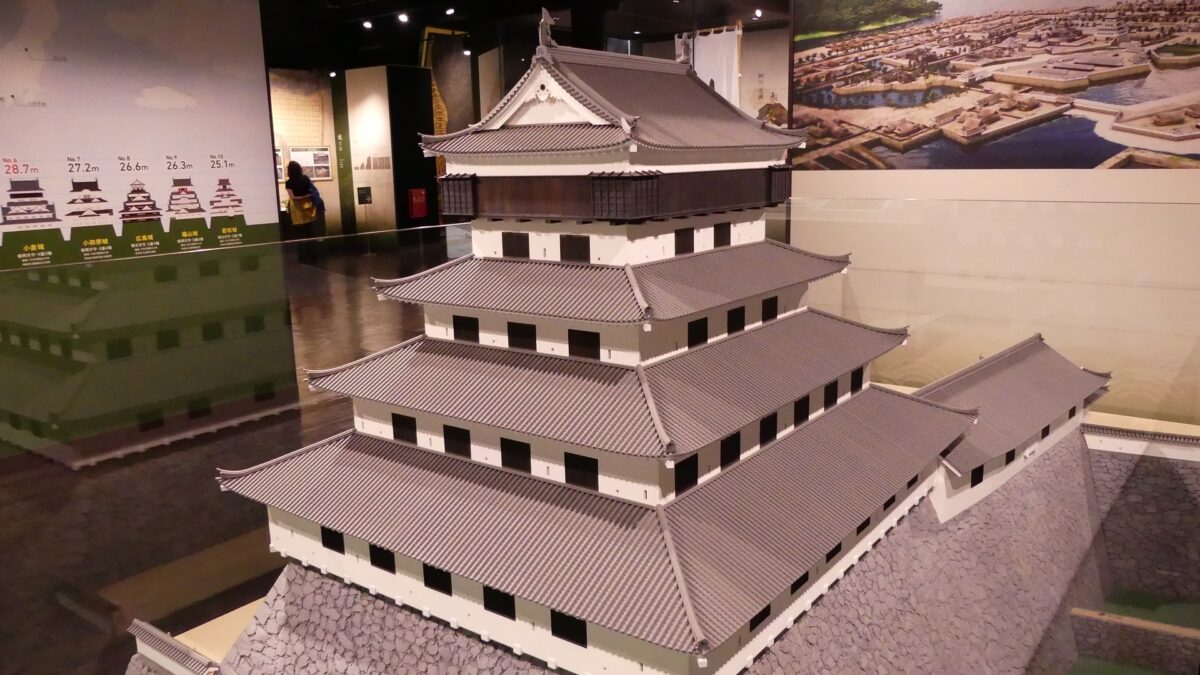
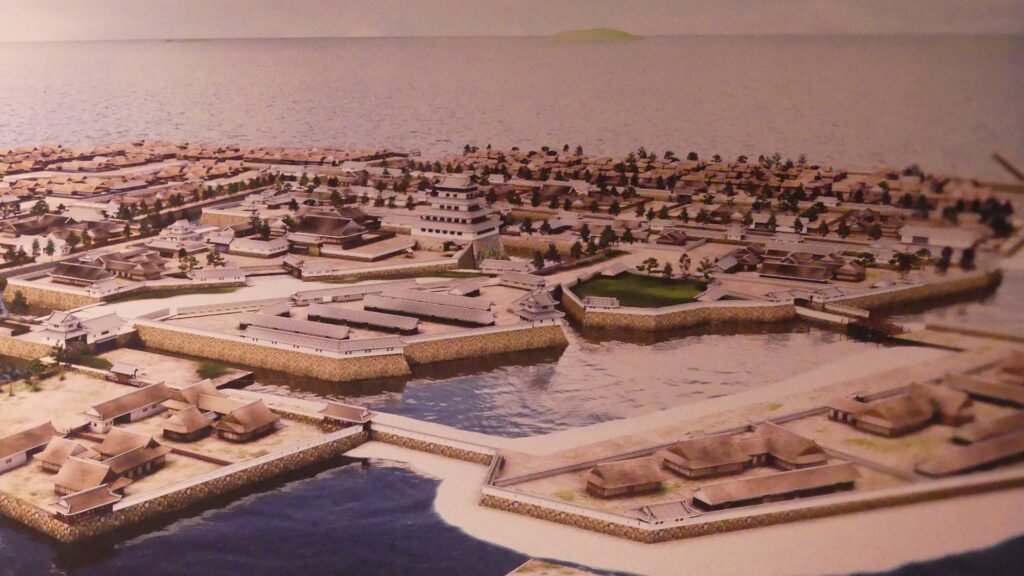
Sakura Castle, which was built on a large plateau, had several distinctive features. First, the castle wisely used the natural shapes of the plateau. The plateau was basically a natural hazard, which was about 20m above the foot of the hill and surrounded by Takasaki and Kashima Rivers. The main enclosure was built at the western edge of the plateau, and other enclosures were built around it. Large dry moats and the main gate were also constructed to the east for fortification. The Samurai residences and the castle town with Narita Road were built over the gate. Overall, the castle and town were all created on the plateau.
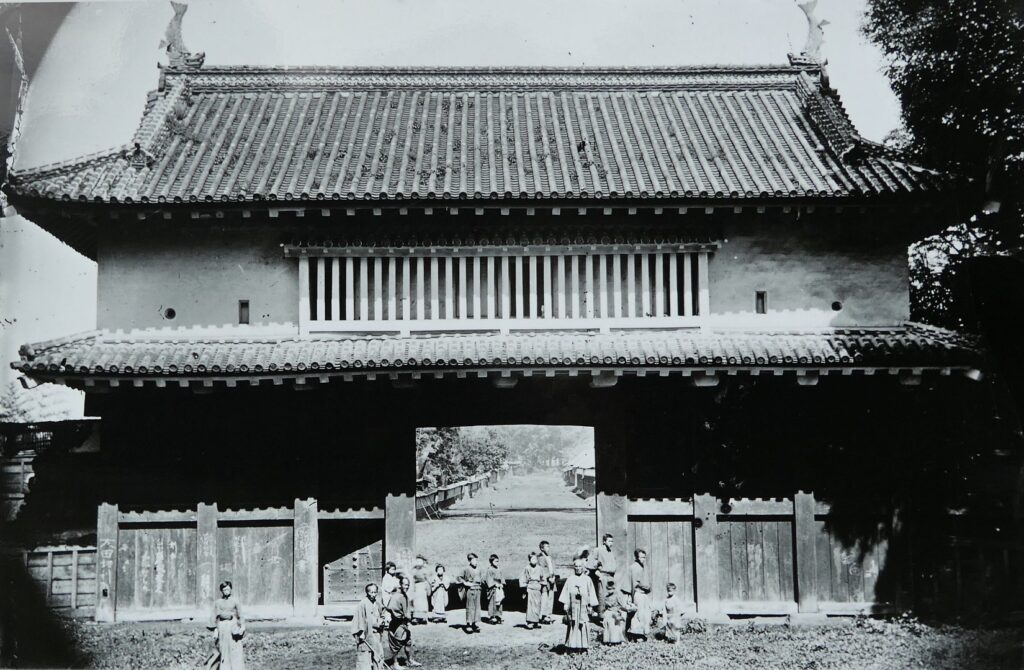
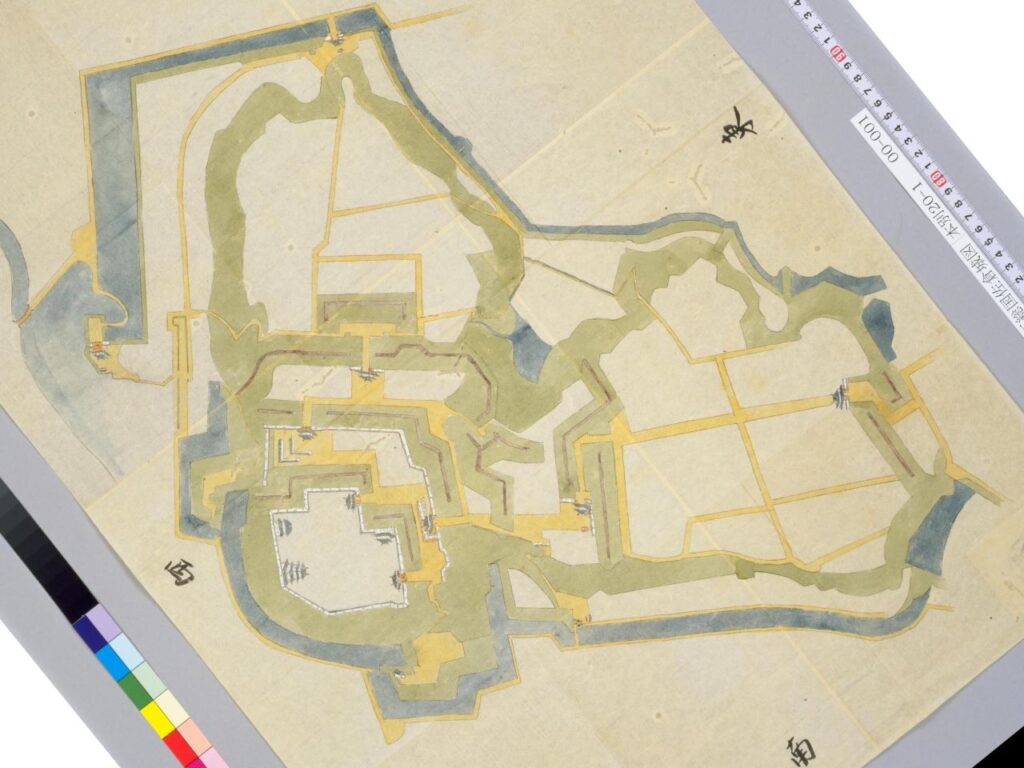


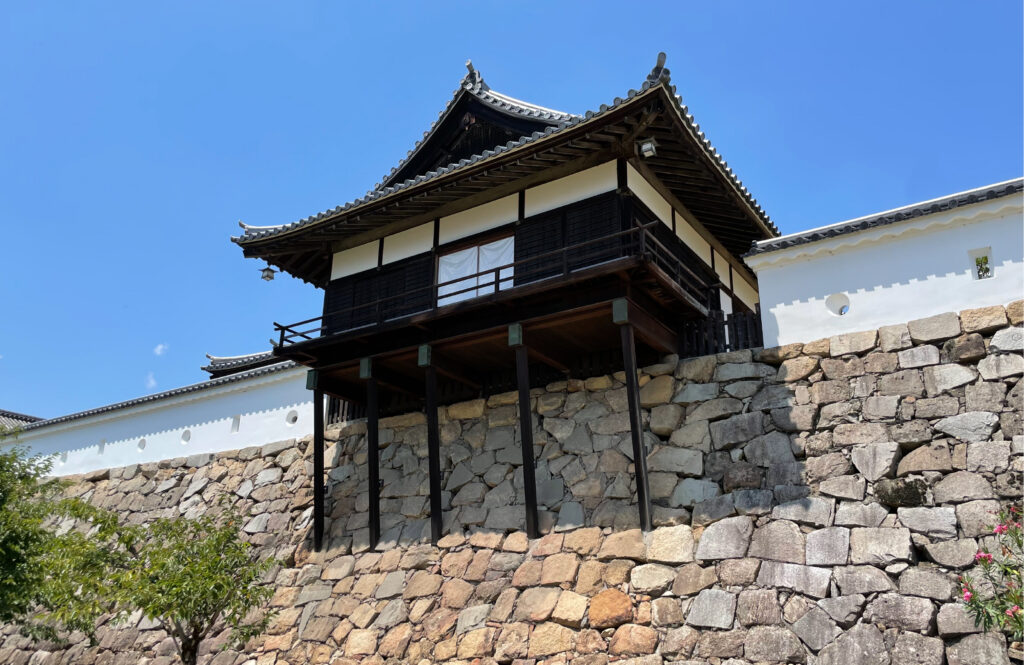
Secondly, the castle foundations were all made from soil, not using stone walls. When the battle of Odawara Castle happened, Hideyoshi Toyotomi built a castle made of pure stone walls, called Ishigakiyama Castle, for the first time in the Kanto Region. Since then, similar castles, such as Edo Castle, were built in the region. However, Sakura Castle kept the traditional method of the region, using only soil. Other castle used the same method, such as Kawagoe and Utsunomiya Castles. On the other hand, the castle had some of the latest defensive systems at that time. There were two defensive positions, called Umadashi, in front of the gate of the third enclosure. There were also huge enclosures outside the third enclosure, which could accommodate lots of soldiers and was used as a parade ground. Furthermore, the belt enclosures were built on the slopes of the plateau where the defenders were able to move easily. Finally, the enclosures connected to two barbican enclosures outside the plateau.
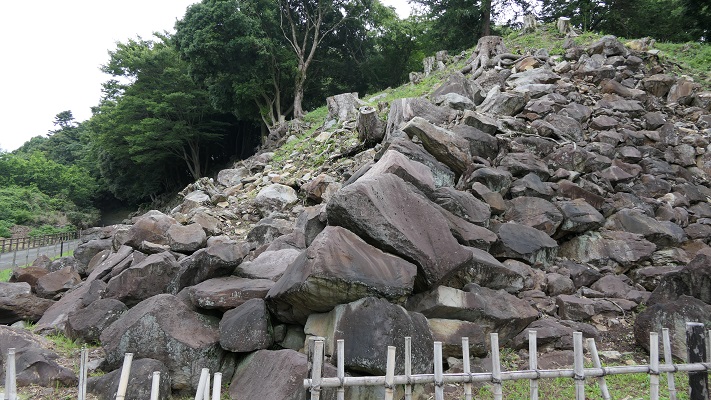
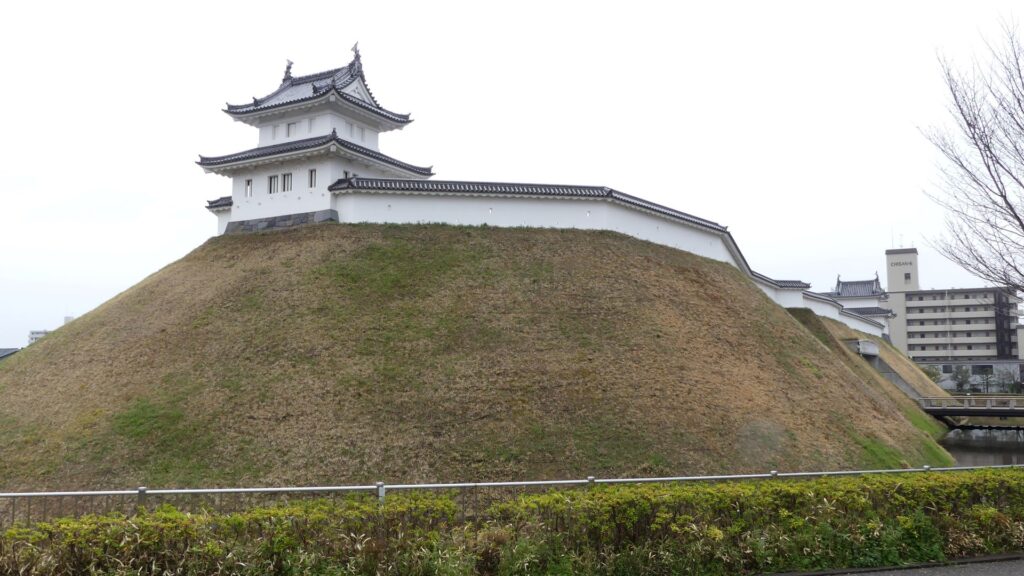






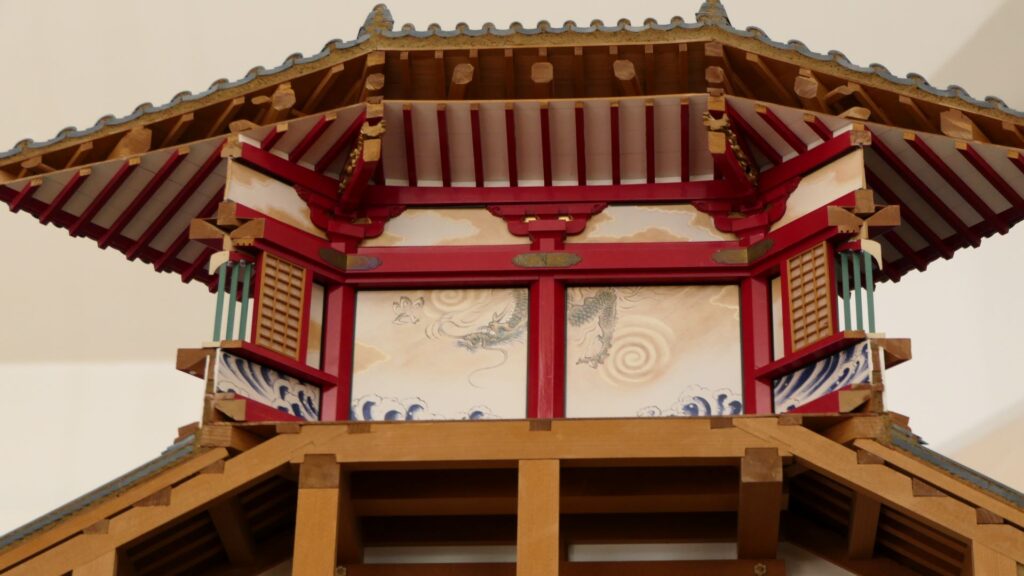
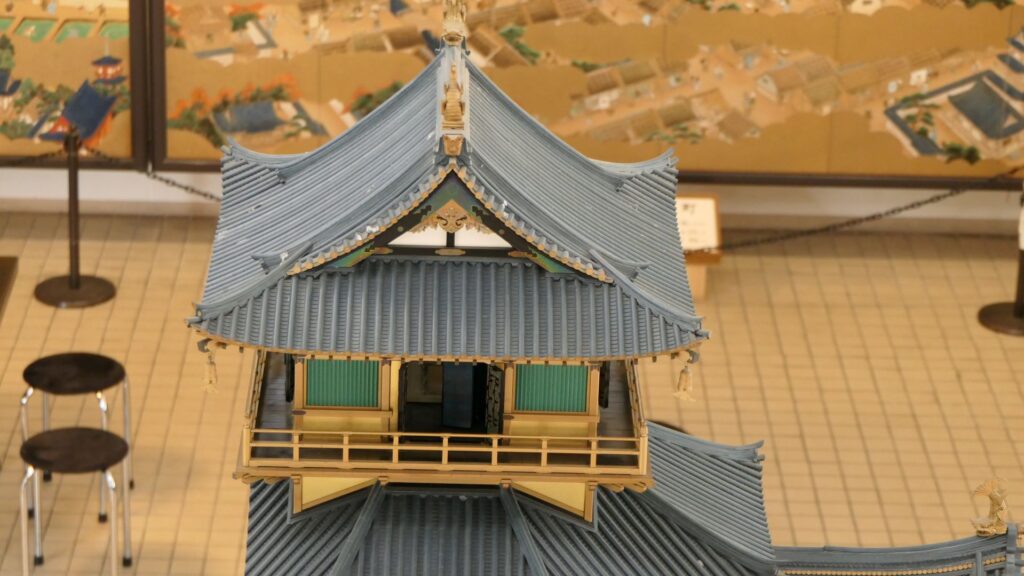
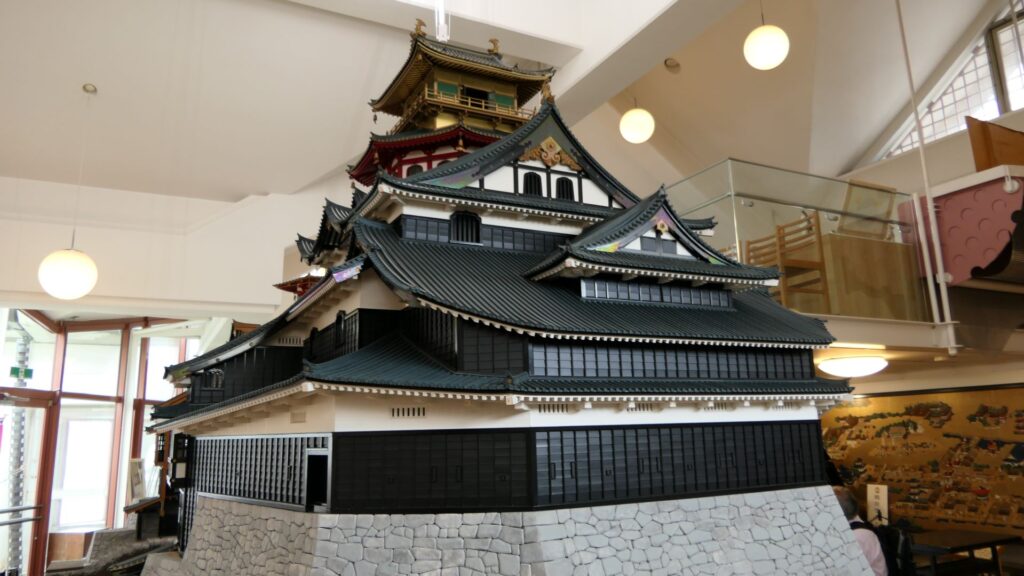
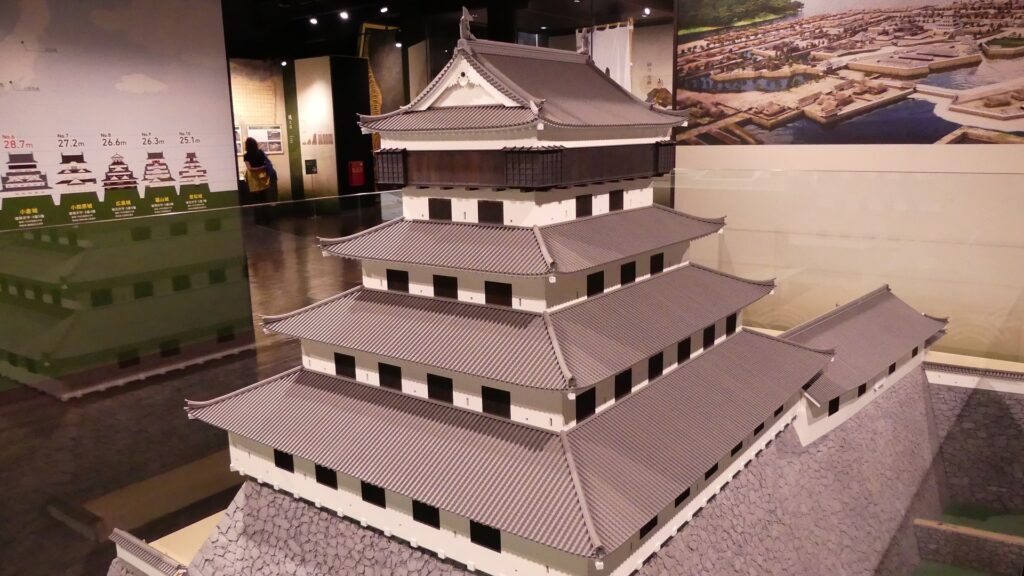
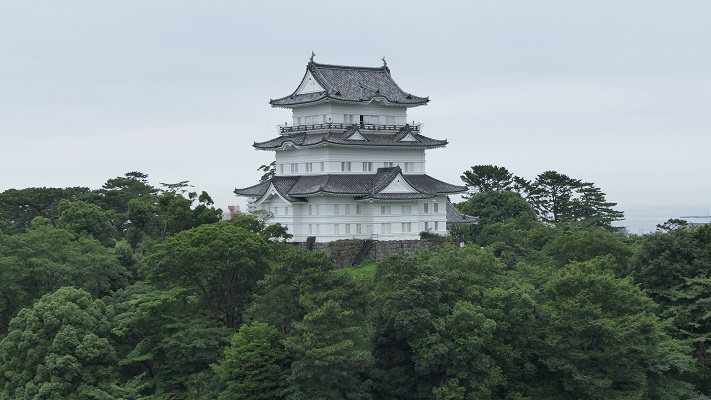
The final feature is about the buildings of the castle. There was the main tower in the main enclosure, which was about 22m high and had three levels (four floors). It was extremely rare for that type of castle to be built at that time. (The shogunate basically didn’t allow new castle constructions after its rules were established.) The tower was said to have moved from Edo castle. Its details are unknown, however, because it was unfortunately burned down by an accidental fire during the Edo Period. Historians speculate that it was similar to that of Koga Castle, which Toshikatsu also built later on. There were also Do-yagura (Copper Turret) and Sumi-yagura (Corner Turret) in the main enclosure. The enclosure also had the main hall inside but was barely used. This was because it was once used by Ieyasu Tokugawa, so it was considered exclusive to the shoguns. Instead, the lord of the castle lived in the main hall of the second enclosure. Atter the hall deteriorated; a new hall was built outside the third enclosure.
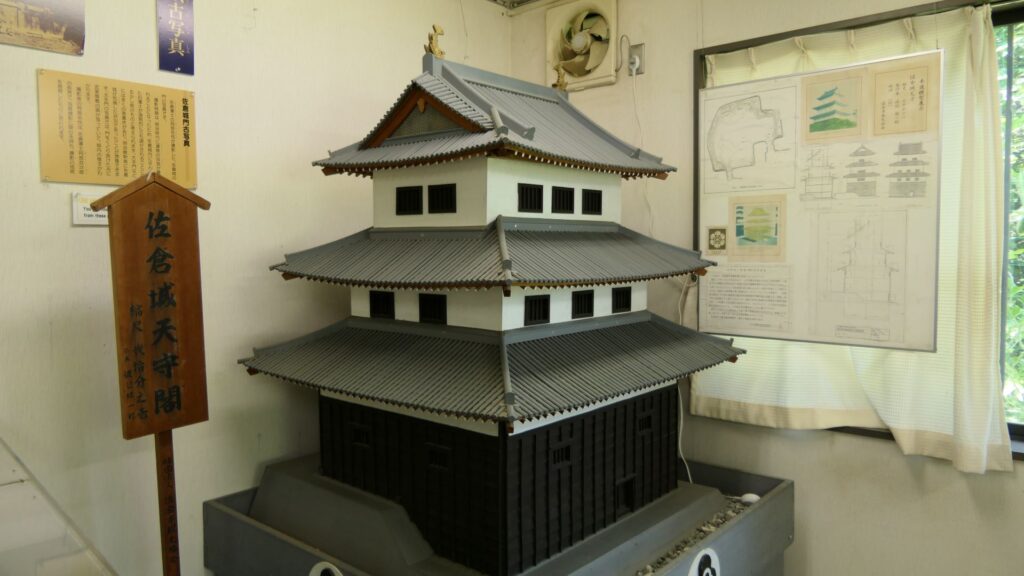

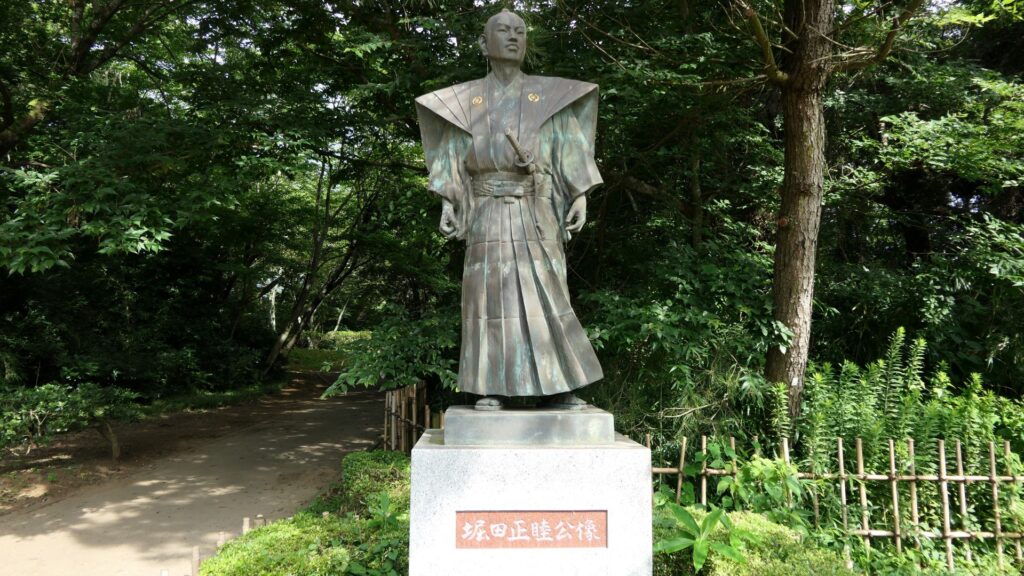
Masayoshi Hotta comes up with an idea to Open the Country from Sakura Castle
After Toshikatsu Doi moved to the Koga Domain in 1633, several lord families ruled the Sakura Domain during the Edo Period. In particular, the Hotta Clan owed the domain and castle for a long time until the end of the period. I will describe Masayoshi Hotta who was one of the lords and how he devoted his life to reforming and opening the country to the rest of the world. Masayoshi was born in 1810 and became one of the core members of the central government when he was 32 years old. However, he quit the position 2 years later because he didn’t really get along with Tadakuni Mizuno, the top of the government under the shogun. However, he kept in touch with his colleagues like Masahiro Abe and Naosuke Ii.
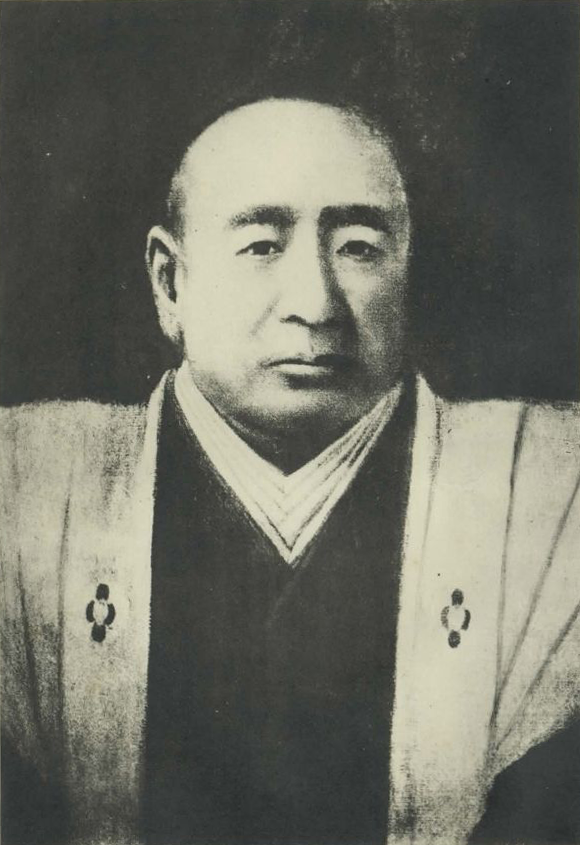

He also reformed the government of the Sakura Domain. He declared the reform to the retainers of the domain at the main hall in the third enclosure of Sakura Castle. One idea was to include the military system of the domain. He changed it to the western style and he allowed the soldiers to exercise in the castle. Another major change from the reform was that Masayoshi introduced the western medicine to the domain. He invited a famous doctor, Taizen Sato from Edo City, who opened a medical school, called Sakura-Juntendo. Lots of students gathered there from all around Japan, which gave Sakura the name Rangaku (Dutch studies) town similar to Nagasaki. (At that time, the western science was provided from the Netherlands, one of the few countries which had diplomatic relationship with Japan.) Masayoshi was also called “Ranpeki” which means a person who devotes oneself entirely to Dutch studies and way of life. As a result, the scenery of Sakura Castle and the town dramatically changed.

After the arrival of Matthew Perry’s fleet in 1853, Masahiro Abe, who was the top of the government, asked the country to vote on whether or not Japan should open the rest of the world. Despite Masayoshi’s wishes to open Japan, most people voted against it. Masayoshi was suddenly assigned the top of the government (the chief of the members of shogun’s council of elders) in 1855. However, the reason why Masayoshi was appointed the top official was still uncertain. One of his tasks was to negotiate with Townsend Harris, the council of the U.S. about the trade treaty. Masayoshi actively dealt with Harris because both of them really wanted Japan to open to the rest of the world. The treaty was still unfair, however. For example, Japan didn’t have autonomy to tariffs. On the other hand, Masayoshi decided to open Yokohama Port which would become a worldwide port even today.


Even after the deal with Harris was finalized, Masayoshi still needed to handle a more difficult task. It was to get approval of the treaty from many relative lords in the government. When Toshikatsu Doi was the top, the system was simpler than the period of Masayoshi. However, the system had completely changed. The result was that only 4 of the 18 relative lords supported it. Therefore, Masayoshi’s second option was to get approval from the emperor, which had ever not been done. It would be the most effective way to overrule the lords. He visited the imperial court in Kyoto in 1558 to persuade the emperor and the nobles but he failed. This was because the emperor Komei himself did not want to open the country to the rest of the world.

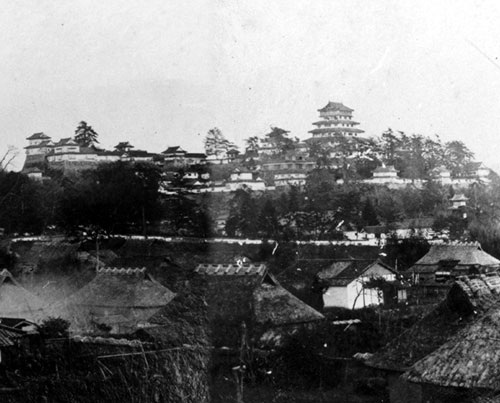
Masayoshi was unfortunately fired, and the matter of the treaty was contnued by Naosuke Ii. He went back to the hall of Sakura Castle and lived there until his retirement and until his death in 1864. After the Meiji Restoration, the castle was used as a base for the Japanese Imperial Army. The mission of the base was to guard the eastern areas of Tokyo, the new imperial capital and the former shogun’s capital. That meant the role of the castle was the same between the Edo Period and the Meiji Era. After World War II, it became Sakura Castle Park and part of the park is used as National Museum of Japanese Histories today. The location of the castle is very suitable for such a large museum.