Location and History
Node of Land and Sea Transportation
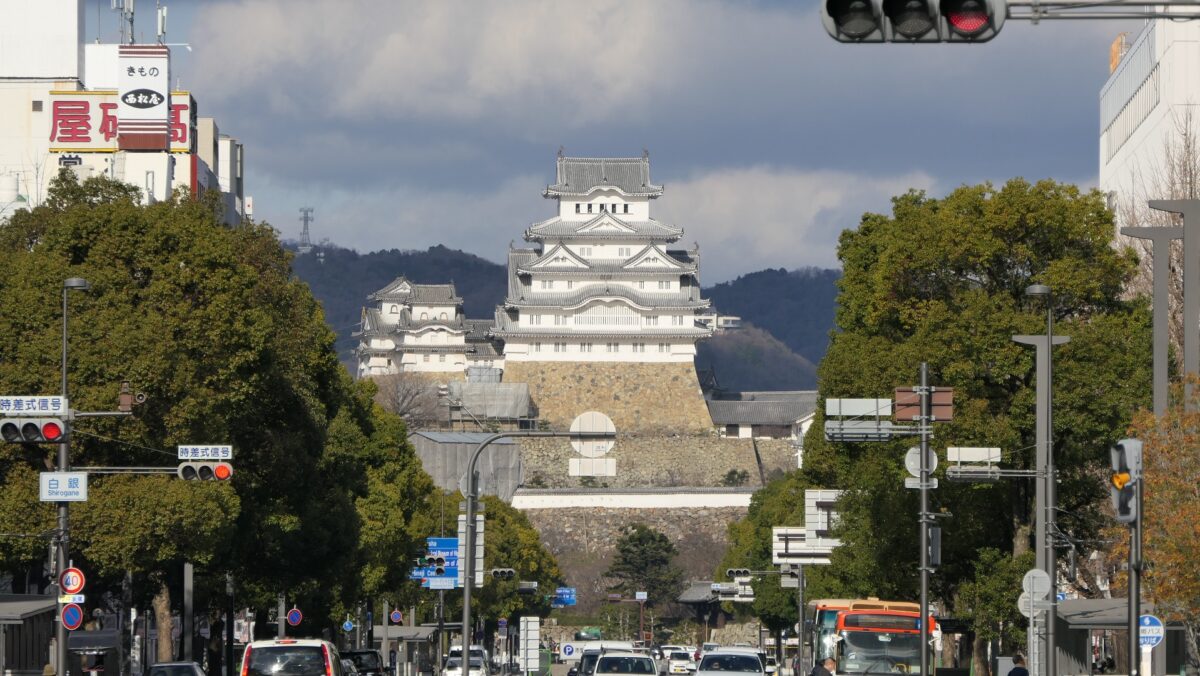
Akashi City is located in the southern part of Hyogo Prefecture alongside Seto Island Sea. The city is connected to Kinki and Chugoku Regions, as an important point for land transport. The area is also close to Awaji and Shikoku Islands, where people got on board ships to the islands in the past. People can go across the Akashi-Kaikyo Bridge to get to the islands now.
The location of the castle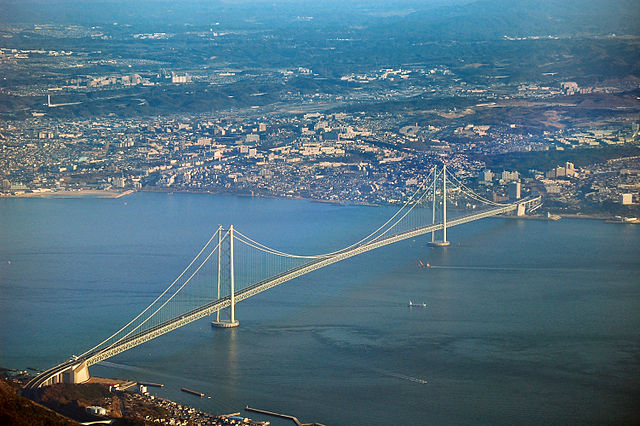
Castle to monitor Lords in western Japan
In 1615, Tokugawa Shogunate defeated the largest rival, Toyotomi Clan. It also ordered other lords to have no other castles than one castle where they lived (Law of One Castle per Province).
Its governance got stable, but it was never satisfied with that. The Shogun, Hidetada Tokugawa told one of the hereditary feudal lords, Tadazane Ogasawara to build a new castle around the Akashi area.


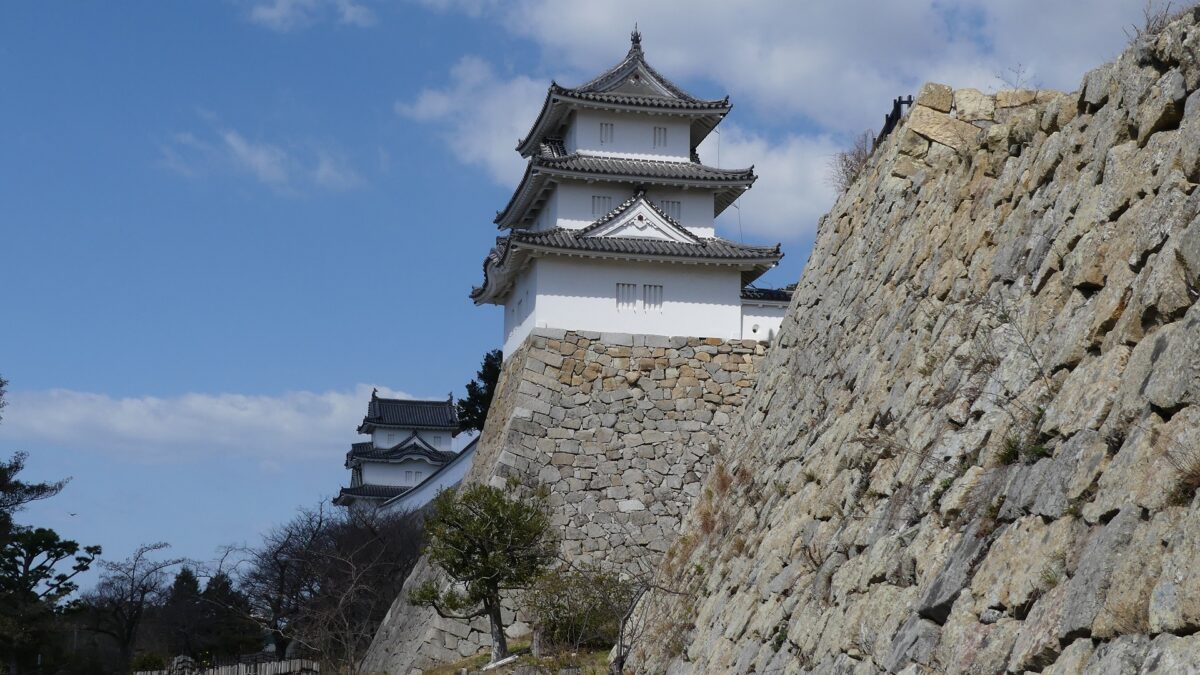
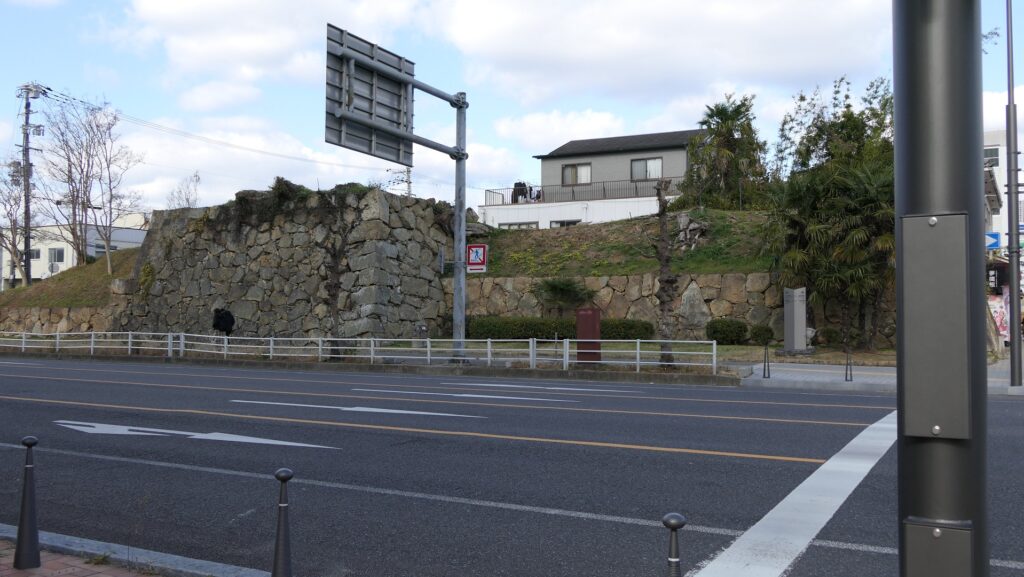
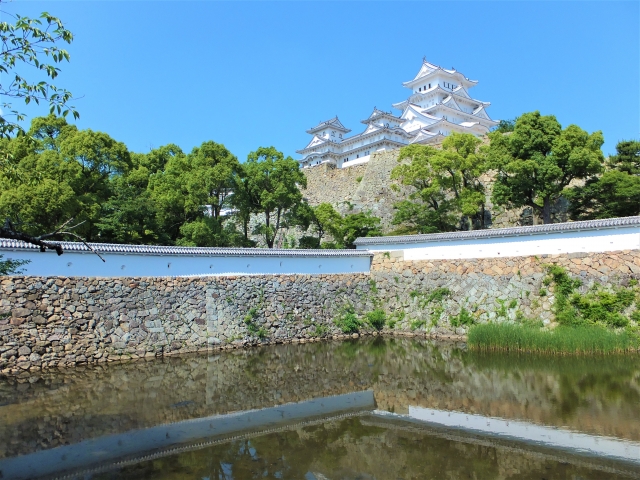
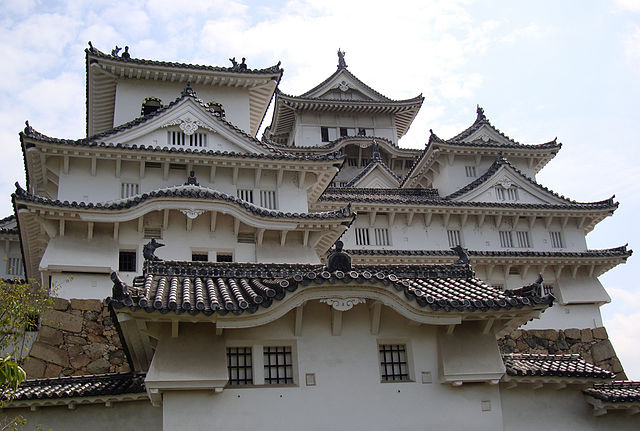
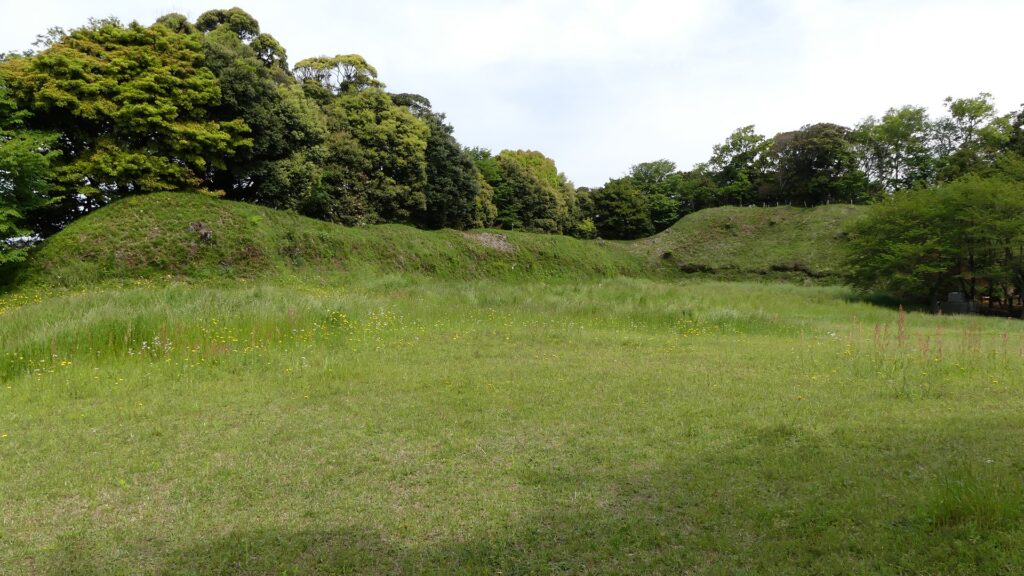
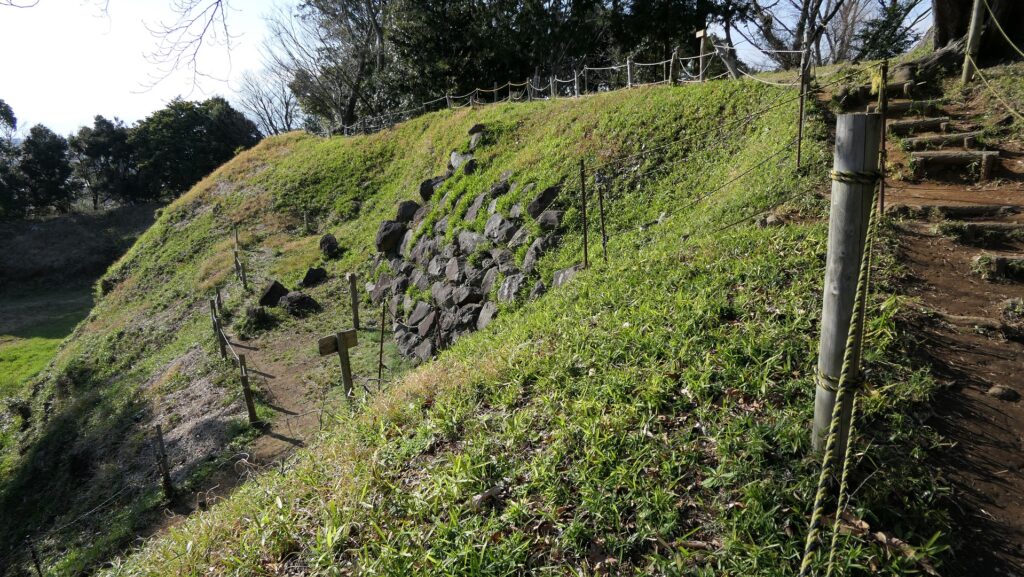
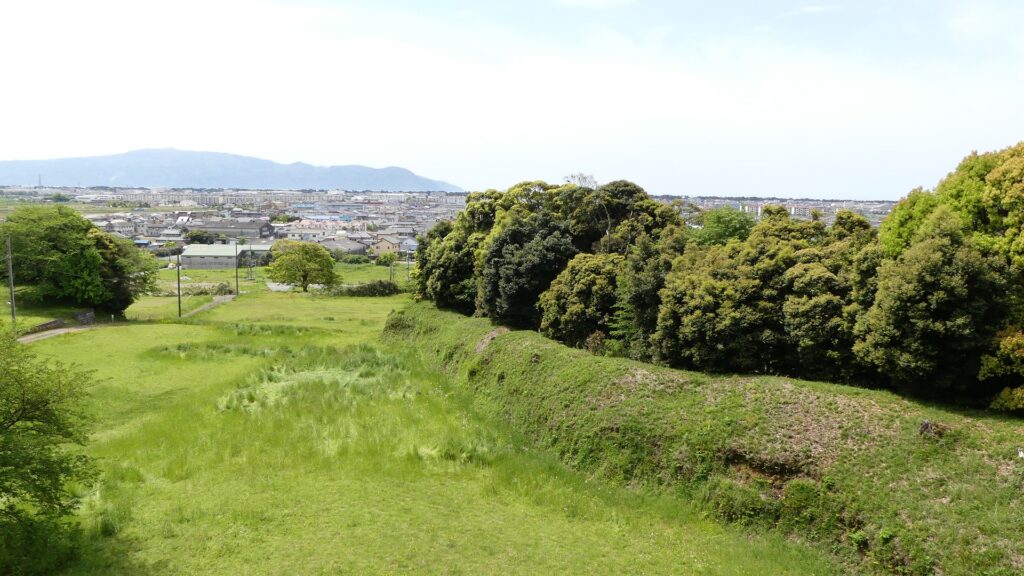
The purpose of the castle was to monitor the non-hereditary feudal lords in western Japan, who would be against the Shogunate. Himeji Castle was already being used for that purpose, but the Shogunate thought it was not enough. The new castle was named “Akashi Castle”. Akashi Castle was built using natural terrain such as the edge of the hill and the plain areas. The hilly area in the north had the main portion of the castle such as the Main Enclosure and the Second Enclosure, which provided much defense. The area originally had a natural pond called Ko-no-ike which was also used as a moat. The plain area in the south had the Main Hall for the lord and the houses for the retainers. The area was guarded by gates such as the Main Gate, and the water moats surrounding the area tripled.
The relief map around the castle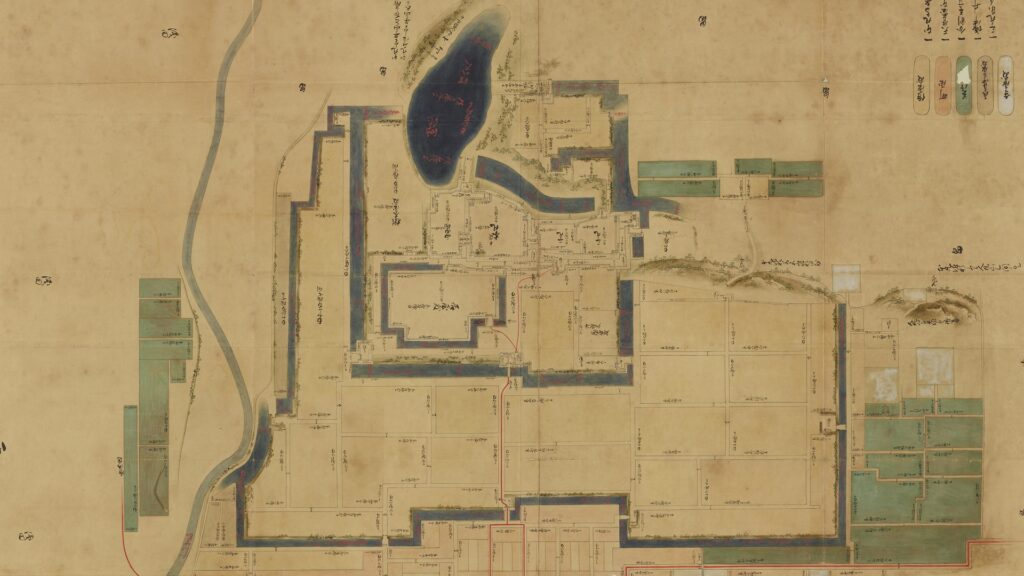
Castle was built by Rush work
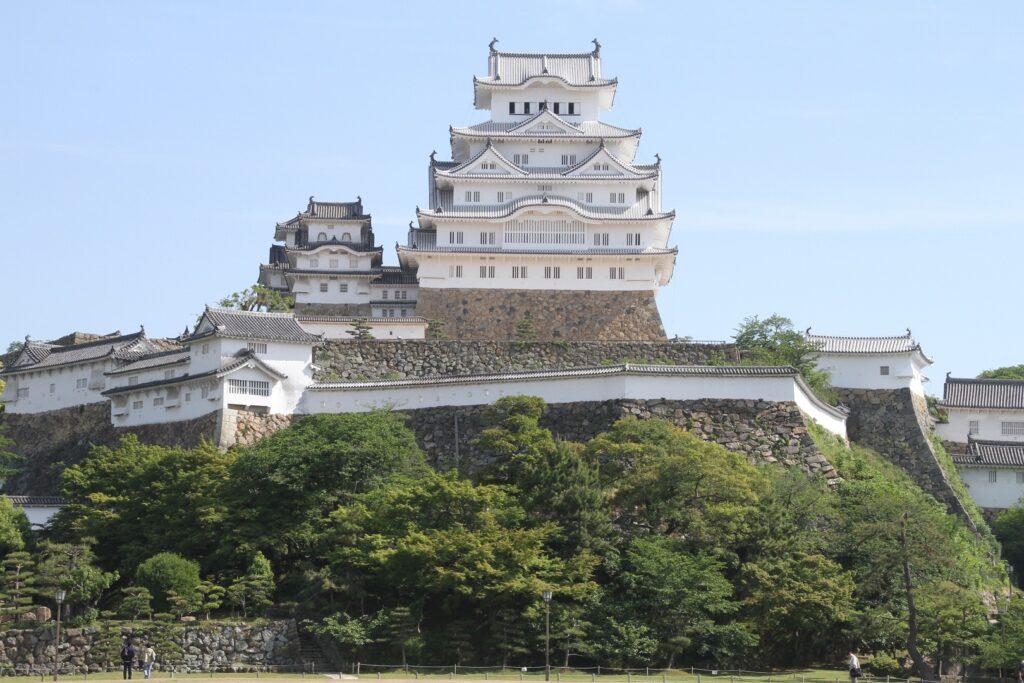
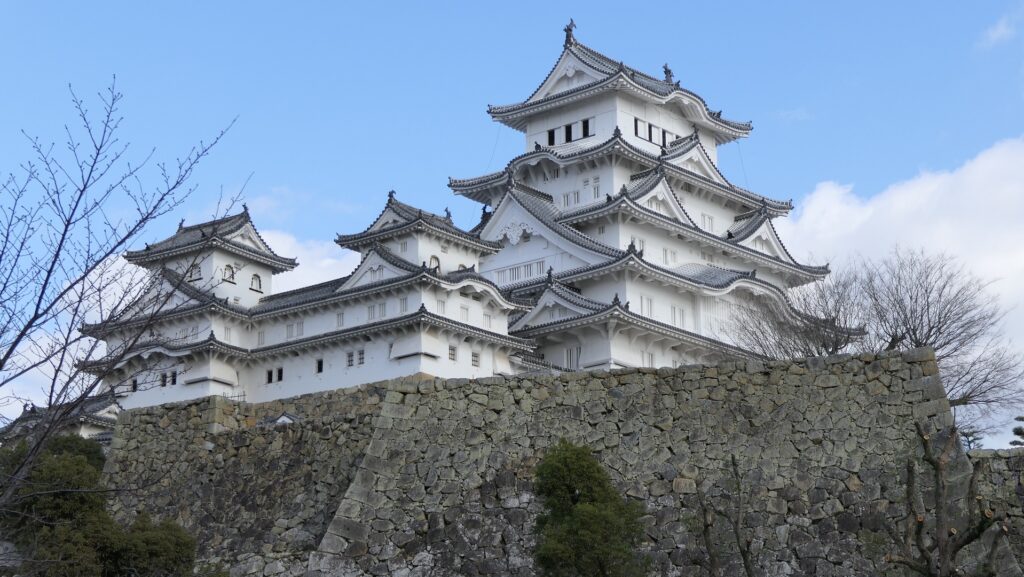
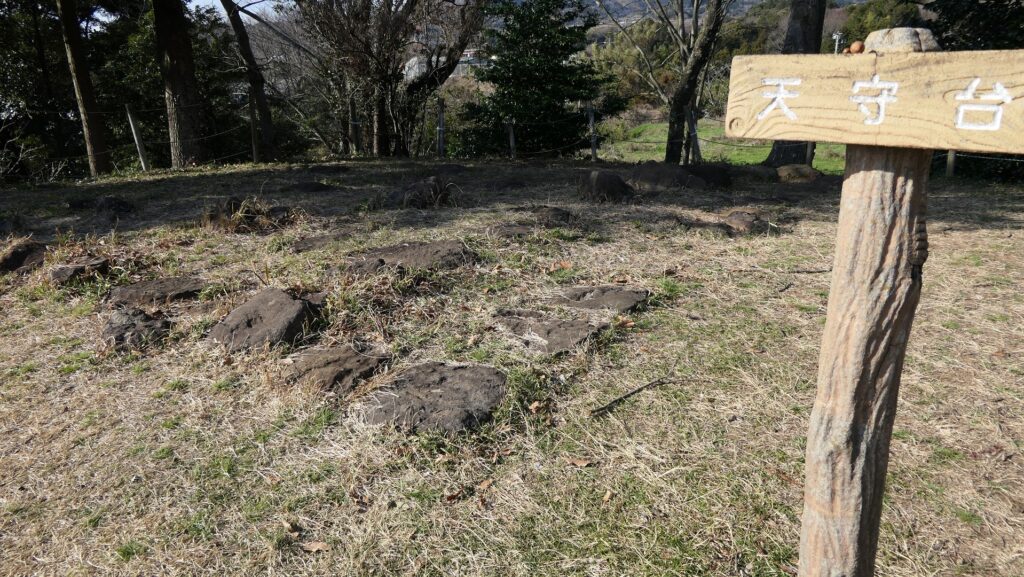
The construction for the castle was rapidly completed within one year in 1619. This was due to the construction using moved buildings and waste materials from abandoned castles by the Law of One Castle per Province. Four three-story turrets were built in each corner of the Main Enclosure. These turrets were connected by the plaster walls which surrounded the enclosure. The large stone wall base for a Main Tower was also built, but the Main Tower itself was never built. The main portion of the castle including the Main Enclosure was covered by the high stone walls.
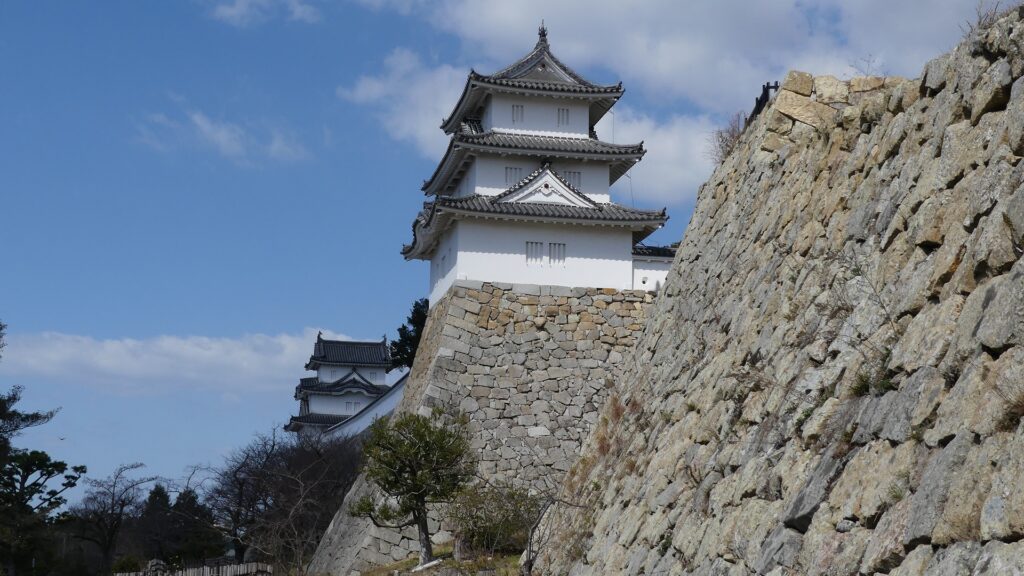

After the completion of the castle, Tadazane was promoted to be the lord of Kokura Castle in 1632, getting more earnings than when he was at Akashi Castle. For about 50 years after that, several lords governed the castle before the Matsudaira Clan came to the castle in 1682. The clan governed the castle until the end of the Edo Period. No war happened during that time, but they often had to repair the buildings which were not new ones when the castle was first built.






























