Location and History
Perry’s Arrival leads Construction of Batteries
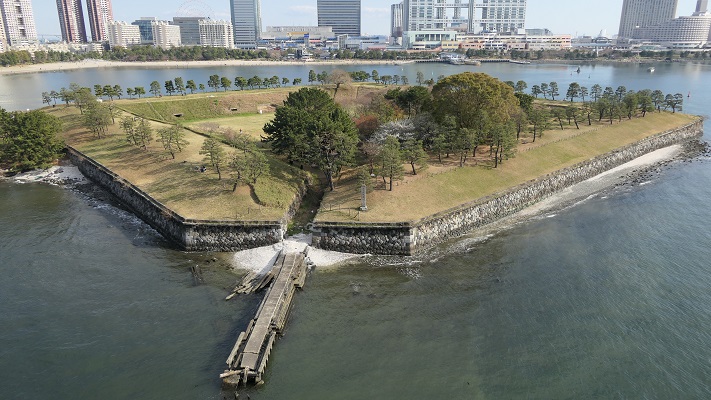
The map around Tokyo BayOdaiba is one of the popular tourist spots in the waterfront area of Tokyo. The land’s name directly means the honorific of batteries and originates from Shinagawa Batteries which were built by the Tokugawa Shogunate to protect Edo City during the end of the Edo Period. The area still has a few of the ruins of the batteries.

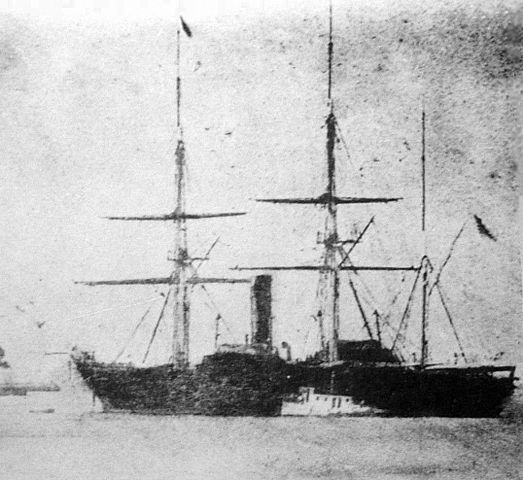
When Western ships often appeared around Japan at that time, the shogunate ordered some feudal domain lords and its own divisions to protect the inside and outside of Edo Bay (the current Tokyo Bay) from possible invasions by the ships. However, they were actually not able to protect even the 8km wide Uraga Channel, the mouth of the bay by their batteries because they didn’t have Blue water navy due to their isolationism. That’s why the shogunate’s basic policy of how to treat the Western ships coming to Japan was to hear their purposes, give materials they needed, and persuade them to return their countries. Therefore, the first arrival of Matthew Perry’s fleet from the U.S. in 1853 gave a big impact on the shogunate’s policy. His fleet intentionally broke the line of the bay mouth and demonstrated its power in the bay to ask the shogunate to open the country.



Hidetatu Egawa builds Batteries at Sea off Shinagawa
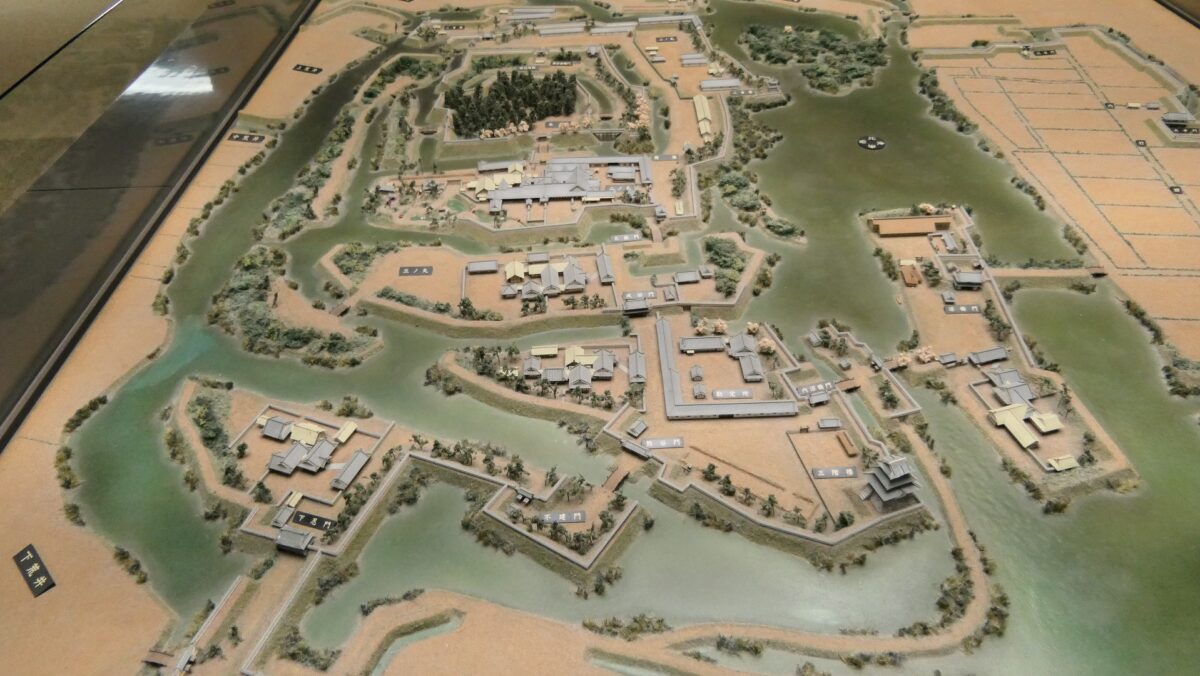
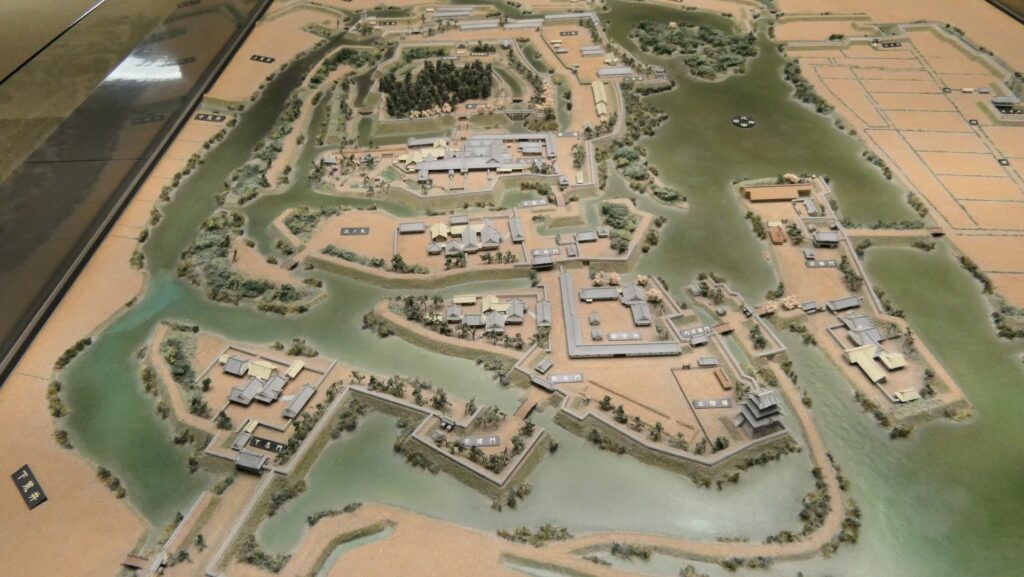
After that, the shogunate ordered Hidetatsu Egawa who was an excellent official and learned the Western sciences to build the certain defensive system in Edo Bay immediately before Perry’s second arrival. Hidetatsu thought it would be the priority to build the final protective line for the Shogun’s Edo Castle and the city area, about 2km off the coast beside the Shinagawa Post Station. The line would consist of several batteries in coastal castles which would bring a cross fire to enemies’ ships. Another reason for the location was that the coastal area was too shallow that the large Western battle ships, like Perry’s flag ship, Susquehanna, would not be able to enter it. In addition, the batteries were out of their range, therefore, they would only be able to confront with gun boats.

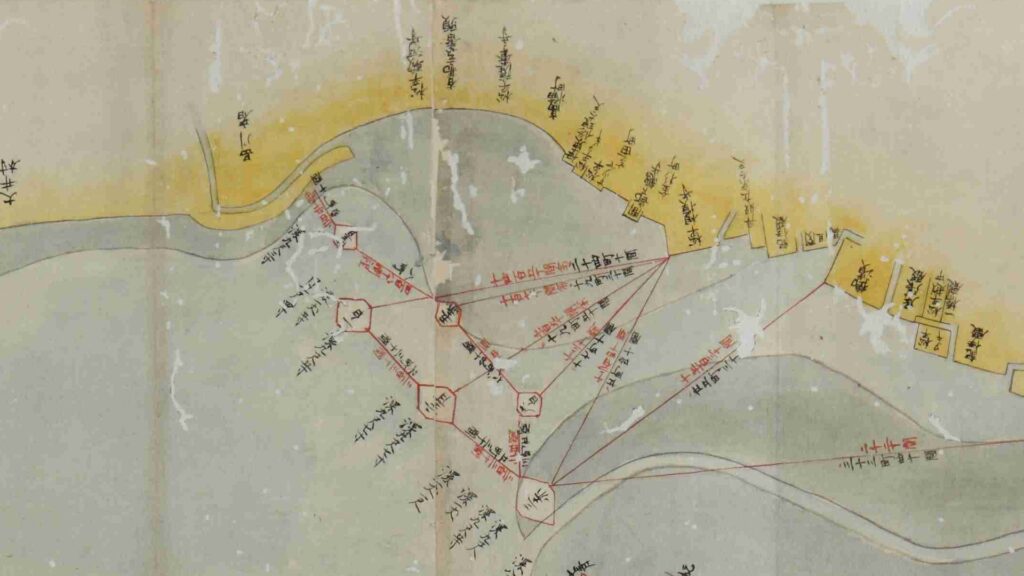

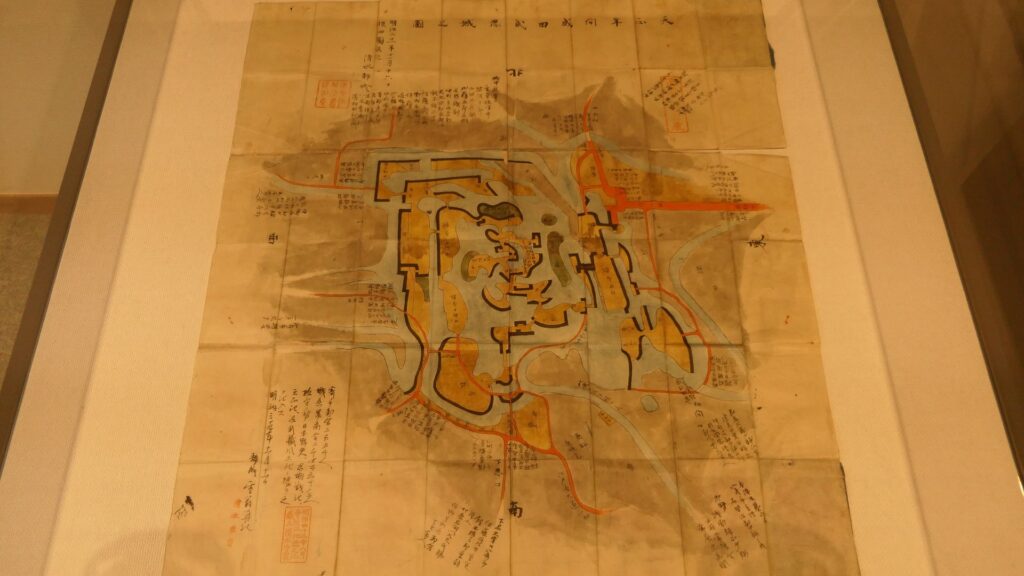
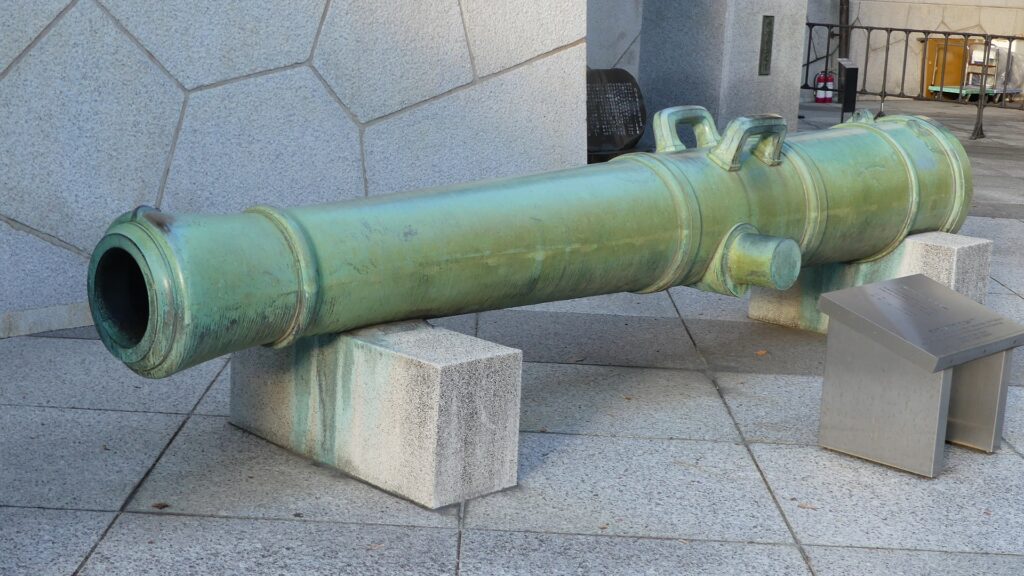
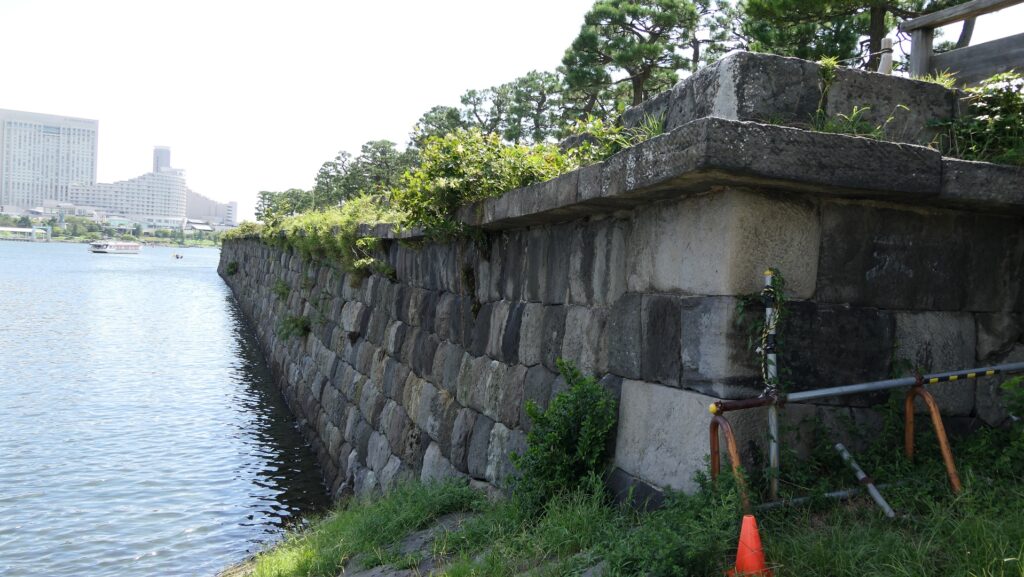
The number of the batteries in the original plan was 11 and the first three ones (No.1 to 3) were completed within a year before Perry’s return, which would be called Shinagawa Batteries. Each battery was on an artificial isolated square island which was surrounded by stone walls and equipped with cannons and related items, which were generally called redoubts. The basic design of the batteries came from several books of the Western military sciences which Hidetatsu and his staff translated. The canons were provided domestically by emulating the Western canons’ designs. However, some of them were cast iron canons the Saga Domain had just succeeded in producing, which were close to the worldwide level. The stone walls were built in the Japanese style, but the top of them was built using a new method called Hanedashi which emulated the European castles. In addition, one of the original ideas for the batteries was to build breakwater piles around them. They would also be used to prevent enemies’ gun boats from getting close to the batteries.
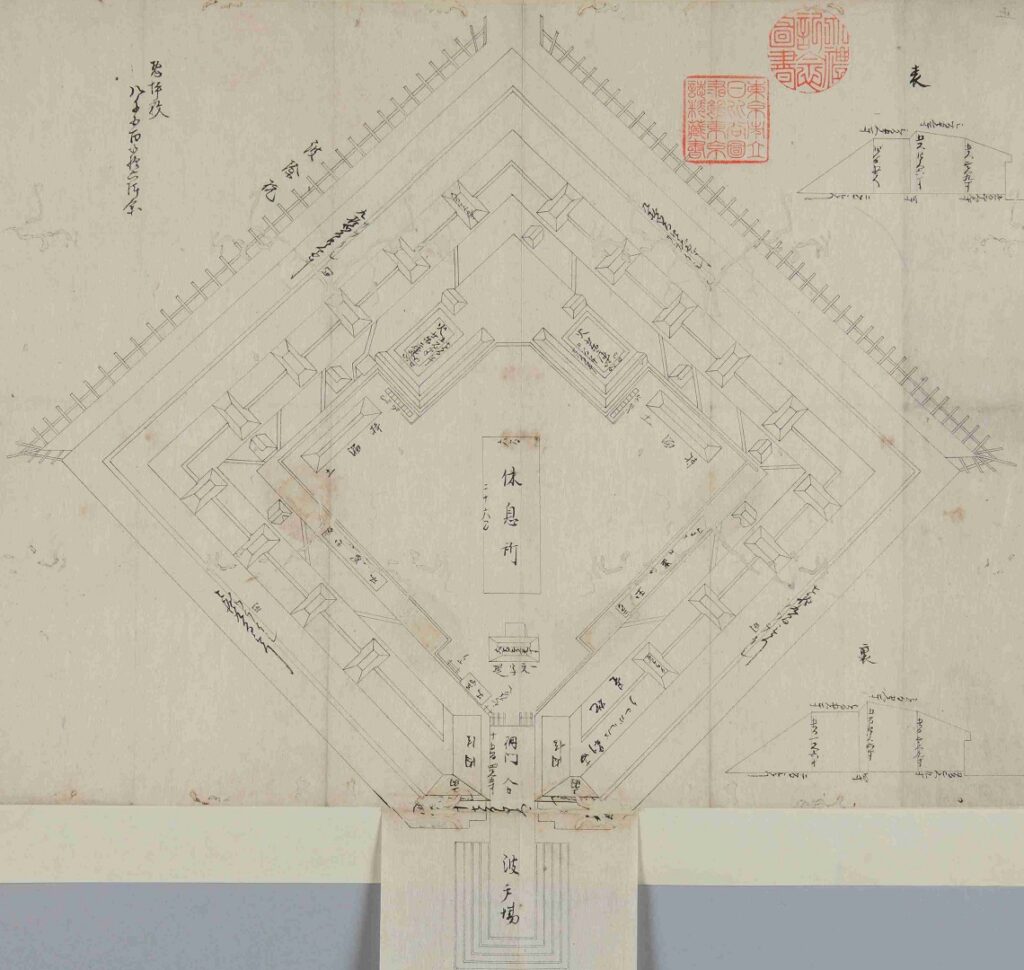


System is maintained until End of Edo Period
The shogunate concluded a treaty with Perry in 1854, known as the Japan–US Treaty of Peace and Amity. The constructions of Shinagawa Batteries continued, but only five (No.1 to 3, 5 and 6) out of the planned 11 were completed and 2 (No.4 and 7) out of 11 were canceled in the middle of their constructions. The reason for it was the shortage of the budget and the stabilization of the diplomatic relationship with the Western Countries after the treaty. The operations of the batteries were done by warriors from several feudal domains. For example, the Oshi Domain, which was based in Oshi Castle, was in charge of the No.3 Battery. The warriors went to the isolated sea battery by using small boats and stayed in the barrack inside with no baths until the next team came.
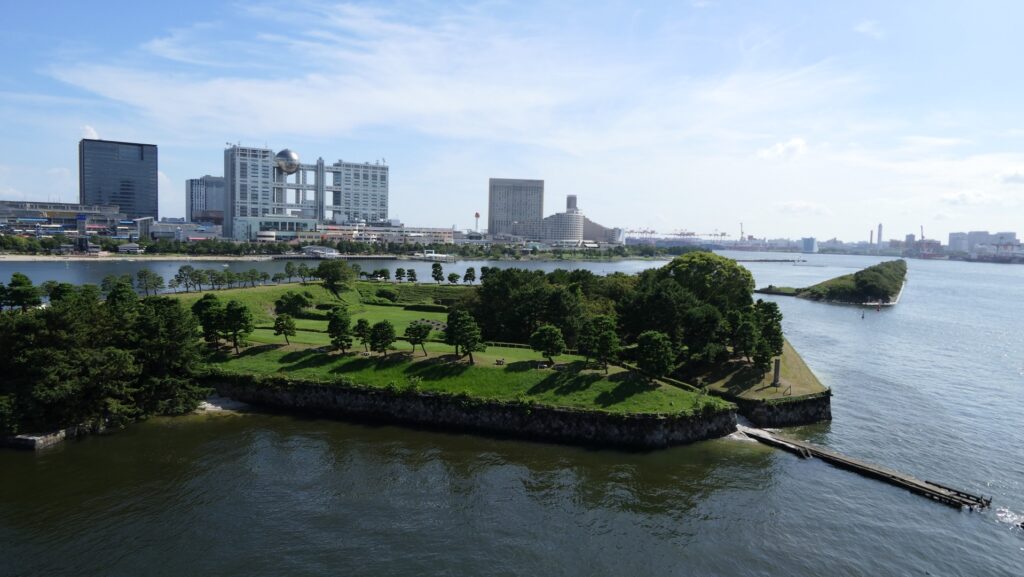

The shogunate also thought the defense system was still not enough. It built coast batteries instead of the uncompleted sea batteries, such as the Battery below Goten-yama Mountain, to support the completed sea batteries. It also built their own gun boats to work closely with these batteries. Each sea battery had its pier where the boats were able to stop. The operation of the defense line lasted until 1868 when the shogunate was defeated by the New Government, known as the Meiji Restoration.
The aerial photo around the batteries around 1945 to 1950, the grounds for them remained until then
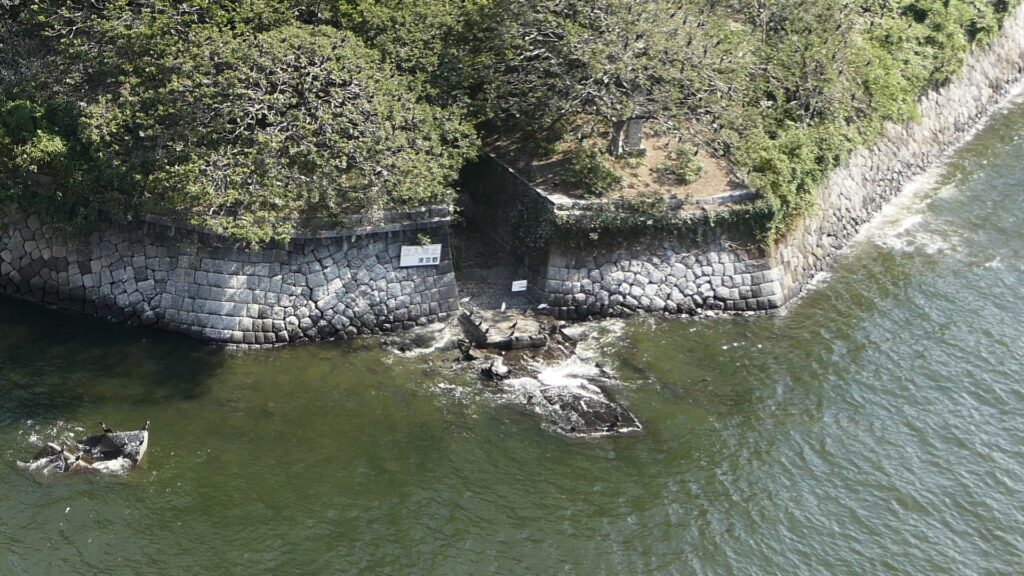

The evaluation of Shinagawa Batteries may be difficult because they were actually not used for battles and the specs of the cannons installed in the batteries became obsolete quickly. However, historians say the batteries worked as a deterrence for invasion by the Western countries. They pointed out that the qualities of the canons in the batteries were at the same level as those equipped in Perry’s fleet. A diplomat from the U.K., who saw the batteries, reported to his government that the batteries had technology levels which were equivalent to the Western cannons.
































