Location and History
Castle is built as Bridgehead in Kyushu
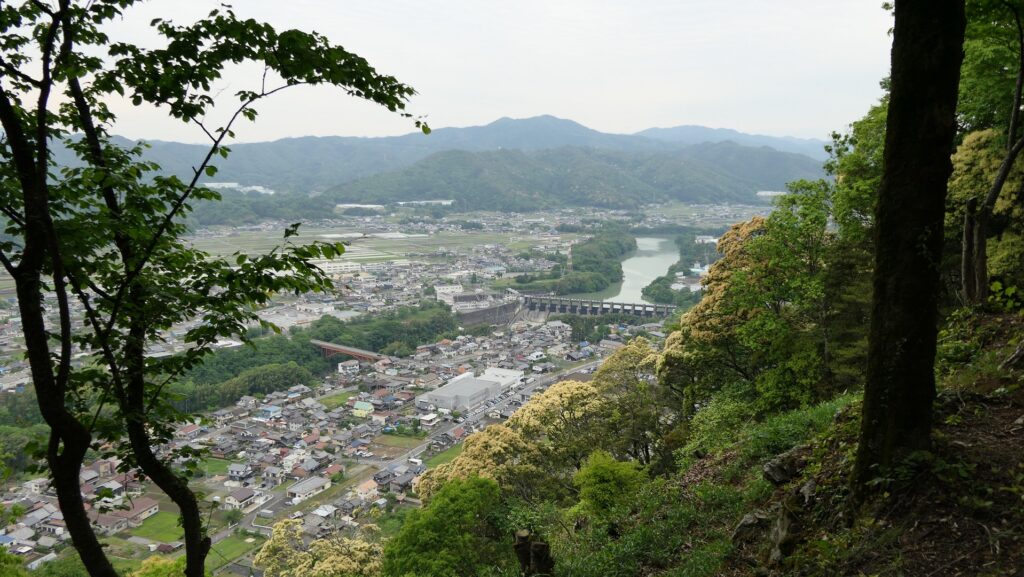
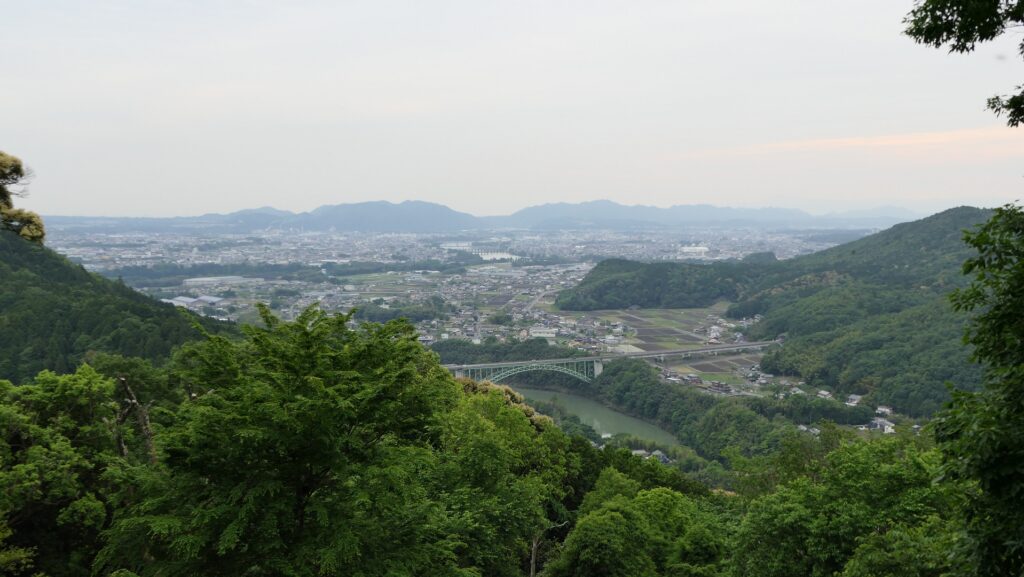
Kokura Castle is located in the Kokura area of Kitakyushu City at the northern edge of the Kyushu Region. For example, if you visit the region using a Shinkansen super express, the first station will be Kokura Station near the castle. The area was more well known as the entrance of the region, which had Kokura Port facing the Kanmon Strait, sandwiched by Kyushu Island and the main island of Japan. That’s why warlords, who wanted to invade the region from the mainland, tried to build a bridgehead in this area. Certain records say that Motonari Mori, who was a great warlord of the Chugoku Region, built it in 1569, which would be the former Kokura Castle. After the ruler, Hideyoshi Toyotomi invaded the region in 1587, he gave the castle to his trusted vassal, Katsunobu Mori. However, Katsunobui was eventually fired because he was against Ieyasu Tokugawa, who would become the next ruler, in the decisive battle in 1600.
The range of Buzen Province and the location of the castleTadaoki Hosokawa renovates Castle
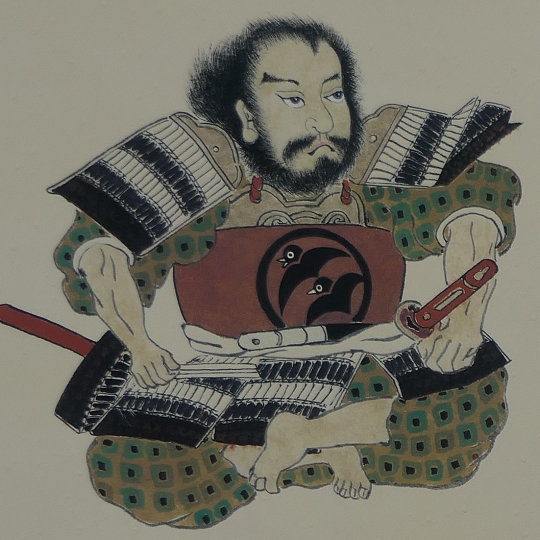
Instead, Tadaoki Hosokawa (also known as Sansai after his retirement), who had greatly supported Ieyasu in the battle, was assigned as the lord of Buzen Provence including the Kokura area and would be the founder of the Kokura Domain. He first lived in Nakatsu Castle, which the former lord of the castle, the Kuroda Clan had built, but soon started to renovate the castle in Kokura in 1602 as his new home, which would be what we call Kokura Castle.


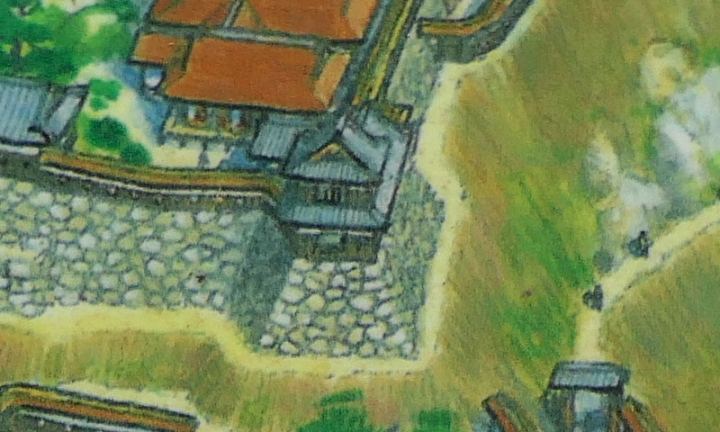
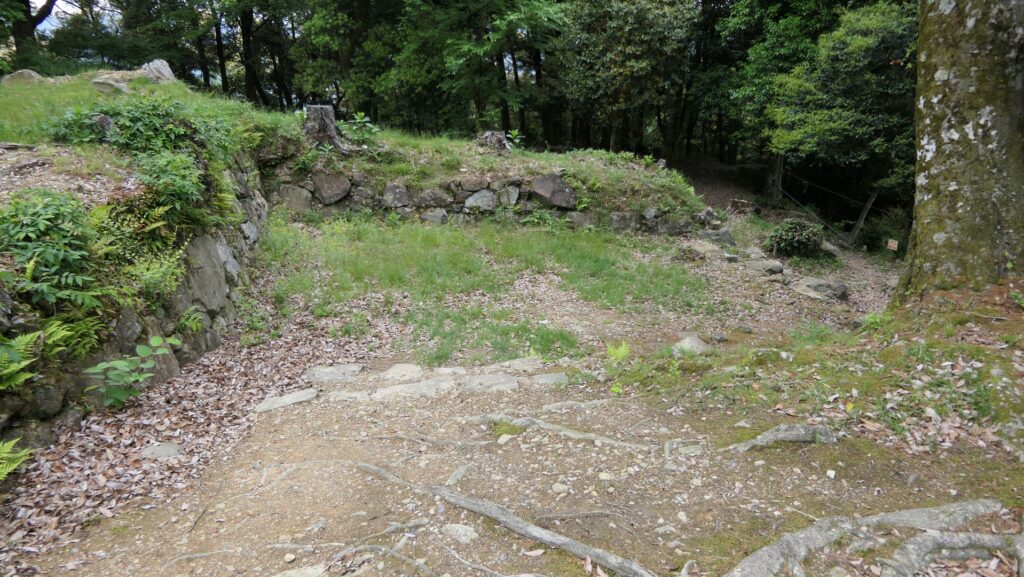
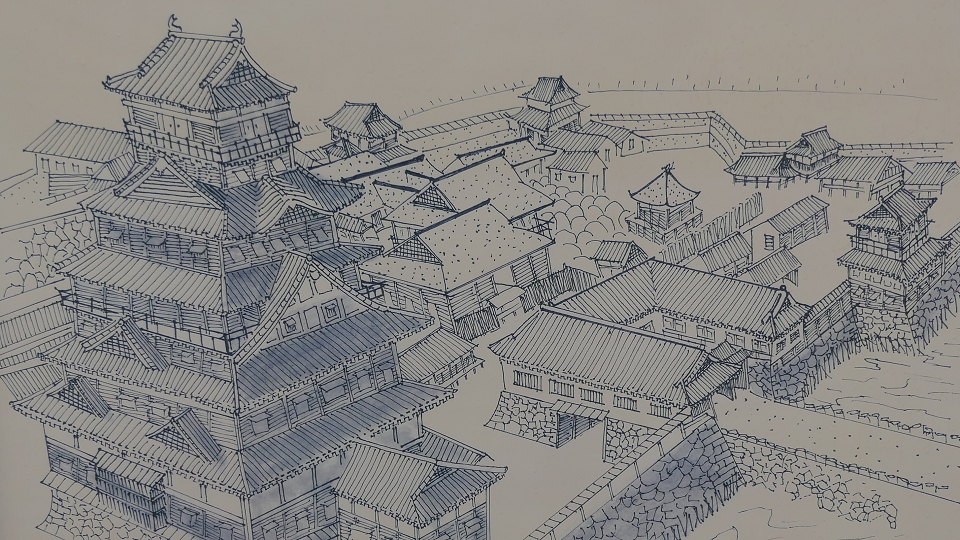
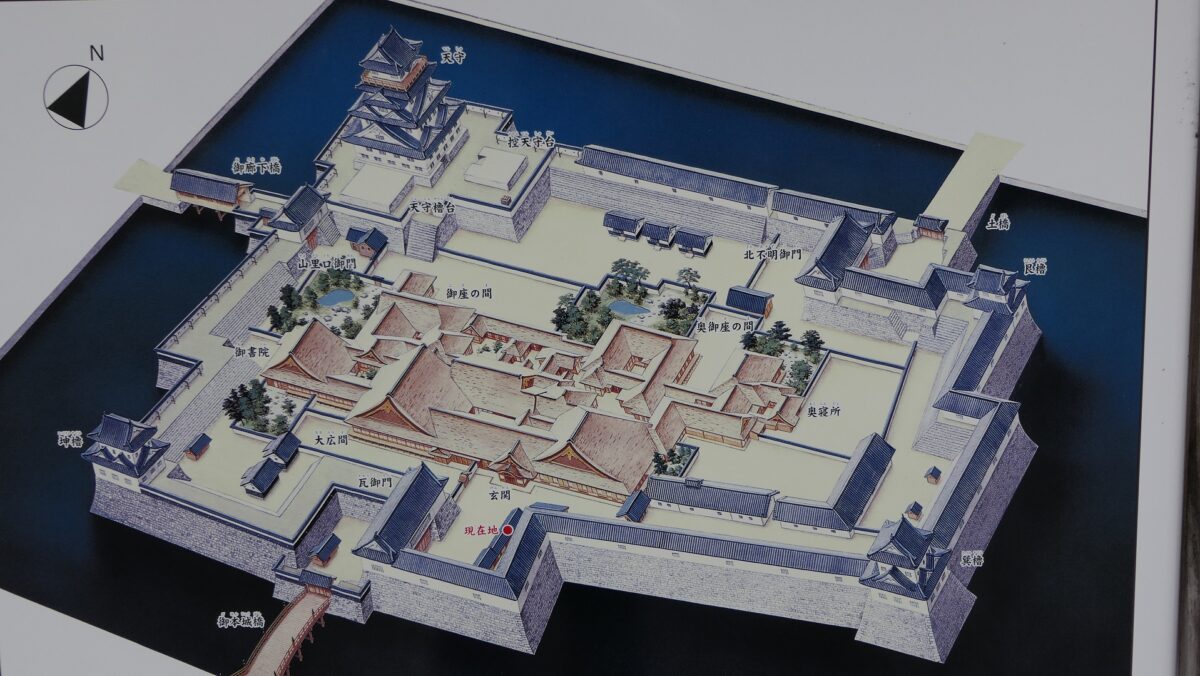
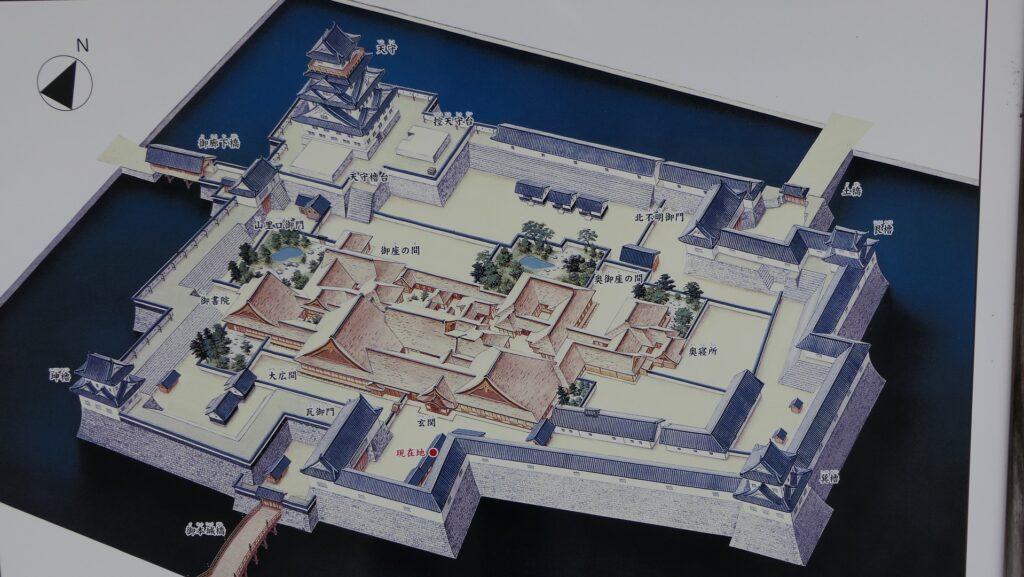
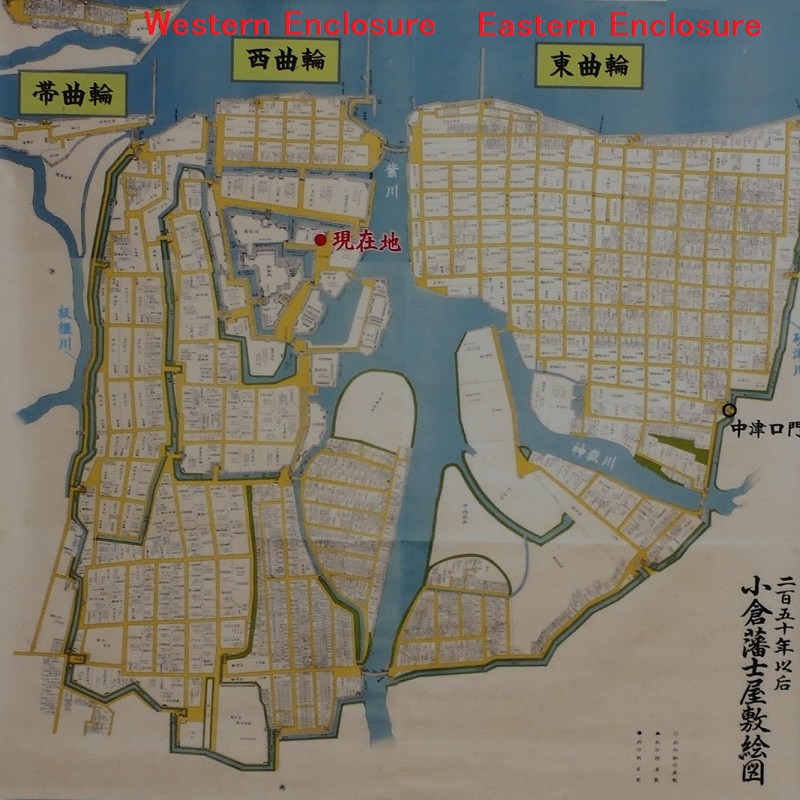
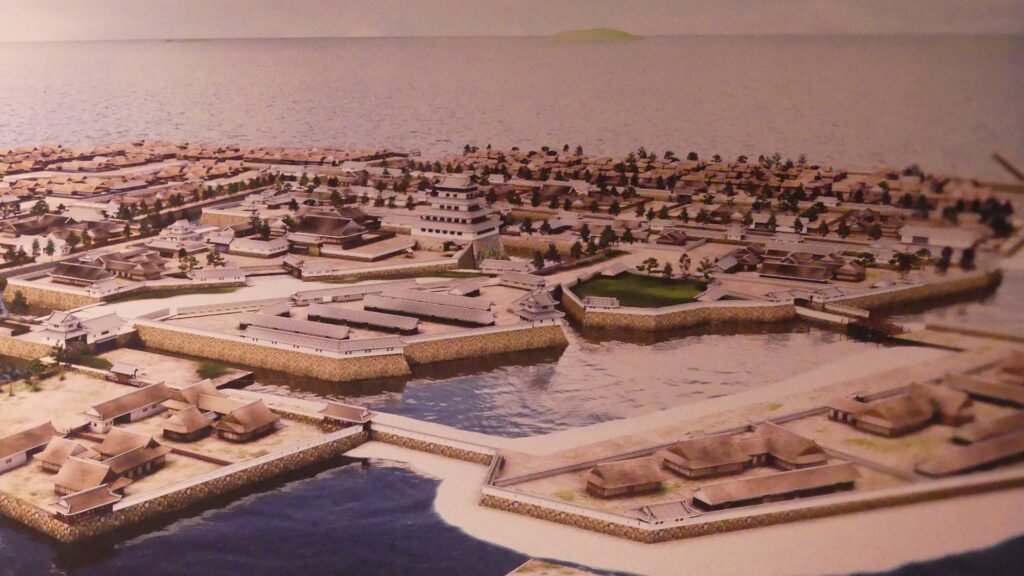
The former castle and the port was along the large estuary of Murasaki River, like a bay, when Tadaoki greatly developed the area. The area was broadly separated into the Western and Eastern Enclosures, binding the river. The Western Enclosure was also divided by water moats into smaller sub enclosures, such as the Main Enclosure, for the lord and warriors. The Eastern Enclosure became the castle town for people like merchants, craftsmen and monks. Furthermore, the whole area was surrounded by other natural or artificial rivers as the outermost moat whose perimeter was about 8km. Tadaoki thought if a large enemy force attacked the castle, he would flood the enemy by breaking the banks of the rivers.

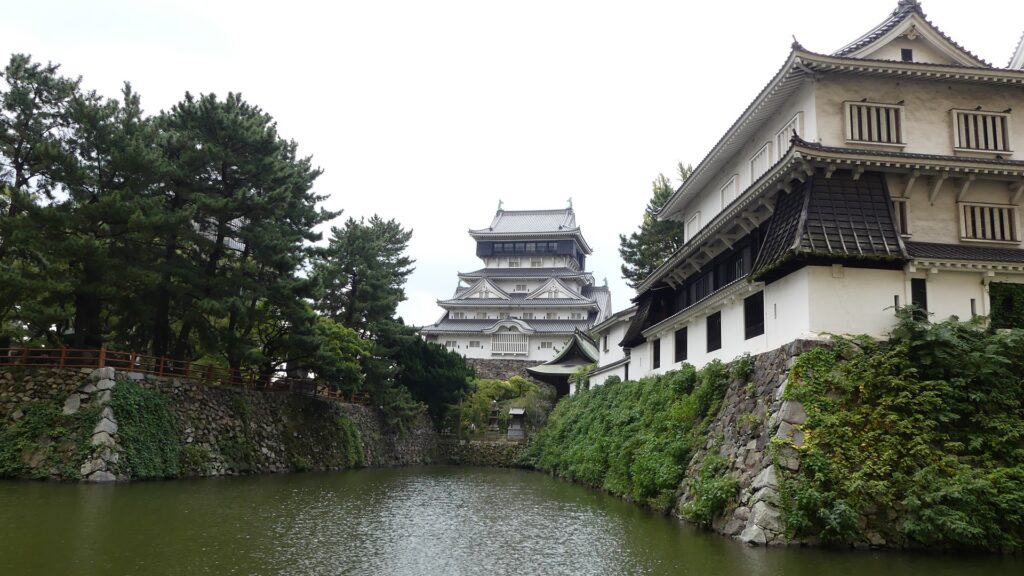
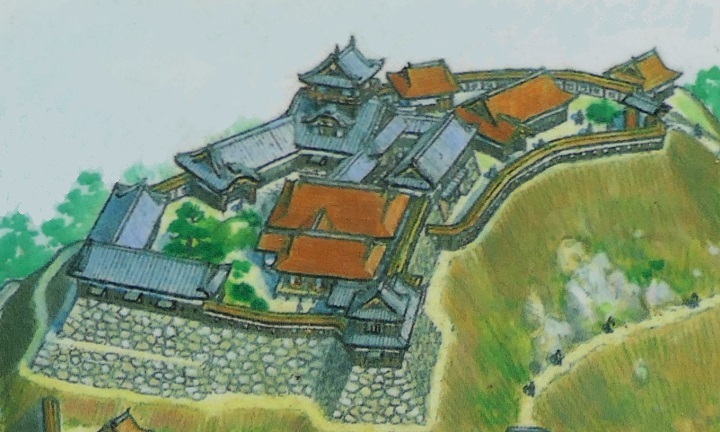
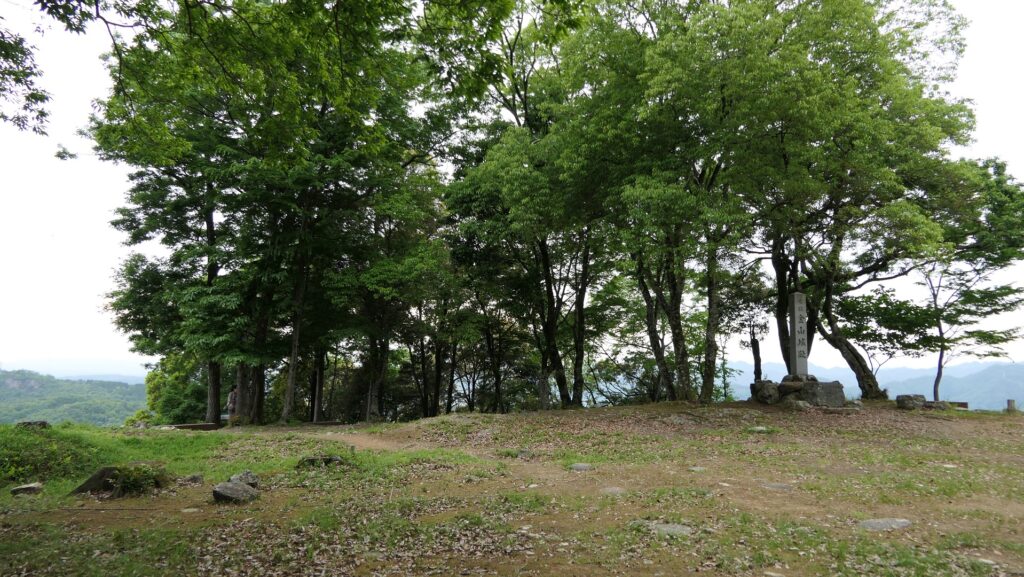
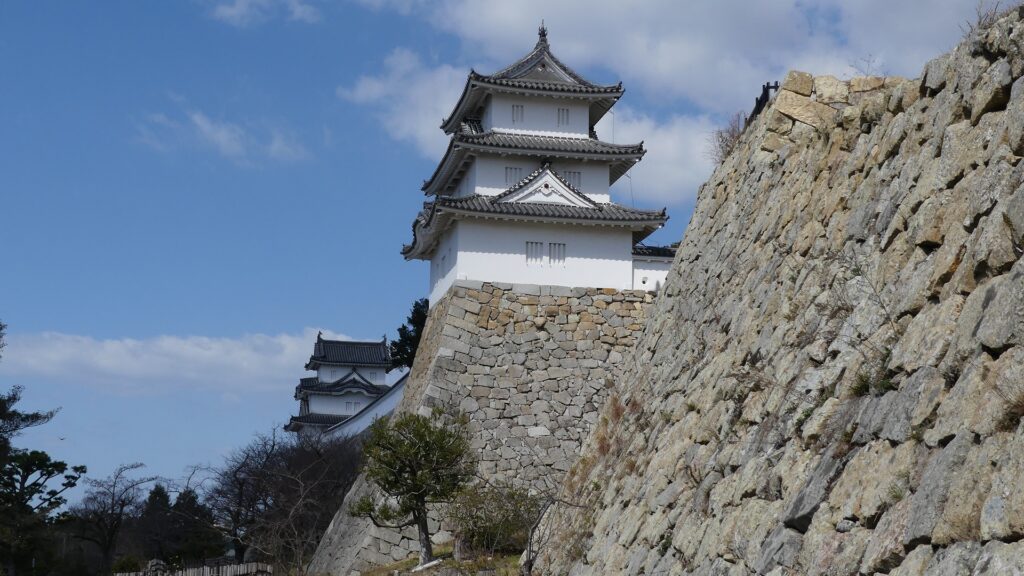
Characteristic Main Tower
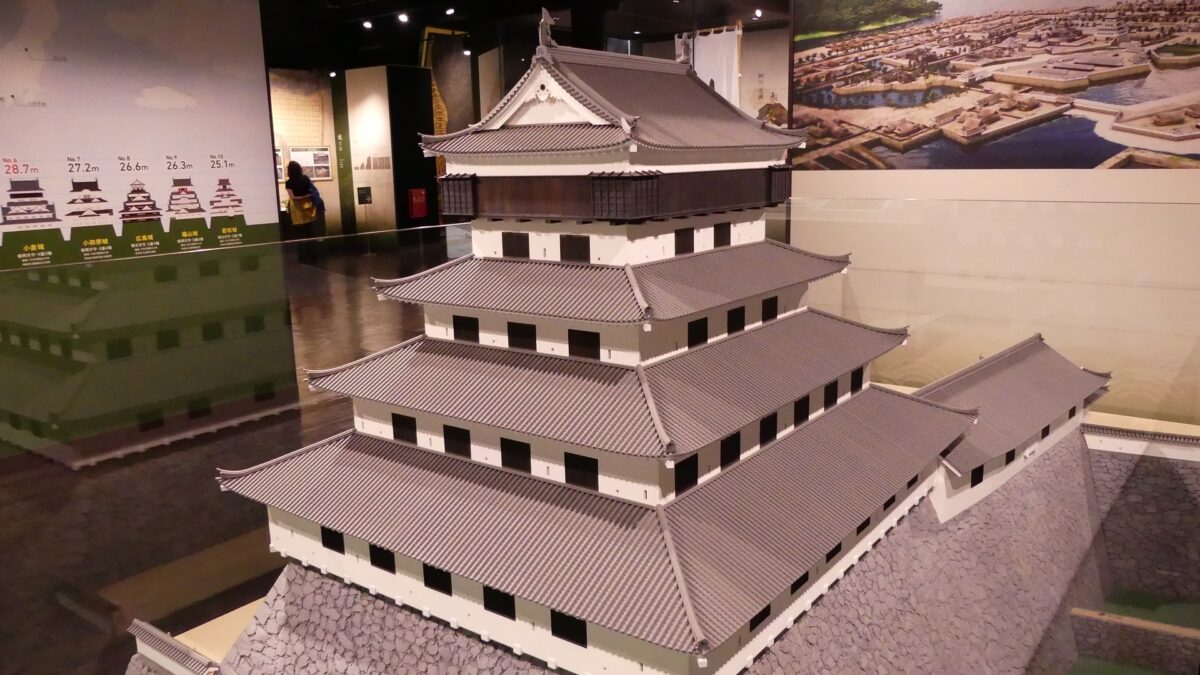
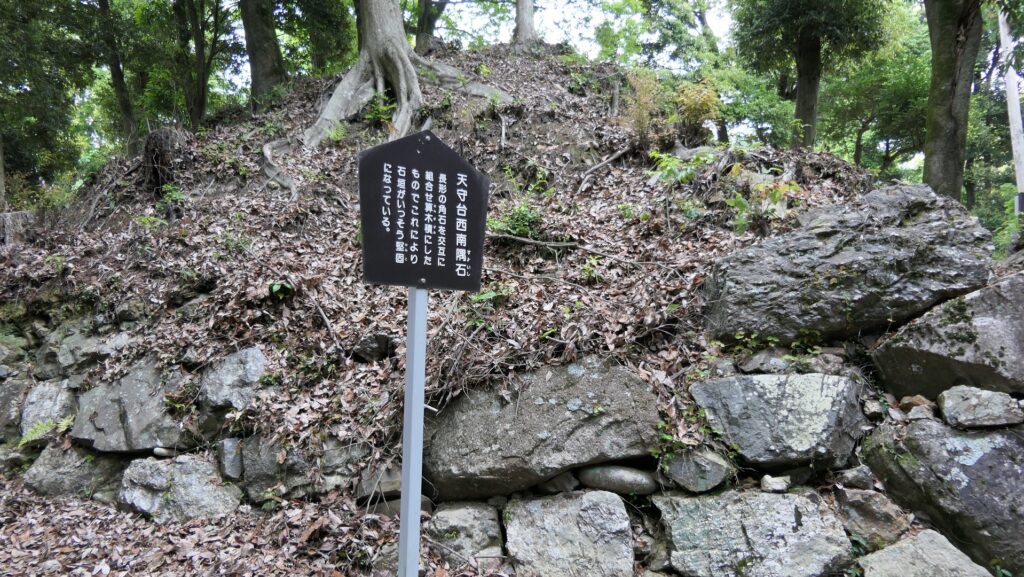
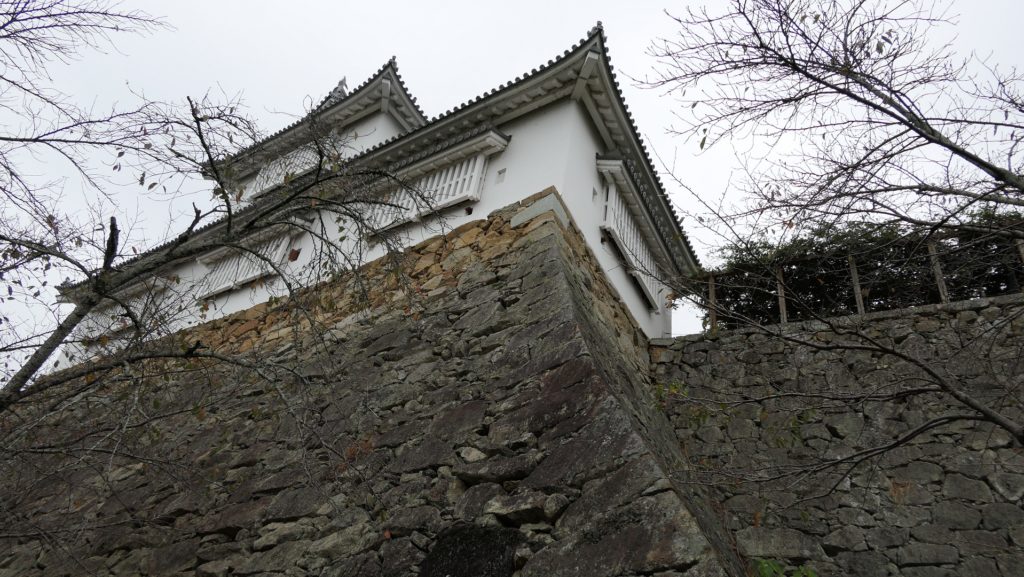
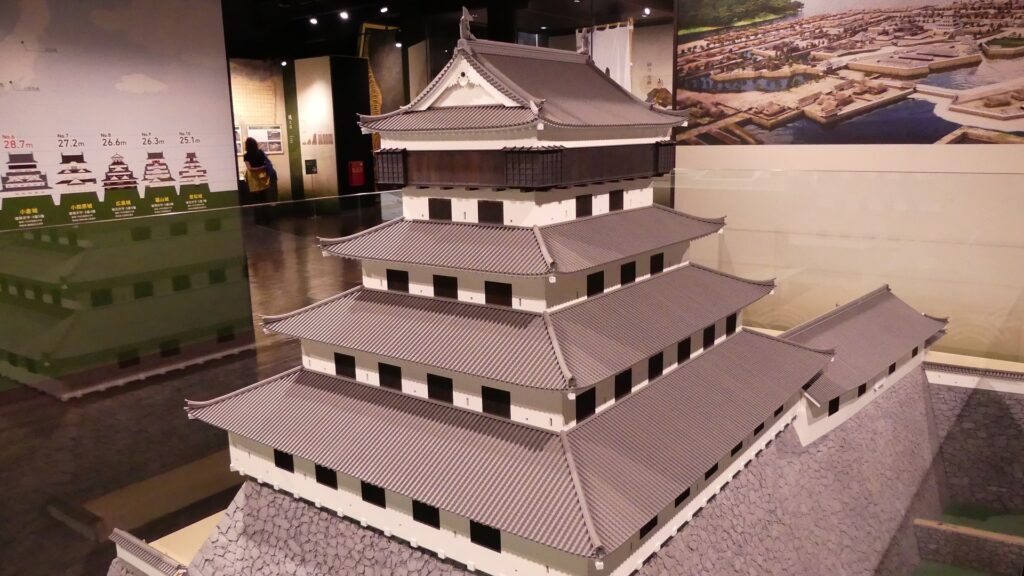
The main portion of the castle was surrounded by high stone walls. In particular, the stone wall base for the Main Tower was built at the northeastern corner of the Main Enclosure and was 18.8m high. The Main Tower itself was 22.8m high, so 41.6m in total. The tower had 4 levels and 5 floors inside because they were no roofs between the fourth and fifth floors. Also, the existing roofs were very simple without any decorations except for the top. It is a method called Soto-siki (meaning multi-storied type). This method made the builders efficient and made the tower easier to protect. The defenders would actually look out over the surronding area and counterattack the enemies at any direction from the tower. In addition, the tower had one more feature called Nanban-zukuri (meaning Western Style) or Kara-zukuri (the Chinese Style). It refers to some of the levels or floors hanging out over the other levels of the tower. In the case of Kokura Castle, it was the top floor because its balcony and handrails were covered by black outer walls to prevent damage from bad weather and strong wind. This Kokura style would be later emulated by other castles like Tsuyama and Takamatsu Castles.
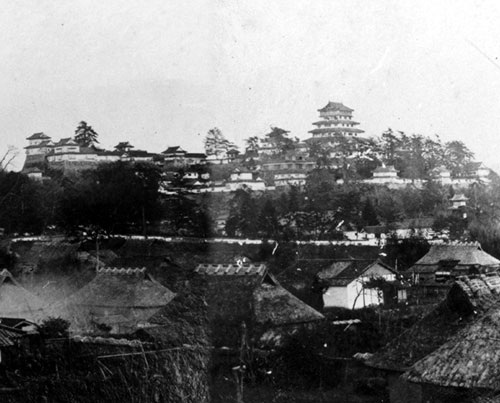




Prosperity and Destruction of Ogasawara Clan
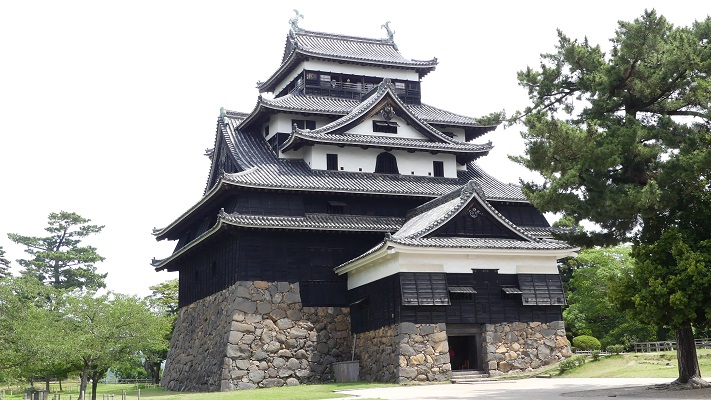
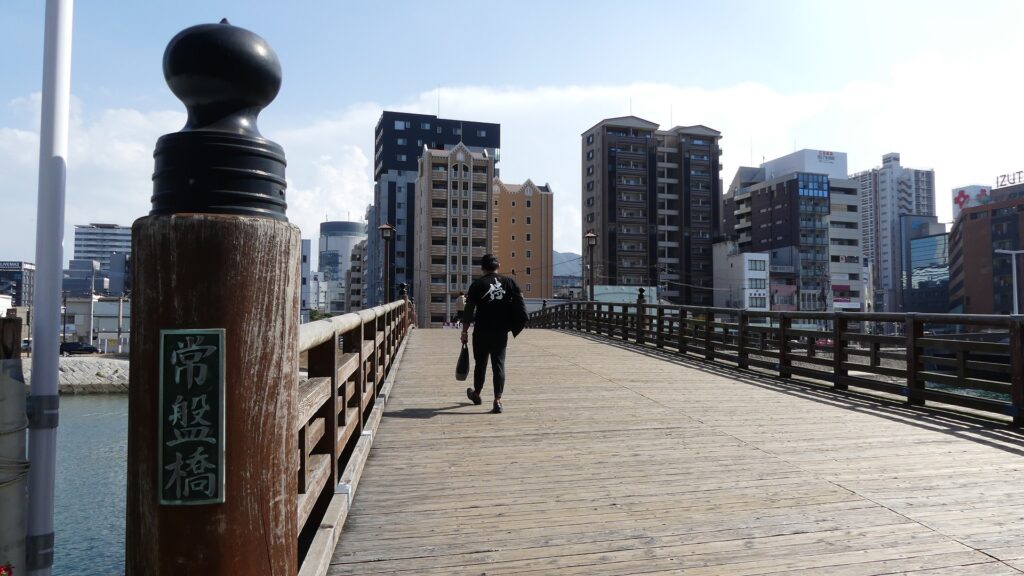
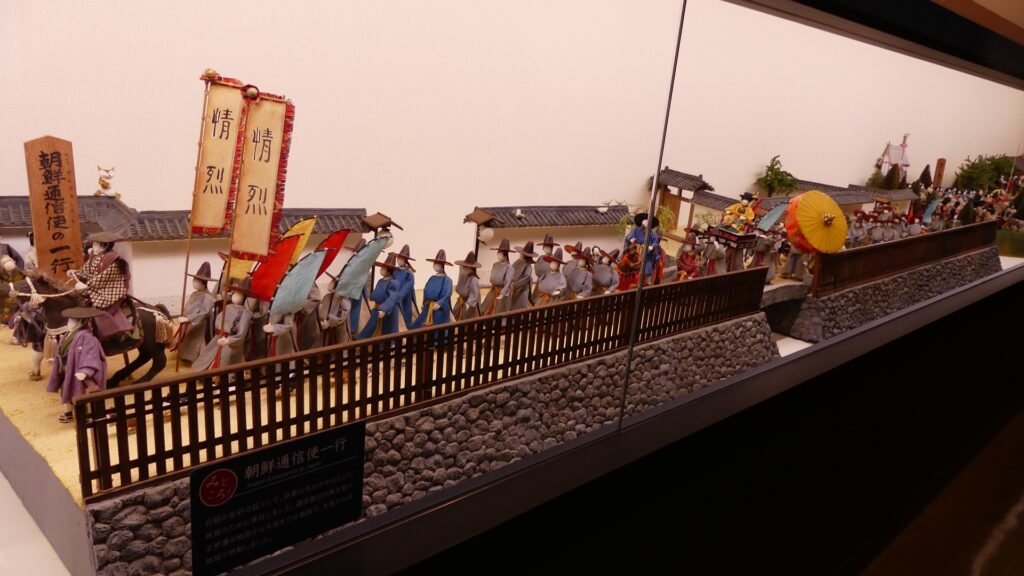
The castle and the domain were followed by Tadazame Ogasawara Ogasawara in 1632 after the Hosokawa Clan was transferred to Kumamoto Castle of the Kumamoto Domain. The Ogasawara Clan was a hereditary feudal lord family of the Tokugawa Shogunate, so it was expected to monitor non-hereditary feudal domains in the Kyushu Region. While the government of the Kokura Domain became stable, its castle town commercially prospered, especially around Tokiwa Bridge which connected the Western and Eastern Enclosures over the Murasaki River. The bridge was also the starting point of the Nagasaki Road where many passengers came and went between the main land and the region. the lords in the region and the Korean Envoys also used the road when they went to Edo.




Meanwhile, a bad sign for the castle occurred in 1837. The Main Tower was unfortunately burned down by an accidental fire though it had survived through some lightning strikes. The tower was not rebuilt by the domain after that. Next, a severe event happened to the castle at the end of the Edo Period. The Choshu Domain at the edge of the mainland over the Kanmon Strait rebelled against the shogunate twice. The Second Conquest of Choshu was planned by the shogunate in 1866. The shogunate ordered the Kokura Domain and its allies to attack the Choshu through the Kokura Route, one of the four battlefields.
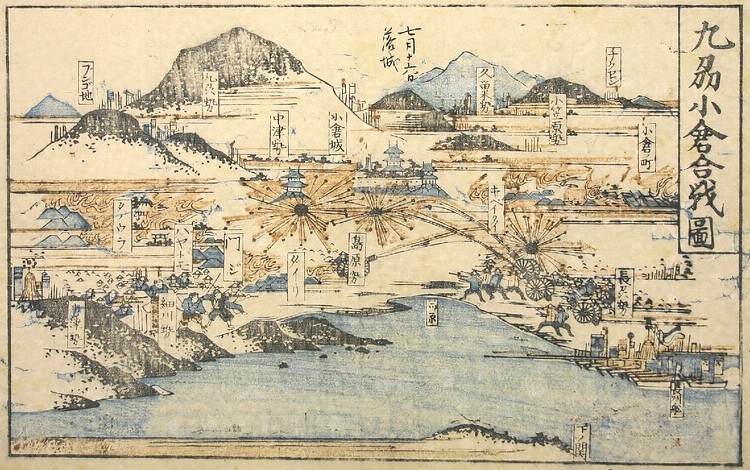

The battles on the Kokura Route started in June. Against all odds, the Choshu troops landed on the Kokura area and counterattacked the shogunate side instead. Moreover, all the allies withdrew after they heard about the death of the shogun, Iemochi Tokugawa, by illness on the 20th of July. The Kokura troops, which were left alone, finally fired at the castle by themselves on the 1st of Aug and continued to fight against the Choshu like a guerrilla army. However, the fall of the castle and the Choshu capturing it became a symbol of the shogunate’s big failure in the battles which would accelerate its destruction and the Meiji Restoration by the New Government including the Choshu Domain.