Features
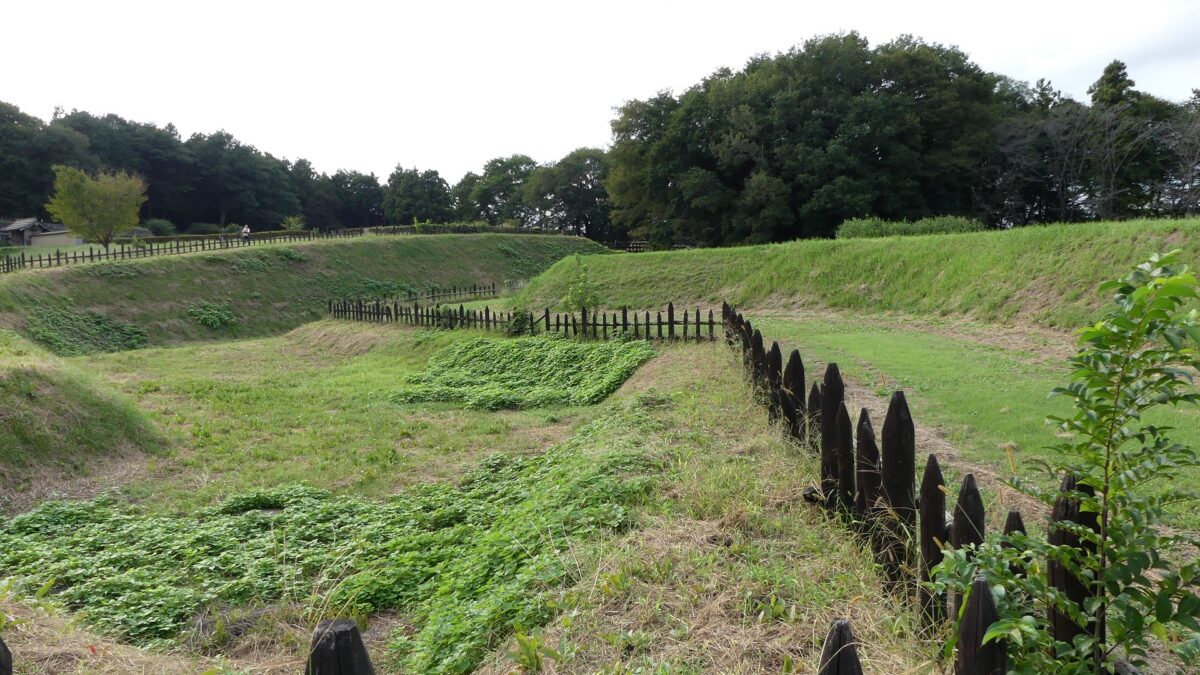
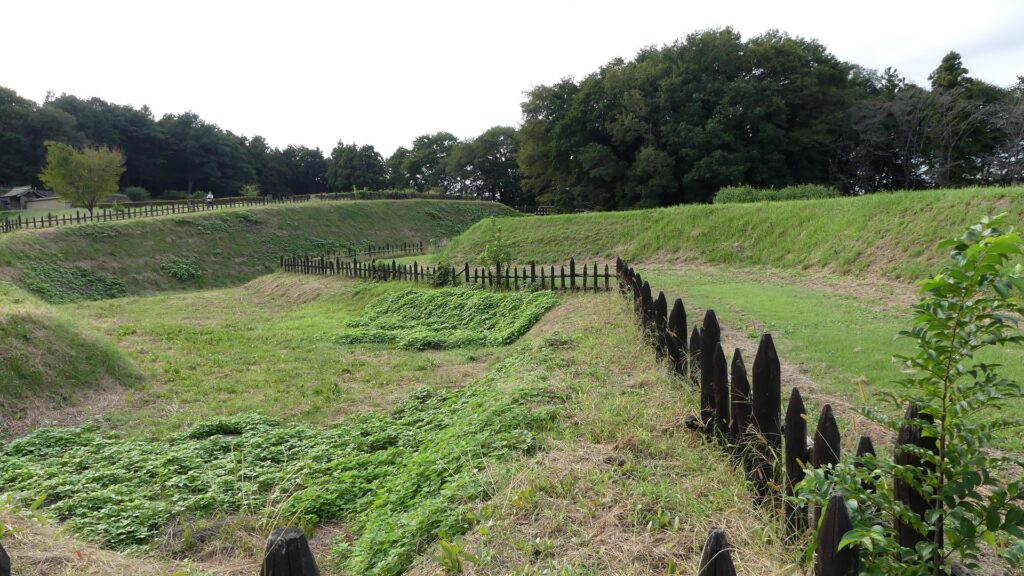
Well-Restored Dry Moats
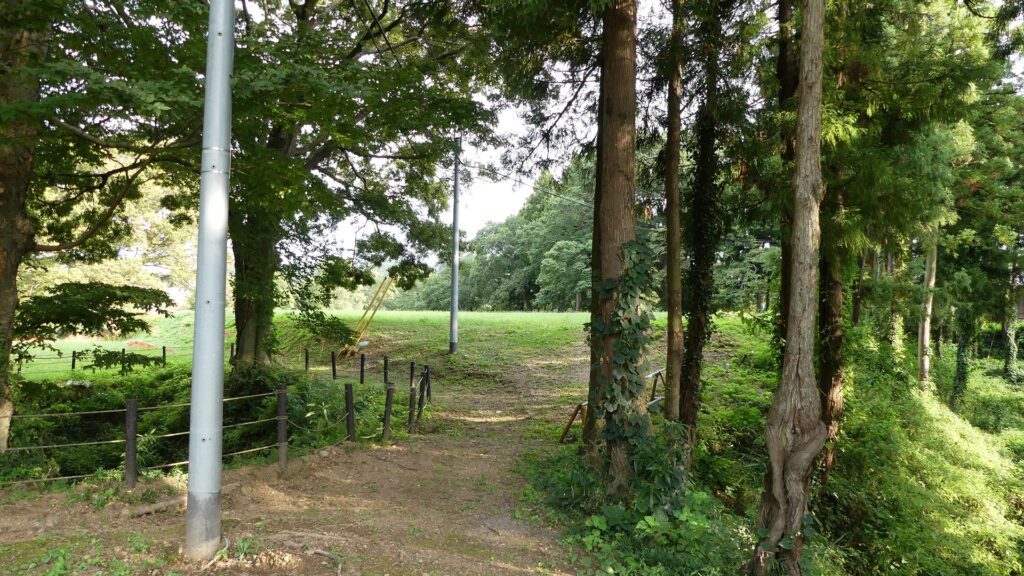
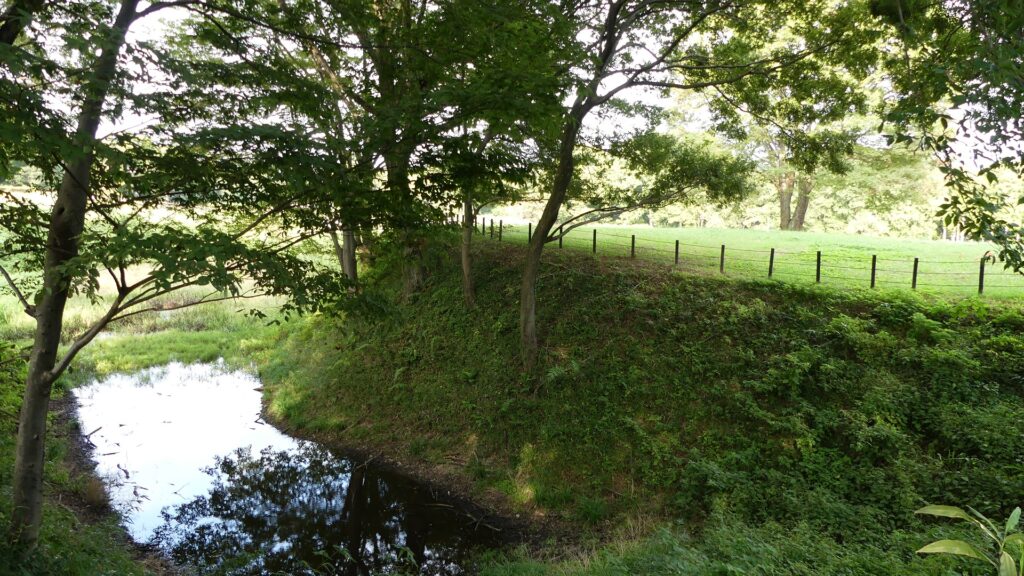
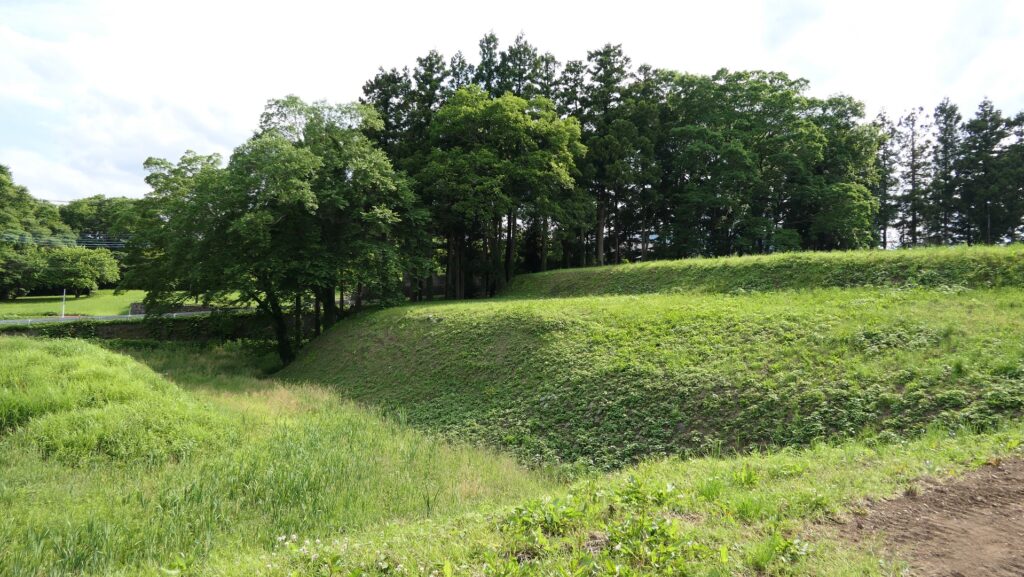
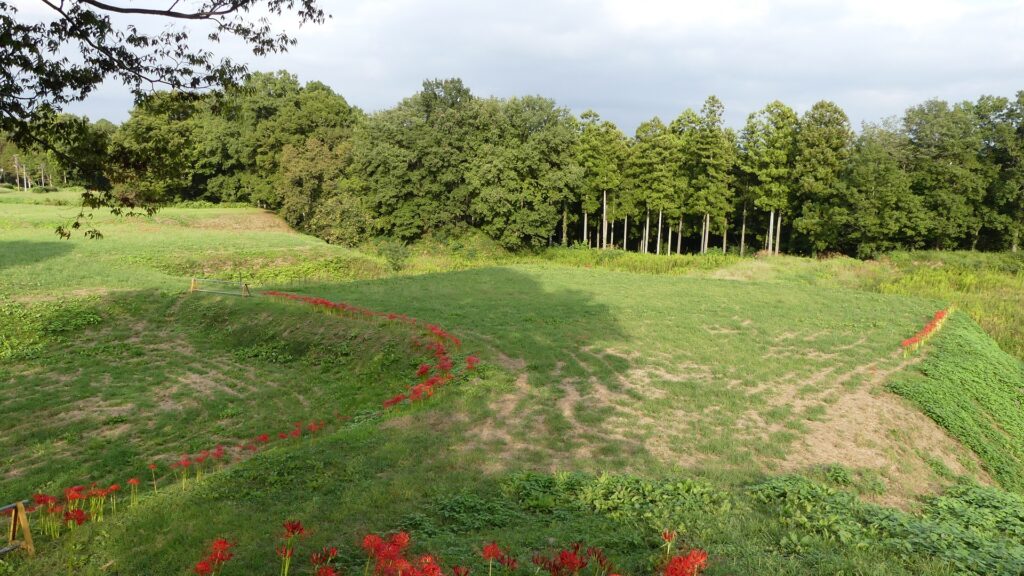
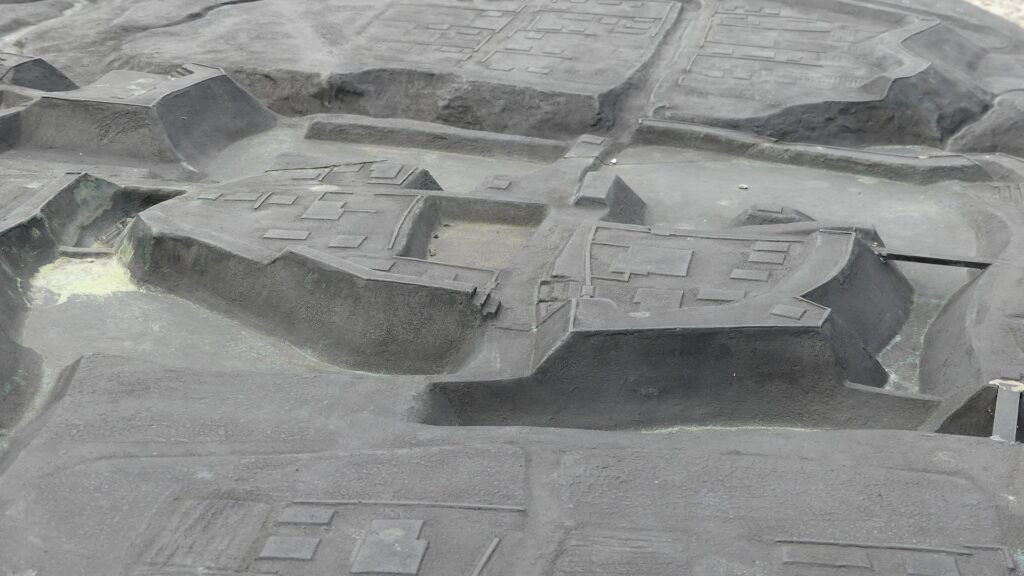
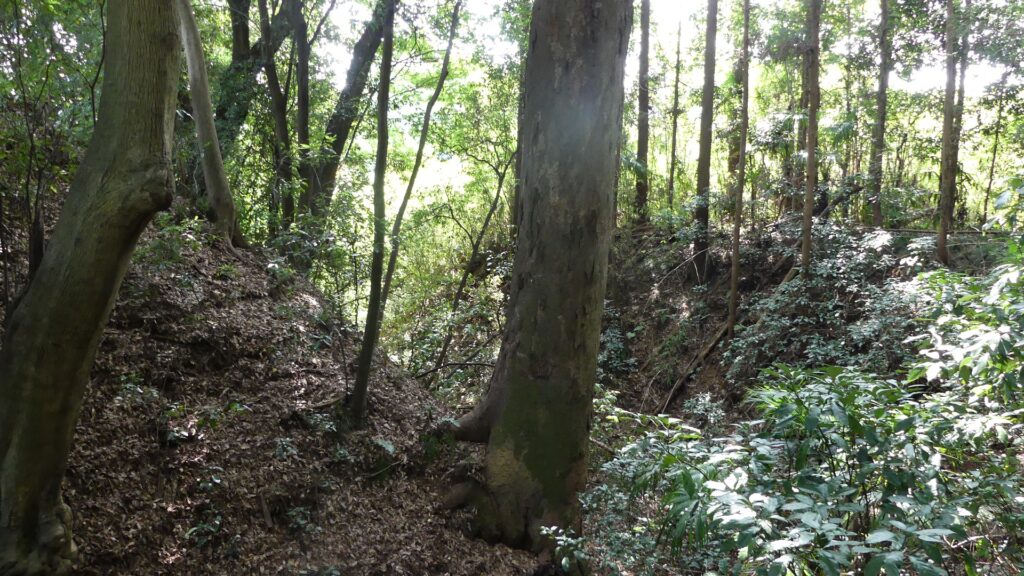
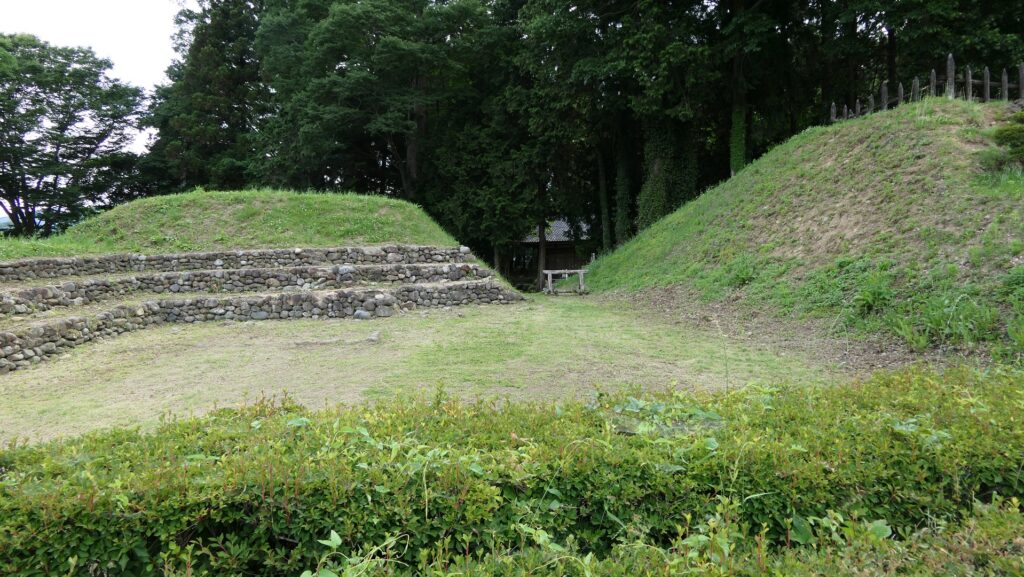
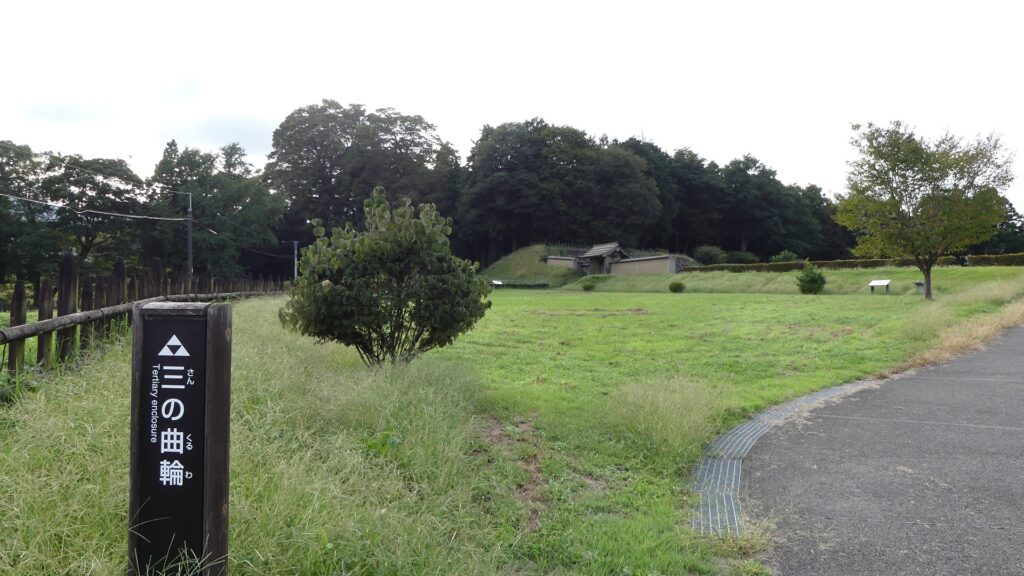
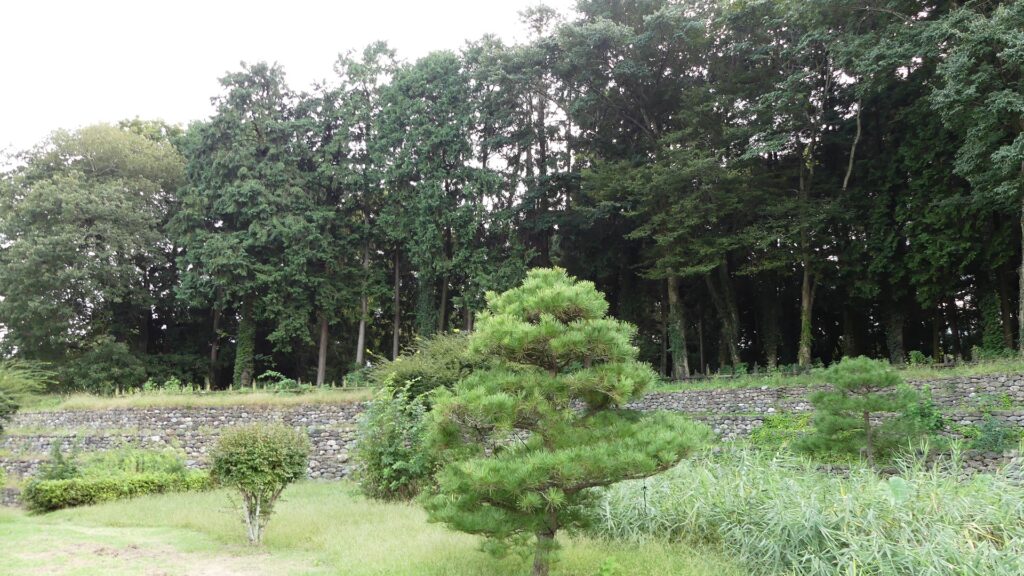
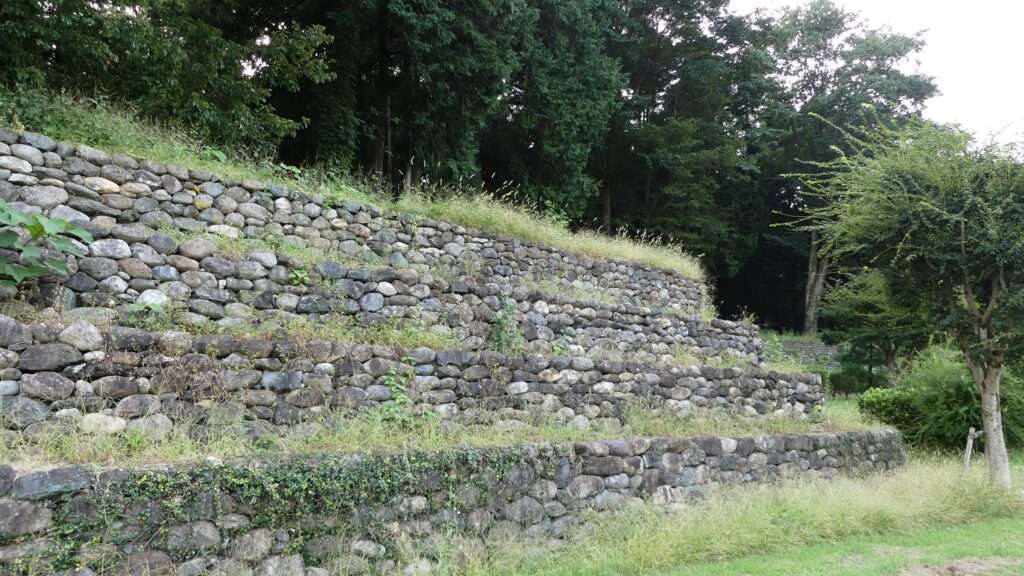
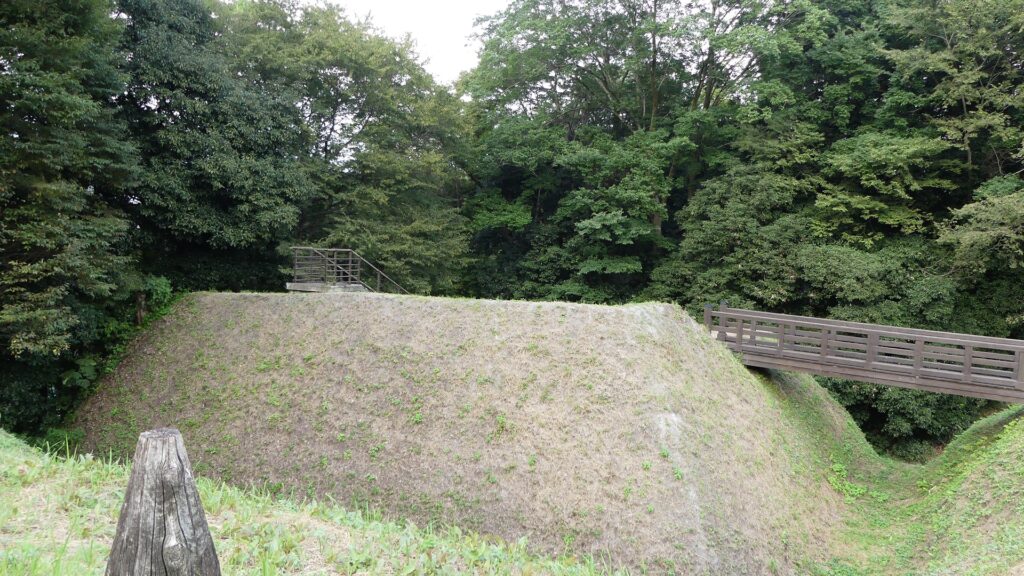
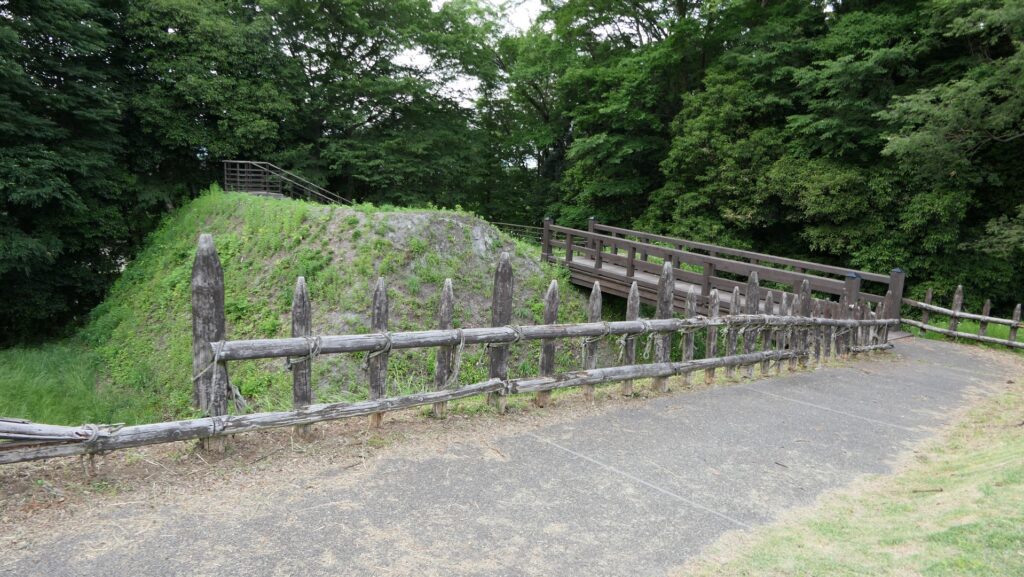
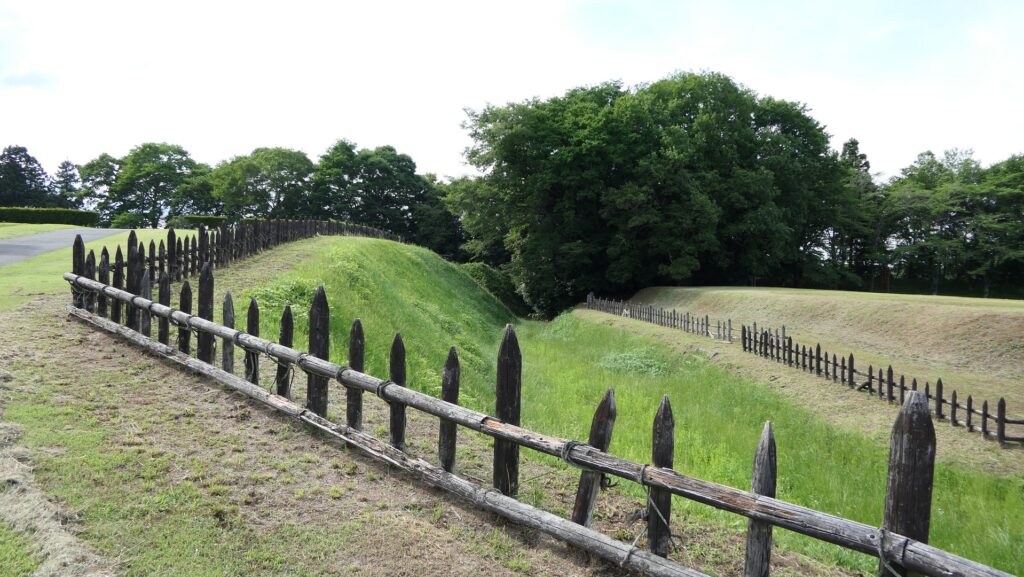
Zigzagged large dry moats with wooden fences between the Third and Second Enclosures, which allowed the defenders to attack enemies’ sides, have also been restored. Only two routes were available between them – the one via the Main Route and the other via the well restored Umadashi system. Also, if you compare the two enclosures, you will find the Third is higher than the Second. In other castles, the Second (which is closer to the Main Enclosure) is usually higher than the Third. However, in the case of Hachigata Castle, it is the other way around. In addition, the Third Enclosure had strong defense systems with four Umadashi which are originally designed by the Hojo Clan. That’s why author, Jun Ito says the Hojo Clan might have moved the center of the castle from the Main Enclosure to the Third in the final stages of the castle.
The aerial photo around the castle. the red markers indicates the four Umadashi systems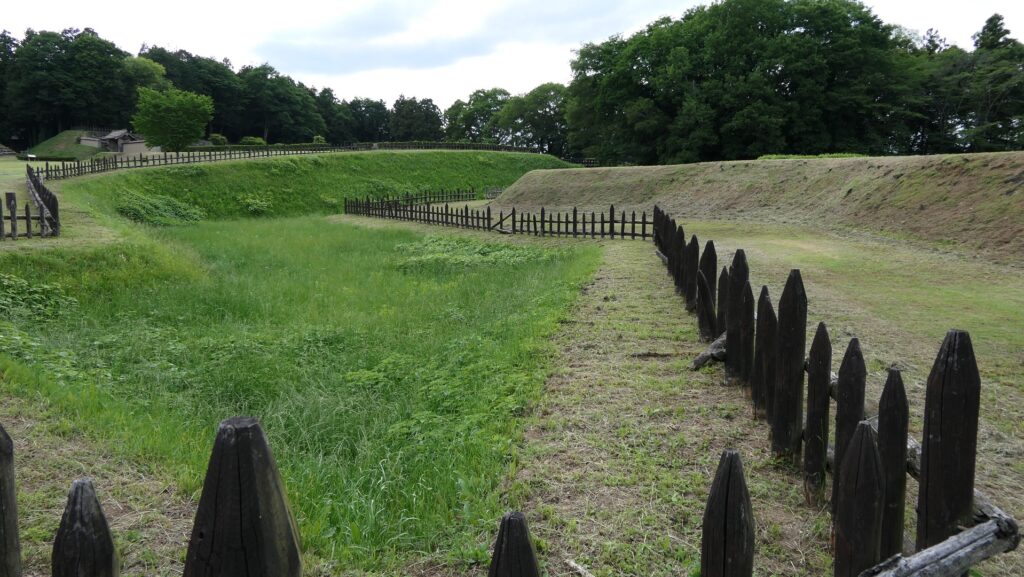



Panorama of Main Enclosure
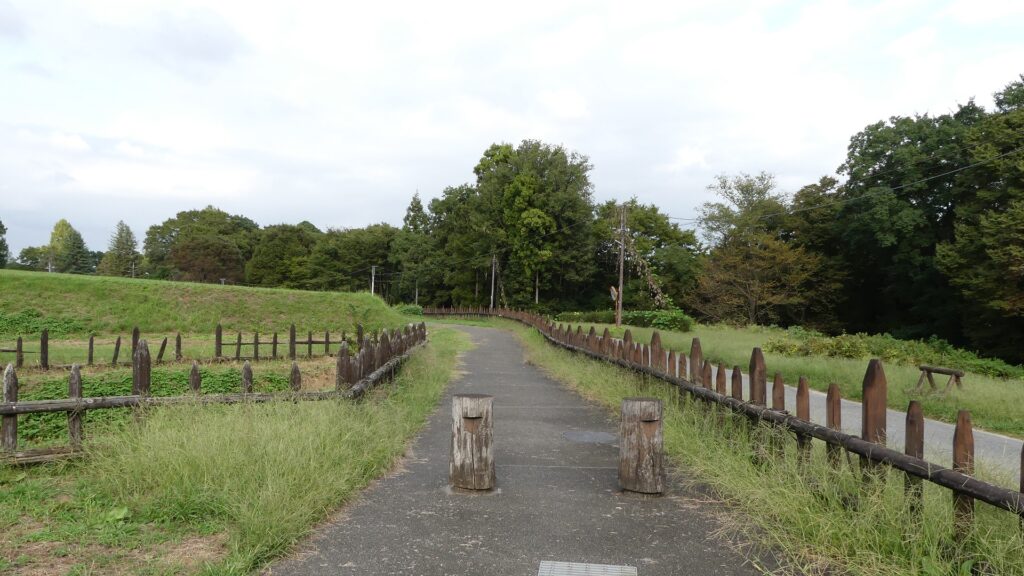
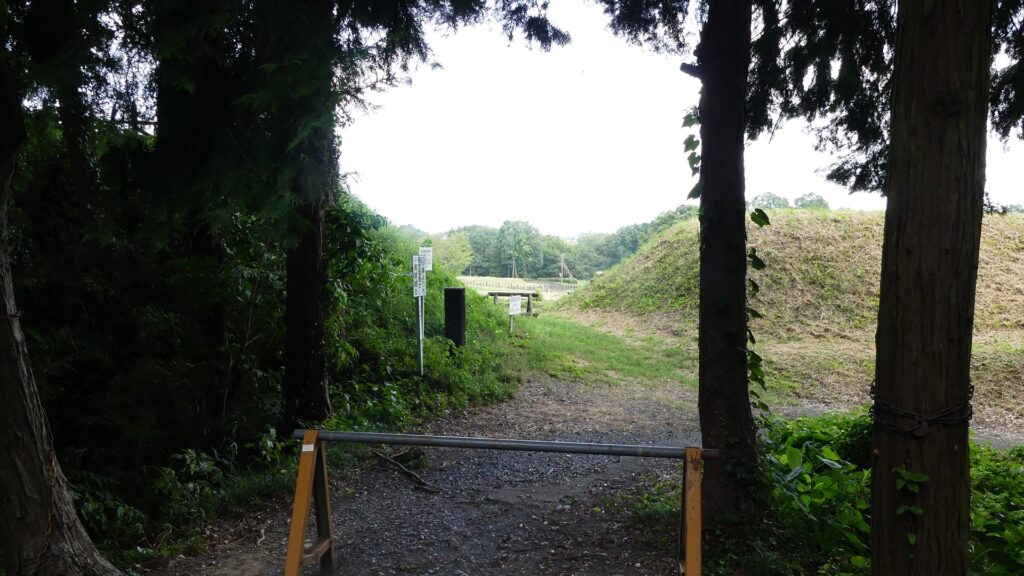
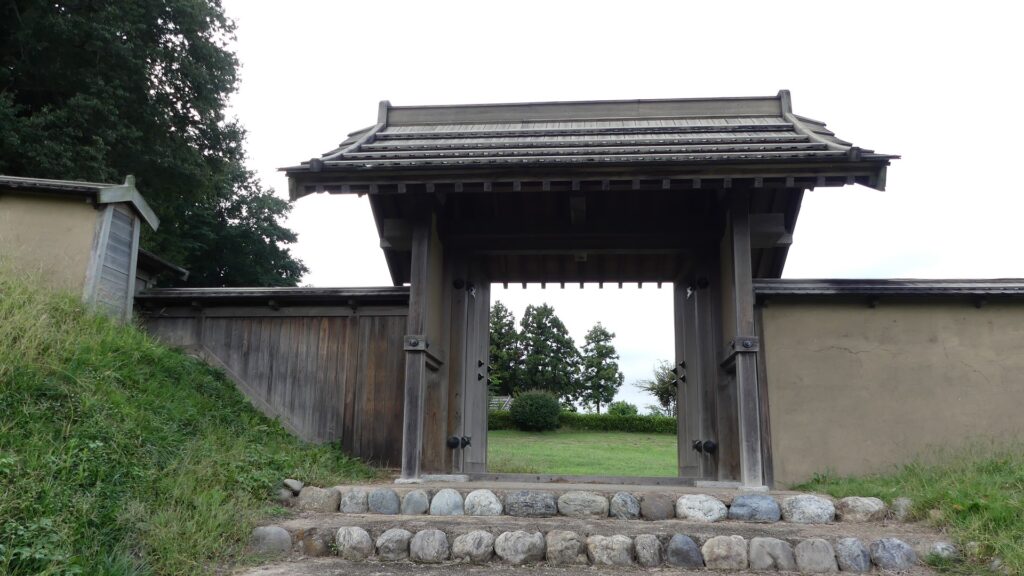
A paved car road goes between the Second and Main Enclosures, so it may be difficult to imagine what it used to look like. According to information at the Hachigata Castle History Museum, there used to be a large gate to the Main Enclosure and a wooden bridge over the deep dry moat in front of the gate.
The map around the castle

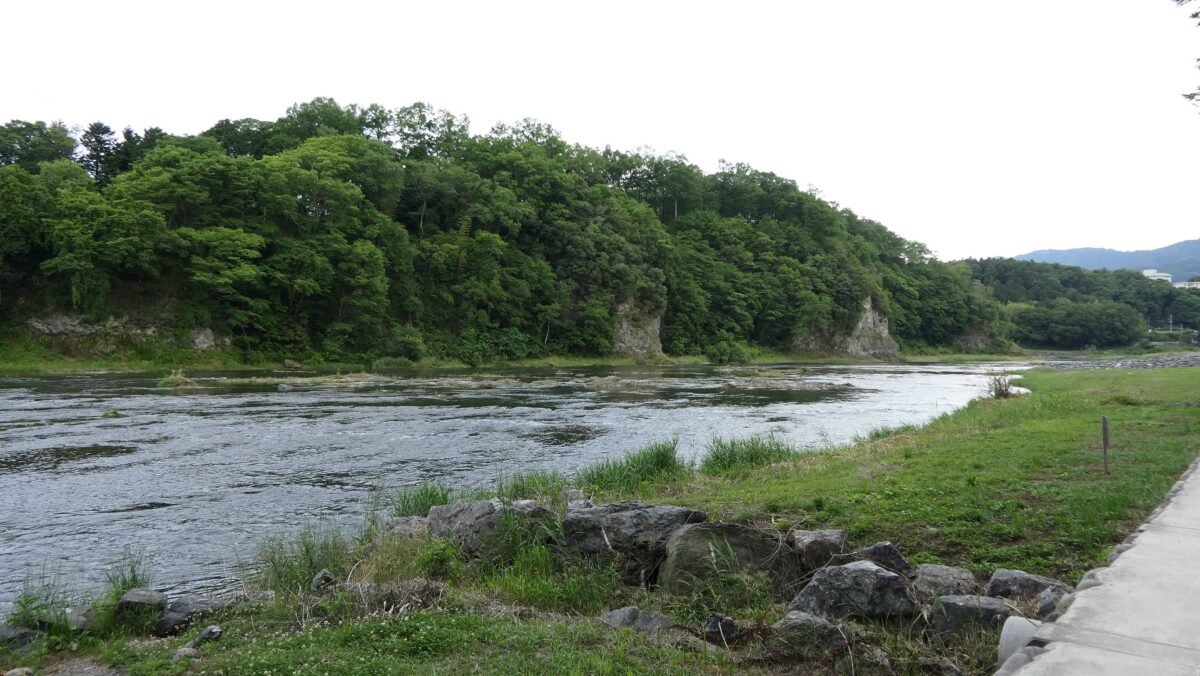
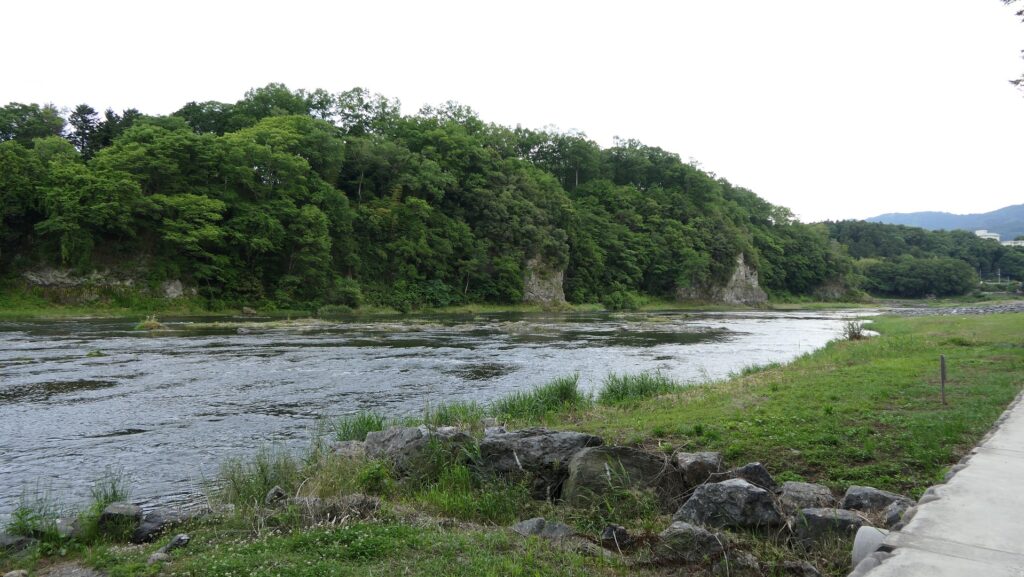
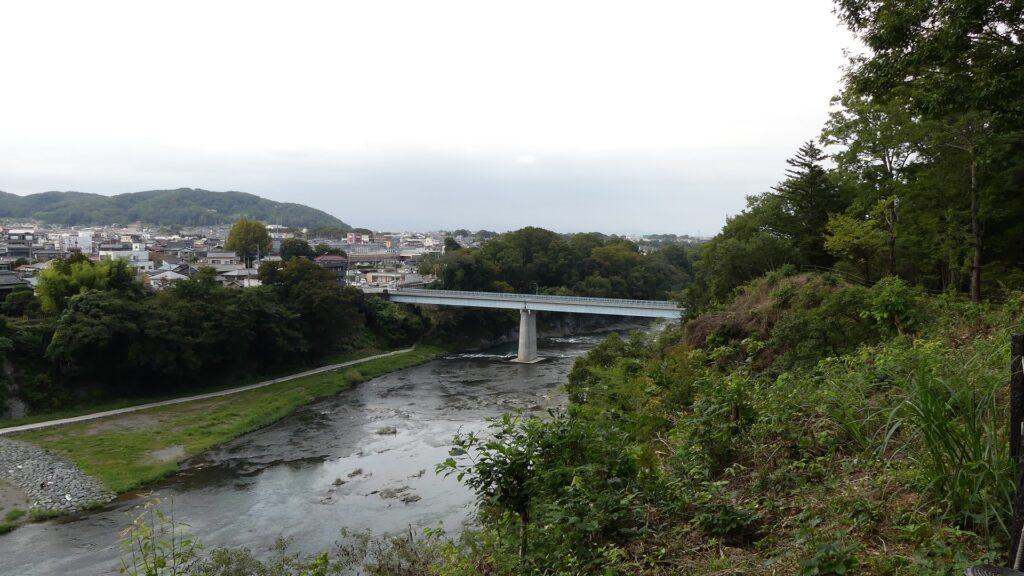
The enclosure has the other peak of the castle, standing beside a 30m tall cliff. no castle buildings remain, and it is purely made of soil, but the ground is still leveled so you can imagine the Main Hall for the lord as it was in the past. You can enjoy a great view of the Arakawa River and the surrounding area from the peak. You can also understand how the castle was naturally protected.
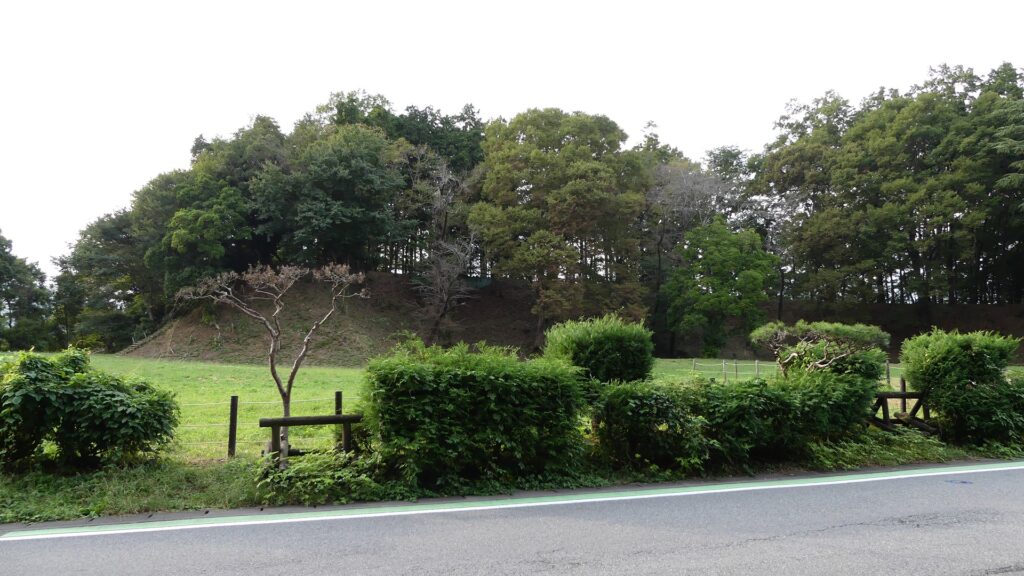
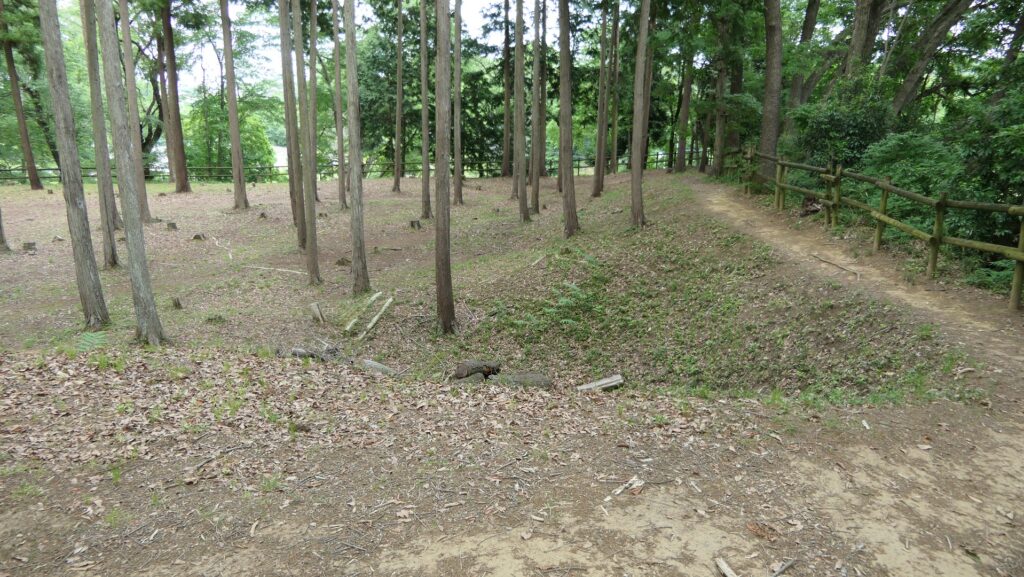



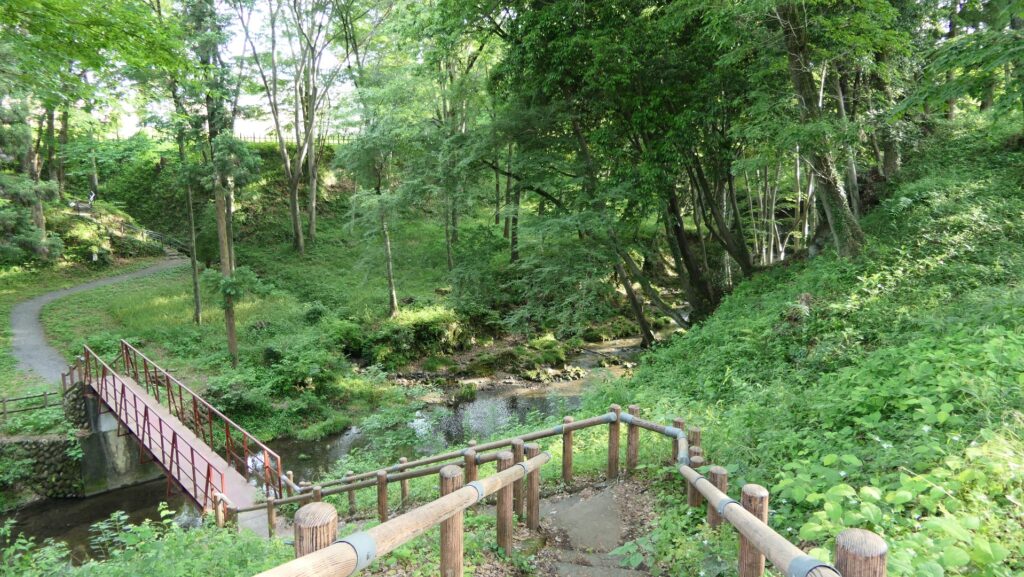
You will finally reach the Sasa Enclosure, near the tip, which is lower than the Main Enclosure. It is another entrance to the castle ruins, beside Shoki-bashi Bridge.
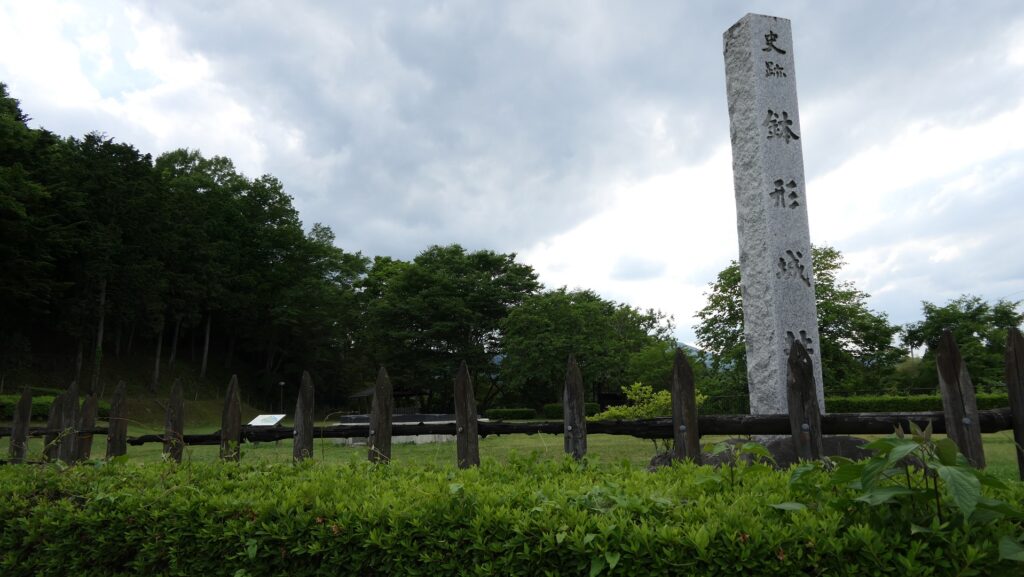
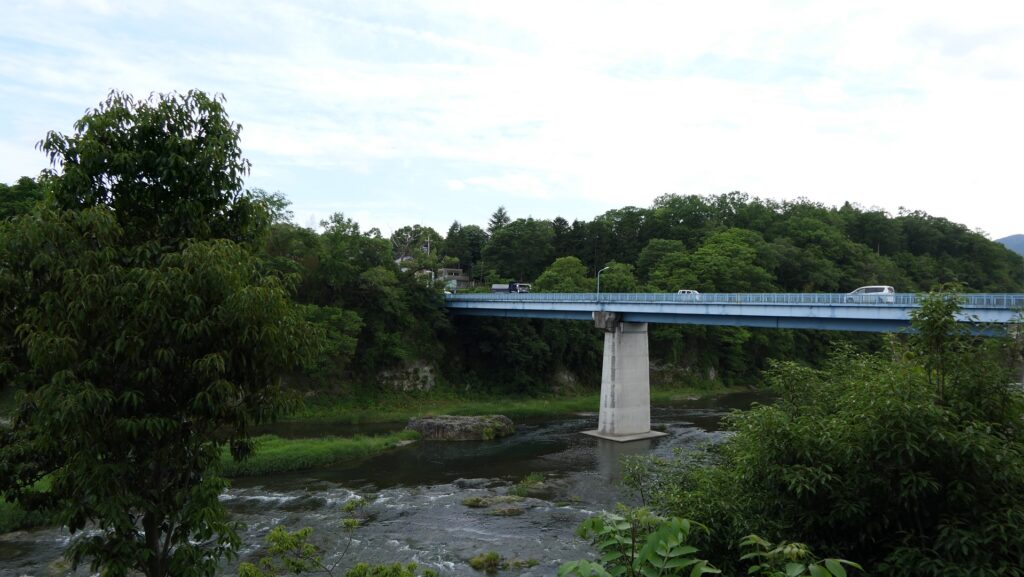


The tip area is a private area where visitors can’t enter, so you can only see this area from the opposite side of the river. If you cross to the opposite, you should check out another great view of the castle ruins on the cliff from the Tamayodo riverbed beside the bridge.
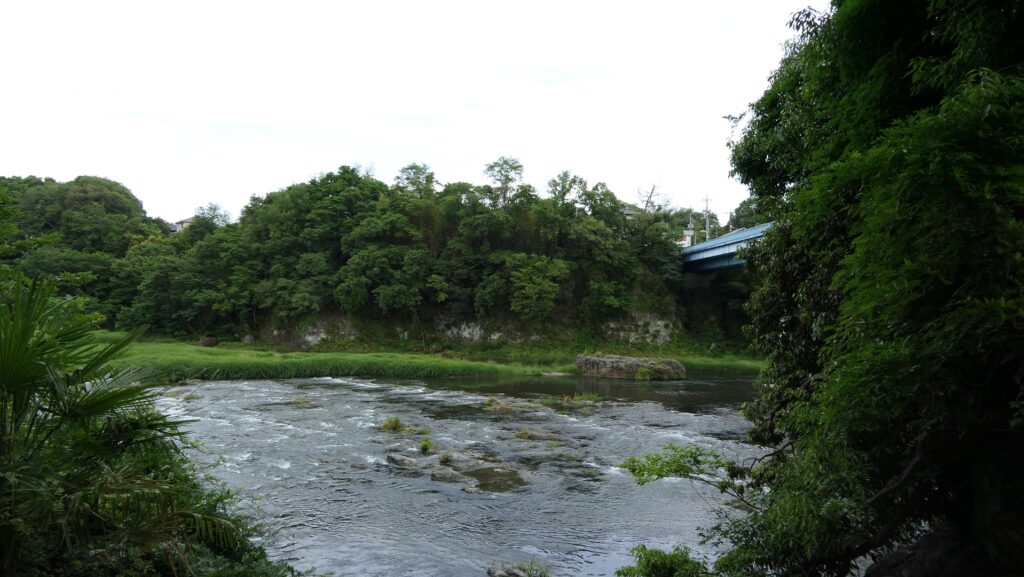
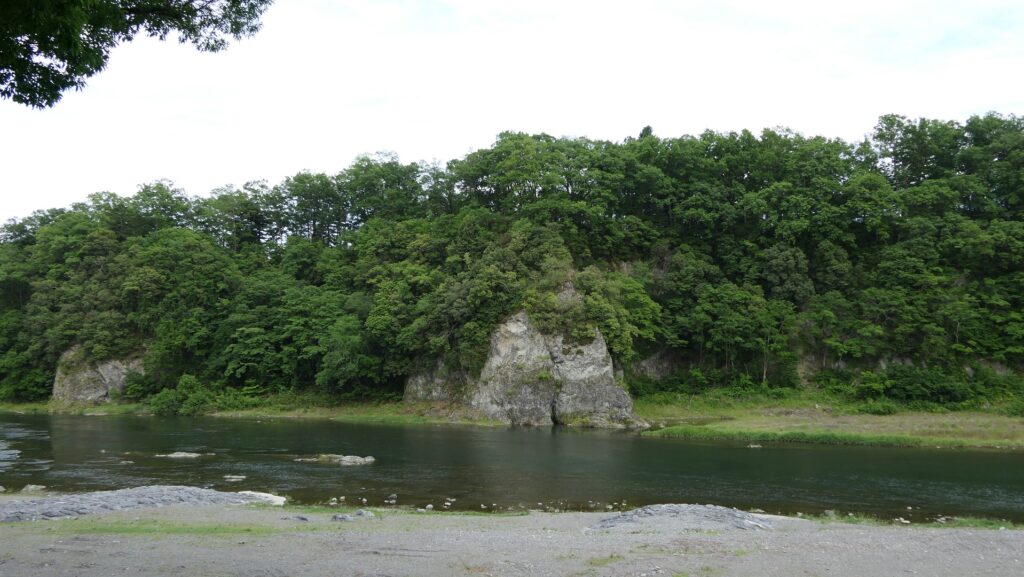


Later History
At the beginning of the Showa era (around 1930), the JR Hachiko line was planned to be constructed through the ruins. Locals argued the plan needed to be changed and asked the government to preserve the ruins. They were successful and the ruins was designated as a National Historic Site in 1932. Yorii Town excavated and researched the Second, Third and Sasa Enclosures between 1997 and 2001. Based on these achievements, the town developed the Hachigata Castle Park and restored some structures of the castle. It also opened the Hachigata Castle History Museum in 2004 to display and educate people about the history of the castle and the studies into it.

My Impression
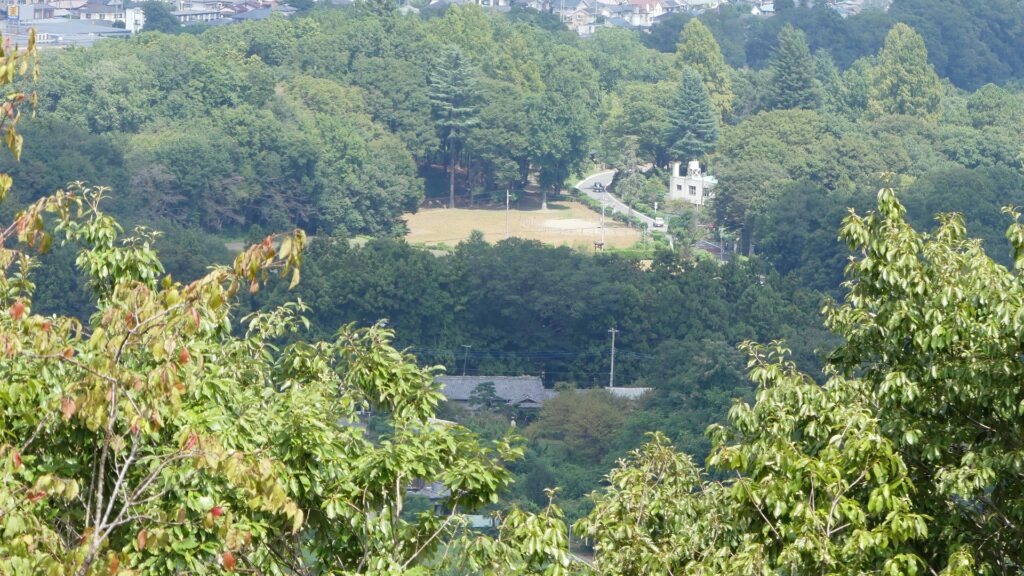
I climbed Kuruma-yama Mountain to its top to confirm that the idea of the attackers firing upon the castle in the battle in 1590 would was realistic. It is widely accepted that General, Tadakatsu Honda brought large guns, fired upon the castle, and broke the Main Gate. The mountain is 227m above sea level and about 100m above the castle, which is about 1km away (the Third Enclosure). A view of the castle ruins from above was actually not good because of the trees surrounding. My conclusion is that not all of the wildly accepted lore is correct. I think the firing itself is the fact, because a large gun shell of several cm in diameter was excavated from the Outer Enclosure of the castle. However, I don’t think shooting from the mountain would have been useful. In the winter campaign of the siege of Osaka in 1614, Ieyasu Tokugawa borrowed the large Western guns and fired upon Osaka Castle from his stronghold on a river delta , about 500m away the castle. Considering this case, shooting at the castle using (probably) Japanese guns 24 years previously, from more than 500m away, even from a mountain could not be done. My speculation is that Tadakatsu put his stronghold on the mountain but fired upon the castle from a place much closer to it than the mountain.




How to get There
I recommend using a car when you visit the castle ruins because there are only a few buses available. It is about a 20-minute drive away from Hanazono IC on the Kanetsu Expressway. There are several parking lots in the park.
If you want to use public transportation, it takes about 30 minutes on foot to get there form Yorii Station.
From Tokyo to Yorii Station.: Take the Tobu-Tojo line from Ikebukuro Station, or take the Joetsu Shinkansen super express from Tokyo Station to Kumagata Station, and transfer to Chichibu Railway.
That’s all. Thank you.
Back to “Hachigata Castle Part1”
Back to “Hachigata Castle Part2”