根城は、地元の人たちと行政の多大な努力により再建された城です。
Ne Castle is a castle which has been rebuilt thanks to the great effort of the local people and officials.

Location and History
この城は現在の青森県八戸市にありました。この地域は東北地方の北部としては開けた場所で、中世から商業で栄えてきました。
The castle was located in what is now Hachinohe City, Aomori pref. which has been the opening for the northern Tohoku region and has flourished through trading since the Middle Ages.

南北朝時代において南朝方により、南部師行が陸奥国にこの地域を統治するために派遣されてきました。彼は1334年に、以前の支配者であった北条氏の館があった糠部郡の丘の上に、初めて根城を築きました。
In the period of the Northern and Southern Courts, Moroyuki Nanbu was sent to Mutsu Province by the Southern Court to govern this area. He first built Ne Castle on a hill in Nukanobu district after the former ruler Hojo’s hall in 1334.

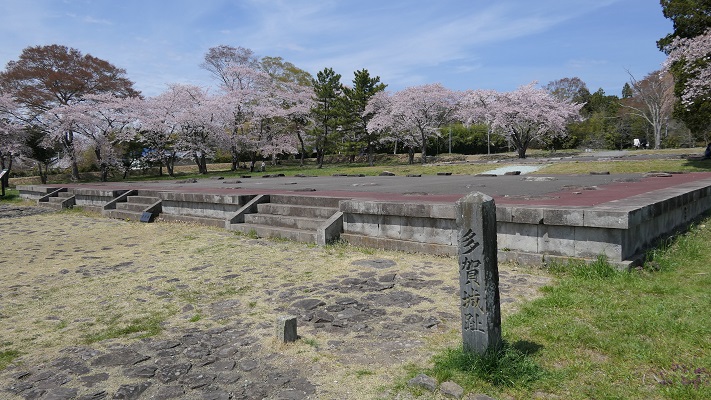
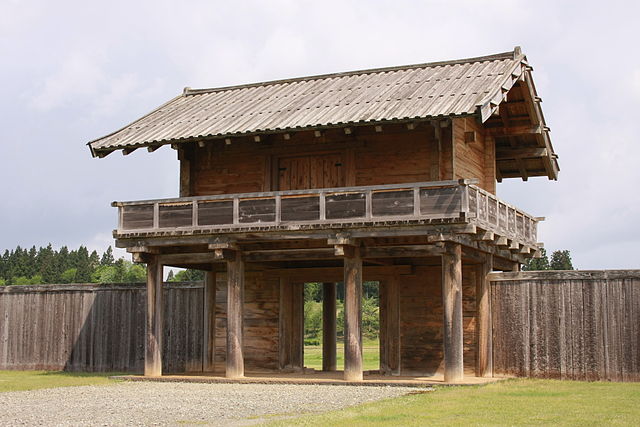
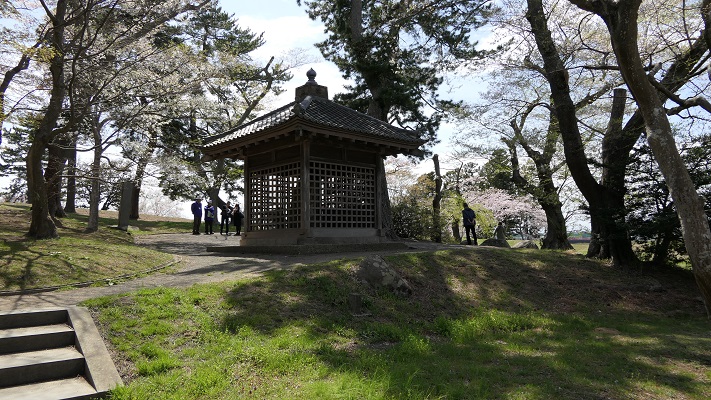
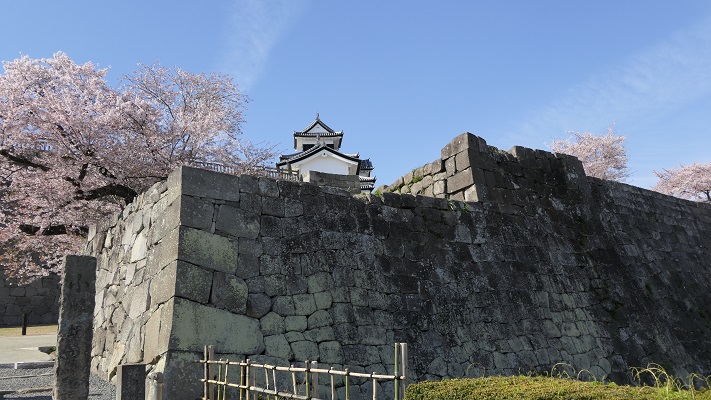
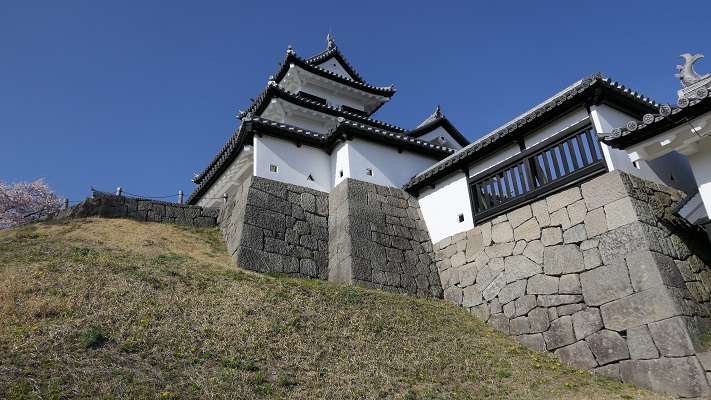
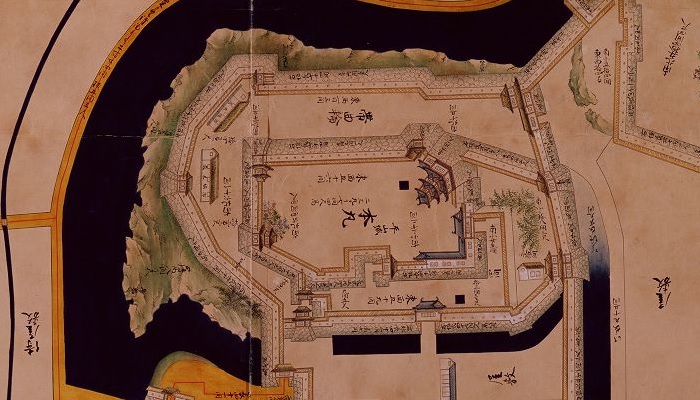
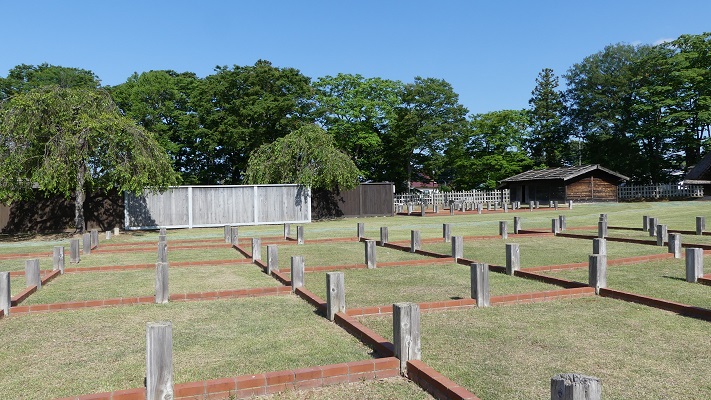
この城には、主殿及び関連する建物が立つ本丸があり、柵と空堀により囲まれていました。「虎口」と呼ばれたその入り口は、橋によりつながれており、非常時には落とされました。主殿は、代替わりなどのときを含め16回建て替えられました。その間、城の領域は、「館」と呼ばれる7つの同様の曲輪により拡張されました。これは中世における典型的な城の作り方の一つでした。
The castle had the main enclosure “Honmaru” with the main palace and related buildings surrounded by fences and dry moats. The entrance called “Koguchi” was accessed by a bridge which would be destroyed in an emergency. The main hall was rebuilt even16 times ,for example, when inheritance. During that time, the castle area was expanded adding seven similar enclosures called “Date”. This is one of typical castle styles in the Middle Ages.

南部氏は、250年以上に渡ってこの城に居続けましたが、戦国時代の終わりに三戸城にいた一族の南部信直が力を持ち、天下人の豊臣秀吉に南部の頭領であると認められました。秀吉は根城の破却を命じましたが、実際には虎口が壊され、堀が埋められた程度でした。その後主殿はしばらく使用されましたが、1627年にはついに廃城になりました。
The Nanbu clan had been staying at the castle for over 250 years, but at the end of the Warring States Period, Nobunao Nanbu, a relative in Sannohe Castle had great influence and was admitted to be the head of the Nanbu clan by the ruler Hideyoshi Toyotomi. Toyotomi ordered Ne Castle to be destroyed, however, it was not done as completely as just the Koguchi was removed and moats were filled. After that, the main hall was used for a while, but it was finally abandoned in 1627.

Features
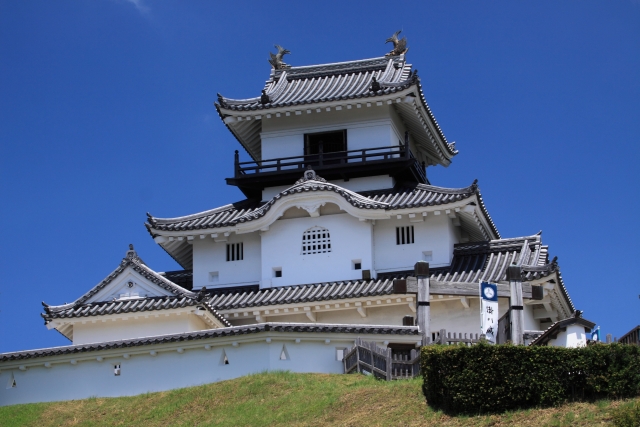
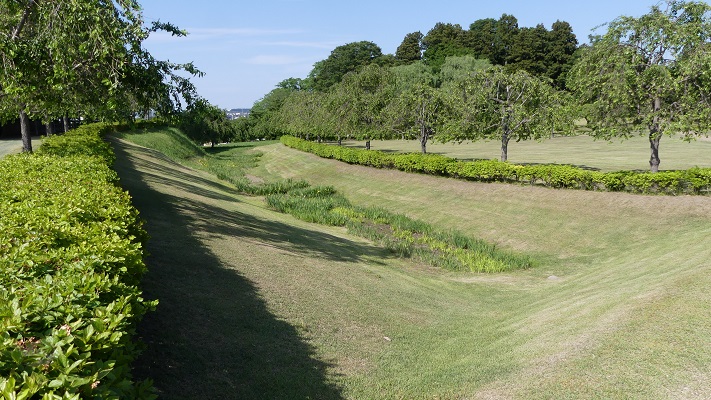
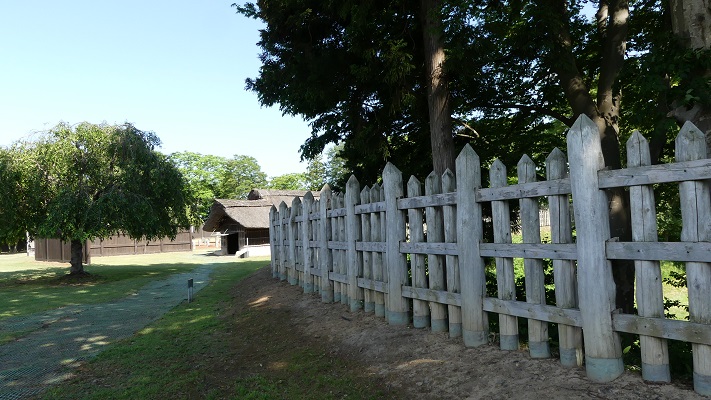
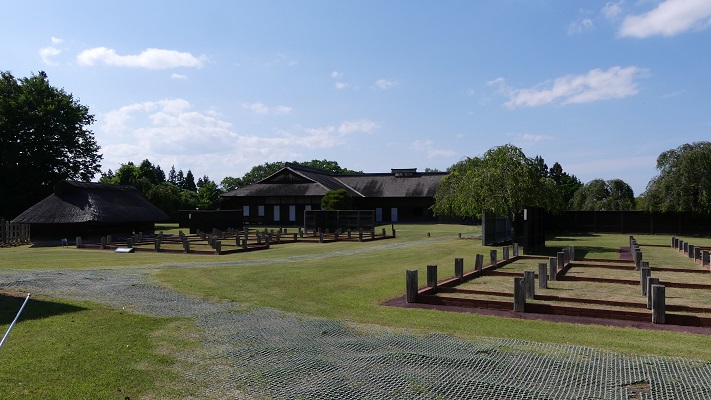
現在、本丸部分はかつてのように復元されています。空堀の上の橋を渡り、虎口を通ってそこに入ります。本丸の内部は木柵により囲まれています。
Now, the Honmaru area is restored to show it was. You can go across the bridge on the dry moat and pass the Koguchi to enter the area. The inside is surrounded by a wood fence.

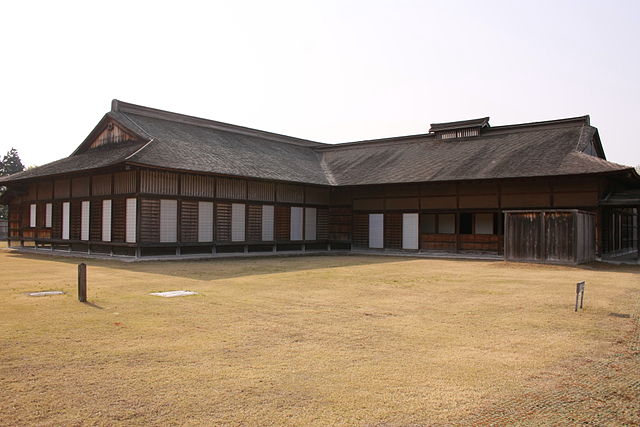
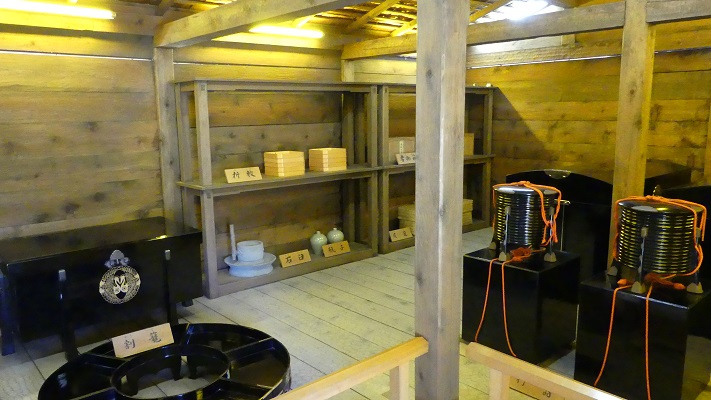
また、復元された本殿に入ることもでき、中では新年の儀式の様子を再現した人形や、城の歴史の説明パネルを見学できます。
You can also see and enter the restored main palace where figures represent a new-year ceremony and panels of its history are shown.

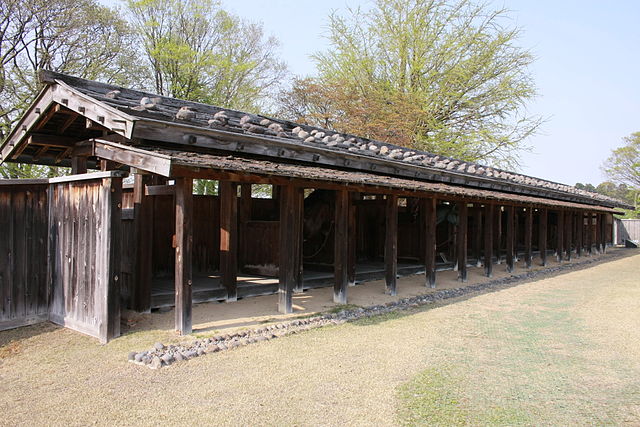
更に関連する建物として、馬小屋、工房、倉庫、鍛冶場などがあります。鎧や什器などがそっくりそのままに作られて置かれています。
There are also restored related buildings such as a stable, workshops, warehouses, and a forge. Many things like armor and utensils are placed inside exactly like the original ones.
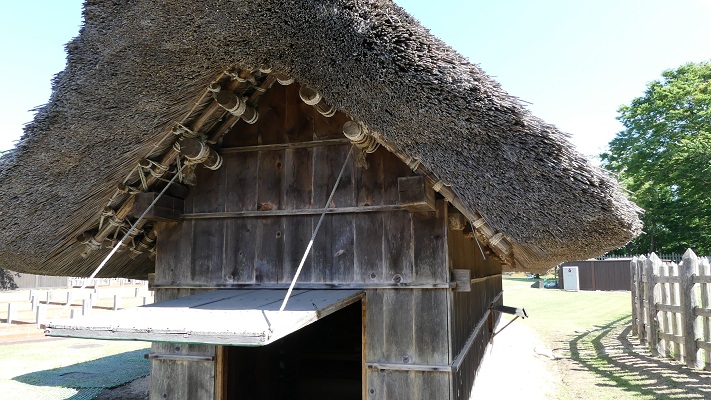
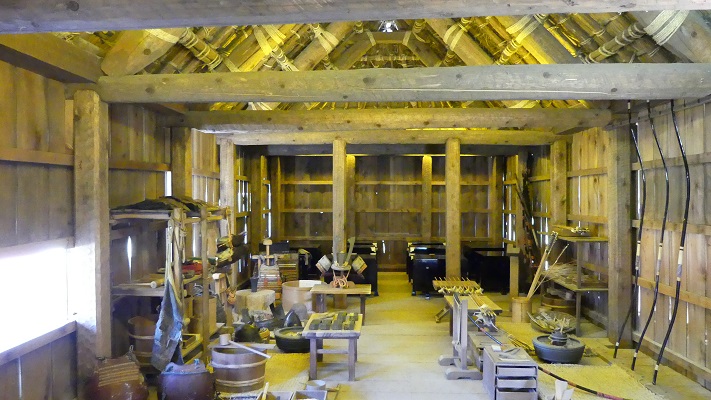



これらの文物を見ていると、中世の世界に入り込んだような気がしてきます。ここにあるものは、1592年に城が廃城となる直前の時代を想定して再現されています。
These items make you feel like you are in the world of the Middle Ages. They are recreated according to the same specifications as the period just before the destruction of the castle in 1592.

Later Life
廃城となった後、根城の辺りは畑か住居として使われたようです。ここは1941年という比較的早い時期に国の史跡に指定されました。第二次世界大戦後、行政側は遺跡が開発され完全に破壊されてしまうことを心配していました。そこで1972年から土地の公有化を進め、1978年に遺跡の環境整備計画を作成しました。そして1989年までに本丸が発掘され、その後どのように遺跡を展示するか考えるにあたり、平面展示ではなく、多くの人に理解してもらえるよう復元することにしました。
After being abandoned, the area of Ne Castle seemed to be used for farming and residences. It was designated as a national historic site, comparatively early in 1941. After World War II, officials were worried about the ruins being developed and completely destroyed. They started to make the land public in1972, make the plan for developing environment of the ruins in 1978, and excavated Honmaru area until 1989. After that, they also thought about how to show the ruins not a flat exhibit, but a restoration to make them understood by many people.
根城の航空写真、一部が住宅化している(The aeriel photo of Ne Castle, Part of it has become residential area)
しかしながら、いくつか問題がありました。最も困難だったのは、建物の詳細です。発掘して出てくるのはほとんどがおびただしい柱の穴でした。研究者は何とかそれを分類し、個々の建物のレイアウトを推定しました。次には、類似の地域や時代の事例から3次元で建物の復元設計を行いました。ついには、1994年にこの再建工事が完成し、「史跡根城の広場」として一般に公開されました。
However, there would be some problems.. The most difficult one was the unclear details of the buildings. The excavation mostly shows plenty of holes for pillars. Researchers somehow managed to sort them and estimate the layout of each building. Next, they tried to design three-dimensional restored buildings from examples in similar regions and periods. Finally, the reconstruction was completed and the site was open to the public in 1994 as “Nejo Castle Site”.

My Impression
八戸市の人たちや行政は、50年近くの長きに渡り根城史跡の整備を行ってきました。これは驚くべき成果であり、心から尊敬します。復元された建物や文物は、伝統的手法で作られており、その維持には特別な修繕や多額の予算が必要です。ここを訪れることもその維持に貢献します。もちろん根城は、訪れるに値しますし、是非中世の雰囲気を味わっていただきたいです。
People and officials in Hachinohe City have been developing the Ne Castle Site for nearly 50 years. This is a significant achievement. I really respect them. The restored buildings and objects are made in the traditional way. Keeping them for a long time requires specific maintenance and much funding. Visiting the site helps keep it as well. Of course Ne Castle is worth visiting to feel the atmosphere of the Middle Ages.

How to get There
車で行く場合:八戸自動車道八戸ICから約10分かかります。
八戸駅からバスで行く場合:バス1番乗り場から南部バスに乗り、根城バス停で降りてください。
東京から八戸駅まで:東北新幹線に乗ってください。
If you want to go there by car: It takes about 10 minutes from the Hachinohe IC on Hachinohe Expressway.
If you want to go there by bus from Hachinohe station: Take the Nanbu bus at the bus terminal plarfoem 1, and take off at the Ne-Jo bus stop.
From Tokyo to Hachinohe st.: Take the Tohoku Shinkansen super express.
Links and References
・VISITはちのへ(VISIT HACHINOHE)
・「日本の遺跡19根城跡/佐々木浩一」同成社(Japanese Book)