立地と歴史~Location and History
岡山市の起源~The origin of Okayama City
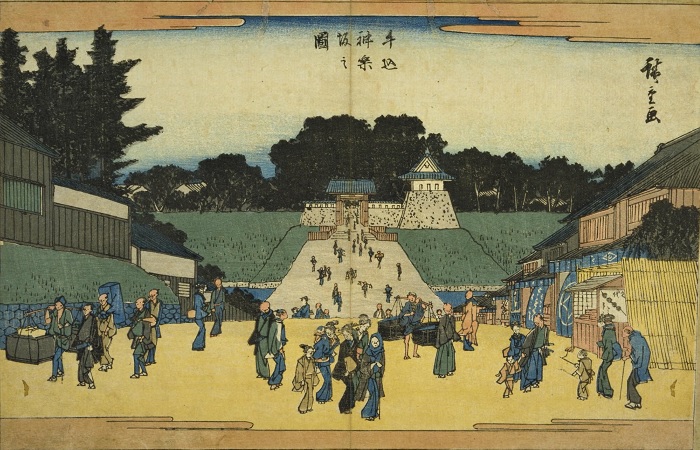
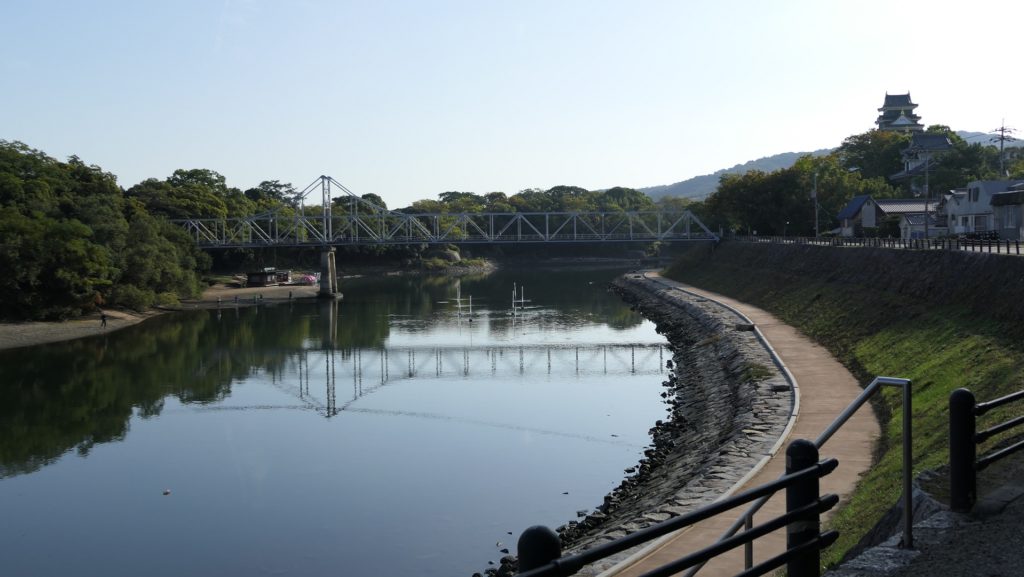
岡山市は中国地方の岡山県の県都です。この市は岡山城を基盤に発展してきました。この城は現在、日本有数の庭園である後楽園と共に旭川に沿った観光地として知られています。しかし実際には多くの市街地がこの城の一部分から派生しているのです。
Okayama City is the capital of Okayama prefecture, Chugoku Region. The city has been developing based around Okayama Castle. The castle is now known for as a tourist spot alongside Asahigawa River with Korakuen, one of the most famous gardens in Japan. Actually, a lot of the city area comes from the part of the castle.

戦国時代、宇喜多氏が最初に旭川のデルタ地帯にあった丘の一つ、石山に城を築きました。宇喜多秀家は石山の東にあったもう一つの丘に城を拡張しました。この丘は岡山と呼ばれており、岡山城と、岡山市という名前両方の起源だったのです。
In the “Sengoku” or Warring States Period, the Ukita clan first built a castle on one of the hills called Ishiyama on the delta of Asahigawa River. Hideie Ukita expanded the castle into another hill in the east of Ishiyama. The hill was called Okayama, the origin of Okayama Castle and the name of the city.


古い形式の天守~Old type Main Tower
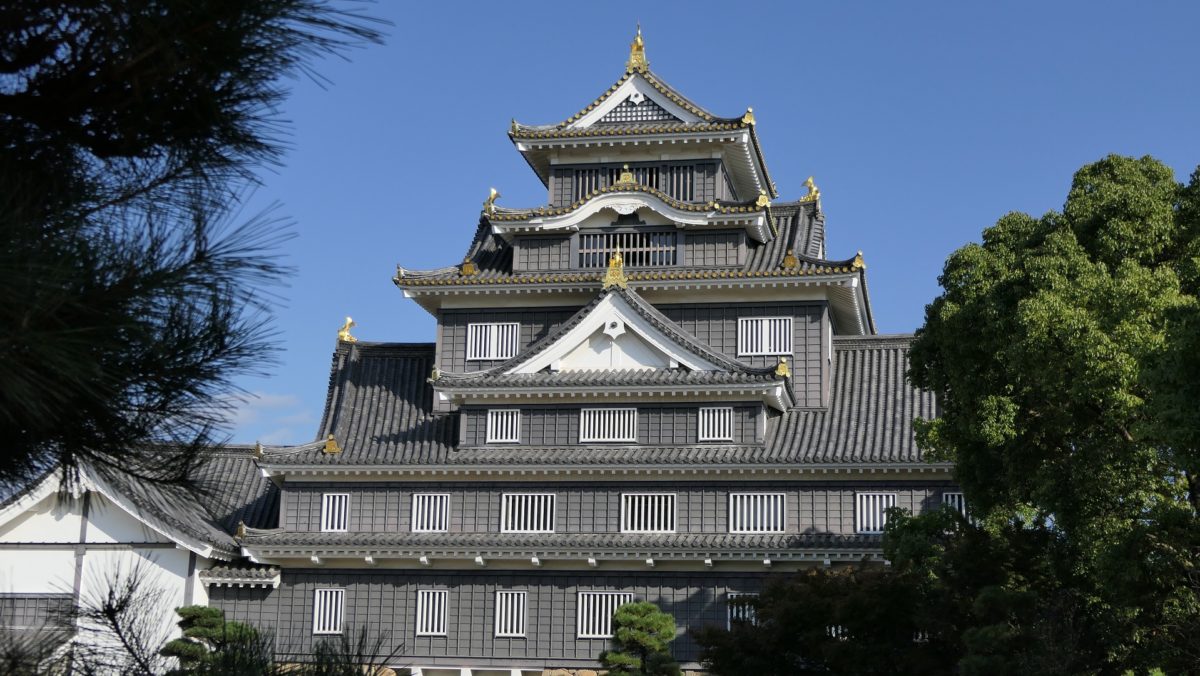
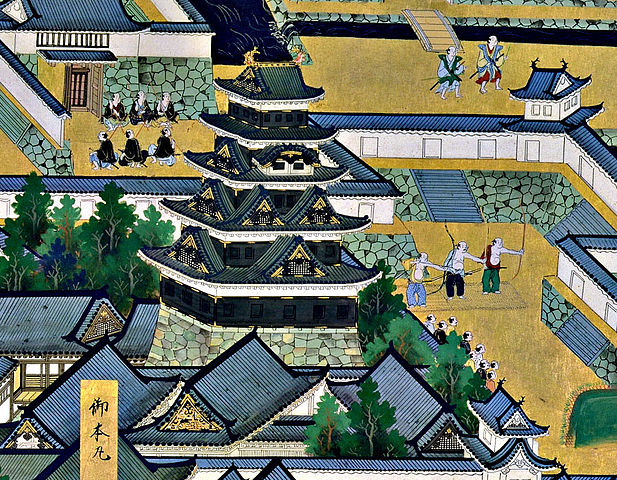
秀家は天下人の豊臣秀吉に気に入られ、五大老の一人になり、大きな天守の建造を許されました。この天守は第二次世界大戦まで残っており、五階建てで、古い型である「望楼型」と呼ばれるものでした。入母屋造りの屋根を持った大きな櫓の上に、小さな望楼がありました。その石垣の基礎とその上の一階は、丘の形に沿って建造されました。これらは最も初期の天守の形式を残していると言われ、日本最初の本格的天守を持った安土城とも比較できるものです。
Hideie who was trusted by the ruler, Hideyoshi Toyotomi, became one of the five chief ministers, and was allowed to build a large Main Tower or “Tenshu”. The Tenshu remained until World War II. It was a five story building in an old style called “boro-gata” or look-out tower style. It had a small look-out tower on a large scale turret with hip-and-gable roofs. Its base stone walls and the first story above were constructed along the shape of the hill. They are said to remain the very first Tenshu style compared with that of Azuchi Castle, the first typical Tenshu in Japan.


岡山城の完成~Completion of Okayama Castle
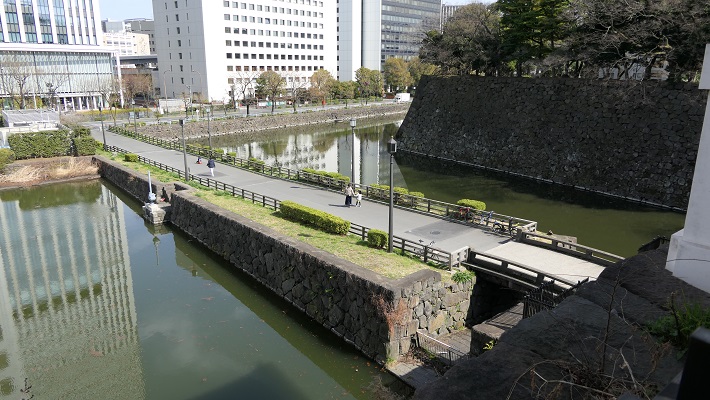
この城の城主は、秀家が1600年の関ヶ原の戦いで敗れた後変わります。江戸時代には、小早川氏、そして池田氏が城と城下町の拡張を続けました。旭川は、自然の障壁として城のデルタ地帯の北から南東へ流れています。結果として城は西の方角へ広がりました。水堀はその方角に向かって五重にも掘られました。
The lords of the castle were changed after Hideie was defeated in the battle of Sekigahara in 1600. The Kobayakawa clan, then the Ikeda clan continued to improv the castle and the castle town in the Edo Period. Asahigawa River flows along the delta of the castle from the north to the southeast being a natural hazard. As a result the castle was expanded into the west direction. They made water moats quintupled towards the direction.
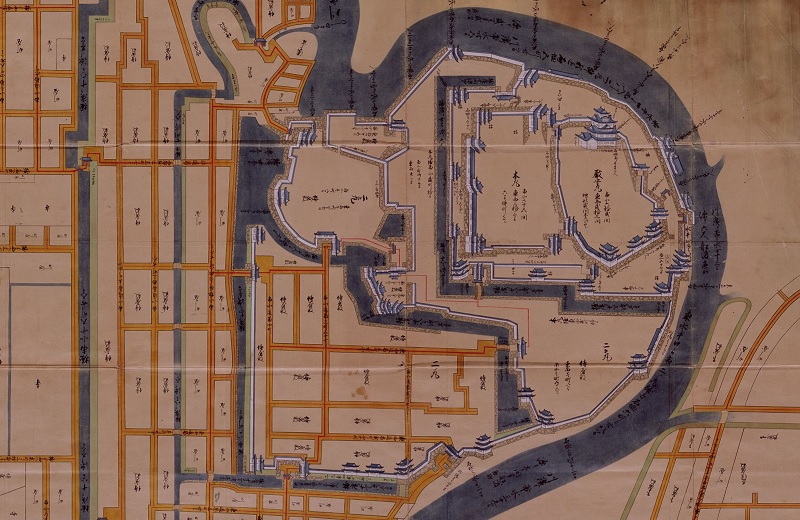
城を守るため、多くの門や櫓も建てられました。1700年、後楽園が川向かいの城とは反対側に作られました。その頃には既に平和な時代になっていたのです。
They also built many turrets and gates to protect the castle. In 1700, Korakuen garden was made in the opposite of the castle across the river. It shows it had already been in peace at that time.

特徴~Features
街中の遺跡~Ruins in City Area
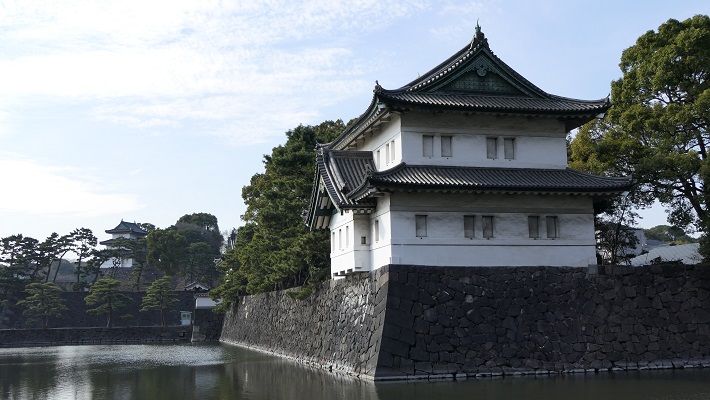
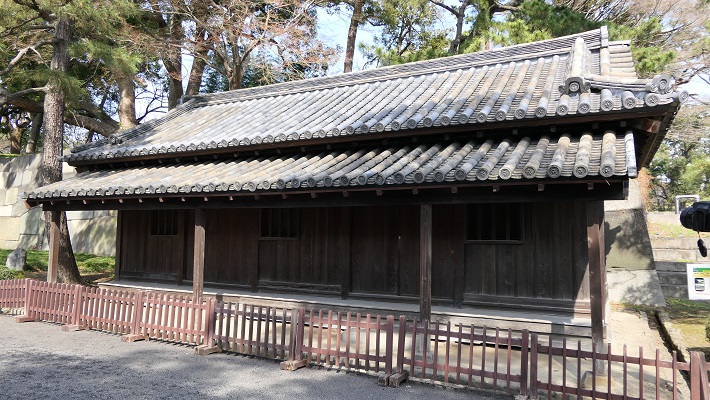
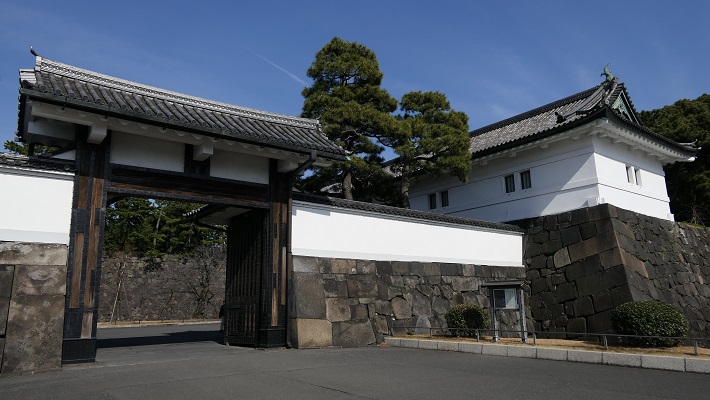
城周辺の航空写真~The aerial photo of around the castle現在、岡山城の中心部である本丸は、烏城(カラスの城という意味)公園として整備されています。この名前は天守が黒く塗られていたことによります。公園は岡山駅から2kmのところにあります。城はかつてはその中間辺りまで広がっていました。そのため、公園の外にもいくつか城の遺跡があります。例えば、以前は西の丸で現在の市街地に残っている西手櫓です。この櫓は重要文化財に指定されています。でもビルに囲まれてさみしそうに見えます。
Now, the center of Okayama Castle, Honmaru enclosure has been developed as Ujo Park (Ujo means Crow Castle). The name comes from the Tenshu being painted black. The park is about 2 km from Okayama Station. The castle once spread to half of the way in the past, so there are some ruins of the castle outside the park. For example, Nishite Turret on the former Nishinomaru enclosure remains in the city area. It is designated as an Important Cultural
Property, but it looks lonely among modern buildings.

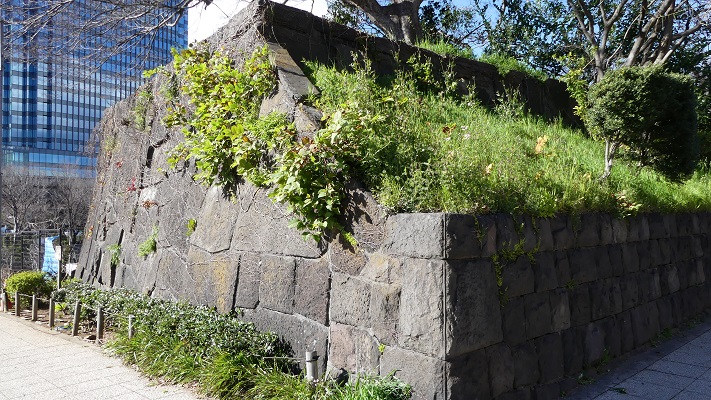
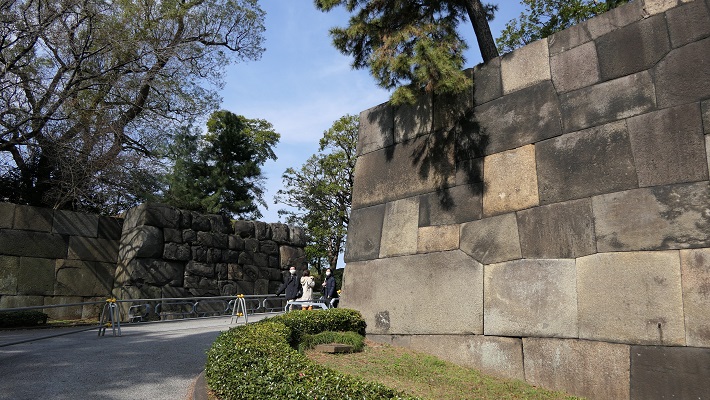
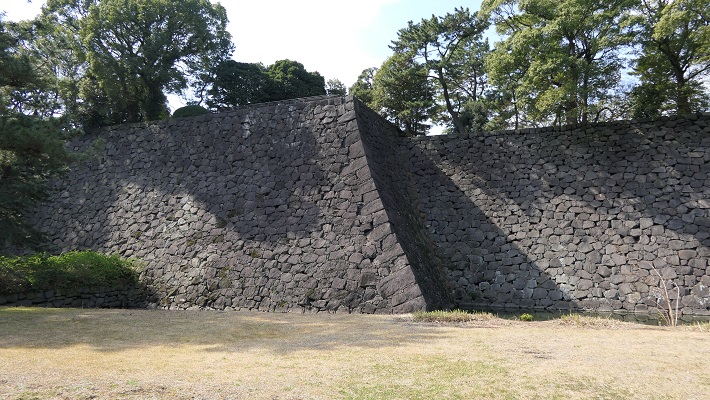
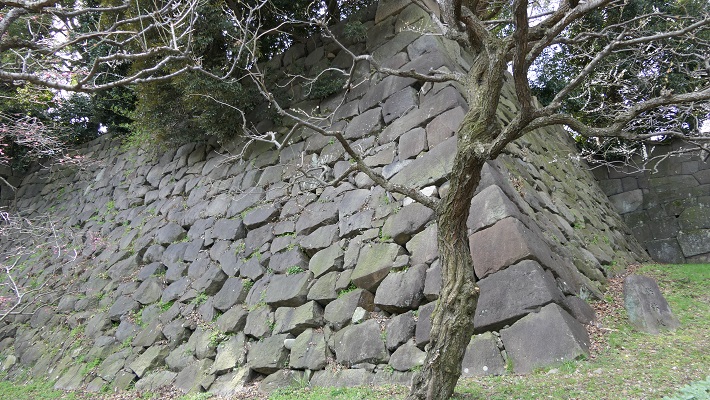
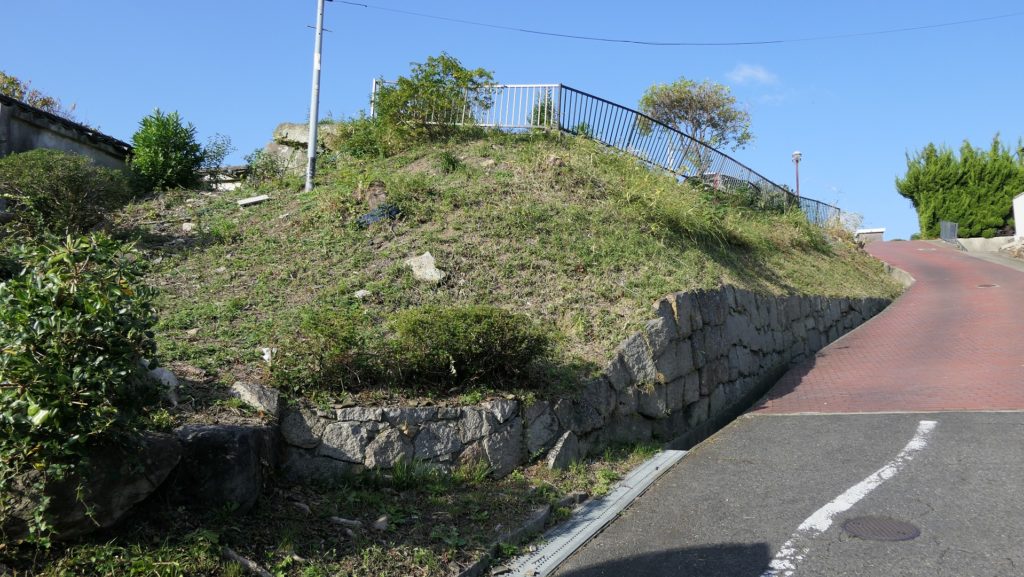
石山曲輪跡は公園の近くにあります。ここは城の最初の中心地でした。現在は駐車場として使われています。曲輪を覆う石垣は江戸時代に作られたようです。
The ruins of Ishiyama enclosure is near the park. It was the first center of the castle, and is now used as a parking lot. The stone walls covering the enclosure seem to be built in the Edo Period.

本丸の遺跡~Ruins in Honmaru
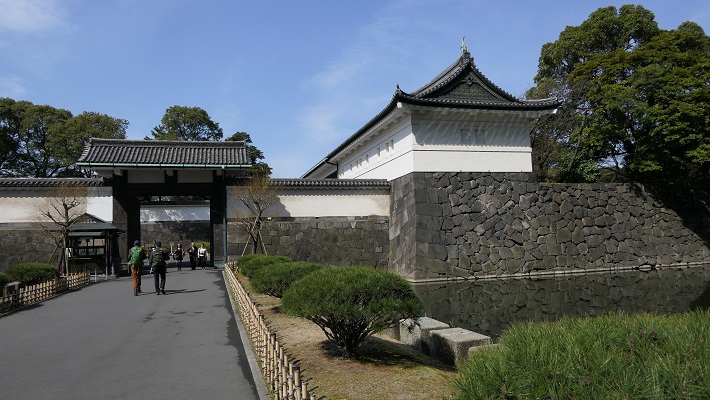
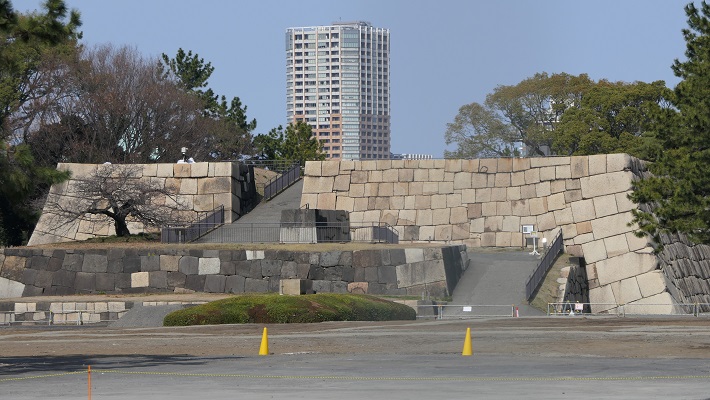
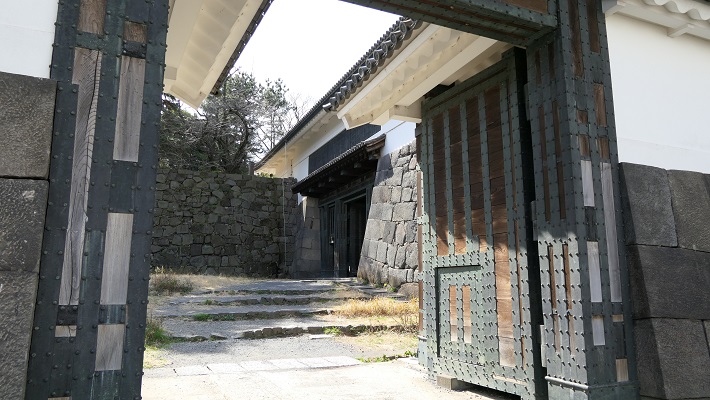
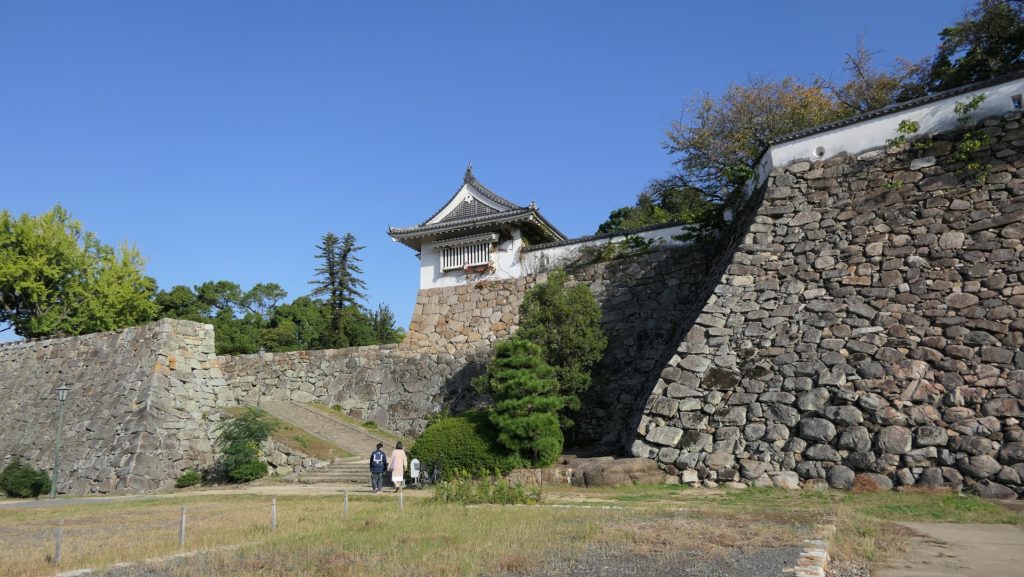
本丸周辺の航空写真~The aerial photo of around Honmaru以前の本丸であった公園には二つの入口があります。その一つは内堀の上の目安橋を渡っていくルートです。これは本丸に至る大手道でした。もう一つは川沿いにある廊下門を通るもので、本丸の裏門に当たります。ここからは川にたたずむ城の姿が望めます。
The park, the former Honmaru, has two entrances. One of them is the route crossing Meyasu-bashi Bridge over the inner moat. It was the Main Route or “Ote-Michi” to Honmaru. The other is going through Roka-mon Gate beside the river, the back gate of Honmaru. You can have a good view of the castle with the river.


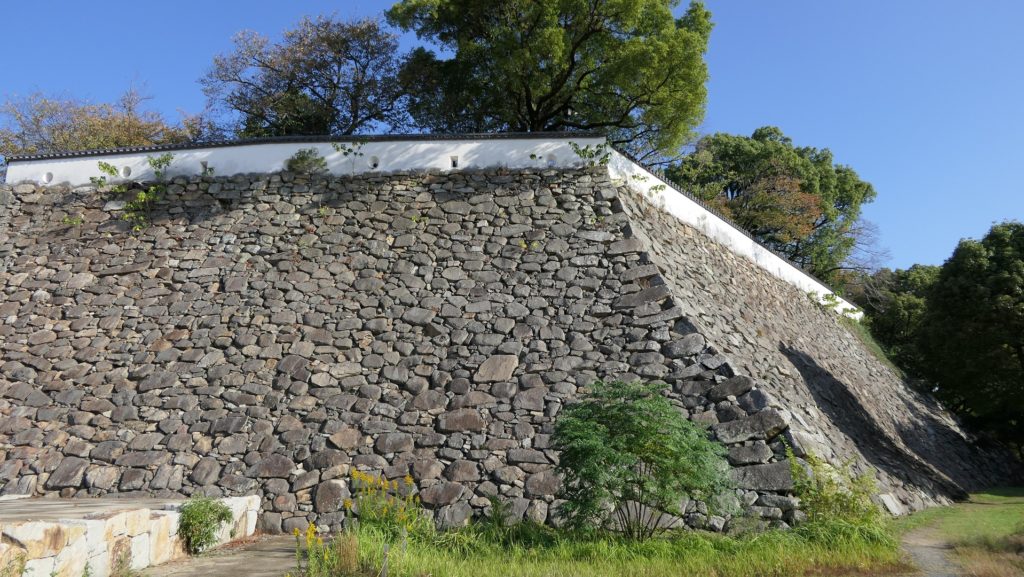
本丸は三段に分かれています。低い段は「下の段」と呼ばれ、門の周辺を指します。真ん中の段は「表向」と呼ばれ、居住や統治のための御殿がありました。ここには重要文化財である月見櫓が残っています。この櫓は、本末の外側からも素晴らしい石垣とともに鑑賞できます。上の段は、「本段」と呼ばれ、最も古い箇所です。不明門がその入り口にあります。ここには創建以来の天守と、藩主の御殿がありました。
Honmaru has three levels of the ground. The lower level called Genodan is the area around the gates. The middle level called Omotemuki is where the hall for official residence and governance was. Tsukimi Turret remains there as an Important Cultural Property. It can also be seen with excellent stone walls from outside Honnmaru. The upper level called Hondan is the oldest part. Akazuno-mon Gate is its entrance. It had the original Tenshu and the main hall for a lord.
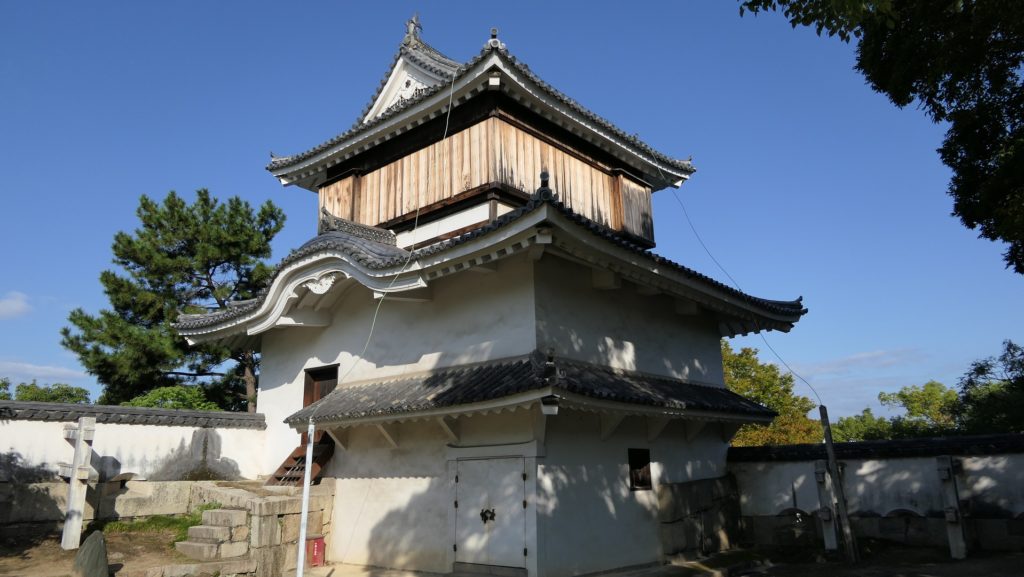
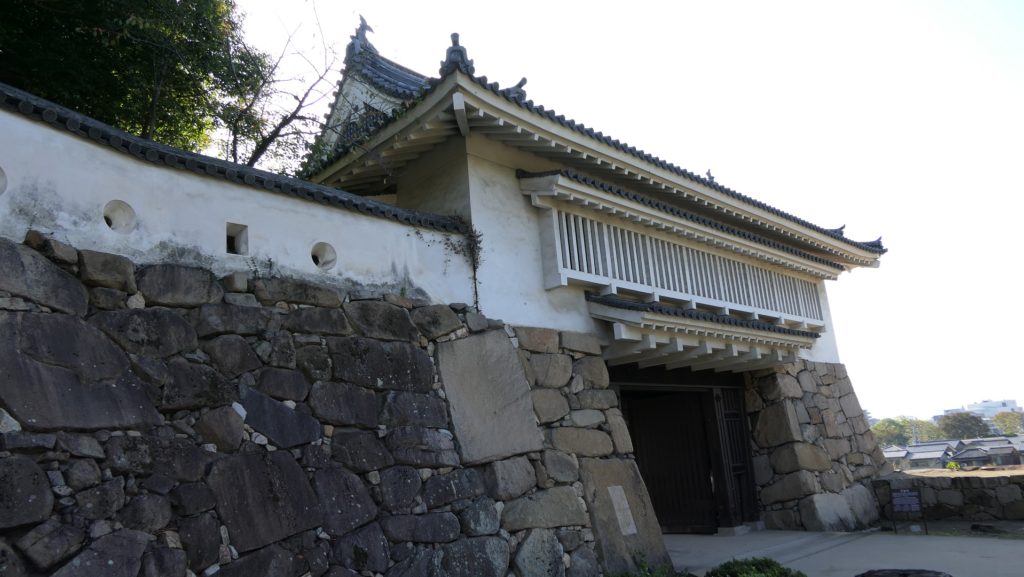






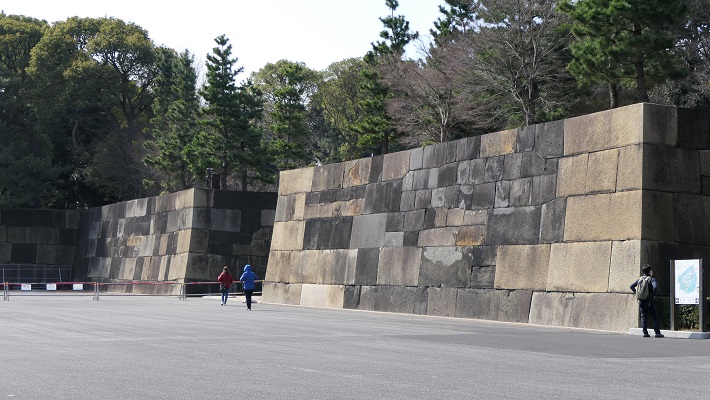
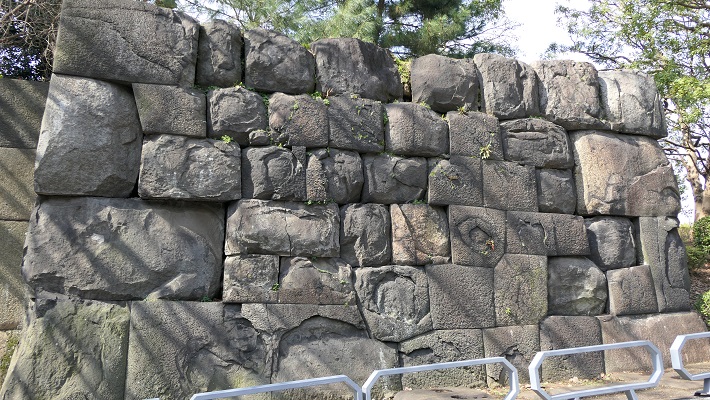
現在の天守は、外観復元され、博物館として使われています。本段を囲む石垣は元々秀家により築かれました。とても古風に見えます。
The present Tenshu has been apparently restored and used as a museum. The stone walls surrounding Hondan were originally built by Hideie. They look very old.


その後~Later History
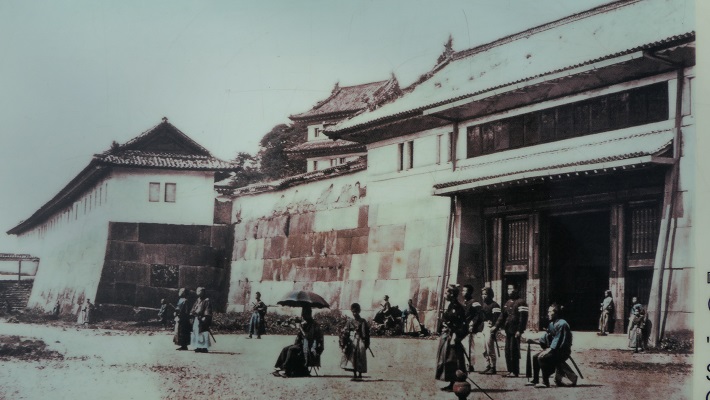
明治維新後、岡山城は廃城となり、ほとんどの建物は撤去されました。本丸であった場所は学校の敷地として使われました。他の場所は市街地に変わっていき、堀は埋められました。元からあった天守は国宝として残りました。しかしながら、残念なことに1945年の岡山空襲で焼け落ちてしまいました。第二次世界大戦後、本丸は烏城公園として整備されました。1966年に天守は外観復元されまます。廊下門と不明門の2つの門も同時に外観復元されました。
After the Meiji Restoration, Okayama Castle was abandoned and almost all of its buildings were demolished. The Honmaru area was used as the ground for a school. The other areas of the castle were turned into the city area with their water moats being filled. The original Tenshu remained as a National Treasure. However, it was unfortunately burned down by the Okayama Air Raid in 1945. After World War II, the Honmaru area was been developed as Ujo Park. Tenshu was apparently restored in 1966. The two gates, Roka-mon and Akazuno-mon , were also restored apparently at the same time.

私の感想~My Impression
今は烏城公園と名付けられた岡山城に是非行っていただきたいです。後楽園と一緒に見学すればとてもよい思い出になります。願わくば、元の天守を見て、中に入ってみたかったです。あと、岡山市にはもっと市民に、岡山城が市の起源であることを知らせてもらいたいです。例えば、現存して街中に残る西手櫓はもっと知られるべきと思います。
Okayama Castle which is now named Ujo Park is a good place to visit. You can have great views and experience together with Korakuen Garden. I wish I could see and enter the original Tenshu. I also hope that officials will let people know the castle is the origin of Okayama City. For example, the remaining Nishite Turret among the city area should be known more to people.

ここに行くには~How to get There
車で行く場合:山陽自動車道の岡山ICから約20分かかります。公園に駐車場があります。
岡山駅から行く場合:駅の東口の岡山駅前電停から路面電車に乗って、城下電停で降りてください。岡山駅から歩いた場合、約20~30分かかります。
If you want to go there by car: It takes about 20 minutes from the Okayama IC on the Sanyo Expressway. The park offers a parking lot.
From Okayama Station: Take the tram from the Okayama-ekimae stop in front of the east exit of the station, and get off at the Joka stop. Or It takes about 20 to 30 minutes on foot from the station.
リンク、参考情報~Links and References
・岡山城-川面に映える漆黒の城~Okayama Castle
・岡山城-川面に映える金烏城(Okayama City Museum)
・「よみがえる日本の城5」学研(Japanese Book)