立地と歴史~Location and History
六角氏は近江国(現在の滋賀県)の南部を中世の長期間に渡って支配してきました。六角氏は最初繖山の麓に住んでいました。1467年の応仁の乱後、戦が日常的になり、戦国時代となりました。この状況に対処するため、家臣とともに丸ごと山の上に引っ越すことにしました。これが観音寺城の始まりです。
The Rokkaku clan governed the area in the south part of Omi Province (now called Shiga Pref.) for a long time in the Middle Ages. They at first lived on foot of Mt.Kinugasa. After the Onin War in 1467, battles became usual. This was known as the Warring States Period. The way to deal with such a situation for them was to move to the mountain top with their retainers in their entirety. It was the origin of Kannnoji Castle.

六角は、城の領域を分割し、それぞれの家臣に割り当てました。その場所の名前は「平井丸」「池田丸」「淡路丸」といった氏族の名前を使っていました。約100年間で、城は山を覆って広がり、曲輪は石垣に囲まれていました。
Rokkaku divided the castle area and assigned an enclosure to each retainer, which was named using their name like “Hirai-Maru”, “Ikeda-Maru” and “Awaji-Maru”. For about 100 years, the castle grew over the whole mountain, with enclosures surrounded by stone walls.
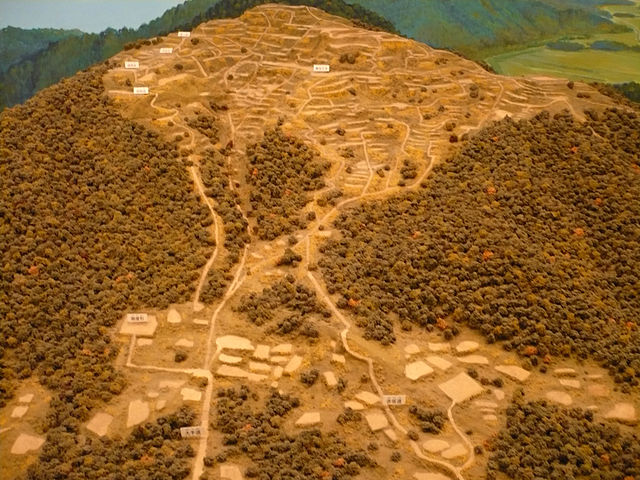

全盛期には、城には1000以上の曲輪があり、1532年には六角氏の頭領、六角定頼は、京都から逃れてきた将軍、足利義晴を受け入れました。義晴は、城中の桑実寺に臨時幕府を設立し、3年間滞在しました。
At its peak, the castle had over 1,000 enclosures. In 1532, the head of the clan, Sadayori Rokkaku accommodated the Shogun, Yoshiharu Ashikaga who escaped from Kyoto. Yoshiharu established the temporary government at Kuwanomi-Tera Temple in the castle and stayed there for three years.
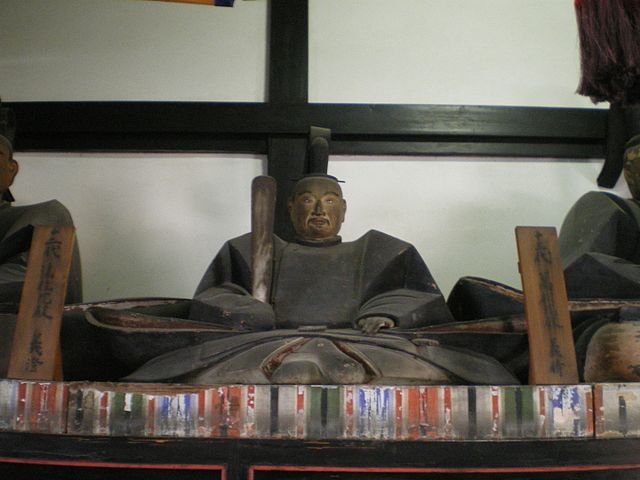

定頼は、将軍に豪華な館を提供しました。彼はまた、本丸に客人をもてなすため二階建ての会所を作りました。ところが、城はその見かけほどは強くはありませんでした。重臣たちには独立の風があり、主君に対して反抗する可能性がありました。彼らの館は戦いのためというより、居住のためでした。つまるところ、この城は長い籠城戦には向いていなかったようです。
Sadayori prepared luxury palaces for the Shogun. He also built a two-story meeting club to host visitors at his Honmaru enclosure. However, the castle was not so strong compared to its appearance. The senior vassals were likely independent, possibly be against their master. Their halls were built for living rather than for battle. Overall, the castle might have not been suitable for a long siege.
結果的に、六角はよく奇妙な戦術を行いました。戦いが起き、大軍が観音寺城に迫ったとします。六角は前もって城から逃亡します。敵は簡単に城を占領できます。それから六角は、周りの支城とともにゲリラ戦を開始しました。当然観音寺城の弱点は知り尽くしており、勘どころを得て反撃できたのです。最後には城を奪回できるという訳です。
As a result, Rokkaku often took a little strange tactic. When a battle happened, if large troops attached Kannonji Castle. They escaped from the castle in advance. That made the enemy capture the castle easily. Then, Rokkaku started a guerrilla fighting with their branch castles around. They knew the weak points of Kannnonji Castle, could attack their enemy efficiently, and finally got the castle back.
1568年、織田信長が京都に上洛しようとしたとき、六角氏に協力を要請しました。六角は断り、織田と戦いました。織田が六角の支城、箕作城を占領すると、六角は観音寺城から逃れました。これが従来のやり方だったのでしょうが、再び戻ることはできませんでした。全ての支城が織田に降伏し、ほとんどの家臣は織田に臣従しました。六角にはもう成す術がありませんでした。織田はしばらく観音寺城を使ったようですが、程なく廃城となりました。
In 1568, when Nobunaga Oda tried to come to Kyoto, he asked Rokkaku for cooperation. Rokkaku refused and fought with Oda. As soon as Oda quickly took Rokkaku’s branch Mitsukuri Castle, Rokkaku escaped from Kannnoji Castle. This might be their traditional way, but they couldn’t return again. As all the branch castles surrendered to Oda, and most of former Rokkaku retainers served to Oda. There would be nothing to do for Rokkaku. Oda seemed to use Kannouji Castle for a while, before abandoning it.

特徴~Features
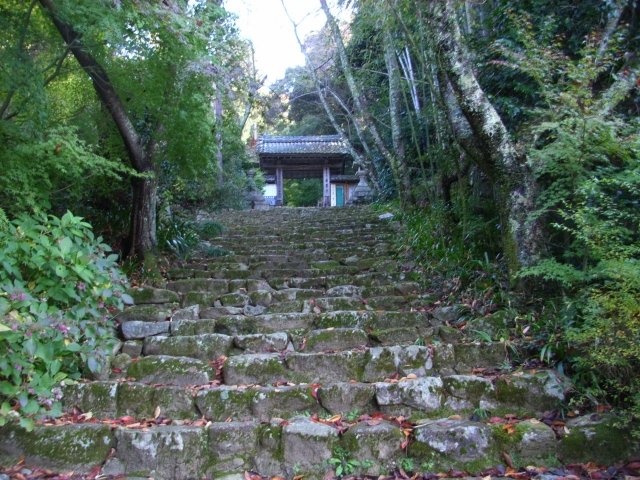
城周辺の航空写真~The aerial photo around the castle城跡に登っていくにはいくつかルートがあります。2つの主なルートのうち、一つは観音正寺を通るものです。この寺は城よりも古くからあり、六角氏から保護を受けていました。寺の下の方で、観音寺山林道有料道路の終点にある駐車場に車を止め、約15分程歩けば城跡の中心に着きます。
There are several routes for climbing up to the castle ruins. One of the two major ones is through Kannonshoji Temple. The temple is older than the castle, and was supported by Rokkaku. You can park at the end of Kannnonji-Sanrindo Tollway under the temple, walk to the center of the ruins in about 15 minutes.
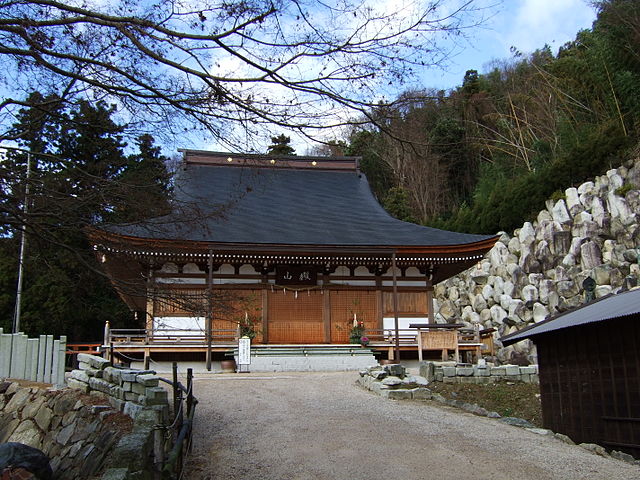
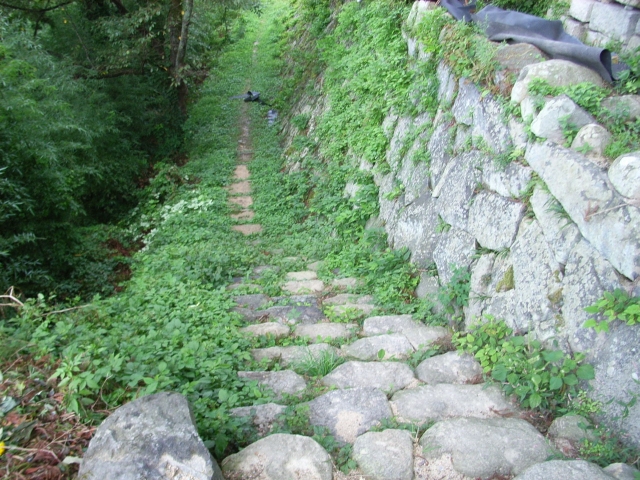


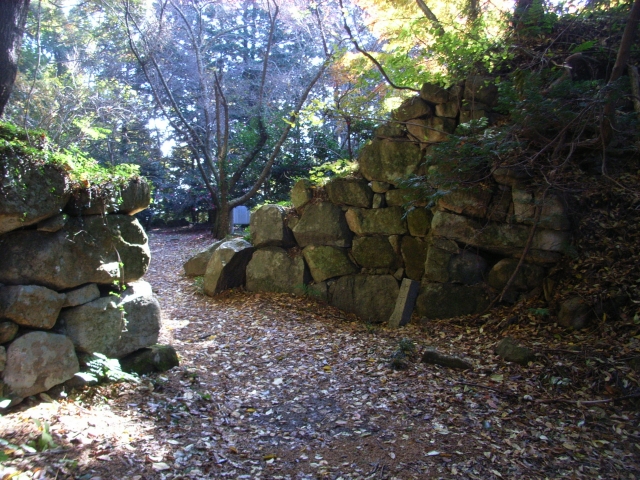
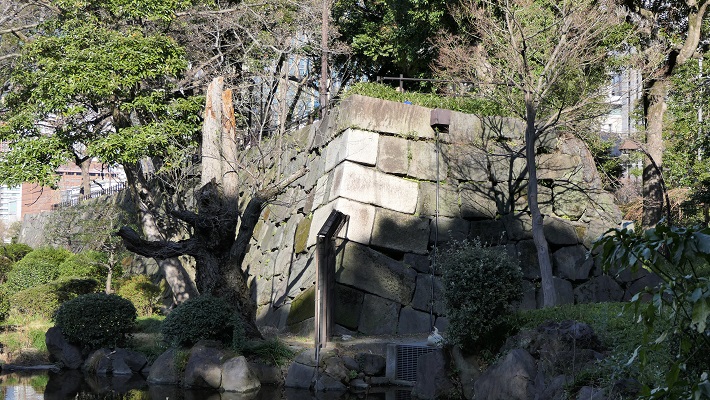
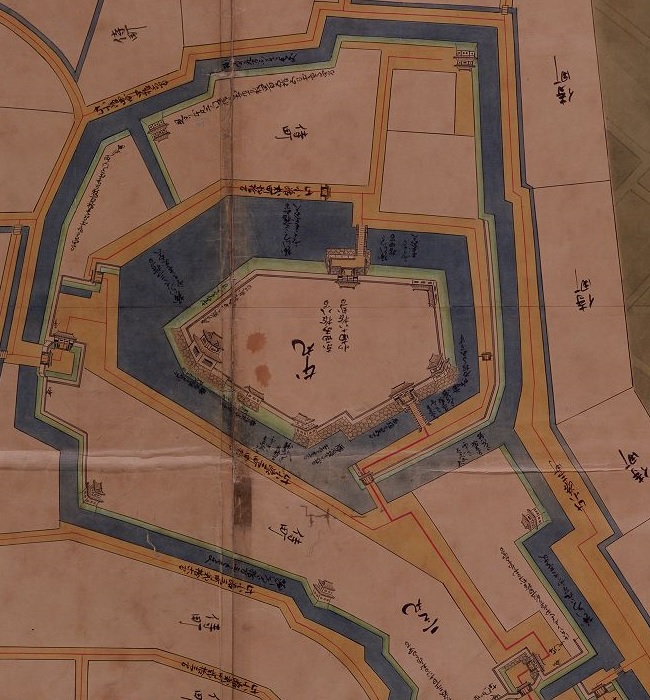
頂上周辺には、本丸、池田丸、平井丸の跡地があります。3つとも広々としていて、周りには石垣があります。石垣は自然石を積み上げるやり方で「野面積み」と呼ばれます。これは本格的に城に対して石垣が使われた最も早い事例の一つです。歴史家はまた、主君と家臣の曲輪の大きさが似ていることが彼らのパワーバランスを表していると言います。主君の力が比較的小さいということが言えるでしょう。
There are the ruins of Honmaru, Ikeda-Maru and Hirai-Maru around the top area. All three are spacious and have large stone walls around. The walls are piled with natural stones called “Nozura-Zumi”. It is one of the earliest examples of stone walls being used in earnest for castles. Historians also say the similar size of enclosures among the lord’s Honmaru and the retainer’s others shows their power balance. The power of the lord might have been relatively weak.
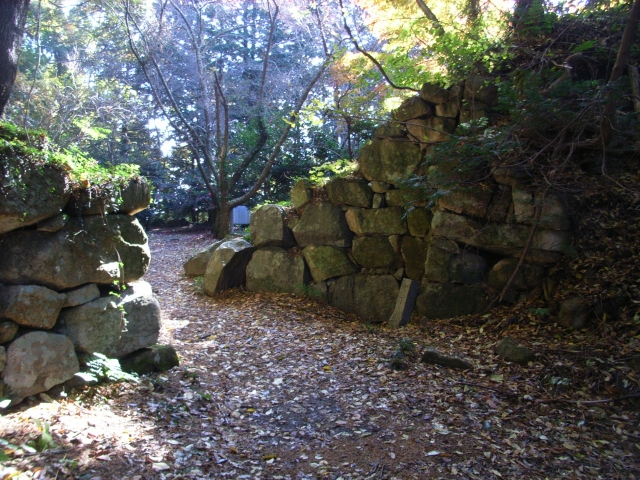
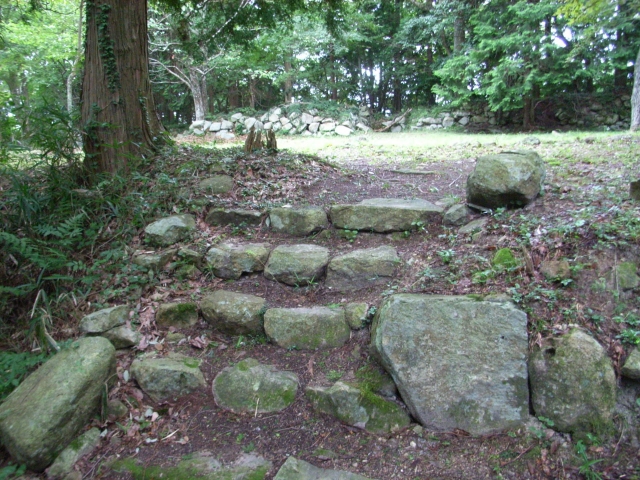
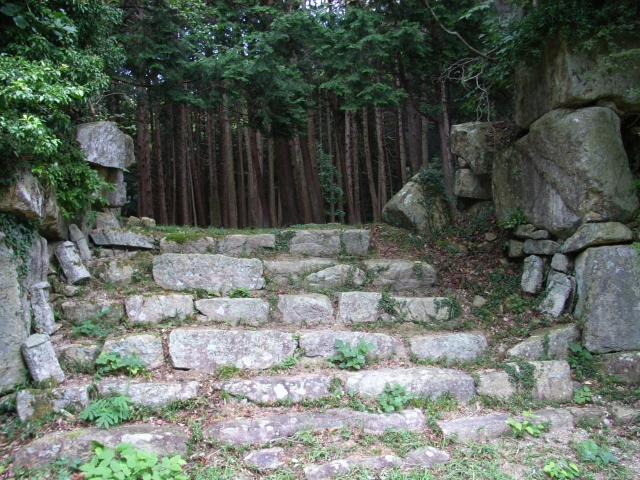



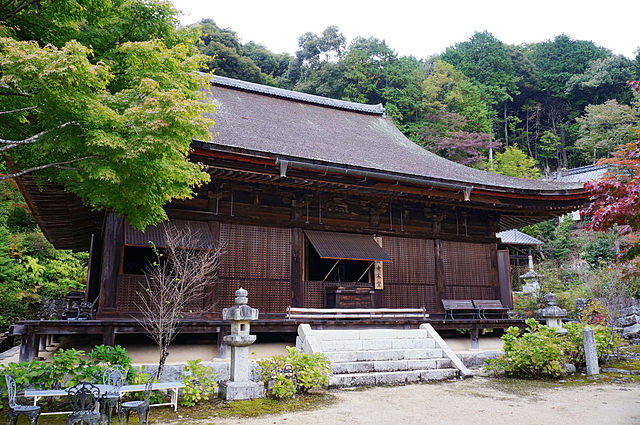
もう一つの主要ルートは桑実寺を通るものです。安土城考古博物館に車を止め、そこから北西の方角にある山道の入り口に歩きます。そして寺に向かう美しい階段を上がっていきます。寺には700年近く前に建てられ現存している本堂があり、国の重要文化財に指定されています。山道は更に川の谷に沿って進みます。曲輪跡から崩れ落ちた多くの巨石も見ることができるでしょう。合わせて30分から1時間ほどの歩きで山上に着きます。
The other of the major routes is through Kuwanomi-Tera Temple. You can first park at Azuchi Archeological Museum, then walk to the start point of the trail in the northeast direction. Climb up beautiful stairways to the temple. It has the remaining Mail Hall built nearly 700 years ago and designated as a National Important Property. The trail goes up further along the river valley. You can also see a lot of abandoned huge stones that are from the ruins of enclosures. You will reach the top after 30 minutes to 1 hour walk in total.


その後~Later Life
観音正寺と桑実寺は別として、城跡の一部は他の寺にも使われていたようです。城跡は、1982年に国の史跡に指定されました。
Beside Kannnonshoji and Kuwanomi-Tea temples, part of the ruins seemed to be used for other temples. The castle ruins were designated as a National Historic Site in 1982.

私の感想~My Impression
この城跡の多くは謎のままです。詳細の研究はまだ始まったばかりです。地元の人々もまた城跡を調査しています。それを受けて、行政は少しずつ史跡を整備してきています。近いうちにまた新しい体験ができればと思います。
The ruins of the castle have a lot of mysteries. The study of their details is still very new. Some local people also try to explore the ruins. In response, officials have been developing the ruins little by little. I’m looking foward to having a new experience in the near future.

ここに行くには~How to get There
車で行く場合は、名神自動車道の八日市ICか竜王ICから約30分かかります。観音寺山林道有料道路は8:30~16:30の間しか開いていませんので気を付けて下さい。
電車の場合は、レンタル自転車を使うことをお勧めします。JR安土駅から城跡まで約3キロあるからです。駅前に2件のレンタル店があります。そこに荷物を預けることもできます。
東京から安土駅まで:東海道新幹線で米原駅まで行き、JR琵琶湖線に乗り換えてください。
大阪から安土駅まで:大阪か新大阪駅からJR京都線に乗ってください。
この情報はほとんど安土城と一緒なので、両方の城をセットで巡ってみてはいかがでしょう。
If you want to go there by car, it takes about 30 minutes from the Yokaichi IC or the Ryuo IC on Meishin Expressway. Please make sure that Kannnonji-Sanrindo Tollway is only open between 8:30 and 16:30.
When using train, I recommend you to use a rental bicycle, because the ruins and about 3km from JR Azuchi Station. There are two rental bicycle shops in front of the station. You can also leave your baggage there.
From Tokyo to Azuchi st.:
Take the Tokaido Shinkansen superexpress to Maibara station, and transfer for JR Biwako line.
From Osaka to Azuchi st.:
Take the train on JR Kyoto line from Osaka or Shin-Osaka station.
This information is almost the same as Azuchi Castle. How about visiting the set of both castles.
リンク、参考情報~Links and References
・観音寺城跡(滋賀県観光情報)(Only Japanese?)
・あづち周遊(Only Japanese)
・観音寺城|散策の備忘録(Only Japanese)
・「六角定頼/村井祐樹著」ミネルヴァ書房(Japanese Book)
・「幻の観音寺城/南條範夫著」文春文庫(Japanese Book)
・「石垣の名城完全ガイド/千田嘉博著」講談社(Japanese Book)