Introduction
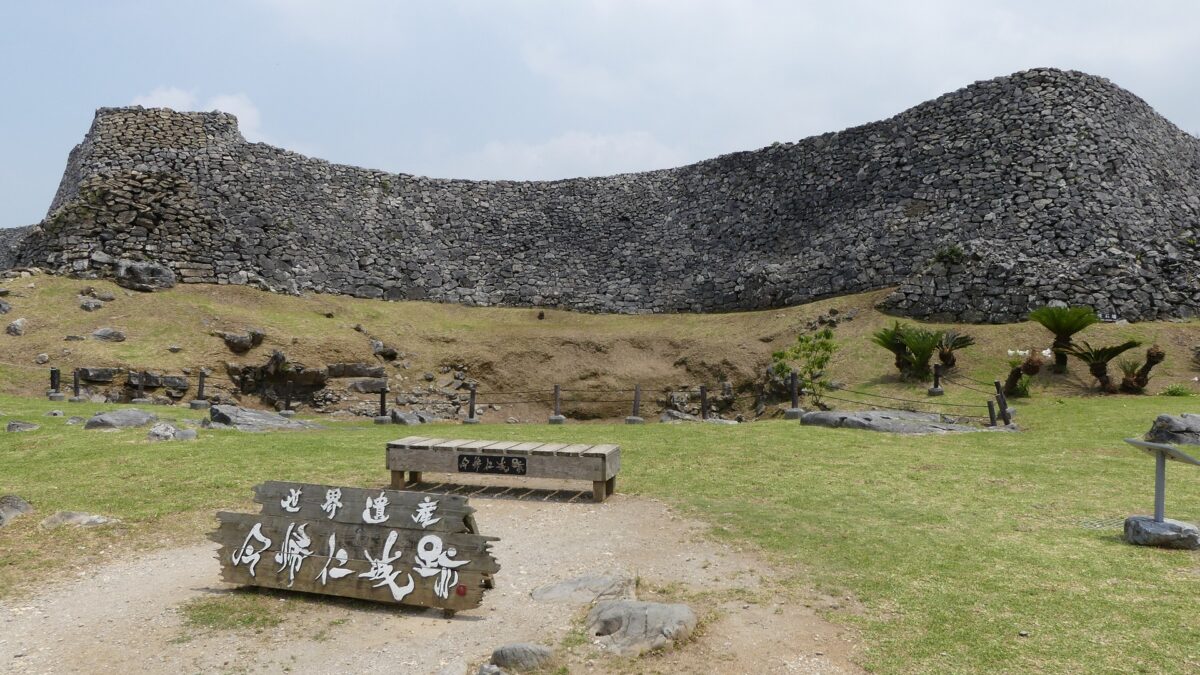
今回からまた沖縄シリーズの始まりです。最大級のグスクの一つ、今帰仁城(なきじんじょう)をご紹介します。以前、琉球王国につながる浦添城や、琉球統一を果たした尚巴志のことをご紹介しましたが、今帰仁城は、そのころ並び立っていた北山王国の本拠地だったのです。北山王国は、浦添城の中山王国や、南山王国とともに、貿易によって栄えたのですが、尚巴志によって滅ぼされてしまったために、その歴史ははっきりとはわからないのです。今回は、今帰仁城について、定説とされるもの以外にも、情報を集めましたので、その歴史ストーリーを考えてみたいと思います。

今回の内容を趣向を変えて、Youtube にも投稿しています。よろしかったらご覧ください。
立地と歴史
三山時代と北山王国
グスクが築かれる前、沖縄の多くの人たちは、漁労・狩猟・採集を中心とした生活を送っていたと考えられています。沖縄の時代区分では「貝塚時代」と呼ばれています。日本本土では、この地域から輸入した貝製品や、貝を加工した螺鈿細工が重宝されました。

11世紀ころからは、貿易の恩恵が沖縄全体に及んできました。中国との貿易もさかんになり、高価な中国製陶磁器が輸入される一方、沖縄からは夜光貝や硫黄が輸出されました。その結果「按司(あじ」)」と呼ばれるたくさんの有力領主たちが現れ、グスクを築きます。琉球王国が成立するまでの時代は「グスク時代」と呼ばれています。
14世紀になると、沖縄本島では有力な按司のもと、3つの王国が成立しました。今帰仁城を本拠地とした北山王国、浦添城の中山王国、島添大里城の南山王国です。王国の本拠地になった大型グスクの建設も、その動きに沿ったものと考えられます。
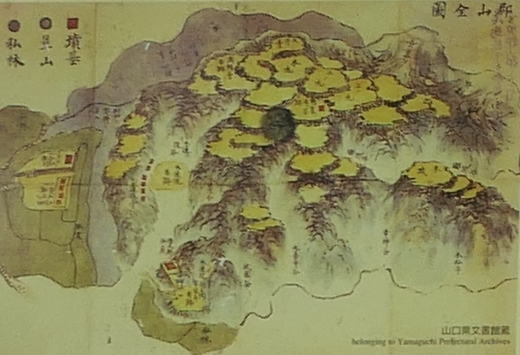
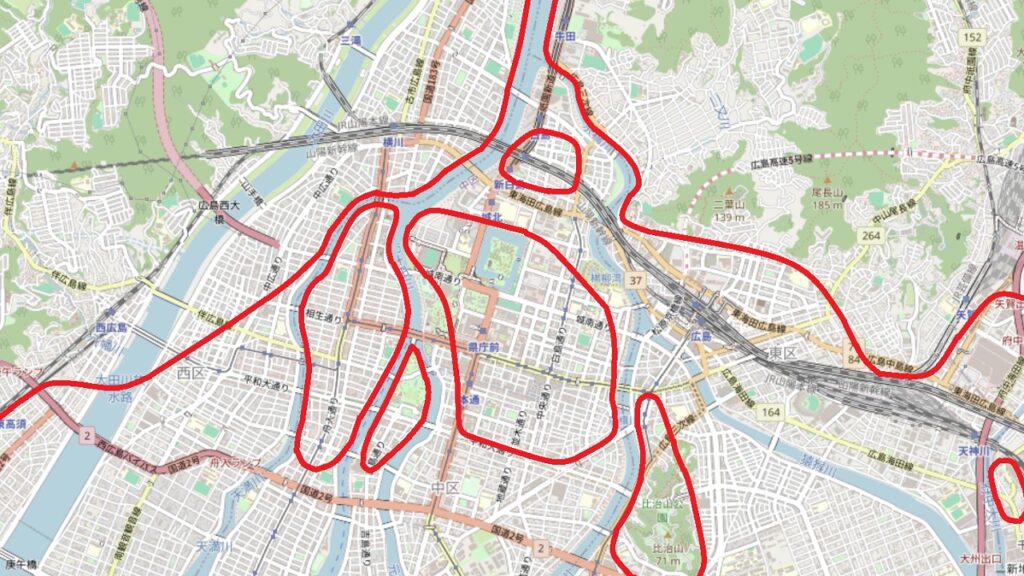
グスクの位置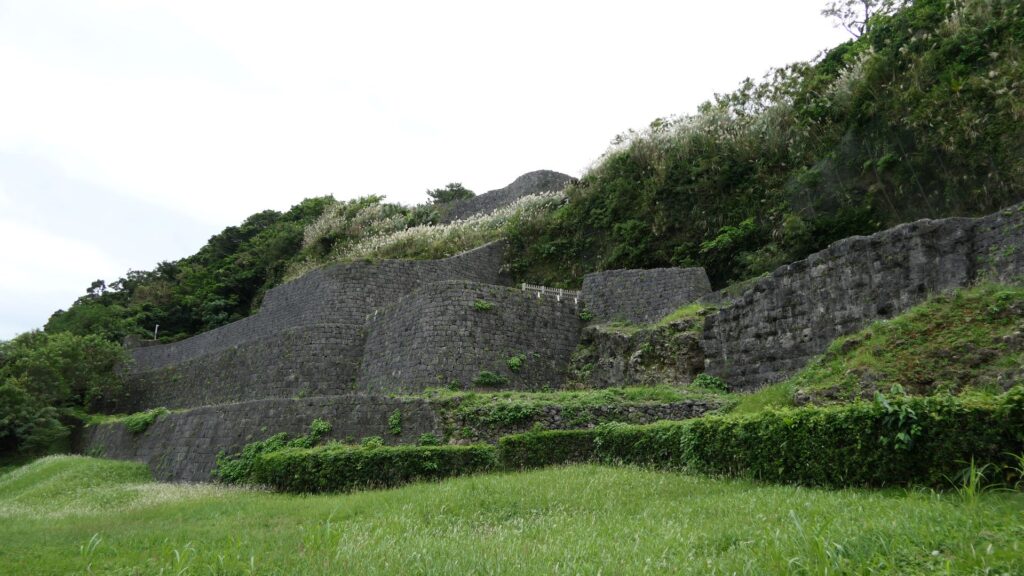

同じ頃、中国では明が建国されました。創立者の洪武帝は、反対勢力や倭寇を取り締まるために「海禁」政策(私的な海外貿易や海外渡航の禁止)を実行しました。また、漢民族が再建した王朝の正当性(以前の「元」は異民族国家)を示すため、日本を含む周りの国々に、宗主国(明)への朝貢を求めたのです(招撫使)。1372年には中山王国に使節が送られました。当時の王、察度は直ちにその弟を進貢使として明に派遣しています。続いて、南山王や北山王も明への朝貢を始めました。この時代はグスク時代の中でも、特に「三山時代」と呼ばれています。

ここから北山王国と今帰仁城を、外部の記録から追ってみます。中国の史書(「明実録」)によると、北山王は1383年から1415年の間に、19回明と交易を行っています。その間の王は、怕尼芝(はにじ)、珉(みん)、攀安知(はんあんち)の3代です。公的な場では、馬や硫黄などを献上し、冠帯衣服や貨幣などを賜っていました。きっと、他の場所でも色々なものを交易していたのでしょう。ただ、中山王国と比べると、回数はだいぶ劣りますので、それが国力の差になっていったとも考えられます。

次に、琉球国最古の現存地図を見てみます。真ん中には初期の首里城の姿が描かれていて、15世紀中ごろの状況と考えられています。この頃は、北山王国はなくなっているのですが、北(上)の方に、今帰仁城が「伊麻奇時利(いまきじり)城」として載っているのです。もう一つ注目は「雲見泊」として現在の運天港も記載されていることです。運天港は那覇港と並ぶ天然の良港だったのです。
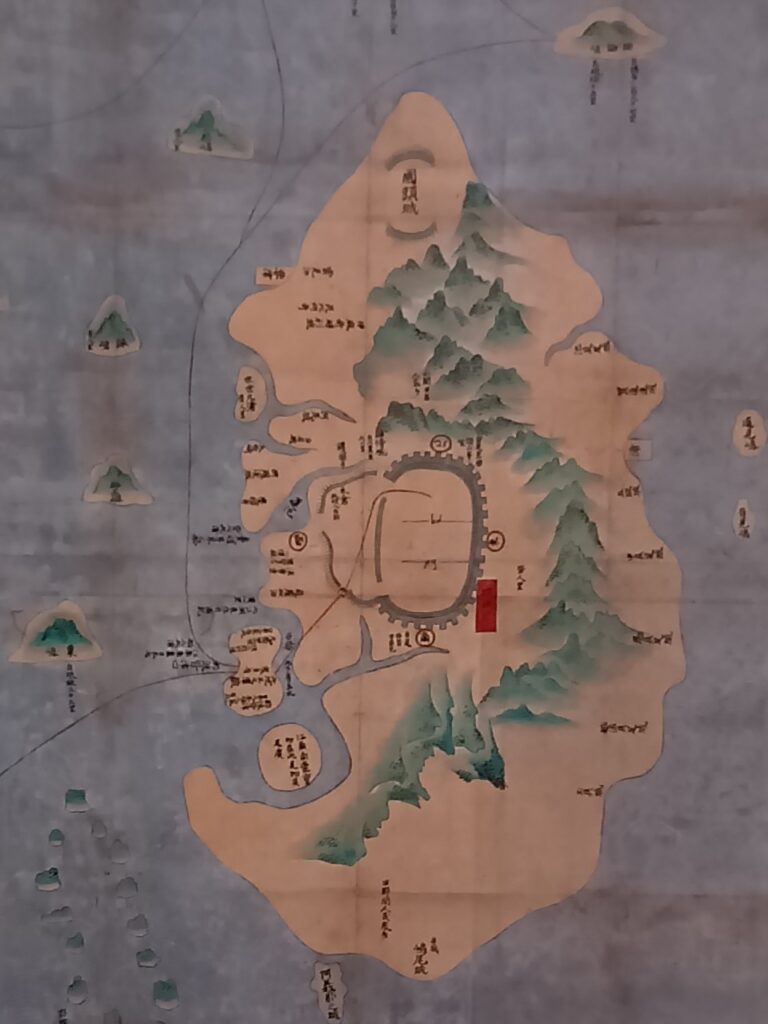
今までのストーリーは、いかがだったでしょうか。客観的なデータのおかげで、北山王国や今帰仁城の存在と繁栄が理解いただけたと思います。ただ、グスクの名前が今と全然ちがっていて、今でも漢字とその読み方が変わっているのが気になります。「新参者の統治」という意味の「いまきじり」が、「みやきせん」→「いまきじり」→「なきじん」と変化してきたと言われます。しかし他にも、最初から「みやきせん」と呼んでいたのではないかという説や、語源についても、魚が寄り付く場所という意味の「なきずみ」であるという説もあります。名前だけでも奥が深いものです。
今帰仁城の伝説と実態
次は外部からはわからない、王国とグスクの生い立ちを、沖縄内部の情報から探りましょう。地元の言い伝えや琉球王国の史書によると、はるか昔、天帝の子孫・天孫氏が首里城を築いてから、その流れをくむ者が、今帰仁城主になったとされています。これは、神話ということなのでしょう(前北山時代)。
次に出てくるのは、浦添城のときにもご紹介した源為朝で、なんと彼は運天港に上陸したというのです。ここにも為朝伝説があるのです。そして、その子が琉球王に、孫が今帰仁城主になったそうです。13世紀くらいのことになるでしょうか(中北山時代)。そしてその後、一つの王国が3つに分かれたというストーリーです(後北山時代)。

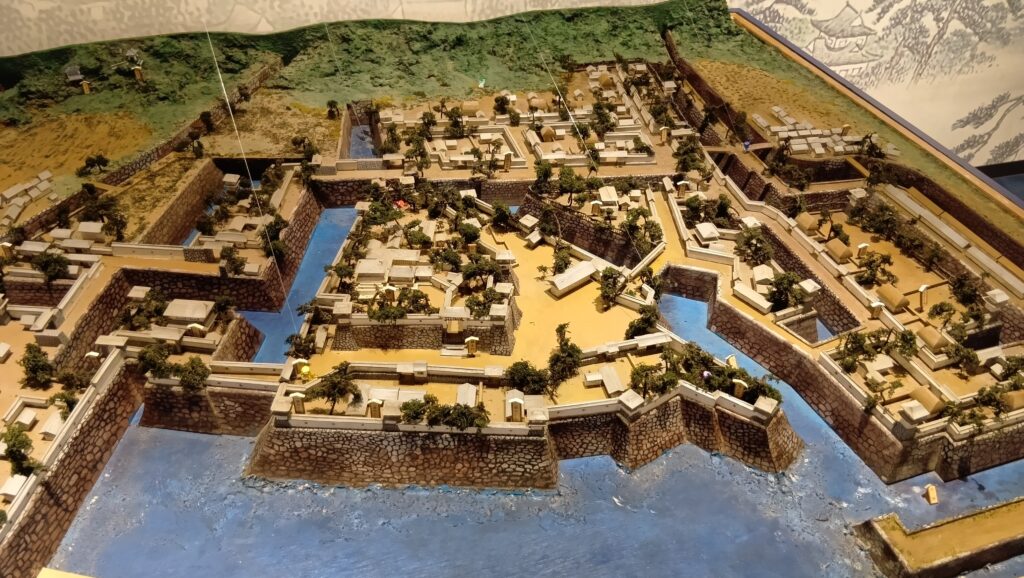
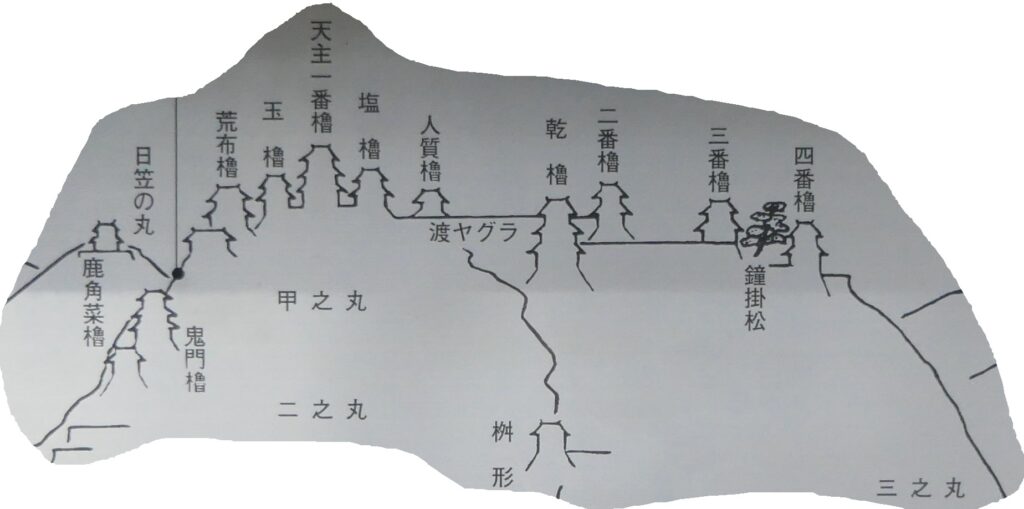
続いて、今帰仁城の発掘成果をご紹介します。これまでに中心部の主郭などが発掘され、グスクには、4つの時代区分があることがわかりました。主郭の様子を時代順にご説明します。まず第1期です(13世紀末~14世紀前期)。時期は、先ほどの伝承では2番目の終わり頃でしょうか。発掘した結果では、その頃にグスクができたことになります。館は掘立柱で、防御のための柵で囲われていて、周りも本格的石垣ではなく、石積や版築による土塁でした。使っていた土器も、地元産が多かったとのことです。
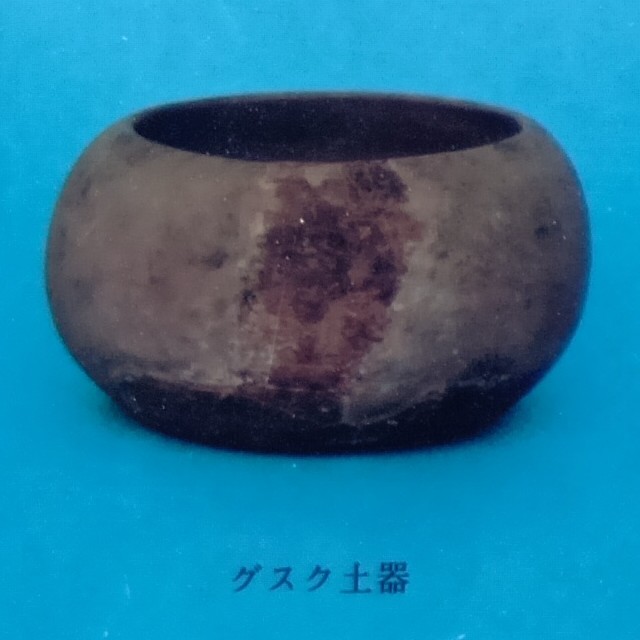
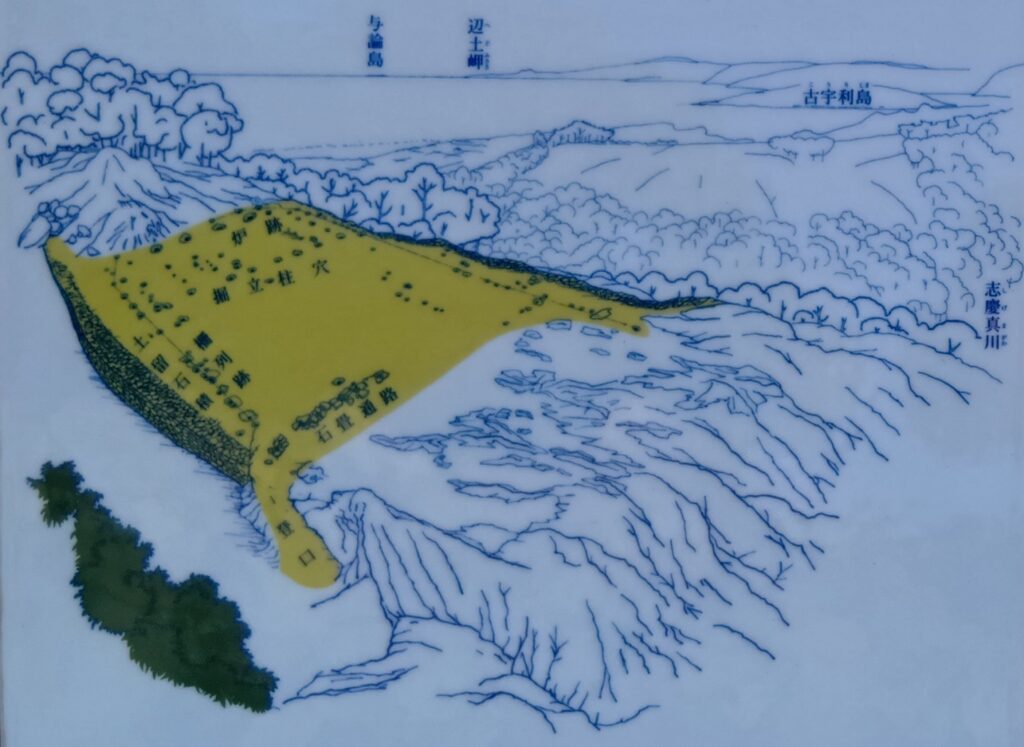

次が第2期です(14世紀中期)。時期は、三山時代に入った頃です。大発展した感じです。中にはグスクらしい礎石建ての正殿が建てられ、規模が大きくなって、周りに石垣も築かれました。中国産の陶磁器の使用も増えてきました。
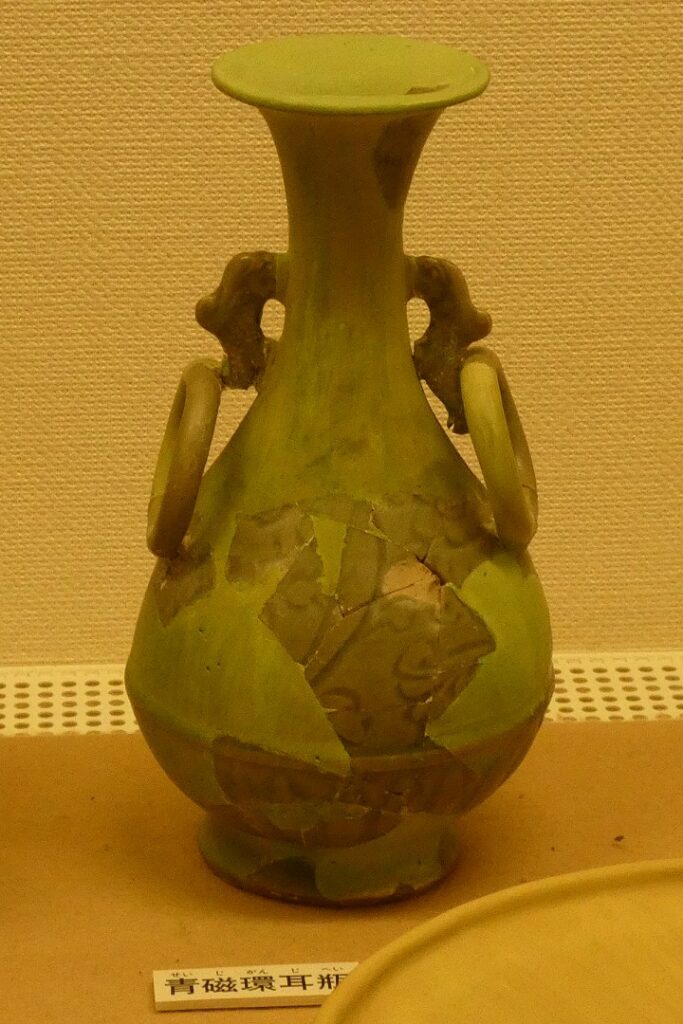
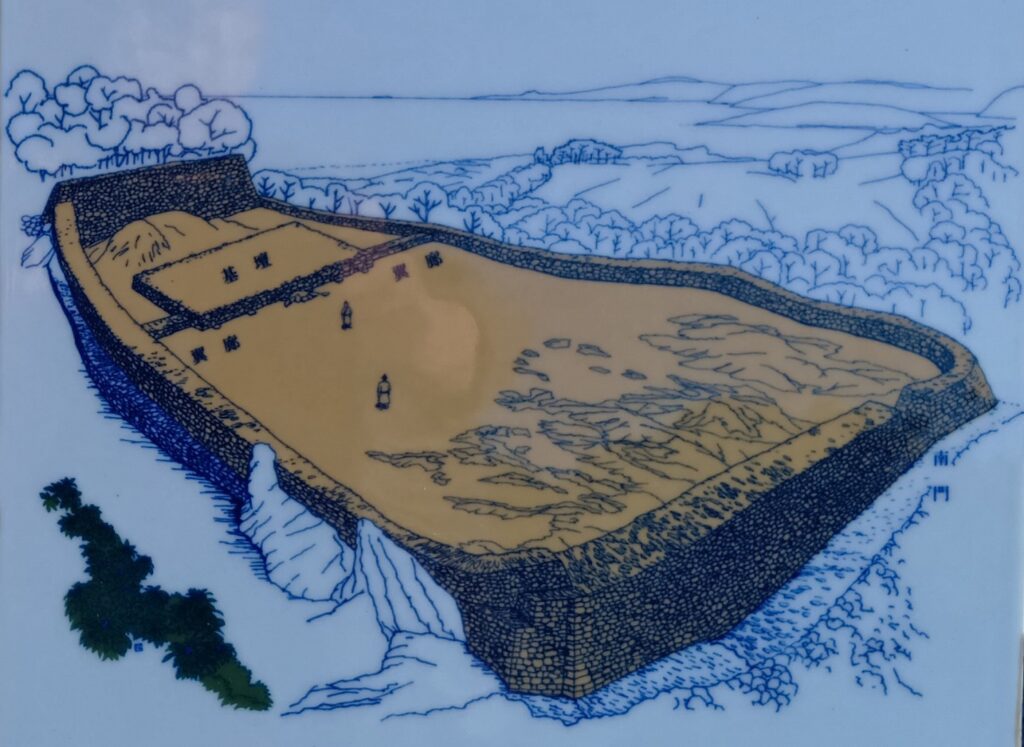

そして最盛期の第3期です(14世紀後半~15世紀前期)。北山王国が明と交易をおこなっていた時期と一致しています。規模も最大になったのですが、なによりも、出土した当時の交易品が、その繁栄を表しています。
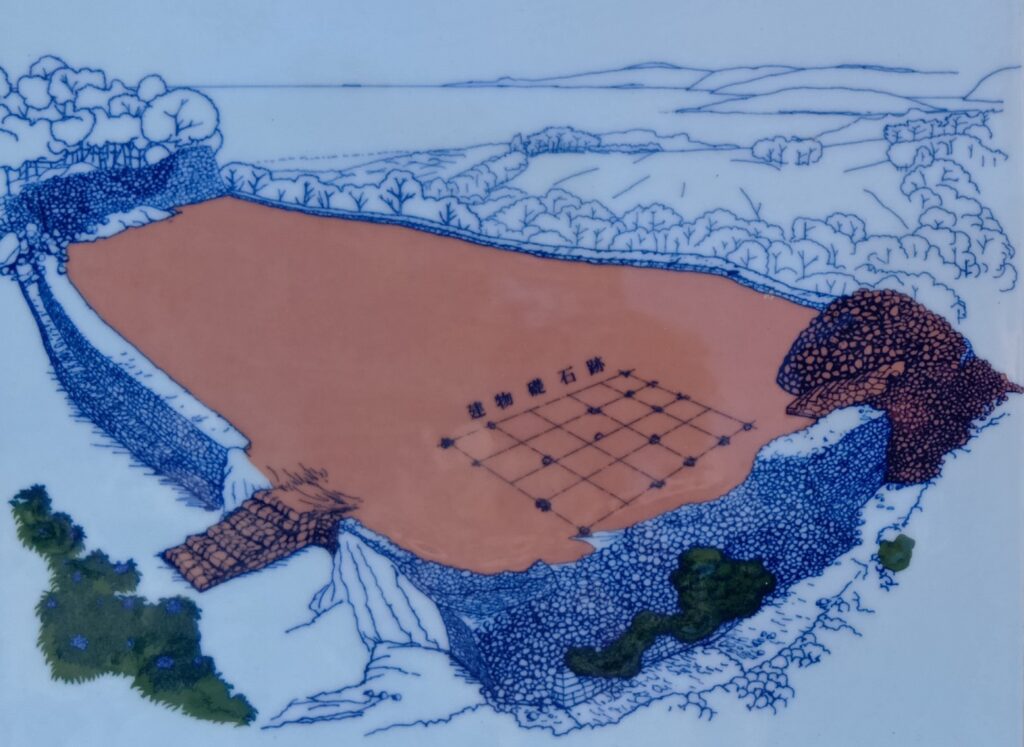

特にびっくりするが、以下の出土品です。これら6つの中国産青磁碗は、土の中からそのまま出てきたのです。意図的に埋められていたようです。重要な祈りの儀式が行われたのかもしれません。
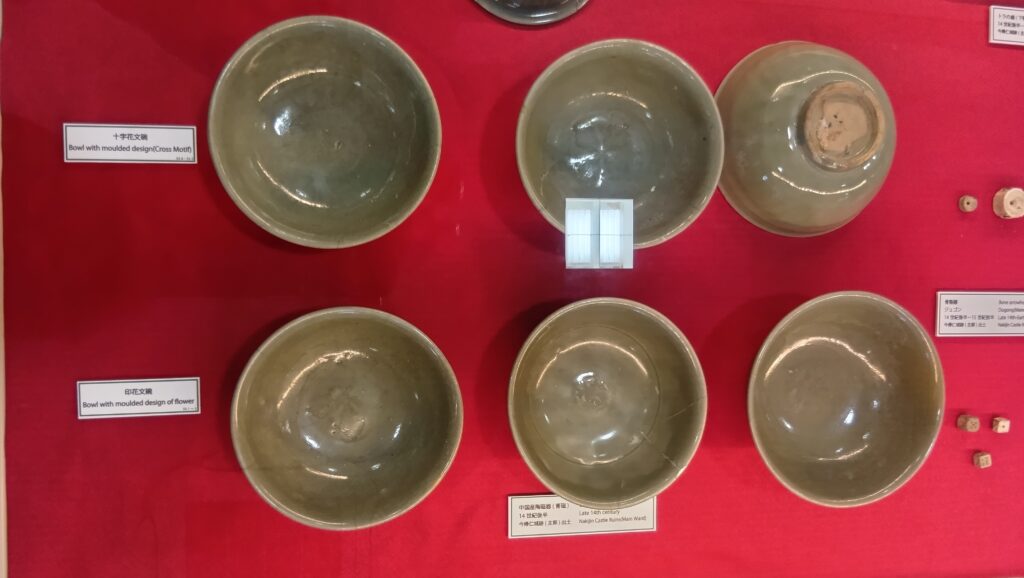

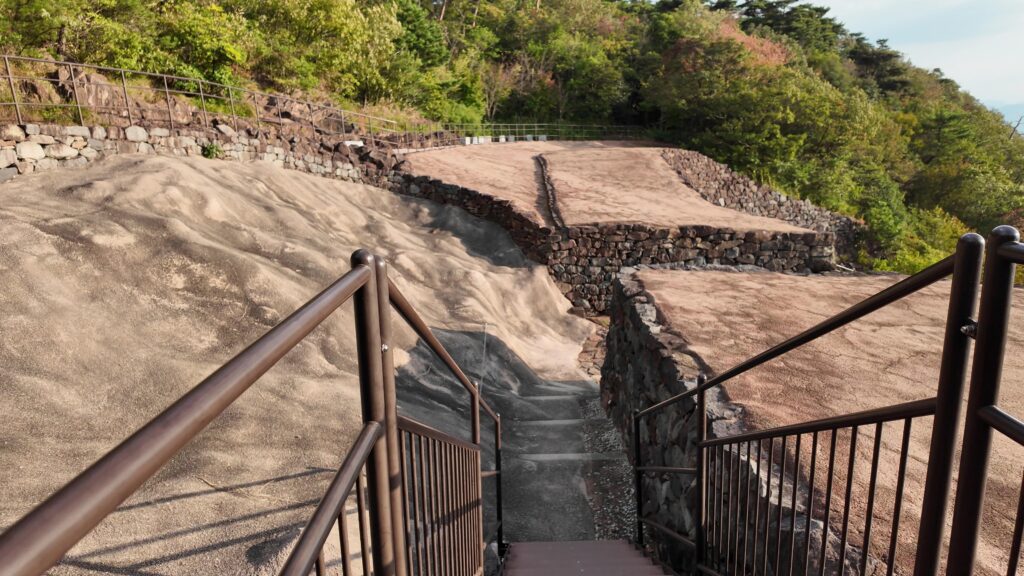
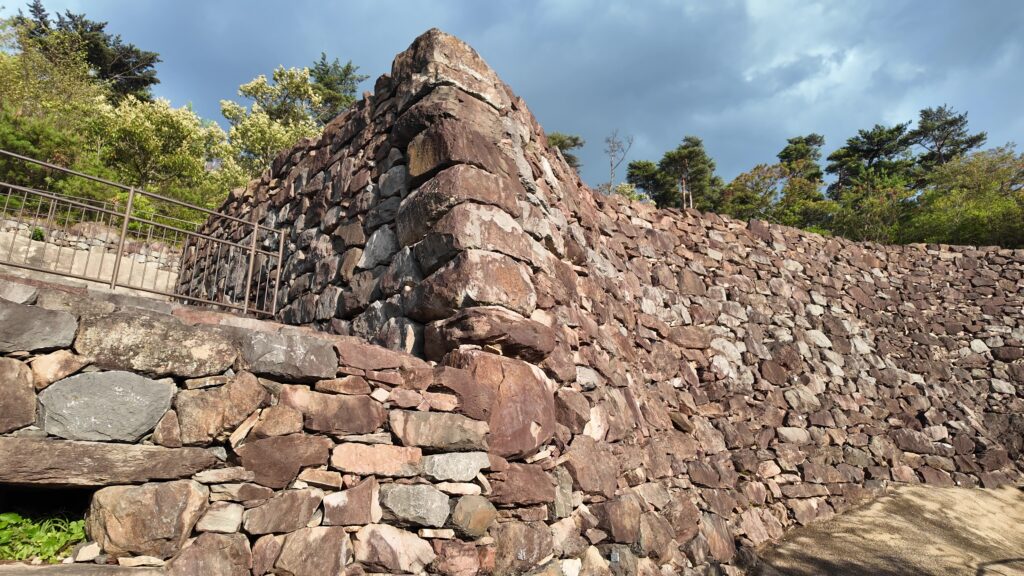
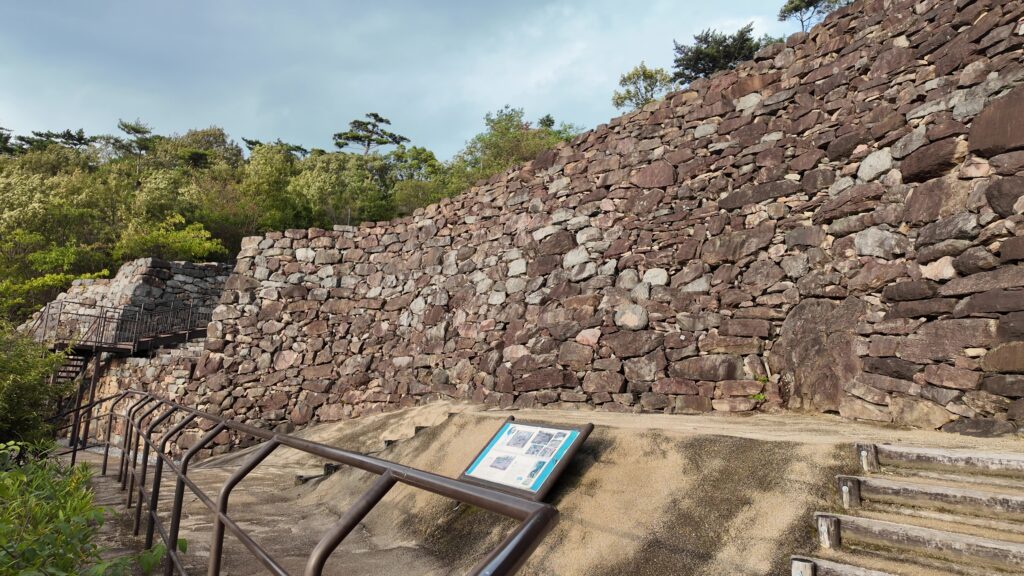
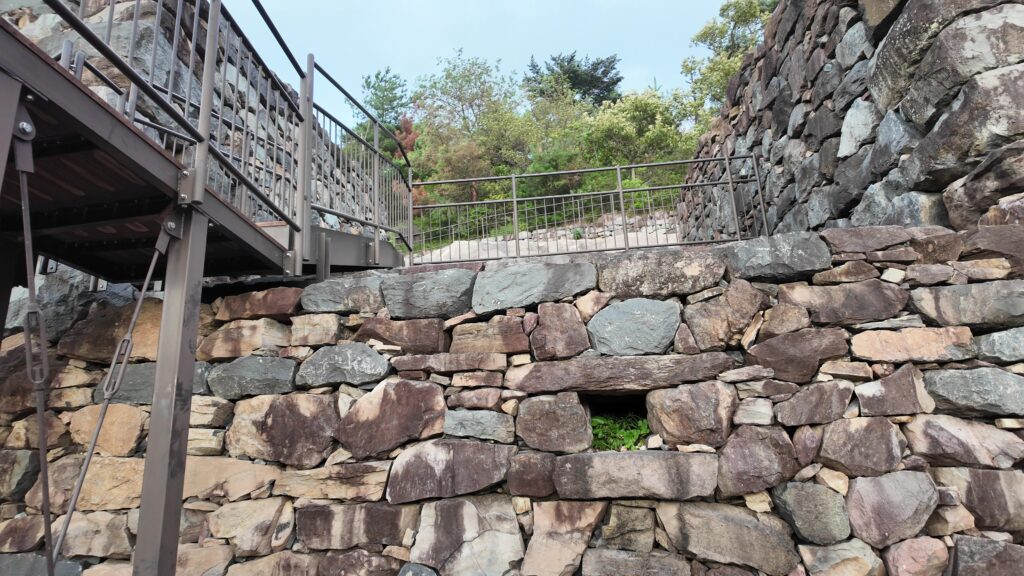
グスク全体の規模としても、このときまでに並行して拡張され、10の曲輪を持つとされる、沖縄屈指の大型グスクになったと考えられます。
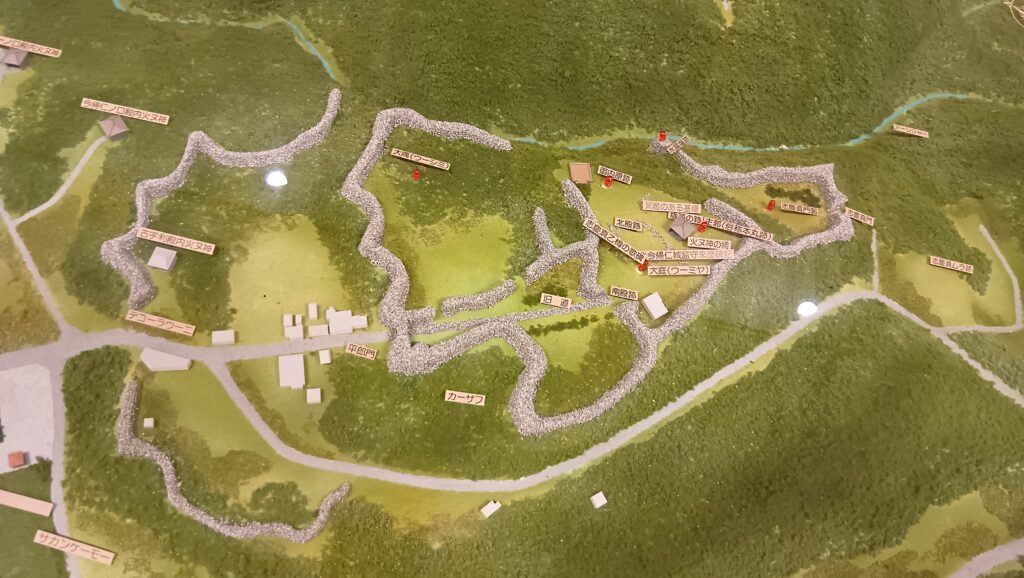

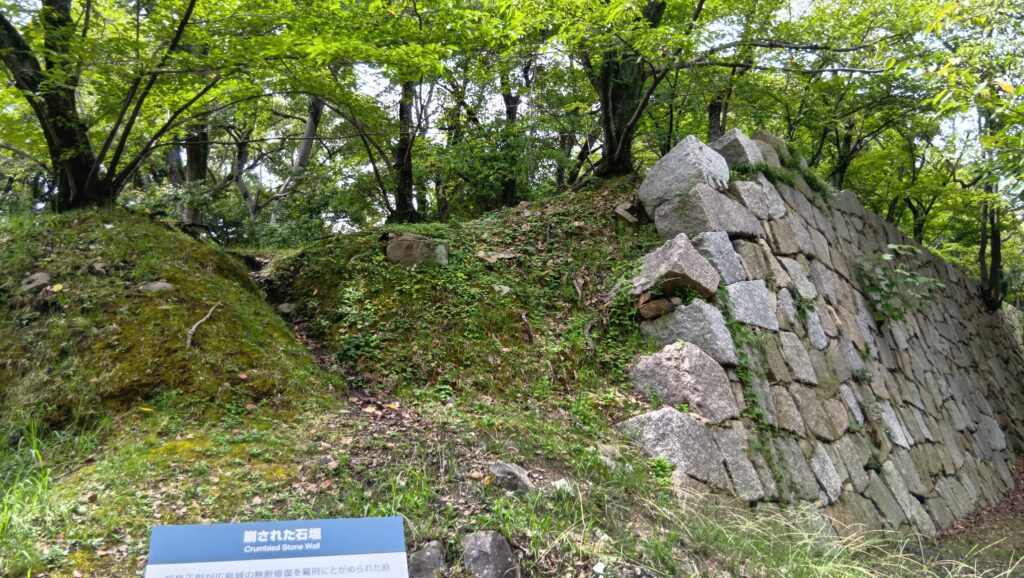
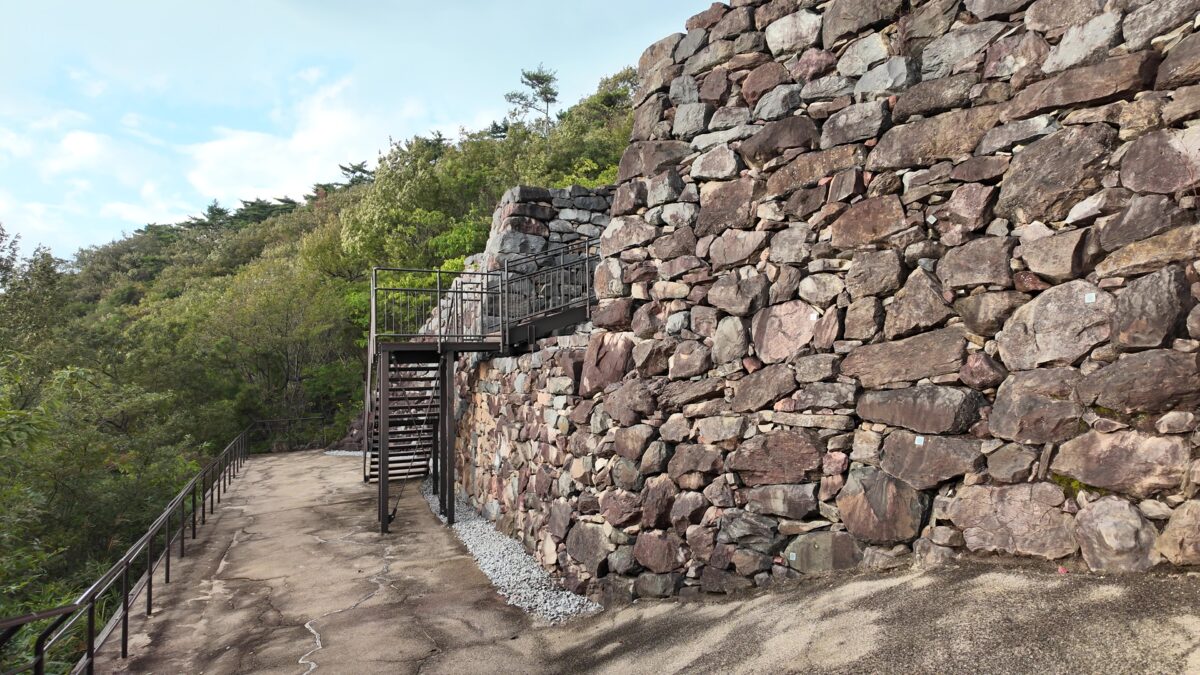
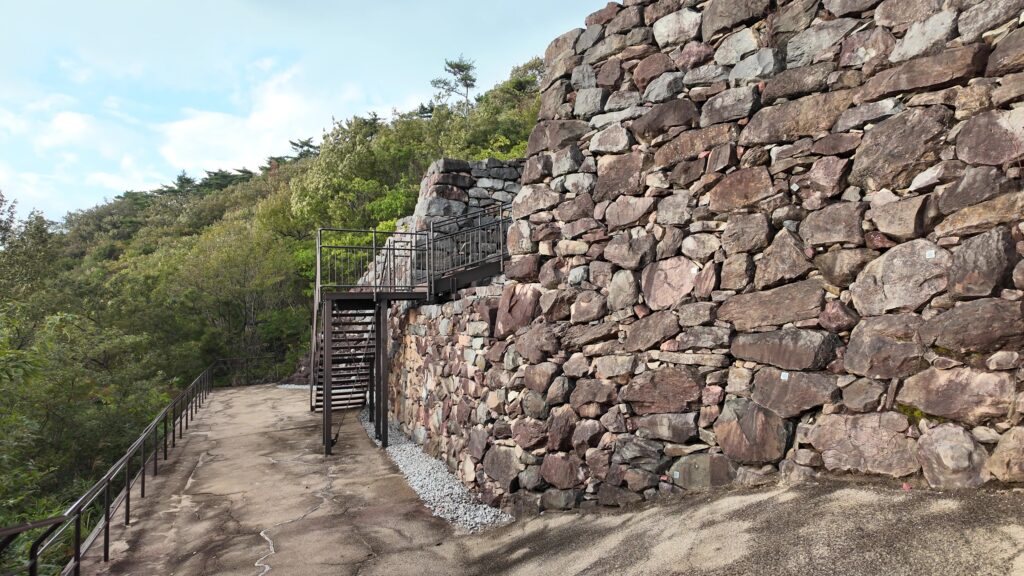
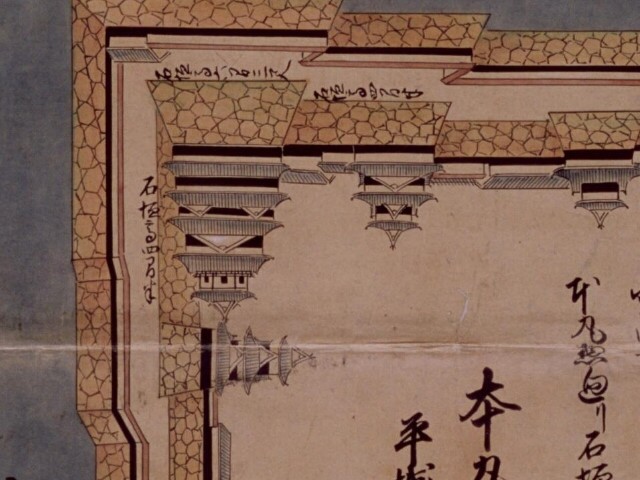
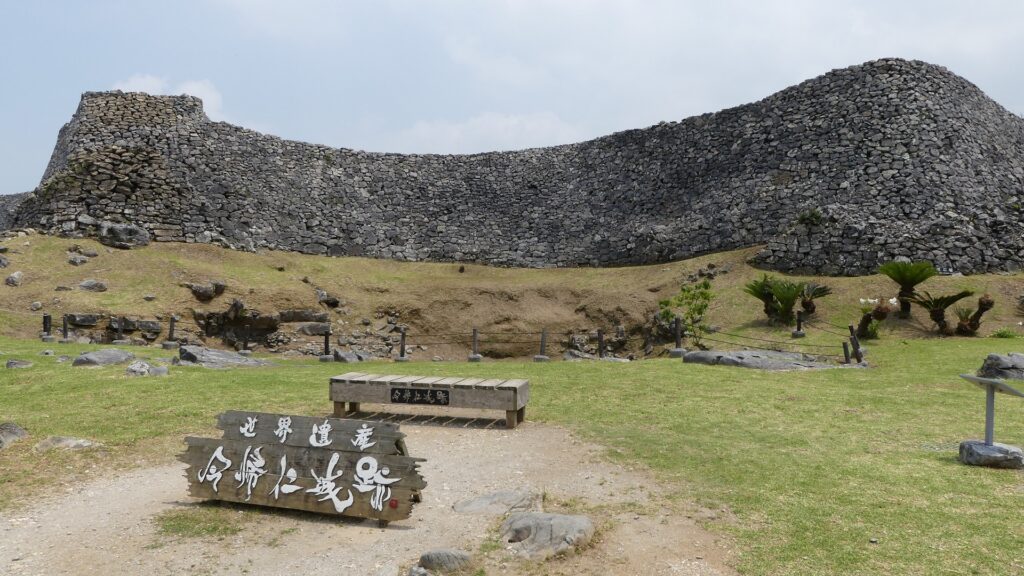
そして、優美な石垣も築かれたのです。本土の城と違って、当時はこの石垣の上を直接、兵士が走り回っていたそうです。塀とか櫓はなかったとのことです。

王国と今帰仁城の生い立ちストーリー、いかがだったでしょうか。為朝伝説にも夢があっておもしろいのですが、発掘の成果などから考えると、やはり小さな按司が、貿易などで成長して、王国を築いたと思えます。現在のところ、この見解が定説になっています。
北山王国の滅亡
いよいよ、クライマックスです。実は北山王国滅亡のストーリーも、尚巴志の琉球統一のプロセスとともに、2つの説があるのです。定説の方からご説明します。こちらのプロセスは、琉球国史書のうち、新しい方の記載をもとにしています(「中山世譜」など)。古い史書の記載を、中国の記録などと照合し、改めているとのことです。こちらは、尚巴志が北山王国(1416年)、南山王国(1429年)の順に攻略しています。
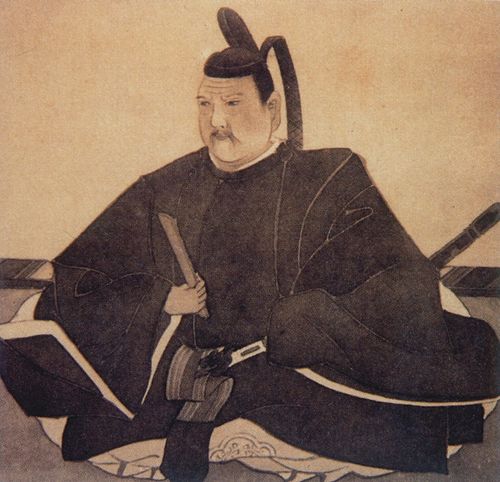
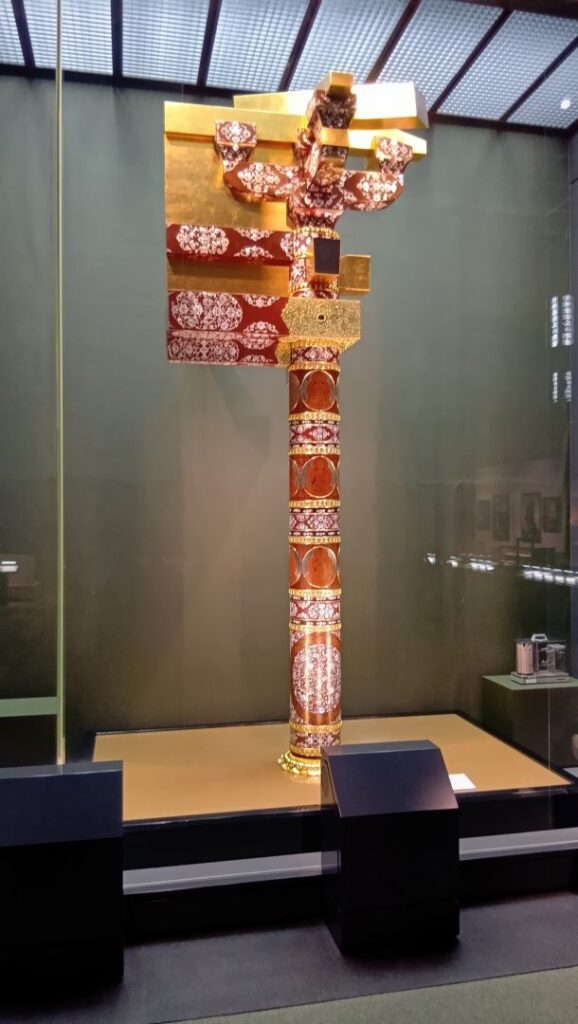
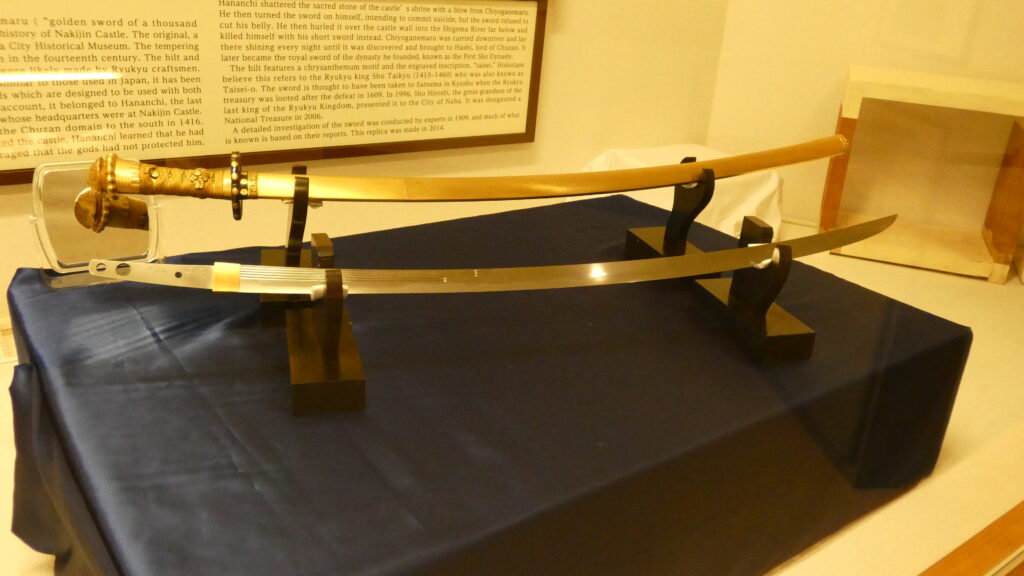
定説での北山王・攀安知(はんあんち)は、武勇に優れていましたが、淫逆無道であったとされます。彼は、重臣の本部平原(もとぶていばら)とともに、中山王国を攻めることを計画します。北山配下の按司たちは、そのことを中山王・思昭に告げたのです。思昭の子・尚巴志が、按司たちと今帰仁城を攻めることになりました。尚巴志軍は優勢でしたが、堅固な城を攻めあぐね、計略を用います。重臣の本部平原を買収したのです。平原は、攀安知を城外で戦うように仕向け、城に火を放ちました。異変に気付いた攀安知は、平原を伝家の宝剣「千代金丸」で成敗しますが、時すでに遅し・・・。悲運を嘆き、グスクを守護する霊石を切りつけ、自害しようとしてもなぜか切れなかったので、宝剣を川に投げ捨て、別の刀で自害しました。これが定説による今帰仁落城のストーリーです。悪人は滅ぶべくして滅ぶ、みたいな筋書です。

次は「異説」として、古い史書(「中山世鑑」)による統一プロセスをご紹介します。この説では、北山攻略をもって琉球統一(1422年)としていますが、事実としてその後も南山王国が明と交易をしています(1429年まで)。だから定説では修正されたのですが、この時期の南山は、尚巴志の傀儡だったという意見もあるのです。こちらも捨てたものではないように思います。それに城攻めの内容は、中国の史書とは関係ないのに、全然ニュアンスが違うのです。
異説では、北山王国が存在するうちに琉球統一が進んでいて、配下の按司も中山王国に服属していきました。劣勢となった攀安知は、一族郎党を集め、彼らを鼓舞し、中山と最後の決戦をすべく、城の防備を固めました(下記補足1)。それを周りの按司たちから聞いた尚巴志は、今帰仁城に大軍で攻め寄せます。しかし堅固な城は、いくら攻めてもなかなか落ちません。そこで尚巴志軍は一計を案じます。その地を知る按司が、夜裏側(グスクの南西側)から忍び寄り、グスクに火を放ったのです。それを合図に総攻撃が始まりました。最期を悟った攀安知は、尚巴志軍に突撃、ついには宝剣で切腹し、引き抜いた剣でグスクを守護するイベの岩を切り刻み、剣を川に投げました(下記補足2)。定説と比べると潔い最期と感じます。
(補足1)「今の人々の多くは心変わりして、我が方は小勢となったが、多数を恐れて一戦もせずに降参するのは、如何にも口惜しいことだ。そして、山北国をうち建てた祖先に恥をさらすことにもなる。さあ、中山の軍は攻め寄せて来るがよい。これを一蹴して手柄を見せようではないか。攻め寄せる中山軍がたとえ数万騎あろうと、これを打ち破ることは雑作もないことだ。もし命運尽きて、この戦に敗れることがあれば、そのときは潔く自害して、名を後世に残そうぞ。さあ者共、仕度をせよ。怖気づいて世の笑いものになるな」(山北王(攀安知)のことば、「訳注 中山世鑑」より)
(補足2)「さあ、イベも、そしてイベにおわす神も供に冥土に旅立ちましょう」(山北王(攀安知)のことば、「訳注 中山世鑑」より)

その剣はその後、中山王に献上され、現在国宝になっています。2つのストーリー、いかがだったでしょうか。もちろん定説の重みは感じますが、どちらも沖縄の伝承がもとであれば、古い方が事実を伝えているかもしれないし、異説の方が真に迫っているようにも思えます。皆さんはどうお感じでしょうか。
その後
北山王国を滅ぼした尚巴志は、次男の尚忠を、北山監守として今帰仁城に置きました。尚忠は、尚巴志が亡くなると、琉球国王を継いだ人物です。今帰仁城は、琉球統一後も、重要な拠点であり続けたのです。この監守制度は、王統が第二尚氏になっても続き、第二監守時代と呼ばれています。一世から十四世まで続き、「山北今帰仁城監守来歴碑記」にその由来が刻まれています。

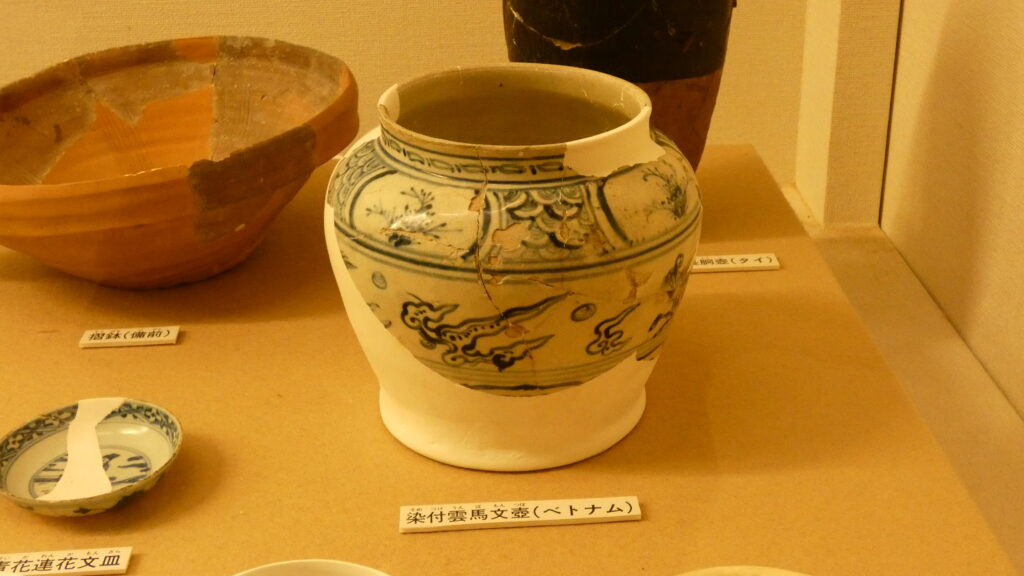
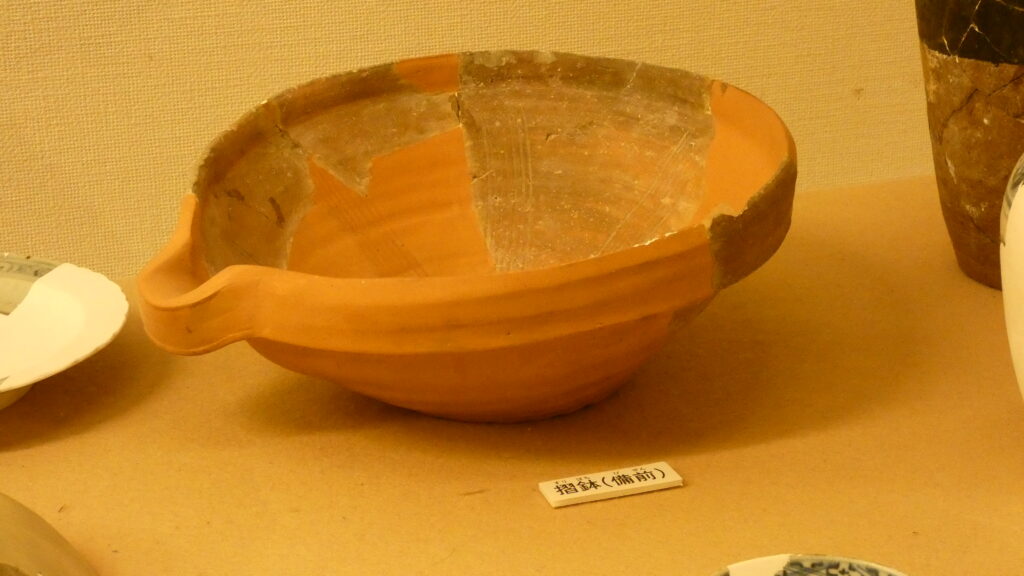
発掘調査による時代区分だと第4期に当たります。この時代にも監守の住居と思われる建物がありました。面白いのは、この時代のものとして、ベトナム製・タイ製の陶磁器や、本土の備前焼も出土していることです。
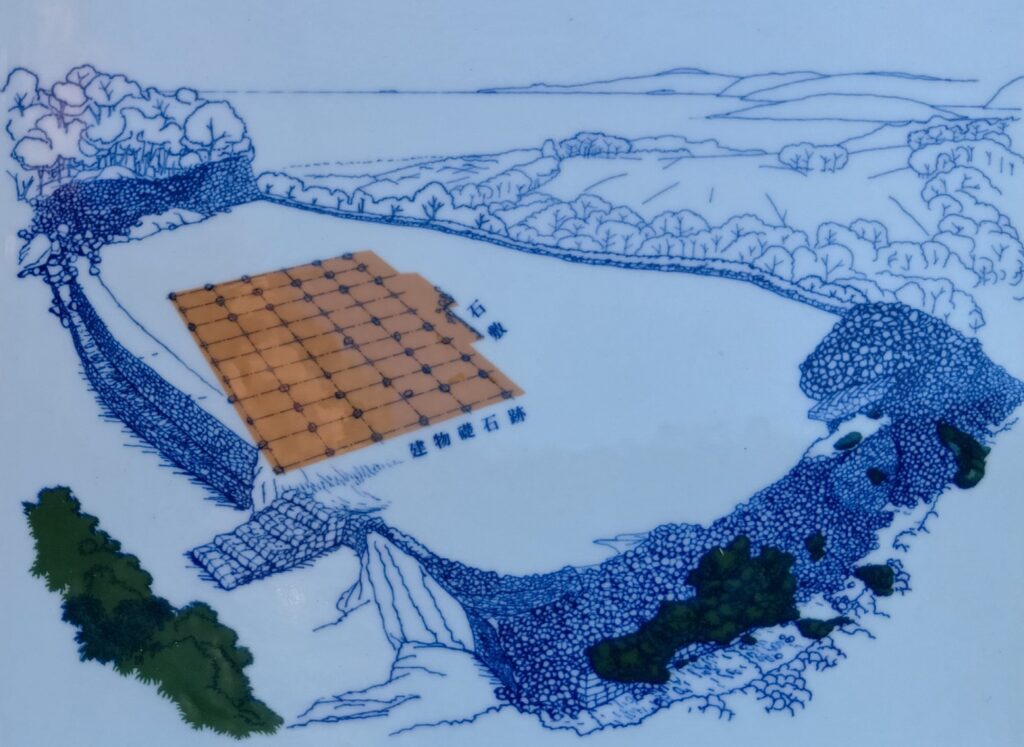


ところが、第二監守五世・向克祉(しょうかくし)の時代に大事件が起こるのです。1609年、薩摩藩の島津氏による琉球侵攻があったのです。慶長14年3月7日、約3千名の薩摩軍は、80艘以上の船に乗り出航しました。7日に奄美大島に到着、まず奄美諸島を制圧します。ここは、琉球王国の支配下にありましたが、この侵攻をきっかけに薩摩藩の直轄地になりました。薩摩軍が次に向かったのが、運天港でした。3月25日のことです。そして薩摩軍が滞在した数日間のうちに、今帰仁城や城下が放火されたととれる記録があります(下記補足3)。更にその間に、北山監守の向克祉が謎の最期を遂げるのです。29日、薩摩軍は浦添、那覇方面に向かいました。今帰仁城は廃城になり、北山監守は城下、そして首里に移っていきました。
(補足3)今きじんの城は無人であるらしい。不意に掃討を開始し、方々へ放火などした。(「琉球渡海日々記」、現代語訳は「広報なきじん」より)
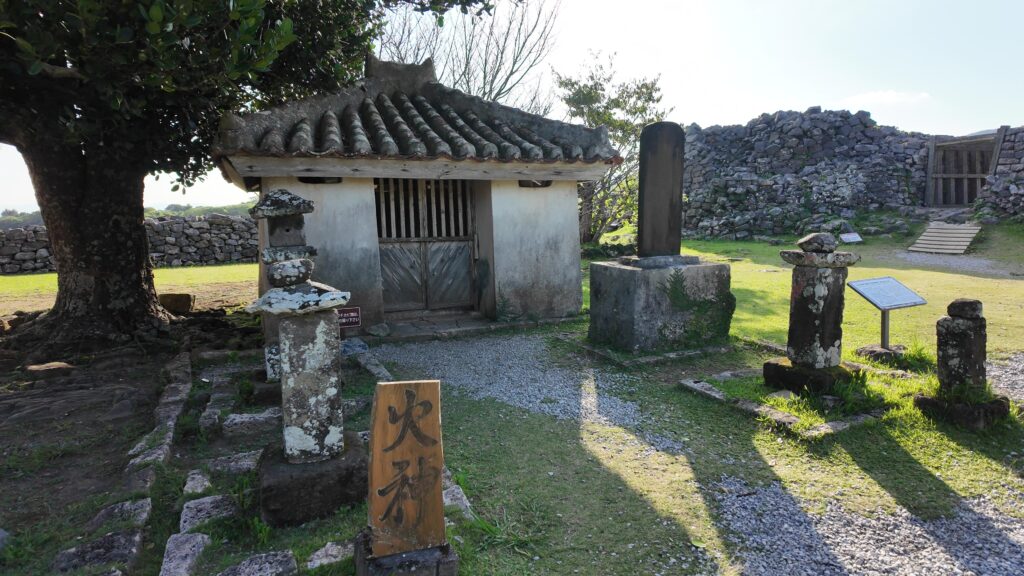


グスク跡には火神(ひのかん)の祠が建てられ、祈りの場所になりました。ようやく静かな時を迎えたと言えるでしょう。監守の石碑が建てられたのもこの時代のことです。文化財として注目されるようになったのは、戦後のことでした。1972年には国の史跡に指定され、2000年には世界文化遺産に登録されました。並行して現存する石垣の修復、失われた石垣の復元など、史跡整備も進められました。それで私たちが今、すばらしいグスクを見学できるのです。