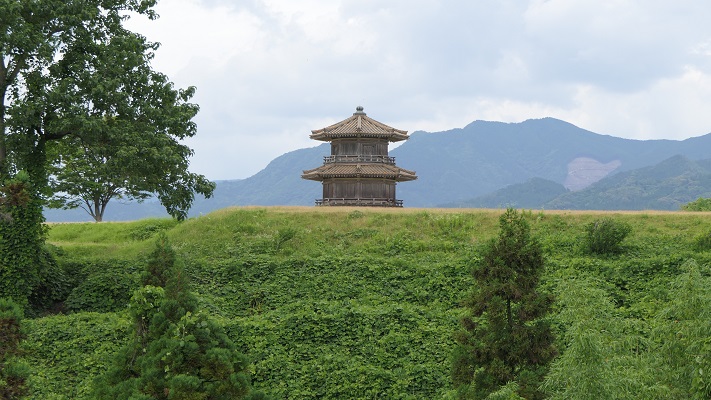
江戸城は間違いなく日本で最大の城です。なぜなら城が東京そのものになったからです。時々、外国からの旅行者の方は、どこに有名な城や城跡があるのかと尋ねられます。もし、そこが東京の中心地であるなら、もうそこは城の中かもしれません。
Edo Castke was definitely the largest castle in Japan, because it became Tokyo itself. Some foreign tourists ask that where famous Japanese castles and ruins are. They may be standing among castles if they are in the center of Tokyo.
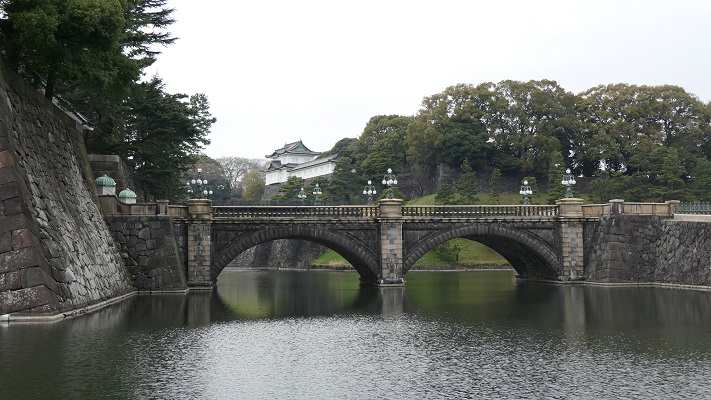

立地と歴史~Location and History
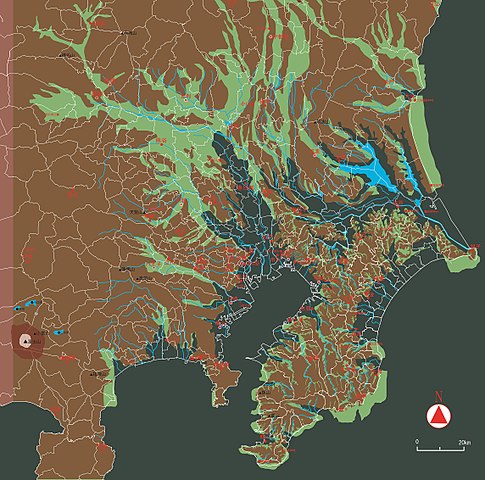
東京を含む関東平野には、中世までは大きな湿地帯がありました。この理由から、はるか昔の東海道は西日本から伸びてきて、 海を越えて房総半島に至っていました。利根、渡良瀬、隅田といった大河が直接江戸湾に注いでいたのです
The Kanto Plain including Tokyo had large waterlogged area until the Middle Ages. For this reason, the Tokaido road went from eastern Japan to Boso peninsula over the sea hundreds years ago. Large rivers like Tone, Watarase, and Sumida directly flow into what is now Tokyo Bay.
江戸城は1457年に太田道灌によって最初に築かれました。彼には敵との境界線であった利根川の近くに城を築く必要があったのです。その後この城は、戦国時代の間関東地方の支配者であった北条氏の支城の1つであり続けました。しかし、地理的な制約から武士たちの都とするには不十分でした。
Edo Castle was first built by Dokan Ota in 1457. He needed to build the castle near the border with his enemy, Tone River. After that, the castle had been one of the branch castles of the Hojo clan who were the ruler of Kanto region during the Warring States Period. But the castle still didn’t deserve warrior’s capital because of its geographical features.

豊臣秀吉は1590年に北条氏を滅ぼし、徳川家康に対し、北条氏に代わり関東地方に転封するよう命じました。秀吉はまた、家康の首府として江戸を指定したと言われています。秀吉は、彼による攻撃を3ヶ月間も耐えた北条氏の首府、小田原に家康が居座るのを恐れたからといいます。
Hideyoshi Toyotomi defeated Hojo clan in 1590, and ordered Ieyasu Tokugawa to move to Kanto region instead of Hojo. It is said that he also designated Edo as Ieyasu’s capital because he feared Ieyasu would settle at Hojo’s capital Odawara which could withstand Toyotomi’s attack for three months.

家康は江戸に到着した直後から、江戸城への驚くべき大改造を開始しました。これは、日本人による湾岸地域での都市作りの初めての試みと言われています。
Immediately after Ieyasu arrived at Edo, he started an incredible renovation of Edo Castle. It is said that it was the first attempt for Japanese people to build a city on a waterfront area.

初期の江戸城は、現在の山の手地域にありました。現在の下町地域は、海面下か湿地帯でした。そして、江戸前島と呼ばれた砂州がありました。また、陸地と砂州の間には日比谷入江が入り込んでいました。
The first Edo Castle was in the present uptown area. The present down town area was below the Sea or waterlogged. There was a sand bank called Edo-Maeto. There was also the Hibiya arm of the sea between the land and the bank.
徳川家臣団は、水上交通のために江戸前島を横切る運河を掘り、川の流路を付け替えたりしました。彼らはまた、このような湾岸都市であったため、上下水道の設備も整えなければなりませんでした。その結果、江戸は水の都となったのです。
Tokugawa team created a canal across Edo-Maeto and change the route of rivers for water transportation. They also had to build a system for water supply and sewerage on such a waterfront city. As a result, Edo became a city of waterways.
家康が1600年に天下を取った後、彼は全国の諸大名に天下普請と呼ばれる城の拡張工事を命じました。日比谷入江は城の用地拡大と防衛上の必要のため、埋め立てられました。この大規模な工事により、天守を含む多くの建物が作られ、多くの堀が掘られ、石垣が高く積まれました。
After Ieyasu got the power in 1600, he ordered lords of the whole country to improve the castle called Tenka-Bushin. They reclaimed Hibiya arm of the sea to spread the ground for the castle as well as the need for defense. Many buildings including Tenshu keep were built, many moats were dug, and high stone walls were built by the large scale construction.
大名たちは少なくとも6万個もの百人石と呼ばれた4トン石を、伊豆半島から海を越えて江戸まで運ばねばなりませんでした。1603年から1660年まで続いた天下普請は江戸を日本一の大城郭に仕立てたのです。
These lords had to carry at least 60,000 four ton stones called Hyakunin-Ishi from Izu Peninsula to Edo over the sea. Tenka-Bushin between 1603 and 1660 resulted in Edo Castle being the largest castle in Japan.
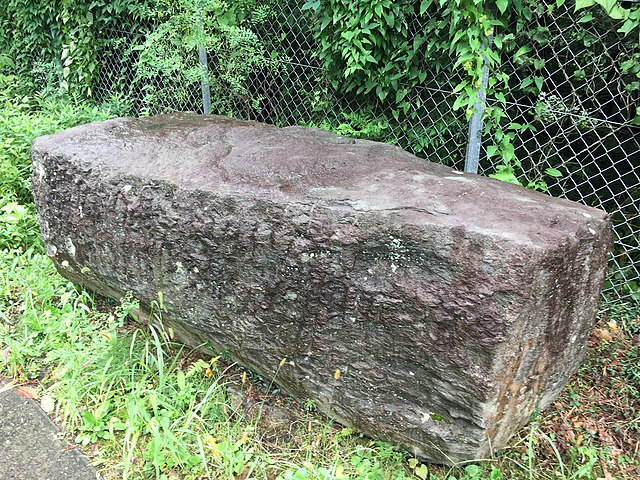

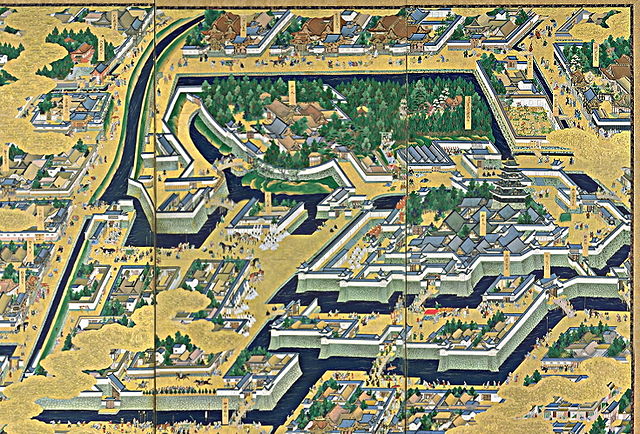
江戸城は、内郭と外郭に分かれていました。内郭は内堀の内側で、城の中心部分で、主要な曲輪である本丸、二の丸、西の丸から構成されていました。その外周は8km近くありました。そこには天守、それぞれの曲輪に御殿があり、そして警備のために多くの櫓や門がありました。
Edo castle was divided into Naikaku and Gaikaku. Naikaku was the inside of the inner moat, and consisted of the center portion of the castle including main enclosures Honmaru, Ninomaru, and Nishinomaru. Its perimeter was nearly 8 km. It had the Tenshu keep, halls for each main enclosure, many turrets and gates for security.
外郭は、外堀に囲まれていた区域で、その外周は約16kmもありました。見附と呼ばれた大型の門と橋のセットが約50ヶ所、主要街道と堀との交差点に置かれ、民衆と交通を監視していました。
Gaikaku was the surrounding area by outer moat whose perimeter was about 16 km, even including the city area. About 50 sets of a large gate and bridge called Mitsuke were placed at the intersections of the moat and major roads to check people and transportation.

その完璧な構造にも関わらず、この城は敵からではなく、火災による被害を受けました。もっとも有名なのは1657年に発生した明暦大火です。この大火により、大半の江戸市域、江戸城、そして3代目の天守が焼け落ちました。大火の後、4代目天守の再建工事が開始されましたが、中止となりました。そのための天守台は今でも見ることができます。
Despite the perfect structure, the castle suffered not from enemies, but from fires. The most famous one was the great fire of Meireki in 1657. It burned out most of Edo City, Edo Castle, and the third Tenshu keep. After the fire, the rebuilding of a fourth Tenshu was launched, but canceled. We can now see the prepared Tenshu base for it.
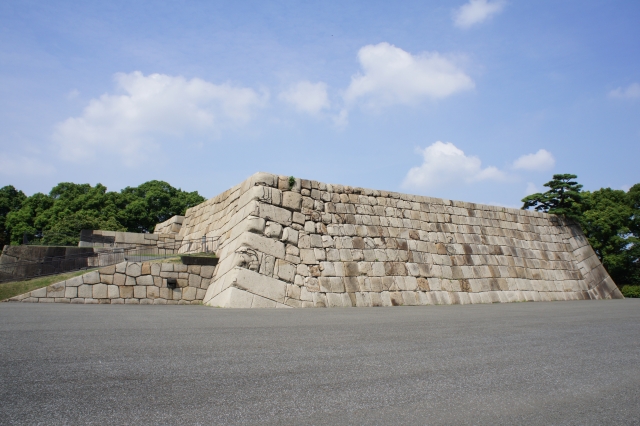

将軍は本丸御殿に住み、統治を行いましたが、御殿も火災での焼失と再建を繰り返しました。幕末になってから、将軍は焼けた本丸御殿から通常は隠居した将軍が住む西の丸御殿に移らなければなりませんでした。予算がなかったからです。
Shogun lived and governed in Honmaru hall, but the hall was also burned down and restored several times. At the end of the Edo Period, Shogun had to move from the burned Honmaru hall to Nishinomaru hall where retired Shogun usually lived, because of the lack of money.

明治維新のとき、西日本の方で新政府と幕府の間で戦いが起こりました。結果として、西郷隆盛と勝海舟との会談が行なわれ、江戸城は新政府に平和裏に引き渡されました。
During the Meiji Restoration, a battle between the New Government and Shogunate was fought in eastern Japan. As a result, Edo Castle was handed over to New Government without war after the meeting between Takamori Saigo and Kaishu Katsu.

1869年、江戸は東京と名前を変え、日本の首都となりました。そして明治天皇が将軍と入れ替わりで、古都京都から東京の江戸城西の丸御殿に移りました。そのため、現在西の丸は皇居の一部となっています。
In 1869, Edo was renamed Tokyo which became the capital of Japan, before the Emperor Meiji move from old capital Kyoto to Nishinomaru hall of Edo Castle in Tokyo instead of Shogun. That’s why Nishinomaru is now part of the Imperial Palace.