Later History
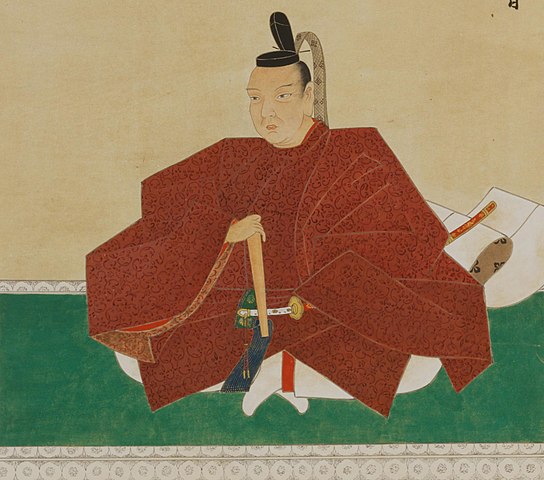
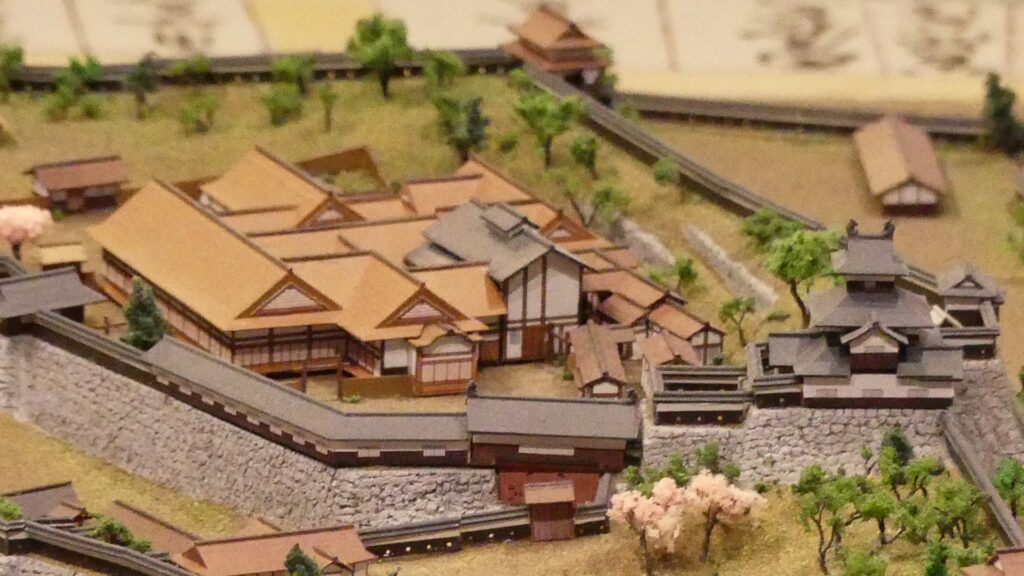
During the Meiji Era, the ruins of the castle were turned into a park in which the baseball stadium was constructed in during the Showa Era. Officials changed their policy for developing the ruins because a lot of citizens complained and the detailed drawings of the castle buildings were left by Sadanobu Matsudaira. They were wondering if the castle would be restored to its original condition. That would be the first attempt in the way large castle buildings are rebuilt in the present time of Japan.
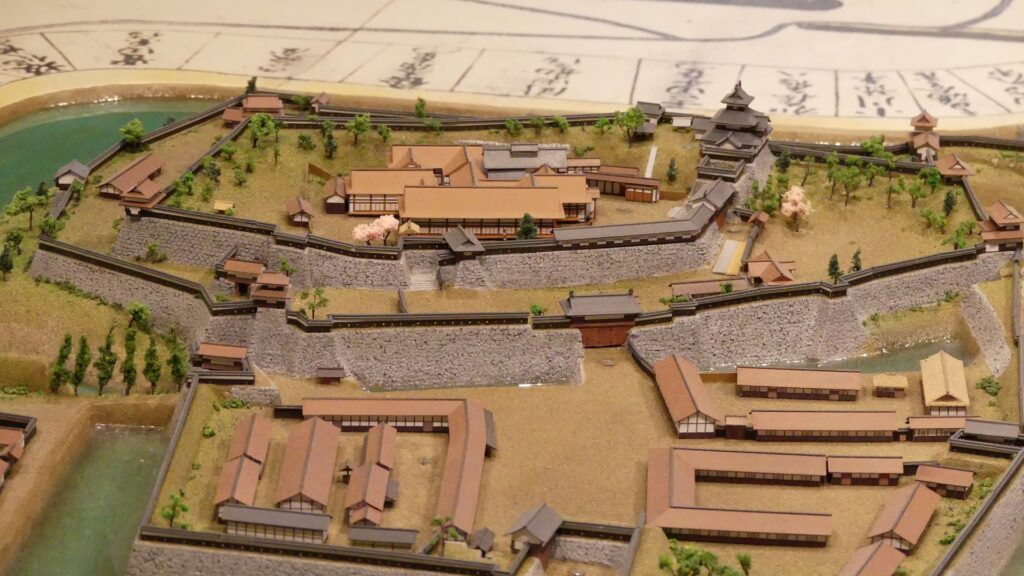
The aerial photo around the castle during the 1970’s
However, there was a big problem with the law. Japan’s Building Standard Act has very strict restrictions on wooden buildings which are over 13m tall. According to this law, new large old-style wooden buildings like the Shirakawa-Komine castle turret are not allowed to be built. So officials continued the restoration of the turret not as a building, but as a structure that would be allowed by the law. It was finally completed in 1991. However, another problem occurred as the government made the most part of the turret inaccessible to visitors, because it was not “a building”. At last, the law had the provisions to be exempt for historical buildings in 1993. The three story-level was finally opened to visitors.
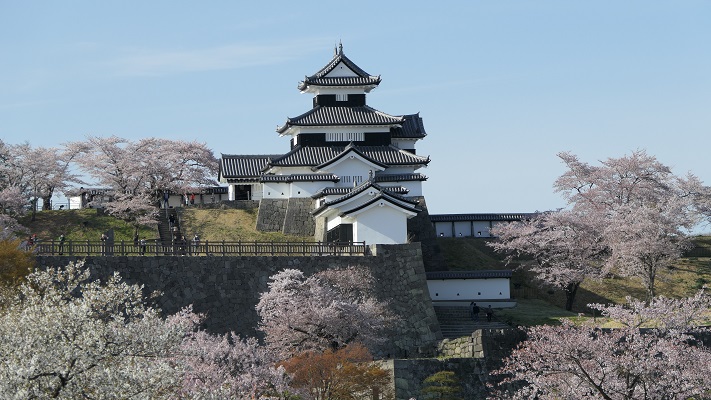

Features
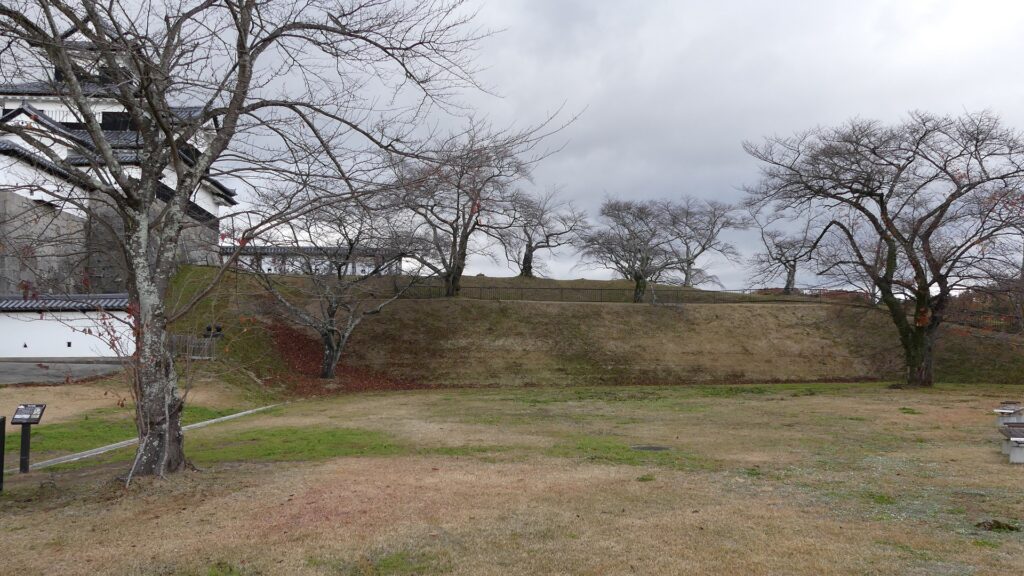
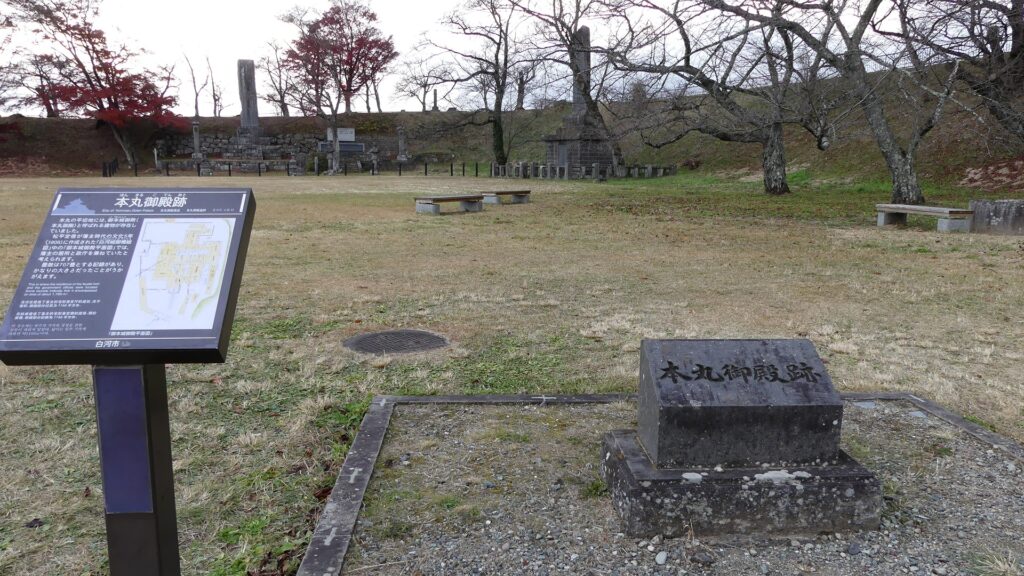
Castle Ruins still look Strong
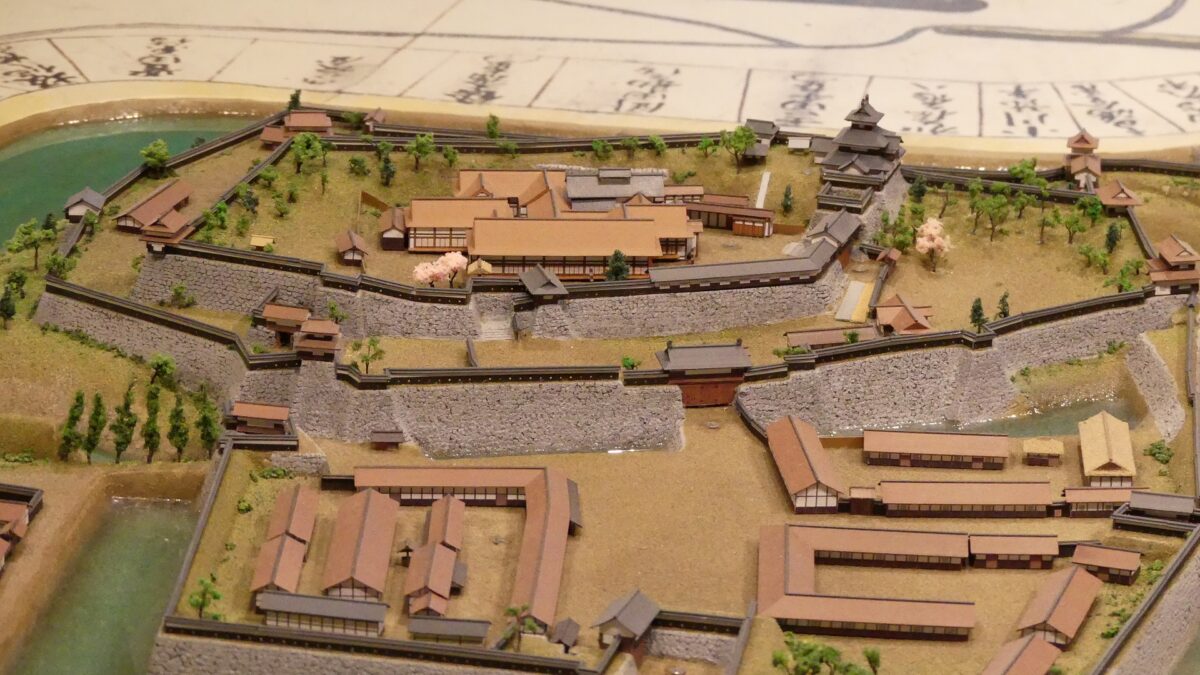
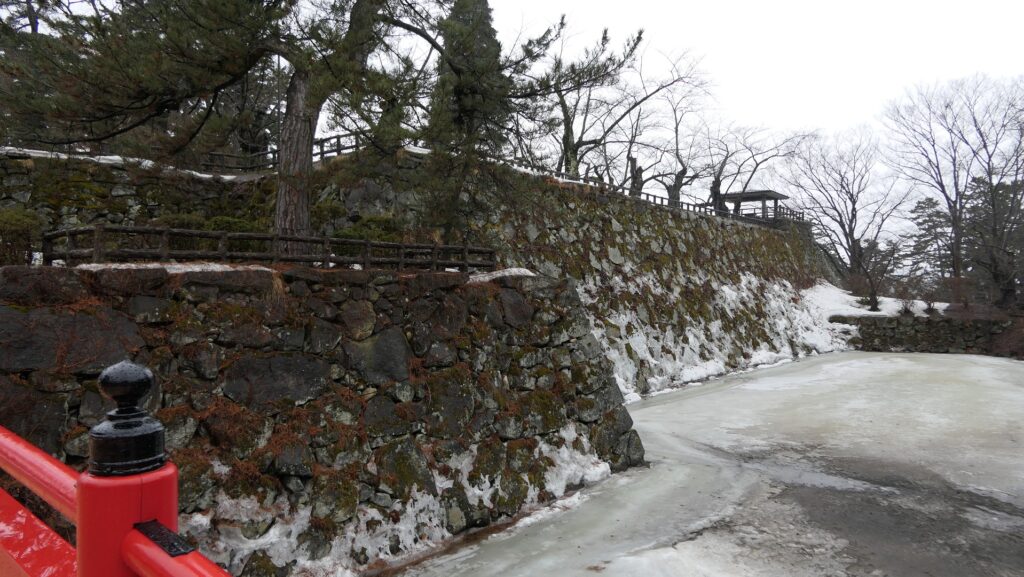
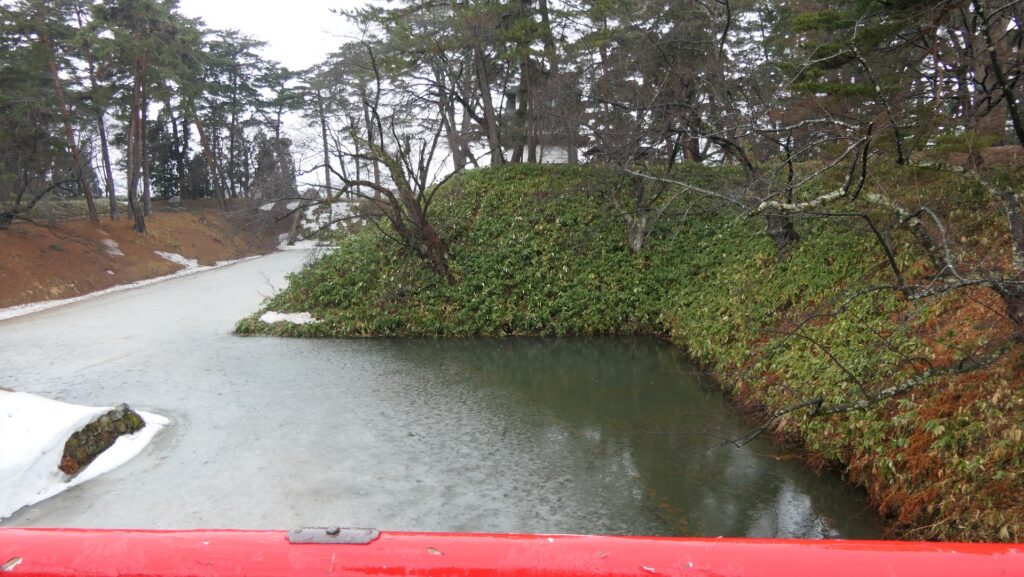
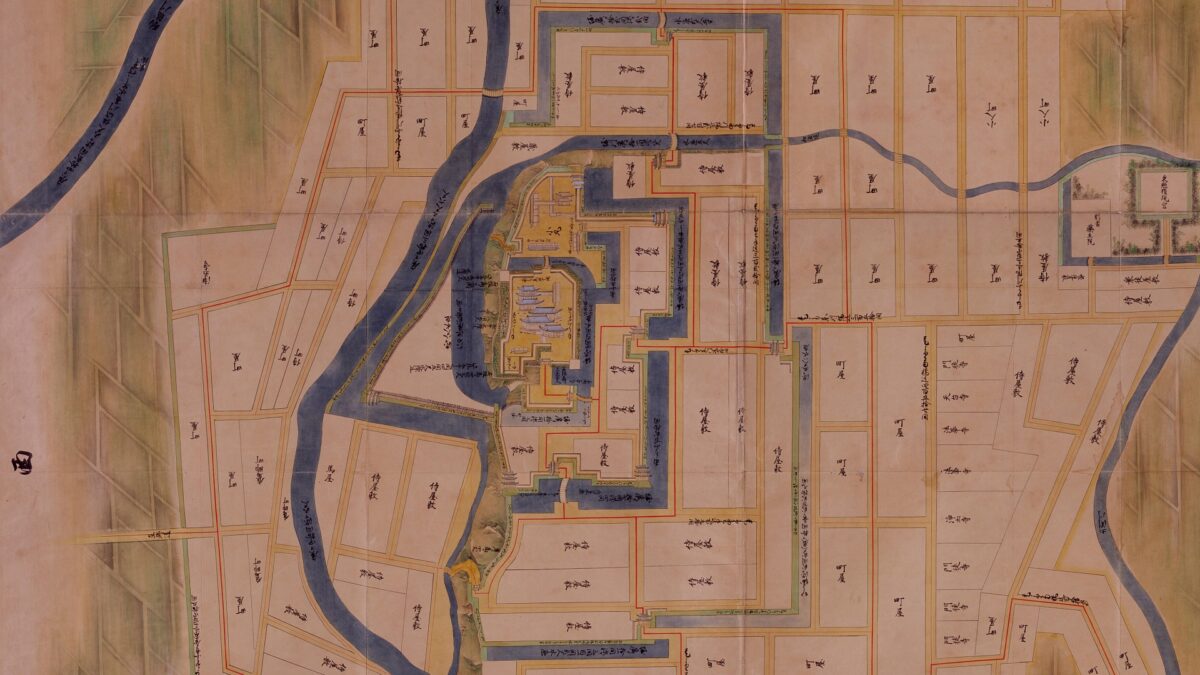
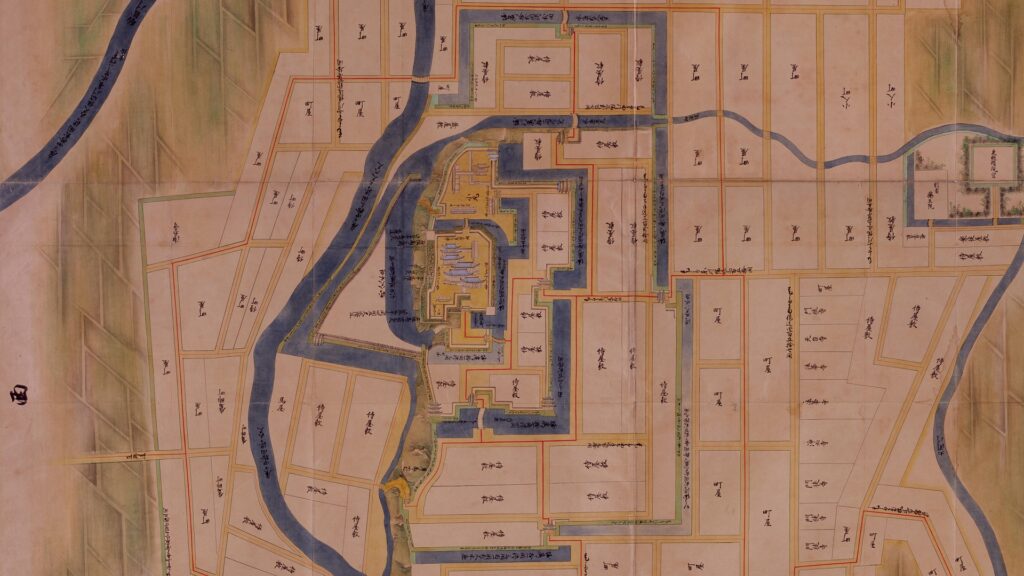
Today, if you stand in front of the ruins of Shirakawa-Komine Castle, called Shiroyama Park, you will be impressed by its wide remaining stone walls and the slim restored three-level turret on the top. The entrance of the park was that of the second enclosure, which had Taiko (drum)-mon Gate. The enclosure has become an open space where people can enjoy relaxing and exercising. It is also partially used by public facilities such as Komine-jo(castle) History Museum and a tea house.
The aerial photo around the castle
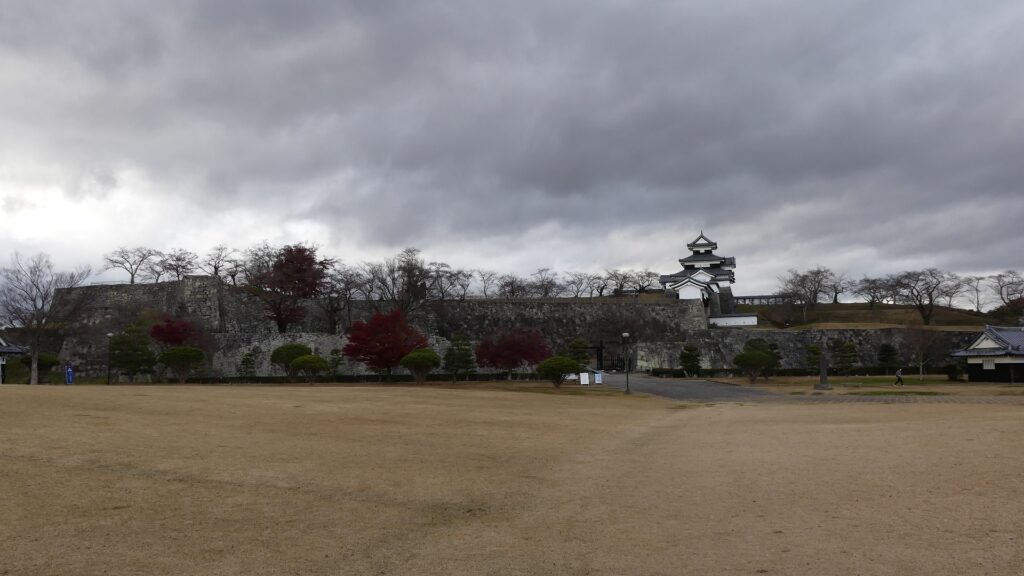
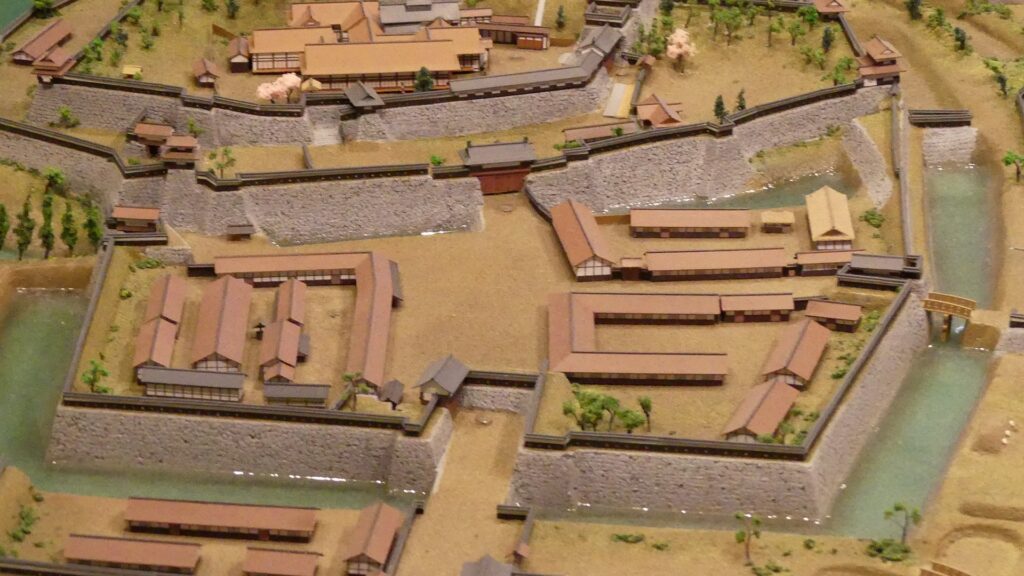


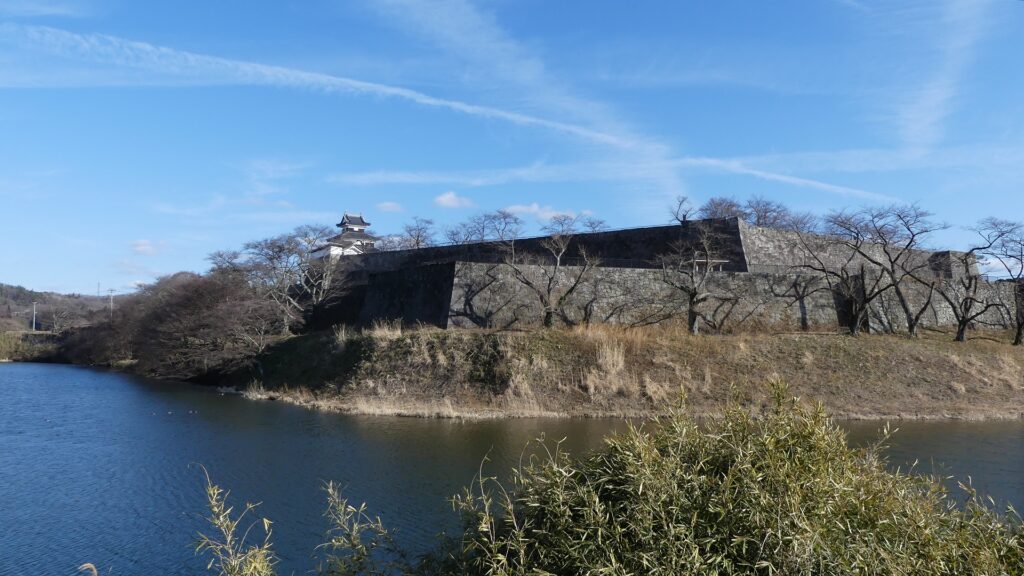
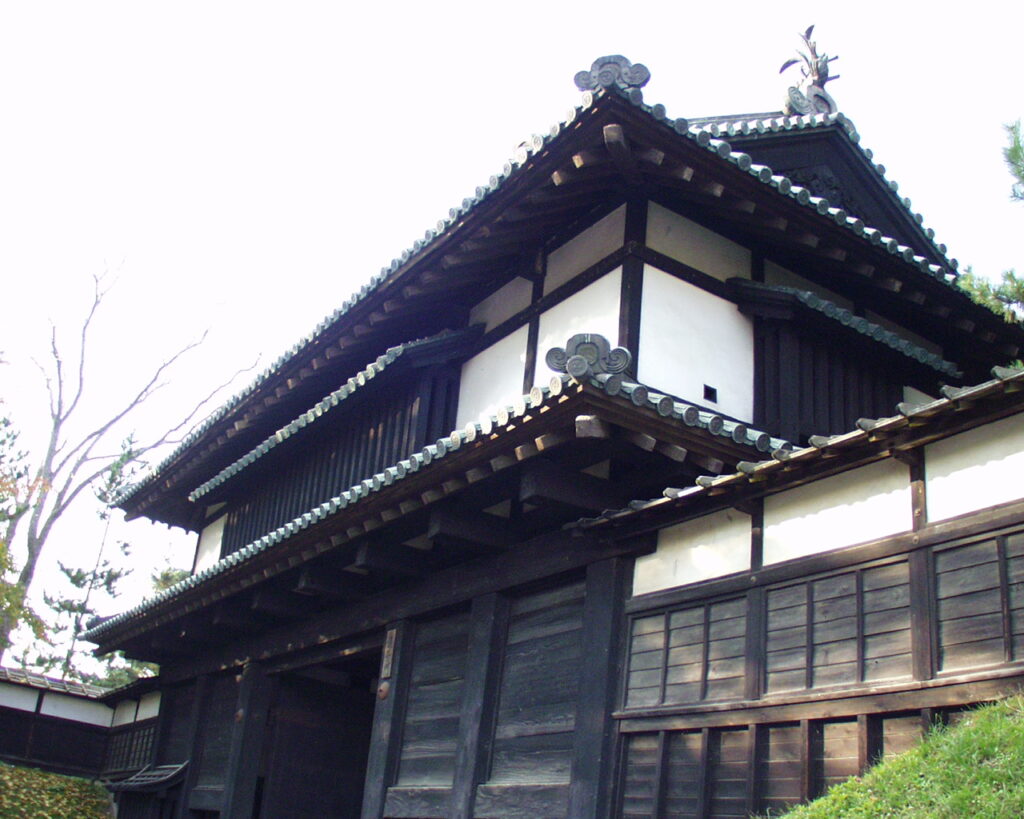
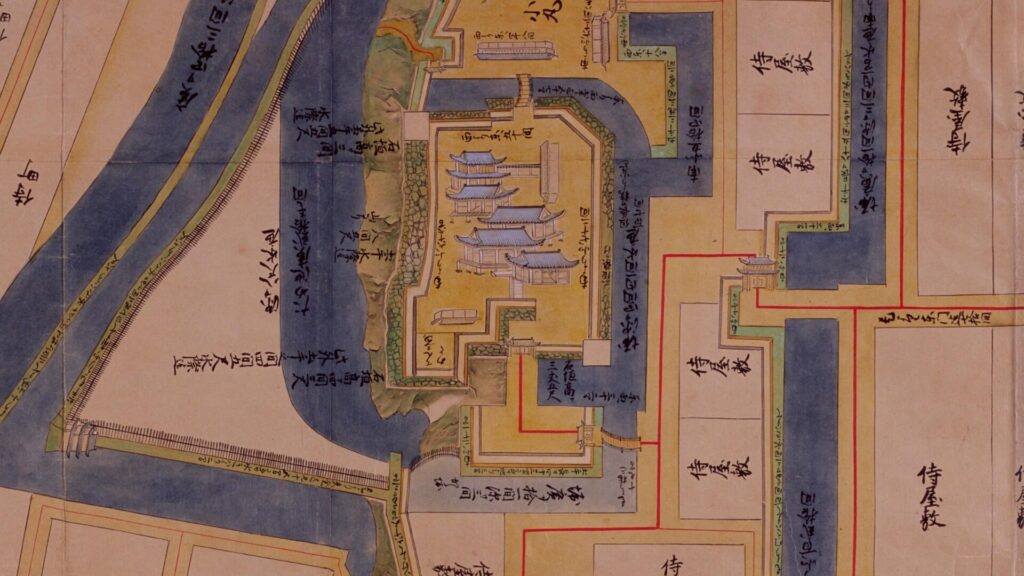
The main portion of the castle ahead still looks very strong, which is surrounded by the inner moat and two-tiered high stone walls. These tiers consist of the main enclosure on the top and the surrounding Take (bamboo)-no-maru Enclosure. You need to go across the earthen bridge over the moat and the ruins of Shimizu(pure water or spring)-mon Gate to enter it. The gate was the largest one in the castle and Shirakawa City is actually planning to restore it by 2026 (as of January 2024). Next, if you climb the stone steps and turn right on the Take-no-maru Enclosure, you will see the three-level turret close by.
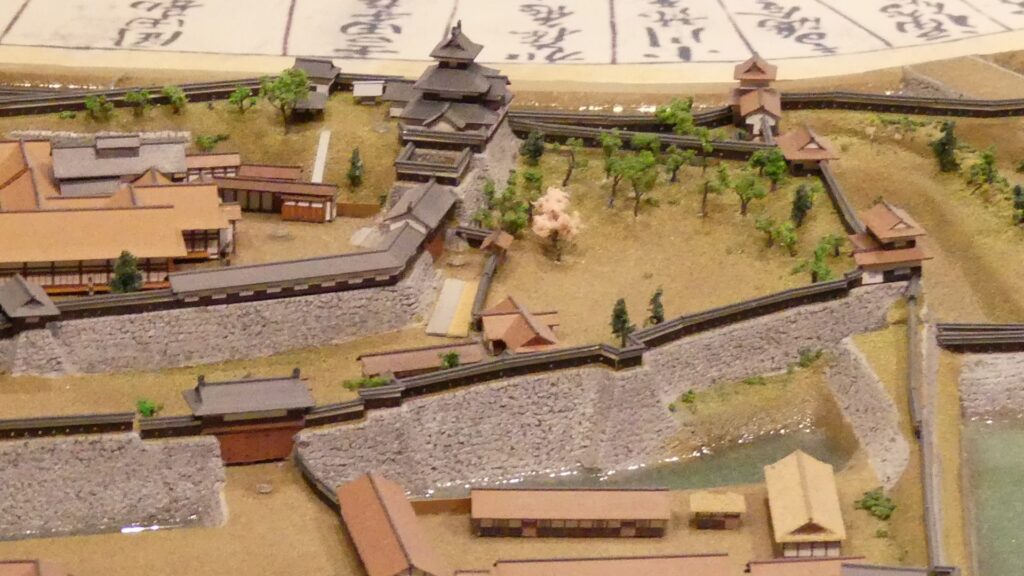




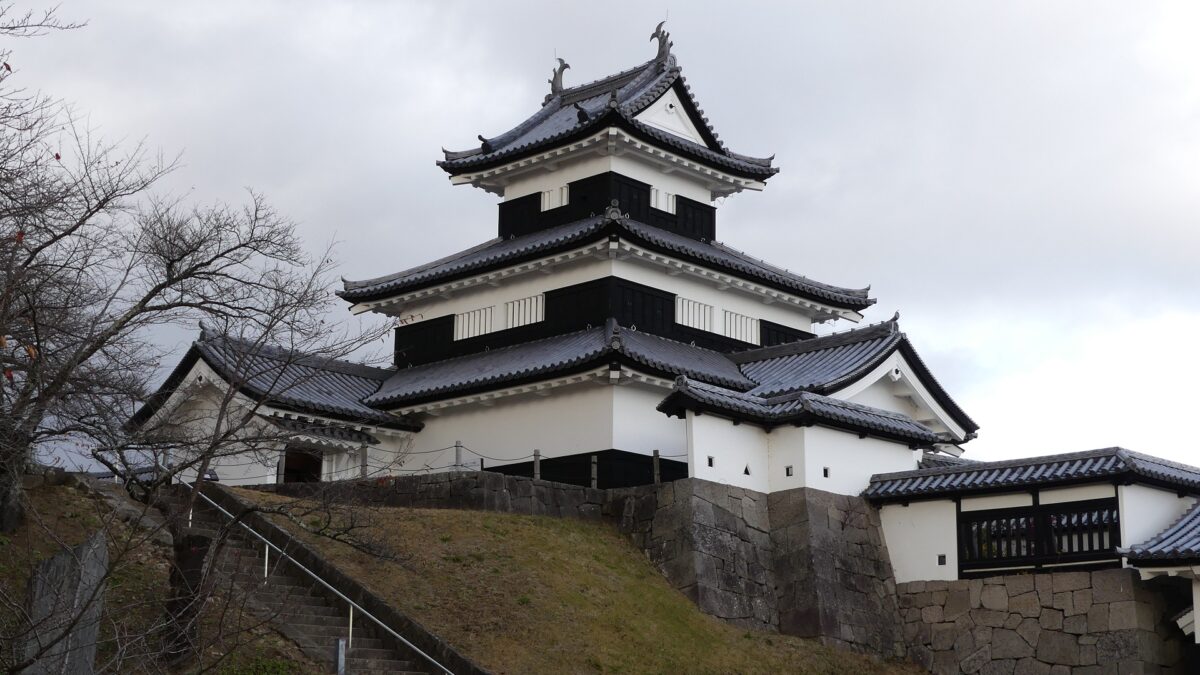
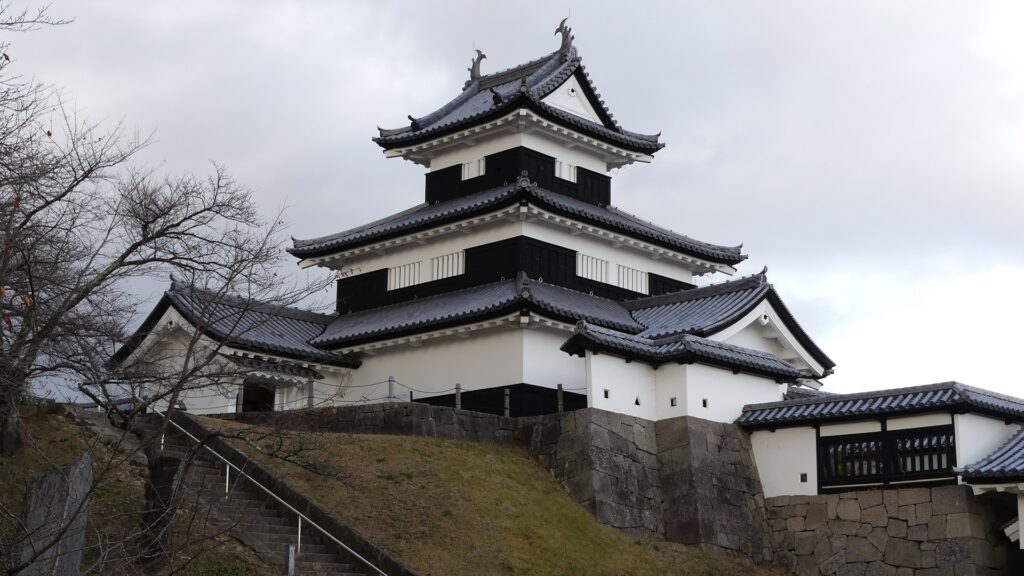
Good Combination of restored Turret and Gate
You can also see Mae-gomon (meaning the front gate) next to the turret which has been restored in the original way since 2004, following the turret. The set of the turret and the gate looks very good and shows the authority of the castle. If you enter the gate, you will be at the main enclosure, which is an empty space but had the main hall for the lord in the past.
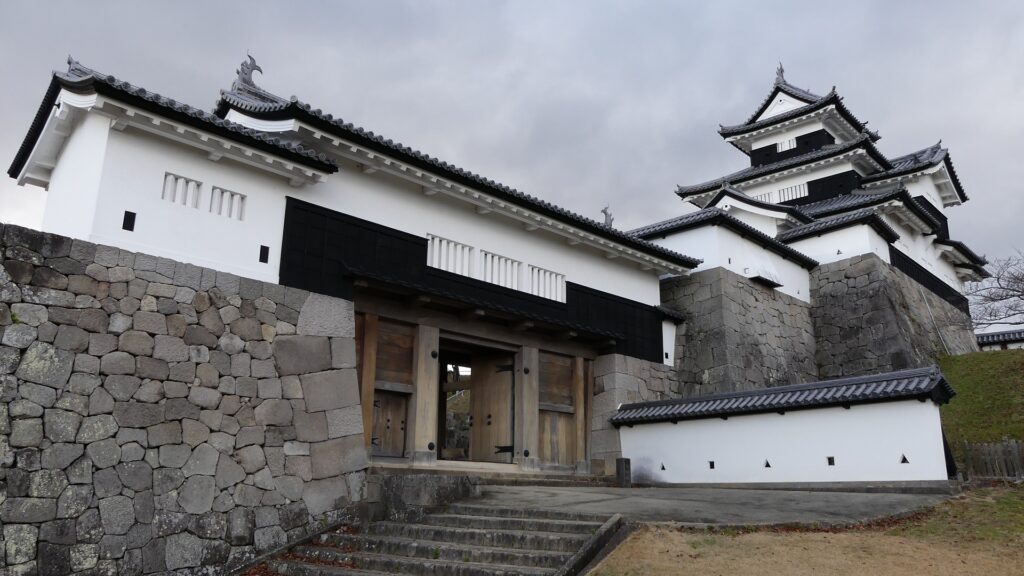



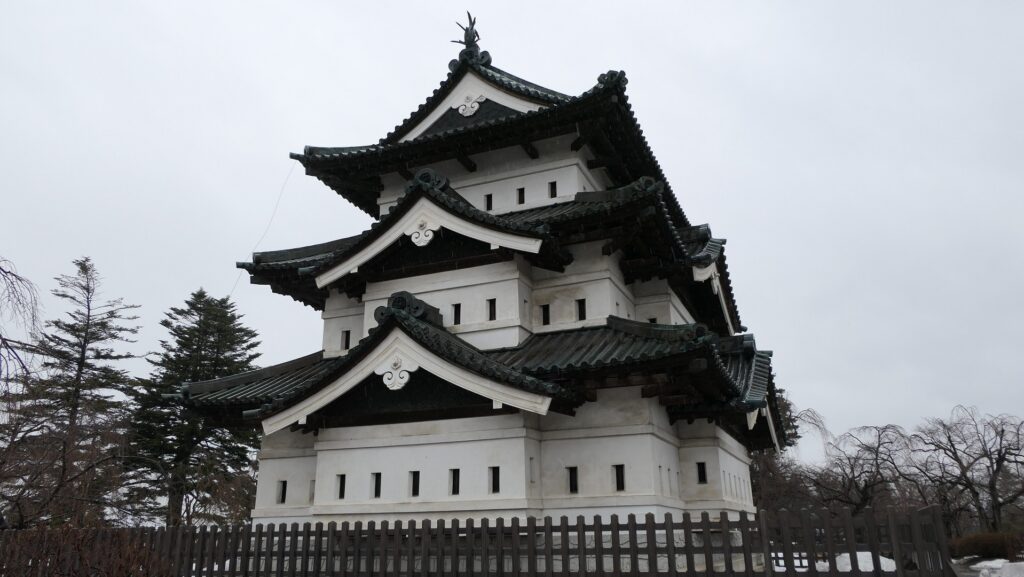
The three-level turret stands on the northeastern corner of the enclosure. Its three floors are simply built with the 11.7meters (6 Ken in the traditional Japanese unit of length) square of fist floor, the 7.8 meters (4 Ken) square of the second one and the 3.9 meters (2 Ken) square of the top one. Each level also has simple roofing and has two-tones of colored walls from white plaster and black-painted lumber. Overall, the tower looks very beautiful with its good design and color arrangement.

Interior of Turret is completely restored as well
You can enter the turret from the inside of the enclosure. From the processes of restoring this turret, officials always stay inside and monitor the safety of the visitors. For example, only five visitors can stay above the first floor at the same time under the current regulations. That’s because the turret was restored exactly in the same way as the original one except for the minimum safety equipment and explanation boards. If you walk around the first floor, you will find that it is not bright and many columns standing inside. Some of the columns came from pine trees of Inari Mountain, one of the hills where the severe battles occurred in 1868 during the Boshin War. That’s why you can see the bullet marks, caused by the war, on one of them.
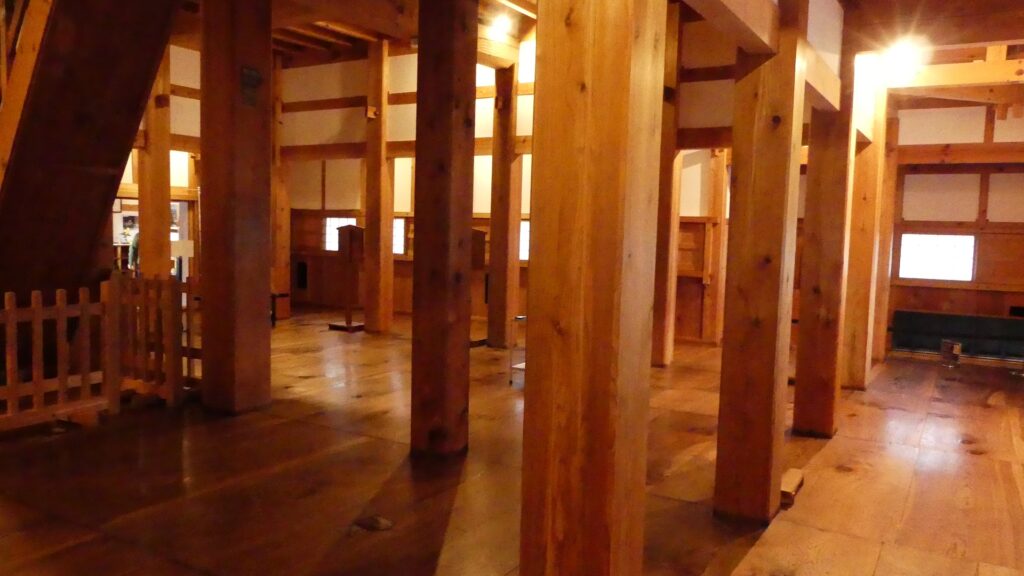


You can also see the defense systems like machicolations, loopholes and bay windows at the northern and eastern sides of the floor. These sides face the outsides of the enclosure, which could have been attacked by enemies.


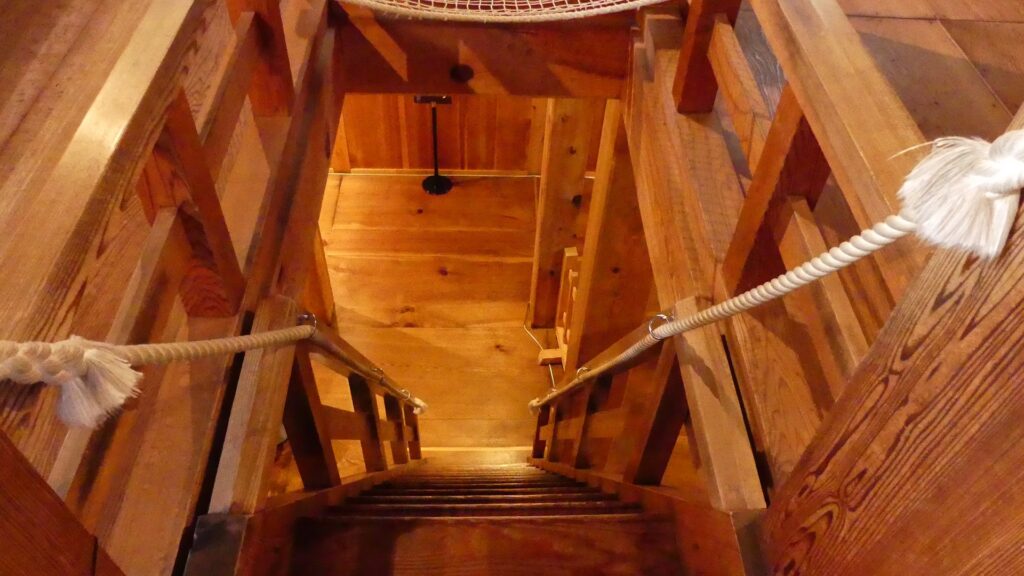
If you want to go to the second and third floors, please be careful when climbing the very steep stairways, but you can use the handrails and ropes.


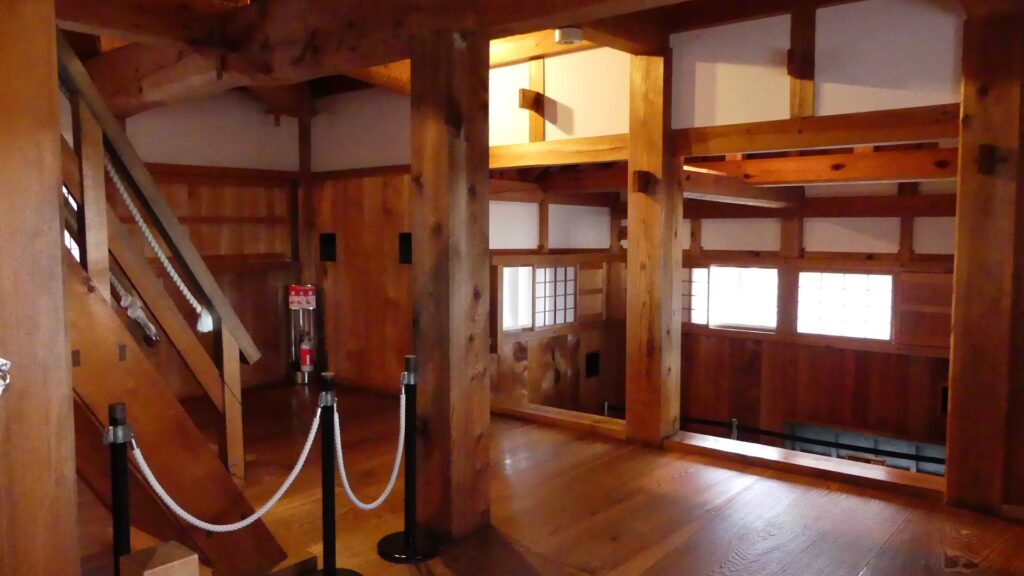
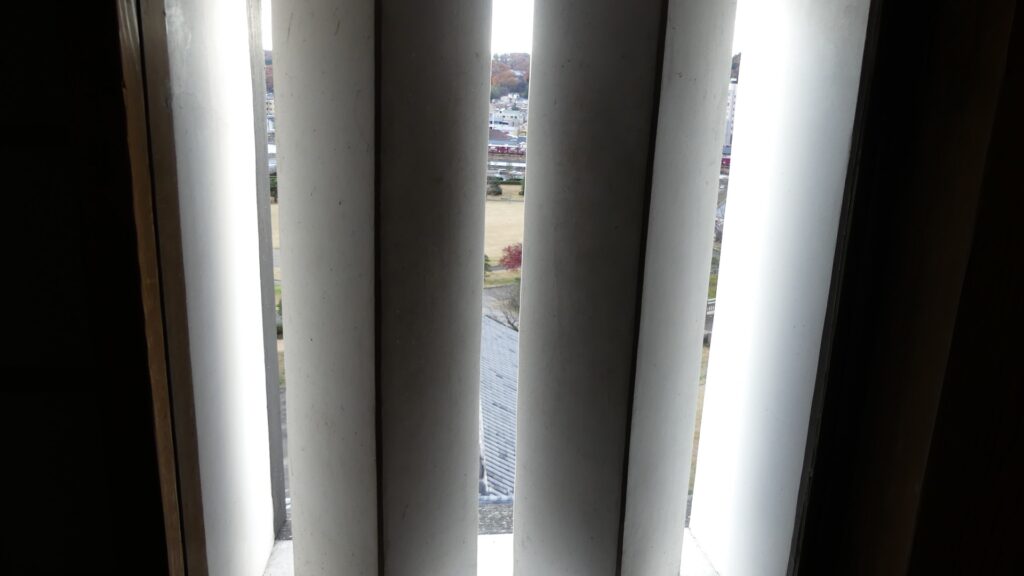
As you go above, the floor becomes smaller and you may feel you are in a box on the top floor. The floor also has defense systems similar to other floors, where you can understand the turret is very practical for battles. In addition, you can see views of the outside through the lattice windows of the floor.



To be continued in “Shirakawa-Komine Castle Part3”
Back to “Shirakawa-Komine Castle Part1”