立地と歴史~Location and History
舟運で繁栄した出羽国~Dewa Province Prospering by Ships
近代以前、大量輸送は船によって行われましたが、海上での航海は危険でした。船が十分発達していなかったからです。日本の場合、中世においては、商業船は主には太平洋ではなく、瀬戸内海や日本海などの内海を航行していました。そのため、当時は内海沿いの大きな港をもつ地域が繫栄しました。出羽国(現在の秋田、山形県を合わせた範囲)はそのような地域でした。
Before the Modern times, mass transportation was done by ships, but sailing on ocean could be dangerous because ships were not developed enough. In the case of Japan, in the Middle Ages, merchant ships sailed mainly on islands seas, such as the Seto Island Sea and the Japan Sea, not on the Pacific Ocean. For this reason, areas with a large port along the island seas prospered at that time.
Dewa Province (combining what is now Akita and Yamagata Prefectures) was one such areas.

秋田で力をつけた安東氏~Ando Clan has power at Akita
安東氏は、北出羽(大体今の秋田県)を根拠地として海上交通を支配して大きな勢力となりました。戦国時代(日本中の地方大名が覇権をめぐって争った時代)には安東氏は、檜山安東氏と湊安東氏の2つのグループに分かれていました。檜山安東氏は北秋田にあった檜山城に住み、湊安東氏は南秋田にあった湊城を拠点としていました。
The Ando Clans had a great power to manage the marine transportation based in the north Dewa (roughly now Akita Prefecture). In the “Sengoku” Period- a period when local clans around Japan were fighting for control over all of the country- the Ando Clans was divided into two groups namely the Hiyama-Ando Clan and the Minato-Ando Clan. The Hiyama-Ando Clan lived in Hiyama Castle which was located on the northern part of Akita, while the Minato-Ando Clan lived in Minato Castle located on the southern part of Akita.
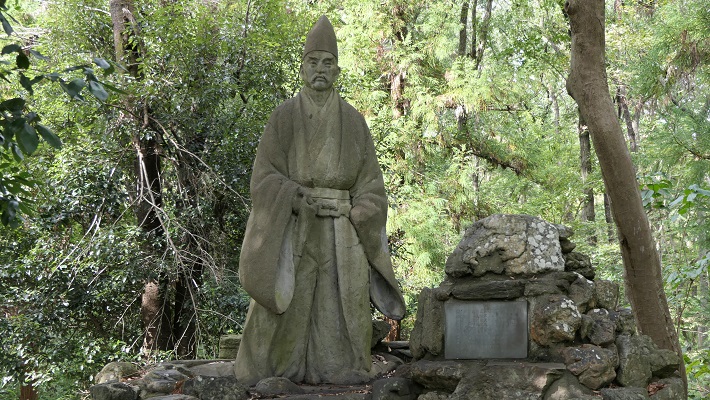
安東愛季は、最初は檜山安東氏の総領でしたが、湊安東氏に固有の跡継ぎがいなかったため、取り込むことに成功しました。彼は、秋田全域を統治することで最も有力な戦国大名の一人になったのです・
Chikasue Ando was at first the lord of the Hiyama-Ando, but was able to take over the Minato-Ando as it didn’t have its own successor. As a result, he ruled over the entire Akita and became known as one of the greatest warlords.

安東愛季が脇本城を拡張~Chikasue Ando develops Wakimoto Castle
愛季は1577年、彼の本拠地を檜山城と湊城の間にある城に移しました。彼が選んだ城が脇本城だったのです。この城は最初は15世紀に築かれたと言われていますが、その後愛季が東日本では有数の規模の山城にまで拡張しました(約150ヘクタール)。この城は、男鹿半島の根元にある100mの高さの丘の上に築かれ、重要な商業港であった土崎湊の近くでもありました。また、主要道路の「天下道」が城の中を通っているため、非常に戦略的な立地であり、城の領主は完全に交通を制御することができました。
Chikasue moved his home base to a castle located between Hiyama and Minato Castles in 1577. The castle that he chose was the Wakimoto Castle. The castle is said to be first built in the 15th century, then Chikasue developed the castle as one of the largest mountain castles in eastern Japan (about 150 hectare). The castle was located on a 100m high hill in the connecting part of Oga Peninsula, near an important trading port called Tsuchizaki-minato. This location proved to be very strategic as a main road called “Tenga-michi” ran between the two sides of the castle giving the Lord full control over transportation.
愛季は支配者として絶頂期にあって、領土を拡張する一方、織田信長といった外の有力戦国大名とは手紙や贈り物により親交を深めました。ところが、1587年の戦いのさ中、彼は突然の病に倒れ、亡くなってしまいます。彼の息子、実季は湊城に住み、最終的には1602年に徳川幕府により関東地方に移されてしまいました。脇本城はそれから廃城となってしまったようです。
Chikasue was at the peak of his career as an administrator expanding his territory and building relationship with other great warlords such as Nobunaga Oda by sending letters and gifts. However, during a battle in 1587 he suddenly fell ill and died. His son, Sanesue lived in Minato Castle and was lastly transferred to Kanto Region by the Tokugawa Shogunate in 1602. Wakimoto Castle seemed to be abandoned since then.

特徴~Features
城跡へ登っていく~Walking up to Castle Ruins
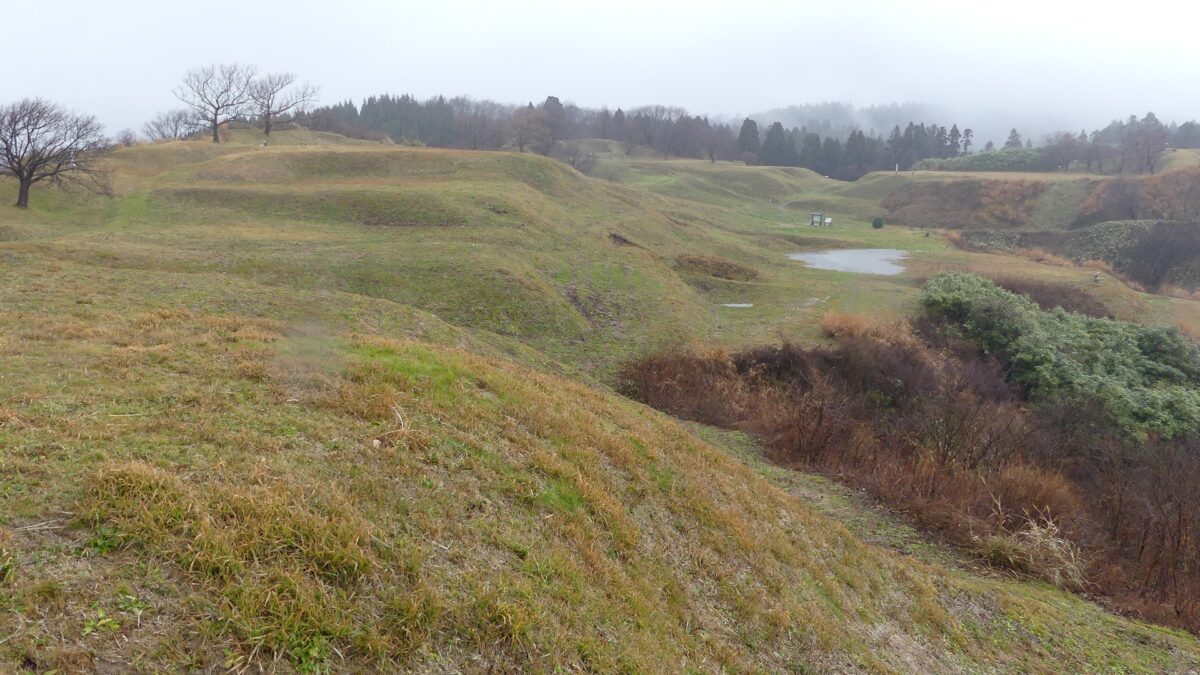
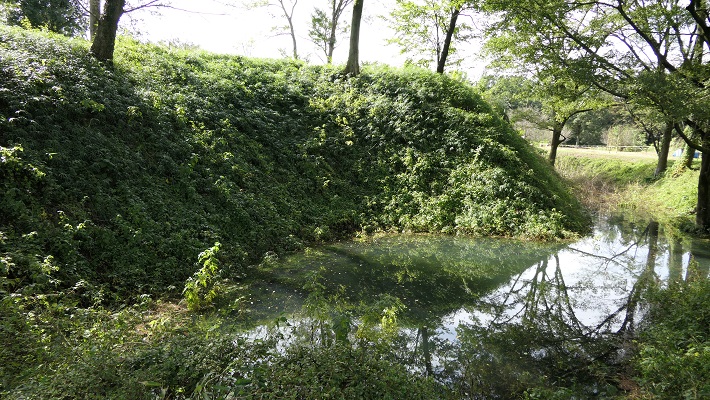
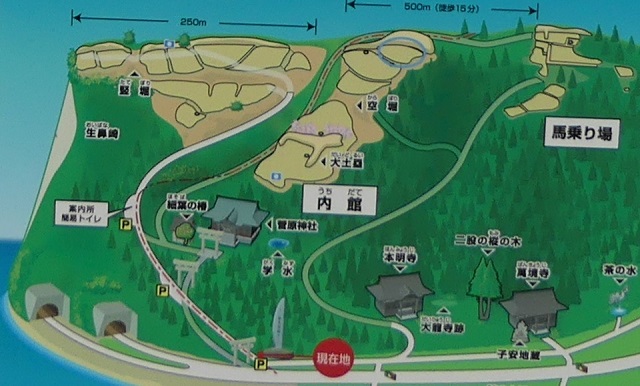
現在、脇本城跡は今もって非常に広大であり、5つの地区に分けられています。しかしながら、5つの地区全てが等しく整備されているわけではありません。そこで、私の訪問時には、一番整備されている「内館」1箇所を見学しました。ここは城の中心部分であり、現在はより整備されていて、観光客が訪れやすいようになっています。
Now, the ruins of Wakimoto Castle are still very large, and they are divided into five areas. However, not all the 5 areas have been developed equally. So, when I visited, I covered the one that was most developed which is “Uchidate”. This was the main portion of the castle, and now is further developed for tourists to visit easily.
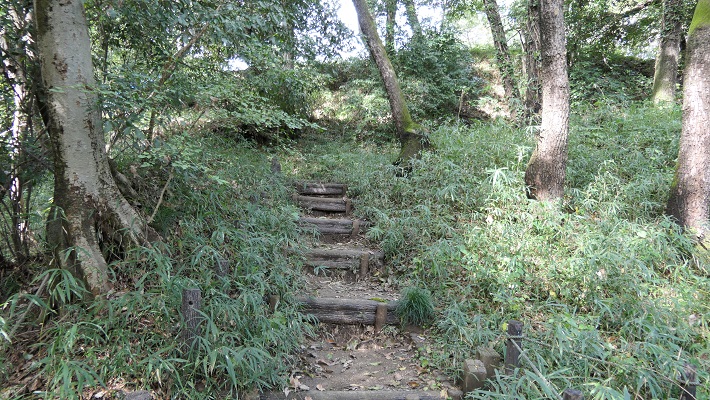
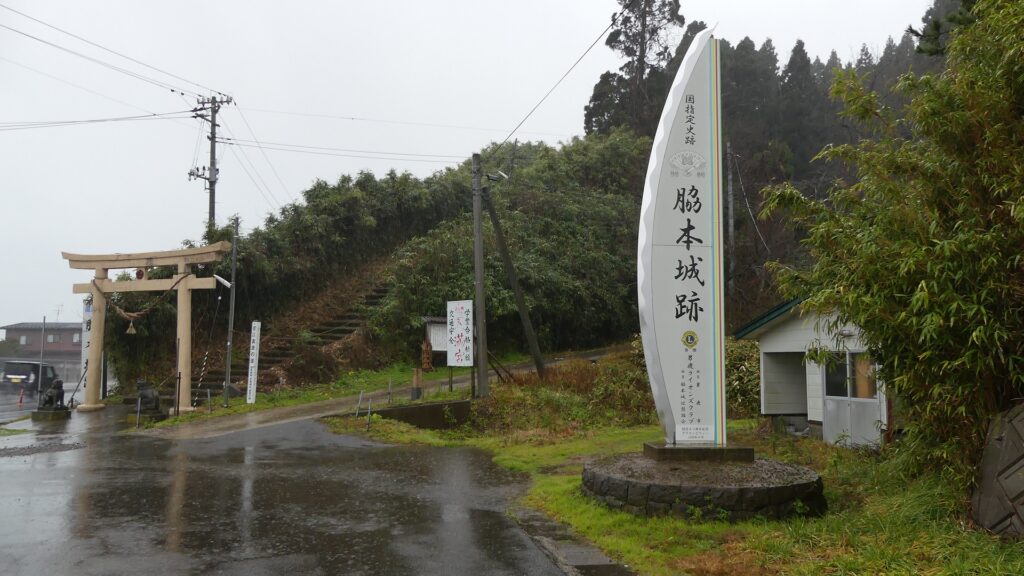
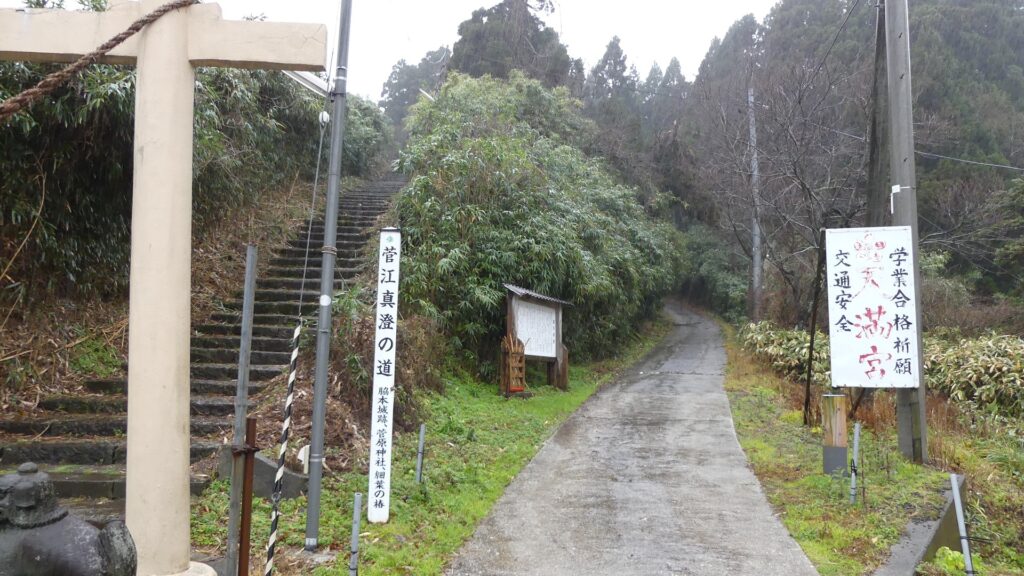
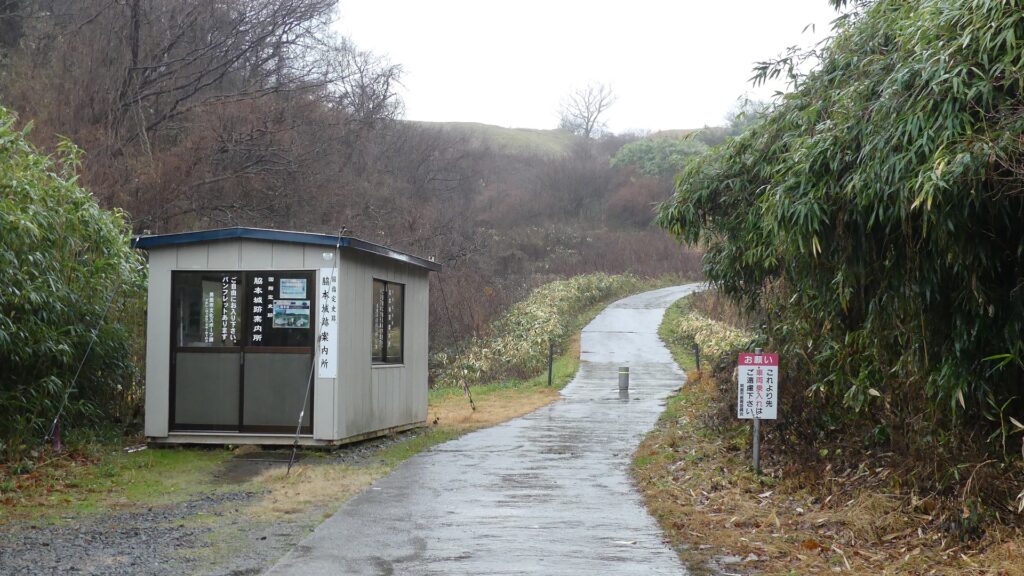
城跡の入口は国道101号線沿いにあります。車で来られた方のために駐車場があります。そこから城跡への道を登っていく必要がありますが、それはかつてからある「天下道」の一部分です。更に進んで城跡の案内所を過ぎると、丘の頂上部分が見えてきます。
The entrance of the ruins is alongside National Route 101. You can park at a parking lot if you are driving. Then, you need to walk up the road to the ruins which was part of the old road, “Tenga-michi”. When you go farther passing through the guide house of the ruins, you will see the top of the hill.



生鼻崎周辺~Around Oihana-saki Cape
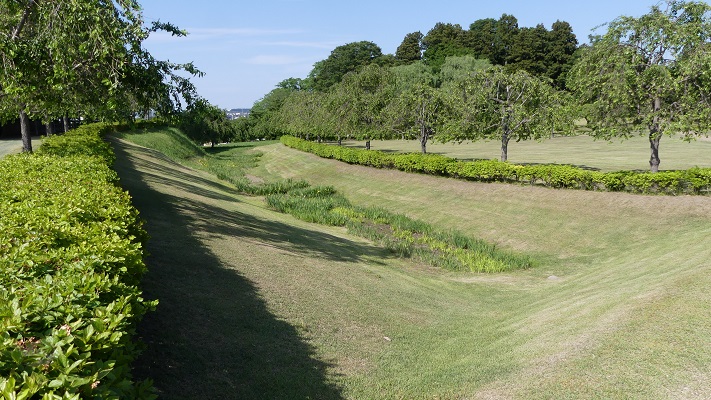
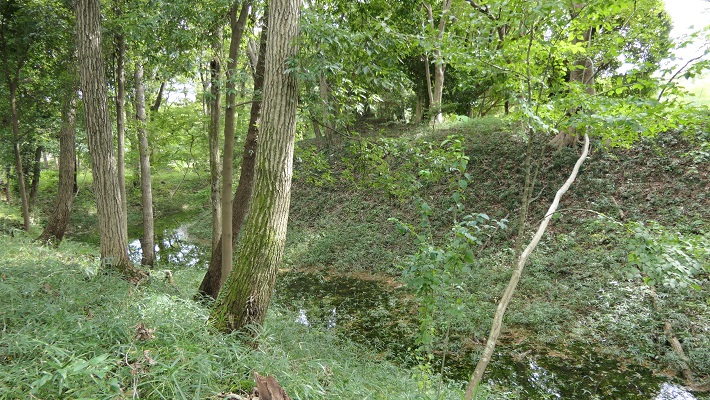
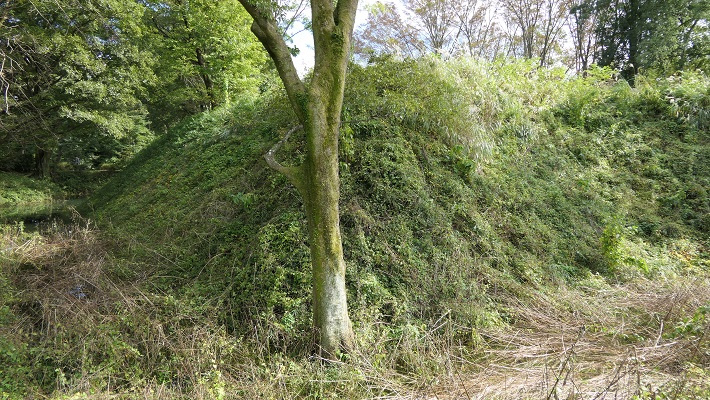
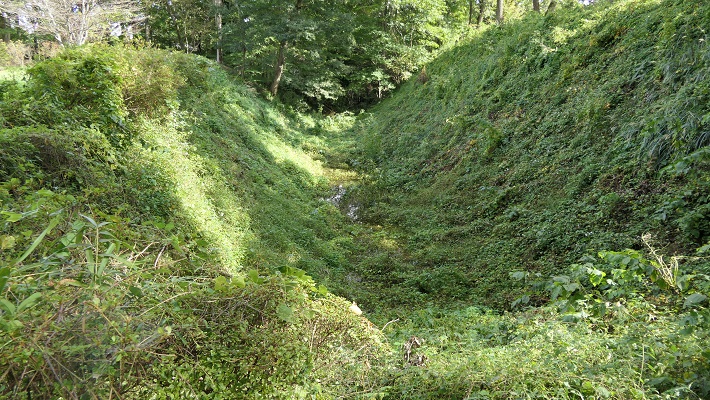
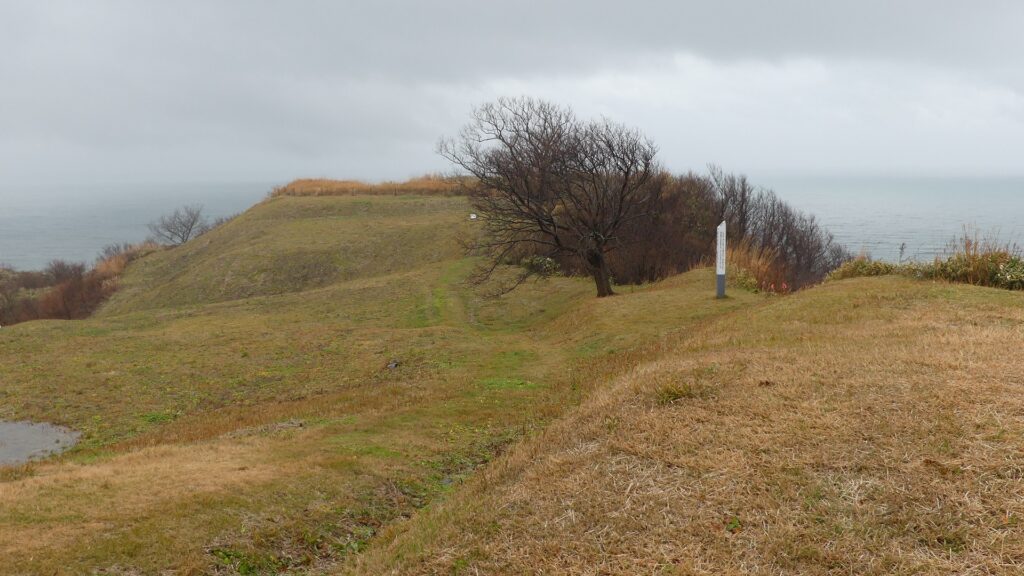
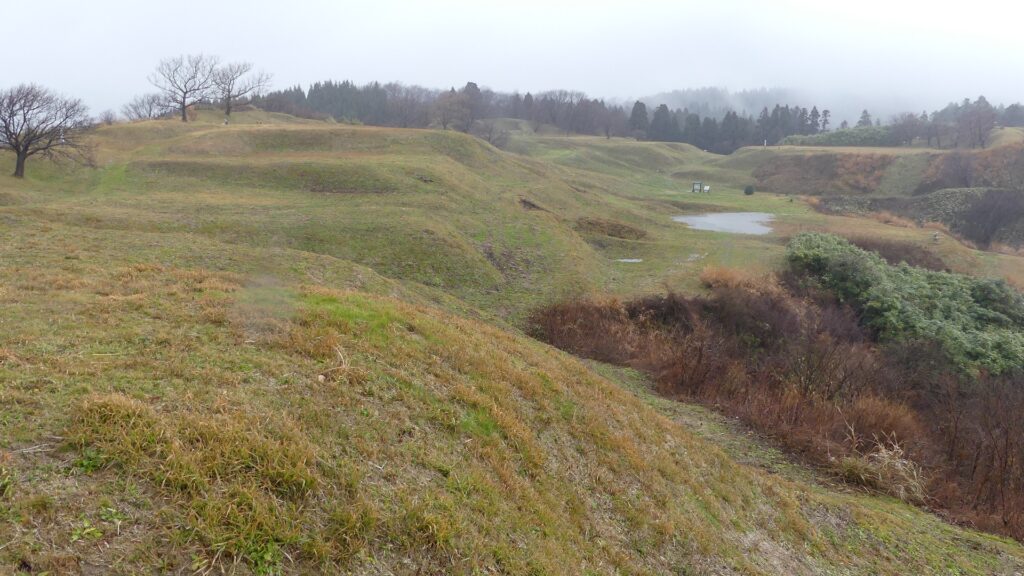
基本的に、戦国時代の東日本では、城の基礎部分は土造りでした。城跡には建物はありませんが、土塁、空堀、虎口などが残っています。丘の頂上に登ってみると、左手(西の方角)には、海に突き出ている「生鼻崎」という岬の上にたくさんの曲輪があるのがわかります。それらの曲輪は岬の先端に向かって列を作って並んでいます。実はかつてはもっと多くの曲輪が岬と共に海に伸びていたのですが、江戸時代の地震のときに崩壊してしまいました。歴史家はこれらの曲輪は安東氏の家臣の屋敷地として使われたのではないかとしています。岬の先端では、日本海の荒々しい姿が見えます。
Basically, the foundations of the castles, in eastern Japan during the Sengoku Period, were made out of soil. The ruins have no buildings, instead they have earthen walls, dry moats, entrances, etc. When you climb on top of the hill, you will see a lot of enclosures on a cape called “Oibana-saki”, sticking out to the sea on the left on the west direction. You can see that these enclosures are in lines towards the top of the cape. In fact, there were many more enclosures with the cape spread to the sea in the past, but they collapsed when an earthquake happened in the Edo Period. Historians speculate that they were used for the Ando clan’s retainers’ houses. At the top of the cape, you can also have a wild view of the Japan Sea.
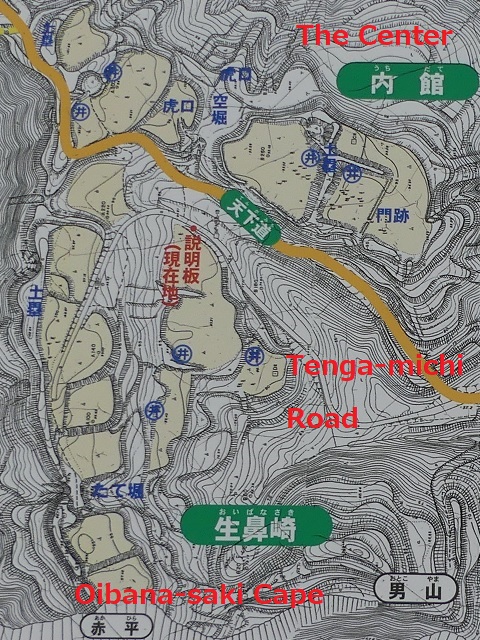



城の中心部分~Center of Castle
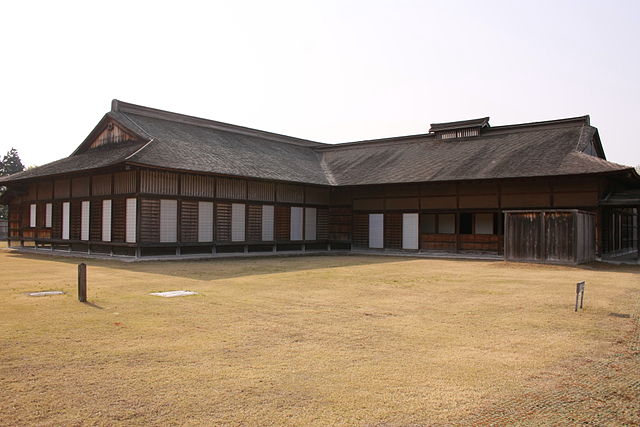
道の反対側の東の方向には、空堀に囲まれたもっと大きな曲輪があります。この辺りが、城の中心地であったと考えられます。歴史家は、北側には別々の目的で作られた2つの建物があったと推定しています。一つは公式の儀式で使われた「主殿」という建物で、もう一つはお客をもてなす「会所」という建物です。
There are two larger enclosures surrounded by dry moats on the opposite side of the route on the east direction. They are supposed to be the center of the castle. Historians also speculate that two buildings on the northern side were used for other purposes. For example one of them was used as the building for the public ceremonies called “Shuden’ and the other for hosting the guests called “Kaisho”.
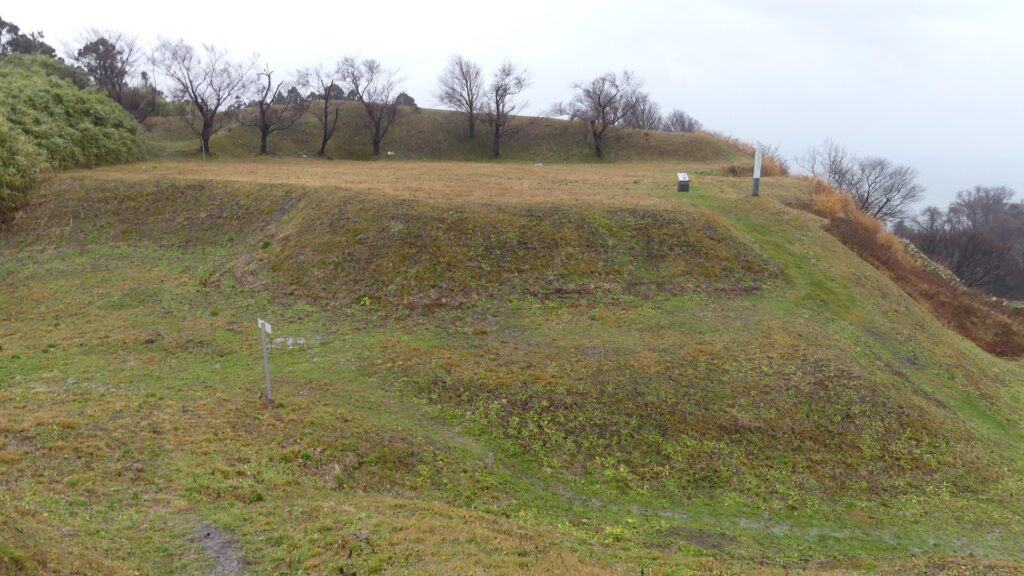
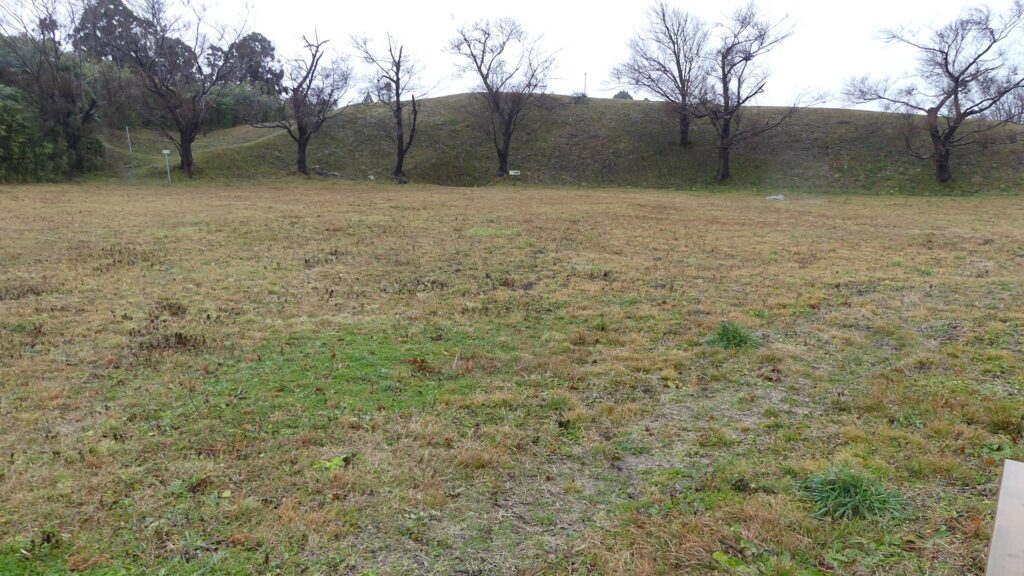



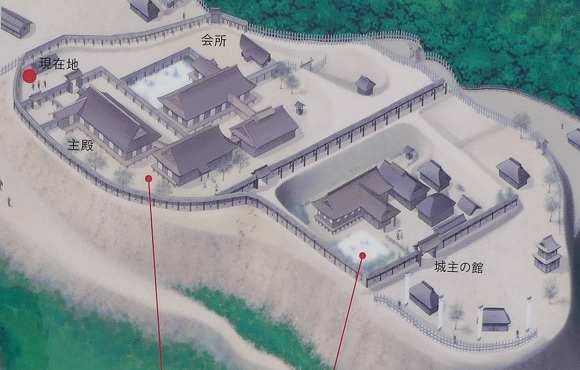
もう一つの南側の曲輪は高くて太い土塁に囲まれており、これもまたとても大きいものです。ここには城主の館があったと考えられています。愛季が住んでいたのでしょうか。この曲輪からは、海岸線とかつては城下町であった街並みの素晴らしい景色が望めます。
The other southern enclosure is surrounded by high thick earthen walls, and it is also very large one. This is thought to be used as the house of the lord. I wonder if Chikasue lived in it. From the enclosure, you can also have a great view of the coast line and the town which was once the castle town.
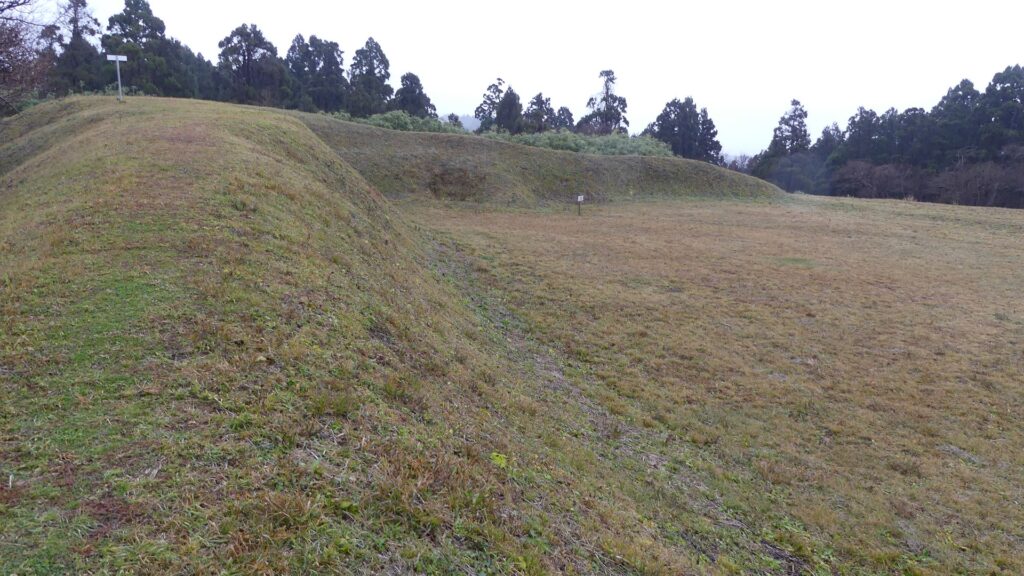


その後~Later History
江戸時代の1804年、有名な旅行家の菅江真澄が脇本城の城跡を訪れています。彼は日記に城跡のことを記録し、スケッチも残しました。1993年からは調査が行われており、この城が非常に大きな規模であったことがわかりました。そのため、城跡は2004年に国の史跡に指定されました。
In 1804 of the Edo Period, a famous traveler, Masumi Sugae visited the ruins of Wakimoto Castle. He recorded the ruins on his diary and left his sketches of them. Investigations have been done since 1993 and it was found out that the castle had a huge scale. Because of it, the ruins were designated as a National Historic Site in 2004.

私の感想~My Impression
私が脇本城跡に行ったときは、ひどい天気でした。更に「内館」地区しか行っていません。それでもこの城跡が大変な規模だということは言えます。もし晴れた日に十分時間が取れれば、もっと城跡を満喫できると思います。他の有名な城に比べてこの城の研究は始まったばかりです。この城から新たな発見がもたらされるのが楽しみです。
When I visited the ruins of Wakimoto Castle, the weather was very bad. In addition, I saw only one area called “Uchidate”, but I was able to witness the large scale of the ruins. If you have enough time to visit the ruins in a fine day, you can enjoy them more! I think the study for the castle have just started compared with other famous castles. I will be looking forward to seeing the new discovery from the castle.

ここに行くには~How to get There
車で行く場合:秋田自動車道昭和男鹿ICから約30分かかります。城跡の入口に駐車場があります。
電車の場合、JR男鹿線脇本駅から城跡まで歩いて約30分かかります。
東京から脇本駅まで:新幹線に乗り、秋田駅で男鹿線に乗り換えてください。
If you want to go there by car: It takes about 30 minutes from the Showa-Oga IC on Akita Expressway. There is a parking lot at the entrance of the ruins.
By train, It takes about 30 minutes from Wakimoto Station on JR Oga line to the ruins on foot.
From Tokyo to Wakimoto Station: Take the Shinkansen super express and transfer to Oga line at Akita Station.
リンク、参考情報~Links and References
・脇本城跡、男鹿市観光協会(Oga city tourism association)
・「日本の城改訂版第150号」デアゴスティーニジャパン(Japanese Book)
・「土崎港(秋田港)の「みなと文化」/渡辺英夫」(Japanese Paper)