Location and History
Ogasawara Clan is driven away from Castle, but is waiting for their long-cherished plan to revive
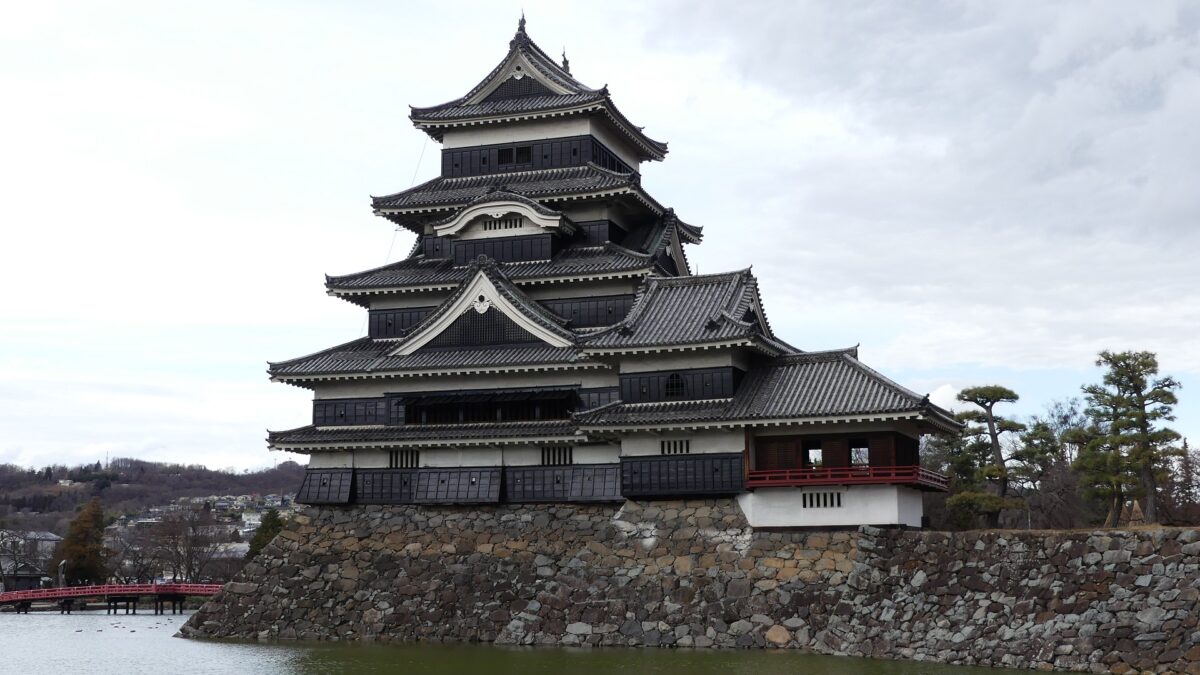
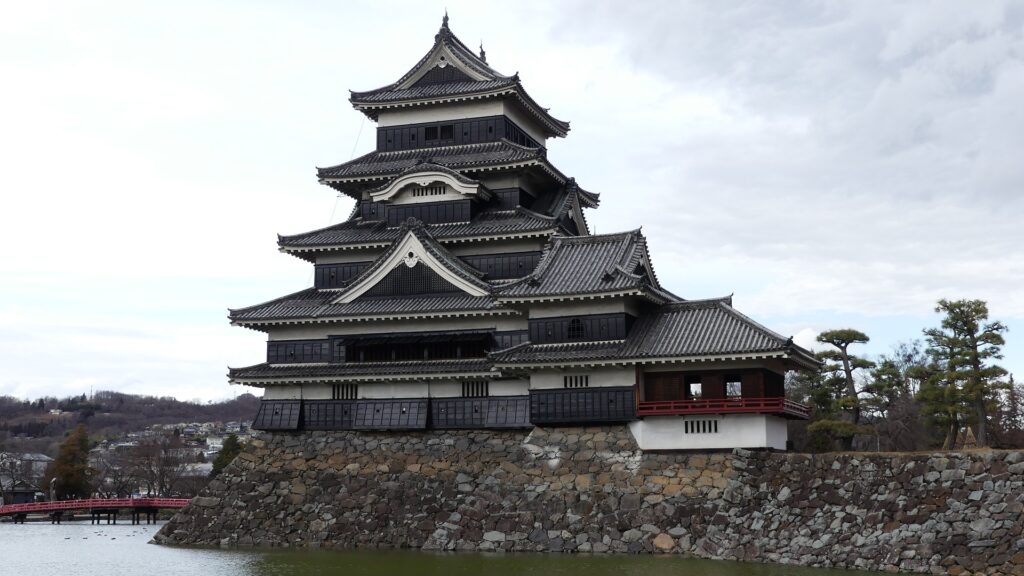
Matsumoto Castle is located in Matsumoto City, Nagano Prefecture, which is known for its wonderful remaining five-level Main Tower. Matsumoto Basin, in which the city is located, has also been known for abundant springs flowing from the surrounding mountains since Ancient Times (we can still see many wells in the city area). That’s why the area was originally called “Fukase” or “Fukashi” which seem to have meant “waters running deep”. The Ogasawara Clan, which became the governor of Shinano Province (now Nagano Pref.), was based in this area during the Middle Ages. Many battles occurred during the Sengoku Period, and Ukon Shimadate, who was a retainer of the clan, built Fukashi Castle (the former Matsumoto Castle) in 1504 to protect the clan’s home, Hayashi Castle. However, they were driven away by the Takeda Clan in 1550, following the Siege of Fukashi.


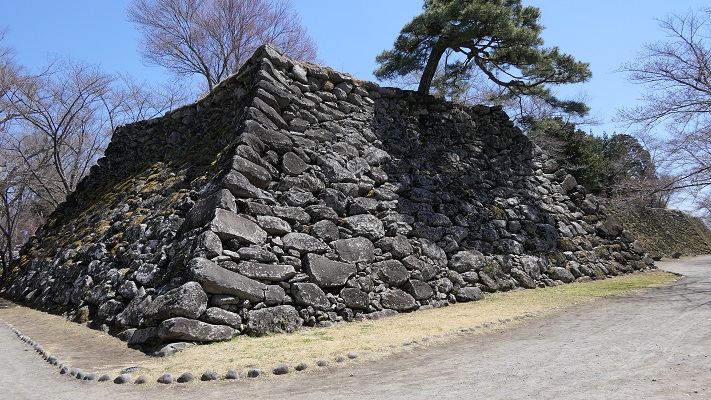
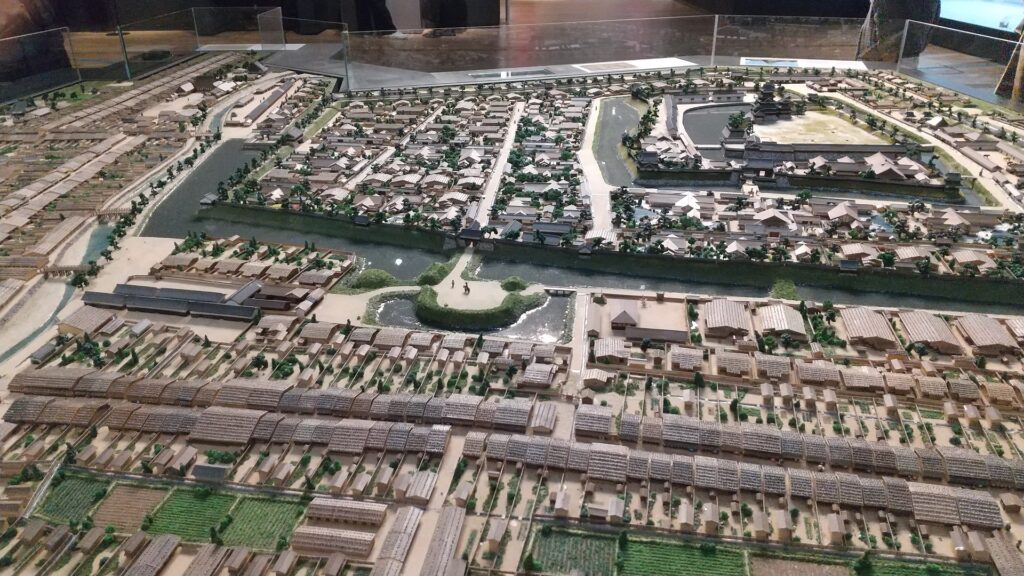
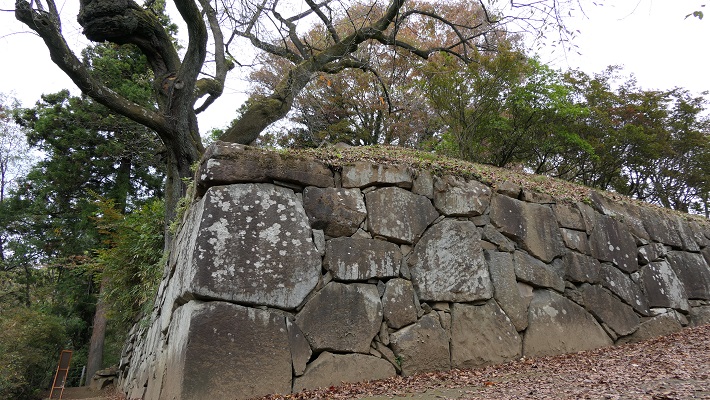
The Takeda Clan fortified Fukashi Castle to be a defensive stronghold even on the flat lands of the basin. The clan had the castle surrounded by tripled water moats. The lands inside the moats were called (from the center) the main, second, and third enclosures. The flow of the Metoba River was diverted to run alongside the outer moat, which made the castle more defensive. The clan also improved the gates of the castle by adding Umadashi systems in front of them. The system refers to a small round enclosure connected by a narrow path to the gate. It was a defense system created and frequently used by the clan. It was said that the basic structures of the castle was completed by the Takeda Clan. However, the castle was still basically made of soil at this point.
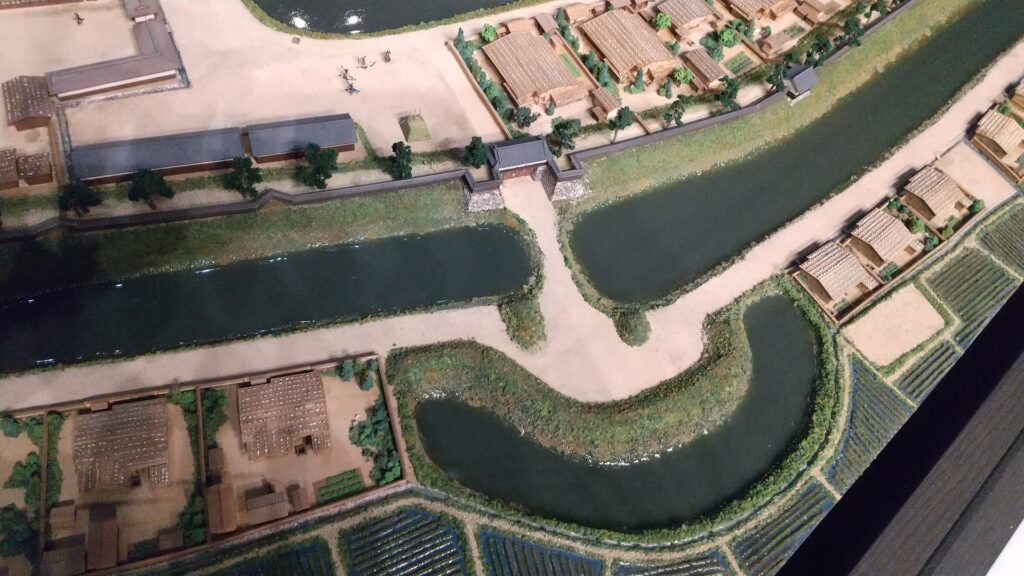





A chance for the Ogasawara Clan to revive suddenly came in 1582 when Nobunaga Oda defeated the Takeda Clan before he was also killed by Mitsuhide Akechi in the Honnoji Incident. Sadayoshi Ogasawara who served Ieyasu Tokugawa returned to Fukashi Castle the following year – for the first time in 33 years, his clan held the castle. He renamed the castle Matsumoto to celebrate the event. The new name was said to come from waiting (matsu) for his long-cherished plan (hon-kai, the Chinese symbol for “hon” is also pronounced “moto”). However, the situation rapidly changed. He and his master, Ieyasu were transferred to the Kanto Region in 1590 by the ruler, Hideyoshi Toyotomi. Hideyoshi gave the castle to Kazumasa Ishikawa who had been a senior vassal of Ieyasu but was acquired by Hideyoshi.


Ishikawa Clan modernizes Castle by building Main Tower
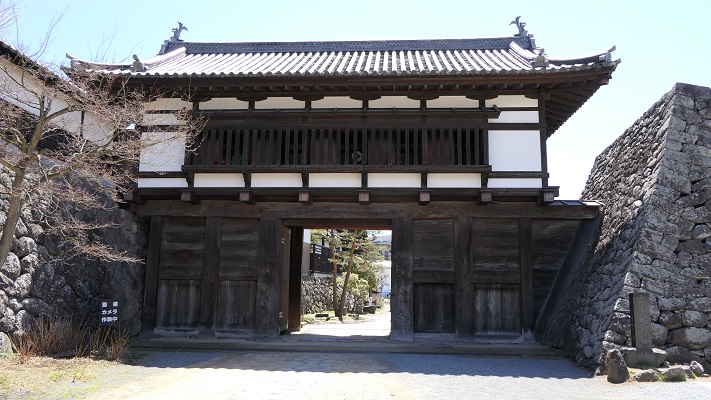
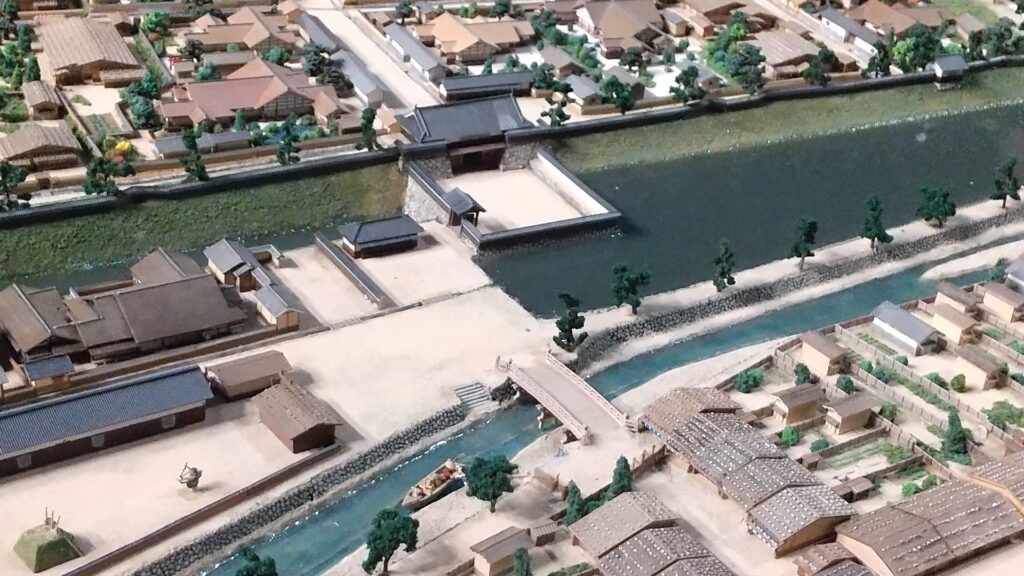
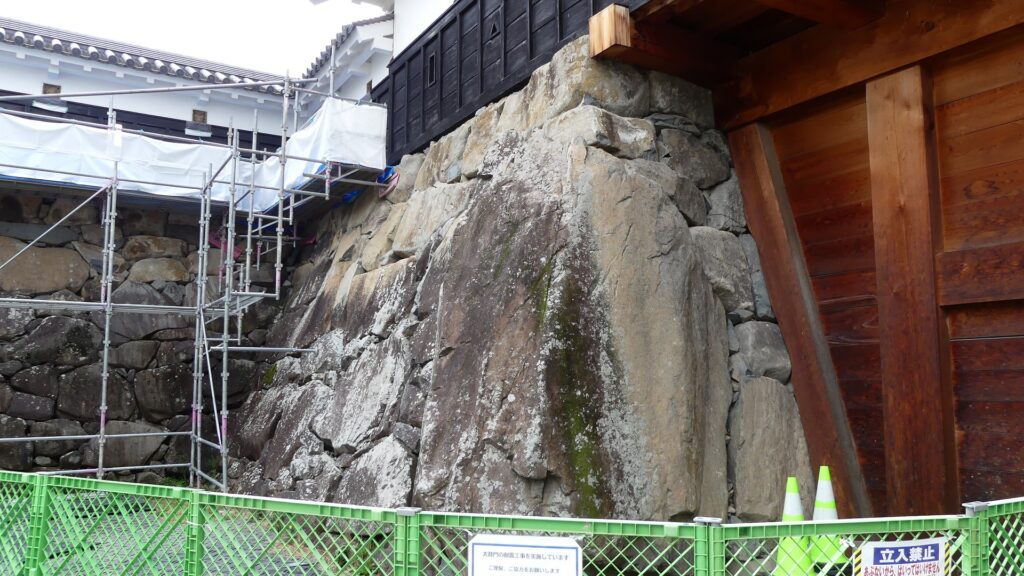
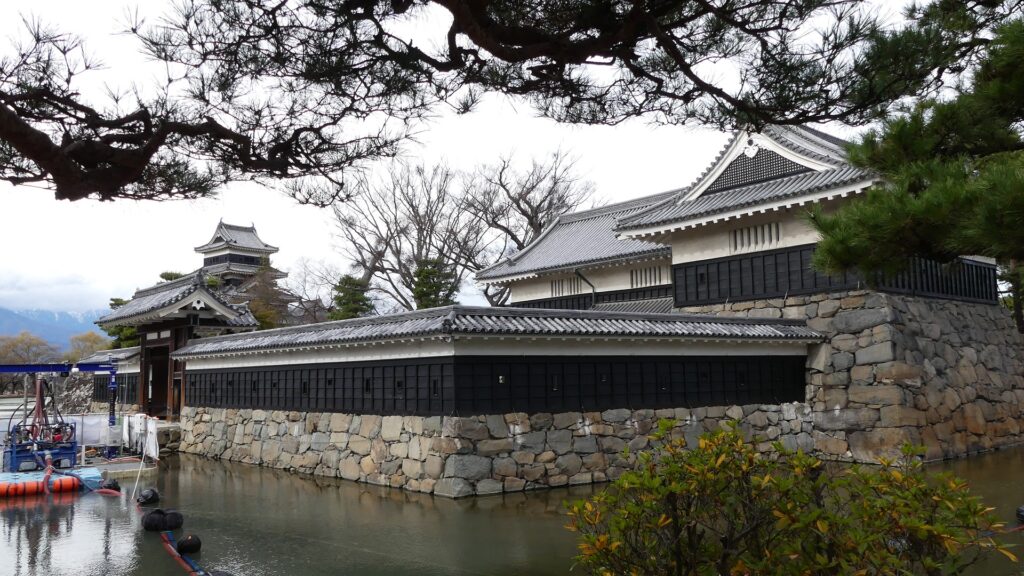
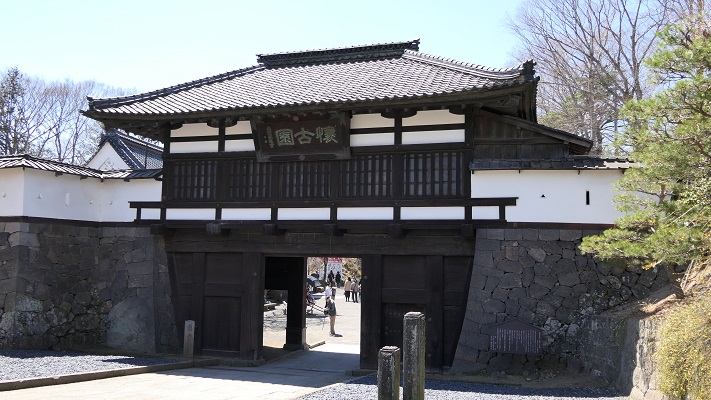
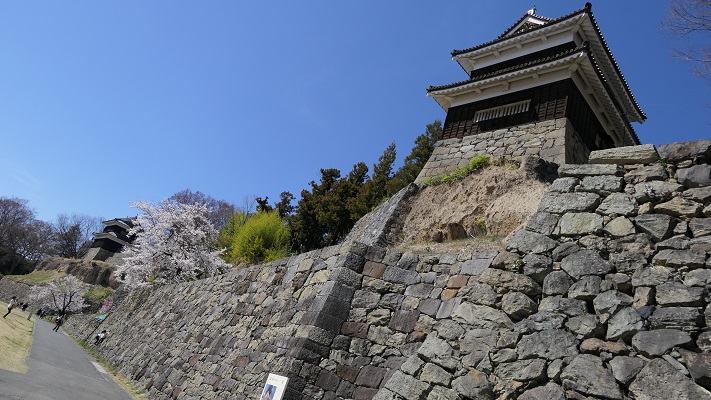
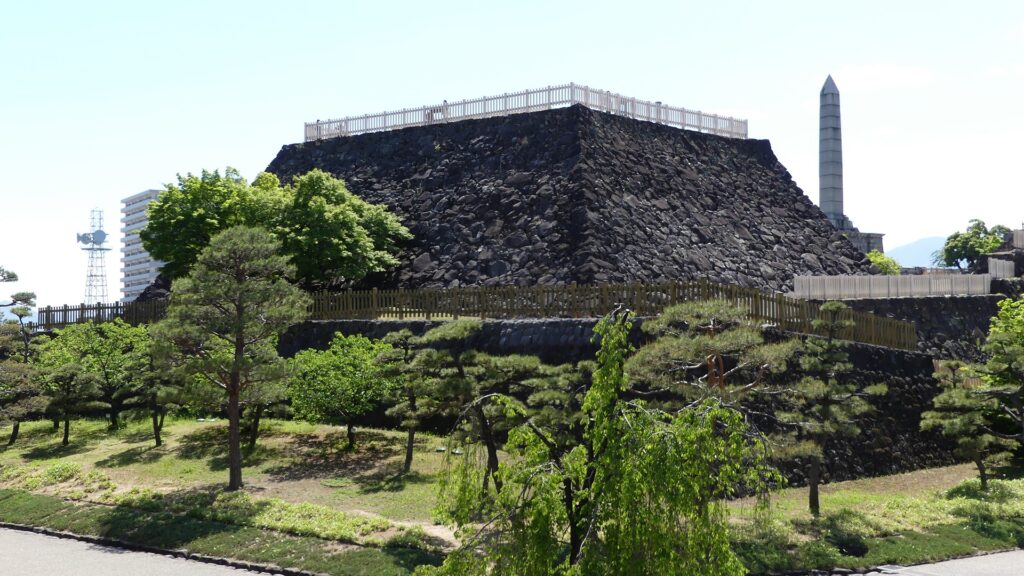
Kazumasa started to modernize the castle using advanced techniques favoured by Hideyoshi, which was continued by his son, Yasunaga after Kazumasa’s death in 1592. Yasunaga built stone walls surrounding each enclosures, including the five-level Main Tower inside the main enclosure. He also replaced the Umadashi system of major gates with the Masugata system. The system refers to a defensive square space surrounded by stone walls and gated buildings. The gates were called Ote-mon (main gate) for the third enclosure, Taiko-mon (drum gate) for the second enclosure, and Kuro-mon (black gate) for the main enclosure. They were completed in 1594. However, local people suffered because of these rapid construction projects. A local legend says that when a worker, who had carried a huge stone for the Taiko-mon Gate, complained about it, Yasunaga heard about it and immediately executed him. Since then, the stone has been called Genba-ishi(stone). Genba was the name of Yasunaga’s official position.
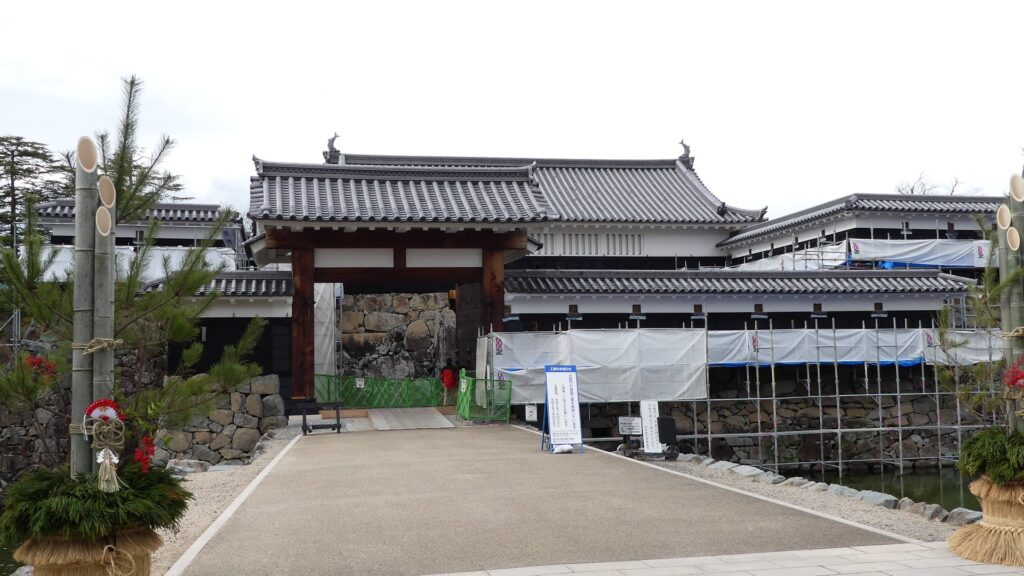





The castle buildings were allowed to use roof tiles with gold leaf with the special permission of Hideyoshi. Such permission was only given to Hideyoshi’s relatives and trusted senior vassals. Other castles of the trusted vassals, which also used the golden roof tiles, were built around Ieyasu’s Kanto Region in places such as Komoro, Ueda, Kofu, Numata, and Sumpu Castle. These castles (including Matsumoto) formed the anti-Ieyasu network to monitor and threaten him. Yasumasa somehow survived even when Ieyasu gained power after Hideyoshi’s death (the golden roof tiles were then scraped). However, he was finally removed by Ieyasu in 1613. The reasons for this remain unclear, but it was possibly Ieyasu’s revenge against the Ishikawa Clan which had abandoned him.
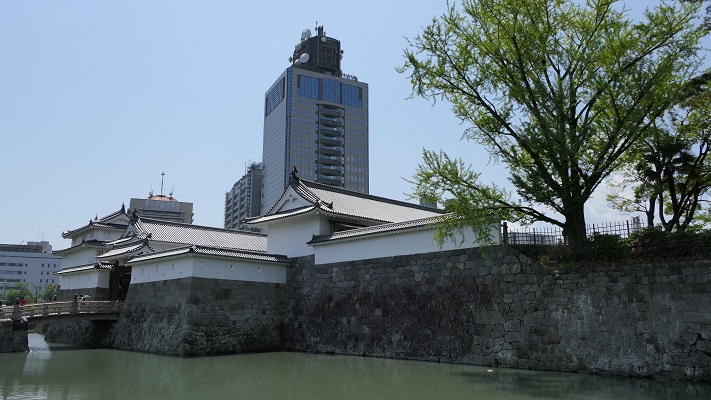





Castle is completed with building Tsukimi Turret
After that, the Ogasawara Clan returned to the castle again but were soon transferred to Akashi Castle in 1617. The castle and the area around it, called the Matsumoto Domain, were followed by the shogun’s relatives and several hereditary feudal lords during the Edo Period. There were also a few important subsequent events for the castle. One of them occurred when Naomasa Matsudaira lived there. He heard about a plan of the shogun, Iemitsu Tokugawa, to visit the castle (though it would be canceled later) and added a new turret called Tsukimi (seeing the moon) Yagura to the Main Tower in 1634. So far, the tower had entirely been designed with battles in mind. This turret, however, was completely built for entertainment. The tower became what we see now, influenced by different tastes.
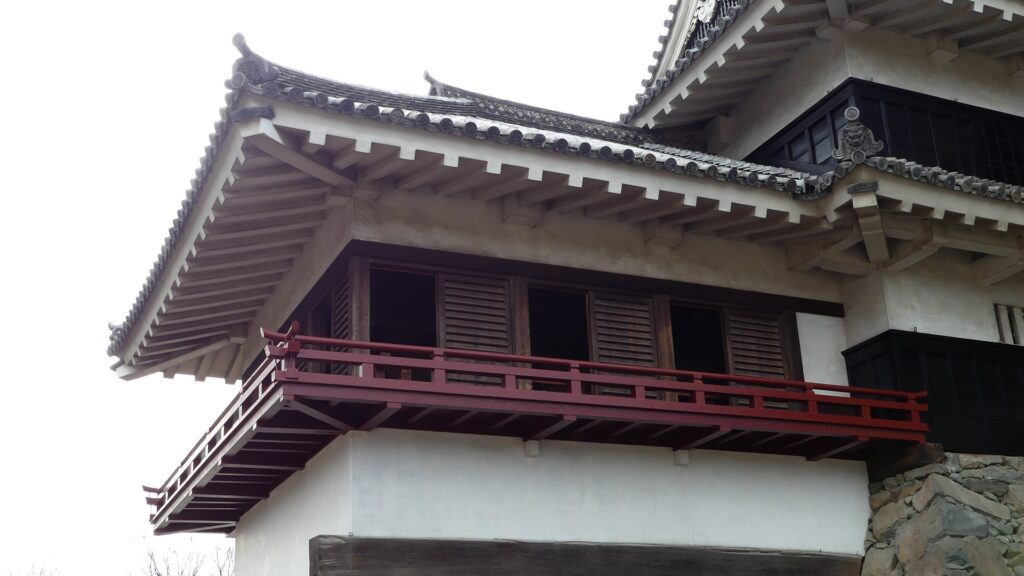
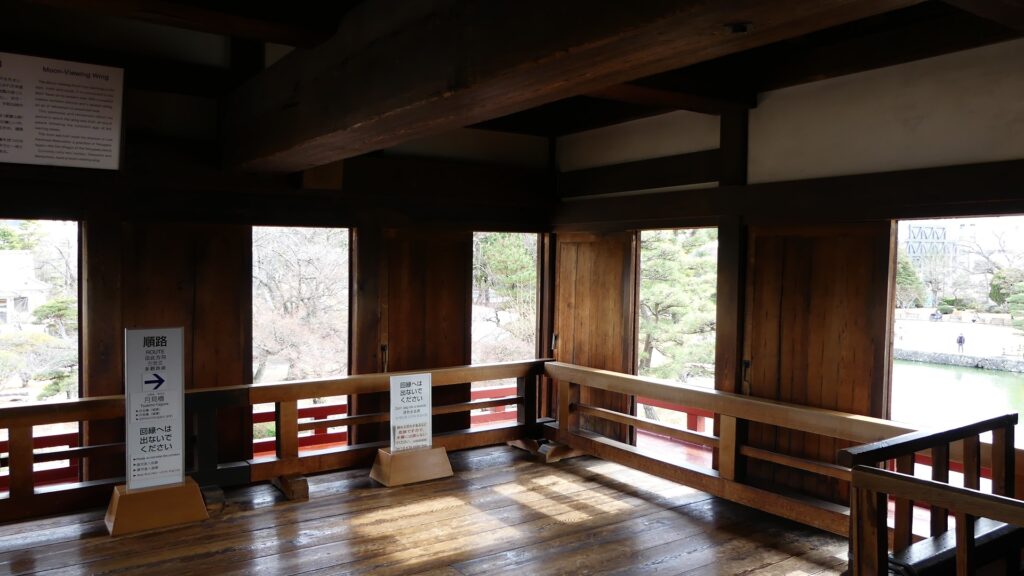




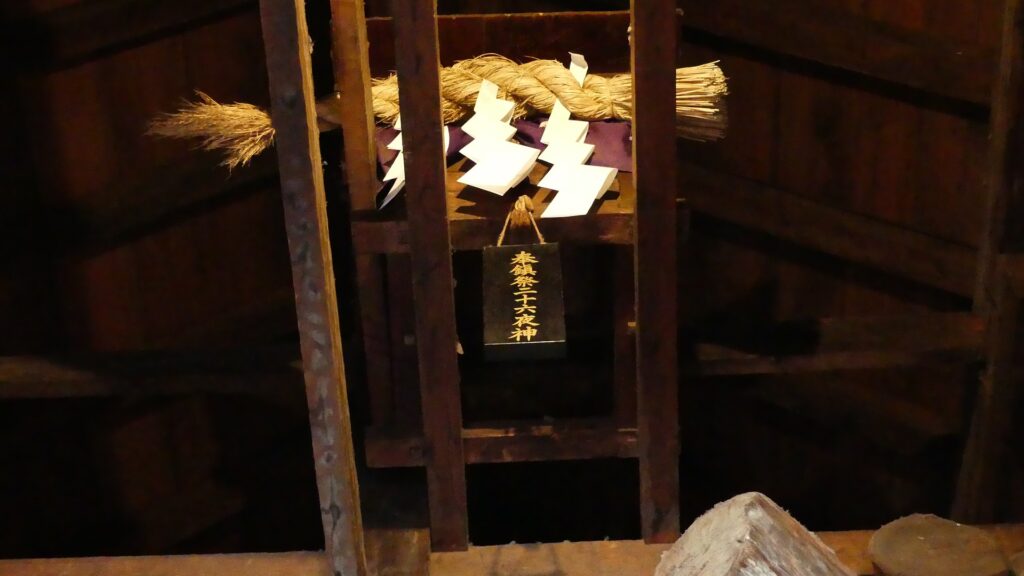
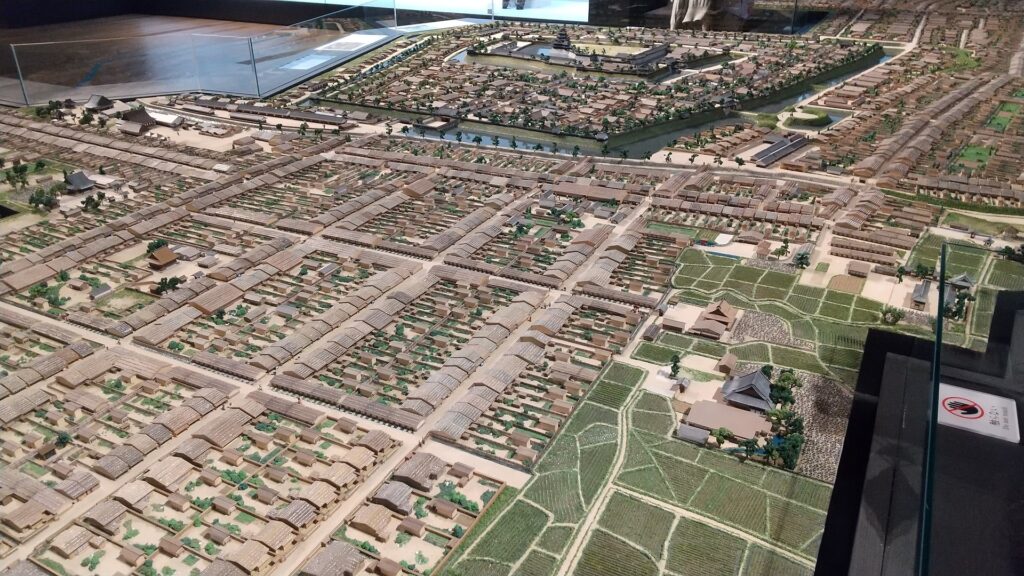
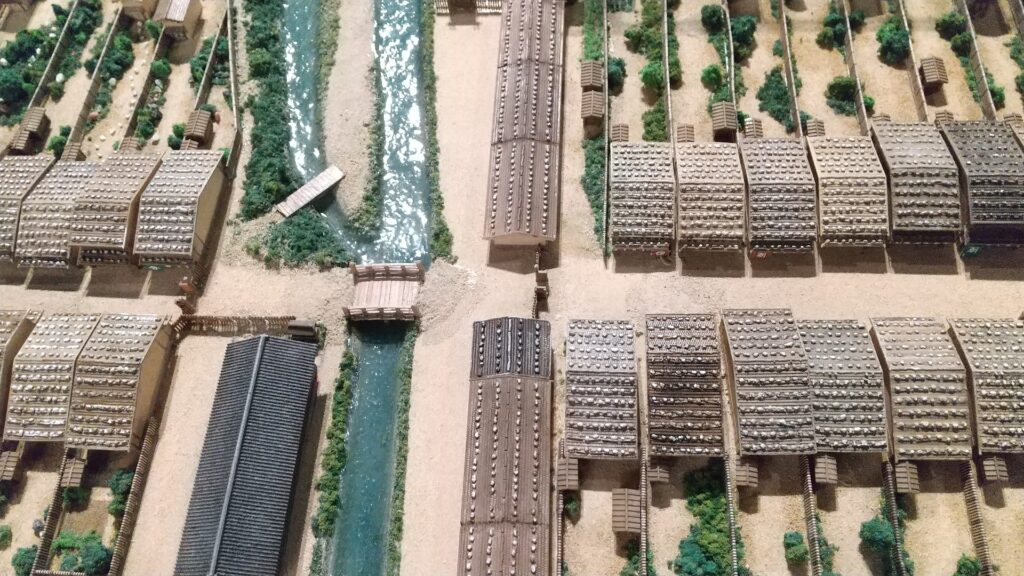
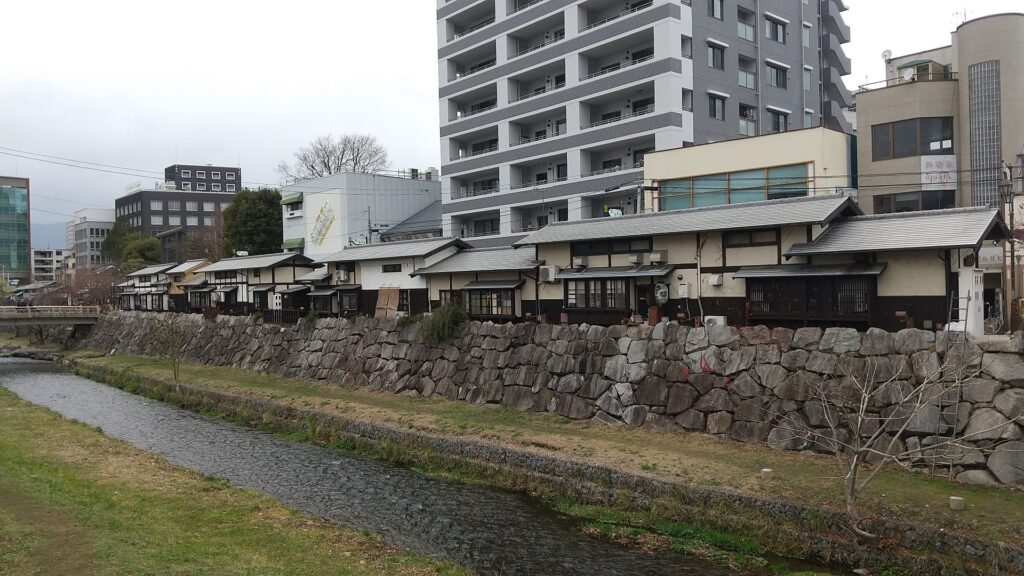
The second occurred during the great fire of Matsumoto in 1727. The Main Hall next to the tower was burned down by the fire; the tower itself fortunately survived. People thought that a god called Nijurokuyashin (the god of the 26th night moon), which was worshiped in the tower, had saved it. In addition, the castle town prospered as the intersection of the Zenkoji Road (from north to south) and the Nomugi Road (from east to west). The town also had many guardhouses to make sure to prevent enemies from reaching the castle easily.