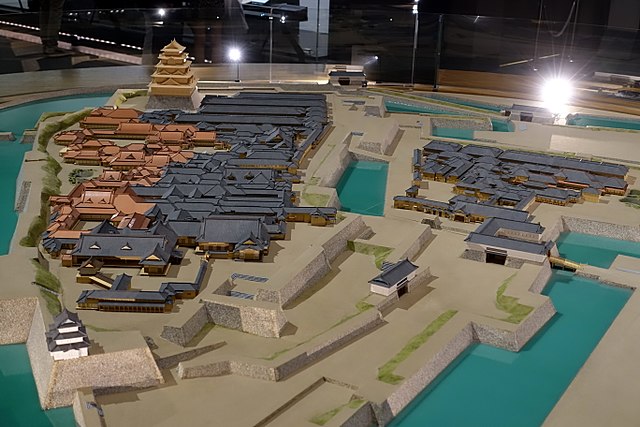
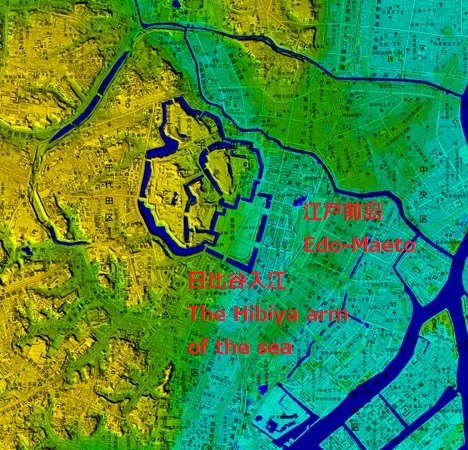
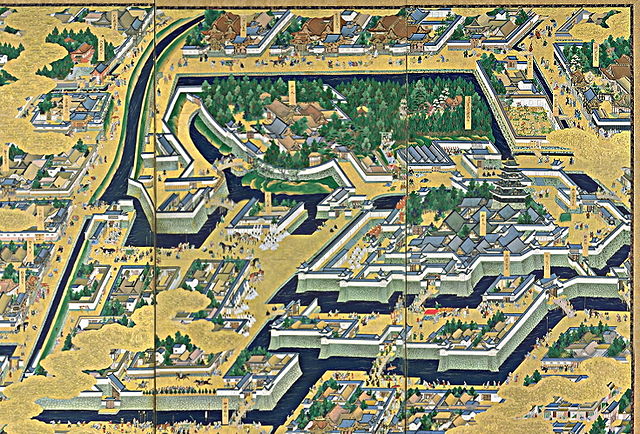
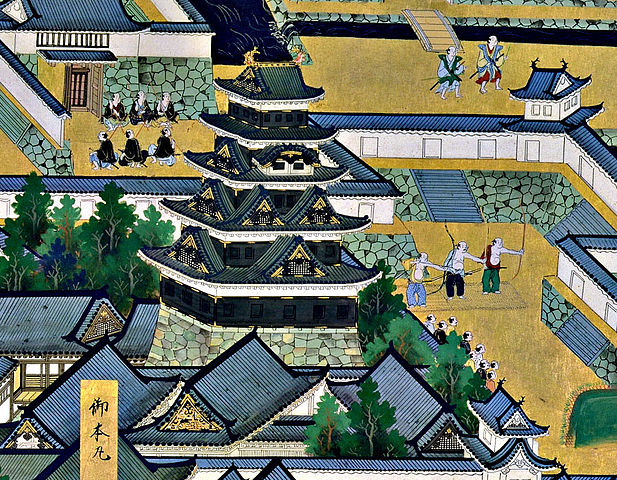
江戸城は内郭と外郭に分かれていました。内郭は内堀の内側にあって城の中心的機能を果たしていて、本丸、北の丸、西の丸といった主要な曲輪から成っていました。その外周は8km近くです。そこには天守、豪華な御殿があり、多くの櫓や門によって警備されていました。現在、内郭は4つの部分に区切られています。一つずつ見ていきましょう。
Edo castle was divided into Naikaku and Gaikaku. Naikaku was the inside of the inner moat, and consisted of the center portion of the castle including primary enclosures such as Honmaru, Kitanomaru, and Nishinomaru. Its perimeter was nearly 8 km. It had the Tenshu keep, luxurious halls, many turrets and gates for security. Now, Naikaku is separated into four parts. Let’s look at each part one by one.
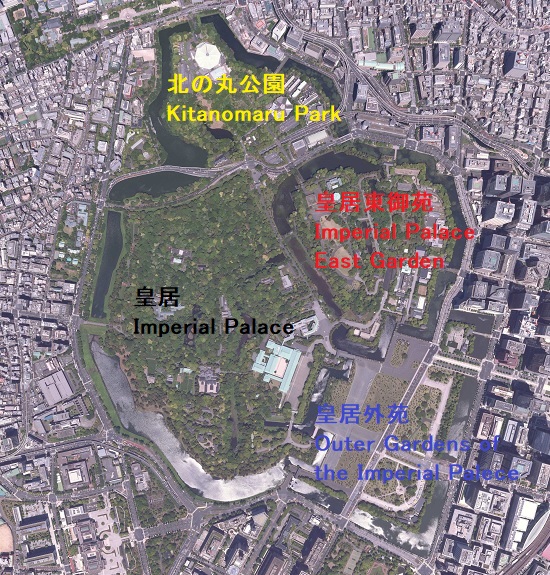
皇居東御苑~Imperial Palace East Garden
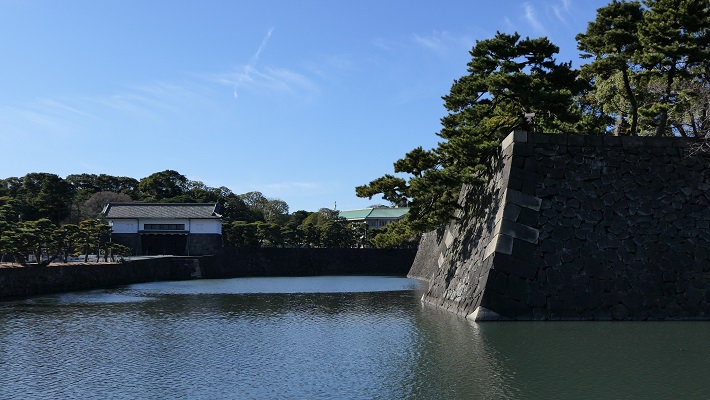
ここは、本丸、二の丸、そして三の丸の各曲輪を由来としています。将軍は長年本丸にあった御殿に住んでいましたが、1863年の火災の後は西の丸に移り、本丸には戻りませんでした。明治維新後、明治天皇もまた西の丸に住み続けました。そのため本丸とその周辺は宮内庁によって使われてきました。そして1968年からは、その多くの部分が庭園として公開されています。
It is derived from the enclosures, Honmaru, Ninonaru and Sannomaru. The Shogun usually lived the main hall at Honmaru for many years. But after the fire in 1863, they moved to Nishinomaru, didn’t returned to Honmaru. After the Meiji Restoration, Emperor Meiji also continued to lived in Nishinomaru. So Honmaru and the area around were used for Imperial Household Agency. Many parts of them have lastly been open to the public as the garden since 1968.
・三の丸巽二重櫓:江戸城に現存している4つの櫓のうちの一つです。庭園の外側からは、本丸富士見三重櫓を背景に、素晴らしい姿を眺めることができます。
・Tatsumi two-story turret at Sannomaru: It is one of four remaining turrets in Edo Castle. You can see a great view of the turret with the background of Fujimi three-story turret at Honmaru from outside the garden.
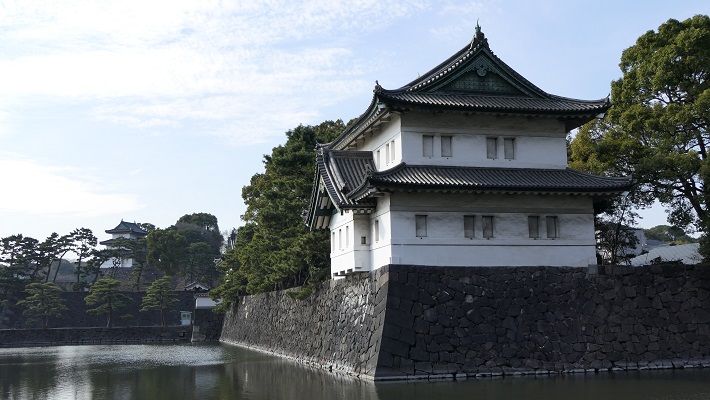

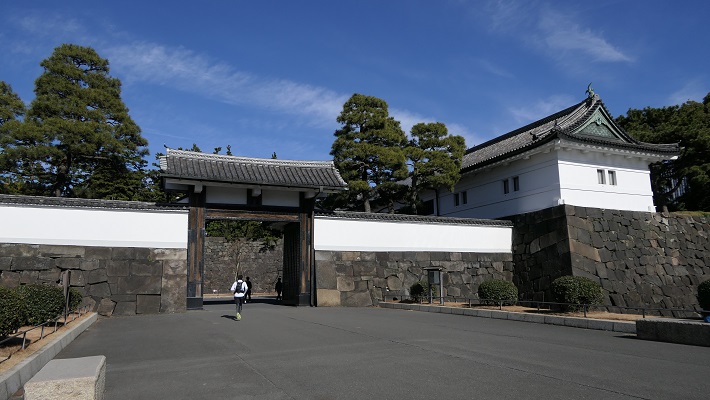
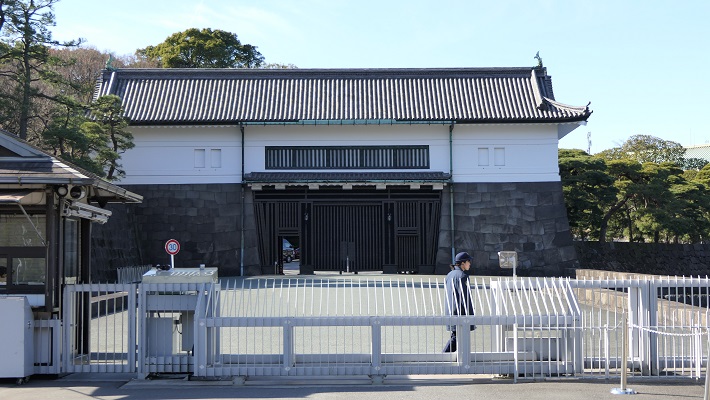
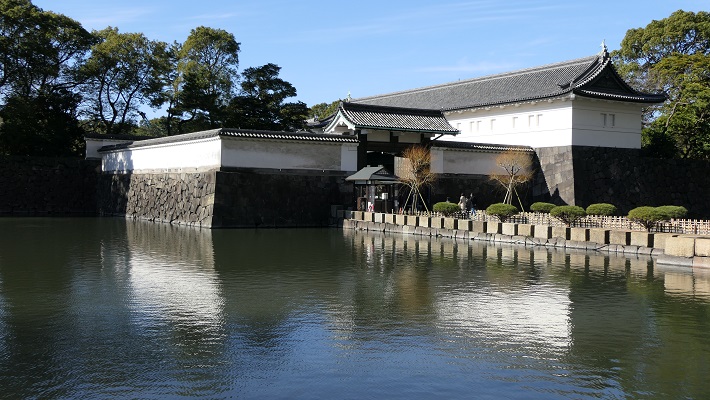
・大手門:この門は、江戸城の正門でした。現存するのは一部分で、残りは復元されています。庭園の入り口の一つでもあります。皇宮警察の人たちが荷物チェックをします。この内側が三の丸となります。
・Ote-mon Gate: This gate was the main entrance of the castle. It is partly original and the rest has been restored. It is also one of the entrances of the garden. The Imperial Guards will check your baggage. The inside of the gate is Sannomaru.
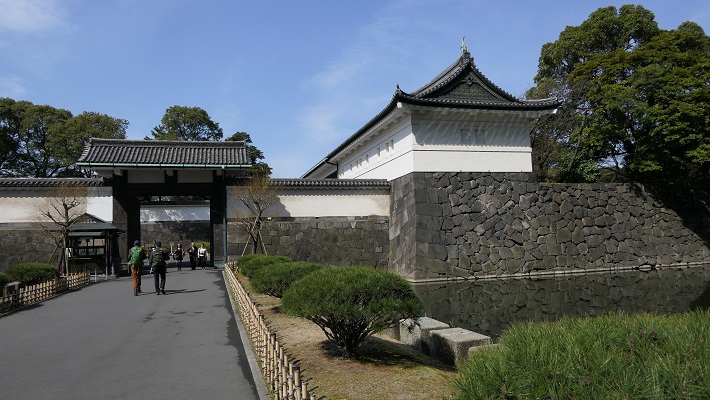

・大手三の門跡:ここは二の丸の入り口でした。過去には大きな櫓と門の前には内堀がありました。残念なことに全て撤去されてしまいました。
・The ruins of Ote-Sannomon Gate: this was the entrance of Ninomaru enclosure. There were large turrets around and the inner moat in front of the gate in the past. Unfortunately, they have all been demolished.


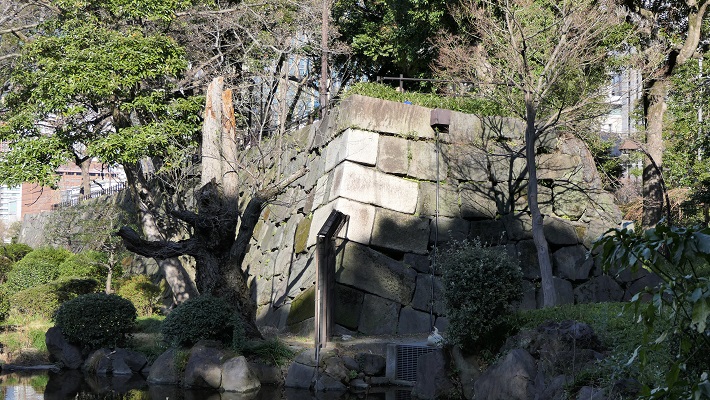
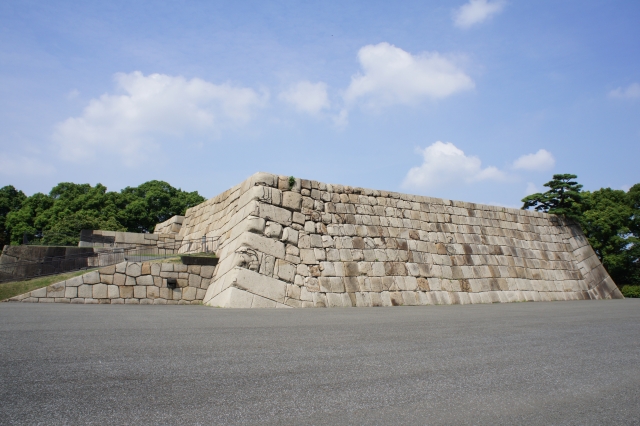
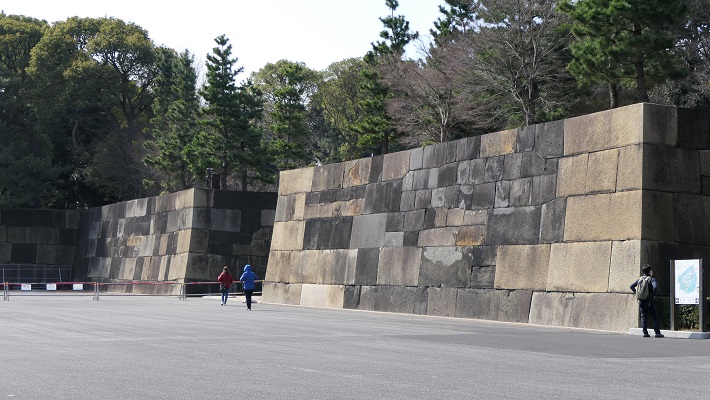
・中の門跡:ここは本丸の入り口でした。ここにも建物は残っていませんが、残っている巨大な石垣には驚かれるでしょう。これらの石は、瀬戸内海から運ばれてきたものです。
・The ruins of Nakanomon Gate: this was the entrance of Honmaru enclosure. They also have no buildings, but you will be surprised to see huge remaining stone walls. These stones were brought from Seto Islands Sea area.
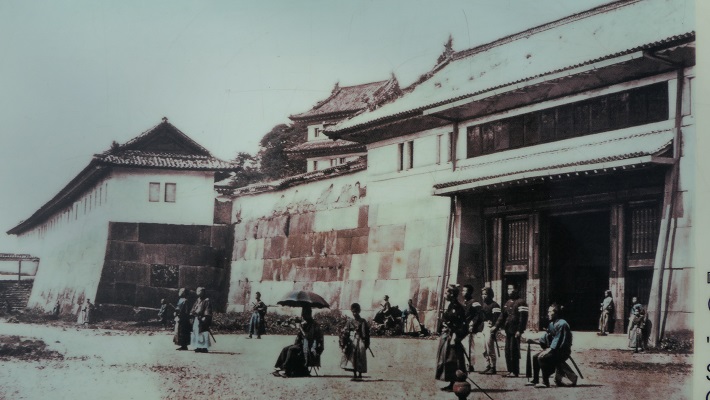


・三つの現存している番所:これらは前述の門の周辺にあります。武士が厳しく訪問者をチェックしていました。その中には忍者もいたそうです。
・The three remaining guard stations: they are around the gates mentioned before. Warriors did security check strictly. Some of them are said to be Ninja.
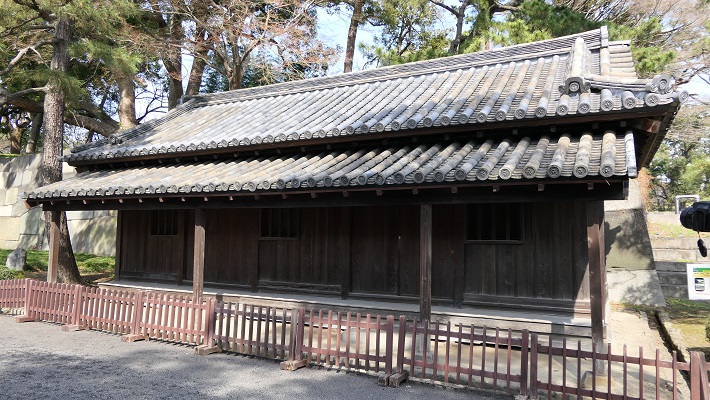



・中雀門跡:この門は、本丸御殿に至る最後の門でした。残っている石垣が黒ずんでいるのは1863年の火災による影響のようです。
・The ruins of Chujaku-mon Gate: this gate was the last one that led to Honmaru main hall. Their remaining stone walls look dark that might have been caused by the fire in 1863.
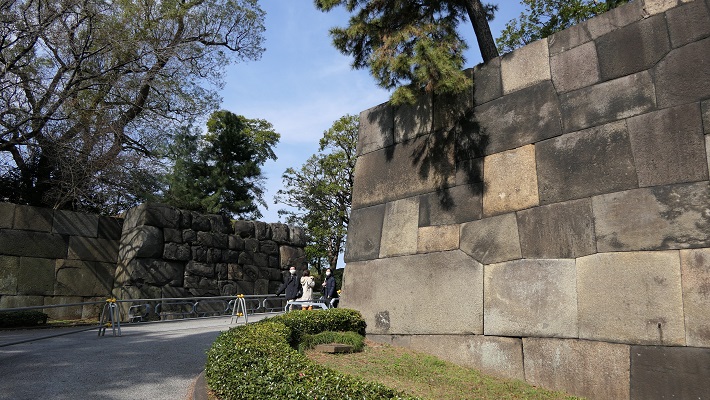
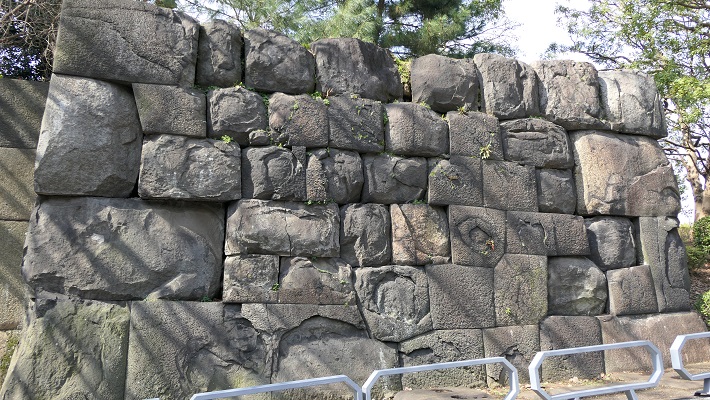


・本丸御殿跡:広大な土地に御殿がひしめいていました。ここは今は花と木の庭園になっています。
・The ruins of Honmaru main hall: this spacey area was packed with the hall. They are now used for a garden with flowers and trees.
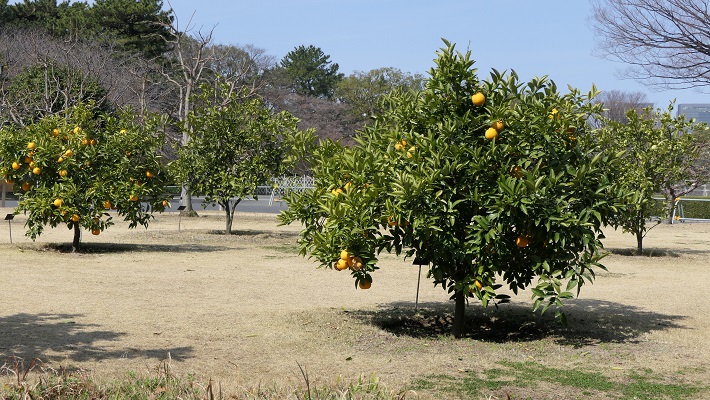


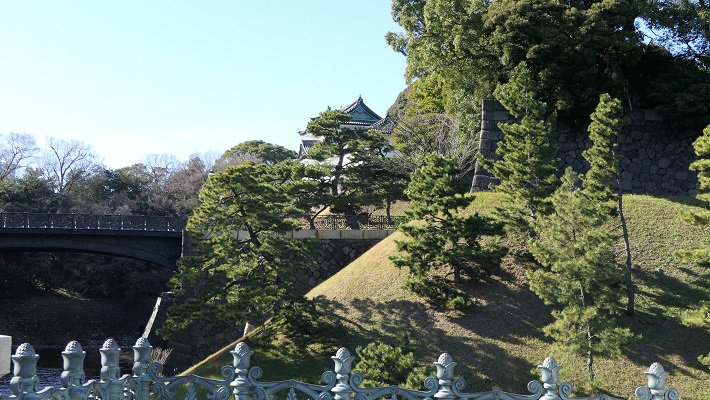
・富士見三重櫓:江戸城で唯一現存している三重櫓です。三代目の天守が焼けた後は代用天守として使われました。本丸からはその背面を見物できます。
・Fujimi three-story turret: it is the only remaining three-story turret in Edo Castle. It was used as the alternative Tenshu keep after the third Tenshu was burned down. We can see the back side of it at Hommaru.


・本丸展望台:ここからは二の丸庭園越しに東京中心地の景色を楽しめます。ここには台所前三重櫓がありました。過去には武士たちが見張りをしていたはずです。
・The viewing platform at Honmaru: You can have a good view of the center of Tokyo looking over Ninomaru Garden. The Daidokoro-mae three-story turret was there. Warriors should be likely looking over for security in the past.
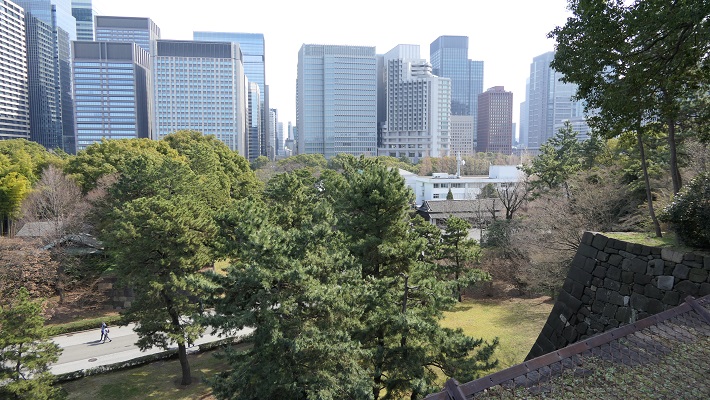
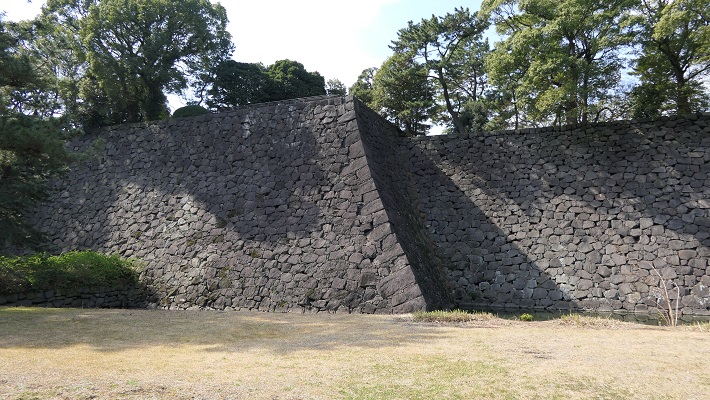


・天守台石垣:この城には天守がありました。最初の三人の将軍は、先代の天守に代わる自身の天守を築きました。三代目の天守は特に史上最大と言われる程巨大でした。ところが、1657年の明暦大火で焼け落ちてしまいます。その後四代目の天守再建が始まりますが、中止となりました。現在その四代目用の天守台が残っています。
・The stone walls for Tenshu keep: the castle had the Tenshu keep. The first three Shoguns built their own Tenshu instead of using the previous one. The third Tenshu was especially big which might have been the biggest one in history. However, it was burned down by the great fire of Meireki in 1657. After the fire, the rebuilding of a fourth Tenshu was launched, but canceled. We can now see the prepared Tenshu base for it.
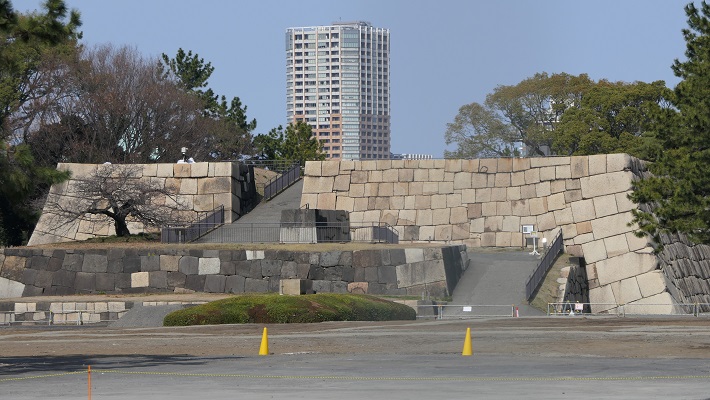


・梅林坂:この城の創始者である太田道灌が梅の木を植え、神社を作った所と言われています。梅林の合間に、より古風な石垣が残ります。
・Bairin (Plum Grove) Slope: it is said that the founder of the castle, Dokan Ota planted plum trees and built a shrine there. We can now see the trees among older looking stone walls.
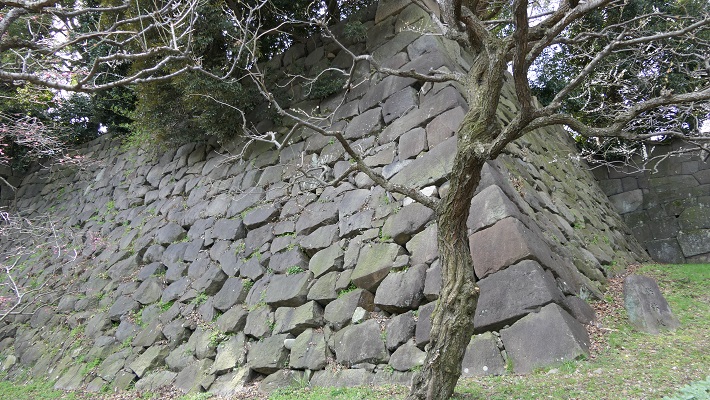


・平川門:ここは城の裏門で、現存しています。この門は、鬼門である東北を向いています。このため、城での罪人はこの門を通して追放されたとのことです。
・Hirakawa-mon Gate: this was the back gate of the castle and remains now. The gate faces the traditional taboo direction – the northeast. For this reason, the offenders in the castle were banished through the gate.

皇居外苑~Outer Gardens of the Imperial Palace
ここは「皇居前広場」とも呼ばれています。江戸時代には「西の丸下」と呼ばれており、多くの大名屋敷が建っていました。明治時代に皇室の園地となりましたが、市民にとって親しみのある場所でもありました。皇居がすぐ近くに見えるからです。第二次世界大戦が終わったとき、敗戦を嘆く人たちがここに集まったことで有名です。現在の人たちも似たような状況です。簡単に来れるので、いつも多くの観光客が集まっています。現在ここは一般に公開されています。
It is called “The Palace Plaza” as well. This area was called “Under Nishinomaru” where many halls for lords were in the Edo Period. In the Meiji Era, it was turned into the garden for Imperial Families, but also familiar to citizens because they could see the Imperial Palace closely. At the end of World War II, it became a well known place for people mourning the loss of the war. This idea is similar to people in the present. Many tourists always visit there due to easy access. Now, garden is open to the public.
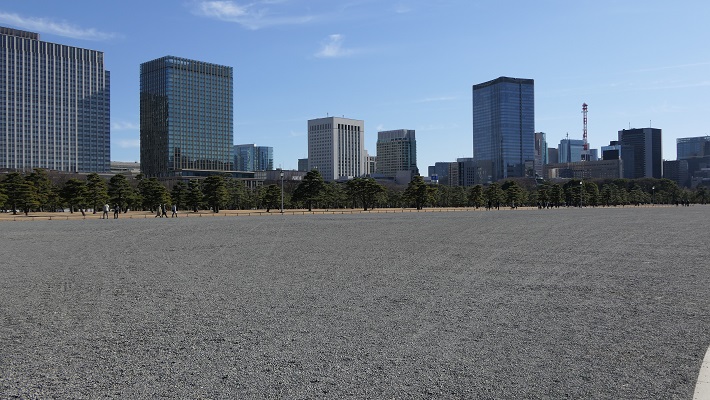
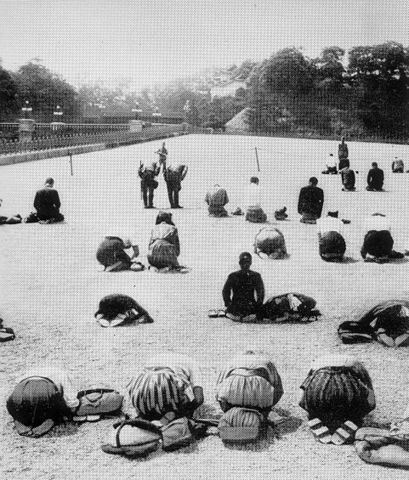


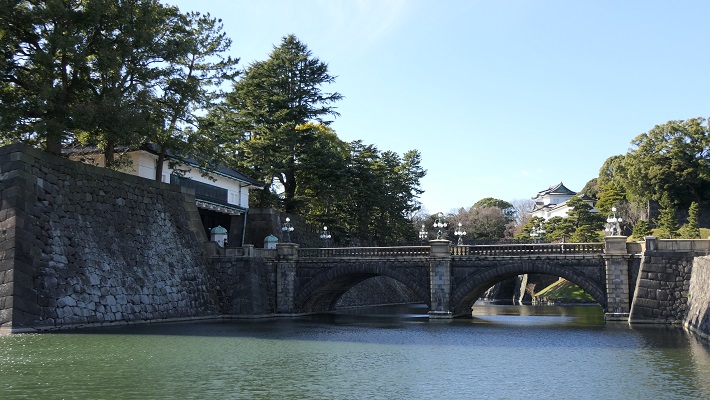
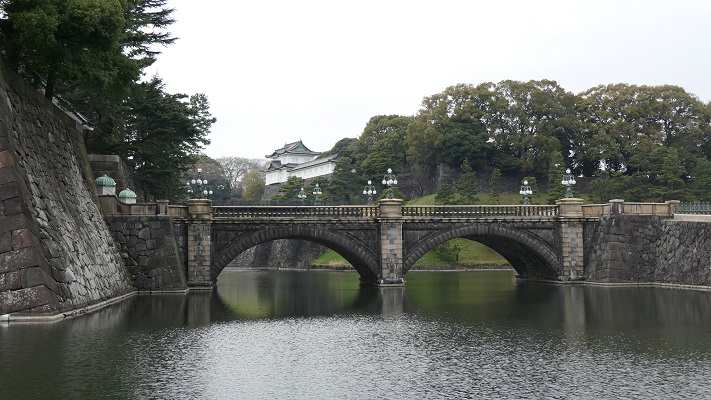
・皇居正門石橋と現存する伏見櫓の風景:外苑そのものは広大な広場です。なので多くの観光客は皇居と江戸城建物の景色を愛でています。この取り合わせは一番有名なものです。
・The view of the Palace Stone Bridge and the remaining Fushimi Turret: The garden itself is an extensive square. So many tourists enjoy the views of Imperial Palace and Edo Castle buildings. This is the most popular one.
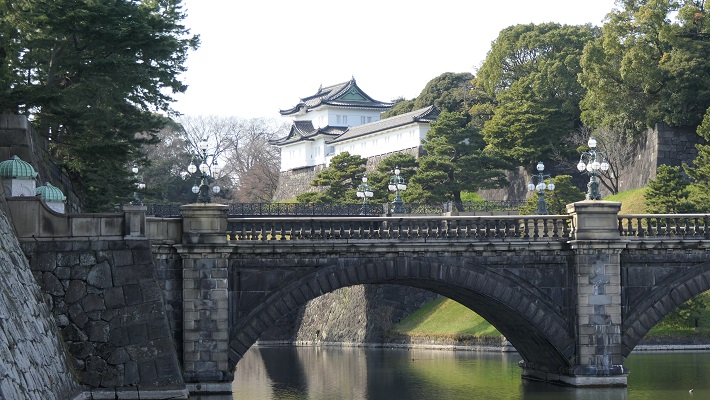

・桜田門:これは最も有名な江戸城の建物の一つです。1860年に桜田門外の変が起こった所です。幕府大老であった井伊直弼が暗殺され、幕府の権威失墜を招きました。この門は現存しており、重要文化財に指定されています。
・Sakurada-mon Gate: This is one of the most popular buildings of Edo Castle. Because this is where Sakuradamon Incident in 1860 happened. The chief minster of Shogunate, Naosuke Ii was assassinated and it caused Shogunate’s the authority to decreas. The gate remains now and has been designated as a Important Cultural Property.
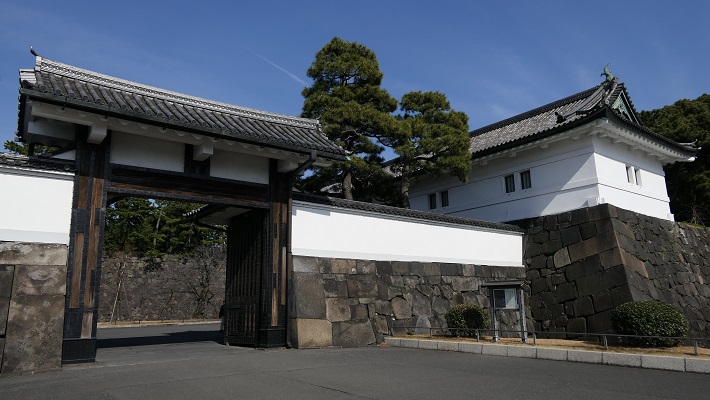

北の丸公園~Kitanomaru Park
北の丸曲輪は、本丸の搦め手を北の方角から守る任務があり、とても重要でした。将軍の親族である清水家と田安家が江戸時代の後期に住んでいました。明治維新後は、近衛師団の兵舎がありました。第二次世界大戦後は公園になり、日本武道館や科学技術館などの施設が置かれています。
Kitanomaru enclosure was very important because it had to guard the rear of Honmaru in the north. The Shogun’s relatives, the Simizu and Tayasu clans lived in the late Edo Period. After the Meiji Restoration, the barracks of the Imperial Guard division were there. After the World War II, it became the park where facilities, like Japan Budokan, Science and Technology Museum, are located.
・清水門:清水家の屋敷の門として使われました。とても優れた構造で、重要文化財になっています。この門は、内堀が窪んでいる奥に設置されていて、誰もが長く細い土橋を渡って入らなければなりません。侵入者は堀に沿った塀から反撃されてしまいます。
・Shimizu-mon Gate: It was used as the gate for Shimizu clan’s hall. It has a excellent structure and has become an Important Cultural Property. The gate is set at the back of the curved inner moat. Everyone has to go on a long and narrow earthen bridge to enter. Invaders were countered by defenders on walls along the moat.
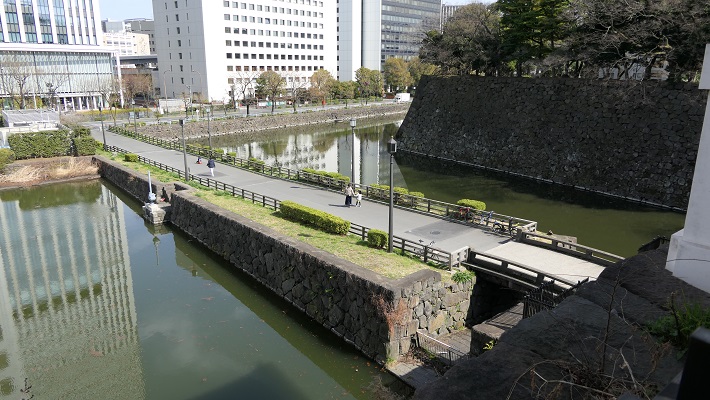


この門はまた2つの「桝形」と呼ばれる方形の区画が外と内両方にありました。守備側は背後から敵を攻撃できたのです。実に強靭な防御力です。私が思うにこの門はもっと有名になってしかるべきです。
The gate also has two square shape blocks called “Masugata” both outside and inside. Defenders were able to counter the enemy from the back. The gate is very strongly defensive. By I think it should be more well-known.
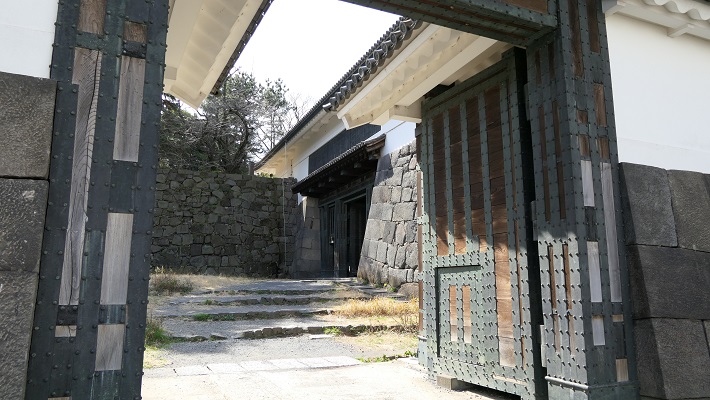
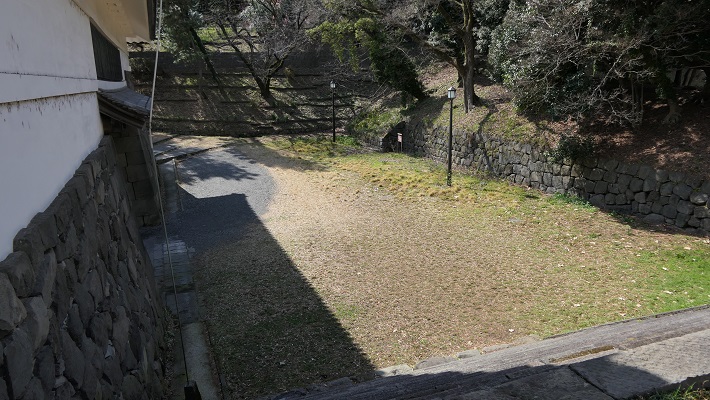


・田安門:ここは田安家の門でした。地下鉄から武道館に行く人は皆、この門を通ります。この門もまた重要文化財に指定されています。
・Tayasu-mon Gate: It was the gate of Tayasu clan’s hall. Now, all people from the subway station to Budokan go through the gate. It looks just like the Budokan gate. It has also been designated as a Important Cultural Property.
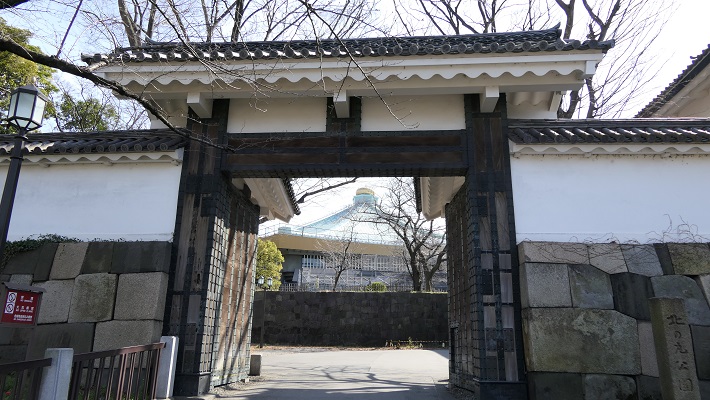

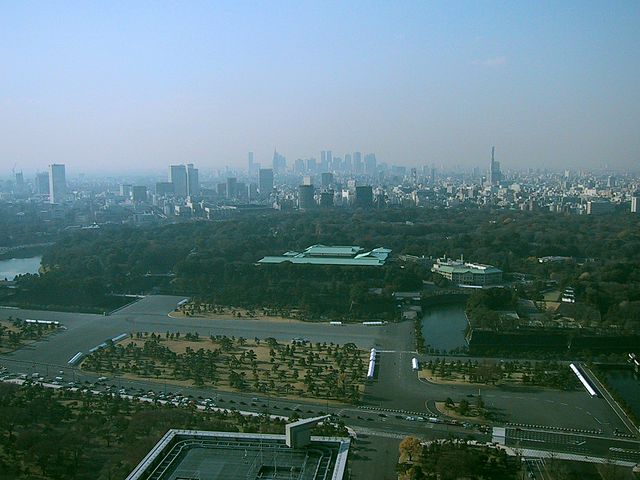
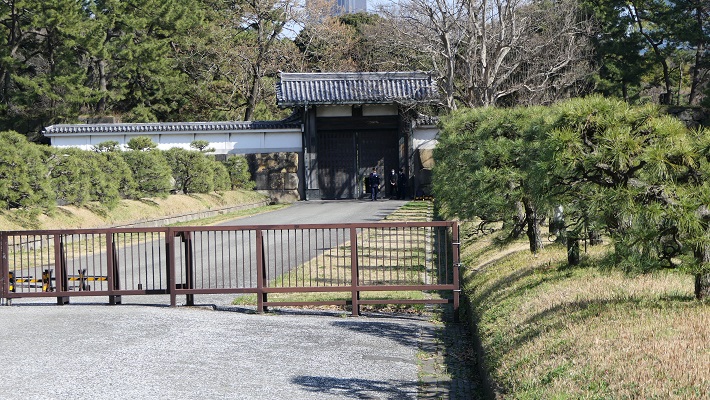
皇居~Imperial Palace
この区域は元々西の丸曲輪と吹上と呼ばれる場所でした。将軍は江戸時代末期に西の丸にある御殿に住んでいました。明治維新のとき、明治天皇はこの御殿に入り、使い続けました。そのため西の丸周辺が皇居になったのです。一般の人は通常皇居には入れませんが、年始や天皇誕生日といった特別な日には一部開放されます。今回は、外側から見ることができる2つの興味ある景色をご紹介します。
This area includes the original Nishinomaru enclosure and a place called Fukiage. The Shogun lived in the hall at Nishinomaru at the end of the Edo Period. During the Meiji Restoration, Emperor Meiji got the hall and continued to use. That’s why Ninomaru around has become Imperial Palace. Visitors can’t usually enter the palace, but it is partly open to people on special days such as New Year Celebration and the Emperor’s birthday. This time, I will show you two of interesting views of the area from outside.

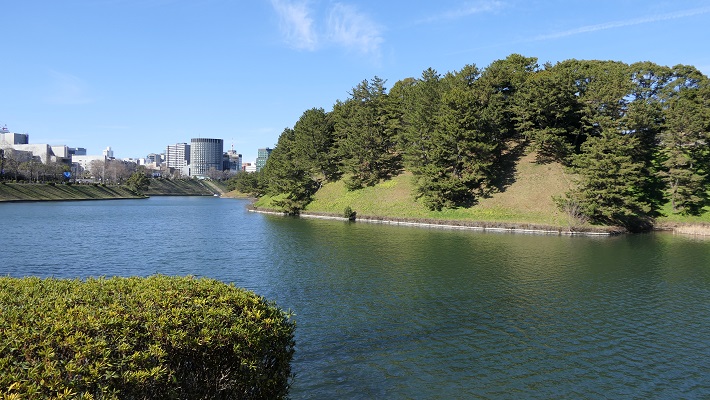
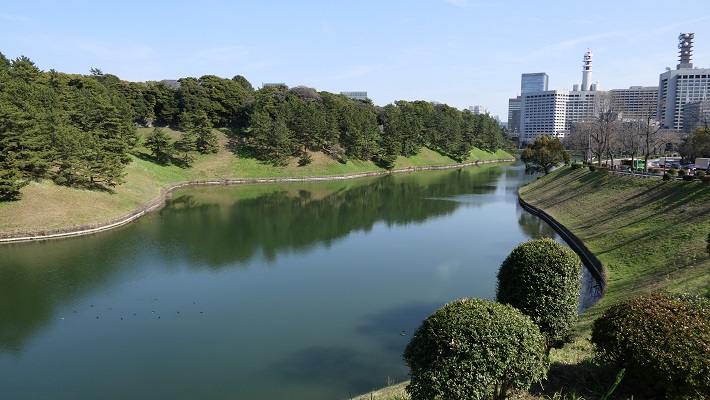
・千鳥ヶ淵:ここは今は内堀の一部になっていますが、元来は川だったようです。「淵」はこの場合、水流をせき止めて作った沼を意味します。この堀は全国的に桜の名所として知られています。春になると、堀の上にはボートで花見をする人たちで溢れます。
・Chidori-ga-Fuchi moat: it is now a part of the inner moat, but seemed to be originally a river. “Fuchi” means a lake made by damming the water in this case. The moat is known around the whole country for cherry blossoms. A lot of people seeing them are on the boats in the moat in the early spring.
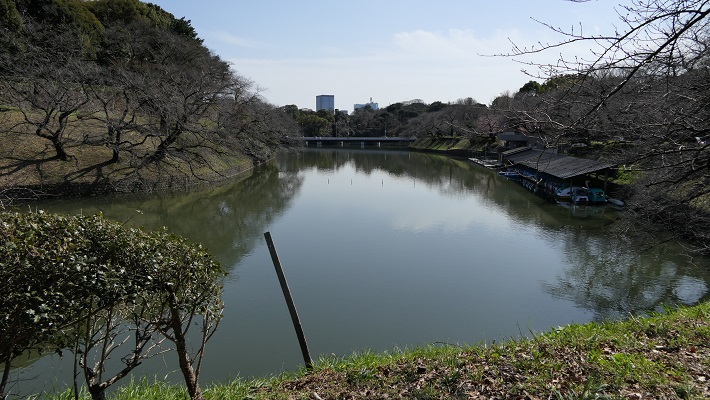

・半蔵門~この名前は、この門を警護していた忍者の頭領、服部半蔵に由来します。外側から門に伸びる土橋はまるでダムのように見えます。実際、この橋は水位を維持するために築かれました。橋の片側の水位は反対側よりかなり高くなっています。
・Hanzo-mon Gate: its name comes from the leader of Ninja, Hanzo Hattori who kept the gate. The earthen bridge from outside to the gate looks just like a dam. Indeed, the bridge was built to hold back the water. You can see the one side of the bridge keep much higher level of the water than the other side.



「江戸城その4」に続きます。~To be continued in “Edo Castle Part4”
「江戸城その2」に戻ります。~Back to “Edo Castle Part2”
「江戸城その1」に戻ります。~Back to “Edo Castle Part1”