特徴~Features
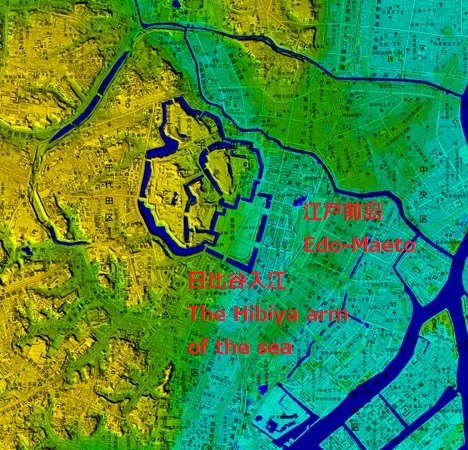
今となっては、ほとんどの人が東京が水の都とは思わないでしょう。ところが、実は江戸はそうだったのです。徳川氏が江戸に移ってきたとき、江戸城は現在の山の手区域にありました。現在の下町にあたる地域は海の下にあったか、湿地帯でした。そして江戸前島と呼ばれた砂州が存在していました。また、陸地と砂州の間には日比谷入江が入り込んでいました。徳川の家臣団は、江戸前島を横切る運河を掘り、水運の便のために川筋を変更したのです。
These days, most people don’t realize that Tokyo is a city of waterways. However, Edo actually was. When the Tokugawa clan moved into Edo, Edo Castle was in the present uptown area. The present down town area was below the sea or waterlogged. There was a sand bank called Edo-Maeto. There was also the Hibiya arm of the sea between the land and the bank. Tokugawa’s team created a canal across Edo-Maeto and change the route of rivers for water transportation.
日比谷入江から江戸前島の東側に川筋を変更して作られた運河が、日本橋川でした。そこには現在日本橋がかかっています。この橋は昔ながらの姿で知られており、多くの主要道路の出発地点でもあります。
A canal created for changing the route of the river from the Hibiya arm of the sea to east of Edo Maeto is Nihonbashi River, where Nihonbashi Bridge goes across. The bridge is known for a traditional view and the starting point of many major roads.
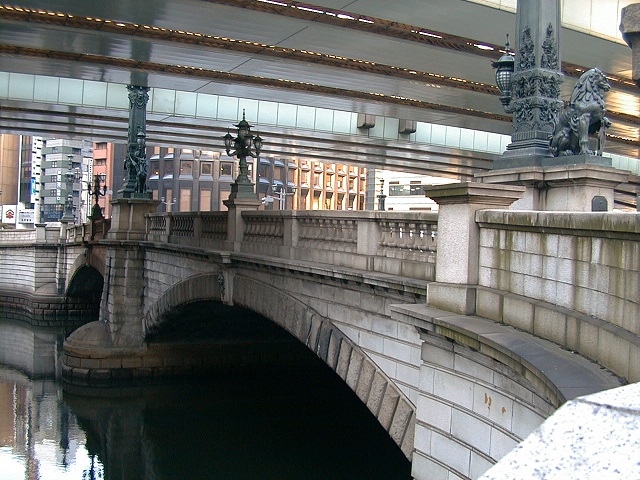
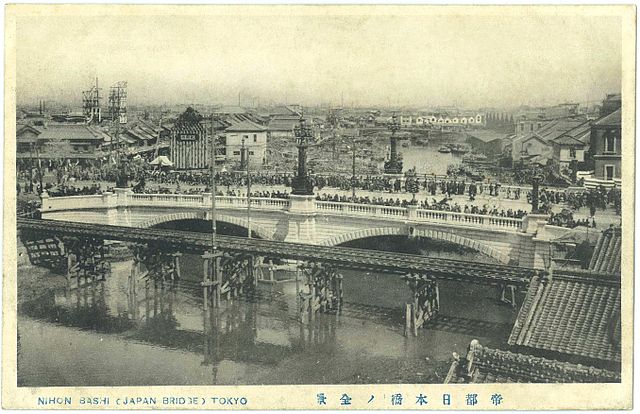




事実、この橋の下を流れる川は人工物で、それは400年以上前に作られたものなのです。この川からは、江戸前島の中心を通る外堀が分かれていました。
In fact, the river below the bridge is artificial and was created over 400 years ago. From the river, the outer moat separated out trough the center of Edo Maeto.
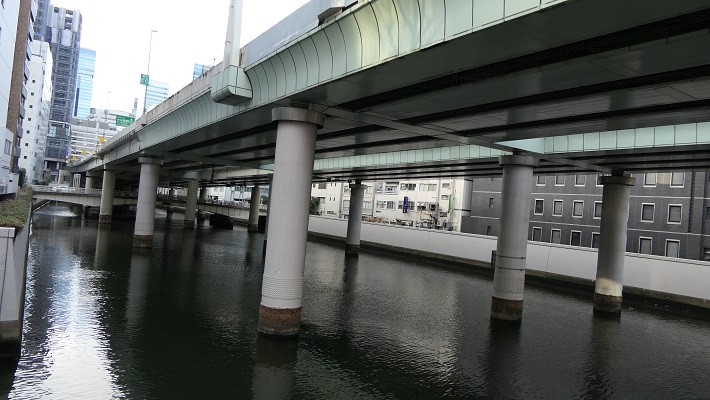
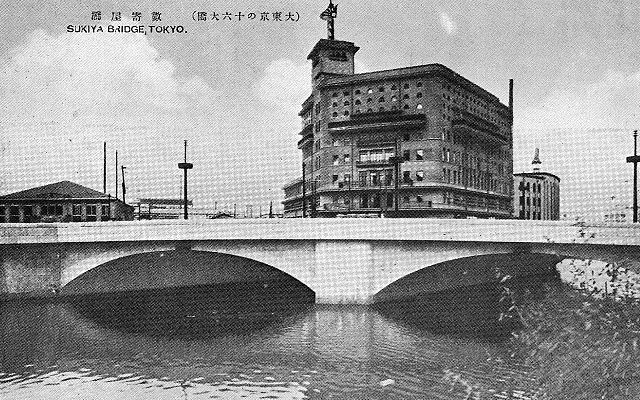


徳川は、城の敷地を広げるためと防衛上の必要から日比谷入江を埋め立てました。更に、江戸前島の周りの海も市街地の確保のため埋め立てたのです。一方で、海の一部分は埋め残して堀、川や運河としました。結果として、江戸は水路とともに広がっていきました。今だにその痕跡は現代の地図上に残っています。それらをいつくか巡ってみましょう。
Tokugawa reclaimed the Hibiya arm of the sea to expand the ground for the castle as well as the need for defense. They also filled the sea around Edo Maeto to create the city area. Meanwhile, they left part of the sea as moats, rivers and canals. As a result, Edo city was spread with waterways. There are still traces of them on the present map. Let’s see some examples.

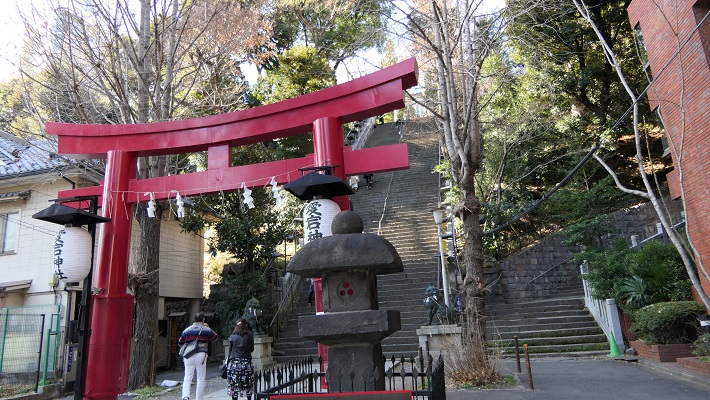
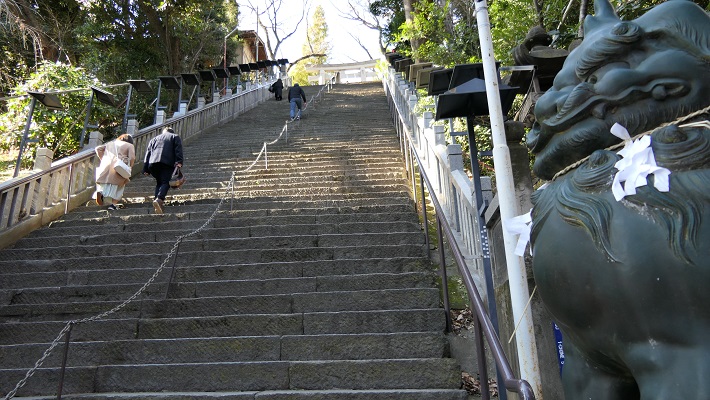
愛宕神社~Atago Shrine
ここは急坂に「出世」の階段があることで有名です。日比谷入江の入り口の近くにあたります。
It is famous for its steep steps of “success”. It was near the entrance of the Hibiya arms of the sea.


赤坂1丁目交差点~Akasaka-icchome intersection
ここは溜池から流れる川の河口でした。外堀の一部に転用されました。
This was the estuary of the river from Tameike. It was turned into a part of the outer moat.



潮見坂~Shiomi slope
霞ヶ関官庁街の中にあります。ここは日比谷入江の西際だったようです。
It is among Kasumigaseki governmental ministries. It seems to be the west edge of the Hibiya arm.

桜田門周辺~Aroud Sakurada-mon Gate
この門の近くに別の川の河口があったようです。内堀の一部として残っています。
This seems to be the estuary of another river near the gate. It remains a part of the inner moat.
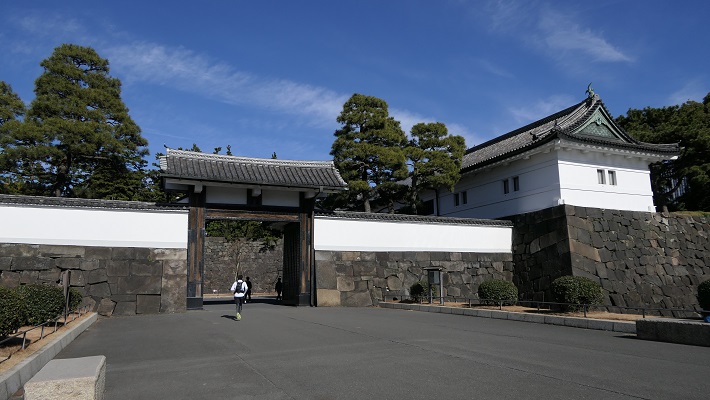


皇居正門~The main entrance of Imperial Palace
宮殿は西の丸だった所にあります。正門前の内堀は元は海でした。
The palace is on what was Nishinomaru enclosure. The inner moat in front of it was originally the sea.
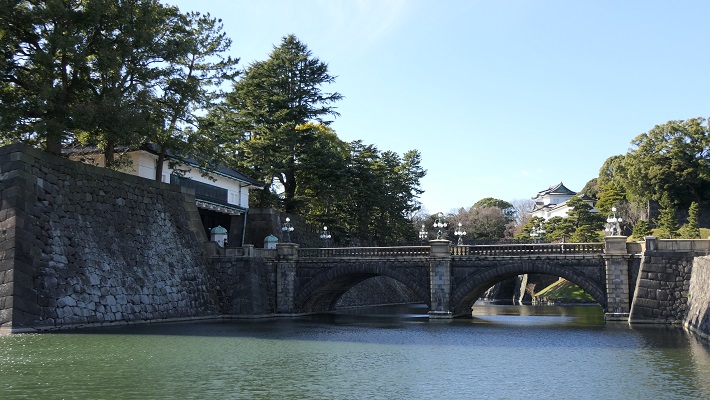


皇居外苑~The Outer Gardens of the Imperial Palace
ここは完全に海で、周りの内堀を残して埋め立てられました。
This was completely a sea, and filled without the inner moat around.

坂下門~Sakashita-mon Gate
門の周辺の内堀は、もともと川や谷だった所を使っています。
The inner moat around the gate uses the original rivers and valleys.
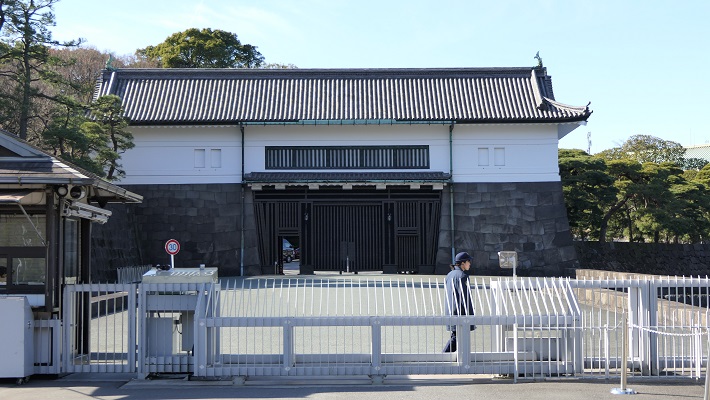
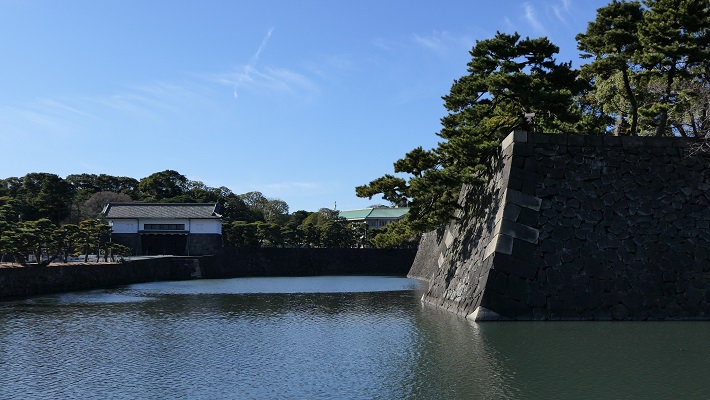


大手門周辺~Around Ote-mon Gate
ここには日比谷入江に注ぐ平川の河口がありました。
This was the estuary of Hirakawa River emptied into the Hibiya arms of the sea.
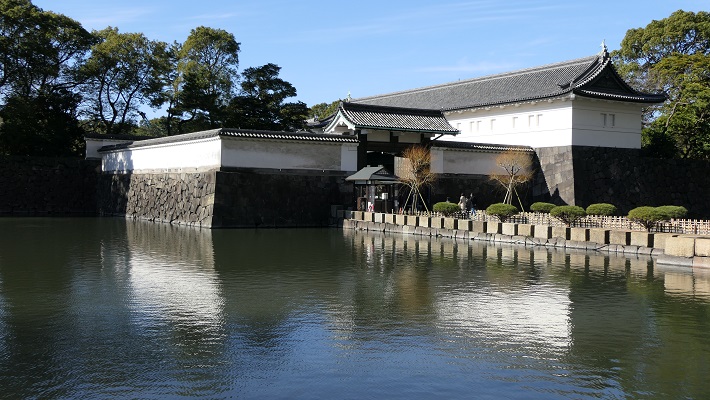


和田倉門~Wadakura-mon Gate
日比谷入江の一番奥の場所にあたります。和田倉とは海岸にある倉庫の意味です。
This was the inmost place of the Hibiya arm of the sea. Wadakura means warehouse st seashore.
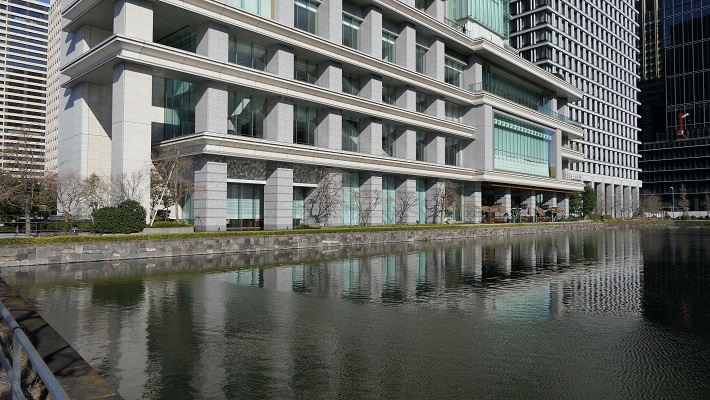


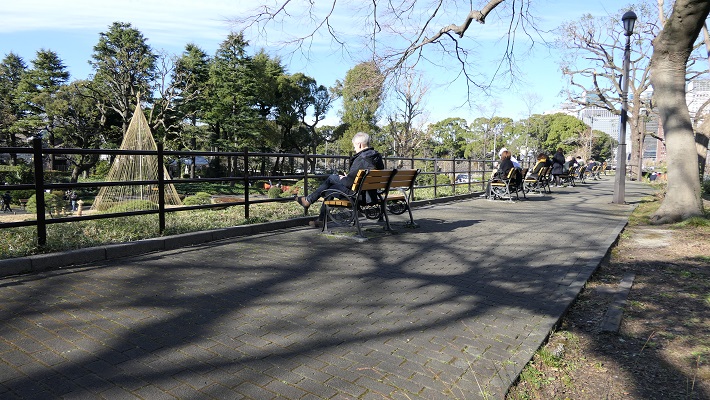
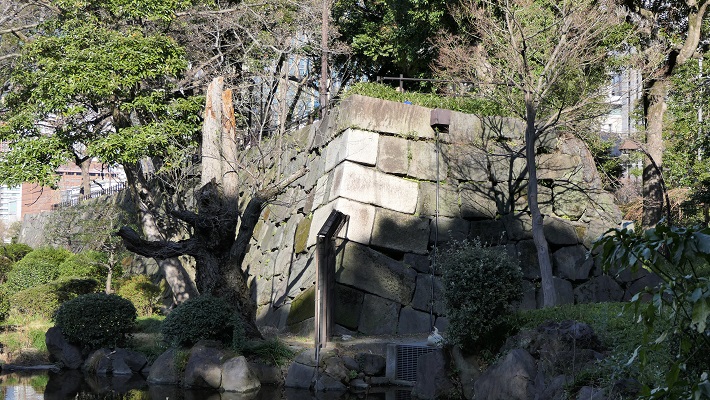
日比谷公園~Hibiya Park
内堀の石垣跡が休憩所として活用されています。
The ruins of stone walls for the inner moat is used for a resting place.


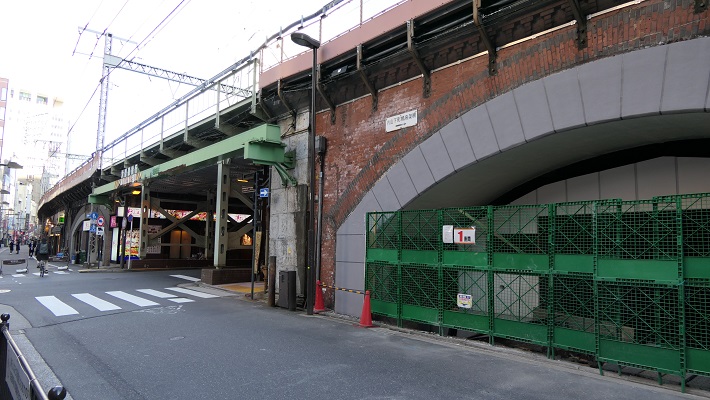
山手線の側面~The side of Yamanote line
レンガ造りの高架鉄道は元から陸地の所だから可能だったと言われています。
It is said that the elevated red brick railway could be available on the primary land.

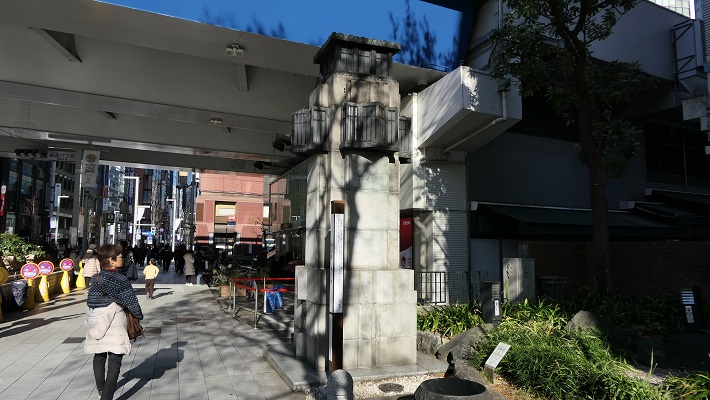
新橋跡~The ruins of Shinbashi bridge
この橋は汐留川にかかっていましたが、元は江戸前島の突端にあたります。
The bridge went across Shiodome-gawa River which was originally the edge of Edo Maeto.

銀座の裏通り~The back street of Ginza
江戸前島の東海岸を利用して作られた三十間堀川がここを流れていました。
Sanjukkenbori River went through it and it was built using the east coast of Edo Maeto.

首都高速都心環状線~The Tokyo Metropolitan Expressway Ring Route
ここは楓川と、ドックのような形の舟入堀がありました。この川は日本橋川につながっていました。
This was Kaedegawa River with several Funairi moats like docks. The river connected to Nihonbashi River.


その後~Later Life
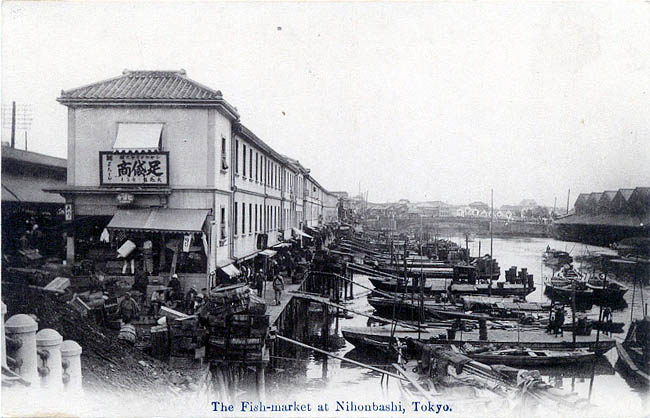
明治維新後、城の多くの建物は撤去されましたが、多くの水路は残りました。人々がまだ使っていたからです。一例として、東京の魚市場は1923年の関東大震災まで日本橋川沿いにありました。地震の後になって築地に移転したのです。
After the Meiji Restoration, many buildings of the castle were demolished, but many waterways remained, because people still used them. For instance, the fish market in Tokyo was along Nihonbashi River until the Great Kanto Earthquakes in 1923. After that, the market moved to Tsukiji.


第二次世界大戦後、一部の外堀が焼けた建物の残骸により埋められました。今の外堀通りです。
After World War II, part the outer moat was filled by the debris of burned buildings. It has become Sotobori Street.

昭和の中期に車が普及し、1959年には、1964年の夏のオリンピックが東京で開催されることが決まりました。東京の交通インフラ、特に高速道路を整備するための時間はわずかしかありません。政府は高速道路の用地として残っていた水路を使わざるをえませんでした。買収する必要がないからです。東京のほとんど全ての水路が消え失せました。
In the mid Showa Era, motorization came and it was decided in 1959 that the 1964 summer Olympics in Tokyo would be held. There would be little time to develop the infrastructure for transportation in Tokyo, especially an expressway. The government had to use the remaining waterways as the land for the expressway. Because they didn’t need buy them. Almost all of the waterways in Tokyo died out.

日本橋と日本橋川は歴史的価値があるため、かろうじて残されました。そのため高速道路がその上を走っているのです。日本橋地域の人たちは、古き良き景観を取り戻すため政府に対し高速道路を地下に移すよう請願しています。
Nihonbashi Bridge and Nihonbashi River have survived due to their historical values. That’s why the expressway goes above them. Now, people in the Nihonbashi area urge the government to move the expressway underground to get its good old landscape back.

「江戸城その3」に続きます。~To be continued in “Edo Castle Part3”
「江戸城その1」に戻ります。~Back to “Edo Castle Part1”