立地と歴史~Location and History
海に面した城~A castle facing the sea
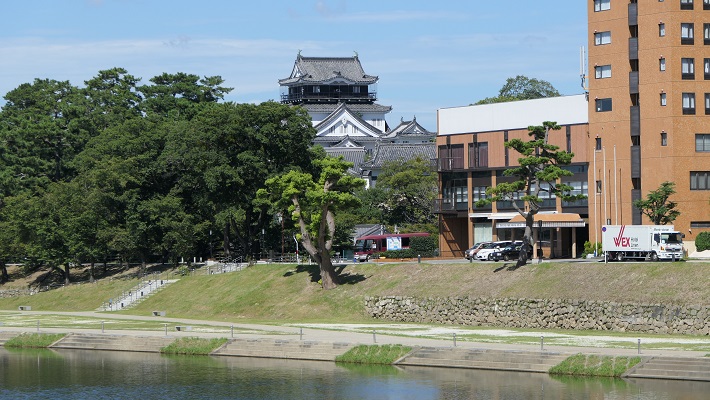
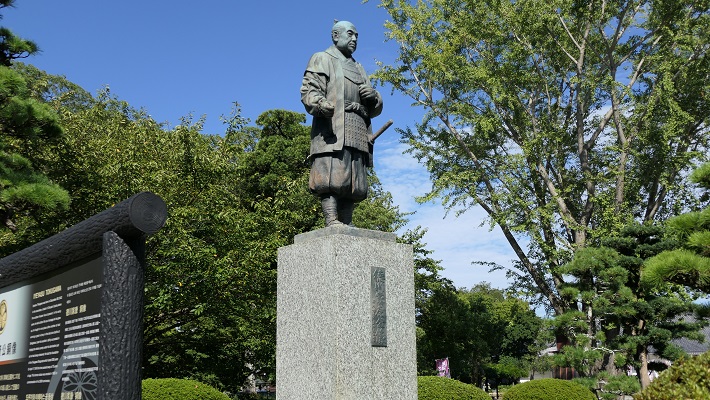
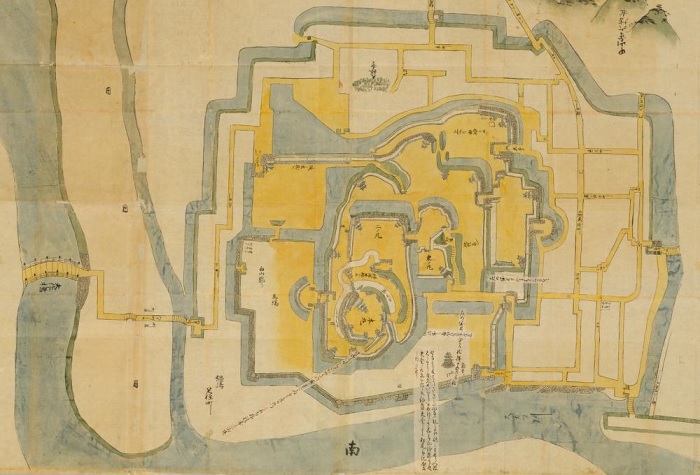
米子市は、中国地方の鳥取県西部にあり、ゆったりした雰囲気を感じる所です。戦国時代には中国地方のほとんどを毛利氏が支配していました。その一族である吉川広家は、天下人の豊臣秀吉に海の近くに新しい城を築くよう命じられ、それは1592年の秀吉の朝鮮侵攻の補給基地の役割がありました。この辺りは朝鮮に近かったからです。それが米子城でした。
Yonago City has a relaxed atmosphere, located in the western part of Tottori Prefecture, Chugoku Region. In the “Sengoku”, or Warring States Period, the Mori clan governed most of this region. Its relative Hiroie Kikkawa was ordered to build a new castle near the sea by the ruler Hideyoshi Toyotomi as a supply base for Hideyoshi’s invasion of Korea in 1592. Because the area is close to Korea. That was Yonago Castle.
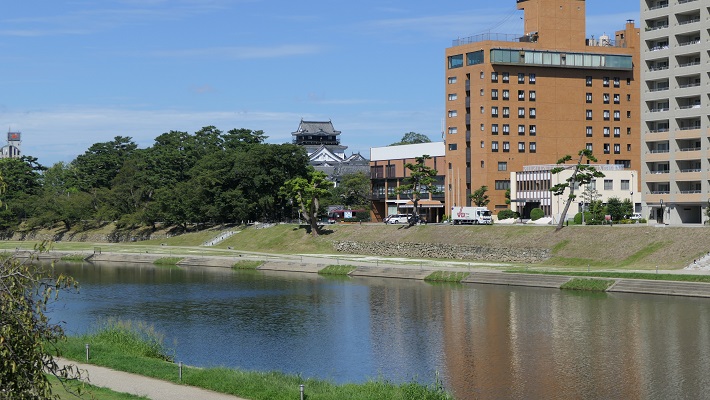
この城は、湊山と呼ばれる90mの高さの山の上に築かれました。城の背後はちょうど中海に面しており、港として使われていました。初期の城に関する詳細は不明なのですが、頂上には4階の天守がありました。
The castle was built on a 90 m mountain called Minato-yama. The back of the castle just faced Nakaumi Lake, and was used as a port. The details regardomg the first castle are uncertain, but there was a four-story main tower or Tenshu on the top.
2つの天守が並ぶ~Two Main towers stands
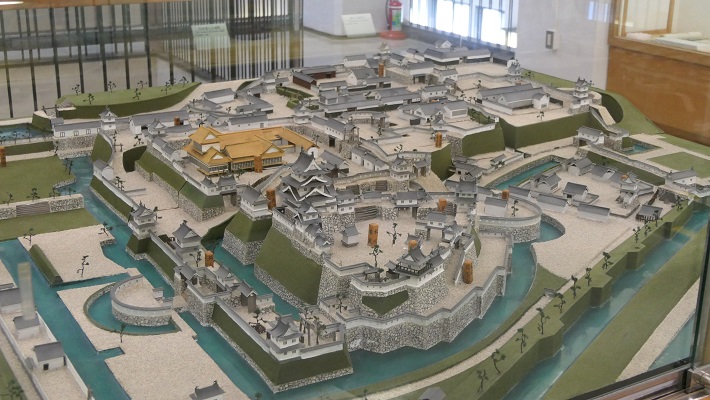
徳川幕府が設立された後は、1600年に米子城と米子藩の領主として、中村一忠が配置されました。一忠は城と城下町の拡張を続け、完成させました。彼はまた、新しく元あった天守より大きな5階の天守を築きました。その当時、大きな天守を築くことが大名たちの間でブームとなっていました。民衆に権威を示すためです。既に古い天守があった場合には、大抵は置き換えられました。
After the Tokugawa Shogunate was established, they placed Kazutada Nakamura as the lord of Yonago Castle and the Yonago feudal Domain in 1600. He continued to improve and complete the castle along with the castle town. He also built a new five-story Tenshu that was larger than the old one. At that time, building large Tenshu was a boom for lords, as they tried to show their authority to people. If there was already an old Tenshu, it was often replaced with the new one.

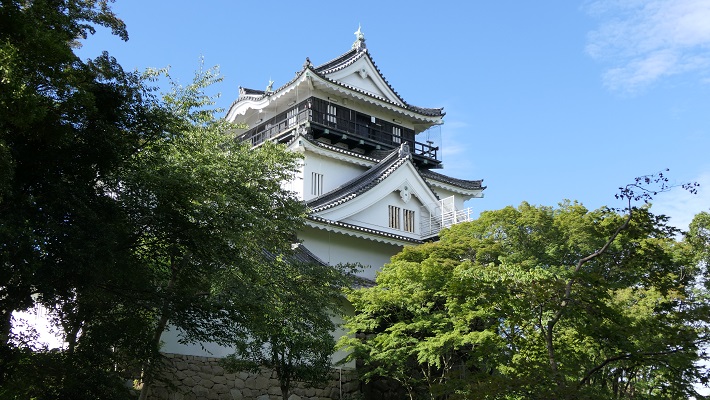
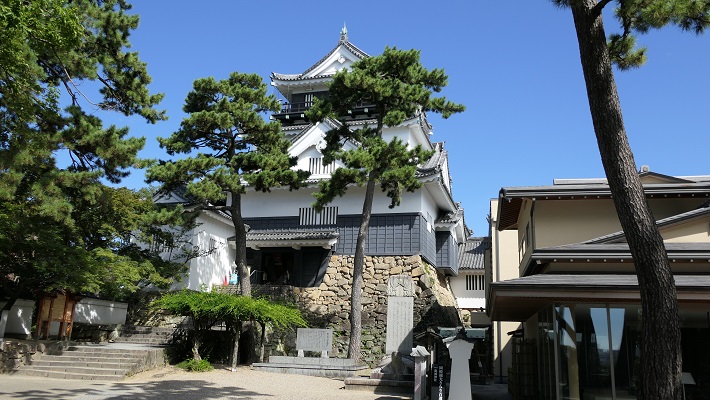
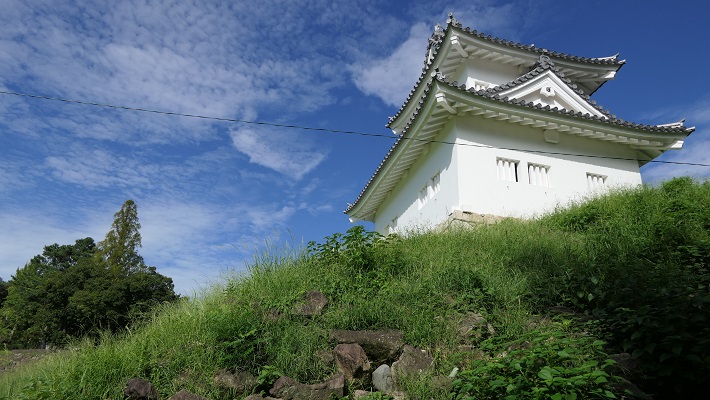
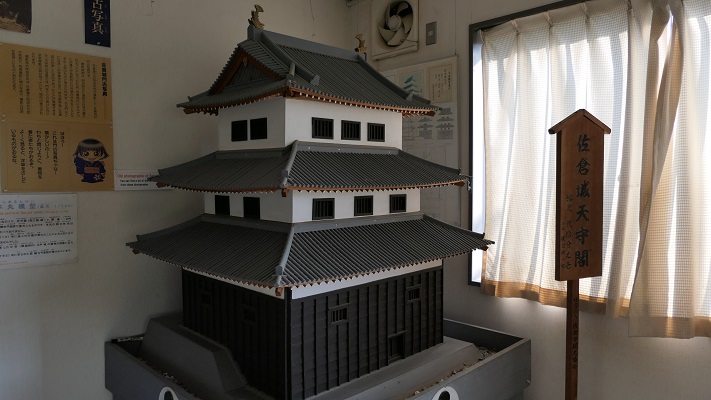
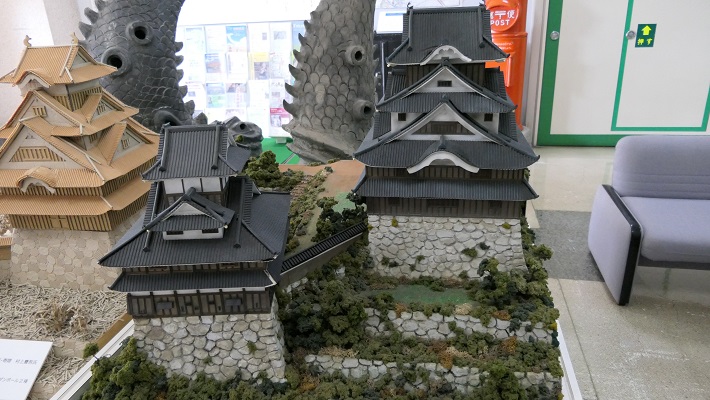
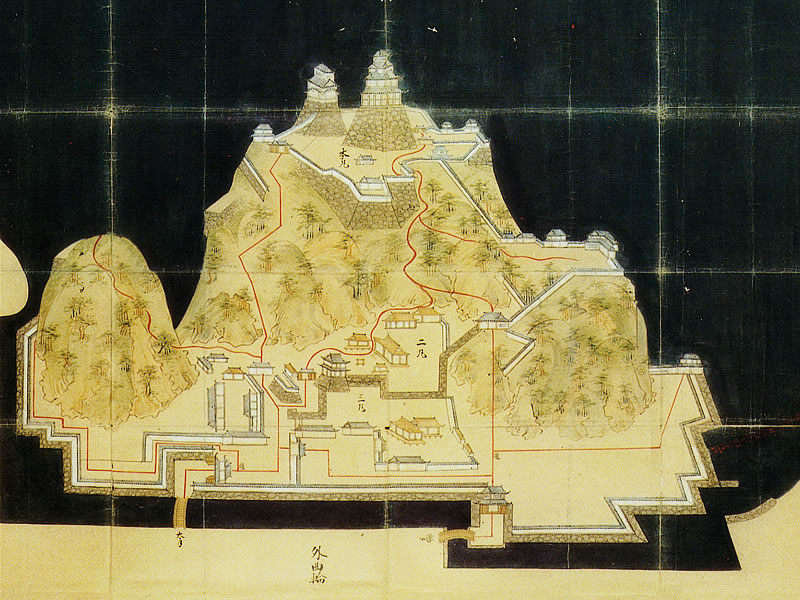
しかし、米子城の場合は、元あった4階の天守は残され、単に名前が副天守または四階櫓と変えられただけでした。つまりそれ以来、2つの天守が並び立っていたのです。何と勇壮な姿だったことでしょう。
However, in the case of Yonago Castle, the old four-story Tenshu remained and was just renamed the Sub Main Tower or the Four-Story Turret. That meant two Tenshu were standing in a row since then. They must have looked so great!

鳥取藩の所有となる~Tottori feudal Domain owns
1609年、一忠は若くして亡くなり、彼には後継ぎとなる子どもがいなかったため、改易となってしまいました。最終的には米子は池田氏による鳥取藩に属することになります。池田氏は一時、当時の本拠地である鳥取城から、米子城に移り、ここを新本拠地にすることを検討しました。それだけ米子城が魅力的だったのですが、結局は中止になりました。結果、鳥取藩の家老である荒尾氏が米子城とその城下町を江戸時代いっぱい統治しました。
In 1609, Kazutada died young, then his clan was disbanded because he didn’t have children or successors. Lastly the Yonago area belonged to the Tottori feudal Domain owned by the Ikeda clan. The clan once considered Yonago Castle as their new home base by moving from their current home base, Tottori Castle. Yonago Castle was attractive to them, but the plan was canceled. Finally, the Arao clan, chief retainer of Tottori Domain governed Yonago Castle and the castle town until the end of the Edo Period.
特徴~Features
城周辺の地図~The map aroud the castle頂上へ上る~Climbing up to the top
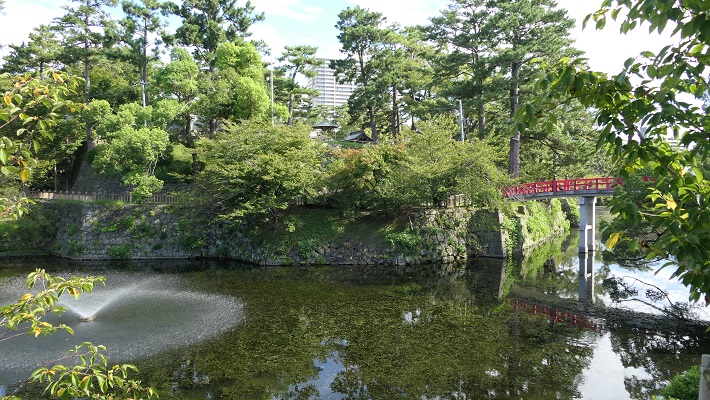
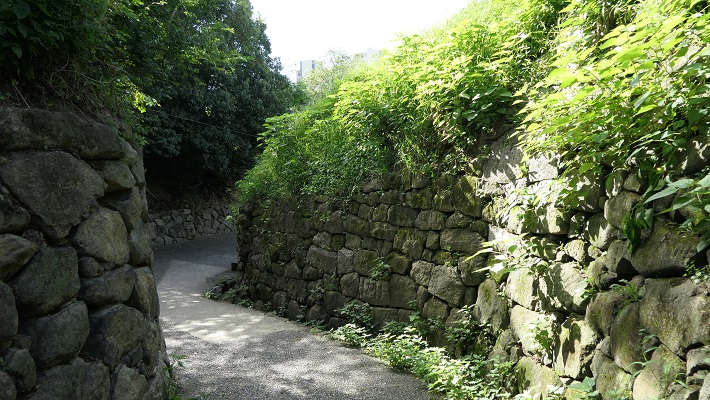
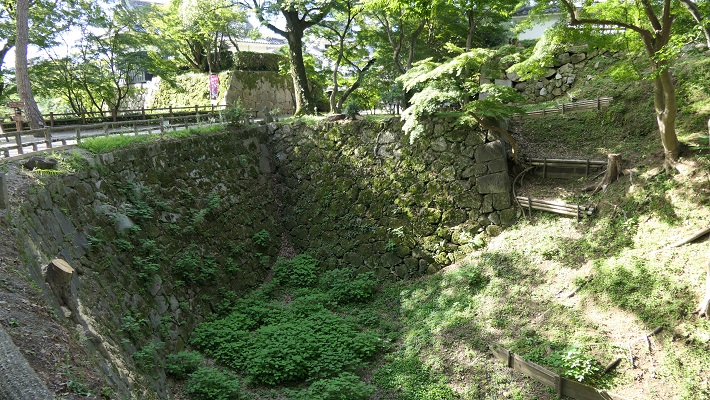
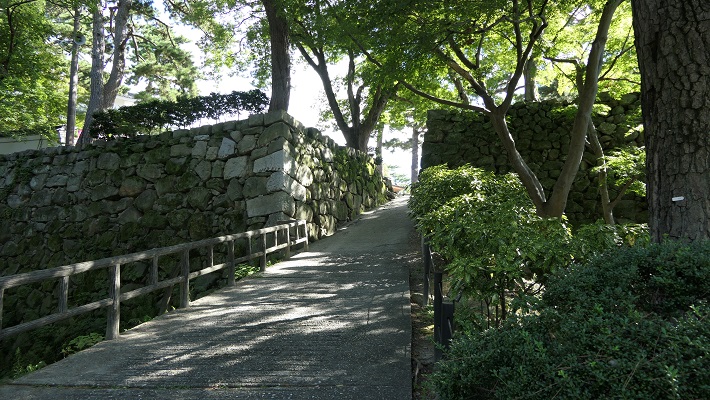
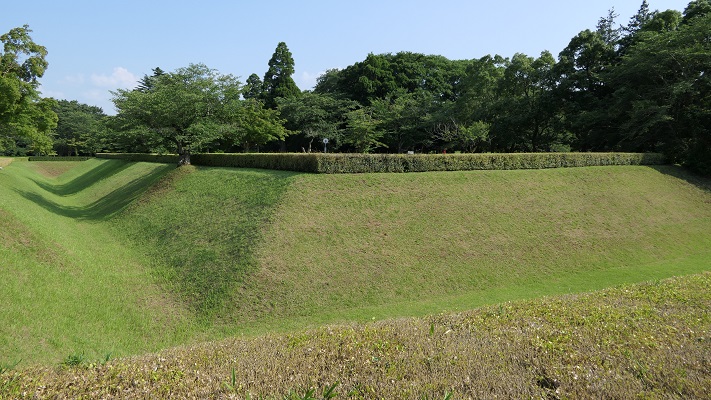
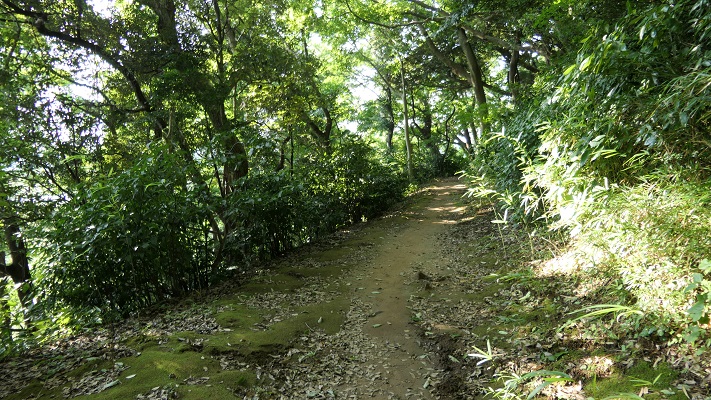
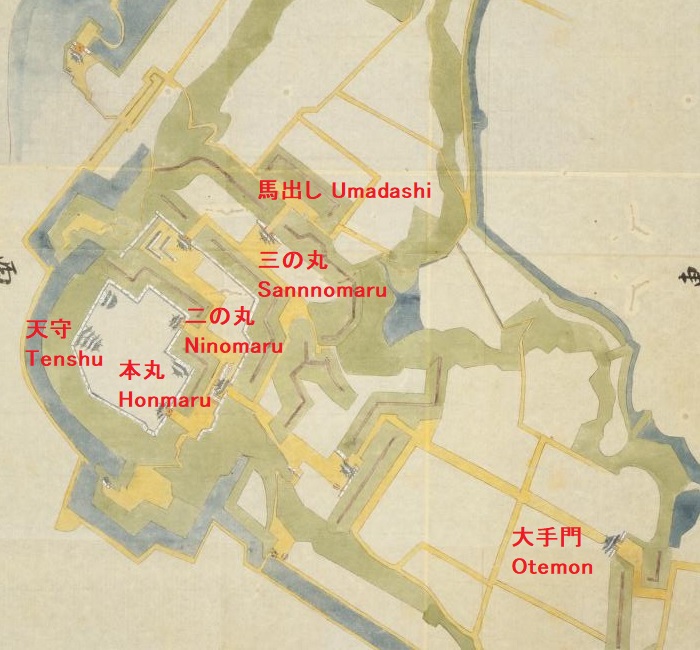
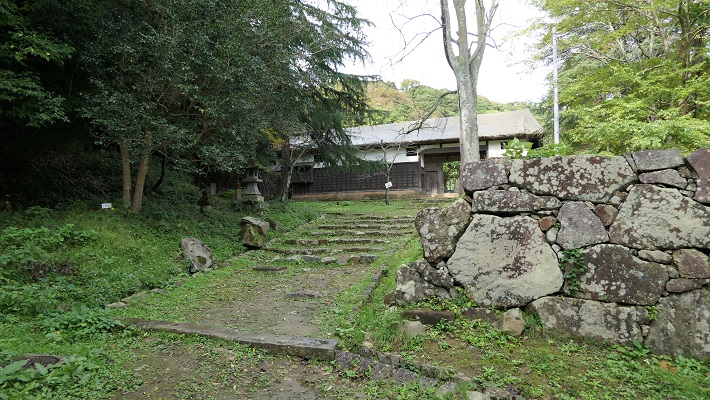
現在、米子城の城跡は湊山公園として残っています。基礎の上に石垣がありますが、現存する建物はありません。城を訪れる人は通常は城の正門であった大手門跡から頂上の方に上っていきます。他にもいくつか登り口があります。
Now, the ruins of Yonago Castle remain as Minato-yama Park. There are stone walls on their foundation, but with no remaining buildings. Visitors can usually climb up to the top from the ruins of the Main Gate or Ote-mon which was the front entrance of the castle. There are also several trails to climb.


山はそれ程高くありませんので、15分か20分くらいあれば頂にある城の中心地に到達できます。
The mountain is not so high, so you can reach the center of the castle at the peak in around 15 to 20 minutes.

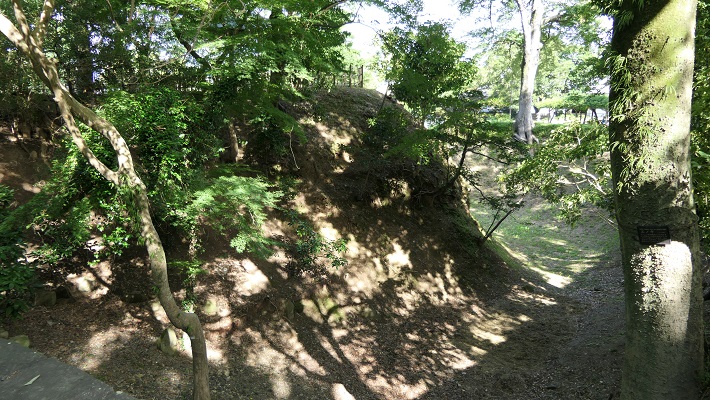
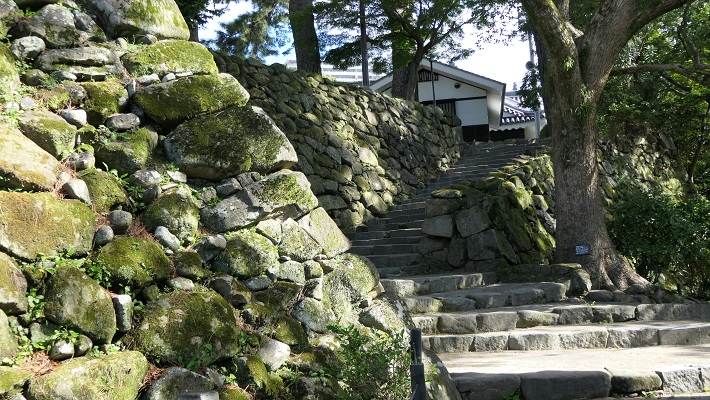
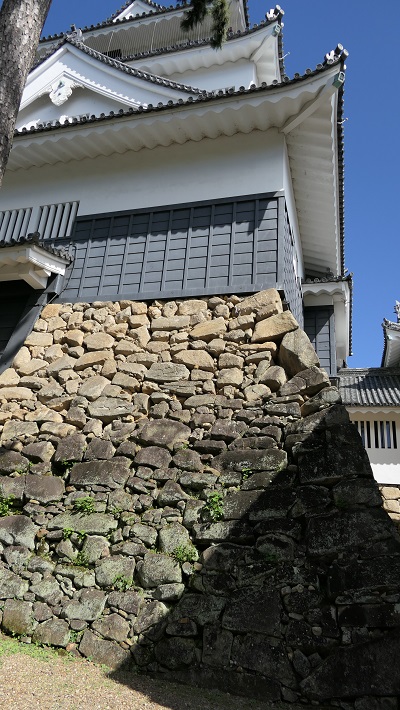
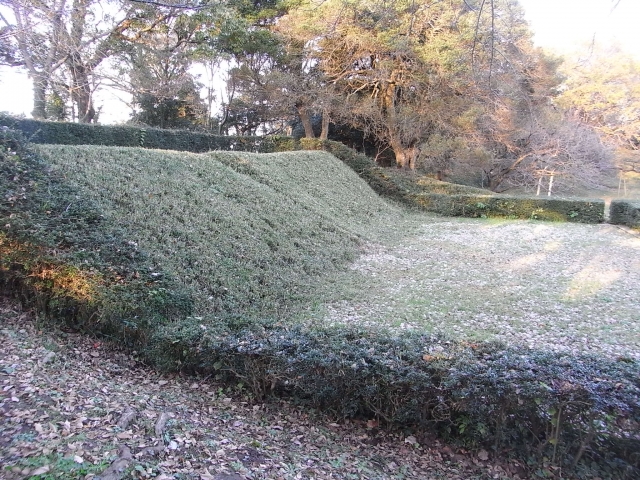
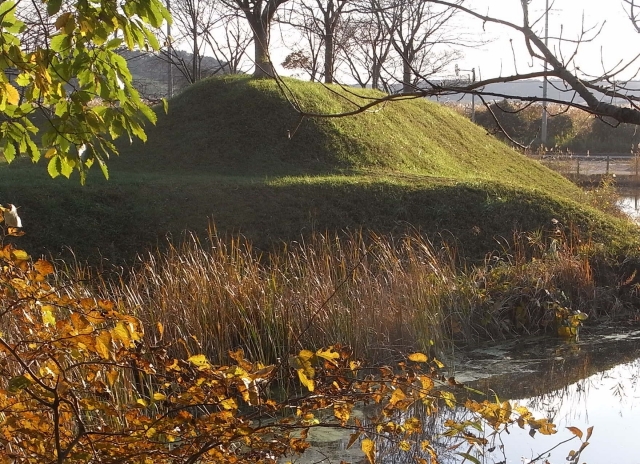
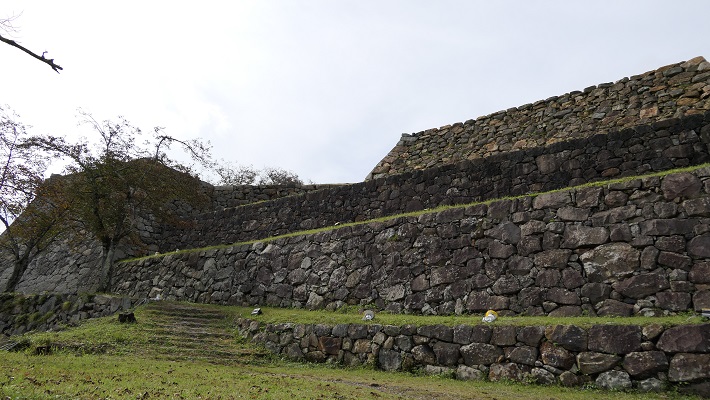
2つの天守台~The two stone wall bases for Tenshu
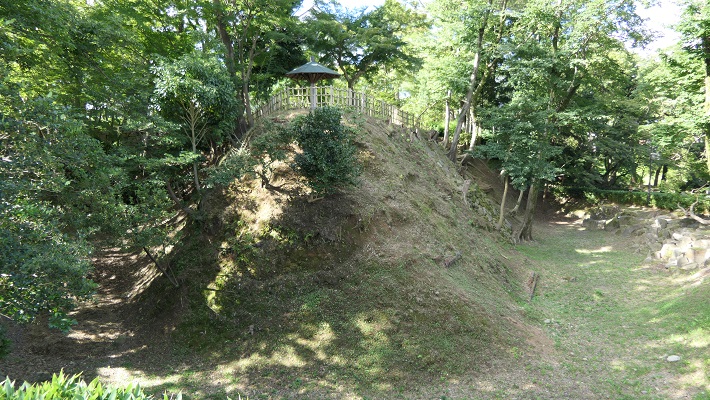
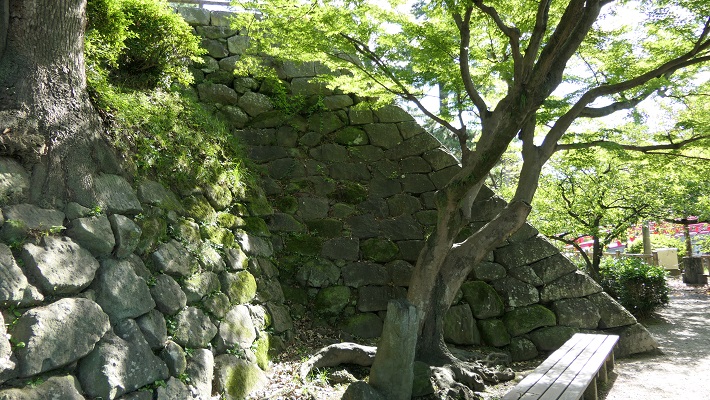
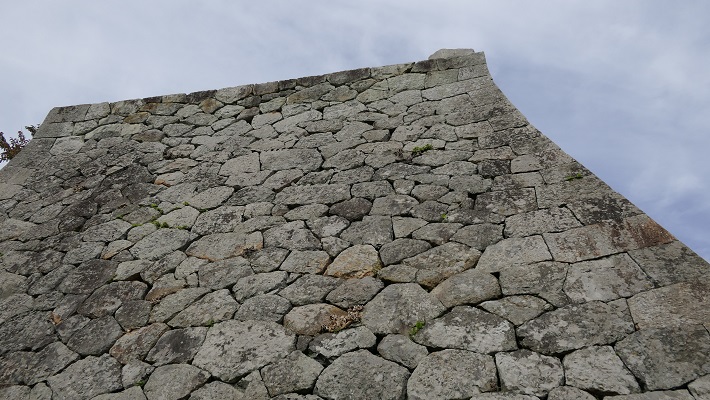
そこには2つの天守のための天守台石垣があります。新しい天守用の方は古い石を使い、三段積みの形式となっています。
There are stone wall bases for two Tenshu. The one for the new Tenshu has a three-layer style using older stones.
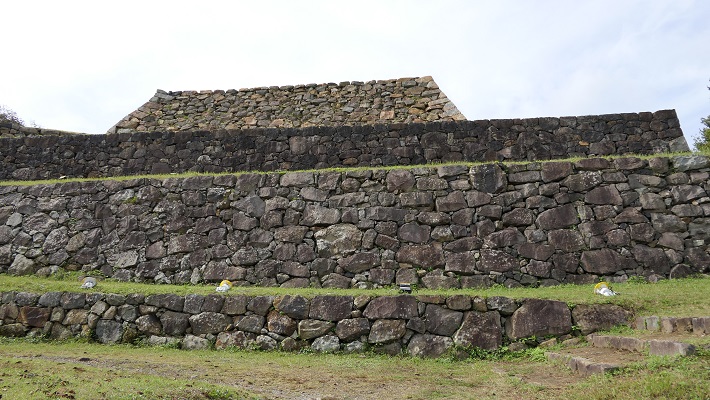


一方、古い天守(副天守)用には新しい石を使い、一層積みとなっています。これは、江戸時代後期に古い天守が大改装されたからです。この時、天守台が置き換えられたと言います。
On the other hand, the one for the old Tenshu (Sub Main Tower) has a single-layer style using newer stones. This is because the old Tenshu was renovated in the late Edo Period. It is said its base was replaced then.

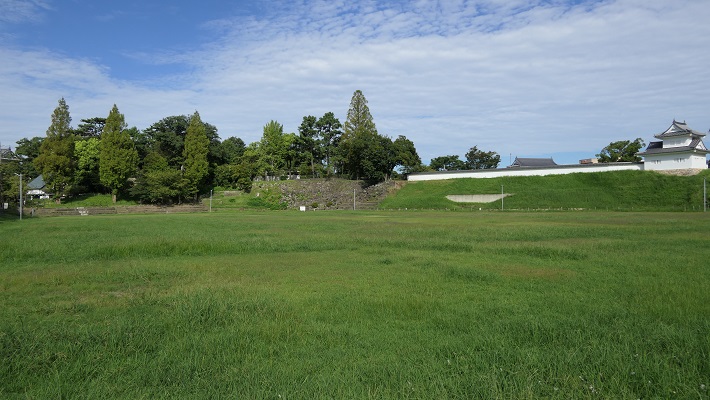
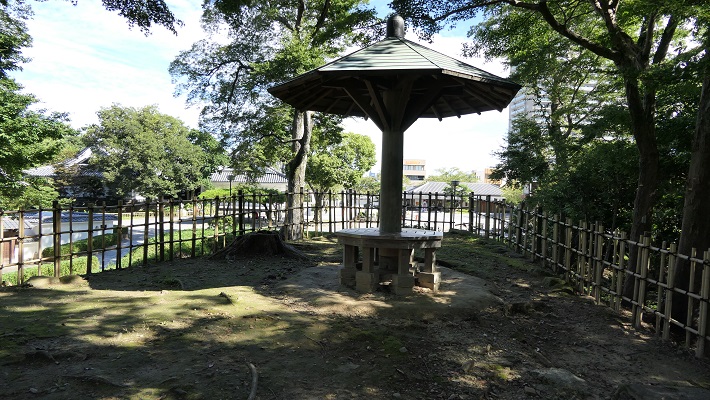
本丸とその他の曲輪~Main and other enclosures
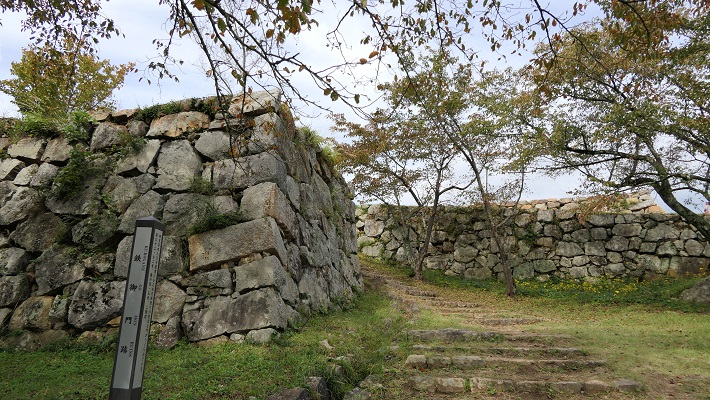
鉄門と呼ばれる正門跡を通り過ぎると、本丸に入っていきます。
Going through the front gate ruins called Kurogane-mon, you will enter the Main enclosure or “Honmaru”.

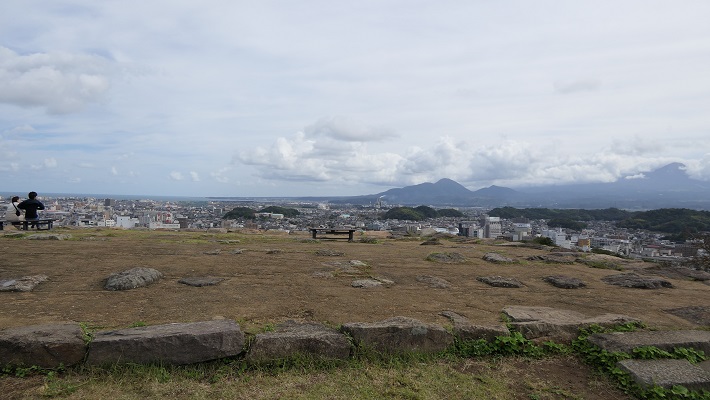
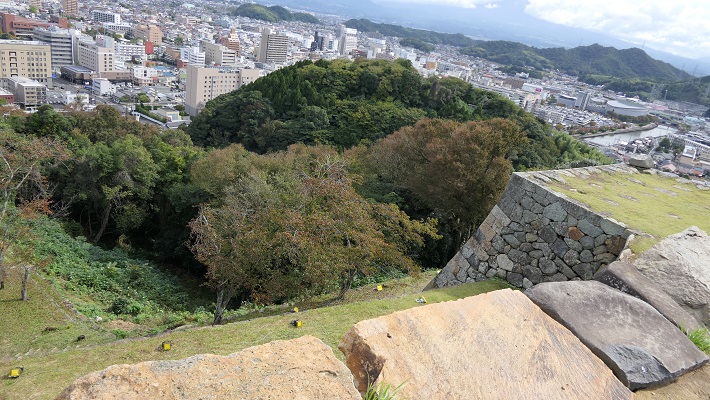
この曲輪からは、城を囲む市街地、海そして山の素晴らしい景色を堪能できます。但し、周りに柵がありませんので、足元お気を付けてください。
From the enclosure, you can get a great view of the surrounding area such as the city, the sea and mountains, but watch your steps, because there are no fences.
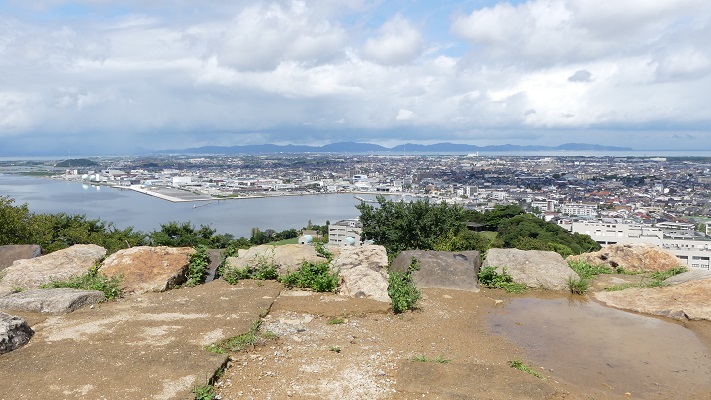



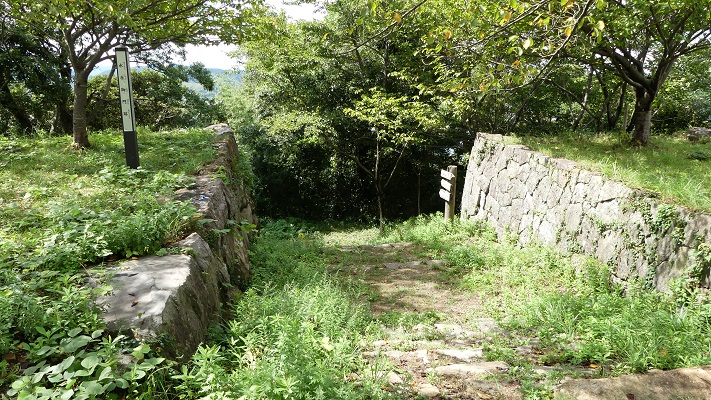
本丸には水手門という裏門もあり、かつては港につながっていました。
Honmaru also has the back gate ruins called Mizunote-mon which led to the port in the past.


城には、他にも山麓に二の丸があり、内膳丸というのもありました。内膳丸は山の中腹なり、見張りや連絡のために使われました。最近の発掘調査により、かつてはこの曲輪から本丸にまっすぐ通じる石垣でできた通路があり、登り石垣と呼ばれました。歴史家は、朝鮮侵攻のときに日本軍が似たような仕組みを作ったことから、これは吉川氏がその時の経験を基に作ったのではないかと考えています。
The castle had other enclosures like the Second enclosure or “Ninomaru” on the foot and “Naizen-maru” enclosure. Naizen-maru is on the midslope and was used for observation and connection. A recent excavation found that this was the direct route made with stone walls called Nobori-Ishigaki from this enclosure to Honmaru in the past. Historians say it might have been built by Kikkawa from the experience of the invasion of Korea where Japanese warriors built similar systems.


その後~Later History
明治維新後、米子城は廃城となり、元藩士に無償で譲渡されました。しかしながら、城をそのまま維持するは大変困難でした。すべての城の建物は、廃材として売られていきました。1933年、米子市が城跡を取得し、しばらくして湊山公園として整備しました。2006年に城跡は国の史跡に指定されました。それ以来、発掘調査が進められています。
After the Meiji Restoration, Yonago Castle was abolished and assigned to former warriors for free. However, it was too difficult for them to keep the castle as it had been. They had to sell all of the buildings in the castle as waste materials. In 1933, Yonago City owned the castle ruins, then developed them as Minato-yama Park after a whole. The ruins were designated as a National Historic Site in 2006. Since then, excavation and investigations have been ongoing.
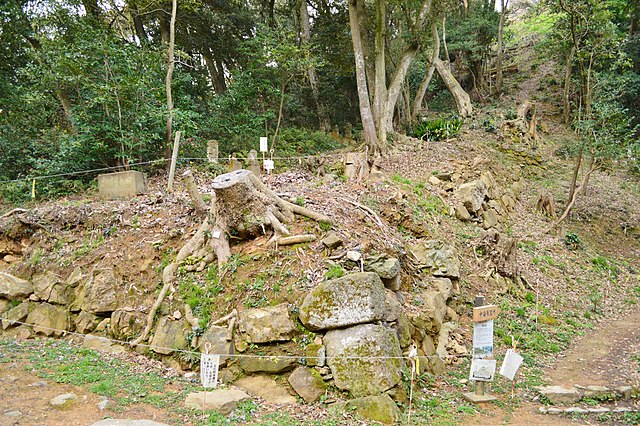

私の感想~My Impression
もし藩士たちが少しでも城の建物を残していてくれたらと思います。そうであったなら現在の松江城のようになっていたでしょう。どちらにしろ米子城跡に訪れる価値はあります。とてもゆったりできますし、観光客も市民も歴史を学ぶ場になります。
I wish the warriors could have kept some of the castle buildings so I could see them today like Matsue Castle. In any case, the ruins of Yonago Castle are still attractive. Visiting the ruins can be relaxing, an exercise and an opportunity to learn history for tourists and citizens.
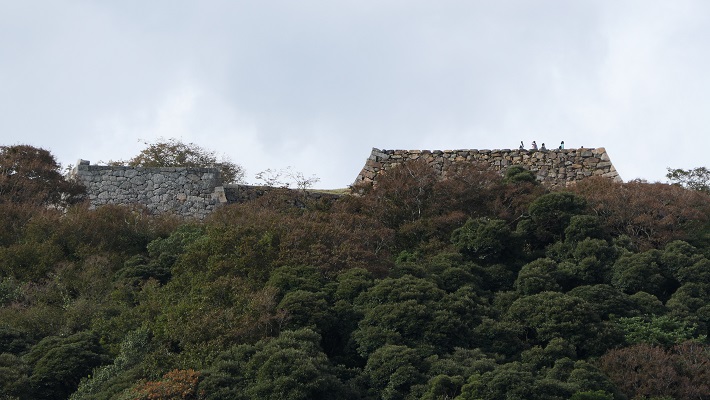

ここに行くには~How to get There
車で行く場合:山陰自動車道米子西ICから約4kmです。公園に駐車場があります。
電車では、JR米子駅から歩いて約20分です。
米子空港から米子駅まで:米子空港駅から境線に乗るか、空港連絡バスに乗ってください。
If you want to go there by car: It is about 4 km from the Yonago-Nishi IC on San-in Expressway. The park offers a parking lot.
By train, it takes about 20 minutes on foot from JR Yonago station.
From Yonago Airport to Yonago station :Take the Sakai line from Yonago-Kuko station, or take the connecting bus for Yonago station.

リンク、参考情報~Links and References
・国史跡 米子城跡(Yonago City Official Website)
・「歴史群像150号、戦国の城/伯耆米子城」学研(Japanese Magazine)
・「よみがえる日本の城6」学研(Japanese Book)