概要~Overviews
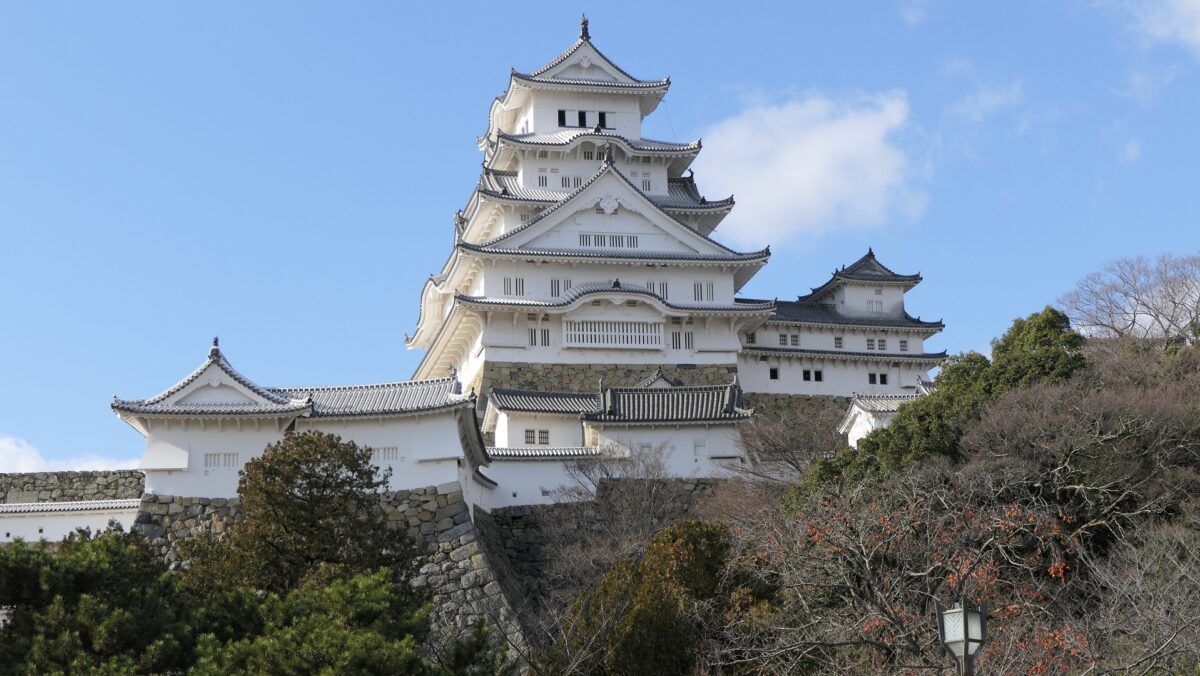
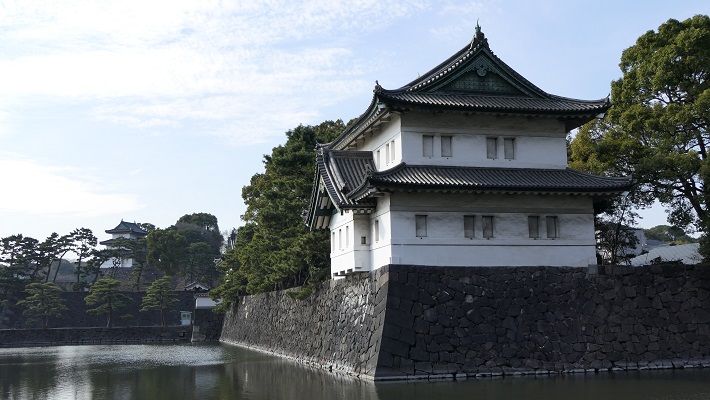
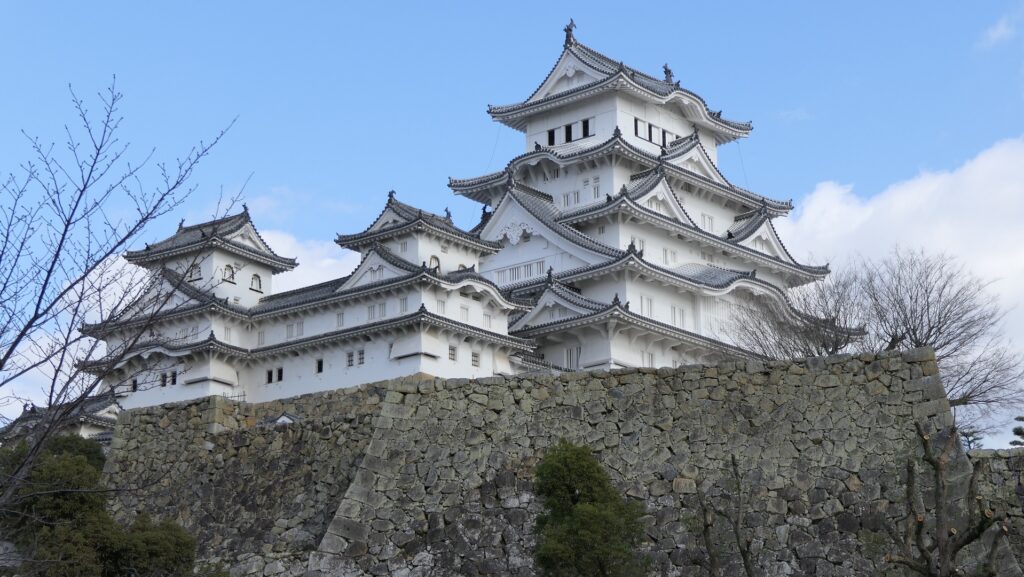
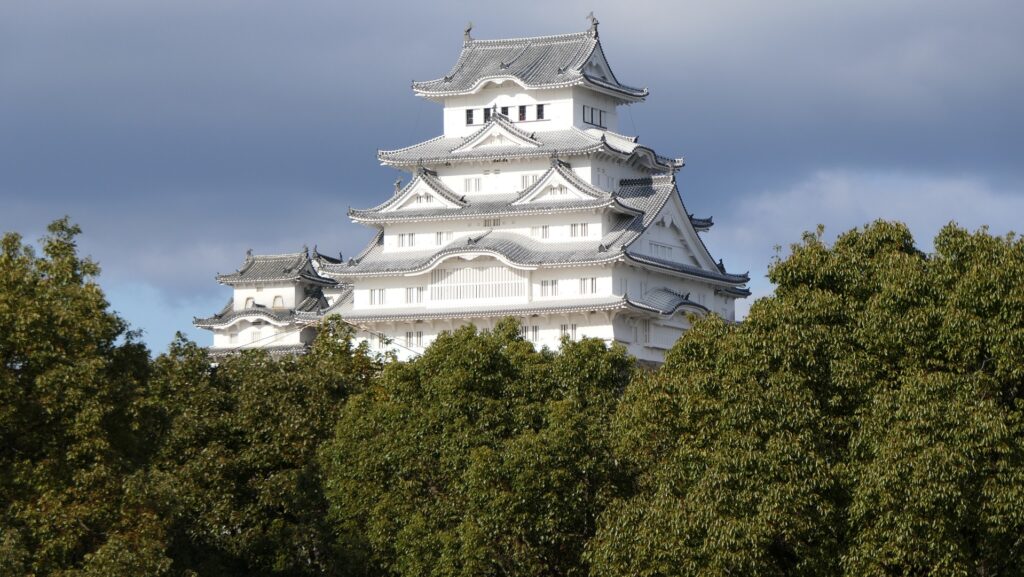
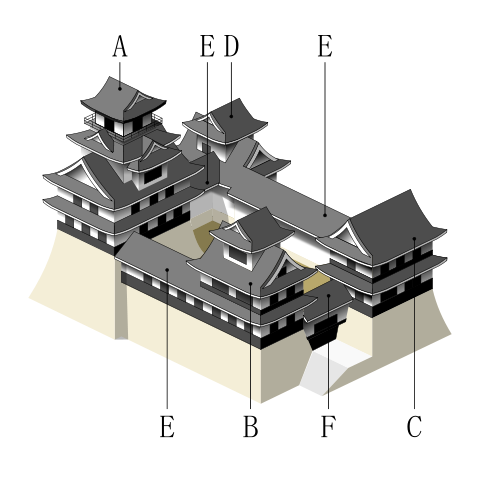
姫路城は、その白亜の天守群を世界中に知られており、よく「白鷺城」という別名で呼ばれたりしています。大天守は、日本の城で現存している12天守の中では最大のものであり、31.5mの高さ(天守台石垣を含めると45.35m)があります。大天守、3基の小天守、その他の構造物と合わせた一体が国宝に指定されています。
Himeji Castle is known around the world for its beautiful group of white Main Towers and is often nicknamed White Heron Castle or “Shirasagi-jo”. The Large Main Tower is the largest one out of the 12 remaining main towers in Japanese castles, which is 31.5m high (45.35m including the stone wall base). The Large Main Tower, the three Small Main Towers, and the other structures on the property have been designated as National Treasures of Japan.

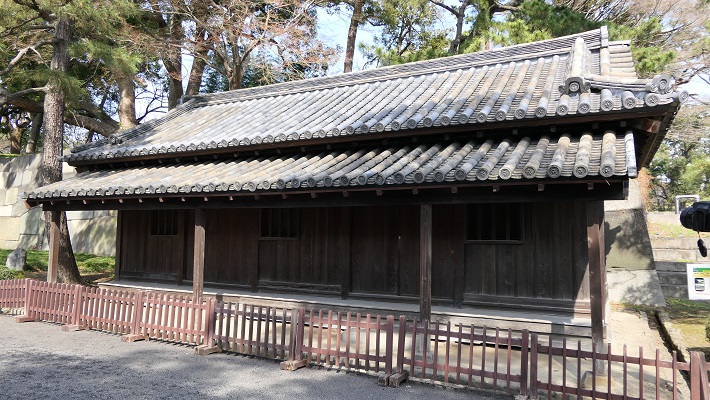
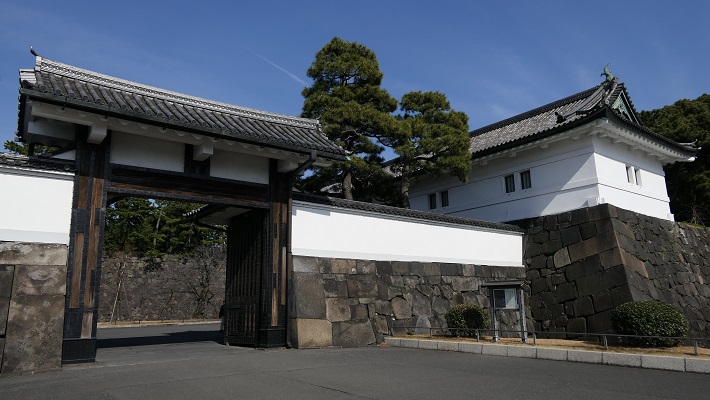
更には、多くの曲輪、石垣、水堀など、城の基礎部分が、ほとんどそのまま残っていて、天守を取り囲んでいます。これら城の主要部分はまた、国の特別史跡に指定されています。27基の櫓、15基の門、32枚の塀という、数多くの建物がその基礎の上に現存しています。これらは全て国の重要文化財に指定されています。
In addition, the current structure of the castle mostly consists of a lot of enclosures, stone walls, and water moats surrounding the Main Tower. The main portion of the castle is designated as a National Special Historic Site. The remaining buildings on the structure include as many as 27 turrets, 15 gates and 32 walls. They have all become Important Cultural Properties.
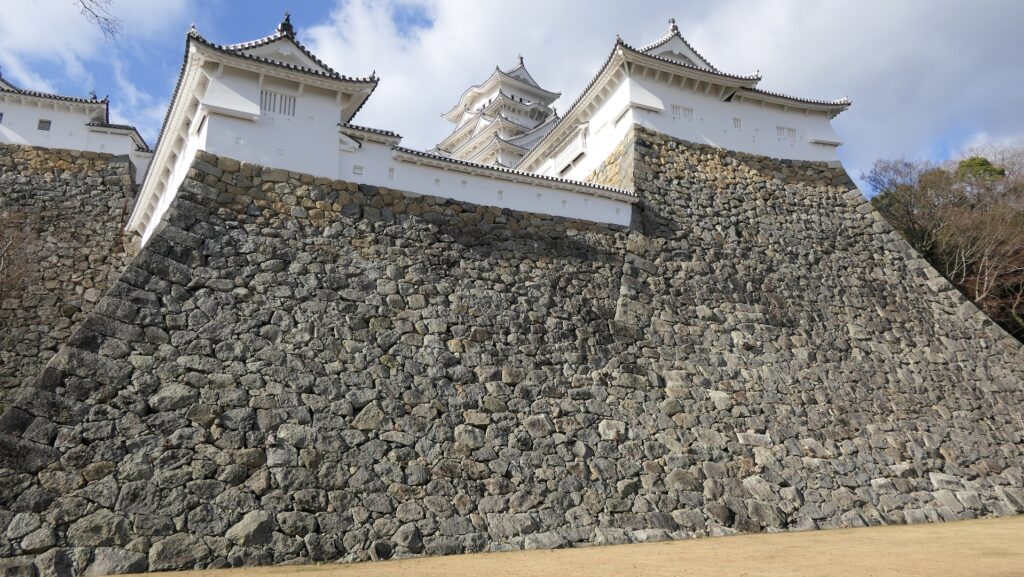

その上に、この城は日本の歴史の中で重要な役割を担いましたが、それは後述します。その役割を終えた後でも、幸運もあったかもしれませんが、日本の人々はこの城を守り続けました。現在この城は、姫路市の最も有名で且つ大事なシンボルとなっています。1993年からは日本では初となる世界文化遺産にも指定されています。
Moreover, the castle had an important role in Japanese history, which I will describe later.
Even after that role ended, the people of Japan continued to maintain the castle, although some people might say it survived by good luck. Now, people consider the castle as the greatest, most respected symbol in Himeji City. It has been a cultural site on the World Heritage List since 1993, which was the first case in Japan.

これらのことから私は、一般的に日本のどの城がベストかと聞かれた場合、それぞれの方に好みがあるにしても、それは姫路城ですと明言できます。
For those reasons, if I am asked from someone which castle is the best in Japan generally, I can clearly answer it is Himeji Castle, though each has his/her own preference.
立地と歴史~Location and History
姫路城は、兵庫県西部の播州平野にある標高45.6m姫山の上にあります。この城は、最初は14世紀に赤松氏によって築かれたと言われていますが、詳細は不明です。城周辺の地域は肥沃で交通の要所であり、山陽街道が通っていました。ただしこの城は、周りにある多くの城のうちの一つに過ぎませんでした。この状況は戦国時代の16世紀、黒田官兵衛が城を所有していた時に変わりました。東には織田氏、西には毛利氏が姫路城周辺の地を狙っている中、官兵衛は織田氏に味方することを決意しました。官兵衛は、姫路城を織田の家臣である羽柴秀吉に差し出したのです。秀吉は、後に天下人である豊臣秀吉となります。
Himeji Castle is located on 45.6m high Himeyama mountain in the Banshu Plain, the western part of Hyogo Prefecture. It is said that the castle was first built by Akamatsu Clan in the 14th century, but the details are uncertain. The area around the castle was fertile and important for transportation where the Sanyo Road passed through, but the castle was among the many castles around. The situation changed in the late 16th century during the Sengoku Period when Kanbe Kuroda owned the castle. With the Oda Clan on the east and the Mori Clan on the west, aiming to invade the area around the Himeji castle, Kanbe decided to support the Oda Clan. He offered his Himeji Castle to Oda’s retainer, Hideyoshi Hashiba, who later became the ruler of Japan and subsequently changed his name to Hideyoshi Toyotomi.

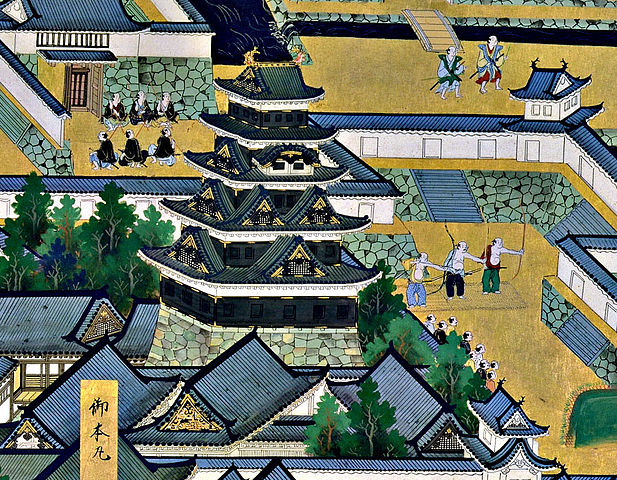
秀吉は毛利の領地を侵略するため、この城を根拠地とし、城の拡張を行いました。秀吉時代の城には三層の天守がありましたが、詳細はその遺跡が現在の天守の下にあるため明らかになっていません。城の基本的な構造はこの時代に確立したと言われています。1582年、秀吉と官兵衛は姫路城から100km近く西方にある備中高松城を攻撃していました。そのとき本能寺の変が起こり、秀吉と官兵衛の主君である織田信長が明智光秀により殺されました。秀吉は直ちに西方の毛利氏と講和を結びます。これにより秀吉は、主には徒歩による移動で重い荷物を自ら運ぶしかなかった前近代の軍隊を、わずか3日で姫路城に戻すことができたのです。彼はこの城で準備を整えてから出陣し、光秀を倒した後、天下を掌握することに成功しました。
Hideyoshi was based at the castle to invade Mori’s territory, and developed the castle. The castle of Hideyoshi’s period had a three-layer Main Tower; the details of which are uncertain because its ruins are under the present Main Tower. It is said that the basic structure of the castle was established at that time. In 1582, Hideyoshi with Kanbe attacked Bicchu-Takamatsu Castle, nearly 100km away from Himeji Castle on the west. The Honnoji Incident happened where Hideyoshi’s and Kanbe’s boss, Nobunaga Oda was killed by Mitsuhide Akechi. Hideyoshi quickly made peace with the Mori Clan. This allowed Hideyoshi to quickly return to Himeji Castle within 3 days with pre-modern large troops travelling mainly by foot and transporting heavy items. He prepared and left the castle to beat Mitsuhide and was successful in taking over control of Japan.


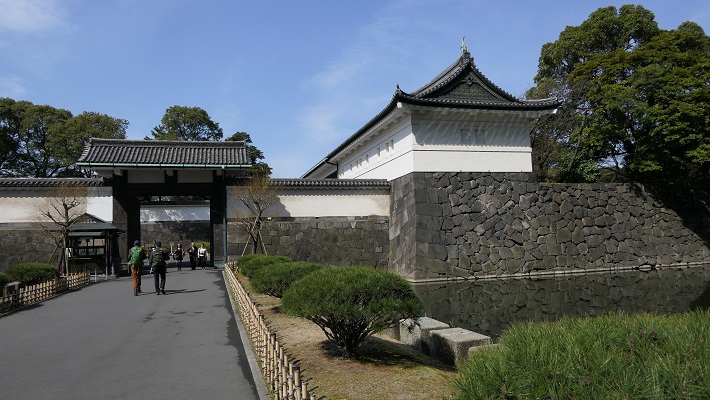
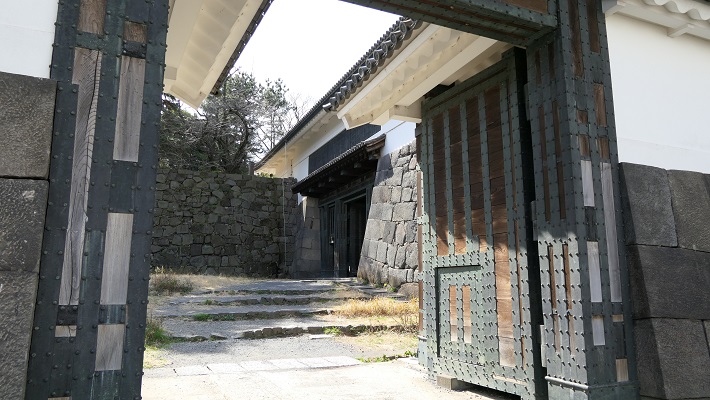
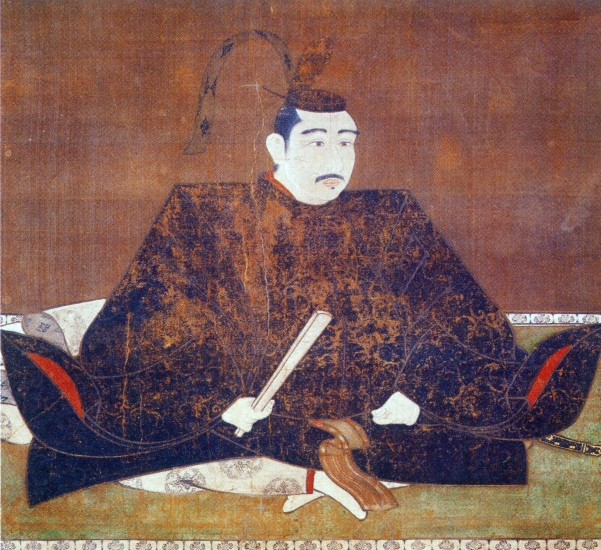
秀吉の死後、豊臣氏に代わって徳川家康が1600年に実権を握りました。家康は、娘婿である池田輝政を吉田城から姫路城に移しました。輝政は後に姫路藩の初代藩主になります。輝政の役目は、大坂城にいた豊臣氏をいまだ支持するかもしれない西国大名を監視することでした。彼は1601年から1609年の間に城の大改修を行います。天守は、5層の大天守と3基の小天守に置き換えられました。これらは、渡櫓によりつながっていて「連立式」天守と呼ばれます。輝政は姫山の上にある秀吉の城の構造を引き継ぎつつも、多くの櫓、門、練塀、石垣を加えたのです。結果的に城は、小さな曲輪を複雑に組み合わせたものとなりました。例えば、今でも観光客は天守にたどり着くまで10以上もの門を通らなければなりません。
After Hideyoshi died, Ieyasu Tokugawa got the power instead of the Toyotomi Clan in 1600. Ieyasu transferred his son-in law, Terumasa Ikeda, from Yoshida Castle to Himeji Castle. Terumasa later became the founder of the Himeji Domain. Terumasa’s role was to monitor the lords in western Japan, who might still support the Toyotomi Clan at Osaka Castle. He did major renovations to the castle between 1601 and 1609. The Main Tower was replaced with the five-layer Large Main Tower and three Small Main Towers. They are connected by the Roofed Passage Turrets, which are called Connected Type or “Renritsu-shiki”. Terumasa followed Hideyoshi’s structure of the castle on Himeyama mountain, but he added lots of turrets, gates, plaster walls, and stone walls. As a result, the center of the castle became very complex with combined small enclosures. For example, visitors must pass through as many as over 10 gates to reach the Main Tower.

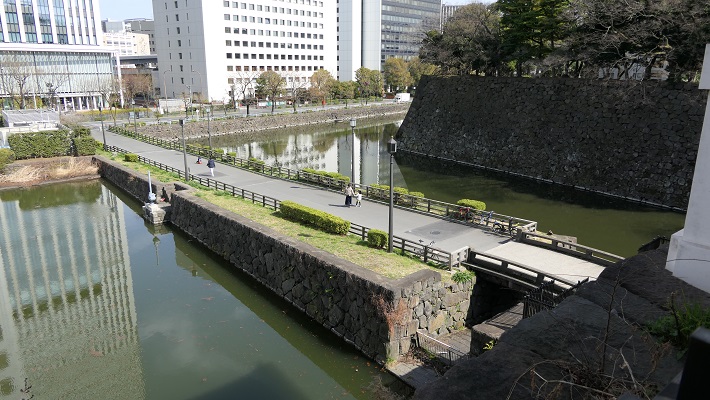
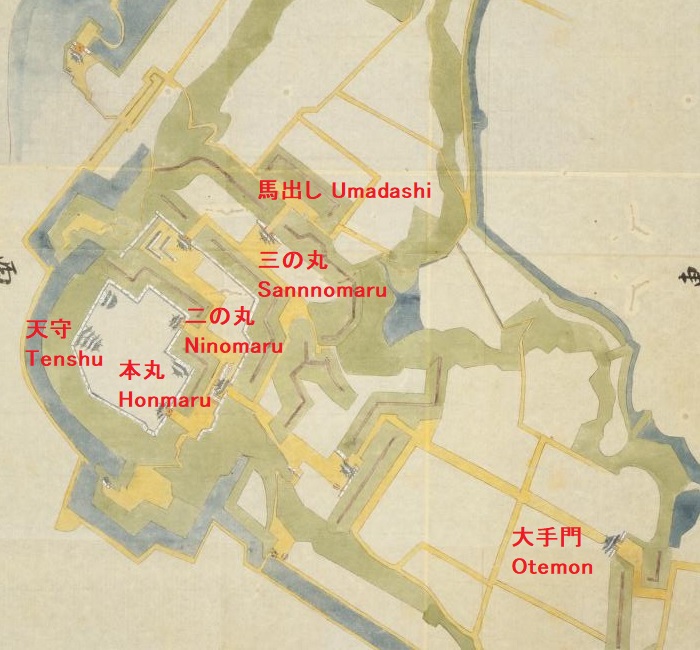
更には、城は姫山の西にある鷺山を取り込んで拡大しました。鷺山の上には西の丸が築かれました。三の丸が姫山の南の平地に築かれました。城の水堀は、城の裏側から渦巻き状に広がっていました。一周目は、姫山の上にある城の中心部と、二の丸と三の丸を囲んでいて、内堀と呼ばれました。二周目は中堀と呼ばれ、武士の屋敷を含む区域を囲んでいました。外堀は、中堀の途中から分かれ出て、南方と東方にあった城下町までも囲んでいました。輝政は、現在私たちが見ているものと、ほとんど近い所まで城を築き上げました。
In addition, the castle was extended to take in the Sagiyama mountain, the west of Himeyama. The Nishinomaru or the Western Enclosure was built on the Sayima mountain. The Sannomaru or the Third Enclosure was built on the plain area to the south of Himeyama. The water moats of the castle started from the back and spread like swirling. The first turn surrounded the center of the castle on Himeyama, Nishinomaru, and Sannnomaru, which was called the Inner Moat. The second turn called the Middle Moat surrounded the area including warriors’ houses. The Outer Moat separated from the halfway of the Middle Moat and even surrounded the castle town on the south and east directions. Terumasa built the castle nearly like what we see now.
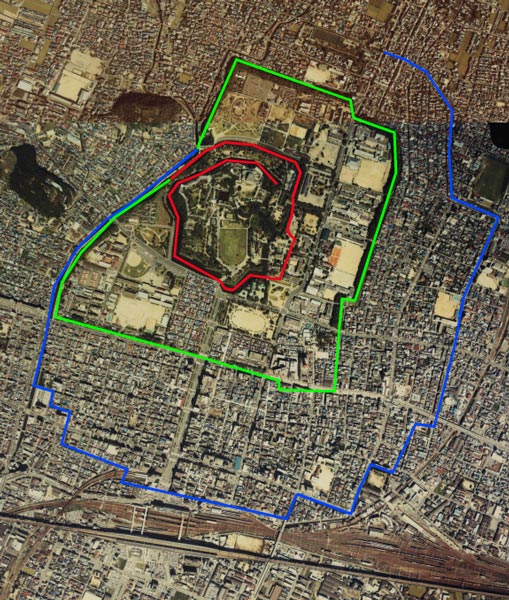
輝政は残念ながら1613年に亡くなってしまいます。徳川幕府は城主を、幕府の重臣である本多忠政に変えました。忠政は城の造営を続け、西の丸を改築したり、運河を掘ったりしました。西の丸は更に広大となり、多くの兵士を収容できるようになりました。よって、中心部の曲輪とは異なる広々とした外観です。。1615年に豊臣氏は幕府により倒されましたが、幕府は姫路城主に西国大名の監視を担わせ続けました。そのため、有能な人材を宛がうため、何度も城主は交替させられます。18世紀の中頃からは、酒井氏が幕末まで城を統治しました。恐らくは社会が安定したからでしょう。城の創建以来、一度もここで戦が起こらなかったため、度々「不戦の城」とも呼ばれています。
After Terumasa unfortunately died in 1613, the Tokugawa Shogunate changed the lord of the castle to Tadamasa Honda, a senior vassal of the Shogunate. Tadamasa continued work on the castle such as improving the Nishinomaru and developing a canal. Nishinomaru became more spacious which could accommodate large troops, so it looks different from other central enclosures. Though the Toyotomi Clan had been defeated by the Shogunate in 1615, it still made the lord of Himeji Castle stay to monitor the lords in western Japan. For this reason, the lord of the castle was replaced by a capable person several times by the Shogunate. From the middle 18th century, the Sakai Clan continued to govern the castle until the end of the Edo Period. Perhaps it could be because the society became stable. No battles have occurred at the castle since it was built, so it is sometimes called “an anti-war castle”.

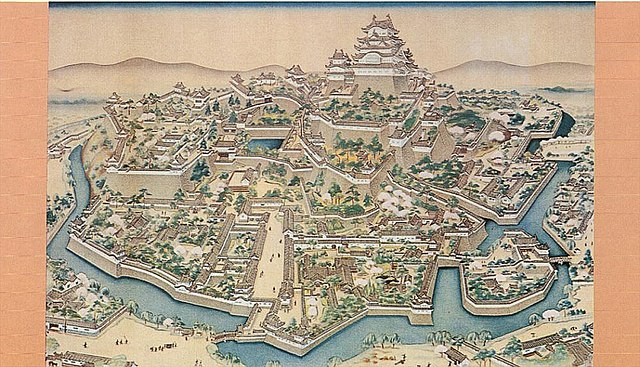
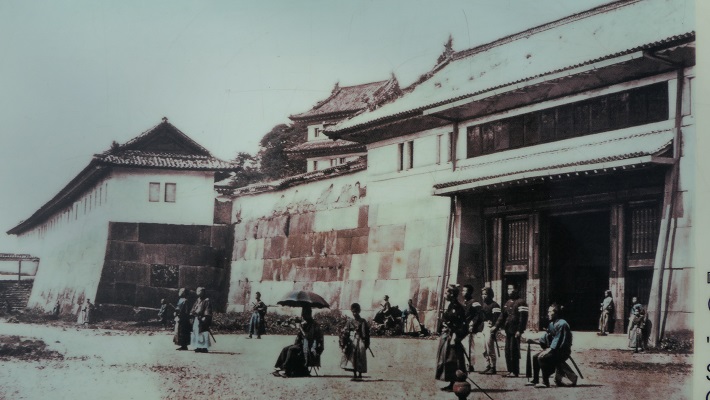
しかしながら、幕末になってこの城は初めての危機を迎えます。1868年に岡山藩などの他藩を含む新政府軍により包囲されたのです。これは酒井氏が幕府の要職についていたためです。城にいた武士たちは降伏を申し出ましたが、攻撃側は受け入れず砲撃を始めました。備前門という門の瓦が幾枚か破損しましたが、それだけでした。単なるパフォーマンスだったのかもしれません。その後城の武士たちは降伏し、城を新政府に引き渡しました。
However, at the end of the Edo Period, the castle faced its first crisis. The New Government Army including other domains, such as Okayama, surrounded the castle in 1868. This is because the Sakai Clan was in charge of an important position for the Shogunate. The warriors in the castle had sworn allegiance, but the attackers didn’t accept it and opened fire. Some tiles of a gate called Bizen-mon were destroyed, but that was all. It may have been like a performance. The warriors in the castle later surrendered and handed over control of the castle to the New Government.

その後~Later History
明治維新後、姫路城の一部は日本陸軍によって使用されました。三の丸周辺の建物は撤去されました。天守を含む他の建物も売られたが、買主は撤去する費用が高すぎたために権利を放棄したとも言われています。真相は不明です。もし本当なら、城にとって第2の危機でした。
After the Meiji Restoration, part of Himeji Castle was used for the Japanese Army. Some buildings around Sannomaru were demolished. It is said that other buildings including the Main Tower were also sold, but the buyer waived the right, because it was too expensive for him to demolish them. This story is unclear. If true, it was the second crisis of the castle.

1878年、中村重遠大佐が姫路城と名古屋城を保存することを陸軍に提案しました。その提案は政府によって認められ、城を維持するための予算が組まれました。これは、城が文化遺産として認められた最初の事例であり、画期的なことでした。1910年に明治の大修理が行われました。実は、天守がその自重により少しずつ傾いてきていたのです。
In 1878, a military officer, Shigeto Nakamura suggested the need to preserve Himeji and Nagoya Castles to the Japanese Army. It was allowed by the government who created a budget to maintain the castles. This is the epoch-making event that castles were considered as cultural properties for the first time. The Meiji Great Repairs was done in 1910. In fact, the Main Tower was leaning little by little due to its own weight, before it was repaired.

第二次世界大戦中の1945年、姫路空襲の時に最後の危機が城に迫りました。姫路市の市街地はほとんど焼き尽くされましたが、城は無事でした。焼夷弾が天守に飛び込んできたのですが、幸い不発だったのです。残念ながら、同じく政府により維持されてきた名古屋城は、爆撃により燃えてしまいました。終戦直後、姫路の人たちは無傷であった姫路城に大変勇気づけられたといいます。現在、2回の大修理(昭和と平成)の後、姫路城は往時のような輝きを取り戻しています。城のために大変な努力をした人々と幸運に感謝しなければならないでしょう。
The last crisis came to the castle when the Himeji Air Raid happened in 1945 during World War II. The town area of Himeji City was mostly burned, but the castle wasn’t affected. A firebomb was dropped into the Main Tower, luckily it didn’t explode. Unfortunately, the Nagoya Castle, which was also being maintained by the government was burned down by bombs. People in Himeji were very encouraged by the fact that Himeji Castle was still intact just after the war. Today, after two more great repairs (Showa and Heisei), Himeji Castle gets the brilliance back like its peak time. I think we have to be thankful for the great effort of the people at the castle and for good fortune.