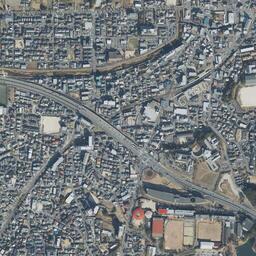
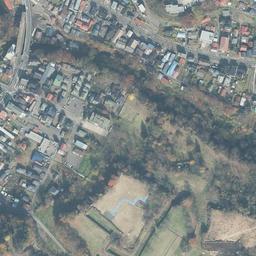
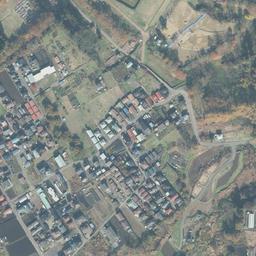
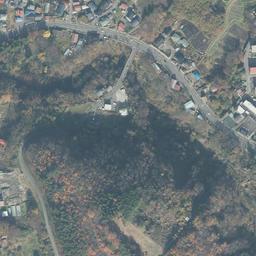
立地と歴史~Location and History
大宰府を守る防衛線~Difense Line to protect Dazaifu
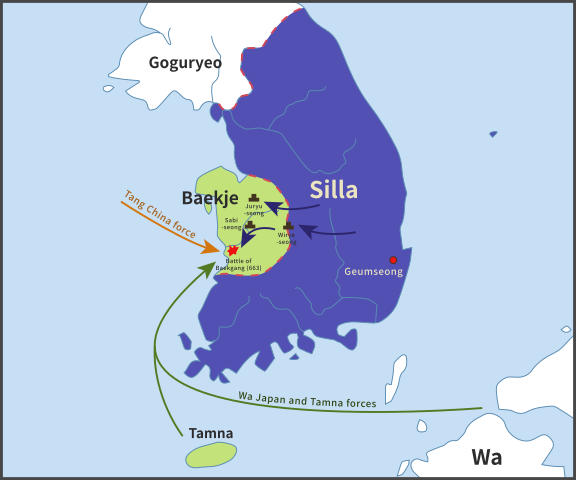
水城は、663年の朝鮮での白村江の戦いで日本が唐と新羅の連合軍に敗れた直後、国が初めて作った本格的な軍事施設です。それは、連合軍の侵攻から古代日本の地方政府であった「大宰府」を守るための防衛ラインでした。つくられたのは664年で、大野、麹智、基肄などの古代山城と呼ばれた西日本の軍事施設より以前のことでした。そのため水城は、日本の城のうちの一つとみなされています(その名前自体が水の城です)。
Mizuki was the first national full-scale military facility built immediately after Japan was beaten by the ally of Tang and Silla in the Battle of Baekgang, Korea in 663. It was a defense line to protect the ancient Japanese local government, “Dazaifu” in Kyushu Island from the ally’s invasion. It was first built in 664 before other military facilities in western Japan called ancient mountain castles such as Ono, Kikuchi, and Kii. That’s why Mizuki is regarded as one of the castles of Japan (The name means Water Castle in Japanese).
戦略的な設計~Strategic Design
この防衛ラインは東は四王寺山の麓と、西にあるもう一つの丘との間に設けられており、福岡平野では最も狭い部分に当たり、大宰府政庁の北にありました。幅80m、高さ10mの土塁が1.2kmに渡っていました。そして両側に水堀がありました。この地域の地盤が弱かったので、土塁は丈夫な枝葉の基礎の上に設置されました。この構成により土塁を強固にする方法は「敷そだ」と呼ばれました。土塁自体を強固にするためには、土を突き固める版築という方法が採用されました。水堀は、土塁の下を通る木樋によってつながっていました。その水は内側の堀から外側の堀に流れていました。
The defense line is located between the foot of Shioji-yama mountain on the east and another hill on the west, which is the narrowest part of the Fukuoka Plain, and the north of Dazaifu government. It consisted of earthen walls that were 1.2km long, 80m wide and 10m high. It was surrounded by water moats on both sides. As the earth was weak in that area so the walls were laid on a foundation of strong branches. And this method of making the structure or wall strong was called “Sikisoda”. To make the walls sturdy the workers use to ram soil on the wall and this method was called Rammed earth. The water moats were connected under the earthen walls through wooden water pipes. The water flowed from the inside into the outside part of the moat.
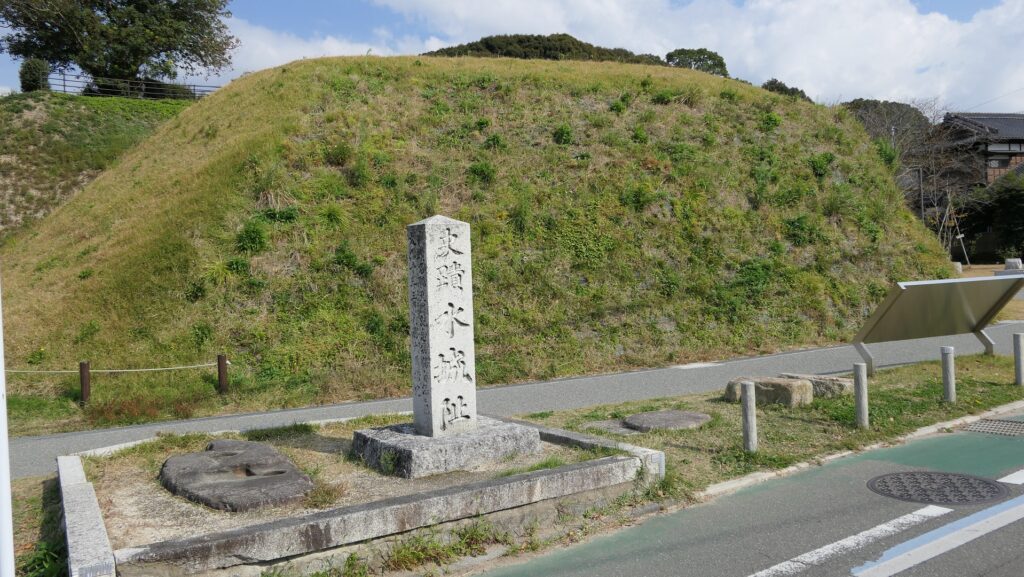
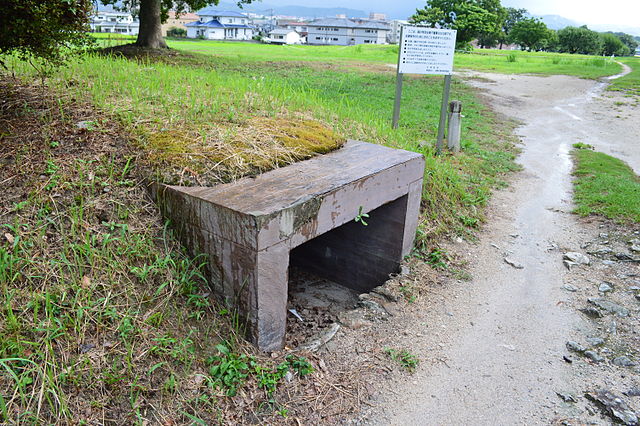


土塁の幅は戦略的に設計されており、守備兵の矢は土塁の高い位置から放たれ外側に届くが、敵の矢は外側の低い位置から放たれ、内側には届かないようになっていました。歴史家は、朝鮮からの亡命者がこれを設計したと推定しています。
Its width was strategically designed so that when the defender’s arrows shot from the upper part of the wall, it could reach outside but when the enemy shot from lower part outside the moat, it couldn’t reach inside. Historians speculate that this method was designed by Korean refugees.

交通の要地~Important Point for Traffic
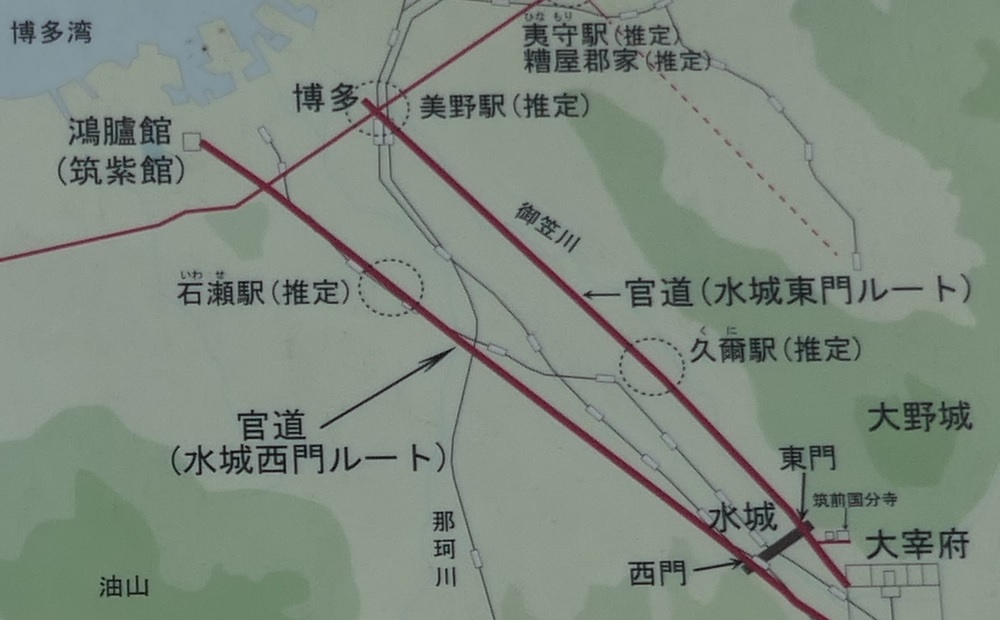
このラインには2つの門があり、それぞれ官道が通っていました。一つは東門から博多港の方に伸びており、もう一つは西門から鴻臚館と呼ばれた中国や朝鮮からの人々をもてなす迎賓館の方に伸びていました。大宰府政庁の出入口としても使われており、この地域の交通や旅行者の出入りを監視していました。
The line had two gates for two government-run roads. One of them went through the East Gate to Hakata Port, and the other went through the West Gate to the guest house called Kouro-kan that was used to host people from China and Korea. It was also used as the entrance of Dazaifu government, and it checked transportation and passengers in and out of that region.
幸いにも、連合軍は日本を攻撃しませんでした。水城は大宰府政庁の道しるべとなりました。多くの人々が訪問客の出迎えや見送りのためにここを使ったのです。
Fortunately, the ally did not attack Japan. Mizuki became a landmark of Dazaifu government. Many people used it to welcome or say good-bye to visitors.
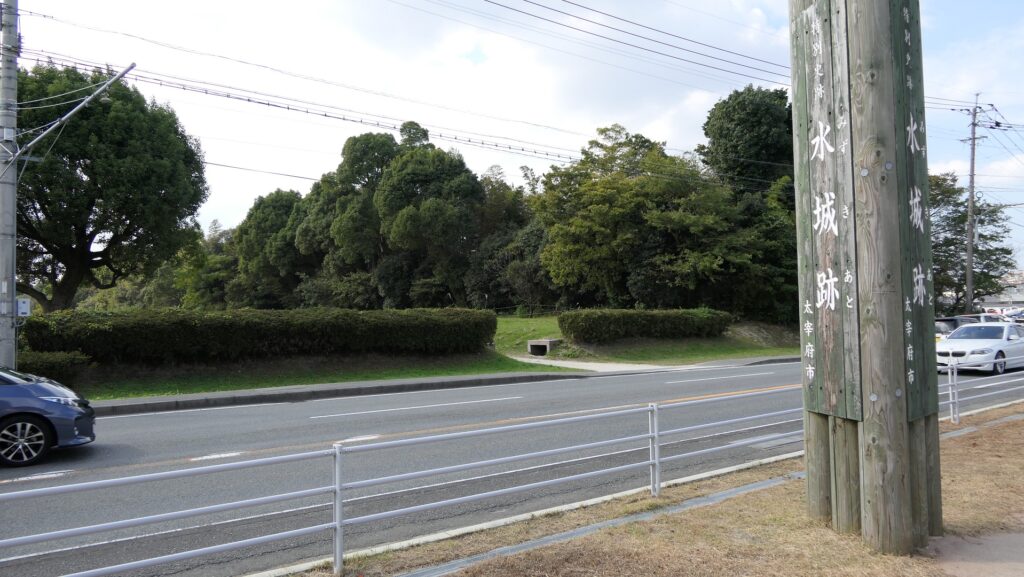

特徴~Features
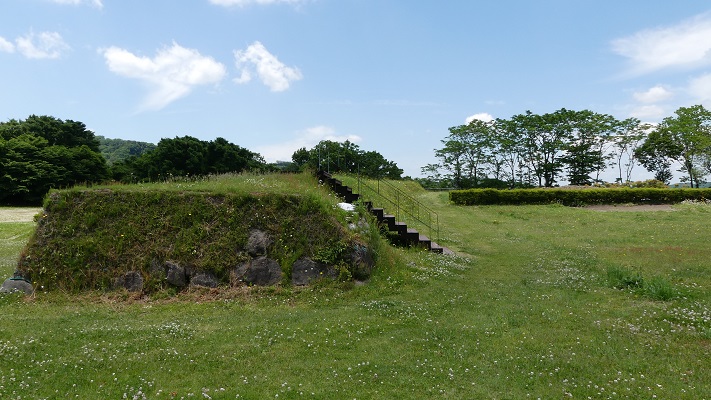
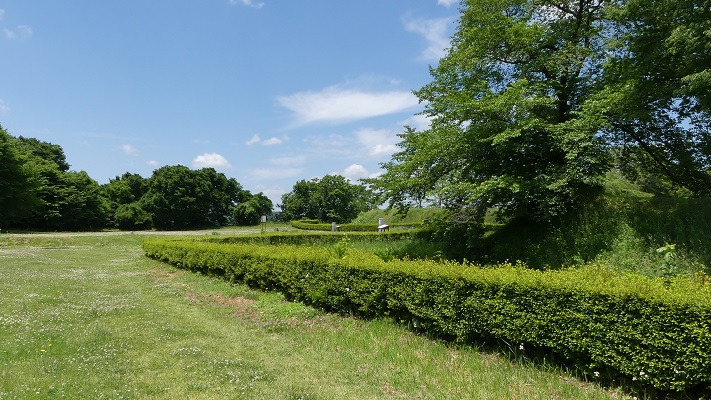
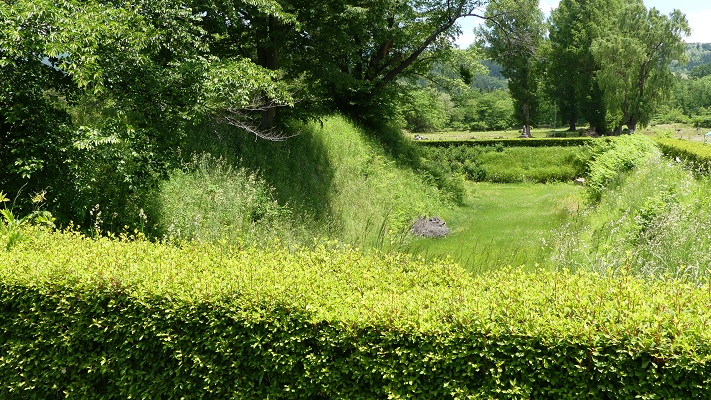
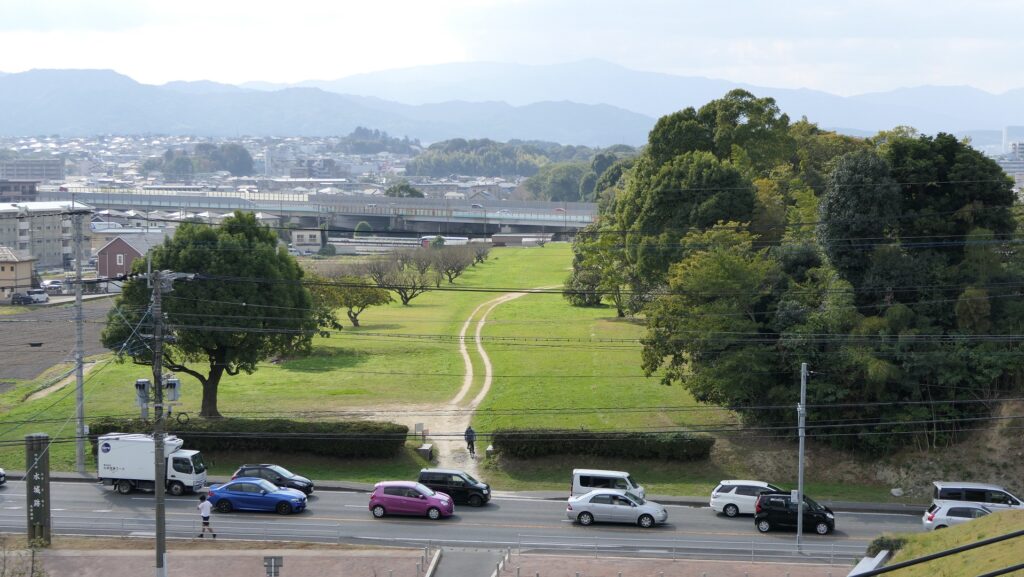
現在、この辺りを通る人たちの多くは、水城跡をはっきりと見ることができます。なぜなら、この遺跡は緑地帯のように今だにこの一帯に横たわっていて、公道、高速道路、鉄道といった多くの現代の交通網もまたこの遺跡を横切っているからです。この遺跡は緑の林に覆われた土塁として残っているのです。素晴らしいことだと思いませんか。
Now, many people who go through the area around the ruins of Mizuki can clearly see them. This is because the ruins still lay across the area like a green belt, and a lot of modern transportation such as public roads, Expressways and Railways, also go across the ruins. The ruins remain as earthen walls covered with green forests. Isn’t that fantastic?
土塁周辺を歩く~Waking around Earthen Walls
この土塁からは既に水堀は失われています。そして、ところどころ現代の交通網により寸断されてしまってもいます。しかしながら、土塁の周辺を歩いてみれば、少なくとも高さが違っている構造になっていることはわかると思います。また、JR鹿児島本線により寸断されている箇所では、どのように土塁が積み上げられているかがわかります。The earthen walls have already lost their water moats, and the walls are partly destroyed by the modern transportation. However, when you walk around the walls, you can at least see the different levels of the structure. You can also see how the walls were rammed at the cross section of the walls which are cut through by the JR Kagoshima Line.
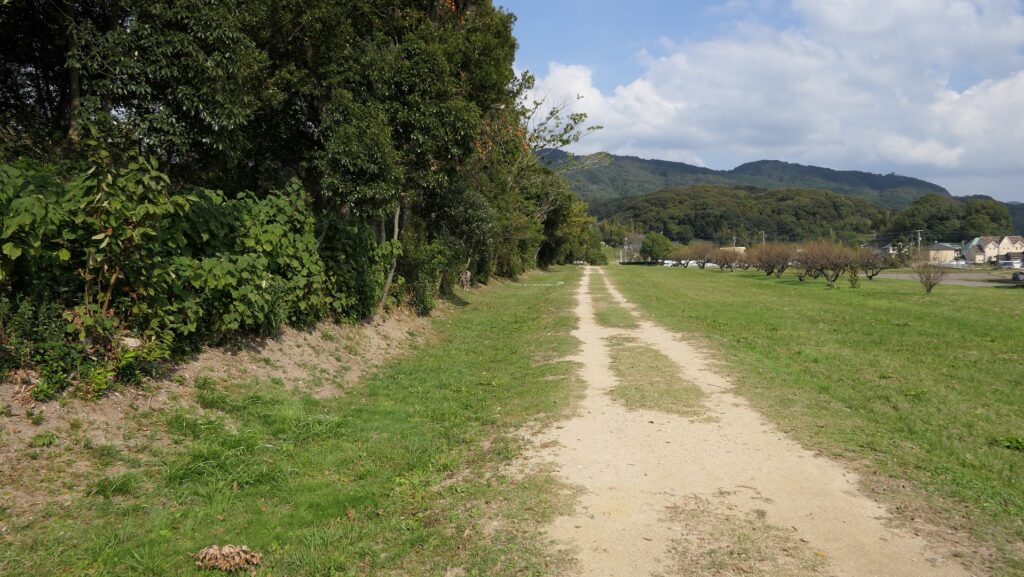
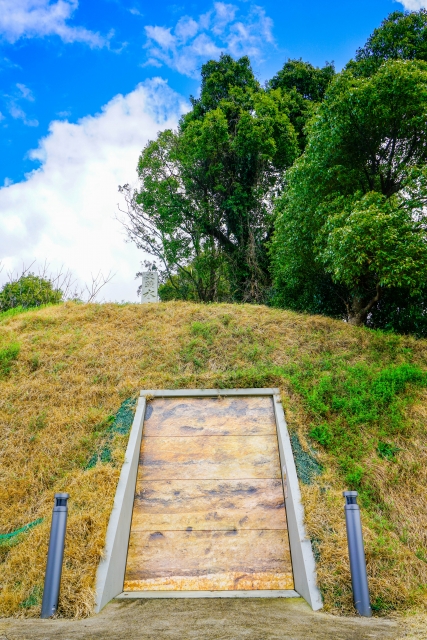



東門周辺~Around East Gate
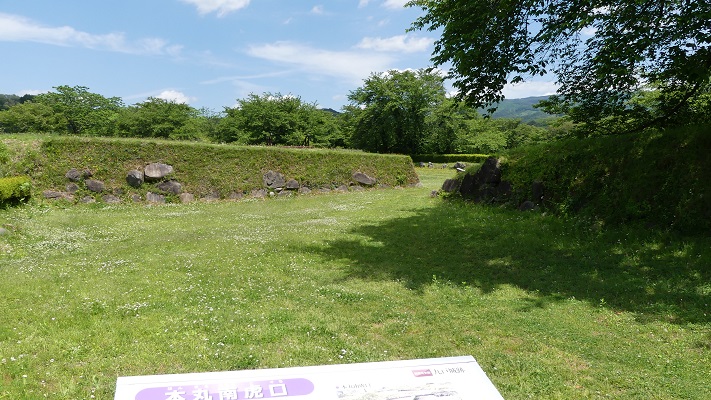
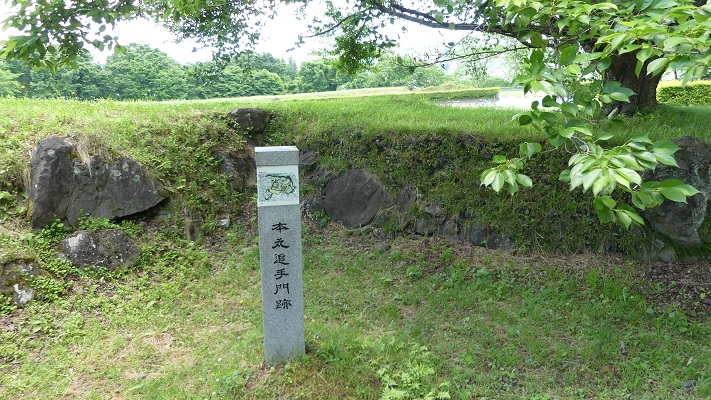
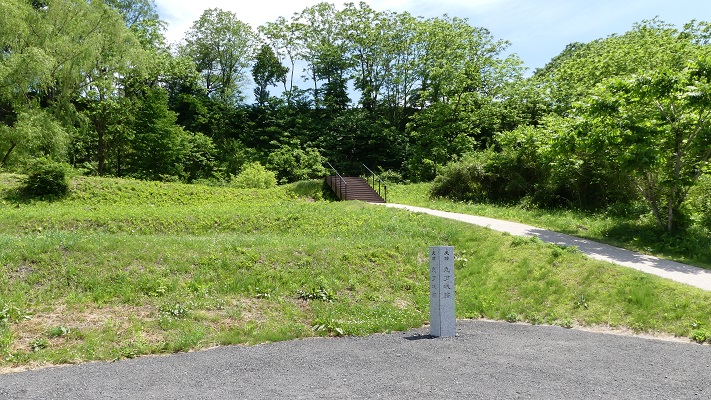
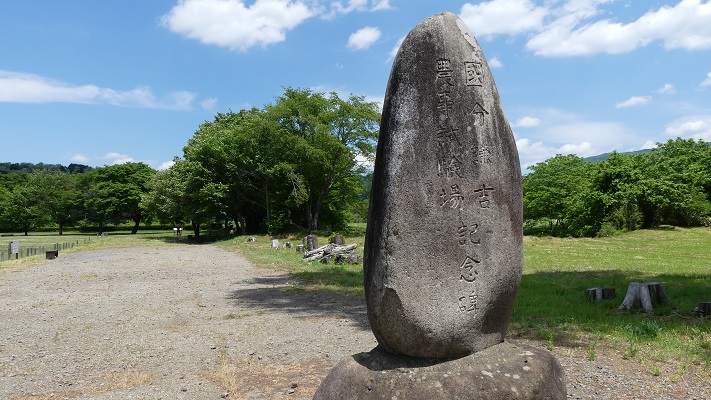
東門跡では、国道112号線がかつての古代官道のように遺跡を通り抜けています。後になって人々は門が元々あった場所に石碑を作って設置しました。門の礎石はまだ残っていて、遺跡を見に来た人であれば、すぐ見つけられます。また、水城館という展示施設があって、水城の歴史や使われている技術を学ぶことができます。この辺りは土塁の東端に当たるため、山裾の方に登って行って、遺跡の全景を見ることもできます。
At the ruins of the East Gate, the National Route 112 goes through the ruins like the ancient government road. Later on, people made and placed stone structures where the gates use to stand originally. The cornerstones of the gate still exists and anybody who visits the ruins can see them . You can also visit the guest house called Mizuki-kan which exhibits the history and technology of the ruins. The area is near the eastern edge of the earthen walls, so you can walk up to the foot of the mountain and have the whole view of the ruins.
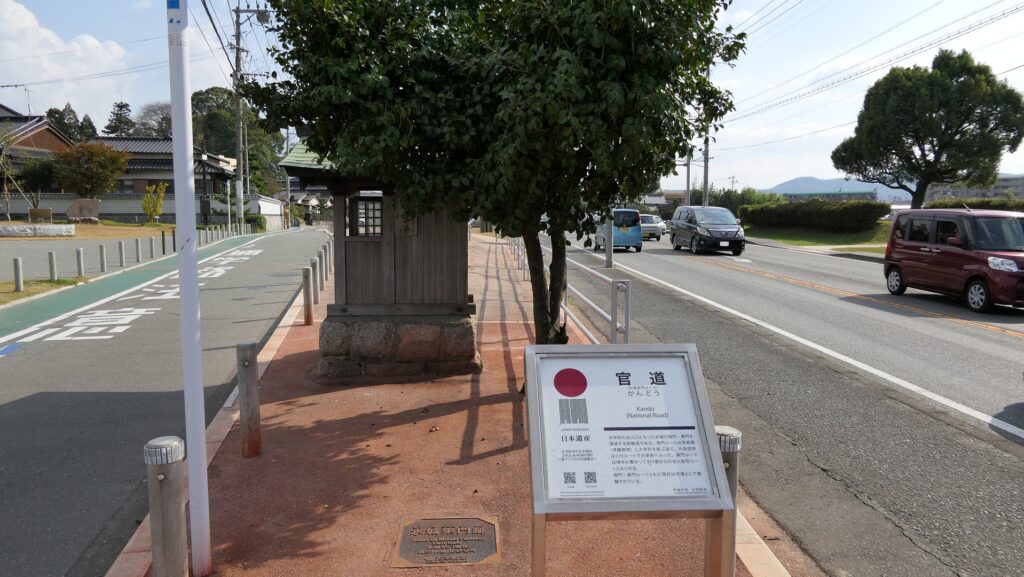
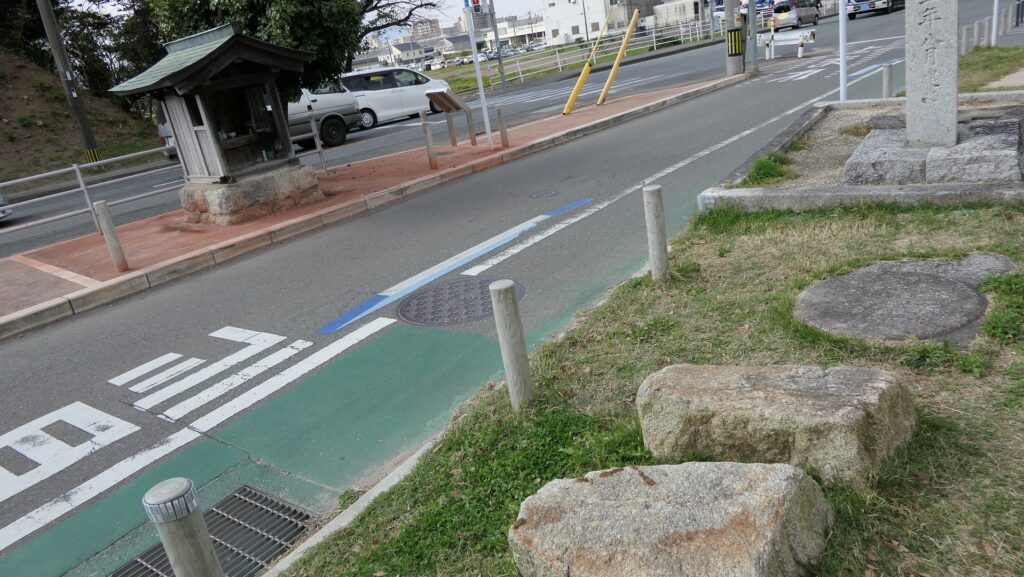
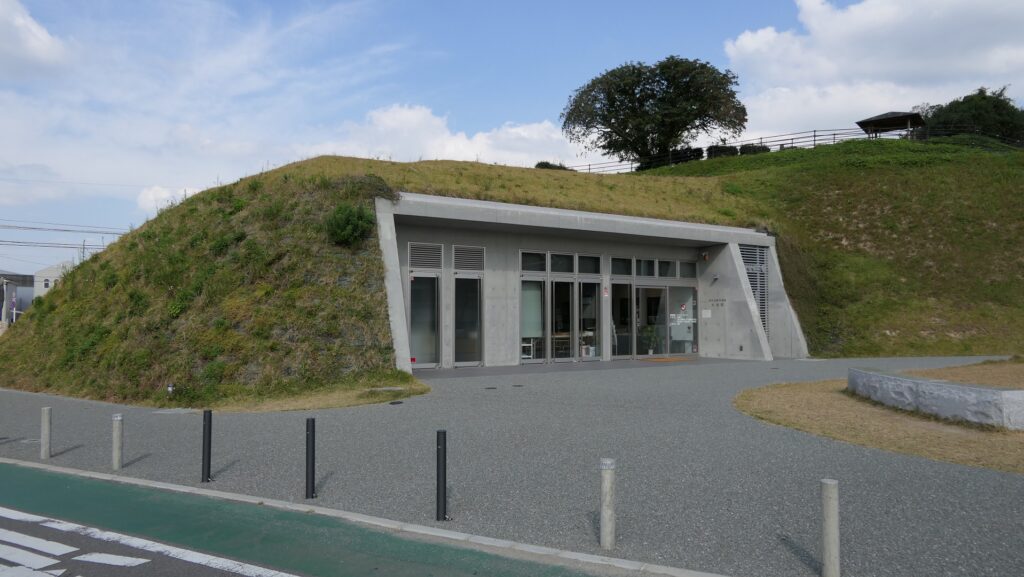





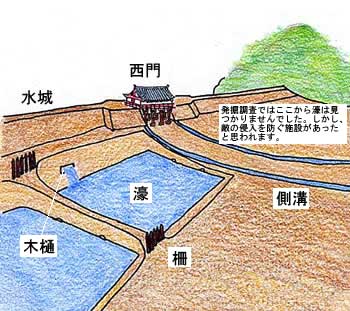
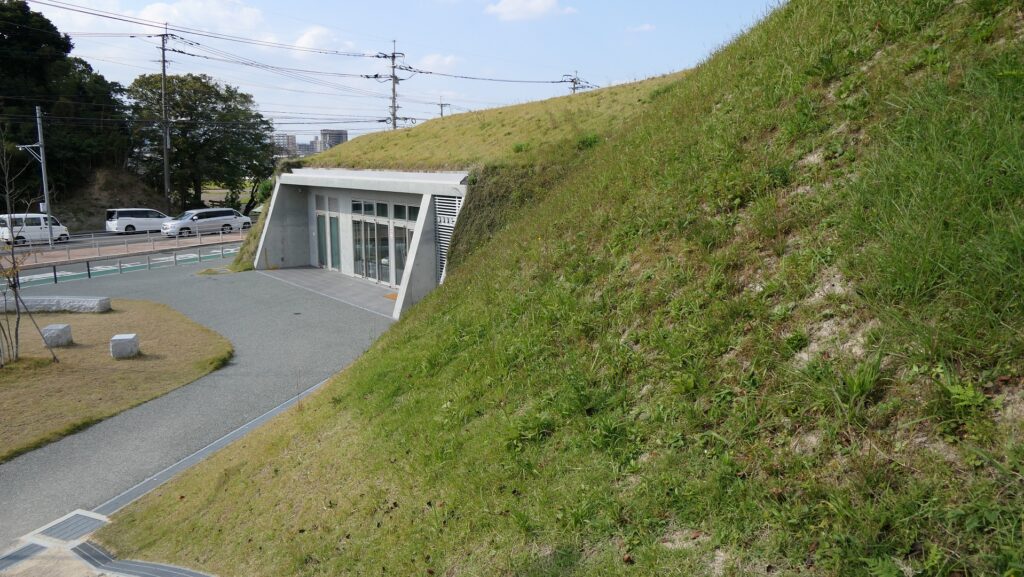
西門周辺~Around West Gate
西門の跡については、ここもまた地方道路により壊されてしまっています。発掘によれば、西門は3回立て直されています。門はその時代ごとの要請によって、機能が違っており、外交関係が悪いときは関門として機能し、関係がよくなると飾り立てられていたようです。
At the ruins of the West Gate, they are also destroyed by a local road. The excavation found that the gate had been rebuilt three times. It was a functional gate that was built as per requirement. The gate served as a barrier when foreign relations were bad. However, when relations were good it was more decorative.
その後~Later History
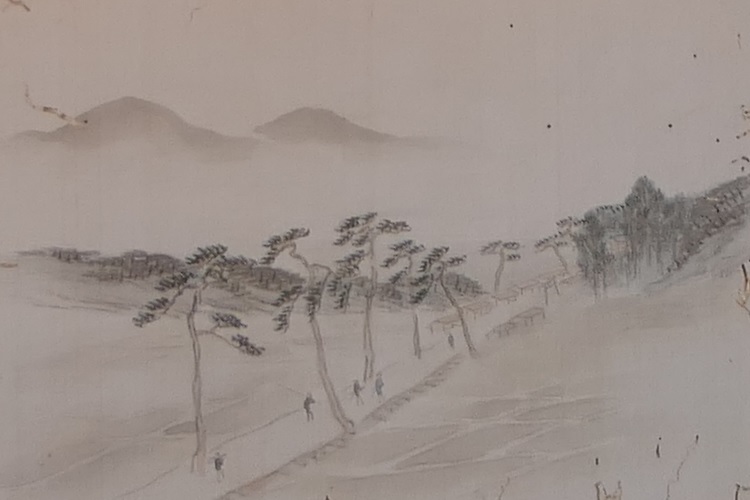
中世の13世紀頃、門は失われていました。しかし武士たちはモンゴル襲来のときに跡地を陣地として使用したようです。江戸時代には東側の官道は日田街道となり、多くの人々が往来しました。人々は水城を著名は遺跡として認識していました。1953年には国の特別史跡に指定されます。
Around the 13th century of the Middle Ages, the gates had been lost, but warriors seemed to use the ruins as a position against the Mongol Invasion. In the Edo Period, the eastern government road was being turned into Hita Road many people used. The people had already recognized Mizuki as famous ruins. The ruins have been designated as a Special National Historic Site since 1953.

私の感想~My Impression
白村江の戦いは、日本の歴史において重要な出来事でした。水城跡は、多くの人々が近くを通るだけで目にすることができる、とても分かりやすい遺跡だと思うのです。歴史の知識があれば、水城がなぜ築かれたか多分わかるでしょう。知識がなくとも、遺跡を見てもっと知りたいと思うかもしれません。水城が永久に守られることを切に望みます。
The battle of baekgang is an important event in the history of Japan. I think that the ruins of Mizuki are very easy to understand for many people, because they can have many chances to see the ruins when they pass by. If they have the knowledge of history, they will probably understand why Mizuki was built easily. Even if not, they may want to learn more about the ruins seeing them. I really hope that Mizuki will be kept forever.

ここに行くには~How to get There
東門跡に行くには:
車では、九州自動車道の大宰府ICから数分のところです。展示施設に駐車場があります。
電車の場合は、西鉄天神大牟田線の下大利駅から歩いて約20分です。
西門跡に行くには:
車では、九州自動車道の大宰府ICから約10分かかります。水城ゆめ広場に駐車場があります。
電車の場合は、JR鹿児島本線の水城駅から歩いて数分のところです。
To the ruins of the East Gate:
By car, it takes few minutes from the Dazaifu IC on Kyushu Expressway. The guest house offers a parking lot.
By train, it takes about 20 minutes on foot from Shimo-ori Station on Nishitetsu Tenjin-Omuta Line.
To the ruins of the West Gate:
By car, it takes about 10 minutes from the Dazaifu IC on Kyushu Expressway.
Mizuki-Yumehiroba Park offers a parking lot.
By train, it takes few minutes on foot from Mizuki Station on JR Kagoshima Line.
リンク、参考情報~Links and References
・水城跡、大野城市(Onojo City Website)
・水城館、古都大宰府保存協会(Japanese Association Website)