立地と歴史~Location and History
勝頼、長篠城を狙う~Katsuyori tries to get the castle
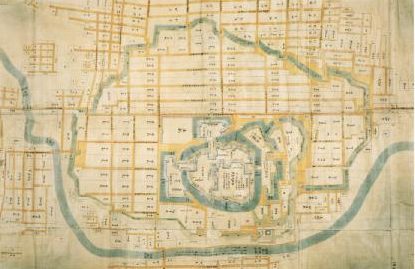
長篠城は三河国(愛知県の東側に相当)の山側に位置しており、二つの川の合流地点にある崖の上に築かれました。城そのものよりも、1575年の長篠の戦いによって有名なのかもしれません。
Nagashino Castle was located in a mountain side of Mikawa Province (what is the eastern part of Aichi Pref.), on a cliff at the meeting point of two rivers. It may be more famous for the battle of Nagashino in 1575 than for itself.
戦国時代の1574年、武田勝頼は遠江国にある高天神城を徳川家康より奪いました。武田は東方にある甲斐国(山梨県)と駿河国(静岡県の中部)を領しており、徳川は西方にある遠江国(静岡県西部)と三河国を有していました。勝頼は、高天神城の更に西方にある長篠城を手に入れようとします。家康にとっては脅威でした。そして盟友の織田信長に援軍を要請します。
In 1574, the “Sengoku” or Waring State Period, Katsuyori Takeda took Takatenjin Castle in Totoumi Province away from Ieyasu Tokugawa. Takeda owned Kai (Yamanashi Pref.) and Suruga (mid Shizuoka Pref.) Provinces in the east, and Tokugawa had Totoumi (west Shizuoka Perf) and Mikawa Provinces in the west. Katsuyori aimed to capture Nagashino Castle, further west than Takatenjin. That was a threat to Ieyasu. He asked his ally, Nobunaga Oda for help.

勝頼、決戦を挑む~Katsuyori wants a decisive battle
1575年5月、勝頼は医王寺にある丘に本陣を置き、武田騎馬隊を含む1万人以上の軍勢で長篠城を包囲しました。一方、城の守備兵は僅か5百名でした。信長と家康は3万人以上の兵を率いて城の西方約4キロにある設楽原に至り、現地に陣地を築き、鉄砲隊を配置しました。
In May 1575, Kstduyoti set his stronghold on a hill at Ioji Temple, and surrounded the Nagashino Castle with over 10,000 soldiers including the Takeda Cavalry. On the other hand, defenders in the castle were only 500 in number. Nobunaga and Ieyasu took more than 30,000 soldiers to Shitara-ga-Hara field, about 4km west from the castle, and built fortresses along the field and brought gun troops.
城の運命はさておき、両方の陣営はこれは決着をつける場であると考えました。勝頼は本陣の丘を下り、信長の方に向かっていきました。しかしながら、それは信長の罠だったのです。
Beside the destiny of the castle, both sides thought it would be the chance to have a showdown. Katsuyori went down the hill and headed towards Nobunaga. However, he was going to be trapped by Nobunaga.

勝頼、信長に突撃~Katsuyori attacks Nobunaga
5月21日、信長は別働隊を勝頼の背後に送り出しました。勝頼は当惑し、すぐさま信長の陣地に突撃するしかなくなりました。設楽原は狭い上に真ん中に連吾川が流れており、周囲は湿地帯となっていました。武田騎馬隊は機動力と攻撃力で知られていましたが、このような状況では普段の力を発揮できません。武田は陣地に向かって一部隊ずつ攻撃せざるをえません。信長の陣地は、設楽原の西側の丘状の場所に築かれ、鉄砲隊の前には木柵が幾重にも設置されていました。まるで城のようだったのでしょう。武田は柵に阻まれ、鉄砲で撃たれ、各個撃破されていきました。
On May 21, Nobunaga sent his detached force to the back of Katsuyori. Katsuyori was confused and there was no other way than charging Nobunaga’s fortresses right away. Shitara-ga-Hara field is narrow with the Rengogawa River flowing at the center, and was waterlogged around. Takeda Cavalry was known for its mobile and strong power, but its power was less than usual under such conditions. Takeda had to attack from one troop to another against the fortresses. Nobunaga’s fortresses were constructed in a hilly area on the western side of the field, which installed several wooden fence layers in front of gun troops. They seemed to look like castles. Takeda was blocked by the fences, shot by the guns, and defeated one by one.

勝頼、完敗す~Katsuyori completely defeated
勝頼は攻略を諦め、撤退しました。そして信長は追撃を開始します。この戦いの間、武田の軍勢のうち約半数が失われたと言われています。武田の多くの重臣や指揮官も戦死しました。この戦いの結果は、信長の天下統一事業と、武田氏の滅亡への動きを加速しました。大きな歴史の節目となりました。
Katsuyori gave up and withdrew. Then Nobunaga started to chase them. It is said that about half of Takeda’s soldiers were lost during the battle. Many senior vassals and troop leaders of Takeda were also killed. The result of the battle would lead to the boost of Nobunaga’s unification of Japan and the destruction of the Takeda clan. It was a big turning point.

多くの歴史家は、この戦いの勝敗の要因は、戦術革命(鉄砲対騎馬隊)にあると言います。しかし、そんなに単純な話ではなく、信長は強力な武田軍に対処するため考え抜いたと指摘する人もいます。彼の決断は、自軍を防御することに徹しながらも、有利な条件下に武田を誘いこむことでした。実際彼は兵士に対し、武田が撤退するまでは陣地から出ないよう命令しました。彼はまた、戦略的にも完勝したのです。
Many historians have said that the result was caused by the tactics revolution (gun vs cavalry). However, it was not so simple. Others point out that Nobunaga considered how they should deal with strong Takeda. His decision was to be devoted to protecting themselves, but to invite Takeda there under advantage. He actually ordered his soldiers that they were no to go out of the fortresses until Takeda withdraw. He was completely successful by his strategy, too.

特徴~Features
長篠城だけではなく、関連遺跡も一緒に回ってみることをお勧めします。歴史への理解をより深めることができます。
I recommend you to visit not only Nagashino Castle but also relative ruins. That will help you to learn more about history.
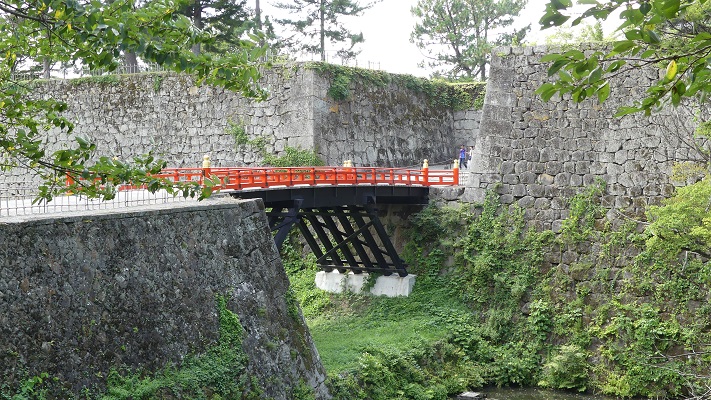
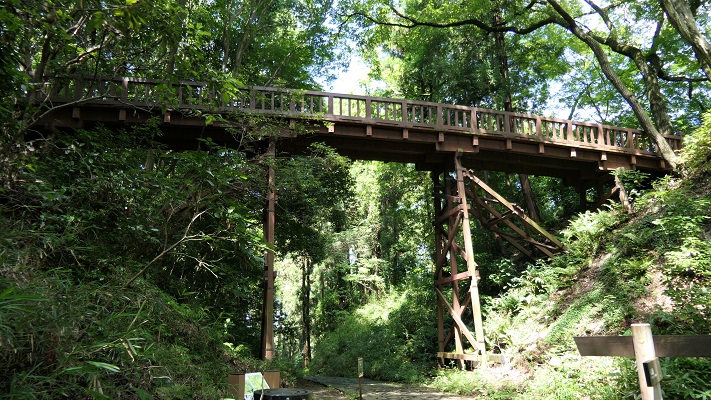
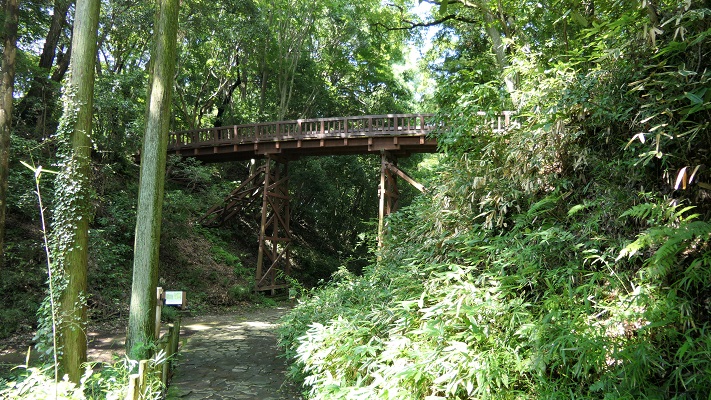
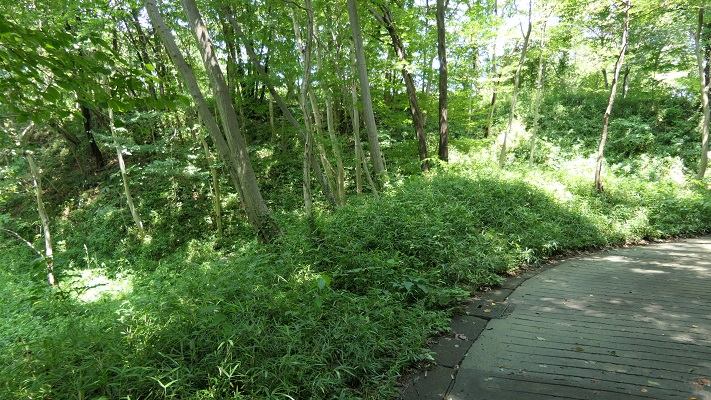
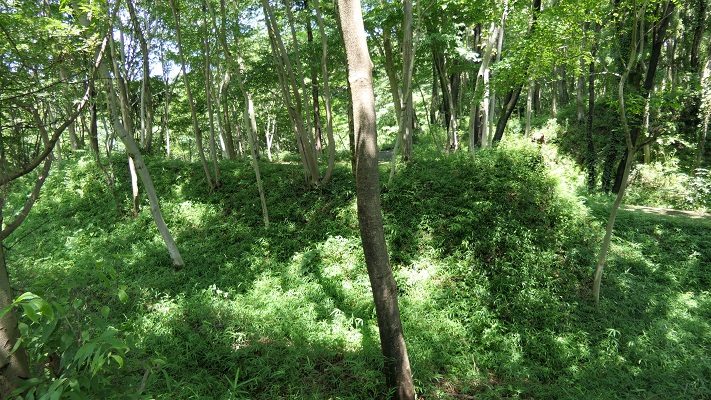
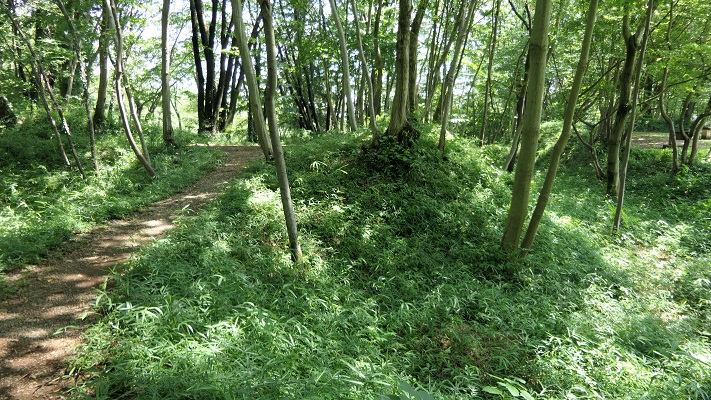
長篠城跡~Nagashino Castle Ruins
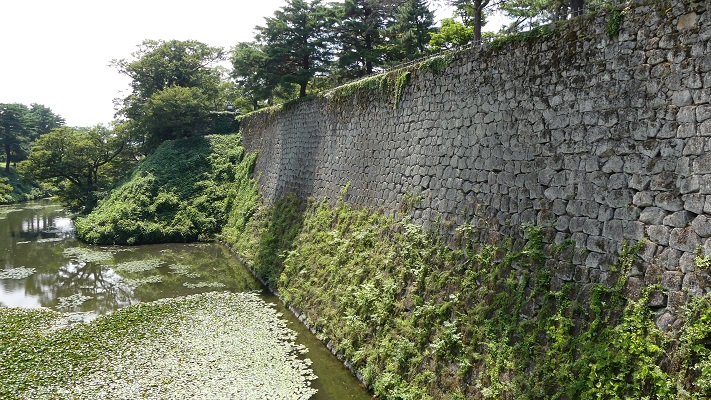
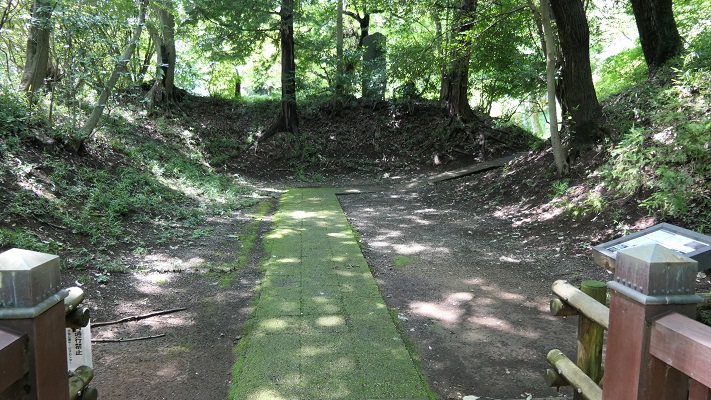
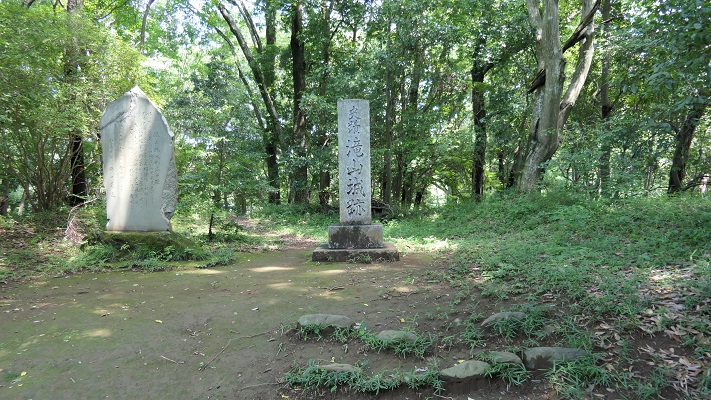
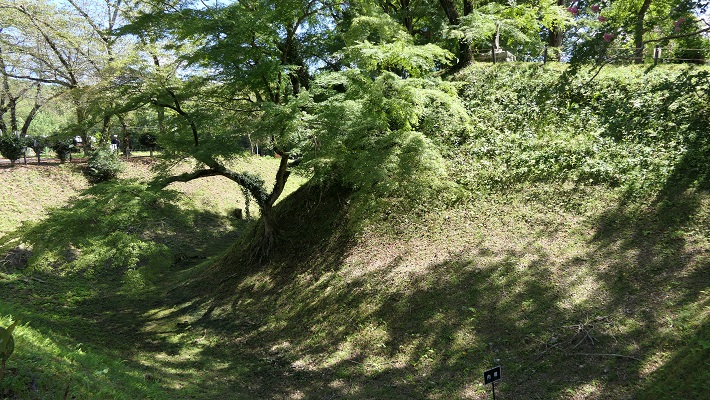
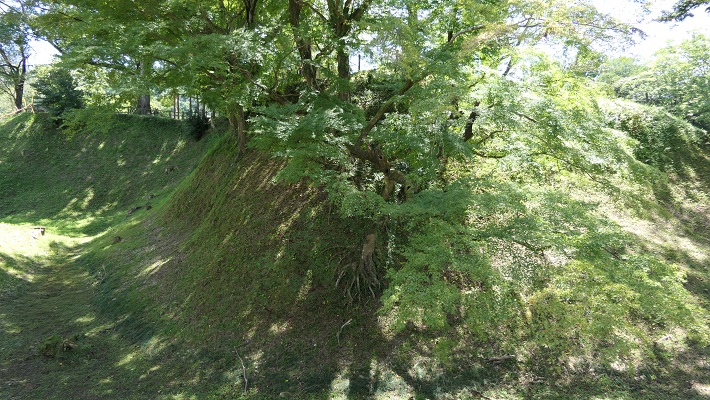
現在、崖の上の本丸が残っています。本丸は土塁で囲まれていて、外側とは空堀で隔てられています。過去にはもっと多くの曲輪が広がっていました。城跡は国の史跡に指定されています。
Now, the Main enclosure or “Honmaru” remains on the cliff. It is surrounded by earthen walls and divides from outside by a deep dry moat. More enclosures spread out in the past. The ruins have been designated as a National Historic Site.
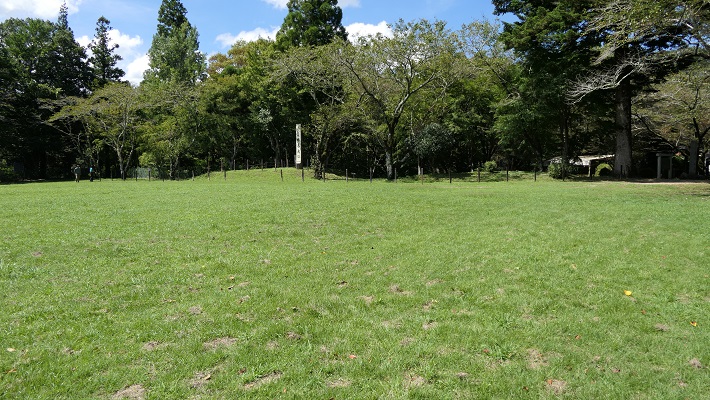


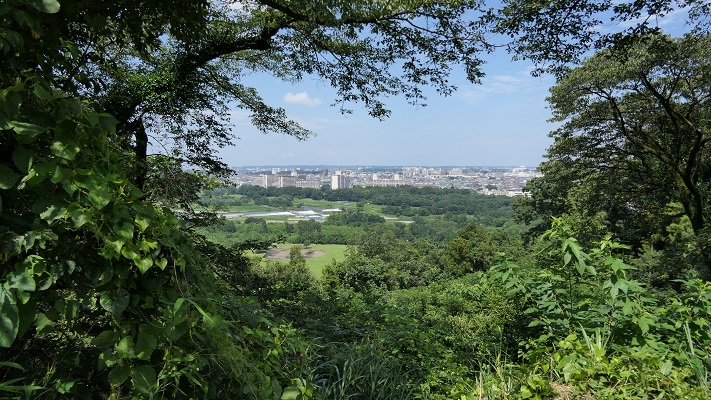
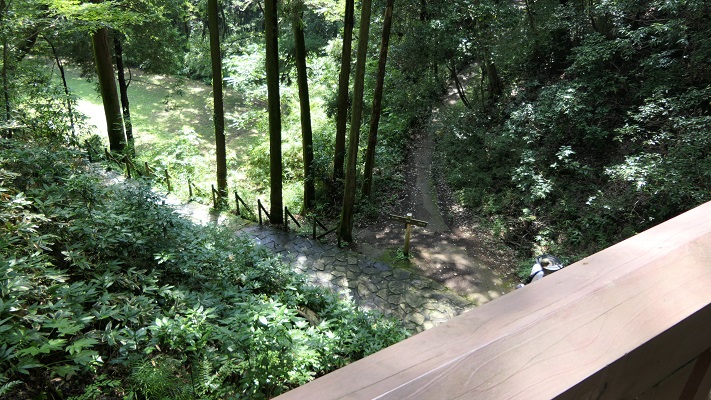
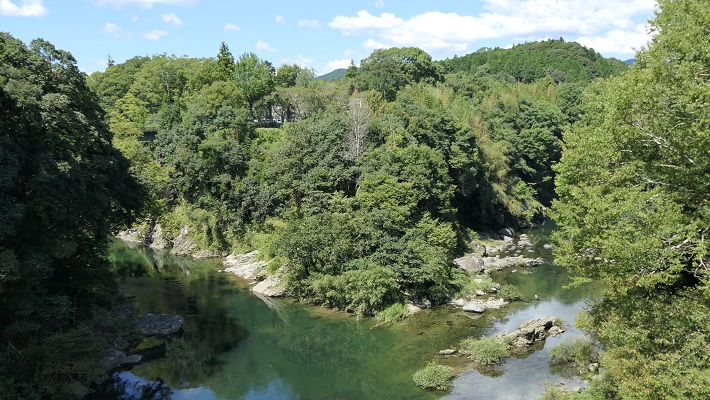
川を越えて城の反対側に行ってみると、崖の下の川の合流地点を見下ろす、素晴らしい景色です。城が自然の要害の上にあったこともわかると思います。
If you go to the opposite of the castle across the rivers, you can see a great view of the meeting point of the revers under the cliff. You can also realize that the castle was on a natural fortress.

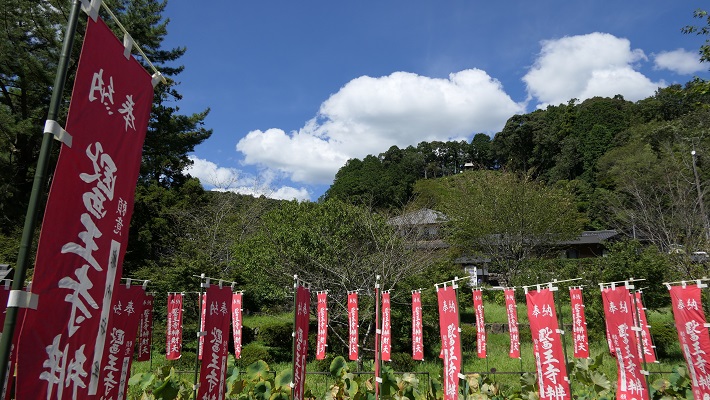
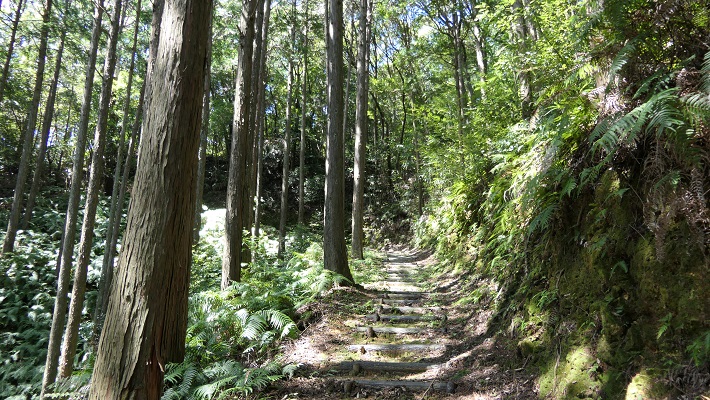
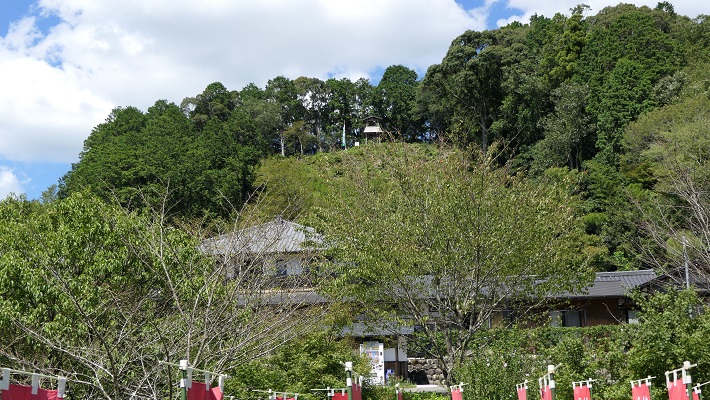
医王寺(勝頼の本陣跡)~Ioji Temple (The ruins of Katsuyori’s stronghold)
本陣は、この寺の裏山にありました。山道を通って簡単に登ることができます。
The stronghold was on the back hill of the temple. You can easily climb up to the top through the trail.


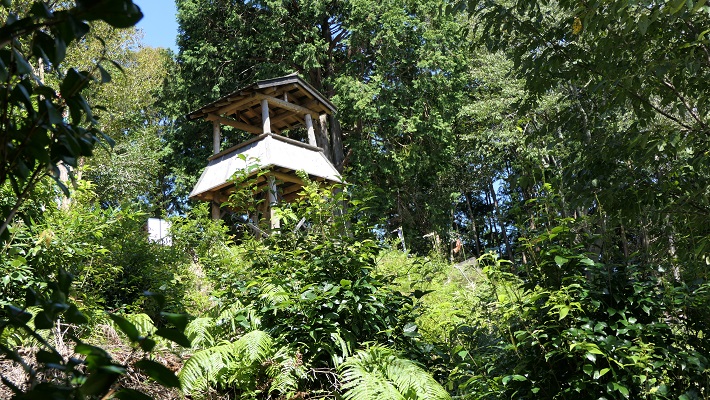
頂上には簡単な物見やぐらが復元されています。ここからは長篠城は見えるのですが、信長の陣地があった設楽原は見えません。十分な情報なしに勝頼がなぜ山を下り、信長の方に向かっていったのか考えてみるのも一興です。
There is a restored simple watch tower on the top. You can see Nagashino Castle from the tower, but can’t see Shitara-ga-Hara where Nobunaga’s fortresses were. It may be interesting to speculate why Katsuyori decided to go down the hill and head towards Nobunaga without enough information.
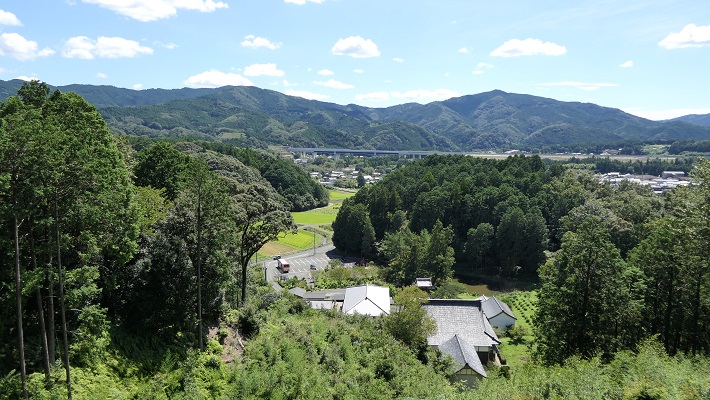


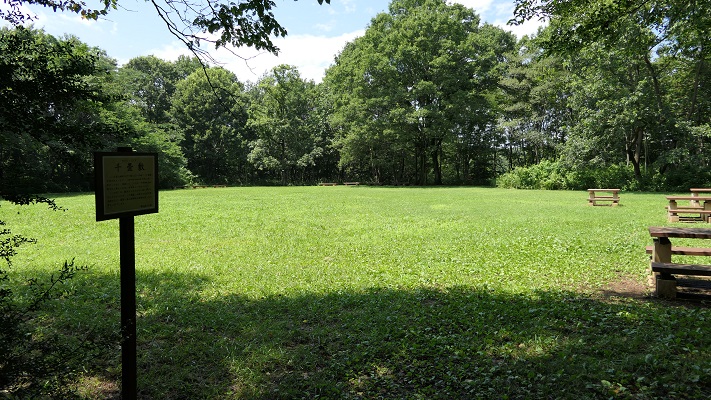
設楽原古戦場~Shitara-ga-Hara Battlefield
この場所は現在は水田になっていますが、丘状の地形に囲まれた谷のようになっているのが今でもわかります。ここが更に湿地帯であったなら、騎馬隊は十分な能力を発揮できなかったでしょう。
This place has now become a rice field, but you can still see it is like a valley surrounded by hilly areas. If it was also waterlogged, troops with horses couldn’t fulfill their potential.

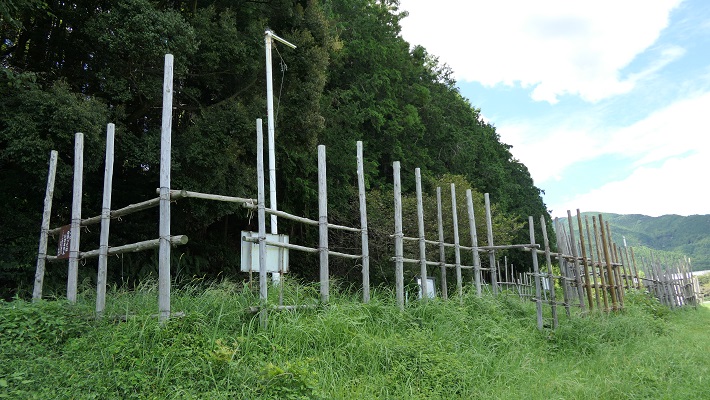
設楽原の西側には木柵と空堀がいくらか復元されています。実際にはもっと縦横に広がっていたはずです。武田は明らかに不利な状況で織田・徳川連合軍と戦わざるをえなかったのです。それが信長の戦略眼だったのです。
There are some restored wooden fences and dry moats on the western side of the field. They must have been spread wider and deeper. Takeda clearly had to fight with the allied forces of Oda and Tokugawa under disadvantage. That was the idea of Nobunaga’s strategy.

その後~Later History
長篠城は、長篠の戦いのわずか1年後、1576年に廃城となりました。ここの城主が新しい城を作り、移っていったからです。その後は、江戸時代には城跡の地に旗本や庄屋の屋敷があったようです。城跡は最終的には1929年に国の史跡に指定されました。
Nsgashino Castle was abandoned 1n 1576, just one year later the battle of Nagashino, because the lord of the castle built and moved to another castle. After that, a shogunal retainer and local administrator seemed to have their residences at the ruins of the castle in the Edo Period. The ruins were lastly designated as a National Historic Site in 1929.

私の感想~My Impression
長篠の戦いから得られる教訓は3つあると思います。
1.リーダーは普段は乾坤一擲の戦いは避けなければならない。
2.どうしても避けられないときは、十分な情報を基にした決断が必要である。
3.リーダーは常にいかに安全に撤退するかも考えておくべきである。
信長は、もし勝頼に敗れたとしてもどう撤退するか考えていたと思うのです。
I think we can learn three lessons from the battle of Nagashino.
1.Leaders must usually avoid playing for all or nothing.
2.If they can’t avoid it, informed decision will be essential, or withdraw immediately.
3.Leaders must always consider how to withdraw safely.
I believe that Nobunaga had considered how to withdraw if he was beaten by Katsuyori.


ここに行くには~How to get There
これまで述べた遺跡を回るには、車を使うのが便利です。みな新東名自動車道の新城ICの近くです。
長篠城だけでよければ、電車で行くこともできます。JR長篠城駅から徒歩10分くらいで現地に着きます。東京または名古屋からでしたら、東海道新幹線で豊橋まで行き、飯田線に乗り換えてください。
I recommend you using car to visit these ruins mentioned above. They are all near Shinshiro IC on Shin-Tomei Expressway.
If you want to visit only Nagashino Castle, it is also accessible by train. It takes about 10 minutes to get there on foot from JR Nagashino-Jo Station. From Tokyo or Nagoya, take the Tokaido Shinkansen super express to Toyohashi Station, then transfer for Iida local line.
リンク、参考情報~Links and References
・史跡長篠城跡、新城市(Multilingual service is available)
・新城市設楽原歴史資料館、新城市(Multilingual service is available)
・「長篠の戦い/藤本正行著」洋泉社(Japanese Book)
・「籠城/榎本秋著」宝島社(Japanese Book)
・「現代語訳 信長公記/太田牛一著、中川太古訳」新人物文庫(Japanese Book)